1570:
size, Pom1 concentration decreases in the middle and becomes concentrated at cell ends. Small cells in early G2 which contain sufficient levels of Pom1 in the entirety of the cell have inactive Cdr2 and cannot enter mitosis. It is not until the cells grow into late G2, when Pom1 is confined to the cell ends that Cdr2 in the medial cortical nodes is activated and able to start the inhibition of Wee1. This finding shows how cell size plays a direct role in regulating the start of mitosis. In this model, Pom1 acts as a molecular link between cell growth and mitotic entry through a Cdr2-Cdr1-Wee1-Cdk1 pathway. The Pom1 polar gradient successfully relays information about cell size and geometry to the Cdk1 regulatory system. Through this gradient, the cell ensures it has reached a defined, sufficient size to enter mitosis.
1544:-tagged proteins and mutant proteins indicates that the medial cortical nodes are formed by the ordered, Cdr2-dependent assembly of multiple interacting proteins during interphase. Cdr2 is at the top of this hierarchy and works upstream of Cdr1 and Blt1. Mitosis is promoted by the negative regulation of Wee1 by Cdr2. It has also been shown that Cdr2 recruits Wee1 to the medial cortical node. The mechanism of this recruitment has yet to be discovered. A Cdr2 kinase mutant, which is able to localize properly despite a loss of function in phosphorylation, disrupts the recruitment of Wee1 to the medial cortex and delays entry into mitosis. Thus, Wee1 localizes with its inhibitory network, which demonstrates that mitosis is controlled through Cdr2-dependent negative regulation of Wee1 at the medial cortical nodes.
1566:, a member of the dual-specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation regulated kinase (DYRK) family of kinases, localizes to cell ends. In Pom1 knockout cells, Cdr2 was no longer restricted to the cell middle, but was seen diffusely through half of the cell. From this data it becomes apparent that Pom1 provides inhibitory signals that confine Cdr2 to the middle of the cell. It has been further shown that Pom1-dependent signals lead to the phosphorylation of Cdr2. Pom1 knockout cells were also shown to divide at a smaller size than wild-type, which indicates a premature entry into mitosis.
921:
1808:
1824:, the DNA content of a cell can be represented as the amount Z (the cell has Z chromosomes). After the DNA replication process, the amount of DNA in the cell is 2Z (multiplication: 2 x Z = 2Z). During Binary fission and mitosis the duplicated DNA content of the reproducing parental cell is separated into two equal halves that are destined to end up in the two daughter cells. The final part of the cell reproduction process is
759:
1474:
1466:. For some cells, there is a mechanism by which cell division is not initiated until a cell has reached a certain size. If the nutrient supply is restricted (after time t = 2 in the diagram, below), and the rate of increase in cell size is slowed, the time period between cell divisions is increased. Yeast cell-size mutants were isolated that begin cell division before reaching a normal/regular size (
20:
2017:. The total mass of a cell, which comprises the mass of all its components including its water content, is a dynamic magnitude and it can be measured in real-time and tracked over hours or even days using an inertial picobalance. A cell's buoyant mass, which corresponds to the total mass of the cell minus that of the fluid it displaces, can be measured using suspended microchannel resonators.
746:
44:
1537:, was found to colocalize with Cdr2 in the medial interphase nodes. Blt1 knockout cells had increased length at division, which is consistent with a delay in mitotic entry. This finding connects a physical location, a band of cortical nodes, with factors that have been shown to directly regulate mitotic entry, namely Cdr1, Cdr2, and Blt1.
1926:. This process can also produce new combinations of genes, some of which may be adaptively beneficial and influence the course of evolution. However, in organisms with more than one set of chromosomes at the main life cycle stage, sex may also provide an advantage because, under random mating, it produces
1831:
After the completion of binary fission or cell reproduction involving mitosis, each daughter cell has the same amount of DNA (Z) as what the parental cell had before it replicated its DNA. These two types of cell reproduction produced two daughter cells that have the same number of chromosomes as the
1403:
A postulated model for mammalian size control situates mass as the driving force of the cell cycle. A cell is unable to grow to an abnormally large size because at a certain cell size or cell mass, the S phase is initiated. The S phase starts the sequence of events leading to mitosis and cytokinesis.
1660:
cell size is controlled by a simple mechanisms in which cell division occurs after a constant volume has been added since the previous division. By always growing by the same amount, cells born smaller or larger than average naturally converge to an average size equivalent to the amount added during
1569:
Pom1 forms polar gradients that peak at cell ends, which shows a direct link between size control factors and a specific physical location in the cell. As a cell grows in size, a gradient in Pom1 grows. When cells are small, Pom1 is spread diffusely throughout the cell body. As the cell increases in
1399:
One disputed theory proposes that many different mammalian cells undergo size-dependent transitions during the cell cycle. These transitions are controlled by the cyclin-dependent kinase Cdk1. Though the proteins that control Cdk1 are well understood, their connection to mechanisms monitoring cell
1504:
removes the inhibitory phosphorylation, and thus activates Cdc2 to allow mitotic entry. A balance of Wee1 and Cdc25 activity with changes in cell size is coordinated by the mitotic entry control system. It has been shown in Wee1 mutants, cells with weakened Wee1 activity, that Cdc2 becomes active
1876:
Immediately after DNA replication a human cell will have 46 "double chromosomes". In each double chromosome there are two copies of that chromosome's DNA molecule. During mitosis the double chromosomes are split to produce 92 "single chromosomes", half of which go into each daughter cell. During
1376:
activity so that when animals are well fed they will grow rapidly and when they are not able to receive sufficient nutrients they will reduce their growth rate. Recently it has been also demonstrated that cellular bicarbonate metabolism, which is responsible for cell growth, can be regulated by
1025:
can be unusually large cells in species for which embryonic development takes place away from the mother's body within an egg that is laid externally. The large size of some eggs can be achieved either by pumping in cytosolic components from adjacent cells through cytoplasmic bridges named ring
1869:
1424:
of cells should be twice as numerous as the previous generation. However, the number of generations only gives a maximum figure as not all cells survive in each generation. Cells can reproduce in the stage of
Mitosis, where they double and split into two genetically equal cells.
1779:
division processes. Binary fission is similar to eukaryote cell reproduction that involves mitosis. Both lead to the production of two daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parental cell. Meiosis is used for a special cell reproduction process of
1865:. There are two distinct sex chromosomes, the X chromosome and the Y chromosome. A diploid human cell has 23 chromosomes from that person's father and 23 from the mother. That is, your body has two copies of human chromosome number 2, one from each of your parents.
1445:
can be 330 μm long, while a typical human cell might be 10 μm. How these cells "decide" how big they should be before dividing is an open question. Chemical gradients are known to be partly responsible, and it is hypothesized that mechanical stress detection by
1803:
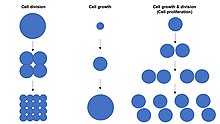
The rest of this article is a comparison of the main features of the three types of cell reproduction that either involve binary fission, mitosis, or meiosis. The diagram below depicts the similarities and differences of these three types of cell reproduction.
2039:
All these assays may correlate well, or not, depending on cell growth conditions and desired aspects (activity, proliferation). The task is even more complicated with populations of different cells, furthermore when combining cell growth interferences or
1913:
events. Information from the chromosome 2 DNA gained from one parent (red) will transfer over to the chromosome 2 DNA molecule that was received from the other parent (green). Notice that in mitosis the two copies of chromosome number 2 do not interact.
