269:
abnormally highly arched palate is also seen in affected individuals causing dental problems and the thrusting forward of the lower jaw. Individuals affected by
Carpenter syndrome often experience cutaneous syndactyly (fusion of the digits) or polydactyly (presence of extra digits) of the toes more often than fingers. Individuals also have short fingers. Approximately one third of individuals born with Carpenter syndrome have a type of heart defect. Commonly seen heart defects may include: narrowing of the pulmonary artery, transposition of the major blood vessels, or the presence of an abnormally large vena cava, which delivers blood back to the heart from the head, neck, and upper limbs. The testes of males affected by Carpenter syndrome may also fail to descend (Paul A. Johnson, 2002).
191:, (ACPS) (RN, 2007). There were originally five types of ACPS, but this number has been decreased because they have been found to be closely related to one another or to other disorders (Paul A. Johnson, 2002). The most common physical manifestation of Carpenter syndrome is early fusing of the fibrous cranial sutures which results in an abnormally pointed head. The fusion of the skull bones is evident from birth (National Organization for Rare Disorders, Inc., 2008). Babies' mobile cranial bones form a cone shape as they pass through the birth canal and soon thereafter return to a normal shape; however, a baby affected by carpenter syndrome maintains a cone shaped head.
278:
easier to do when the skull is still constantly growing and changing. In surgery the doctor breaks the fused sutures to allow for brain growth. Doctors remove the cranial plates of the skull, reshape them and replace them back onto the skull in an attempt to reshape the head to appear more normal. Although the sutures are broken during surgery they will quickly refuse, and in some cases holes form in the plates allowing cerebral spinal fluid to escape into cyst like structures on the external surface of the head.
64:
265:
much smaller than normal and often cause visual impairment. Complications may include damage to the optic nerve, resulting in a decrease in visual clarity, bulging eyeballs as a result of shallow eye orbits which usually causes some sort of damage to the cornea (the outer layer of the eye). Bicoronal craniosynostosis may also result in widely spaced eyes and narrowing of the sinuses and tear ducts that may result in inflammation of the mucous membranes of the exposed portion of the eye.
40:
127:
208:
135:
261:
posterior (front to back) diameter of the skull. An increased A-P diameter indicates a malformed fusion of the sagittal suture. Individuals affected with sagittal craniosynostosis have narrow, prominent foreheads and the back of the head is much larger than normal. The "soft spot" is very small or missing altogether with this particular type of craniosynostosis.
199:
fingers are commonly missing an interphalangeal joint. Roughly half of the babies born with
Carpenter syndrome have some type of heart defect, and seventy five percent of individuals with this disease will experience some degree of development delay due to mild intellectual disability (Carpenter syndrome-description).
268:
In addition to the previously named complications of bicoronal craniosynostosis, many babies will also be affected by hydrocephalus, more commonly known as water on the brain. Hydrocephalus results in increased pressure on the brain which can cause permanent brain damage if not treated promptly. An
251:
The diagnosis of
Carpenter syndrome is made based on the presence of the bicoronal and sagittal skull malformations, which results in a pointed, cone-shaped or short, broad head. The diagnosis is also made based on the presence of extra or fused digits. X rays and/ or CT scans of the skull may be
194:
A baby affected by
Carpenter syndrome will also display malformations of the face. An individual affected by the syndrome may have broad cheeks, a flat nasal bridge, and a wide upturned nose with abnormally large nasal openings. Their ears will most commonly be low, unevenly set, and malformed in
264:
The second common type of skull malformation is bicoronal craniosynostosis is characterized by a wide, short skull. In this particular type of craniosynostosis the A-P diameter is smaller than in normal individuals. These individuals have malformed eye sockets and foreheads. The eye sockets are
281:
If an individual with
Carpenter syndrome has a serious heart defect they will require surgery to correct the malformation of the heart. Other elective surgeries may also be performed. Some parents opt to have their child's webbed fingers or toes separated which improves their appearance but not
198:
Other physical abnormalities associated with
Carpenter syndrome include extra digits. Extra toes are more commonly seen than fingers. Often both the toes and fingers are webbed, a process that occurs before the sixth week gestational period. Often their digits will be abnormally short, and the
297:
Carpenter syndrome is an autosomal recessive disease which means both parents must have the faulty genes in order to pass the disease onto their children. Even if both parents possess the faulty gene there is still only a twenty five percent chance that they will produce a child affected by the
260:
The primary diagnostic factor is a malformation of the skull. The two most common types of craniosynostosis are sagittal and bicoronal. Sagittal craniosynostosis manifests itself by causing a long narrow skull, resembling a football. It is quantitatively determined by measuring the anterior to
277:
Operations to correct the malformations of the skull should be performed within the first year of infancy in patients affected by
Carpenter syndrome. Performing surgery at a young age increases the likelihood of obtaining a greatly improved appearance of the head because modifying bone is much
195:
structure. In addition to these facial abnormalities, individuals also have an underdeveloped maxilla and/or mandible with a highly arched and narrow palate which makes speech a very difficult skill to master. Teeth are usually very late to come in and will be undersized and spaced far apart.
