582:
clear-cut, and some researchers believe the signs and symptoms reflect a spectrum instead of distinct types: Cockayne syndrome Type A (CSA) is marked by normal development until a child is 1 or 2 years old, at which point growth slows and developmental delays are noticed. Symptoms are not apparent until they are 1 year. Life expectancy for type A is approximately 10 to 20 years. These symptoms are seen in CS type 1 children. Cockayne syndrome type B (CSB), also known as "cerebro-oculo-facio-skeletal (COFS) syndrome" (or "Pena-Shokeir syndrome type B"), is the most severe subtype. Symptoms are present at birth and normal brain development stops after birth. The average lifespan for children with type B is up to 7 years of age. These symptoms are seen in CS type 2 children. Cockayne syndrome type C (CSC) appears later in childhood with milder symptoms than the other types and a slower progression of the disorder. People with this type of
Cockayne syndrome live into adulthood, with an average lifespan of 40 to 50 years. These symptoms are seen in CS type 3.
381:, particularly the DNA in active genes. DNA damage is caused by ultraviolet rays from sunlight, radiation, or free radicals in the body. A normal cell can repair DNA damage before it accumulates. If either the ERCC6 or the ERCC8 gene is altered (as in Cockayne Syndrome), DNA damage encountered during transcription isn't repaired, causing RNA polymerase to stall at that location, interfering with gene expression. As the unrepaired DNA damage accumulates, progressively more active gene expression is impeded, leading to malfunctioning cells or cell death, which likely contributes to the signs of Cockayne Syndrome such as premature aging and neuronal hypomyelination.
190:) and is much more severe than CS Type 1. It involves very little neurological development after birth. Death usually occurs by age seven. This specific type has also been designated as cerebro-oculo-facio-skeletal (COFS) syndrome or Pena-Shokeir syndrome Type II. COFS syndrome is named so due to the effects it has on the brain, eyes, face, and skeletal system, as the disease frequently causes brain atrophy, cataracts, loss of fat in the face, and osteoporosis. COFS syndrome can be further subdivided into several conditions (COFS types 1, 2, 3 (associated with
278:. The resulting accumulation of oxidative damage could impair the normal functions of the DNA and may even result in triggering a program of cell death (apoptosis). The children with this disease do not repair the active genes where oxidative damage occurs. Normally, oxidative damage repair is faster in the active genes (which make up less than five percent of the genome) than in inactive regions of the DNA. The resulting accumulation of oxidative damage could impair the normal functions of the DNA and may even result in triggering a program of cell death (
75:
565:
Syndrome patients are very sensitive to UV radiation. Optimal nutrition can also help. Genetic counseling for the parents is recommended, as the disorder has a 25% chance of being passed to any future children, and prenatal testing is also a possibility. Another important aspect is the prevention of recurrence of CS in other siblings. Identification of gene defects involved makes it possible to offer genetic counseling and antenatal diagnostic testing to the parents who already have one affected child.
169:(1880–1956) who first described it in 1936 and re-described in 1946. Neill-Dingwall syndrome was named after Mary M. Dingwall and Catherine A. Neill. These two scientists described the case of two brothers with Cockayne syndrome and asserted it was the same disease described by Cockayne. In their article, the two contributed to the signs of the disease through their discovery of calcifications in the brain. They also compared Cockayne syndrome to what is now known as
48:
274:. Each lesion—a damaged section of DNA—must be snipped out and the DNA repaired to preserve its normal function. Unrepaired DNA can lose its ability to code for proteins. Mutations also can result. These mutations can activate oncogenes or silence tumor suppressor genes. According to research, oxidative damage to active genes is not preferentially repaired, and in the most severe cases, the repair is slowed throughout the whole
291:
499:, or involuntary eye movement, and pupils that fail to dilate demonstrate a loss of control of voluntary and involuntary muscle movement. A salt and pepper retinal pigmentation is also a typical sign. Diagnosis is determined by a specific test for DNA repair, which measures the recovery of RNA after exposure to UV radiation. Despite being associated with genes involved in
420:, particularly inter-strand cross-links, double-strand breaks and some monoadducts. CSB protein is also normally recruited to DNA damaged sites, and its recruitment is most rapid and robust as follows: interstrand crosslinks > double-strand breaks > monoadducts > oxidative damage. CSB protein forms a complex with another DNA repair protein, SNM1A (
491:), and serious sensitivity to sunlight are common, even in individuals without XP-CS. Often patients with Cockayne Syndrome will severely burn or blister with very little heat exposure. The eyes of patients can be affected in various ways and eye abnormalities are common in CS. Cataracts and cloudiness of the cornea (
590:
Cockayne syndrome is rare worldwide. No racial predilection is reported for
Cockayne syndrome. No sexual predilection is described for Cockayne syndrome; the male-to-female ratio is equal. Cockayne syndrome I (CS-A) manifests in childhood. Cockayne syndrome II (CS-B) manifests at birth or in infancy,
200:
Xeroderma pigmentosum-Cockayne syndrome (XP-CS) occurs when an individual also has xeroderma pigmentosum, another DNA repair disease. Some symptoms of each disease are expressed. For instance, freckling and pigment abnormalities characteristic of XP are present. The neurological disorder, spasticity,
568:
Currently, there are two ongoing projects focused on the development of gene therapy for
Cockayne syndrome. The first project, led by the Viljem Julijan Association for Children with Rare Diseases, aims to develop gene therapy specifically for Cockayne syndrome type B. The second project, led by the
564:
There is no permanent cure for this syndrome, although patients can be symptomatically treated. Treatment usually involves physical therapy and minor surgeries to the affected organs, such as cataract removal. Also wearing high-factor sunscreen and protective clothing is recommended because
Cockayne
581:
for those with
Cockayne syndrome is poor, as death typically occurs by the age of 12. The prognosis for Cockayne syndrome varies by disease type. There are three types of Cockayne syndrome according to the severity and onset of the symptoms. However, the differences between the types are not always
161:
mechanism. Unlike other defects of DNA repair, patients with CS are not predisposed to cancer or infection. Cockayne syndrome is a rare but destructive disease usually resulting in death within the first or second decade of life. The mutation of specific genes in
Cockayne syndrome is known, but the
182:
CS Type I, the "classic" form, is characterized by normal fetal growth with the onset of abnormalities in the first two years of life. Vision and hearing gradually decline. The central and peripheral nervous systems progressively degenerate until death in the first or second decade of life as a
599:
The recent research on Jan 2018 mentions different CS features that are seen globally with similarities and differences: CS has an incidence of 1 in 250,000 live births, and a prevalence of approximately 1 per 2.5 million, which is remarkably consistent across various regions globally:
376:
Mutations in the ERCC8 (also known as CSA) gene or the ERCC6 (also known as CSB) gene are the cause of
Cockayne syndrome type A and type B. Mutations in the ERCC6 gene mutation makes up ~70% of cases. The proteins made by these genes are involved in repairing damaged DNA via the
125:
and neurological disorders are criteria for diagnosis, while photosensitivity, hearing loss, eye abnormalities, and cavities are other very common features. Problems with any or all of the internal organs are possible. It is associated with a group of disorders called
2345:
2325:
487:), due to a loss of subcutaneous fat. Their small chin, large ears, and pointy, thin nose often give an aged appearance. The skin of those with Cockayne syndrome is also frequently affected: hyperpigmentation, varicose or spider veins (
519:
Laboratory studies are mainly useful to eliminate other disorders. For example, skeletal radiography, endocrinologic tests, and chromosomal breakage studies can help in excluding disorders included in the differential diagnosis.