1832:
parental cell. Chromosomes duplicate prior to cell division when forming new skin cells for reproduction. After meiotic cell reproduction the four daughter cells have half the number of chromosomes that the parental cell originally had. This is the
956:
and thus undergo cell growth at only half the rate of two cells. Hence, two cells grow (accumulate mass) at twice the rate of a single cell, and four cells grow at 4-times the rate of a single cell. This principle leads to an
2008:
allows combining cell counts ('events') with other specific parameters: fluorescent probes for membranes, cytoplasm or nuclei allow distinguishing dead/viable cells, cell types, cell differentiation, expression of a
3109:
2570:
2566:
1840:
organisms to produce haploid gametes. In a diploid organism such as the human organism, most cells of the body have the diploid amount of DNA, 2N. Using this notation for counting chromosomes we say that human
976:, with a disproportionate increase in the rate of cell growth leading to production of larger cells and a disproportionate increase in the rate of cell division leading to production of many smaller cells.
1505:
when the cell is smaller. Thus, mitosis occurs before the yeast reach their normal size. This suggests that cell division may be regulated in part by dilution of Wee1 protein in cells as they grow larger.
1996:, using suitable stains. But the increase of cells number is usually more significant. It can be measured by manual counting of cells under microscopy observation, using the dye exclusion method (i.e.
3242:
Cuny, Andreas P.; Tanuj Sapra, K.; Martinez-Martin, David; Fläschner, Gotthold; Adams, Jonathan D.; Martin, Sascha; Gerber, Christoph; Rudolf, Fabian; Müller, Daniel J. (2022-06-22).
3195:
Martínez-Martín, David; Fläschner, Gotthold; Gaub, Benjamin; Martin, Sascha; Newton, Richard; Beerli, Corina; Mercer, Jason; Gerber, Christoph; Müller, Daniel J. (October 2017).
1984:
tissues, misregulation of cellular size can induce packing defects and disperse aberrant cells. But the consequence of atypical cell growth in other animal tissues is unknown.
1619:. Under the influence of certain plant hormones the cell wall can be remodeled, allowing for increases in cell size that are important for the growth of some plant tissues.
3125:
1828:, when daughter cells physically split apart from a parental cell. During meiosis, there are two cell division steps that together produce the four daughter cells.
2879:
Schulz HN, Brinkhoff T, Ferdelman TG, Mariné MH, Teske A, Jorgensen BB (April 1999). "Dense populations of a giant sulfur bacterium in
Namibian shelf sediments".
1496:
modification of the molecular structure of Cdc2 inhibits the enzymatic activity of Cdc2 and prevents cell division. Wee1 acts to keep Cdc2 inactive during early
1404:
A cell is unable to get too small because the later cell cycle events, such as S, G2, and M, are delayed until mass increases sufficiently to begin S phase.
1877:
meiosis, there are two chromosome separation steps which assure that each of the four daughter cells gets one copy of each of the 23 types of chromosome.
790:
2028:-AM measure (fluorimetrically) not only the membrane functionality (dye retention), but also the functionality of cytoplasmic enzymes (esterases). The
80:
1728:. This is the physical division of mother and daughter cells. The M phase has been broken down into several distinct phases, sequentially known as
1901:
Though cell reproduction that uses mitosis can reproduce eukaryotic cells, eukaryotes bother with the more complicated process of meiosis because
3299:
Burg, Thomas P.; Godin, Michel; Knudsen, Scott M.; Shen, Wenjiang; Carlson, Greg; Foster, John S.; Babcock, Ken; Manalis, Scott R. (April 2007).
1631:
1492:
in humans), a cyclin-dependent kinase, on a tyrosine residue. Cdc2 drives entry into mitosis by phosphorylating a wide range of targets. This
3368:
3119:
3092:
2588:
2407:
2305:
1909:. Notice that when meiosis starts, the two copies of sister chromatids number 2 are adjacent to each other. During this time, there can be
1562:), cells divide at a defined, reproducible size during mitosis because of the regulated activity of Cdk1. The cell polarity protein kinase
696:
477:
1635:
691:
1552:
Cell polarity factors positioned at the cell tips provide spatial cues to limit Cdr2 distribution to the cell middle. In fission yeast
2703:
Moseley JB, Mayeux A, Paoletti A, Nurse P (June 2009). "A spatial gradient coordinates cell size and mitotic entry in fission yeast".
1525:) are localized to a band of cortical nodes in the middle of interphase cells. After entry into mitosis, cytokinesis factors such as
1946:
A series of growth disorders can occur at the cellular level and these consequently underpin much of the subsequent course in
3082:
1892:
1767:, a process that includes DNA replication, chromosome segregation, and cytokinesis. Eukaryotic cell division either involves
783:
2930:
Taheri-Araghi, S; Bradde, S; Sauls, J. T.; Hill, N. S.; Levin, P. A.; Paulsson, J; Vergassola, M; Jun, S (February 2015).
1117:
1980:
progression. Despite the prevalence of pleomorphism in human pathology, its role in disease progression is unclear. In
3412:
1136:, and the expression of each gene occurs to various different levels in a cell-type specific fashion (in response to
2981:
Campos, M; Surovtsev, I. V.; Kato, S; Paintdakhi, A; Beltran, B; Ebmeier, S. E.; Jacobs-Wagner, C (December 2014).
2021:
1439:
being a single cell several meters in length. Plant cells are much larger than animal cells, and protists such as
2657:"Spatial and temporal pathway for assembly and constriction of the contractile ring in fission yeast cytokinesis"
2561:
2020:
Beside the increasing number of cells, one can be assessed regarding the metabolic activity growth, that is, the
1554:
1541:
1450:
structures is involved. Work on the topic generally requires an organism whose cell cycle is well-characterized.
1338:
1331:
1223:
via regulation of translation initiation factors, including the 'translational elongation initiation factor 4E' (
776:
59:
1673:. For most of the constituents of the cell, growth is a steady, continuous process, interrupted only briefly at
2337:
Ali E, Liponska A, O'Hara B, Amici D, Torno M, Gao P, Asara J, Yap M-N F, Mendillo M, Ben-Sahra I (June 2022).
1915:
1896:
1862:
1137:
686:
2832:"A positive feedback loop between Dumbfounded and Rolling pebbles leads to myotube enlargement in Drosophila"
1973:
1596:
have revealed several genes that are required for the formation of multinucleated muscle cells by fusion of
1592:
1534:
1202:
1144:
1121:
1143:
To drive cell growth, the global rate of gene expression can be increased by enhancing the overall rate of
920:
1960:(spread to other locations in the body via lymph or blood). Several key determinants of cell growth, like
1935:
681:
287:
2288:
Hafen, E. (2004). "Interplay
Between Growth Factor and Nutrient Signaling: Lessons from Drosophila TOR".
984:
rates that maintain a roughly constant cell size in the exponentially proliferating population of cells.
1910:
1369:
1346:
1327:
1303:
1240:
1220:
1206:
1155:
1129:
874:
372:
347:
327:
162:
142:
2791:"The cell-end factor pom1p inhibits mid1p in specification of the cell division plane in fission yeast"
2888:
2712:
2613:
2250:
1670:
1186:
714:
592:
402:
352:
3407:
1992:
The cell growth can be detected by a variety of methods. The cell size growth can be visualized by
1902:
1605:
1323:
1272:
1244:
1171:
729:
719:
507:
377:
69:
2604:
Wu L, Russell P (June 1993). "Nim1 kinase promotes mitosis by inactivating Wee1 tyrosine kinase".