285:
In order to address the vision problems that are associated with bicoronal craniosynostosis, the individual must seek consultation from an ophthalmologist. If the palate is severely affected dental consultation may be necessary to correct the malformation. Obesity is often associated with
282:
necessarily the functionality of the digits. In order to address the occupational challenges of the disease, many children with
Carpenter Syndrome go through speech and occupational therapy in order to achieve more independence in everyday tasks and activities (RN, 2007).
286:
Carpenter syndrome, so a lifelong diet plan is often utilized to maintain a healthy weight. In addition surgery must be performed if the testes fail to descend (Paul A. Johnson, 2002). If the procedure is not performed the individual will become infertile.
1254:
252:
performed in order to accurately diagnose the individual; however, other genetic disorders, which have available genetic tests, are also characterized by skull malformations. A positive result on these tests can rule out a
Carpenter syndrome diagnosis.
676:
1247:
536:
Jenkins, D; Seelow, D; Jehee, Fs; Perlyn, Ca; Alonso, Lg; Bueno, Df; Donnai, D; Josifova, D; Mathijssen, Im; Morton, Je; Orstavik, Kh; Sweeney, E; Wall, Sa; Marsh, Jl; Nurnberg, P; Passos-Bueno, Mr; Wilkie, Ao (June 2007).
586:
Twigg, SR; Lloyd, D; Jenkins, D; Elçioglu, NE; Cooper, CD; Al-Sannaa, N; Annagür, A; Gillessen-Kaesbach, G; Hüning, I; Knight, SJ; Goodship, JA; Keavney, BD; Beales, PL; Gileadi, O; McGowan, SJ; Wilkie, AO (Nov 2, 2012).
1240:
298:
syndrome. Their children who do not have the disease will still be carriers and possess the ability to pass the disease onto their offspring if their spouse is also a carrier of the particular gene.
294:
There are approximately three hundred known cases of
Carpenter syndrome in the United States. Only 1 in 1 million live births will result in an infant affected by Carpenter syndrome (RN, 2007).
787:
2009:
2039:
780:
1787:
1036:
773:
1639:
1966:
843:
501:
Frias, Jl; Felman, Ah; Rosenbloom, Al; Finkelstein, Sn; Hoyt, Wf; Hall, Bd (1978). "Normal intelligence in two children with Carpenter syndrome".
1385:
838:
312:
2029:
1718:
1994:
1502:
1457:
1395:
938:
691:
331:
1856:
1326:
1306:
1316:
1051:
976:
1871:
453:
1076:
1566:
1375:
1331:
539:"RAB23 mutations in Carpenter syndrome imply an unexpected role for hedgehog signaling in cranial-suture development and obesity"
1041:
2034:
1138:
350:
Perlyn, Ca; Marsh, Jl (March 1909). "Craniofacial dysmorphology of Carpenter syndrome: lessons from three affected siblings".
