1203:
have a high swelling ratio. Since they are noncovalently bound to the fibrils, they may reversibly associate and disassociate so that the bridges between fibrils can be broken and reformed. This process may be involved in allowing the fibril to elongate and decrease in diameter under tension. However, the proteoglycans may also have a role in the tensile properties of tendon. The structure of tendon is effectively a fibre composite material, built as a series of hierarchical levels. At each level of the hierarchy, the collagen units are bound together by either collagen crosslinks, or the proteoglycans, to create a structure highly resistant to tensile load. The elongation and the strain of the collagen fibrils alone have been shown to be much lower than the total elongation and strain of the entire tendon under the same amount of stress, demonstrating that the proteoglycan-rich matrix must also undergo deformation, and stiffening of the matrix occurs at high strain rates. This deformation of the non-collagenous matrix occurs at all levels of the tendon hierarchy, and by modulating the organisation and structure of this matrix, the different mechanical properties required by different tendons can be achieved. Energy storing tendons have been shown to utilise significant amounts of sliding between fascicles to enable the high strain characteristics they require, whilst positional tendons rely more heavily on sliding between collagen fibres and fibrils. However, recent data suggests that energy storing tendons may also contain fascicles which are twisted, or helical, in nature - an arrangement that would be highly beneficial for providing the spring-like behaviour required in these tendons.
1387:(TGF-β). These growth factors all have different roles during the healing process. IGF-1 increases collagen and proteoglycan production during the first stage of inflammation, and PDGF is also present during the early stages after injury and promotes the synthesis of other growth factors along with the synthesis of DNA and the proliferation of tendon cells. The three isoforms of TGF-β (TGF-β1, TGF-β2, TGF-β3) are known to play a role in wound healing and scar formation. VEGF is well known to promote angiogenesis and to induce endothelial cell proliferation and migration, and VEGF mRNA has been shown to be expressed at the site of tendon injuries along with collagen I mRNA. Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are a subgroup of TGF-β superfamily that can induce bone and cartilage formation as well as tissue differentiation, and BMP-12 specifically has been shown to influence formation and differentiation of tendon tissue and to promote fibrogenesis.
1396:
after about one week following an acute injury can help to promote the synthesis of collagen by the tenocytes, leading to increased tensile strength and diameter of the healed tendons and fewer adhesions than tendons that are immobilized. In chronic tendon injuries, mechanical loading has also been shown to stimulate fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis along with collagen realignment, all of which promote repair and remodeling. To further support the theory that movement and activity assist in tendon healing, it has been shown that immobilization of the tendons after injury often has a negative effect on healing. In rabbits, collagen fascicles that are immobilized have shown decreased tensile strength, and immobilization also results in lower amounts of water, proteoglycans, and collagen crosslinks in the tendons.
1230:) in some planes when stretched up to 2% along their length, i.e. within their normal range of motion. After this 'toe' region, the structure becomes significantly stiffer, and has a linear stress-strain curve until it begins to fail. The mechanical properties of tendons vary widely, as they are matched to the functional requirements of the tendon. The energy storing tendons tend to be more elastic, or less stiff, so they can more easily store energy, whilst the stiffer positional tendons tend to be a little more viscoelastic, and less elastic, so they can provide finer control of movement. A typical energy storing tendon will fail at around 12–15% strain, and a stress in the region of 100–150 MPa, although some tendons are notably more extensible than this, for example the superficial digital flexor in the
410:, which associate with collagen and are involved in the fibril assembly process during tendon development. Dermatan sulfate is thought to be responsible for forming associations between fibrils, while chondroitin sulfate is thought to be more involved with occupying volume between the fibrils to keep them separated and help withstand deformation. The dermatan sulfate side chains of decorin aggregate in solution, and this behavior can assist with the assembly of the collagen fibrils. When decorin molecules are bound to a collagen fibril, their dermatan sulfate chains may extend and associate with other dermatan sulfate chains on decorin that is bound to separate fibrils, therefore creating interfibrillar bridges and eventually causing parallel alignment of the fibrils.