194:) and 4). Typically patients with this early-onset form of the disorder show more severe brain damage, including reduced myelination of white matter, and more widespread calcifications, including in the cortex and basal ganglia.
2951:
428:, that localizes to inter-strand cross-links in a transcription dependent manner. The accumulation of CSB protein at sites of DNA double-strand breaks occurs in a transcription dependent manner and facilitates
1475:
Bender M, Potocki L, Metry D. What syndrome is this? Cockayne syndrome. Pediatric
Dermatology . November 2003;20(6):538-540. Available from: MEDLINE with Full Text, Ipswich, MA. Accessed April 30, 2015.
2944:
544:
Imaging studies reveal a widespread absence of the myelin sheaths of the neurons in the white matter of the brain and general atrophy of the cortex. Calcifications have also been found in the
2484:
1689:
Laugel V. Cockayne
Syndrome. 2000 Dec 28 . In: Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH, et al., editors. GeneReviews® . Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2015. Available from:
3437:
3392:
2937:
3379:
3427:
2117:
Title: Cockayne
Syndrome Authors: Dr Nita R Sutay, Dr Md Ashfaque Tinmaswala, Dr Manjiri Karlekar, Dr Swati Jhahttp://jmscr.igmpublication.org/v3-i7/35%20jmscr.pdf
2477:
3209:
2235:
Kubota, Masaya; Ohta, Sayaka; Ando, Aki; Koyama, Akiko; Terashima, Hiroshi; Kashii, Hirofumi; Hoshino, Hideki; Sugita, Katsuo; Hayashi, Masaharu (June 2015).
201:
and underdevelopment of sexual organs characteristic of CS are seen. However, hypomyelination and the facial features of typical CS patients are not present.
536:
Prenatal evaluation is possible. Amniotic fluid cell culturing is used to demonstrate that fetal cells are deficient in RNA synthesis after UV irradiation.
2733:
1726:
Vessoni, Alexandre Teixeira; Guerra, Camila Chaves Coelho; Kajitani, Gustavo Satoru; Nascimento, Livia Luz Souza; Garcia, Camila Carrião Machado (2020).
290:
3447:
3085:
2470:
556:
found in patients with Cockayne syndrome could also result in the lack of muscle control, particularly involuntary, and poor posture typically seen.
170:
2102:
2540:
2535:
3412:
1451:
197:
CS Type III, characterized by late-onset, is typically milder than Types I and II. Often patients with Type III will live into adulthood.
2635:
2360:
2992:
2748:
2673:
1623:
Neill CA, Dingwall MM. A Syndrome Resembling Progeria: A Review of Two Cases. Archives of Disease in Childhood. 1950;25(123):213-223.
552:
that regulates movements and aids in some forms of learning, along with the cortex. Additionally, atrophy of the central area of the
3202:
3339:
3046:
2773:
3172:
417:
2738:
3422:
3095:
2835:
2968:
3253:
3151:
2683:
891:
may be grossly deformed ("cactus flowers"), ferruginated dendrites. Dendrites have fewer higher order branches. Purkinje "
2640:
2530:
3442:
3195:
2929:
2743:
710:
2625:
2237:"Nationwide survey of Cockayne syndrome in Japan: Incidence, clinical course and prognosis: Cockayne syndrome in Japan"
2960:
2863:
2655:
1300:
3334:
2799:
2595:
2550:
3344:
3263:
3118:
3073:
3034:
2698:
2605:
952:
500:
456:
410:
378:
3113:
2794:
2678:
2042:"DNA damage during the G0/G1 phase triggers RNA-templated, Cockayne syndrome B-dependent homologous recombination"
1352:
1181:
409:. This deficiency reflects the loss of ability to perform the DNA repair process known as transcription coupled
21:
3324:
3167:
230:. In normal cells, our body repairs the damaged sections. In the case of this disease, due to subtle defects in
2753:
2590:
2502:
2377:
429:
3090:
3432:
2663:
1171:
911:
757:
403:
231:
2668:
3417:
3354:
3308:
3013:
2493:
1292:
1144:
1093:
1049:
1016:
922:
663:
166:
569:
Riaan Research Initiative, is dedicated to the development of gene therapy for Cockayne syndrome type A.
495:) are common. The loss of and damage to the nerves of the optic nerve, causing optic atrophy, can occur.
3359:
3276:
3056:
2902:
2890:
2874:
2846:
2570:
2510:
2450:
2282:
2099:
1134:
1007:
504:
191:
1993:"Cockayne syndrome group B protein regulates DNA double-strand break repair and checkpoint activation"
440:
of the cell cycle, DNA damage can trigger a CSB-dependent recombinational repair process that uses an
2858:
2842:
2830:
2818:
2053:
1362:
2172:
3329:
3281:
3218:
3155:
3077:
2725:
2713:
2349:
1443:
1237:
990:
800:
753:
700:
295:
258:
involving oxygen can generate several highly reactive free radicals. These free radicals can cause
219:
74:
848:. Relative sparing of the cerebral cortex, slight thinning of cortical ribbon may be seen. Normal
2560:
2520:
2264:
2173:"Cockayne syndrome | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program"
1522:
1393:
Bertola; Cao, H; Albano, Lm; Oliveira, Dp; Kok, F; Marques-Dias, Mj; Kim, Ca; Hegele, Ra (2006).
1077:
1035:
994:
986:
939:
899:
815:
680:
672:
476:
528:
Brain CT scanning in Cockayne syndrome patients may reveal calcifications and cortical atrophy.
242:
needed by the body does not operate at normal capacity. Over time, went this theory, results in
2098:
Kyllermen, Marten. Cockayne Syndrome. Swedish Information Centre for Rare Diseases. 2012: 4.0.
3369:
3364:
2823:
2610:
2525:
2388:
2256:
2217:
2081:
2022:
1973:
1924:
1872:
1814:
1765:
1747:
1599:
1557:
1514:
1506:
1447:
1416:
1286:
971:
741:
627:
122:
102:
55:
2907:
2883:
2763:
2758:
2620:
2565:
2248:
2207:
2199:
2186:
Karikkineth, A. C.; Scheibye-Knudsen, M.; Fivenson, E.; Croteau, D. L.; Bohr, V. A. (2016).
2071:
2061:
2012:
2004:
1963:
1955:
1914:
1906:
1862:
1854:
1804:
1796:
1755:
1739:
1728:"Cockayne Syndrome: The many challenges and approaches to understand a multifaceted disease"
1591:
1549:
1498:
1435:
1406:
1367:
1229:
1188:
1163:
649:
451:
The premature aging features of CS are likely due, at least in part, to the deficiencies in
399:
271:
259:
127:
114:
60:
1942:
Iyama T, Lee SY, Berquist BR, Gileadi O, Bohr VA, Seidman MM, McHugh PJ, Wilson DM (2015).
1895:"Elements That Regulate the DNA Damage Response of Proteins Defective in Cockayne Syndrome"
1701:
516:
475:), their eyes appear sunken, and they have an "aged" look. They often have long limbs with
173:(HGPS), then called progeria, due to the advanced aging that characterizes both disorders.
