1048:
382:(1860), some 19th-century and early-20th-century historians have supposed that there may indeed have been a Campanian or Capuan league or (con)federation of cities from the mid-5th century BCE until 211 BCE, but the evidence from primary sources is poor and contradictory. There is no clear evidence of the membership of this supposed league, let alone of its political institutions and thus how it might have functioned in practice, if it existed. Historian Nikoletta Farkas (2006) concluded that Capua did control quite some rural territory – known as the
997:
33:
201:
467:– Roman citizenship without voting rights, meaning they were allowed to trade and intermarry with Romans, and maintained political and legal autonomy. But Capua lost some territory, and was required to supply soldiers to Rome.
508:, although he does not indicate when this supposedly happened. Franco Sartori (1953) argued for a 318 BCE date, but later scholars Sherwin-White (1973) and Frederiksen (1984) reasoned that the Romans did not regularly appoint
180:, is of classical origin. The most accredited hypothesis is that it derives from the name of the ancient inhabitants of Capua. From Capuani, in fact, we would have Campani and, therefore, Campania; furthermore, both
1288:
543:, recorded for the first time in 1092 (although there are doubts about the originality of the document), replaced the name Campania. The new toponym will officially replace the old one in the
559:
toponym
Campania and what it originally indicated was lost in the language: in an emblematic way, the geographical maps, from about 1500 to 1700, show the indication Terra Laboris olim
148:, and later also the plains of the various neighbouring municipalities. It was a very large territory when compared with the other Italic cities of the Roman and pre-Roman period.
354:
in the mid-8th century, that would dominate the region until the 5th century BCE. The evidence suggests that the city of Capua was founded in the 6th or 5th century BCE by
358:, though scholars have not been able to establish an exact date. Several Roman and Greek authors writing centuries later have penned varying and contradictory
374:(written in the 1st century BCE or CE) asserted that Capua became the capital of a league of twelve Campanian cities, mirroring the notion that twelve
342:
suggest the region has been continuously inhabited since the 10th century BCE. Most ancient sources refer to the indigenous peoples of
Campania as
852:
Aniello
Gentile, Da Leboriae (Terrae) a Terra di Lavoro, riflessi linguistici di storia, cultura e civiltà in Campania, in Archivio storico di
1105:
614:
398:
appears to have been a local official of Capua, not someone presiding over a council of a (con)federation or league of cities. The name
985:
939:
116:
50:
963:
953:
97:
1047:
1222:
630:
69:
54:
1192:
1293:
1111:
76:
1142:
1032:
1137:
1132:
83:
43:
524:
1258:
1238:
339:
868:"Rassegna della giurisprudenza della corte di cassazione in materia di lavoro (settembre 2012-dicembre 2013)"
65:
1177:
483:
against Rome, but was defeated after a long siege by the Romans in 211 BCE, ending in its loss of autonomy.
978:
579:
463:
157:
908:
Leadership among the
Samnites and related Oscan-speaking peoples between the fifth and first centuries BC
1243:
1217:
1172:
1079:
1056:
1022:
435:
in 343 BCE, Capua either "surrendered" or "allied" itself to Rome, depending on one's interpretation of
1207:
1017:
906:
200:
1037:
1027:
447:. Either way, Capua soon joined other Latin cities in revolting against Rome during the subsequent
1167:
1089:
1009:
499:
252:
402:
for a geographical region does not appear in Greek and Roman sources until the 2nd century BCE.