1370:
1269:
234:
986:
1574:
1522:
1440:
1792:
1390:
943:
833:
1816:
1770:
1598:
1046:
928:
589:"Mutations in multidomain protein MEGF8 identify a Carpenter syndrome subtype associated with defective lateralization"
307:
1613:
1166:
958:
1698:
1607:
1321:
1102:
898:
853:
1001:
908:
1656:
1550:
1097:
981:
1924:
1485:
1278:
104:
1670:
1232:
1980:
1380:
1354:
1286:
1056:
893:
805:
702:
1758:
1705:
1511:
966:
176:
115:
971:
1684:
1362:
796:
753:
243:
gene, located on chromosome 19 at 19q13.2, have been identified as primary causes of Carpenter syndrome.
1802:
1205:
1193:
1177:
1149:
873:
813:
188:
108:
1161:
1145:
1133:
1121:
476:
88:
84:
63:
1028:
1016:
1840:
1710:
1366:
1296:
863:
375:
179:
is also common with the disorder, although some patients may have average intellectual capacity.
1421:
1126:
913:
903:
828:
713:
618:
568:
518:
449:
424:
367:
52:
443:
1918:
1835:
1732:
1627:
1536:
1210:
1186:
1066:
1061:
923:
868:
608:
600:
558:
550:
510:
414:
406:
359:
57:
1830:
1797:
1724:
1435:
1291:
1198:
1182:
1170:
1154:
1081:
948:
933:
918:
1952:
1810:
1738:
1219:
1071:
818:
613:
588:
563:
538:
419:
394:
363:
2023:
885:
379:
126:
39:
1405:
991:
765:
230:
146:
707:
1781:
1589:
1011:
212:
152:
100:
718:
604:
410:
1899:
1006:
685:
158:
96:
1885:
1345:
724:
514:
134:
622:
572:
428:
371:
207:
995:
858:
748:
522:
220:
81:
668:
1946:
1938:
1932:
1865:
1650:
164:
92:
1974:
1960:
1879:
1824:
1585:
1530:
680:
554:
1692:
1678:
1664:
1621:
1516:
1479:
1465:
1451:
729:
239:
225:
206:
133:
125:
1988:
1893:
1752:
1746:
1544:
1496:
1429:
1415:
696:
335:
1236:
769:
187:
Carpenter syndrome belongs to a rare genetic disorder known as
1263:
Deficiencies of intracellular signaling peptides and proteins
395:"Case of acrocephaly with other congenital malformations"
211:
Carpenter syndrome has an autosomal recessive pattern of
138:
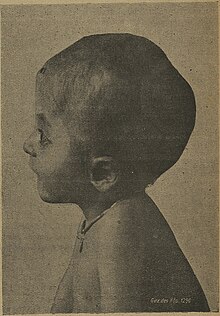
Symptoms of Carpenter syndrome in an 8-year-old boy, 1919
634:
632:
483:. National Center for Advancing Transnational Sciences
448:. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 25.
114:
It was first characterized in 1909, and is named for
658:
1910:
1855:
1769:
1638:
1597:
1583:
1565:
1404:
1353:
1344:
1305:
1277:
1268:
1111:
1090:
1027:
957:
884:
804:
739:
662:
51:
29:
24:
442:Beighton, Peter; Beighton, Greta (2012-12-06).
142:Carpenter syndrome presents several features:
2010:intracellular signaling peptides and proteins
1248:
781:
8:
481:Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center
399:Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine
219:Carpenter syndrome has been associated with
1594:
1350:
1274:
1255:
1241:
1233:
788:
774:
766:
659:
62:
47:Original case described by Carpenter, 1909
38:
21:
2040:Syndromes with craniofacial abnormalities
1872:EDARADD Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
612:
562:
418:
405:(Sect Study Dis Child): 45–53, 199–201.