1187:
the past two decades, much research has focused on the elastic properties of some tendons and their ability to function as springs. Not all tendons are required to perform the same functional role, with some predominantly positioning limbs, such as the fingers when writing (positional tendons) and others acting as springs to make locomotion more efficient (energy storing tendons). Energy storing tendons can store and recover energy at high efficiency. For example, during a human stride, the
Achilles tendon stretches as the ankle joint dorsiflexes. During the last portion of the stride, as the foot plantar-flexes (pointing the toes down), the stored elastic energy is released. Furthermore, because the tendon stretches, the muscle is able to function with less or even
1356:
levels of GAG and water are high. After about six weeks, the remodeling stage begins. The first part of this stage is consolidation, which lasts from about six to ten weeks after the injury. During this time, the synthesis of collagen and GAGs is decreased, and the cellularity is also decreased as the tissue becomes more fibrous as a result of increased production of collagen I and the fibrils become aligned in the direction of mechanical stress. The final maturation stage occurs after ten weeks, and during this time there is an increase in crosslinking of the collagen fibrils, which causes the tissue to become stiffer. Gradually, over about one year, the tissue will turn from fibrous to scar-like.
1281:: non-inflammatory injury to the tendon at the cellular level. The degradation is caused by damage to collagen, cells, and the vascular components of the tendon, and is known to lead to rupture. Observations of tendons that have undergone spontaneous rupture have shown the presence of collagen fibrils that are not in the correct parallel orientation or are not uniform in length or diameter, along with rounded tenocytes, other cell abnormalities, and the ingrowth of blood vessels. Other forms of tendinosis that have not led to rupture have also shown the degeneration, disorientation, and thinning of the collagen fibrils, along with an increase in the amount of glycosaminoglycans between the fibrils.
1195:
fibres have some flexibility due to the absence of hydroxyproline and proline residues at specific locations in the amino acid sequence, which allows the formation of other conformations such as bends or internal loops in the triple helix and results in the development of crimps. The crimps in the collagen fibrils allow the tendons to have some flexibility as well as a low compressive stiffness. In addition, because the tendon is a multi-stranded structure made up of many partially independent fibrils and fascicles, it does not behave as a single rod, and this property also contributes to its flexibility.
1502:
1179:
82:
383:, the tropocollagen molecules spontaneously assemble into insoluble fibrils. A collagen molecule is about 300 nm long and 1–2 nm wide, and the diameter of the fibrils that are formed can range from 50–500 nm. In tendons, the fibrils then assemble further to form fascicles, which are about 10 mm in length with a diameter of 50–300 μm, and finally into a tendon fibre with a diameter of 100–500 μm.
3945:
1520:, portions of the tendon can become ossified. In this process, osteocytes infiltrate the tendon and lay down bone as they would in sesamoid bone such as the patella. In birds, tendon ossification primarily occurs in the hindlimb, while in ornithischian dinosaurs, ossified axial muscle tendons form a latticework along the neural and haemal spines on the tail, presumably for support.
3955:
1360:
capable of degrading collagen I fibrils. The degradation of the collagen fibrils by MMP-1 along with the presence of denatured collagen are factors that are believed to cause weakening of the tendon ECM and an increase in the potential for another rupture to occur. In response to repeated mechanical loading or injury,
1202:
components of tendons also are important to the mechanical properties. While the collagen fibrils allow tendons to resist tensile stress, the proteoglycans allow them to resist compressive stress. These molecules are very hydrophilic, meaning that they can absorb a large amount of water and therefore
422:
produce the collagen molecules, which aggregate end-to-end and side-to-side to produce collagen fibrils. Fibril bundles are organized to form fibres with the elongated tenocytes closely packed between them. There is a three-dimensional network of cell processes associated with collagen in the tendon.