1278:
To inhibit cell growth, the global rate of gene expression can be decreased or the global rate of
3389:
2912:
2736:
2637:
2483:
2232:
2116:
1435:
1417:
1413:
1198:
1179:
977:
966:
958:
941:
862:
676:
622:
602:
587:
412:
407:
76:
64:
1868:
1820:
The DNA content of a cell is duplicated at the start of the cell reproduction process. Prior to
1388:
activity, although this mode of regulation is more important in single-celled organisms than in
1950:, in which a group of cells display uncontrolled growth and division beyond the normal limits,
1692:
that are required for DNA replication. The second part of the cell cycle is the S phase, where
1500:
when cells are still small. When cells have reached sufficient size during G2, the phosphatase
3364:
3338:
3330:
3281:
3263:
3224:
3216:
3177:
3115:
3088:
3063:
3014:
2963:
2904:
2861:
2812:
2771:
2728:
2678:
2629:
2584:
2539:
2464:
2413:
2403:
2368:
2339:"The mTORC1-SLC4A7 axis stimulates bicarbonate import to enhance de novo nucleotide synthesis"
2319:
2311:
2301:
2270:
2224:
2216:
2175:
2157:
2108:
2100:
1906:
1842:
1705:
1194:
1148:
1008:
988:
878:
724:
607:
487:
342:
175:
113:
3320:
3312:
3271:
3255:
3208:
3167:
3159:
3053:
3045:
3004:
2996:
2953:
2945:
2896:
2851:
2843:
2802:
2763:
2720:
2668:
2621:
2529:
2521:
2454:
2444:
2395:
2358:
2350:
2293:
2262:
2206:
2165:
2147:
2090:
2053:
1886:
1190:
1175:
763:
332:
171:
834:
or anabolism) is greater than the overall rate of cellular degradation (the destruction of
3384:
3325:
2936:
2014:
1821:
1693:
1583:
1485:
861:, which are distinct processes that can occur alongside cell growth during the process of
617:
582:
3244:"High-resolution mass measurements of single budding yeast reveal linear growth segments"
2892:
2716:
2617:
1807:
3276:
3243:
3172:
3147:
3108:
El-Naggar, A.K.; Chan, J.C.K.; Grandis, J.R.; Takata, T.; Slootweg, P.J. (2017-01-23).
3058:
3033:
3009:
2987:
2982:
2958:
2931:
2856:
2831:
2534:
2510:"Coupling among Growth Rate Response, Metabolic Cycle and Cell Division Cycle in Yeast"
2509:
2363:
2338:
2005:
1764:
1357:
1319:
914:
894:
811:
750:
472:
282:
2767:
2673:
2656:
2459:
2432:
2399:
2211:
2194:
2193:
Neufeld, Thomas P; de la Cruz, Aida Flor A; Johnston, Laura A; Edgar, Bruce A (1998).
2170:
2135:
2095:
2078:
3401:
2577:
1825:
1725:
1601:
1459:
1389:
1228:
1217:
1152:
1125:
1106:
981:
973:
962:
937:
933:
929:
898:
870:
866:
854:
552:
447:
337:
312:
307:
2916:
2236:
2120:
2000:) to count only viable cells. Less fastidious, scalable, methods include the use of
1488:
that normally phosphorylates the Cdc2 cell cycle regulatory protein (the homolog of
1473:
3148:"Cell-Size Pleomorphism Drives Aberrant Clone Dispersal in Proliferating Epithelia"
2740:
2641:
1931:
1857:
have 23 chromosomes (N = 23). Humans have 23 distinct types of chromosomes, the 22
1850:
1776:
1733:
1717:
1709:
1447:
1279:
1082:
1078:
1060:
1056:
1052:
1048:
953:
949:
835:
831:
827:
819:
597:
577:
542:
537:
527:
522:
502:
482:
392:
362:
322:
302:
292:
272:
267:
262:
257:
157:
2292:. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology. Vol. 279. pp. 153–167.
19:
3163:
2900:
2354:
2297:
1997:
1721:
1697:
1530:
1518:
1514:
1393:
1381:
1033:
1004:
647:
642:
612:
567:
512:
452:
437:
432:
397:
357:
247:
237:
232:
152:
98:
3259:
3000:
745:
3300:
3196:
3146:
Ramanathan, Subramanian P.; Krajnc, Matej; Gibson, Matthew C. (October 2019).
3049:
2949:
2807:
2790:
2266:
1993:
1981:
1965:
1956:
1927:
1923:
1756:
1681:
1615:
are complicated by the fact that almost all plant cells are inside of a solid
1612:
1441:
1421:
1189:
is an example of a regulatory protein that can induce the overall activity of
1064:
1028:
902:
897:
occur repeatedly without cell growth. Conversely, some cells can grow without
890:
858:
839:
632:
627:
572:
557:
497:
462:
457:
427:
387:
367:
297:
277:
137:
132:
3385:
A comparison of generational and exponential models of cell population growth
3334:
3267:
3220:
2315:
2220:
2161:
2104:
1622:
Most unicellular organisms are microscopic in size, but there are some giant
2525:
2033:
2029:
2010:
2001:
1846:
1752:
1745:
1737:
1623:
1616:
1579:
1529:
are recruited to similar nodes; these nodes eventually condense to form the
1526:
1350:
1307:
1291:
1283:
1267:
also directly phosphorylates and activates the ribosomal protein S6-kinase (
1072:
1016:
847:
823:
815:
672:
547:
532:
517:
467:
442:
195:
147:
108:
103:
3342:
3285:
3228:
3181:
3114:. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer (also known as Adman).
3081:
Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, B.; Burke, A.P; Marx, A.; Nicholson, A.G. (2015).
3067:
3018:
2967:
2908:
2865:
2816:
2775:
2732:
2682:
2543:
2468:
2449:
2417:
2372:
2323:
2274:
2253:(2010). "Developmental control of cell growth and division in Drosophila".
2179:
1634:—Dense populations of a giant sulfur bacterium in Namibian shelf sediments—
865:, where a cell, known as the mother cell, grows and divides to produce two
3301:"Weighing of biomolecules, single cells and single nanoparticles in fluid"
2847:
2633:
2228:
2152:
2112:
1604:
between myocytes and some are involved in adhesion-dependent cell-to-cell
2041:
1858:
1760:
1741:
1729:
1627:
1597:
1497:
1493:
1260:
1213:
1163:
1094:
1068:
843:
637:
562:
492:
422:
417:
242:
211:
190:
3316:
3212:
3197:"Inertial picobalance reveals fast mass fluctuations in mammalian cells"
2724:
2575:
Lodish HF, Berk A, Zipursky LS, Matsudaira P, et al., eds. (2000).
1318:
Many of the signal molecules that control of cellular growth are called
1032:) or by internalisation of nutrient storage granules (yolk granules) by
2025:
1919:
1837:
1833:
1781:
1772:
1768:
1713:
1674:
1587:
1578:
One common means to produce very large cells is by cell fusion to form
1361:
1159:
1133:
1098:
1000:
996:
906:
652:
382:
252:
199:
185:
43:
35:
1433:
Cell size is highly variable among organisms, with some algae such as
1255:
that can directly phosphorylate and inactivate a general inhibitor of
2625:
1977:
1969:
1961:
1947:
1797:
1793:
1785:
1689:
1335:
1252:
1236:
1102:
1022:
1012:
992:
945:
886:
882:
317:
207:
3084:
WHO Classification of
Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart
2136:"Controlling cell division in yeast and animals: does size matter?"