345:
343:
324:
155:– additional digits (fingers and toes)
87:congenital disorder characterized by
7:
1503:Neutrophil immunodeficiency syndrome
1386:Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy
503:American Journal of Medical Genetics
1857:Signal transducing adaptor proteins
647:Carpenter Syndrom-What is it?, 2007
332:Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man
233:in humans. Additionally, three key
1441:KRAS Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome
1332:X-linked intellectual disability 1
1327:Juvenile primary lateral sclerosis
593:American Journal of Human Genetics
543:American Journal of Human Genetics
364:10.1097/01.prs.0000299284.92862.6c
352:Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
130:Polydactyly in original case, 1909
14:
1788:Bannayan–Riley–Ruvalcaba syndrome
1037:Bannayan–Riley–Ruvalcaba syndrome
78:acrocephalopolysyndactyly type II
33:Acrocephalopolysyndactyly type II
1376:Progressive osseous heteroplasia
111:that presents with polydactyly.
1981:PRKCSH Polycystic liver disease
1967:Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome
1371:Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism
1270:GTP-binding protein regulators
844:Bonnet–Dechaume–Blanc syndrome
1:
2030:Autosomal recessive disorders
1575:Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome
1523:Chylomicron retention disease
839:Sakati–Nyhan–Tisdale syndrome
313:Sakati–Nyhan–Tisdale syndrome
1817:X-linked myotubular myopathy
1077:Tatton-Brown–Rahman syndrome
1047:Benign symmetric lipomatosis
1614:X-linked agammaglobulinemia
1458:Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease
1167:Branchio-oto-renal syndrome
1042:Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome
445:The Man Behind the Syndrome
2056:
1317:Marinesco–Sjögren syndrome
1139:Zimmermann–Laband syndrome
1091:Laurence–Moon–Bardet–Biedl
1052:Klippel–Trénaunay syndrome
1002:Caudal regression syndrome
977:Klippel–Trénaunay syndrome
939:Smith–Lemli–Opitz syndrome
909:Cornelia de Lange syndrome
605:10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.08.027
411:10.1177/003591570900201418
229:gene, which is located on
2005:
1925:Neurofibromatosis type II
1759:Pseudohypoaldosteronism 2
1486:Griscelli syndrome type 2
1279:GTPase-activating protein
987:Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome
105:Acrocephalopolysyndactyly
46:
37:
1793:Lhermitte–Duclos disease
1391:McCune–Albright syndrome
1381:Pseudohypoparathyroidism
1287:Neurofibromatosis type I
1057:Neurofibromatosis type I
944:Snyder–Robinson syndrome
894:1q21.1 deletion syndrome
834:Saethre–Chotzen syndrome
708:C563187 C563187, C563187
1551:Bardet–Biedl syndrome 3
967:Adducted thumb syndrome
929:Silver–Russell syndrome
515:10.1002/ajmg.1320020210
308:Cole–Carpenter syndrome
177:Intellectual disability
116:George Alfred Carpenter
80:, is an extremely rare
2035:Rare genetic syndromes
1699:Peutz–Jeghers syndrome
1685:Incontinentia pigmenti
1671:Li–Fraumeni syndrome 2
1322:Aarskog–Scott syndrome
1103:Laurence–Moon syndrome
899:Aarskog–Scott syndrome
854:Baller–Gerold syndrome
797:Congenital abnormality
216:
139:
131:
1803:Proteus-like syndrome
1657:Coffin-Lowry syndrome
1098:Bardet–Biedl syndrome
982:Nail–patella syndrome
874:Pierre Robin sequence
814:Acrocephalosyndactyly
638:Paul A. Johnson, 2002
210:
189:acrocephalosyndactyly
137:
129:
109:acrocephalosyndactyly
1711:Myotonic dystrophy 1
1029:Overgrowth syndromes
477:"Carpenter syndrome"
393:Carpenter G (1909).