456:
Tendon length varies in all major groups and from person to person. Tendon length is, in practice, the deciding factor regarding actual and potential muscle size. For example, all other relevant biological factors being equal, a man with a shorter tendons and a longer biceps muscle will have greater
1194:
The mechanical properties of the tendon are dependent on the collagen fiber diameter and orientation. The collagen fibrils are parallel to each other and closely packed, but show a wave-like appearance due to planar undulations, or crimps, on a scale of several micrometers. In tendons, the collagen
1186:
Traditionally, tendons have been considered to be a mechanism by which muscles connect to bone as well as muscles itself, functioning to transmit forces. This connection allows tendons to passively modulate forces during locomotion, providing additional stability with no active work. However, over
1395:
In animal models, extensive studies have been conducted to investigate the effects of mechanical strain in the form of activity level on tendon injury and healing. While stretching can disrupt healing during the initial inflammatory phase, it has been shown that controlled movement of the tendons
1221:
structures, which means they exhibit both elastic and viscous behaviour. When stretched, tendons exhibit typical "soft tissue" behavior. The force-extension, or stress-strain curve starts with a very low stiffness region, as the crimp structure straightens and the collagen fibres align suggesting
1355:
of tenocytes are initiated. Tenocytes then move into the site and start to synthesize collagen III. After a few days, the repair or proliferation stage begins. In this stage, the tenocytes are involved in the synthesis of large amounts of collagen and proteoglycans at the site of injury, and the
1359:
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) have a very important role in the degradation and remodeling of the ECM during the healing process after a tendon injury. Certain MMPs including MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-8, MMP-13, and MMP-14 have collagenase activity, meaning that, unlike many other enzymes, they are
1245:
in rats resulted in a decrease in the average thickness of the collagen fiber bundles comprising the tendon. In humans, an experiment in which people were subjected to a simulated micro-gravity environment found that tendon stiffness decreased significantly, even when subjects were required to
472:
Tendon length is determined by genetic predisposition, and has not been shown to either increase or decrease in response to environment, unlike muscles, which can be shortened by trauma, use imbalances and a lack of recovery and stretching. In addition tendons allow muscles to be at an optimal
1403:
mechanisms have been proposed as reasons for the response of tenocytes to mechanical force that enable them to alter their gene expression, protein synthesis, and cell phenotype, and eventually cause changes in tendon structure. A major factor is mechanical deformation of the
1306:
It was believed that tendons could not undergo matrix turnover and that tenocytes were not capable of repair. However, it has since been shown that, throughout the lifetime of a person, tenocytes in the tendon actively synthesize matrix components as well as enzymes such as
1444:), lashing tool blades to shafts, etc. It is also recommended in survival guides as a material from which strong cordage can be made for items like traps or living structures. Tendon must be treated in specific ways to function usefully for these purposes.
1314:
The three main stages of tendon healing are inflammation, repair or proliferation, and remodeling, which can be further divided into consolidation and maturation. These stages can overlap with each other. In the first stage, inflammatory cells such as
1297:
Tendinopathies may be caused by several intrinsic factors including age, body weight, and nutrition. The extrinsic factors are often related to sports and include excessive forces or loading, poor training techniques, and environmental conditions.
56:
402:(GAG) side chains have multiple interactions with the surface of the fibrils – showing that the proteoglycans are important structurally in the interconnection of the fibrils. The major GAG components of the tendon are
1990:
Zhang G, Ezura Y, Chervoneva I, Robinson PS, Beason DP, Carine ET, et al. (August 2006). "Decorin regulates assembly of collagen fibrils and acquisition of biomechanical properties during tendon development".
1271:. Tendinopathies can be caused by a number of factors relating to the tendon extracellular matrix (ECM), and their classification has been difficult because their symptoms and histopathology often are similar.
1452:
utilized sinew as the only cordage for all domestic purposes due to the lack of other suitable fiber sources in their ecological habitats. The elastic properties of particular sinews were also used in
3205:
Riley GP, Curry V, DeGroot J, van El B, Verzijl N, Hazleman BL, et al. (March 2002). "Matrix metalloproteinase activities and their relationship with collagen remodelling in tendon pathology".
3240:
Moulin V, Tam BY, Castilloux G, Auger FA, O'Connor-McCourt MD, Philip A, et al. (August 2001). "Fetal and adult human skin fibroblasts display intrinsic differences in contractile capacity".
2717:
Thorpe CT, Klemt C, Riley GP, Birch HL, Clegg PD, Screen HR (August 2013). "Helical sub-structures in energy-storing tendons provide a possible mechanism for efficient energy storage and return".
1367:
A variety of other molecules are involved in tendon repair and regeneration. There are five growth factors that have been shown to be significantly upregulated and active during tendon healing:
1420:, which induce intracellular signaling cascades, may also be important, and ion channels are activated by stretching to allow ions such as calcium, sodium, or potassium to enter the cell.
1682:
Caldini EG, Caldini N, De-Pasquale V, Strocchi R, Guizzardi S, Ruggeri A, et al. (1990). "Distribution of elastic system fibres in the rat tail tendon and its associated sheaths".
1311:(MMPs) can degrade the matrix. Tendons are capable of healing and recovering from injuries in a process that is controlled by the tenocytes and their surrounding extracellular matrix.
1459:
Sinew makes for an excellent cordage material for three reasons: It is extremely strong, it contains natural glues, and it shrinks as it dries, doing away with the need for knots.
1226:) and ex vivo (through mechanical testing of various cadaveric tendon tissue) have shown that healthy tendons are highly anisotropic and exhibit a negative Poisson's ratio (
1416:, and cell-cell junctions. Changes in the actin cytoskeleton can activate integrins, which mediate "outside-in" and "inside-out" signaling between the cell and the matrix.