47:
3243:
3146:
2976:
2964:
2895:
2879:
2867:
2851:
2778:
2645:
2630:
2615:
2106:
1372:
1310:
1159:
967:
907:
880:
811:
766:
729:
714:
492:
118:
1785:"Deficient repair of the transcribed strand of active genes in Cockayne's syndrome cells"
1436:
515:
In Cockayne syndrome patients, UV-irradiated cells show decreased DNA and RNA synthesis.
183:
result of serious neurological degradation. Cortical atrophy is less severe in CS Type I.
2057:
3349:
3248:
3162:
3141:
3063:
2916:
2768:
2515:
2212:
2187:
2076:
2041:
2017:
1992:
1968:
1943:
1919:
1894:
1867:
1842:
1760:
1727:
1357:
1335:
1296:
1225:
1148:
1117:
888:
872:
864:
804:
644:
488:
106:
2354:
1809:
1784:
1783:
van Hoffen A, Natarajan AT, Mayne LV, van Zeeland AA, Mullenders LH, Venema J (1993).
246:
failure and death. Every minute, the body pumps 10 to 20 liters of oxygen through the
162:
widespread effects and its relationship with DNA repair is yet to be well understood.
3406:
3374:
3235:
3135:
3051:
2582:
1667:
Javadzadeh M. Cockayne Syndrome. Iran J Child Neurol. Autumn 2014;8;4(Suppl.1):18-19.
1644:
1314:
1304:
1220:
1200:
1085:
1002:
975:
963:
915:
861:
845:
774:
762:
718:
706:
623:
243:
223:
2128:
1743:
1526:
2688:
2462:
2268:
2040:
Wei L, Nakajima S, Böhm S, Bernstein KA, Shen Z, Tsang M, Levine AS, Lan L (2015).
1215:
1196:
1192:
1185:
1140:
1105:
1057:
1031:
948:
837:
725:
668:
468:
402:
induced by the action of ultraviolet (UV) light on the template strand of actively
391:
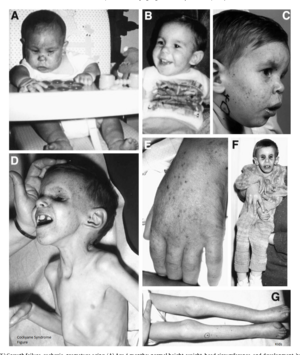
131:
2428:
2382:
1841:
Karikkineth A, Scheibye-Knudsen M, Fivenson E, Croteau D, Bohr B (January 2017).
3105:
2708:
2434:
1327:
1123:
1081:
1069:
790:
737:
425:
299:
68:
1228:
show changes in advanced atherosclerosis and arteriolosclerosis. Unilateral or
652:. Wrinkled and aged appearing skin. Thin dry hair, prematurely gray hair. Poor
3226:
3025:
3002:
2703:
2439:
2393:
2334:
2203:
1910:
1858:
1690:
1502:
1411:
1394:
1331:
1257:
1253:
1204:
1065:
1053:
1027:
825:
808:
786:
749:
553:
452:
263:
255:
187:
158:
1800:
1751:
1582:
Nance M, Berry S (1 January 1992). "Cockayne syndrome: review of 140 cases".
1510:
2423:
2399:
2066:
2008:
1944:"CSB interacts with SNM1A and promotes DNA interstrand crosslink processing"
1595:
1486:
1275:
1113:
1098:
1012:
945:
919:
895:
884:
857:
841:
833:
829:
733:
578:
549:
496:
279:
251:
211:
99:
96:
64:
2260:
2221:
2085:
2026:
1977:
1928:
1876:
1769:
1676:
Cerebrooculofacioskeletal Syndrome 2. Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man.
1561:
1518:
1420:
1959:
1818:
1603:
1553:
3303:
3007:
2986:
2692:
2555:
2445:
2236:
1126:
1109:
1101:
1073:
903:
796:
782:
778:
745:
692:
484:
480:
472:
437:
433:
235:
110:
803:, especially in areas of Metachromatic leukodystrophy, calcification in
622:
Wizened faceies. Sunken eyes, large ears, thin pointy nose. Small chin.
416:
Within the damaged cell, the CSA protein normally localizes to sites of
1321:
1271:
1046:
1043:
959:
935:
876:
868:
819:
696:
545:
421:
239:
226:. This can cause oxidative damage to cellular components including the
17:
3187:
2317:
2252:
1836:
1834:
1832:
1830:
1828:
289:
105:
disorder characterized by growth failure, impaired development of the
2329:
2100:
http://www.socialstyrelsen.se/rarediseases/cockaynesyndrome#anchor_17
1647:
Published April 28, 2015. Reviewed May 2010. Accessed April 30, 2015.
1395:"Cockayne syndrome type A: novel mutations in eight typical patients"
1177:
1155:
1061:
1023:
1020:
982:
979:
892:
688:
684:
676:
653:
275:
267:
215:
1076:
and outer nuclear cell layers. Both the outer and inner segments of
130:, which are conditions characterized by degradation of neurological
1487:"Cockayne syndrome: the expanding clinical and mutational spectrum"
2188:"Cockayne syndrome: Clinical features, model systems and pathways"
1843:"Cockayne syndrome: Clinical features, model systems and pathways"
926:
853:
849:
770:
722:
395:
353:
337:
247:
150:
140:
2404:
3295:
2371:
2368:
2365:
2338:
1677:
1540:
Hoeijmakers JH (October 2009). "DNA damage, aging, and cancer".
640:
636:
617:
406:
398:
deficient cells are unable to preferentially repair cyclobutane
364:
348:
332:
319:
307:
250:, carrying it to billions of cells in our bodies. In its normal
3191:
2933:
2466:
467:
People with this syndrome have smaller than normal head sizes (
445:
441:
270:
occur in the DNA every day. Many of these lesions result from
227:
2152:
479:(inability to relax the muscle at a joint), a hunched back (
1991:
Batenburg NL, Thompson EL, Hendrickson EA, Zhu XD (2015).
989:. Loss of hair cells in pars superior. Loss of neurons in
16:"Cocaine syndrome" redirects here. For the substance, see
2301:
507:, CS is not associated with an increased risk of cancer.
517:
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1115866-workup#c5
262:
to cellular components including the DNA. In an average
222:
produces several highly reactive forms of oxygen called
2300:
This article incorporates some public domain text from
2129:"Cockayne syndrome type b | Viljem Julijan Association"
1375:— thought to be a form (or subset) of Cockayne syndrome
1434:
James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005).
856:. Lamination, neuronal size, and configuration of the
1015:. Usually bilateral, most develop by 4 years of age.