1298:
1269:
1248:
1187:
1127:
971:
935:
883:
610:
432:
284:
217:
90:
604:
461:
of the Roman
Republic, with both obligations and benefits. The inhabitants of Capua received
1253:
875:
476:
346:. Settlers from other peoples arrived in subsequent centuries, first mainly the Greeks from
177:
1182:
1162:
1094:
853:
552:
548:
427:
It is uncertain exactly how Capua and the rest of
Campania came under the dominion of the
379:
375:
359:
315:
1099:
428:
161:
1282:
1147:
213:
378:
also formed a league, which may be indicative of such a foundation myth. Ever since
1152:
1064:
444:
418:
307:
145:
1157:
536:
370:
227:
The main inhabited centers of this historical region were (from north to south)
32:
928:
La storia dell'Ager
Campanus, i problemi della limitatio e sua lettura attuale
504:
335:
311:
17:
887:
867:
448:
422:
355:
303:
879:
1001:
996:
544:
495:
480:
406:
319:
292:
276:
268:
236:
221:
185:
173:
409:
conquered
Etruscan Capua in 423 BCE, and Greek Cumae in 421 or 420 BCE.
1084:
1074:
1069:
291:. Thanks to the fertility of the soil, also due to the presence of the
288:
280:
248:
205:
57: in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
931:
520:
394:), there were no other cities in Campania under its control, and the
387:
365:
347:
272:
260:
232:
512:
in Capua until 211 BCE, and hence the division of
Campania into ten
556:
457:
386:– beyond its urban centre, but apart from the subordinate city of
351:
264:
244:
240:
228:
141:
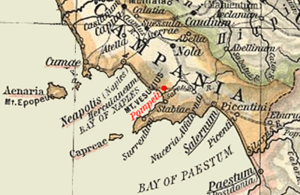
587:
491:
436:
256:
181:
967:
502:
wrote in the 4th century CE that
Campania was divided into ten
26:
731:
729:
727:
631:"Perché Campania Felix: le origini del nome | Visititaly.eu"
479:(218–201 BCE), Capua sided with the Carthaginian army under
140:) originally indicated the territory of the ancient city of
603:
Giordano, Anna; Caprio, Adriana; Natale, Marcello (2003).
192:
with a clear reference to Capua and the surrounding area.
170:
Osci enim a Regione Campaniæ, quae est Oscor, vocati sunt.
872:
Giornale di Diritto del Lavoro e di Relazioni Industriali
824:
822:
797:
795:
746:
744:
168:, the name from which the Osci peoples who lived there (
1289:
Geographical, historical and cultural regions of Italy
666:
664:
954:
Approfondimento sull'archeologia vesuviana e campana
1231:
1206:
1120:
1055:
1008:
523:, became part, in the Augustan subdivision, of the
208:in Ancient Campania. William R. Shepherd (1911).
494:due to the alliance of the city of Capua with
979:
310:river as its boundaries to the south and the
8:
455:340–338 BCE), but was defeated and became a
547:territorial subdivision. In fact, from the
986:
972:
964:
519:The territory of Campania, together with
117:Learn how and when to remove this message
930:(Real sito di S. Leucio 8-9 June 2001),
445:how historically reliable his account is
199:
572:
840:
828:
813:
801:
786:
774:
762:
750:
735:
718:
706:
694:
682:
670:
655:
164:), the pre-Roman name of Campania was
486:Initially Campania also included the
302:Ancient Campania, closed between the
212:Campania extended from the slopes of
7:
598:
596:
55:adding citations to reliable sources
914:(PhD thesis). King's College London
516:should also be dated to that year.
490:, then it was heavily downsized by
156:According to the Roman philologist
25:
856:, VI volume, 1978-1979, pp. 9-61.
1046:
995:
31:
551:, due to the prevalence of the
42:needs additional citations for
1223:List of presidents of Campania
866:Curzio, Pietro (27 May 2014).
390:(and the otherwise unattested
1:
609:(in Italian). Guida Editori.
555:, the connection between the
452:
405:Classical sources agree that
295:river, it earned the name of
176:Campania, dating back to the
1193:Duchy of Apulia and Calabria
586:Parte I, p. 109. Budapest,
584:De verborum significatione.
525:Regio I: Latium et Campania
498:. The late Roman historian
314:to the north. According to
1315:
1106:Cities, towns and villages
905:Farkas, Nikoletta (2006).