1916:
Recombination of genetic information between homologous chromosomes
2983:"A constant size extension drives bacterial cell size homeostasis"
1954:(intrusion on and destruction of adjacent tissues), and sometimes
1867:
1806:
1501:
1472:
1463:
1365:
1256:
1224:
1113:
1086:
919:
203:
18:
2195:"Coordination of Growth and Cell Division in the Drosophila Wing"
965:
rate (mass accumulation) during cell proliferation, owing to the
1854:
1789:
1574:
Other experimental systems for the study of cell size regulation
1563:
1489:
1481:
1385:
1373:
1342:
1299:
1295:
1287:
1264:
1248:
1232:
1167:
1037:
910:
807:
123:
1392:
organisms such as animals that always maintain an abundance of
1368:
family, which circulate as hormones in animals to activate the
987:
Some special cells can grow to very large sizes via an unusual
1684:, has four major parts called phases. The first part, called G
1517:(which negatively regulates Wee1) and the Cdr2-related kinase
1268:
1183:
1090:
2036:
assay (fluorimetric) dose the mitochondrial redox potential.
826:
volume. Cell growth occurs when the overall rate of cellular
1800:, a cell which again has the normal amount of chromosomes.
1716:. The fourth phase, M phase, consists of nuclear division (
924:
Cell division without cell growth during embryonic cleavage
944:. This is because a single cell with only one copy of the
873:
can also occur independently of one another. During early
2754:
Rupes I (September 2002). "Checking cell size in yeast".
1836:
amount of DNA, often symbolized as N. Meiosis is used by
1712:
that are required during the process of division, called
2789:
Padte NN, Martin SG, Howard M, Chang F (December 2006).
1788:) which have half the normal cellular amount of DNA. A
1282:
degradation can be increased by increasing the rate of
3032:
Schmoller, Kurt M.; Skotheim, Jan M. (December 2015).
2655:
Wu JQ, Kuhn JR, Kovar DR, Pollard TD (November 2003).
3087:. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer.
2386:
Mitchison JM (2003). "Growth during the cell cycle".
2830:
Menon SD, Osman Z, Chenchill K, Chia W (June 2005).
1784:
organisms. It produces four special daughter cells (
1059:
exceeds the overall rate of cellular degradation of
1051:
can grow by increasing the overall rate of cellular
1775:. Mitosis and meiosis are sometimes called the two
1341:, which is able to activate another protein kinase
1216:can be increased to boost the global efficiency of
2576:
1677:when the nucleus and then the cell divide in two.
1608:that allows for a cascade of cell fusion events.
1521:(which directly phosphorylates and inhibits Wee1
1412:Cell populations go through a particular type of
1227:) complex, which binds to and caps the 5' end of
936:rarely occurs solely through cell growth without
2433:"Control and maintenance of mammalian cell size"
2072:
2070:
2068:
2932:"Cell-size control and homeostasis in bacteria"
1356:Nutrient availability influences production of
1290:normally directly inhibits the function of the
1239:complex, is an important upstream regulator of
1816:Comparison of the three types of cell division
16:Increase of the total mass of the cancer cells
3034:"The Biosynthetic Basis of Cell Size Control"
1600:. Some of the key proteins are important for
784:
8:
2698:
2696:
2694:
2692:
1533:ring. A previously uncharacterized protein,
1334:and the downstream serine/threonine protein
980:typically involves balanced cell growth and
3111:WHO Classification of Head and Neck Tumours
2569:and the homologous proteins in humans also
1708:occurs, mainly involving the production of
1586:cells are formed by fusion of thousands of
1384:to individual cells also directly promotes
1972:. Therefore, heterogenous cell growth and
1582:. For example, very long (several inches)
1151:(for active genes) or the overall rate of
972:Cell size depends on both cell growth and
791:
777:
26:
3324:
3275:
3171:
3057:
3008:
2957:
2855:
2806:
2672:
2533:
2484:"Algae create glue to repair cell damage"
2458:
2448:
2362:
2210:
2169:
2151:
2134:Grewal, Savraj S; Edgar, Bruce A (2003).
2094:
1724:), accompanied by the formation of a new
1302:activity both reduces the global rate of
23:Cell division, growth & proliferation
2583:(4th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman.
1688:phase is marked by synthesis of various
1630:that are visible to the naked eye. (See
1212:In addition, the activity of individual
2064:
1458:The relationship between cell size and
1330:, which includes upstream lipid kinase
853:Cell growth is not to be confused with
34:
3361:The cell cycle: principles of control
1796:gamete can then combine to produce a
1680:The process of cell division, called
1263:, to promote translation efficiency.
7:
2508:Slavov N.; Botstein D. (June 2011).
2390:. International Review of Cytology.
2079:"Size Control in Animal Development"
1976:is one of the earliest hallmarks of
999:but there is no subsequent mitosis (
1590:. Genetic studies of the fruit fly
806:refers to an increase in the total
2077:Conlon, Ian; Raff, Martin (1999).
901:or without any progression of the
14:
3390:Local Growth in an Array of Disks
1771:or a more complex process called
1751:Cell division is more complex in
1380:In addition, the availability of
1314:Cell growth regulation in animals
1044:Mechanisms of cell growth control
2571:regulate cell entry into mitosis
1462:has been extensively studied in
940:, but most often occurs through
758:
757:
744:
42:
2255:Current Opinion in Cell Biology
1964:and the regulation of cellular
1696:produces two identical sets of
1640:, closely related to the genus
1162:by increasing the abundance of
869:. Importantly, cell growth and
3393:Wolfram Demonstrations Project
3326:11858/00-001M-0000-0014-9C58-F
2482:Peplow, Mark (23 March 2005).
1893:Origin and function of meiosis
1477:Figure 1:Cell cycle and growth
1085:is initiated by expression of
1011:cells have many copies of the
1:
2768:10.1016/S0168-9525(02)02745-2
2674:10.1016/S1534-5807(03)00324-1
2514:Molecular Biology of the Cell
2400:10.1016/S0074-7696(03)01004-0
2212:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81462-2
2096:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80563-2
1704:phase in which a significant
1540:Further experimentation with
3363:. London: Sunderland, Mass.
3164:10.1016/j.devcel.2019.08.005
2901:10.1126/science.284.5413.493
2355:10.1016/j.molcel.2022.06.008
2298:10.1007/978-3-642-18930-2_10
1968:, are commonly disrupted in
1861:and the special category of
1720:) and cytoplasmic division (
1636:Large protists of the genus
1306:and increases the extent of
1648:In the rod-shaped bacteria
1101:that catalyse synthesis of
3429:
3260:10.1038/s41467-022-30781-y
3001:10.1016/j.cell.2014.11.022
1905:such as meiosis confers a
1890:
1884:
1454:Yeast cell size regulation
1261:4E-binding protein (4E-BP)
3359:Morgan, David O. (2007).
3050:10.1016/j.tcb.2015.10.006
2950:10.1016/j.cub.2014.12.009
2808:10.1016/j.cub.2006.11.024
2267:10.1016/j.ceb.2010.08.018
1755:than in other organisms.
1700:. The third part is the G
1611:Increases in the size of
1555:Schizosaccharomyces pombe
1209:and thereby cell growth.
969:increase in cell number.
697:List of unsolved problems
2431:Cooper, Stephen (2004).
1897:Homologous recombination
1748:leading to cytokinesis.
1138:gene regulatory networks
1055:such that production of
991:cell cycle in which the
692:List of research methods
2526:10.1091/mbc.E11-02-0132
2032:(colorimetric) and the
1322:, many of which induce
1310:to reduce cell growth.
163:Response to environment
2579:Molecular cell biology
2450:10.1186/1471-2121-5-35
1873:
1849:(2N = 46) while human
1812:
1654:Caulobacter crescentus
1478:
1400:size remains elusive.
1353:to drive cell growth.