2307:
390:
In contrast to cells with normal repair capability,
134:. There are two primary types of Cockayne syndrome:
3317:
3294:
3262:
3234:
3225:
3127:
3104:
3072:
3033:
3024:
2975:
2808:
2787:
2724:
2654:
2581:
2501:
2414:
2311:
1438:
Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology
54:
37:
32:
1645:http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/cockayne-syndrome
840:. May be seen as a high-intensity white matter on
955:(44%) Most commonly bilateral, rarely unilateral
3438:DNA replication and repair-deficiency disorders
2153:"Riaan Research Initiative — Cockayne Syndrome"
1888:
1886:
3393:DNA replication and repair-deficiency disorder
3203:
2945:
2478:
8:
1663:
1661:
1659:
1657:
1655:
1653:
254:form, oxygen is harmless. However, cellular
1643:Cockayne Syndrome. Genetics Home Reference
1056:deposition, large pigment laden cells in a
3380:Marfanoid–progeroid–lipodystrophy syndrome
3231:
3210:
3196:
3188:
3030:
2952:
2938:
2930:
2485:
2471:
2463:
2308:
602:
73:
29:
3086:Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer
2211:
2075:
2065:
2016:
1967:
1918:
1866:
1808:
1759:
1410:
157:The underlying disorder is a defect in a
1471:
1469:
1467:
1465:
1463:
312:
1619:
1617:
1615:
1613:
1577:
1575:
1573:
1571:
1385:
748:loss at multiple sites, especially the
3428:Syndromes affecting the nervous system
379:transcription-coupled repair mechanism
2302:The U.S. National Library of Medicine
1639:
1637:
1635:
1633:
1631:
1629:
756:due to anterograde and/or retrograde
7:
3304:Hutchinson–Gilford progeria syndrome
1706:The Lecturio Medical Concept Library
1584:American Journal of Medical Genetics
1491:Mechanisms of Ageing and Development
171:Hutchinson–Gilford progeria syndrome
165:It is named after English physician
2133:Cure for Cockayne Syndrome – type B
1442:(10th ed.). Saunders. p.
879:, and in some cases neurons in the
844:sequences signals. No major brain
432:repair of the breaks. During the
186:CS Type II is present from birth (
148:, resulting from mutations in the
14:
2734:Bannayan–Riley–Ruvalcaba syndrome
3448:Diseases named after discoverers
3173:Severe combined immunodeficiency
306:Cockayne syndrome is classified
138:, arising from mutations in the
46:
3096:Mismatch repair cancer syndrome
1744:10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2019-0085
2969:DNA repair-deficiency disorder
2541:Bonnet–Dechaume–Blanc syndrome
1732:Genetics and Molecular Biology
591:and it has a worse prognosis.
483:), and they may be very thin (
146:Cockayne syndrome type B (CSB)
136:Cockayne syndrome type A (CSA)
1:
3413:Autosomal recessive disorders
2536:Sakati–Nyhan–Tisdale syndrome
1678:https://omim.org/entry/610756
867:dominance. Severe cerebellar
3340:DeSanctis–Cacchione syndrome
3047:DeSanctis–Cacchione syndrome
2993:Aicardi–Goutières syndrome 4
2774:Tatton-Brown–Rahman syndrome
2744:Benign symmetric lipomatosis
2046:Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A
918:not commonly seen, although
711:Metachromatic leukodystrophy
709:– is patchy and segmental– "
671:usually beginning at age 2.
2864:Branchio-oto-renal syndrome
2739:Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome
2283:"Orphanet: CAMFAK syndrome"
1893:Iyama T, Wilson DM (2016).
1301:thyroid-stimulating hormone
1088:, axonal loss, and gliosis
238:machinery for synthesizing
3464:
3345:Nijmegen breakage syndrome
3119:Nijmegen breakage syndrome
3035:Nucleotide excision repair
2836:Zimmermann–Laband syndrome
2788:Laurence–Moon–Bardet–Biedl
2749:Klippel–Trénaunay syndrome
2699:Caudal regression syndrome
2674:Klippel–Trénaunay syndrome
2636:Smith–Lemli–Opitz syndrome
2606:Cornelia de Lange syndrome
958:Loss of hair cells in the
953:sensorineural hearing loss
501:nucleotide excision repair
457:DNA damage theory of aging
430:homologous recombinational
411:nucleotide excision repair
109:, abnormal sensitivity to
15:
3388:
3254:Rothmund–Thomson syndrome
3152:Rothmund–Thomson syndrome
2684:Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome
2204:10.1016/j.arr.2016.08.002
1911:10.1016/j.jmb.2015.11.020
1859:10.1016/j.arr.2016.08.002
1738:(1 suppl. 1): e20190085.
1503:10.1016/j.mad.2013.02.006
1412:10.1007/s10038-006-0011-7
1399:Journal of Human Genetics
1353:Accelerated aging disease
1182:gastrointestinal motility
852:pattern with widening of
471:), are of short stature (
294:Cockayne syndrome has an
45:
22:Cockayne (disambiguation)
2754:Neurofibromatosis type I
2641:Snyder–Robinson syndrome
2591:1q21.1 deletion syndrome
2531:Saethre–Chotzen syndrome
2241:Pediatrics International
1485:Laugel, Vincent (2013).
860:are preserved. May show
218:occurs in the body, the
3318:Other/related disorders
2984:Separation/initiation:
2664:Adducted thumb syndrome
2626:Silver–Russell syndrome
2192:Ageing Research Reviews
2067:10.1073/pnas.1507105112
2009:10.15252/embj.201490041
1847:Ageing Research Reviews
1702:"Cell Injury and Death"
1596:10.1002/ajmg.1320420115
1172:Gastrointestinal system
951:. Mixed conductive and
912:neurofibrillary tangles
93:Neill-Dingwall syndrome
41:Neill-Dingwall syndrome
3423:Neurological disorders
3355:Dyskeratosis congenita
3335:Baller–Gerold syndrome
3309:Restrictive dermopathy
3264:NER protein-associated
3014:Dyskeratosis congenita
2800:Laurence–Moon syndrome
2596:Aarskog–Scott syndrome
2551:Baller–Gerold syndrome
2494:Congenital abnormality
1801:10.1093/nar/21.25.5890
1680:. Published 2/12/2007.
1293:sexual characteristics
1274:atrophy. A successful
1145:Aortic root dilatation
1094:Musculoskeletal system
1084:atrophy, with partial
1017:Pigmentary retinopathy
962:, particularly in the
902:enlargement, enlarged
769:(especially depths of
721:are affected. Affects
664:Central nervous system
303:
167:Edward Alfred Cockayne
95:, is a rare and fatal
20:. For other uses, see
3360:Ataxia telangiectasia
3277:Xeroderma pigmentosum
3114:Ataxia–telangiectasia
3057:Xeroderma pigmentosum
2795:Bardet–Biedl syndrome
2679:Nail–patella syndrome
2571:Pierre Robin sequence
2511:Acrocephalosyndactyly
1554:10.1056/NEJMra0804615
1135:Cardiovascular system
1019:("salt and pepper").
1008:Corneal opacification
966:. Loss of neurons in
505:xeroderma pigmentosum
293:
192:xeroderma pigmentosum
117:), eye disorders and
3325:Li–Fraumeni syndrome
3168:Li–Fraumeni syndrome
2726:Overgrowth syndromes
2127:admin (2020-10-23).
1363:Degenerative disease
701:subdural hemorrhages
3443:Progeroid syndromes
3330:Rapadilino syndrome
3282:Trichothiodystrophy
3219:Progeroid syndromes
3156:RAPADILINO syndrome
3091:Muir–Torre syndrome
3078:DNA mismatch repair
2714:VACTERL association
2058:2015PNAS..112E3495W
1960:10.1093/nar/gku1279
1328:production of sweat
1238:Reproductive system
1230:hypoplastic kidneys
1158:medial thickening.
1116:. Stooped posture.
1072:. Loss of cells in
991:vestibular ganglion
832:may show irregular
754:anterior horn cells
296:autosomal recessive
266:, several thousand
220:cellular metabolism
2669:Holt–Oram syndrome
2561:Goldenhar syndrome
2521:Carpenter syndrome
2415:External resources
2105:2015-09-24 at the
1278:has been reported.
1036:palpebral fissures
995:endolymphatic duct
993:. Collapse of the
940:vestibular systems
898:" may be present.