431:. At the beginning of the
416:
350:who founded the colony of
132:(often also identified as
1267:
1044:
216:(to the north) up to the
934:, Jovene Editore, 2002,
340:Santa Maria Capua Vetere
1178:Principality of Salerno
439:'s meaning of the word
338:on the edges of modern
318:, however, the city of
880:10.3280/gdl2014-142003
580:Sextus Pompeius Festus
464:civitas sine suffragio
209:
158:Sextus Pompeius Festus
1218:Elections in Campania
1173:Principality of Capua
417:Further information:
306:and the sea, had the
203:
1090:Sorrentine Peninsula
51:improve this article
1294:History of Campania
926:Gennaro Franciosi,
843:, pp. 107–108.
816:, pp. 106–107.
789:, pp. 105–106.
777:, pp. 104–105.
738:, pp. 136–139.
322:was its boundary.
1168:Duchy of Benevento
697:, pp. 99–101.
685:, pp. 99–100.
331:Pre-Roman Campania
210:
66:"Ancient Campania"
1276:
1275:
1188:Duchy of Sorrento
1128:Kingdom of Naples
658:, pp. 98–99.
616:978-88-7188-774-6
433:First Samnite War
376:cities in Etruria
285:Nuceria Alfaterna
218:Phlegraean Fields
127:
126:
119:
101:
16:(Redirected from
1306:
1198:Ancient Campania
1112:List of communes
1050:
1000:
999:
988:
981:
974:
965:
923:
921:
919:
913:
892:
891:
874:(142): 223–268.
863:
857:
850:
844:
838:
832:
826:
817:
811:
805:
799:
790:
784:
778:
772:
766:
760:
754:
748:
739:
733:
722:
716:
710:
704:
698:
692:
686:
680:
674:
668:
659:
653:
647:
646:
644:
642:
627:
621:
620:
600:
591:
577:
477:Second Punic War
454:
360:foundation myths
178:fifth century BC
130:Ancient Campania
122:
115:
111:
108:
102:
100:
59:
35:
27:
21:
1314:
1313:
1309:
1308:
1307:
1305:
1304:
1303:
1279:
1278:
1277:
1272:
1263:
1227:
1209:
1202:
1183:Duchy of Amalfi
1163:Duchy of Naples
1158:Italia province
1116:
1095:Terra di Lavoro
1051:
1042:
1004:
994:
992:
959:vesuviolive.it.
949:
917:
915:
911:
904:
901:
896:
895:
865:
864:
860:
854:Terra di Lavoro
851:
847:
839:
835:
827:
820:
812:
808:
800:
793:
785:
781:
773:
769:
761:
757:
749:
742:
734:
725:
717:
713:
705:
701:
693:
689:
681:
677:
669:
662:
654:
650:
640:
638:
629:
628:
624:
617:
606:Terra di lavoro
602:
601:
594:
578:
574:
569:
553:Duchy of Naples
549:seventh century
533:
473:
425:
415:
413:4th century BCE
380:Theodor Mommsen
333:
328:
316:Pliny the Elder
198:
154:
123:
112:
106:
103:
60:
58:
48:
36:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1312:
1310:
1302:
1301:
1296:
1291:
1281:
1280:
1274:
1273:
1268:
1265:
1264:
1262:
1261:
1256:
1251:
1246:
1241:
1235:
1233:
1229:
1228:
1226:
1225:
1220:
1214:
1212:
1204:
1203:
1201:
1200:
1195:
1190:
1185:
1180:
1175:
1170:
1165:
1160:
1155:
1150:
1145:
1140:
1135:
1130:
1124:
1122:
1118:
1117:
1115:
1114:
1109:
1102:
1100:Vallo di Diano
1097:
1092:
1087:
1082:
1077:
1072:
1067:
1061:
1059:
1053:
1052:
1045:
1043:
1041:
1040:
1035:
1030:
1025:
1020:
1014:
1012:
1006:
1005:
993:
991:
990:
983:
976:
968:
962:
961:
948:
947:External links
945:
944:
943:
924:
900:
897:
894:
893:
858:
845:
833:
831:, p. 108.
