125:
246:. At local contact temperatures ranging between 305-330 °C, the additive thermally decomposes and the reactive halogen atoms form a surface layer of iron halides on the part surface. Eventual failure of the contact point comes when the contact temperature exceeds the melting point of the iron halide layer. Under such conditions, small particles of
69:
perform well over a range of temperatures, speeds and gear sizes to help prevent damage to the gears during starting and stopping of the engine. Unlike antiwear additives, extreme pressure additives are rarely used in
250:
are generated as well. Some compounds used in lubricant additives are chloroalkanes, trichloromethyl phosphine acids, organic esters of a-acetoxy-b,b,b-trichloroethyl phosphonic acid, trichloromethyl esters of
238:
361:
128:
74:. The sulfur or chlorine compounds contained in them can react with water and combustion byproducts, forming acids that facilitate
379:
155:
and elementary sulfur), and chlorinated compounds. During the 1950s the use of lead soaps was eliminated and replaced by
278:(TCP) typically exceeds 200 °C. Their reaction products form a chemically bonded lubricating film on the surfaces.
271:
109:
conditions. Under such conditions, small irregularities on the sliding surfaces cause localized flashes of high
51:
184:
434:
222:
188:
295:
160:
397:"Monitoring Active Sulfur in EP Gear Oils - And Other Options for Monitoring EP Additive Depletion"
275:
55:
357:
118:
114:
349:
344:
Theo Mang; Jürgen Braun; Wilfried Dresel; Jürgen Omeis (2011). "Lubricants, 2. Components".
255:, trichloromethyl derivates of sulfur, trichloroacetoxy compounds, esters or amine salts of
225:) are cheap and efficient, however they persist in environment and have strong tendency for
383:
299:
266:, with or without zinc, have excellent high-pressure and antiwear properties, and provide
263:
256:
252:
234:
226:
198:
113:(300-1000 °C), without significant increase of the average surface temperature. The
428:
230:
36:
242:
The activity of halogenated hydrocarbons increases with decreasing stability of the
419:
322:
24:
376:
274:(ZDDP) start decomposing at 130-170 °C, while the activation temperature of
281:
209:
110:
396:
294:
compounds decompose under high pressure to form an in-situ deposited layer of
291:
243:
214:
144:
98:
86:
353:
310:
303:
267:
75:
71:
40:
28:
132:
106:
90:
66:
58:
are used with lighter load applications such as hydraulic and automotive
124:
314:
285:
247:
233:, their role is largely confined to formulations for forming complex
180:
94:
82:
59:
105:
compounds, which chemically react with the metal surface under high
50:
Extreme pressure additives are usually used in applications such as
318:
204:
194:
152:
123:
102:
44:
156:
148:
140:
32:
270:
protection especially in presence of chlorinated hydrocarbons.
259:, 1,2,3,4,7,7-hexachloro-5-dimethylbicyclo-2-heptene, etc.
229:. Therefore, they are being replaced with alternatives. In
135:, serving as an antioxidant and protecting metal surfaces.
309:
Sulfur containing extreme pressure additives can cause
35:
exposed to very high pressures. They are also added to
81:
Extreme pressure additives typically contain organic
325:
when high temperature environments are encountered.
139:The early extreme pressure additives were based on
31:with a role to decrease wear of the parts of the
346:Ullmanns Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry
8:
121:and the surface is confined to this area.
339:
337:
284:serve as carriers of inactive and active
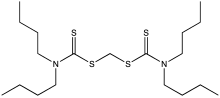
131:is an additive in some extreme pressure
333:
313:problems in gears with parts made of
7:
221:Aliphatic chlorinated hydrocarbons (
151:"), "active sulfur" compounds (e.g.
129:Methylenebis(dibutyldithiocarbamate)
179:Short and medium chain chlorinated
78:of the engine parts and bearings.
14:
159:and phosphorus compounds such as
176:Dark active sulfur hydrocarbon
166:Some of the EP additives are:
1:
272:Zinc dialkyldithiophosphates
170:Dark inactive sulfurized fat
451:
302:are used as additives for
173:Dark active sulfurized fat
17:Extreme pressure additives
354:10.1002/14356007.o15_o04
185:chlorinated hydrocarbons
382:July 15, 2011, at the
136:
101:and sulfur-phosphorus-
223:chlorinated paraffins
189:chlorinated paraffins
127:
93:compounds, including
296:molybdenum disulfide
161:zinc dithiophosphate
395:Shugarman, Arnold.
276:tricresyl phosphate
244:carbon-halogen bond
137:
56:antiwear additives
377:pecuniary.com FAQ
363:978-3-527-30673-2
115:chemical reaction
65:Extreme pressure
442:
408:
407:
405:
403:
392:
386:
374:
368:
367:
341:
300:dithiocarbamates
264:organophosphates
450:
449:
445:
444:
443:
441:
440:
439:
425:
424:
416:
411:
401:
399:
394:
393:
389:
384:Wayback Machine
375:
371:
364:
343:
342:
335:
331:
257:chlorendic acid
253:phosphoric acid
235:stainless steel
227:bioaccumulation
199:chlorendic acid
12:
11:
5:
448:
446:
438:
437:
427:
426:
423:
422:
415:
412:
410:
409:
387:
369:
362:
332:
330:
327:
231:cutting fluids
219:
218:
212:
207:
201:
192:
177:
174:
171:
37:cutting fluids
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
447:
436:
435:Oil additives
433:
432:
430:
421:
418:
417:
413:
398:
391:
388:
385:
381:
378:
373:
370:
365:
359:
355:
351:
348:. Wiley-VCH.
347:
340:
338:
334:
328:
326:
324:
320:
316:
312:
307:
305:
301:
298:. Molybdenum
297:
293:
289:
287:
283:
279:
277:
273:
269:
265:
260:
258:
254:
249:
245:
240:
239:
236:
232:
228:
224:
216:
213:
211:
208:
206:
202:
200:
196:
193:
190:
186:
182:
178:
175:
172:
169:
168:
167:
164:
162:
158:
154:
150:
146:
142:
134:
130:
126:
122:
120:
116:
112:
108:
104:
100:
96:
92:
88:
84:
79:
77:
73:
68:
63:
61:
57:
53:
48:
46:
42:
38:
34:
30:
26:
22:
18:
420:Metalworking
400:. Retrieved
390:
372:
345:
323:copper alloy
308:
290:
282:Polysulfides
280:
262:Oil-soluble
261:
241:
220:
210:Polysulfides
165:
138:
117:between the
80:
64:
49:
21:EP additives
20:
16:
15:
145:fatty acids
111:temperature
329:References
321:and other
292:Molybdenum
215:Molybdenum
99:phosphorus
87:phosphorus
72:motor oils
29:lubricants
402:7 October
311:corrosion
268:corrosion
217:compounds
143:salts of
133:gear oils
119:additives
76:corrosion
67:gear oils
52:gearboxes
41:machining
25:additives
429:Category
414:See also
380:Archived
203:Polymer
107:pressure
91:chlorine
54:, while
304:greases
237:parts.
181:alkanes
147:("lead
60:engines
360:
315:bronze
286:sulfur
248:carbon
205:esters
195:Esters
153:thiols
95:sulfur
83:sulfur
45:metals
23:, are
319:brass
183:(see
149:soaps
103:boron
33:gears
19:, or
404:2012
358:ISBN
187:and
157:zinc
141:lead
39:for
27:for
350:doi
288:.
197:of
89:or
43:of
431::
356:.
336:^
317:,
306:.
163:.
85:,
62:.
47:.
406:.
366:.
352::
191:)
97:-
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.