816:arteriolosclerosis
681:Delayed milestones
673:Mental retardation
511:Laboratory Studies
477:joint contractures
356:(also called CSB)
340:(also called CSA)
304:
3400:
3399:
3370:PIBI(D)S syndrome
3365:De Barsy syndrome
3290:
3289:
3272:Cockayne syndrome
3185:
3184:
3181:
3180:
3043:Cockayne syndrome
2961:Metabolic disease
2927:
2926:
2824:Feingold syndrome
2611:Dubowitz syndrome
2601:Cockayne syndrome
2526:Pfeiffer syndrome
2460:
2459:
2440:Cockayne Syndrome
2253:10.1111/ped.12635
2052:(27): E3495–504.
1948:Nucleic Acids Res
1789:Nucleic Acids Res
1453:978-0-7216-2921-6
1344:
1343:
1291:Normal secondary
1287:Endocrine systems
1189:gastrostomy tubes
1129:, disuse atrophy
997:of pars inferior
972:auditory pathways
742:peripheral nerves
628:enamel hypoplasia
609:Clinical features
548:, an area of the
400:pyrimidine dimers
373:
372:
123:Failure to thrive
103:neurodegenerative
85:Cockayne syndrome
82:
81:
33:Cockayne syndrome
27:Medical condition
3455:
3232:
3212:
3205:
3198:
3189:
3031:
2954:
2947:
2940:
2931:
2908:Donohue syndrome
2884:Timothy syndrome
2764:Proteus syndrome
2759:Perlman syndrome
2621:Robinow syndrome
2566:Moebius syndrome
2487:
2480:
2473:
2464:
2309:
2287:
2286:
2279:
2273:
2272:
2232:
2226:
2225:
2215:
2183:
2177:
2176:
2169:
2163:
2162:
2160:
2159:
2149:
2143:
2142:
2140:
2139:
2124:
2118:
2115:
2109:
2096:
2090:
2089:
2079:
2069:
2037:
2031:
2030:
2020:
2003:(10): 1399–416.
1988:
1982:
1981:
1971:
1939:
1933:
1932:
1922:
1890:
1881:
1880:
1870:
1838:
1823:
1822:
1812:
1780:
1774:
1773:
1763:
1723:
1717:
1716:
1714:
1712:
1698:
1692:
1687:
1681:
1674:
1668:
1665:
1648:
1641:
1624:
1621:
1608:
1607:
1579:
1566:
1565:
1537:
1531:
1530:
1497:(5–6): 161–170.
1482:
1476:
1473:
1458:
1457:
1441:
1431:
1425:
1424:
1414:
1390:
1368:Genetic disorder
1164:arteriosclerosis
906:magna are seen.
650:Photosensitivity
603:
313:
272:oxidative damage
260:oxidative damage
128:leukodystrophies
115:photosensitivity
78:
77:
61:Medical genetics
50:
30:
3463:
3462:
3458:
3457:
3456:
3454:
3453:
3452:
3403:
3402:
3401:
3396:
3384:
3313:
3286:
3258:
3244:Werner syndrome
3236:RecQ-associated
3221:
3216:
3186:
3177:
3147:Werner syndrome
3123:
3100:
3068:
3020:
2977:DNA replication
2971:
2965:DNA replication
2958:
2928:
2923:
2896:Marfan syndrome
2880:Keutel syndrome
2868:CHARGE syndrome
2852:Fraser syndrome
2810:
2809:Combined/other,
2804:
2783:
2779:Weaver syndrome
2720:
2650:
2646:Turner syndrome
2631:Seckel syndrome
2616:Noonan syndrome
2577:
2497:
2491:
2461:
2456:
2455:
2410:
2409:
2320:
2296:
2291:
2290:
2281:
2280:
2276:
2234:
2233:
2229:
2185:
2184:
2180:
2171:
2170:
2166:
2157:
2155:
2151:
2150:
2146:
2137:
2135:
2126:
2125:
2121:
2116:
2112:
2107:Wayback Machine
2097:
2093:
2039:
2038:
2034:
1990:
1989:
1985:
1941:
1940:
1936:
1892:
1891:
1884:
1840:
1839:
1826:
1782:
1781:
1777:
1725:
1724:
1720:
1710:
1708:
1700:
1699:
1695:
1688:
1684:
1675:
1671:
1666:
1651:
1642:
1627:
1622:
1611:
1581:
1580:
1569:
1548:(15): 1475–85.
1542:N. Engl. J. Med
1539:
1538:
1534:
1484:
1483:
1479:
1474:
1461:
1454:
1433:
1432:
1428:
1392:
1391:
1387:
1382:
1373:CAMFAK syndrome
1349:
1322:Eccrine systems
1311:pituitary gland
1160:Atherosclerosis
1042:Patchy loss of
968:spiral ganglion
944:Sensorineural,
908:Amyloid plaques
881:dentate nucleus
812:atherosclerosis
767:cerebral cortex
730:corpus callosum
715:oligodendroglia
597:
595:Recent research
588:
575:
562:
542:
534:
526:
524:Imaging Studies
513:
493:corneal opacity
465:
388:
288:
208:
179:
119:premature aging
91:), also called
72:
28:
25:
12:
11:
5:
3461:
3459:
3451:
3450:
3445:
3440:
3435:
3433:Genodermatoses
3430:
3425:
3420:
3415:
3405:
3404:
3398:
3397:
3389:
3386:
3385:
3383:
3382:
3377:
3372:
3367:
3362:
3357:
3352:
3350:Fanconi anemia
3347:
3342:
3337:
3332:
3327:
3321:
3319:
3315:
3314:
3312:
3311:
3306:
3300:
3298:
3292:
3291:
3288:
3287:
3285:
3284:
3279:
3274:
3268:
3266:
3260:
3259:
3257:
3256:
3251:
3249:Bloom syndrome
3246:
3240:
3238:
3229:
3223:
3222:
3217:
3215:
3214:
3207:
3200:
3192:
3183:
3182:
3179:
3178:
3176:
3175:
3170:
3165:
3163:Fanconi anemia
3160:
3159:
3158:
3149:
3144:
3142:Bloom syndrome
3131:
3129:
3125:
3124:
3122:
3121:
3116:
3110:
3108:
3102:
3101:
3099:
3098:
3093:
3088:
3082:
3080:
3070:
3069:
3067:
3066:
3064:IBIDS syndrome
3061:
3060:
3059:
3049:
3039:
3037:
3028:
3022:
3021:
3019:
3018:
3017:
3016:
2998:
2997:
2996:
2995:
2981:
2979:
2973:
2972:
2959:
2957:
2956:
2949:
2942:
2934:
2925:
2924:
2922:
2921:
2920:
2919:
2917:Fryns syndrome
2911:
2899:
2887:
2871:
2855:
2839:
2827:
2814:
2812:
2806:
2805:
2803:
2802:
2797:
2791:
2789:
2785:
2784:
2782:
2781:
2776:
2771:
2769:Sotos syndrome
2766:
2761:
2756:
2751:
2746:
2741:
2736:
2730:
2728:
2722:
2721:
2719:
2718:
2717:
2716:
2711:
2706:
2701:
2686:
2681:
2676:
2671:
2666:
2660:
2658:
2652:
2651:
2649:
2648:
2643:
2638:
2633:
2628:
2623:
2618:
2613:
2608:
2603:
2598:
2593:
2587:
2585:
2579:
2578:
2576:
2575:
2574:
2573:
2568:
2563:
2558:
2553:
2545:
2544:
2543:
2538:
2533:
2528:
2523:
2518:
2516:Apert syndrome
2507:
2505:
2499:
2498:
2492:
2490:
2489:
2482:
2475:
2467:
2458:
2457:
2454:
2453:
2442:
2431:
2419:
2418:
2416:
2412:
2411:
2408:
2407:
2396:
2385:
2374:
2357:
2342:
2321:
2316:
2315:
2313:
2312:Classification
2306:
2305:
2295:
2294:External links
2292:
2289:
2288:
2274:
2247:(3): 339–347.