818:
806:
804:, p. 106.
791:
779:
767:
765:, p. 101.
755:
753:, p. 102.
740:
723:
711:
709:, p. 100.
699:
687:
675:
660:
648:
622:
615:
592:
571:
570:
568:
565:
561:Campania felix
539:, the toponym
532:
529:
472:
471:Roman Campania
469:
429:Roman Republic
414:
411:
396:meddix tuticus
332:
329:
327:
324:
297:Campania Felix
224:to the south.
197:
194:
153:
150:
134:Campania Felix
125:
124:
39:
37:
30:
24:
18:Campania felix
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1311:
1300:
1297:
1295:
1292:
1290:
1287:
1286:
1284:
1271:
1266:
1260:
1257:
1255:
1252:
1250:
1247:
1245:
1242:
1240:
1237:
1236:
1234:
1230:
1224:
1221:
1219:
1216:
1215:
1213:
1211:
1205:
1199:
1196:
1194:
1191:
1189:
1186:
1184:
1181:
1179:
1176:
1174:
1171:
1169:
1166:
1164:
1161:
1159:
1156:
1154:
1151:
1149:
1148:Magna Graecia
1146:
1144:
1141:
1139:
1136:
1134:
1131:
1129:
1126:
1125:
1123:
1119:
1113:
1110:
1108:
1107:
1103:
1101:
1098:
1096:
1093:
1091:
1088:
1086:
1083:
1081:
1078:
1076:
1073:
1071:
1068:
1066:
1063:
1062:
1060:
1058:
1054:
1049:
1039:
1036:
1034:
1031:
1029:
1026:
1024:
1021:
1019:
1016:
1015:
1013:
1011:
1007:
1003:
998:
989:
984:
982:
977:
975:
970:
969:
966:
960:
956:
955:
951:
950:
946:
941:
940:88-243-1450-3
937:
933:
929:
925:
910:
909:
903:
902:
898:
889:
885:
881:
877:
873:
869:
862:
859:
855:
849:
846:
842:
837:
834:
830:
825:
823:
819:
815:
810:
807:
803:
798:
796:
792:
788:
783:
780:
776:
771:
768:
764:
759:
756:
752:
747:
745:
741:
737:
732:
730:
728:
724:
721:, p. 97.
720:
715:
712:
708:
703:
700:
696:
691:
688:
684:
679:
676:
673:, p. 99.
672:
667:
665:
661:
657:
652:
649:
636:
635:visititaly.eu
632:
626:
623:
618:
612:
608:
607:
599:
597:
593:
589:
585:
581:
576:
573:
566:
564:
562:
558:
554:
550:
546:
542:
541:Terra Laboris
538:
530:
528:
526:
522:
517:
515:
511:
507:
506:
501:
497:
493:
489:
488:ager Falernus
484:
482:
478:
470:
468:
466:
465:
460:
459:
450:
446:
442:
438:
434:
430:
424:
420:
412:
410:
408:
403:
401:
397:
393:
389:
385:
384:ager Campanus
381:
377:
373:
372:
367:
363:
362:about Capua.