1251:is a serine/threonine
1243:initiation as well as
925:
682:List of biology awards
288:Biological engineering
24:
3248:Nature Communications
2848:10.1083/jcb.200501126
2153:10.1186/1475-4924-2-5
1924:repairing DNA damages
1911:genetic recombination
1891:Further information:
1871:
1810:
1669:Cell reproduction is
1548:Cell polarity factors
1476:
1370:PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
1328:PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
995:is replicated during
923:
875:embryonic development
373:Developmental biology
348:Computational biology
328:Cellular microbiology
22:
1936:Hardy–Weinberg ratio
1509:Linking Cdr2 to Wee1
1372:in cells to promote
1187:transcription factor
1003:) or cell division (
905:, such as growth of
715:Agricultural science
593:Reproductive biology
478:Mathematical biology
403:Evolutionary biology
353:Conservation biology
3317:10.1038/nature05741
3311:(7139): 1066–1069.
3213:10.1038/nature24288
2893:1999Sci...284..493S
2725:10.1038/nature08074
2717:2009Natur.459..857M
2618:1993Natur.363..738W
2349:(1): 3284–3298.e7.
1988:Measurement methods
1907:selective advantage
1903:sexual reproduction
1881:Sexual reproduction
1763:cells reproduce by
1632:Table of cell sizes
1606:signal transduction
1513:The protein kinase
1416:called doubling or
1324:signal transduction
1273:ribosome biogenesis
1245:ribosome biogenesis
720:Biomedical sciences
378:Ecological genetics
30:Part of a series on
3413:Cellular processes
3152:Developmental Cell
2251:Thompson, Barry J.
2140:Journal of Biology
1874:
1813:
1479:
1436:Caulerpa taxifolia
1418:cell proliferation
1414:exponential growth
1377:mTORC1 signaling.
1271:), which promotes
1199:RNA polymerase III
1180:RNA polymerase III
978:Cell proliferation
942:cell proliferation
926:
863:cell proliferation
850:, or catabolism).
751:Biology portal
603:Structural biology
588:Relational biology
413:Generative biology
408:Freshwater biology
25:
3370:978-0-9539181-2-6
3207:(7677): 500–505.
3121:978-92-832-2438-9
3094:978-92-832-2436-5
2590:978-0-7167-3136-8
2520:(12): 1997–2009.
2409:978-0-12-364630-9
2307:978-3-642-62360-8
1934:according to the
1922:is a process for
1706:protein synthesis
1661:each generation.
1345:, which promotes
1298:. Thus, reducing
1195:RNA polymerase II
1149:RNA polymerase II
814:, including both
801:
800:
725:Health technology
608:Synthetic biology
488:Molecular biology
343:Cognitive biology
138:Energy processing
3420:
3374:
3347:
3346:
3328:
3296:
3290:
3289:
3279:
3239:
3233:
3232:
3192:
3186:
3185:
3175:
3143:
3137:
3136:
3134:
3133:
3124:. Archived from
3105:
3099:
3098:
3078:
3072:
3071:
3061:
3038:Trends Cell Biol
3029:
3023:
3022:
3012:
2995:(6): 1433–1446.
2978:
2972:
2971:
2961:
2927:
2921:
2920:
2876:
2870:
2869:
2859:
2827:
2821:
2820:
2810:
2786:
2780:
2779:
2751:
2745:
2744:
2711:(7248): 857–60.
2700:
2687:
2686:
2676:
2652:
2646:
2645:
2626:10.1038/363738a0
2612:(6431): 738–41.
2601:
2595:
2594:
2582:
2554:
2548:
2547:
2537:
2505:
2499:
2498:
2496:
2494:
2479:
2473:
2472:
2462:
2452:
2437:BMC Cell Biology
2428:
2422:
2421:
2383:
2377:
2376:
2366:
2334:
2328:
2327:
2285:
2279:
2278:
2247:
2241:
2240:
2214:
2205:(7): 1183–1193.
2190:
2184:
2183:
2173:
2155:
2131:
2125:
2124:
2098:
2074:
2054:Bacterial growth
1887:Evolution of sex
1408:Cell populations
1396:in circulation.
1294:inducing kinase
1201:to drive global
1191:RNA polymerase I
1176:RNA polymerase I
1015:, so are highly
793:
786:
779:
766:
761:
760:
753:
749:
748:
687:List of journals
333:Chemical biology
46:
27:
3428:
3427:
3423:
3422:
3421:
3419:
3418:
3417:
3398:
3397:
3381:
3371:
3358:
3355:
3350:
3298:
3297:
3293:
3241:
3240:
3236:
3194:
3193:
3189:
3158:(1): 49–61.e4.
3145:
3144:
3140:
3131:
3129:
3122:
3107:
3106:
3102:
3095:
3080:
3079:
3075:
3044:(12): 793–802.
3031:
3030:
3026:
2980:
2979:
2975:
2937:Current Biology
2929:
2928:
2924:
2887:(5413): 493–5.
2878:
2877:
2873:
2829:
2828:
2824:
2788:
2787:
2783:
2753:
2752:
2748:
2702:
2701:
2690:
2654:
2653:
2649:
2603:
2602:
2598:
2591:
2574:
2567:small cell size
2555:
2551:
2507:
2506:
2502:
2492:
2490:
2481:
2480:
2476:
2430:
2429:
2425:
2410:
2388:Int. Rev. Cytol
2385:
2384:
2380:
2336:
2335:
2331:
2308:
2287:
2286:
2282:
2249:
2248:
2244:
2192:
2191:
2187:
2133:
2132:
2128:
2076:
2075:
2066:
2062:
2050:
1990:
1944:
1899:
1889:
1883:
1863:sex chromosomes
1822:DNA replication
1818:
1703:
1694:DNA replication
1687:
1667:
1584:skeletal muscle
1576:
1550:
1511:
1486:tyrosine kinase
1456:
1431:
1410:
1316:
1046:
1009:endoreplicating
1007:). These large
989:endoreplication
913:pathfinding in
830:(production of
797:
756:
743:
742:
735:
734:
710:
702:
701:
668:
660:
659:
658:
657:
618:Systems biology
583:Quantum biology
226:
218:
217:
182:
167:
129:
118:
94:
86:
51:
49:Science of life
17:
12:
11:
5:
3426:
3424:
3416:
3415:
3410:
3400:
3399:
3396:
3395:
3387:
3380:
3379:External links
3377:
3376:
3375:
3369:
3354:
3351:
3349:
3348:
3291:
3234:
3187:
3138:
3120:
3100:
3093:
3073:
3024:
2973:
2944:(3): 385–391.
2922:
2871:
2822:
2801:(24): 2480–7.
2781:
2746:
2688:
2647:
2596:
2589:
2549:
2500:
2474:
2423:
2408:
2378:
2343:Molecular Cell
2329:
2306:
2280:
2261:(6): 788–794.
2242:
2185:
2126:
2089:(2): 235–244.