2227:
2178:
2164:
2144:
2119:
2110:
2091:
2032:
1983:
1934:
1882:
1824:
1795:(25): 5890–5.
1775:
1718:
1693:
1682:
1669:
1649:
1625:
1609:
1567:
1532:
1477:
1459:
1452:
1426:
1384:
1383:
1381:
1378:
1377:
1376:
1370:
1365:
1360:
1358:Biogerontology
1355:
1348:
1345:
1342:
1341:
1338:
1324:
1318:
1317:
1307:
1305:calcium levels
1297:growth hormone
1289:
1283:
1282:
1279:
1269:
1265:
1264:
1261:
1251:
1247:
1246:
1243:
1240:
1234:
1233:
1226:Renal arteries
1223:
1218:
1212:
1211:
1208:
1174:
1168:
1167:
1152:
1149:Cardiomyopathy
1137:
1131:
1130:
1121:
1118:Muscle wasting
1096:
1090:
1089:
1080:are affected.
1078:photoreceptors
1060:distribution.
1040:
1005:
999:
998:
976:Scala communis
956:
942:
932:
931:
889:Purkinje cells
805:leptomeningeal
801:String vessels
781:; also of the
777:, cerebellum,
704:
666:
660:
659:
657:
647:
633:
632:
630:
620:
614:
613:
610:
607:
606:Affected parts
596:
593:
587:
584:
574:
571:
561:
558:
541:
538:
533:
530:
525:
522:
512:
509:
503:(NER), unlike
489:telangiectasia
464:
461:
387:
384:
383:
382:
371:
370:
367:
362:
358:
357:
351:
346:
342:
341:
335:
330:
326:
325:
322:
317:
287:
284:
207:
204:
203:
202:
198:
195:
184:
178:
175:
107:nervous system
80:
79:
58:
52:
51:
43:
42:
39:
35:
34:
26:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3460:
3449:
3446:
3444:
3441:
3439:
3436:
3434:
3431:
3429:
3426:
3424:
3421:
3419:
3418:Rare diseases
3416:
3414:
3411:
3410:
3408:
3395:
3394:
3387:
3381:
3378:
3376:
3375:BIDS syndrome
3373:
3371:
3368:
3366:
3363:
3361:
3358:
3356:
3353:
3351:
3348:
3346:
3343:
3341:
3338:
3336:
3333:
3331:
3328:
3326:
3323:
3322:
3320:
3316:
3310:
3307:
3305:
3302:
3301:
3299:
3297:
3293:
3283:
3280:
3278:
3275:
3273:
3270:
3269:
3267:
3265:
3261:
3255:
3252:
3250:
3247:
3245:
3242:
3241:
3239:
3237:
3233:
3230:
3228:
3224:
3220:
3213:
3208:
3206:
3201:
3199:
3194:
3193:
3190:
3174:
3171:
3169:
3166:
3164:
3161:
3157:
3153:
3150:
3148:
3145:
3143:
3140:
3139:
3138:
3137:
3136:RecQ helicase
3133:
3132:
3130:
3126:
3120:
3117:
3115:
3112:
3111:
3109:
3107:
3103:
3097:
3094:
3092:
3089:
3087:
3084:
3083:
3081:
3079:
3075:
3071:
3065:
3062:
3058:
3055:
3054:
3053:
3052:Thymine dimer
3050:
3048:
3044:
3041:
3040:
3038:
3036:
3032:
3029:
3027:
3023:
3015:
3012:
3011:
3010:
3009:
3004:
3000:
2999:
2994:
2991:
2990:
2989:
2988:
2983:
2982:
2980:
2978:
2974:
2970:
2966:
2962:
2955:
2950:
2948:
2943:
2941:
2936:
2935:
2932:
2918:
2915:
2914:
2912:
2909:
2905:
2904:
2900:
2897:
2893:
2892:
2888:
2885:
2881:
2877:
2876:
2872:
2869:
2865:
2861:
2860:
2856:
2853:
2849:
2848:
2844:
2840:
2837:
2833:
2832:
2828:
2825:
2821:
2820:
2816:
2815:
2813:
2807:
2801:
2798:
2796:
2793:
2792:
2790:
2786:
2780:
2777:
2775:
2772:
2770:
2767:
2765:
2762:
2760:
2757:
2755:
2752:
2750:
2747:
2745:
2742:
2740:
2737:
2735:
2732:
2731:
2729:
2727:
2723:
2715:
2712:
2710:
2707:
2705:
2702:
2700:
2697:
2696:
2694:
2690:
2687:
2685:
2682:
2680:
2677:
2675:
2672:
2670:
2667:
2665:
2662:
2661:
2659:
2657:
2653:
2647:
2644:
2642:
2639:
2637:
2634:
2632:
2629:
2627:
2624:
2622:
2619:
2617:
2614:
2612:
2609:
2607:
2604:
2602:
2599:
2597:
2594:
2592:
2589:
2588:
2586:
2584:
2583:Short stature
2580:
2572:
2569:
2567:
2564:
2562:
2559:
2557:
2554:
2552:
2549:
2548:
2546:
2542:
2539:
2537:
2534:
2532:
2529:
2527:
2524:
2522:
2519:
2517:
2514:
2513:
2512:
2509:
2508:
2506:
2504:
2500:
2495:
2488:
2483:
2481:
2476:
2474:
2469:
2468:
2465:
2452:
2448:
2447:
2443:
2441:
2437:
2436:
2432:
2430:
2426:
2425:
2421:
2420:
2417:
2413:
2406:
2402:
2401:
2397:
2395:
2391:
2390:
2386:
2384:
2380:
2379:
2375:
2373:
2370:
2367:
2363:
2362:
2358:
2356:
2352:
2351:
2347:
2343:
2340:
2336:
2332:
2331:
2327:
2323:
2322:
2319:
2314:
2310:
2304:
2303:
2298:
2297:
2293:
2284:
2278:
2275:
2270:
2266:
2262:
2258:
2254:
2250:
2246:
2242:
2238:
2231:
2228:
2223:
2219:
2214:
2209:
2205:
2201:
2197:
2193:
2189:
2182:
2179:
2174:
2168:
2165:
2154:
2148:
2145:
2134:
2130:
2123:
2120:
2114:
2111:
2108:
2104:
2101:
2095:
2092:
2087:
2083:
2078:
2073:
2068:
2063:
2059:
2055:
2051:
2047:
2043:
2036:
2033:
2028:
2024:
2019:
2014:
2010:
2006:
2002:
1998:
1994:
1987:
1984:
1979:
1975:
1970:
1965:
1961:
1957:
1954:(1): 247–58.