361:
357:
353:
349:
345:
341:
337:
330:
325:
323:
321:
317:
313:
309:
305:
300:
298:
294:
290:
286:
282:
278:
274:
270:
266:
262:
258:
254:
250:
246:
242:
238:
234:
230:
225:
223:
222:Vesuvian area
219:
215:
214:Mount Massico
207:
202:
195:
193:
191:
190:Ager Campanus
187:
183:
179:
175:
171:
167:
163:
162:II century BC
159:
151:
149:
147:
143:
139:
138:ager Campanus
135:
131:
121:
118:
110:
99:
96:
92:
89:
85:
82:
78:
75:
71:
68: –
67:
63:
62:Find sources:
56:
52:
46:
45:
40:This section
38:
34:
29:
28:
19:
1259:Coat of arms
1239:Demographics
1208:Politics and
1197:
1153:Samnite Wars
1143:Two Sicilies
1104:
1065:Amalfi Coast
958:
952:
927:
916:. Retrieved
907:
899:Bibliography
871:
861:
848:
836:
809:
782:
770:
758:
714:
702:
690:
678:
651:
639:. Retrieved
637:(in Italian)
634:
625:
605:
583:
575:
560:
540:
534:
518:
514:praefecturae
513:
509:
505:praefecturae
503:
487:
485:
474:
462:
456:
440:
426:
419:Samnite Wars
404:
399:
395:
391:
383:
369:
364:
343:
334:
301:
296:
226:
211:
189:
169:
165:
155:
146:Roman period
137:
133:
129:
128:
113:
104:
94:
87:
80:
73:
61:
49:Please help
44:verification
41:
841:Farkas 2006
829:Farkas 2006
814:Farkas 2006
802:Farkas 2006
787:Farkas 2006
775:Farkas 2006
763:Farkas 2006
751:Farkas 2006
736:Farkas 2006
719:Farkas 2006
707:Farkas 2006
695:Farkas 2006
683:Farkas 2006
671:Farkas 2006
656:Farkas 2006
641:25 February
537:Middle Ages
531:Middle Ages
475:During the
371:Geographica
348:Pithekoūsai
336:Necropoleis
1283:Categories
1270:Categories
1210:government
567:References
312:Garigliano
188:say of an
77:newspapers
1244:Geography
1023:Benevento
1010:Provinces
888:1720-4321
510:praefecti
449:Latin War
423:Latin War
392:Sabatinum
356:Etruscans
304:Apennines
277:Sorrentum
196:Geography
152:Etymology
107:June 2024
1299:Campania
1138:Viceroys
1133:Monarchs
1018:Avellino
1002:Campania
496:Hannibal
481:Hannibal
407:Samnites
400:Campania
320:Sinuessa
293:Volturno
289:Salernum
269:Oplontis
261:Neapolis
237:Liternum
220:and the
186:Polybius
1232:Culture
1121:History
1085:Samnium
1080:Islands
1075:Irpinia
1070:Cilento
1038:Salerno
1028:Caserta
918:23 June
535:In the
441:deditio
326:History
281:Stabiae
253:Acerrae
249:Puteoli
206:Pompeii
204:Map of
174:toponym
172:). The
144:in the
91:scholar
1057:Places
1033:Naples
938:
932:Naples
886:
613:
545:Norman
521:Latium
500:Festus
458:socius
443:, and
388:Atella
366:Strabo
344:Ausoni
273:Pompei
265:Caprae
233:Atella
93:
86:
79:
72:
64:
1249:Music
957:, on
912:(PDF)
557:Latin
352:Cumae
245:Baiae
241:Cumae
229:Capua
182:Livio
166:Oscor
142:Capua
98:JSTOR
84:books
1254:Flag
936:ISBN
920:2024
884:ISSN
643:2021
611:ISBN
588:1889
492:Rome
437:Livy
421:and
308:Sele
287:and
257:Nola
184:and
70:news
876:doi
368:'s
136:or
53:by
1285::
882:.
870:.
821:^
794:^
743:^
726:^
663:^
633:.
595:^
582:,
563:.
527:.
453:c.
299:.
283:,
279:,
275:,
271:,
267:,
263:,
259:,
255:,
251:,
247:,
243:,
239:,
235:,
231:,
987:e
980:t
973:v
942:.
922:.
890:.
878::
645:.
619:.
590:.
451:(
160:(
120:)
114:(
109:)
105:(
95:·
88:·
81:·
74:·
47:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.