149:– tower-shaped skull
1017:VACTERL association
1841:Metachondromatosis
1537:Joubert syndrome 8
1472:Carpenter syndrome
1307:Guanine nucleotide
1297:Tuberous sclerosis
972:Holt–Oram syndrome
864:Goldenhar syndrome
824:Carpenter syndrome
740:External resources
217:
172:Undescended testes
140:
132:
107:is a variation of
74:Carpenter syndrome
25:Carpenter syndrome
2017:
2016:
1851:
1850:
1831:Noonan syndrome 1
1725:Seckel syndrome 1
1561:
1560:
1436:Noonan syndrome 3
1422:Costello syndrome
1340:
1339:
1230:
1229:
1127:Feingold syndrome
914:Dubowitz syndrome
904:Cockayne syndrome
829:Pfeiffer syndrome
763:
762:
71:
70:
19:Medical condition
16:Medical Condition
2047:
1836:LEOPARD syndrome
1739:Oguchi disease 2
1640:Serine/threonine
1628:ZAP70 deficiency
1595:
1351:
1275:
1257:
1250:
1243:
1234:
1211:Donohue syndrome
1187:Timothy syndrome
1067:Proteus syndrome
1062:Perlman syndrome
924:Robinow syndrome
869:Moebius syndrome
790:
783:
776:
767:
660:
648:
645:
639:
636:
627:
626:
616:
583:
577:
576:
566:
533:
527:
526:
498:
492:
491:
489:
488:
473:
467:
466:
464:
462:
439:
433:
432:
422:
390:
384:
383:
347:
338:
329:
67:
66:
58:Medical genetics
42:
22:
2055:
2054:
2050:
2049:
2048:
2046:
2045:
2044:
2020:
2019:
2018:
2013:
2001:
1906:
1847:
1798:Cowden syndrome
1772:
1765:
1641:
1634:
1599:Tyrosine kinase
1579:
1557:
1400:
1336:
1309:exchange factor
1308:
1301:
1292:Watson syndrome
1264:
1261:
1231:
1226:
1199:Marfan syndrome
1183:Keutel syndrome
1171:CHARGE syndrome
1155:Fraser syndrome
1113:
1112:Combined/other,
1107:
1086:
1082:Weaver syndrome
1023:
953:
949:Turner syndrome
934:Seckel syndrome
919:Noonan syndrome
880:
800:
794:
764:
759:
758:
735:
734:
671:
657:
652:
651:
646:
642:
637:
630:
585:
584:
580:
535:
534:
530:
500:
499:
495:
486:
484:
475:
474:
470:
460:
458:
456:
441:
440:
436:
392:
391:
387:
349:
348:
341:
330:
326:
321:
304:
292:
275:
258:
249:
205:
185:
124:
91:malformations,
61:
20:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2053:
2051:
2043:
2042:
2037:
2032:
2022:
2021:
2015:
2014:
2006:
2003:
2002:
2000:
1999:
1998:
1997:
1985:
1984:
1983:
1971:
1970:
1969:
1957:
1956:
1955:
1953:Carney complex
1943:
1942:
1941:
1929:
1928:
1927:
1914:
1912:
1908:
1907:
1905:
1904:
1903:
1902:
1890:
1889:
1888:
1876:
1875:
1874:
1861:
1859:
1853:
1852:
1849:
1848:
1846:
1845:
1844:
1843:
1838:
1833:
1821:
1820:
1819:
1807:
1806:
1805:
1800:
1795:
1790:
1777:
1775:
1767:
1766:
1764:
1763:
1762:
1761:
1743:
1742:
1741:
1729:
1728:
1727:
1715:
1714:
1713:
1703:
1702:
1701:
1689:
1688:
1687:
1675:
1674:
1673:
1661:
1660:
1659:
1646:
1644:
1636:
1635:
1633:
1632:
1631:
1630:
1618:
1617:
1616:
1603:
1601:
1592:
1581:
1580:
1578:
1577:
1571:
1569:
1563:
1562:
1559:
1558:
1556:
1555:
1554:
1553:
1541:
1540:
1539:
1527:
1526:
1525:
1508:
1507:
1506:
1505:
1491:
1490:
1489:
1488:
1476:
1475:
1474:
1462:
1461:
1460:
1446:
1445:
1444:
1443:
1438:
1426:
1425:
1424:
1410:
1408:
1402:
1401:
1399:
1398:
1393:
1388:
1383:
1378:
1373:
1359:
1357:
1348:
1342:
1341:
1338:
1337:
1335:
1334:
1329:
1324:
1319:
1313:
1311:
1303:
1302:
1300:
1299:
1294:
1289:
1283:
1281:
1272:
1266:
1265:
1262:
1260:
1259:
1252:
1245:
1237:
1228:
1227:
1225:
1224:
1223:
1222:
1220:Fryns syndrome
1214:
1202:
1190:
1174:
1158:
1142:
1130:
1117:
1115:
1109:
1108:
1106:
1105:
1100:
1094:
1092:
1088:
1087:
1085:
1084:
1079:
1074:
1072:Sotos syndrome
1069:
1064:
1059:
1054:
1049:
1044:
1039:
1033:
1031:
1025:
1024:
1022:
1021:
1020:
1019:
1014:
1009:
1004:
989:
984:
979:
974:
969:
963:
961:
955:
954:
952:
951:
946:
941:
936:
931:
926:
921:
916:
911:
906:
901:
896:
890:
888:
882:
881:
879:
878:
877:
876:
871:
866:
861:
856:
848:
847:
846:
841:
836:
831:
826:
821:
819:Apert syndrome
810:
808:
802:
801:
795:
793:
792:
785:
778:
770:
761:
760:
757:
756:
744:
743:
741:
737:
736:
733:
732:
721:
710:
699:
688:
672:
667:
666:
664:
663:Classification
656:
655:External links
653:
650:
649:
640:
628:
599:(5): 897–905.
578:
555:10.1086/518047
549:(6): 1162–70.
528:
493:
468:
454:
434:
385:
339:
323:
322:
320:
317:
316:
315:
310:
303:
300:
291:
288:
274:
271:
257:
254:
248:
245:
204:
201:
184:
181:
174:
173:
170:
169:Reduced height
167:
162:
161:– fused digits
156:
150:
123:
120:
76:, also called
69:
68:
55:
49:
48:
44:
43:
35:
34:
31:
27:
26:
18:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2052:
2041:
2038:
2036:
2033:
2031:
2028:
2027:
2025:
2012:
2011:
2004:
1996:
1993:
1992:
1991:
1990:
1986:
1982:
1979:
1978:
1977:
1976:
1972:
1968:
1965:
1964:
1963:
1962:
1958:
1954:
1951:
1950:
1949:
1948:
1944:
1940:
1937:
1936:
1935:
1934:
1930:
1926:
1923:
1922:
1921:
1920:
1916:
1915:
1913:
1909:
1901:
1898:
1897:
1896:
1895:
1891:
1887:
1884:
1883:
1882:
1881:
1877:
1873:
1870:
1869:
1868:
1867:
1863:
1862:
1860:
1858:
1854:
1842:
1839:
1837:
1834:
1832:
1829:
1828:
1827:
1826:
1822:
1818:
1815:
1814:
1813:
1812:
1808:
1804:
1801:
1799:
1796:
1794:
1791:
1789:
1786:
1785:
1784:
1783:
1779:
1778:
1776:
1774:
1768:
1760:
1757:
1756:
1755:
1754:
1749:
1748:
1744:
1740:
1737:
1736:
1735:
1734:
1730:
1726:
1723:
1722:
1721:
1720:
1716:
1712:
1709:
1708:
1707:
1704:
1700:
1697:
1696:
1695:
1694:
1690:
1686:
1683:
1682:
1681:
1680:
1676:
1672:
1669:
1668:
1667:
1666:
1662:
1658:
1655:
1654:
1653:
1652:
1648:
1647:
1645:
1643:
1637:
1629:
1626:
1625:
1624:
1623:
1619:
1615:
1612:
1611:
1610:
1609:
1605:
1604:
1602:
1600:
1596:
1593:
1591:
1587:
1582:
1576:
1573:
1572:
1570:
1568:
1564:
1552:
1549:
1548:
1547:
1546:
1542:
1538:
1535:
1534:
1533:
1532:
1528:
1524:
1521:
1520:
1519:
1518:
1513:
1510:
1509:
1504:
1501:
1500:
1499:
1498:
1493:
1492:
1487:
1484:
1483:
1482:
1481:
1477:
1473:
1470:
1469:
1468:
1467:
1463:
1459:
1456:
1455:
1454:
1453:
1448:
1447:
1442:
1439:
1437:
1434:
1433:
1432:
1431:
1427:
1423:
1420:
1419:
1418:
1417:
1412:
1411:
1409:
1407:
1403:
1397:
1394:
1392:
1389:
1387:
1384:
1382:
1379:
1377:
1374:
1372:
1368:
1364:
1361:
1360:
1358:
1356:
1355:Heterotrimeic
1352:
1349:
1347:
1343:
1333:
1330:
1328:
1325:
1323:
1320:
1318:
1315:
1314:
1312:
1310:
1304:
1298:
1295:
1293:
1290:
1288:
1285:
1284:
1282:
1280:
1276:
1273:
1271:
1267:
1258:
1253:
1251:
1246:
1244:
1239:
1238:
1235:
1221:
1218:
1217:
1215:
1212:
1208:
1207:
1203:
1200:
1196:
1195:
1191:
1188:
1184:
1180:
1179:
1175:
1172:
1168:
1164:
1163:
1159:
1156:
1152:
1151:
1147:
1143:
1140:
1136:
1135:
1131:
1128:
1124:
1123:
1119:
1118:
1116:
1110:
1104:
1101:
1099:
1096:
1095:
1093:
1089:
1083:
1080:
1078:
1075:
1073:
1070:
1068:
1065:
1063:
1060:
1058:
1055:
1053:
1050:
1048:
1045:
1043:
1040:
1038:
1035:
1034:
1032:
1030:
1026:
1018:
1015:
1013:
1010:
1008:
1005:
1003:
1000:
999:
997:
993:
990:
988:
985:
983:
980:
978:
975:
973:
970:
968:
965:
964:
962:
960:
956:
950:
947:
945:
942:
940:
937:
935:
932:
930:
927:
925:
922:
920:
917:
915:
912:
910:
907:
905:
902:
900:
897:
895:
892:
891:
889:
887:
886:Short stature
883:
875:
872:
870:
867:
865:
862:
860:
857:
855:
852:
851:
849:
845:
842:
840:
837:
835:
832:
830:
827:
825:
822:
820:
817:
816:
815:
812:
811:
809:
807:
803:
798:
791:
786:
784:
779:
777:
772:
771:
768:
755:
751:
750:
746:
745:
742:
738:
731:
727:
726:
722:
720:
716:
715:
711:
709:
705:
704:
700:
698:
694:
693:
689:
687:
683:
682:
678:
674:
673:
670:
665:
661:
654:
644:
641:
635:
633:
629:
624:
620:
615:
610:
606:
602:
598:
594:
590:
582:
579:
574:
570:
565:
560:
556:
552:
548:
544:
540:
532:
529:
524:
520:
516:
512:
508:
504:
497:
494:
482:
478:
472:
469:
457:
455:9781447114154
451:
447:
446:
438:
435:
430:
426:
421:
416:
412:
408:
404:
400:
396:
389:
386:
381:
377:
373:
369:
365:
361:
358:(3): 971–81.
357:
353:
346:
344:
340:
337:
333:
328:
325:
318:
314:
311:
309:
306:
305:
301:
299:
295:
289:
287:
283:
279:
272:
270:
266:
262:
255:
253:
246:
244:
242:
241:
236:
232:
228:
227:
222:
214:
209:
202:
200:
196:
192:
190:
182:
180:
178:
171:
168:
166:
163:
160:
157:
154:
151:
148:
145:
144:
143:
136:
128:
121:
119:
117:
112:
110:
106:
102:
98:
94:
90:
86:
83:
79:
75:
65:
59:
56:
54:
50:
45:
41:
36:
32:
28:
23:
2007:
1987:
1973:
1959:
1945:
1931:
1917:
1892:
1878:
1864:
1823:
1809:
1780:
1751:
1745:
1731:
1717:
1691:
1677:
1663:
1649:
1620:
1606:
1543:
1529:
1515:
1495:
1478:
1471:
1464:
1450:
1428:
1414:
1204:
1192:
1176:
1160:
1144:
1132:
1120:
992:Gastrulation
823:
806:Craniofacial
747:
723:
712:
701:
690:
675:
643:
596:
592:
581:
546:
542:
531:
509:(2): 191–9.