1953:
1949:
1945:
1938:
1935:
1930:
1926:
1921:
1916:
1912:
1908:
1904:
1900:
1896:
1889:
1887:
1883:
1878:
1874:
1869:
1864:
1860:
1856:
1852:
1848:
1844:
1837:
1835:
1833:
1831:
1829:
1825:
1820:
1816:
1811:
1806:
1802:
1798:
1794:
1790:
1786:
1779:
1776:
1771:
1767:
1762:
1757:
1753:
1749:
1745:
1741:
1737:
1733:
1729:
1722:
1719:
1707:
1703:
1697:
1694:
1691:
1686:
1683:
1679:
1673:
1670:
1664:
1662:
1660:
1658:
1656:
1654:
1650:
1646:
1640:
1638:
1636:
1634:
1632:
1630:
1626:
1620:
1618:
1616:
1614:
1610:
1605:
1601:
1597:
1593:
1589:
1585:
1578:
1576:
1574:
1572:
1568:
1563:
1559:
1555:
1551:
1547:
1543:
1536:
1533:
1528:
1524:
1520:
1516:
1512:
1508:
1504:
1500:
1496:
1492:
1488:
1481:
1478:
1472:
1470:
1468:
1466:
1464:
1460:
1455:
1449:
1445:
1440:
1439:
1430:
1427:
1422:
1418:
1413:
1408:
1404:
1400:
1396:
1389:
1386:
1379:
1374:
1371:
1369:
1366:
1364:
1361:
1359:
1356:
1354:
1351:
1350:
1346:
1339:
1337:
1333:
1329:
1325:
1323:
1320:
1319:
1316:
1315:thyroid gland
1312:
1308:
1306:
1302:
1298:
1294:
1290:
1288:
1285:
1284:
1280:
1277:
1273:
1270:
1267:
1266:
1262:
1259:
1255:
1252:
1249:
1248:
1244:
1241:
1239:
1236:
1235:
1231:
1227:
1224:
1222:
1221:Renal failure
1219:
1217:
1214:
1213:
1209:
1206:
1202:
1201:liver enzymes
1198:
1194:
1190:
1187:
1183:
1179:
1175:
1173:
1170:
1169:
1165:
1161:
1157:
1153:
1150:
1146:
1142:
1138:
1136:
1133:
1132:
1128:
1125:
1122:
1119:
1115:
1111:
1107:
1103:
1100:
1097:
1095:
1092:
1091:
1087:
1086:demyelination
1083:
1079:
1075:
1071:
1067:
1063:
1059:
1055:
1051:
1048:
1045:
1041:
1039:
1037:
1033:
1029:
1025:
1022:
1018:
1014:
1009:
1006:
1004:
1001:
1000:
996:
992:
988:
987:prototympanum
984:
981:
977:
973:
970:. Atrophy of
969:
965:
961:
957:
954:
950:
947:
943:
941:
937:
934:
933:
930:
928:
924:
921:
917:
916:Hirano bodies
913:
909:
905:
901:
897:
894:
890:
886:
882:
878:
874:
870:
866:
863:
859:
855:
851:
847:
846:malformations
843:
839:
835:
831:
827:
823:
821:
817:
813:
810:
806:
802:
798:
794:
792:
788:
784:
780:
776:
775:basal ganglia
772:
768:
764:
763:Calcification
759:
755:
751:
747:
743:
739:
735:
731:
727:
724:
720:
719:Schwann cells
716:
712:
708:
707:Demyelination
705:
702:
698:
694:
690:
686:
682:
678:
674:
670:
667:
665:
662:
661:
658:
655:
651:
648:
646:
642:
638:
635:
634:
631:
629:
625:
624:Dental caries
621:
619:
616:
615:
611:
608:
605:
604:
601:
594:
592:
585:
583:
580:
572:
570:
566:
559:
557:
555:
551:
547:
539:
537:
531:
529:
523:
521:
518:
510:
508:
506:
502:
498:
494:
490:
486:
482:
478:
474:
470:
462:
460:
458:
454:
449:
447:
444:(rather than
443:
439:
435:
431:
427:
424:), a 5' – 3'
423:
419:
414:
412:
408:
405:
401:
397:
393:
385:
380:
375:
374:
368:
366:
363:
360:
359:
355:
352:
350:
347:
344:
343:
339:
336:
334:
331:
328:
327:
323:
321:
318:
315:
314:
311:
309:
301:
297:
292:
285:
283:
281:
277:
273:
269:
265:
261:
257:
253:
249:
245:
244:developmental
241:
237:
234:, children's
233:
232:transcription
229:
225:
224:free radicals
221:
217:
213:
205:
199:
196:
193:
189:
185:
181:
180:
176:
174:
172:
168:
163:
160:
155:
153:
152:
147:
143:
142:
137:
133:
129:
124:
120:
116:
112:
108:
104:
101:
98:
94:
90:
86:
76:
70:
66:
62:
59:
57:
53:
49:
44:
40:
36:
31:
23:
19:
3390:
3271:
3134:
3042:
3006:
3001:Termination/
2985:
2901:
2889:
2873:
2857:
2841:
2829:
2817:
2689:Gastrulation
2600:
2503:Craniofacial
2444:
2433:
2422:
2398:
2387:
2376:
2359:
2344:
2324:
2299:
2277:
2244:
2240:
2230:
2195:
2191:
2181:
2167:
2156:. Retrieved
2147:
2136:. Retrieved
2132:
2122:
2113:
2094:
2049:
2045:
2035:
2000:
1996:
1986:
1951:
1947:
1937:
1905:(1): 62–78.
1902:
1899:J. Mol. Biol
1898:
1850:
1846:
1792:
1788:
1778:
1735:
1731:
1721:
1709:. Retrieved
1705:
1696:
1685:
1672:
1590:(1): 68–84.
1587:
1583:
1545:
1541:
1535:
1494:
1490:
1480:
1437:
1429:
1405:(8): 701–5.
1402:
1398:
1388:
1216:Renal system
1197:splenomegaly
1193:Hepatomegaly
1186:percutaneous
1184:. Many have
1141:hypertension
1139:Accelerated
1106:Contractures
1068:atrophy and
1058:perivascular
1032:Enophthalmos
1011:
978:, thickened
949:hearing loss
824:
822:is present.
795:
761:
758:degeneration
726:white matter
669:Microcephaly
598:
589:
586:Epidemiology
576:
567:
563:
543:
535:
527:
514:
469:microcephaly
466:
450:
448:) template.
415:
389:
310:as follows:
305:
209:
164:
156:
149:
145:
139:
135:
132:white matter
92:
88:
84:
83:
3106:MRN complex
2811:known locus
2709:Sirenomelia
2435:GeneReviews
1199:, elevated
1180:. Abnormal
1124:Denervation
1082:Optic nerve
1070:hyperplasia
900:Ventricular
875:, granular
836:, multiple
809:accelerated
791:capillaries
738:spinal cord
532:Other Tests
426:exonuclease
404:transcribed
369:none known
308:genetically
300:inheritance
298:pattern of
69:dermatology
38:Other names
3407:Categories
3391:See also:
3227:DNA repair
3026:DNA repair
3003:telomerase
2704:Ectromelia
2389:DiseasesDB
2158:2023-07-06
2138:2023-07-06
1380:References
1326:Decreased
1258:testicular
1256:, smaller
1254:Micropenis
1205:metabolism
1203:. Altered
1154:Increased
1066:epithelial
1054:Lipofuscin
1028:Optic disk
985:, widened
964:basal turn
923:reactivity
871:. Loss of
826:Astrocytes
799:changes -
787:arterioles
752:. Loss of
750:cerebellum
612:pathology
554:cerebellum
453:DNA repair
418:DNA damage
413:(TC-NER).