2063:
2061:
2058:
2057:
2056:
2049:
2046:
2006:flow cytometry
1989:
1986:
1943:
1940:
1885:Main article:
1882:
1879:
1847:46 chromosomes
1817:
1814:
1765:binary fission
1759:cells such as
1701:
1685:
1666:
1663:
1575:
1572:
1549:
1546:
1510:
1507:
1455:
1452:
1430:
1427:
1409:
1406:
1358:growth factors
1320:growth factors
1315:
1312:
1235:, part of the
1231:. The protein
1116:are generally
1045:
1042:
915:nervous system
895:cell divisions
867:daughter cells
799:
798:
796:
795:
788:
781:
773:
770:
769:
768:
767:
754:
737:
736:
733:
732:
727:
722:
717:
711:
708:
707:
704:
703:
700:
699:
694:
689:
684:
679:
669:
666:
665:
662:
661:
656:
655:
650:
645:
640:
635:
630:
625:
620:
615:
610:
605:
600:
595:
590:
585:
580:
575:
570:
565:
560:
555:
550:
545:
540:
535:
530:
525:
520:
515:
510:
505:
500:
495:
490:
485:
480:
475:
473:Marine biology
470:
465:
460:
455:
450:
445:
440:
435:
430:
425:
420:
415:
410:
405:
400:
395:
390:
385:
380:
375:
370:
365:
360:
355:
350:
345:
340:
335:
330:
325:
320:
315:
310:
305:
300:
295:
290:
285:
283:Bioinformatics
280:
275:
270:
265:
260:
255:
250:
245:
240:
235:
229:
228:
227:
224:
223:
220:
219:
216:
215:
193:
188:
181:
180:
166:
165:
160:
155:
150:
145:
140:
135:
128:
127:
122:Properties of
117:
116:
111:
106:
101:
95:
93:Key components
92:
91:
88:
87:
85:
84:
73:
72:
67:
62:
56:
53:
52:
47:
39:
38:
32:
31:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3425:
3414:
3411:
3409:
3406:
3405:
3403:
3394:
3391:
3388:
3386:
3383:
3382:
3378:
3372:
3366:
3362:
3357:
3356:
3352:
3344:
3340:
3336:
3332:
3327:
3322:
3318:
3314:
3310:
3306:
3302:
3295:
3292:
3287:
3283:
3278:
3273:
3269:
3265:
3261:
3257:
3253:
3249:
3245:
3238:
3235:
3230:
3226:
3222:
3218:
3214:
3210:
3206:
3202:
3198:
3191:
3188:
3183:
3179:
3174:
3169:
3165:
3161:
3157:
3153:
3149:
3142:
3139:
3128:on 2019-10-31
3127:
3123:
3117:
3113:
3112:
3104:
3101:
3096:
3090:
3086:
3085:
3077:
3074:
3069:
3065:
3060:
3055:
3051:
3047:
3043:
3039:
3035:
3028:
3025:
3020:
3016:
3011:
3006:
3002:
2998:
2994:
2990:
2989:
2984:
2977:
2974:
2969:
2965:
2960:
2955:
2951:
2947:
2943:
2939:
2938:
2933:
2926:
2923:
2918:
2914:
2910:
2906:
2902:
2898:
2894:
2890:
2886:
2882:
2875:
2872:
2867:
2863:
2858:
2853:
2849:
2845:
2842:(6): 909–20.
2841:
2837:
2833:
2826:
2823:
2818:
2814:
2809:
2804:
2800:
2796:
2792:
2785:
2782:
2777:
2773:
2769:
2765:
2762:(9): 479–85.
2761:
2757:
2750:
2747:
2742:
2738:
2734:
2730:
2726:
2722:
2718:
2714:
2710:
2706:
2699:
2697:
2695:
2693:
2689:
2684:
2680:
2675:
2670:
2667:(5): 723–34.
2666:
2662:
2658:
2651:
2648:
2643:
2639:
2635:
2631:
2627:
2623:
2619:
2615:
2611:
2607:
2600:
2597:
2592:
2586:
2581:
2580:
2572:
2568:
2564:
2563:
2558:
2553:
2550:
2545:
2541:
2536:
2531:
2527:
2523:
2519:
2515:
2511:
2504:
2501:
2489:
2485:
2478:
2475:
2470:
2466:
2461:
2456:
2451:
2446:
2442:
2438:
2434:
2427:
2424:
2419:
2415:
2411:
2405:
2401:
2397:
2393:
2389:
2382:
2379:
2374:
2370:
2365:
2360:
2356:
2352:
2348:
2344:
2340:
2333:
2330:
2325:
2321:
2317:
2313:
2309:
2303:
2299:
2295:
2291:
2284:
2281:
2276:
2272:
2268:
2264:
2260:
2256:
2252:
2246:
2243:
2238:
2234:
2230:
2226:
2222:
2218:
2213:
2208:
2204:
2200:
2196:
2189:
2186:
2181:
2177:
2172:
2167:
2163:
2159:
2154:
2149:
2145:
2141:
2137:
2130:
2127:
2122:
2118:
2114:
2110:
2106:
2102:
2097:
2092:
2088:
2084:
2080:
2073:
2071:
2069:
2065:
2059:
2055:
2052:
2051:
2047:
2045:
2043:
2037:
2035:
2031:
2027:
2023:
2018:
2016:
2012:
2007:
2003:
1999:
1995:
1987:
1985:
1983:
1979:
1975:
1971:
1967:
1963:
1959:
1958:
1953:
1949:
1941:
1939:
1937:
1933:
1932:heterozygotes
1929:
1925:
1921:
1917:
1912:
1908:
1904:
1898:
1894:
1888:
1880:
1878:
1870:
1866:
1864:
1860:
1856:
1852:
1848:
1844:
1839:
1835:
1829:
1827:
1826:cell division
1823:
1815:
1809:
1805:
1801:
1799:
1795:
1791:
1787:
1783:
1778:
1774:
1770:
1766:
1762:
1758:
1754:
1749:
1747:
1743:
1739:
1735:
1731:
1727:
1726:cell membrane
1723:
1719:
1715:
1711:
1707:
1699:
1695:
1691:
1683:
1678:
1676:
1672:
1665:Cell division
1664:
1662:
1659:
1655:
1651:
1646:
1644:
1643:
1639:
1633:
1629:
1625:
1620:
1618:
1614:
1609:
1607:
1603:
1602:cell adhesion
1599:
1595:
1594:
1589:
1585:
1581:
1573:
1571:
1567:
1565:
1561:
1557:
1556:
1547:
1545:
1543:
1538:
1536:
1532:
1528:
1524:
1520:
1516:
1508:
1506:
1503:
1499:
1495:
1491:
1487:
1484:protein is a
1483:
1475:
1471:
1469:
1465:
1461:
1460:cell division
1453:
1451:
1449:
1444:
1443:
1438:
1437:
1428:
1426:
1423:
1420:. Thus, each
1419:
1415:
1407:
1405:
1401:
1397:
1395:
1391:
1390:multicellular
1387:
1383:
1378:
1375:
1371:
1367:
1363:
1359:
1354:
1352:
1349:and inhibits
1348:
1344:
1340:
1337:
1333:
1329:
1325:
1321:
1313:
1311:
1309:
1305:
1301:
1297:
1293:
1289:
1285:
1281:
1276:
1274:
1270:
1266:
1262:
1258:
1254:
1250:
1246:
1242:
1238:
1234:
1230:
1226:
1222:
1219:
1215:
1210:
1208:
1204:
1203:transcription
1200:
1196:
1192:
1188:
1185:
1181:
1177:
1173:
1169:
1165:
1161:
1157:
1154:
1150:
1146:
1145:transcription
1141:
1139:
1135:
1131:
1127:
1126:messenger RNA
1123:
1122:transcription
1119:
1115:
1110:
1108:
1107:carbohydrates
1104:
1100:
1096:
1092:
1089:which encode
1088:
1084:
1080:
1076:
1074:
1070:
1066:
1062:
1058:
1054:
1050:
1043:
1041:
1039:
1035:
1031:
1030:
1024:
1020:
1018:
1014:
1010:
1006:
1002:
998:
994:
990:
985:
983:
982:cell division
979:
975:
974:cell division
970:
968:
964:
963:tissue growth
960:
955:
951:
947:
943:
939:
938:cell division
935:
934:tissue growth
931:
930:multicellular
922:
918:
917:development.