506:
502:
496:
485:. Retrieved
480:
471:
459:. Retrieved
444:
437:
402:
398:
388:
355:
351:
327:
296:
293:
284:
280:
276:
267:
263:
259:
250:
238:
231:chromosome 6
224:
218:
197:
193:
186:
175:
147:Turricephaly
141:
122:Presentation
113:
89:craniofacial
77:
73:
72:
1773:phosphatase
1590:phosphatase
1114:known locus
1012:Sirenomelia
213:inheritance
183:Description
153:Polydactyly
101:polydactyly
30:Other names
2024:Categories
1900:Zaspopathy
1567:MAP kinase
1007:Ectromelia
714:DiseasesDB
487:2021-02-19
319:References
290:Occurrence
159:Syndactyly
97:syndactyly
2008:See also
1886:Cherubism
1406:Monomeric
1346:G protein
1216:Multiple
799:syndromes
730:205813009
725:SNOMED CT
273:Treatment
247:Diagnosis
221:mutations
85:recessive
82:autosomal
53:Specialty
1771:Tyrosine
996:mesoderm
859:Cyclopia
749:Orphanet
623:23063620
573:17503333
461:7 August
429:19974019
380:21493967
372:18317146
334:(OMIM):
302:See also
203:Genetics
1947:PRKAR1A
1939:CADASIL
1933:Notch 3
1866:EDARADD
1651:RPS6KA3
614:3487118
564:1867103
420:2047261
237:in the
223:in the
165:Obesity
93:obesity
1975:PRKCSH
1961:PRKAG2
1880:SH3BP2
1825:PTPN11
1642:kinase
1586:kinase
1584:Other
1531:ARL13B
850:Other
697:201000
621:
611:
571:
561:
523:263437
521:
452:
427:
417:
378:
370:
336:201000
99:, and
60:
1995:XIAP2
1911:Other
1693:STK11
1679:IKBKG
1665:CHEK2
1622:ZAP70
1517:SAR1B
1494:RHO:
1480:RAB27
1466:RAB23
1449:RAB:
1413:RAS:
1396:CGL 2
1367:GNAS1
959:Limbs
754:65759
719:29583
686:Q87.0
376:S2CID
256:Types
240:MEGF8
226:RAB23
1989:XIAP
1894:LDB3
1811:MTM1
1782:PTEN
1753:WNK1
1747:WNK4
1733:GRK1
1706:DMPK
1545:ARL6
1497:RAC2
1452:RAB7
1430:KRAS
1416:HRAS
1363:cAMP
703:MeSH
692:OMIM
619:PMID
569:PMID
519:PMID
463:2018
450:ISBN
425:PMID
368:PMID
235:SNPs
1919:NF2
1719:ATR
1608:BTK
1512:ARF
677:ICD
609:PMC
601:doi
559:PMC
551:doi
511:doi
415:PMC
407:doi
360:doi
356:121
2026::
1514::
1369::
1206:19
1194:15
1185:,
1178:12
1169:,
1150:13
998::
752::
728::
717::
706::
695::
684::
681:10
631:^
617:.
607:.
597:91
595:.
591:.
567:.
557:.
547:80
545:.
541:.
517:.
505:.
479:.
423:.
413:.
401:.
397:.
374:.
366:.
354:.
342:^
118:.
103:.
95:,
1750:/
1588:/
1365:/
1256:e
1249:t
1242:v
1213:)
1209:(
1201:)
1197:(
1189:)
1181:(
1173:)
1165:(
1162:8
1157:)
1153:(
1148:/
1146:4
1141:)
1137:(
1134:3
1129:)
1125:(
1122:2
994:/
789:e
782:t
775:v
679:-
669:D
625:.
603::
575:.
553::
525:.
513::
507:2
490:.
465:.
431:.
409::
403:2
382:.
362::
215:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.