264:human cell
256:metabolism
214:or excess
188:congenital
159:DNA repair
144:gene, and
3296:Lamin A/C
2913:Multiple
2496:syndromes
2424:eMedicine
2400:SNOMED CT
1752:1415-4757
1511:1872-6216
1295:. Normal
1276:pregnancy
1114:scoliosis
1099:Cachectic
1034:, Narrow
1013:Cataracts
946:high tone
920:ubiquitin
896:torpedoes
885:Dendrites
865:occipital
858:neocortex
842:FLAIR MRI
834:cytoplasm
830:microglia
807:vessels,
734:brainstem
579:prognosis
573:Prognosis
560:Treatment
550:forebrain
540:Neurology
497:Nystagmus
463:Diagnosis
386:Mechanism
280:apoptosis
252:molecular
212:hyperoxia
100:recessive
97:autosomal
65:neurology
56:Specialty
2987:RNASEH2A
2693:mesoderm
2556:Cyclopia
2446:Orphanet
2405:21086008
2341:Q87.110)
2261:25851792
2222:27507608
2198:: 3–17.
2103:Archived
2086:26100862
2027:25820262
1978:25505141
1929:26616585
1877:27507608
1853:: 3–17.
1770:32453336
1562:19812404
1527:19137836
1519:23428416
1421:16865293
1347:See also
1207:of drugs
1127:myopathy
1110:Kyphosis
1102:dwarfism
1074:ganglion
1064:pigment
1050:granules
1030:pallor,
929:present
904:cisterna
873:Purkinje
862:parietal
797:Vascular
783:arteries
779:thalamus
746:Neuronal
723:cerebral
713:". Both
693:seizures
485:cachetic
481:kyphosis
473:dwarfism
438:G1 phase
286:Genetics
240:proteins
111:sunlight
2429:ped/424
2383:D003057
2269:5311897
2213:5195851
2077:4500203
2054:Bibcode
2018:4491999
1969:4288174
1920:4738086
1868:5195851
1819:8290349
1761:7250278
1604:1308368
1309:Normal
1272:Ovarian
1268:Females
1176:Severe
1062:Retinal
1047:pigment
1044:melanin
960:cochlea
936:Hearing
877:neurons
869:atrophy
820:Gliosis
765:of the
697:strokes
685:Tremors
656:access.
546:putamen
422:DCLRE1A
268:lesions
236:genetic
18:cocaine
2547:Other
2372:216411
2369:133540
2366:216400
2267:
2259:
2220:
2210:
2084:
2074:
2025:
2015:
1997:EMBO J
1976:
1966:
1927:
1917:
1875:
1865:
1817:
1810:310470
1807:
1768:
1758:
1750:
1711:7 July
1602:
1560:
1525:
1517:
1509:
1450:
1419:
1336:saliva
1178:reflux
1156:intima
1024:pupils
1021:Miotic
1003:Vision
983:curare
980:stapes
893:axonal
838:nuclei
789:, and
740:, and
699:, and
689:ataxia
677:low IQ
654:venous
365:216411
349:133540
333:216400
276:genome
216:oxygen
206:Causes
154:gene.
71:
3128:Other
2656:Limbs
2355:759.8
2335:Q87.1
2265:S2CID
1523:S2CID
1332:tears
1250:Males
927:axons
854:sulci
850:gyral
771:sulci
675:with
645:nails
455:(see
407:genes
354:ERCC6
338:ERCC8
324:Gene
316:Type
248:blood
177:Types
151:ERCC6
141:ERCC8
3008:DKC1
2967:and
2394:2907
2378:MeSH
2361:OMIM
2350:9-CM
2339:ILDS
2257:PMID
2218:PMID
2082:PMID
2023:PMID
1974:PMID
1925:PMID
1873:PMID
1815:PMID
1766:PMID
1748:ISSN
1713:2021
1600:PMID
1558:PMID
1515:PMID
1507:ISSN
1448:ISBN
1417:PMID
1313:and
1260:size
938:and
828:and
814:and
717:and
641:hair
637:Skin
618:Face
577:The
394:and
320:OMIM
3074:MSI
2451:191
2346:ICD
2326:ICD
2249:doi
2208:PMC
2200:doi
2072:PMC
2062:doi
2050:112
2013:PMC
2005:doi
1964:PMC
1956:doi
1915:PMC
1907:doi
1903:428
1863:PMC
1855:doi
1805:PMC
1797:doi
1756:PMC
1740:doi
1592:doi
1550:doi
1546:361
1499:doi
1495:134
1444:575
1407:doi
925:of
887:of
793:).
459:).
446:DNA
442:RNA
396:CSB
392:CSA
282:).
228:DNA
210:If
3409::
3005::
2963::
2903:19
2891:15
2882:,
2875:12
2866:,
2847:13
2695::
2449::
2438::
2427::
2403::
2392::
2381::
2364::
2353::
2333::
2330:10
2263:.
2255:.
2245:57
2243:.
2239:.
2216:.
2206:.
2196:33
2194:.
2190:.
2131:.
2080:.
2070:.
2060:.
2048:.
2044:.
2021:.
2011:.
2001:34
1999:.
1995:.
1972:.
1962:.
1952:43
1950:.
1946:.
1923:.
1913:.
1901:.
1897:.
1885:^
1871:.
1861:.
1851:33
1849:.
1845:.
1827:^
1813:.
1803:.
1793:21
1791:.
1787:.
1764:.
1754:.
1746:.
1736:43
1734:.
1730:.
1704:.
1652:^
1628:^
1612:^
1598:.
1588:42
1586:.
1570:^
1556:.
1544:.
1521:.
1513:.
1505:.
1493:.
1489:.
1462:^
1446:.
1415:.
1403:51
1401:.
1397:.
1340:-
1334:,
1330:,
1303:,
1299:,
1281:-
1263:-
1245:-
1232:.
1210:-
1195:,
1191:.
1166:.
1162:,
1151:.
1147:.
1143:.
1112:,
1108:.
1104:.
1052:.
1038:.
1026:,
1010:.
974:.
914:,
910:,
883:.
818:.
785:,
773:,
760:.
744:.
736:,
732:,
728:,
703:.
695:,
691:,
687:,
679:.
643:,
639:,
626:,
434:G0
361:C
345:B
329:A
121:.
89:CS
67:,
63:,
3211:e
3204:t
3197:v
3154:/
3076:/
3045:/
2953:e
2946:t
2939:v
2910:)
2906:(
2898:)
2894:(
2886:)
2878:(
2870:)
2862:(
2859:8
2854:)
2850:(
2845:/
2843:4
2838:)
2834:(
2831:3
2826:)
2822:(
2819:2
2691:/
2486:e
2479:t
2472:v
2348:-
2337:(
2328:-
2318:D
2285:.
2271:.
2251::
2224:.
2202::
2175:.
2161:.
2141:.
2088:.
2064::
2056::
2029:.
2007::
1980:.
1958::
1931:.
1909::
1879:.
1857::
1821:.
1799::
1772:.
1742::
1715:.
1606:.
1594::
1564:.
1552::
1529:.
1501::
1456:.
1423:.
1409::
1242:-
1120:.
683:.
436:/
302:.
113:(
87:(
24:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.