916:
912:
908:
904:
900:
899:cell division
896:
892:
888:
884:
880:
876:
872:
871:cell division
868:
864:
860:
856:
855:cell division
851:
849:
845:
841:
837:
833:
829:
825:
821:
817:
813:
809:
805:
794:
789:
787:
782:
780:
775:
774:
772:
771:
765:
755:
752:
747:
741:
740:
739:
738:
731:
728:
726:
723:
721:
718:
716:
713:
712:
706:
705:
698:
695:
693:
690:
688:
685:
683:
680:
678:
674:
671:
670:
664:
663:
654:
651:
649:
646:
644:
641:
639:
636:
634:
631:
629:
626:
624:
621:
619:
616:
614:
611:
609:
606:
604:
601:
599:
596:
594:
591:
589:
586:
584:
581:
579:
576:
574:
571:
569:
566:
564:
561:
559:
556:
554:
553:Phylogenetics
551:
549:
546:
544:
541:
539:
536:
534:
531:
529:
526:
524:
521:
519:
516:
514:
511:
509:
506:
504:
501:
499:
496:
494:
491:
489:
486:
484:
481:
479:
476:
474:
471:
469:
466:
464:
461:
459:
456:
454:
451:
449:
448:Human biology
446:
444:
441:
439:
436:
434:
431:
429:
426:
424:
421:
419:
416:
414:
411:
409:
406:
404:
401:
399:
396:
394:
391:
389:
386:
384:
381:
379:
376:
374:
371:
369:
366:
364:
361:
359:
356:
354:
351:
349:
346:
344:
341:
339:
338:Chronobiology
336:
334:
331:
329:
326:
324:
321:
319:
316:
314:
313:Biotechnology
311:
309:
308:Biostatistics
306:
304:
301:
299:
296:
294:
291:
289:
286:
284:
281:
279:
276:
274:
271:
269:
266:
264:
261:
259:
256:
254:
251:
249:
246:
244:
241:
239:
236:
234:
231:
230:
222:
221:
213:
209:
205:
201:
197:
194:
192:
189:
187:
184:
183:
179:
177:
173:
169:
168:
164:
161:
159:
156:
154:
151:
149:
146:
144:
141:
139:
136:
134:
131:
130:
126:
125:
120:
119:
115:
112:
110:
107:
105:
102:
100:
97:
96:
90:
89:
82:
78:
75:
74:
71:
68:
66:
63:
61:
58:
57:
55:
54:
50:
45:
41:
40:
37:
33:
29:
28:
21:
3392:
3360:
3308:
3304:
3294:
3251:
3247:
3237:
3204:
3200:
3190:
3155:
3151:
3141:
3130:. Retrieved
3126:the original
3110:
3103:
3083:
3076:
3041:
3037:
3027:
2992:
2986:
2976:
2941:
2935:
2925:
2884:
2880:
2874:
2839:
2836:J. Cell Biol
2835:
2825:
2798:
2794:
2784:
2759:
2756:Trends Genet
2755:
2749:
2708:
2704:
2664:
2660:
2650:
2609:
2605:
2599:
2578:
2560:
2556:
2552:
2517:
2513:
2503:
2491:. Retrieved
2487:
2477:
2440:
2436:
2426:
2391:
2387:
2381:
2346:
2342:
2332:
2289:
2283:
2258:
2254:
2245:
2202:
2198:
2188:
2143:
2139:
2129:
2086:
2082:
2038:
2019:
1991:
1974:pleomorphism
1955:
1951:
1945:
1900:
1875:
1830:
1819:
1802:
1750:
1734:prometaphase
1718:karyokinesis
1710:microtubules
1679:
1668:
1657:
1653:
1649:
1647:
1641:
1637:
1621:
1610:
1591:
1577:
1568:
1559:
1553:
1551:
1539:
1522:
1512:
1480:
1467:
1457:
1448:cytoskeletal
1440:
1434:
1432:
1411:
1402:
1398:
1379:
1355:
1317:
1280:biomolecular
1277:
1211:
1142:
1111:
1097:, including
1083:biomolecules
1079:Biosynthesis
1077:
1061:biomolecules
1057:biomolecules
1053:biosynthesis
1047:
1027:
1021:
986:
971:
961:increase of
954:biosynthesis
952:can perform
950:cell nucleus
927:
852:
836:biomolecules
832:biomolecules
828:biosynthesis
803:
802:
709:Applications
598:Sociobiology
578:Protistology
543:Photobiology
538:Pharmacology
528:Parasitology
523:Paleontology
503:Neuroscience
483:Microbiology
393:Epidemiology
363:Cytogenetics
323:Cell biology
303:Biosemiotics
293:Biomechanics
273:Biogeography
268:Biochemistry
263:Bacteriology
258:Astrobiology
170:
158:Reproduction
121:
48:
3254:(1): 3483.
2559:mutants of
2394:: 165–258.
1998:trypan blue
1928:homozygotes
1872:Chromosomes
1845:cells have
1811:Cell growth
1757:Prokaryotic
1722:cytokinesis
1698:chromosomes
1658:B. subtilis
1613:plant cells
1531:cytokinetic
1394:amino acids
1382:amino acids
1347:translation
1304:translation
1241:translation
1221:translation
1207:translation
1174:depends on
1156:translation
1130:translation
1128:(mRNA) and
1112:Individual
1034:endocytosis
1005:cytokinesis
967:exponential
959:exponential
932:organisms,
816:cytoplasmic
804:Cell growth
648:Xenobiology
643:Virophysics
613:Systematics
568:Primatology
513:Ornithology
453:Ichthyology
438:Herpetology
433:Gerontology
398:Epigenetics
358:Cryobiology
248:Agrostology
238:Aerobiology
233:Abiogenesis
99:Cell theory
3408:Cell cycle
3402:Categories
3132:2019-10-31
2795:Curr. Biol
2488:Nature.com
2060:References
2030:MTT assays
2002:cytometers
1994:microscopy
1982:epithelial
1966:metabolism
1957:metastasis
1753:eukaryotes
1682:cell cycle
1593:Drosophila
1470:mutants).
1442:Paramecium
1422:generation
1172:biogenesis
1065:proteasome
1029:Drosophila
903:cell cycle
891:blastoderm
885:to form a
859:cell cycle
840:proteasome
633:Toxicology
628:Teratology
573:Proteomics
558:Physiology
498:Neontology
463:Lipidology
458:Immunology
428:Geobiology
388:Embryology
368:Dendrology
298:Biophysics
278:Biogeology
153:Regulation
133:Adaptation
3335:1476-4687
3268:2041-1723
3221:1476-4687
2661:Dev. Cell
2443:(1): 35.
2316:0070-217X
2221:0092-8674
2162:1475-4924
2105:0092-8674
2034:resazurin
2011:biomarker
1942:Disorders
1859:autosomes
1761:bacterial
1746:telophase
1738:metaphase
1617:cell wall
1598:myoblasts
1527:myosin II
1429:Cell size
1351:autophagy
1308:autophagy
1296:Atg1/ULK1
1292:autophagy
1284:autophagy
1214:ribosomes
1164:ribosomes
1118:expressed
1073:autophagy
1017:polyploid
848:autophagy
824:organelle
673:Biologist
548:Phycology
533:Pathology
518:Osteology
508:Nutrition
468:Mammalogy
443:Histology
114:Phylogeny
109:Evolution
104:Ecosystem
3343:17460669
3286:35732645
3229:29072271
3182:31495693
3068:26573465
3019:25480302
2968:25544609
2917:32571118
2909:10205058
2866:15955848
2817:17140794
2776:12175809
2733:19474789
2683:14602073
2562:S. pombe
2544:21525243
2469:15456512
2418:12921238
2373:35772404
2324:14560957
2275:20833011
2237:14608744
2180:12733996
2146:(1): 5.
2121:15738174
2048:See also
2042:toxicity
2013:such as
2004:, while
1952:invasion
1742:anaphase
1730:prophase
1628:protozoa
1624:bacteria
1588:myocytes
1580:syncytia
1560:S. Pombe
1523:in vitro
1494:covalent
1326:via the
1259:, named
1170:, whose
1134:proteins
1095:proteins
1069:lysosome
1063:via the
1026:canals (
879:cleavage
844:lysosome
838:via the
764:Category
730:Pharming
667:Research
638:Virology
623:Taxonomy
563:Pomology
493:Mycology
423:Genomics
418:Genetics
243:Agronomy
225:Branches
212:Protists
191:Bacteria
176:Kingdoms
81:timeline
70:Glossary
3277:9217925
3173:6903429
3059:6773270
3010:4258233
2959:4323405
2889:Bibcode
2881:Science
2857:2171639
2741:4330336
2713:Bibcode
2642:4320080
2634:8515818
2614:Bibcode
2535:3113766
2364:9444906
2229:9657151
2113:9988218
2026:calcein
1920:meiosis
1918:during
1843:somatic
1838:diploid
1834:haploid
1786:gametes
1782:diploid
1777:nuclear
1773:meiosis
1769:mitosis
1714:mitosis
1690:enzymes
1675:M phase
1671:asexual
1650:E. coli
1362:Insulin
1360:of the
1160:protein
1099:enzymes
1093:and/or
1023:Oocytes
1001:M-phase
997:S-phase
948:in the
909:during
907:neurons
881:of the
857:or the
820:nuclear
653:Zoology
383:Ecology
253:Anatomy
200:Animals
196:Eukarya
186:Archaea
178:of life
172:Domains
77:History
65:Outline
36:Biology
3367:
3341:
3333:
3305:Nature
3284:
3274:
3266:
3227:
3219:
3201:Nature
3180:
3170:
3118:
3091:
3066:
3056:
3017:
3007:
2966:
2956:
2915:
2907:
2864:
2854:
2815:
2774:
2739:
2731:
2705:Nature
2681:
2640:
2632:
2606:Nature
2587:
2542:
2532:
2493:4 July
2467:
2460:524481
2457:
2416:
2406:
2371:
2361:
2322:
2314:
2304:
2273:
2235:
2227:
2219:
2178:
2171:156596
2168:
2160:
2119:
2111:
2103:
1978:cancer
1970:tumors
1962:ploidy
1948:cancer
1798:zygote
1794:female
1792:and a
1642:Amoeba
1336:kinase
1253:kinase
1182:. The
1103:lipids
1013:genome
993:genome
946:genome
911:axonal
887:morula
883:zygote
762:
318:Botany
208:Plants
143:Growth
3353:Books
2913:S2CID
2737:S2CID
2638:S2CID
2573:; in
2565:have
2233:S2CID
2117:S2CID
1851:sperm
1638:Chaos
1502:Cdc25
1464:yeast
1366:IGF-1
1257:eIF4E
1237:TORC1
1229:mRNAs
1225:eIF4E
1158:into
1132:into
1124:into
1114:genes
1087:genes
1049:Cells
1038:frogs
810:of a
677:list)
204:Fungi
148:Order
60:Index
3365:ISBN
3339:PMID
3331:ISSN
3282:PMID
3264:ISSN
3225:PMID
3217:ISSN
3178:PMID
3116:ISBN
3089:ISBN
3064:PMID
3015:PMID
2988:Cell
2964:PMID
2905:PMID
2862:PMID
2813:PMID
2772:PMID
2729:PMID
2679:PMID
2630:PMID
2585:ISBN
2557:Wee1
2540:PMID
2495:2016
2465:PMID
2414:PMID
2404:ISBN
2369:PMID
2320:PMID
2312:ISSN
2302:ISBN
2271:PMID
2225:PMID
2217:ISSN
2199:Cell
2176:PMID
2158:ISSN
2109:PMID
2101:ISSN
2083:Cell
2024:and
2022:CFDA
2015:Ki67
1930:and
1895:and
1855:eggs
1853:and
1790:male
1744:and
1656:and
1626:and
1564:Pom1
1535:Blt1
1519:Cdr1
1515:Cdr2
1490:CDK1
1482:Wee1
1332:PI3K
1218:mRNA
1205:and
1197:and
1178:and
1168:tRNA
1166:and
1153:mRNA
1120:via
1105:and
1091:RNAs
889:and
822:and
812:cell
808:mass
174:and
124:life
3321:hdl
3313:doi
3309:446
3272:PMC
3256:doi
3209:doi
3205:550
3168:PMC
3160:doi
3054:PMC
3046:doi
3005:PMC
2997:doi
2993:159
2954:PMC
2946:doi
2897:doi
2885:284
2852:PMC
2844:doi
2840:169
2803:doi
2764:doi
2721:doi
2709:459
2669:doi
2622:doi
2610:363
2530:PMC
2522:doi
2455:PMC
2445:doi
2396:doi
2392:226
2359:PMC
2351:doi
2294:doi
2290:TOR
2263:doi
2207:doi
2166:PMC
2148:doi
2091:doi
1645:.)
1542:GFP
1468:wee
1386:TOR
1374:TOR
1343:TOR
1339:Akt
1300:TOR
1288:TOR
1269:S6K
1265:TOR
1249:TOR
1233:TOR
1184:Myc
1147:by
1140:).
1081:of
1071:or
1040:).
928:In
893:),
846:or
3404::
3337:.
3329:.
3319:.
3307:.
3303:.
3280:.
3270:.
3262:.
3252:13
3250:.
3246:.
3223:.
3215:.
3203:.
3199:.
3176:.
3166:.
3156:51
3154:.
3150:.
3062:.
3052:.
3042:25
3040:.
3036:.
3013:.
3003:.
2991:.
2985:.
2962:.
2952:.
2942:25
2940:.
2934:.
2911:.
2903:.
2895:.
2883:.
2860:.
2850:.
2838:.
2834:.
2811:.
2799:16
2797:.
2793:.
2770:.
2760:18
2758:.
2735:.
2727:.
2719:.
2707:.
2691:^
2677:.
2663:.
2659:.
2636:.
2628:.
2620:.
2608:.
2538:.
2528:.
2518:22
2516:.
2512:.
2486:.
2463:.
2453:.
2439:.
2435:.
2412:.
2402:.
2367:.
2357:.
2347:82
2345:.
2341:.
2318:.
2310:.
2300:.
2269:.
2259:22
2257:.
2231:.
2223:.
2215:.
2203:93
2201:.
2197:.
2174:.
2164:.
2156:.
2142:.
2138:.
2115:.
2107:.
2099:.
2087:96
2085:.
2081:.
2067:^
2044:.
1938:.
1740:,
1736:,
1732:,
1652:,
1498:G2
1286:.
1275:.
1247:.
1193:,
1109:.
1075:.
1067:,
1019:.
842:,
818:,
210:,
206:,
202:,
3373:.
3345:.
3323::
3315::
3288:.
3258::
3231:.
3211::
3184:.
3162::
3135:.
3097:.
3070:.
3048::
3021:.
2999::
2970:.
2948::
2919:.
2899::
2891::
2868:.
2846::
2819:.
2805::
2778:.
2766::
2743:.
2723::
2715::
2685:.
2671::
2665:5
2644:.
2624::
2616::
2593:.
2546:.
2524::
2497:.
2471:.
2447::
2441:5
2420:.
2398::
2375:.
2353::
2326:.
2296::
2277:.
2265::
2239:.
2209::
2182:.
2150::
2144:2
2123:.
2093::
1702:2
1686:1
1558:(
1364:/
1036:(
877:(
792:e
785:t
778:v
675:(
214:)
198:(
83:)
79:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.