2259:
1717:
461:
will generally have shorter tendons. Conversely, in sports requiring athletes to excel in actions such as running or jumping, it is beneficial to have longer than average
1928:
Fukuta S, Oyama M, Kavalkovich K, Fu FH, Niyibizi C (April 1998). "Identification of types II, IX and X collagens at the insertion site of the bovine achilles tendon".
1267:
or tendon injuries due to overuse. These types of injuries generally result in inflammation and degeneration or weakening of the tendons, which may eventually lead to
2541:
Screen HR, Lee DA, Bader DL, Shelton JC (2004). "An investigation into the effects of the hierarchical structure of tendon fascicles on micromechanical properties".
1246:
perform restiveness exercises. These effects have implications in areas ranging from treatment of bedridden patients to the design of more effective exercises for
398:, which are capable of binding to the collagen fibrils at specific locations. The proteoglycans are interwoven with the collagen fibrils – their
161:
4193:
2633:
Gupta HS, Seto J, Krauss S, Boesecke P, Screen HR (February 2010). "In situ multi-level analysis of viscoelastic deformation mechanisms in tendon collagen".
1234:, which stretches in excess of 20% when galloping. Positional tendons can fail at strains as low as 6–8%, but can have moduli in the region of 700–1000 MPa.
1364:
may be released by tenocytes and can induce the release of MMPs, causing degradation of the ECM and leading to recurring injury and chronic tendinopathies.
2797:|volume=35 |issue=3 |pages=314–8. Are the material properties and matrix composition of equine flexor and extensor tendons determined by their functions?
3991:
3285:"Quantitative variation in vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA expression during early flexor tendon healing: an investigation in a canine model"
3899:
1626:"A Tppp3+Pdgfra+ tendon stem cell population contributes to regeneration and reveals a shared role for PDGF signalling in regeneration and fibrosis"
220:. The difference is that ligaments connect bone to bone, while tendons connect muscle to bone. There are about 4000 tendons in the adult human body
427:, and this signalling gives them the ability to detect and respond to mechanical loading. These communications happen by two proteins essentially:
2273:
1456:
favoured by the steppe nomads of
Eurasia, and Native Americans. The first stone throwing artillery also used the elastic properties of sinew.
2816:
1237:
Several studies have demonstrated that tendons respond to changes in mechanical loading with growth and remodeling processes, much like
309:
1376:
390:(a compound consisting of a protein bonded to glycosaminoglycan groups, present especially in connective tissue) components including
252:, which is a delicate loose connective tissue containing thin collagen fibrils and elastic fibers. A set of fascicles is bound by an
4490:
4155:
2465:
Ker RF (December 2002). "The implications of the adaptable fatigue quality of tendons for their construction, repair and function".
1551:
257:
2832:
Nakagawa Y, Totsuka M, Sato T, Fukuda Y, Hirota K (1989). "Effect of disuse on the ultrastructure of the achilles tendon in rats".
351:, many minor collagens are present that play vital roles in tendon development and function. These include type II collagen in the
4186:
3435:
2303:
363:, type V collagen in the vascular walls, and type X collagen in the mineralized fibrocartilage near the interface with the bone.
438:
Blood vessels may be visualized within the endotendon running parallel to collagen fibres, with occasional branching transverse
4507:
4068:
2430:
Silver FH, Freeman JW, Seehra GP (October 2003). "Collagen self-assembly and the development of tendon mechanical properties".
1384:
229:
2967:
2877:"Influence of 90-day simulated microgravity on human tendon mechanical properties and the effect of resistive countermeasures"
2502:"Tendon response to tensile stress: an ultrastructural investigation of collagen:proteoglycan interactions in stressed tendon"
1380:
1372:
445:
The internal tendon bulk is thought to contain no nerve fibres, but the epitenon and paratenon contain nerve endings, while
2077:"Proteoglycan-collagen arrangements in developing rat tail tendon. An electron microscopical and biochemical investigation"
4073:
3984:
156:
2218:
1844:
Kjaer M (April 2004). "Role of extracellular matrix in adaptation of tendon and skeletal muscle to mechanical loading".
1368:
1231:
473:
distance from the site where they actively engage in movement, passing through regions where space is premium, like the
1412:
and therefore affect cell shape, motility, and function. Mechanical forces can be transmitted by focal adhesion sites,
4455:
4367:
4179:
4078:
4063:
2036:"Structural aspects of the extracellular matrix of the tendon: an atomic force and scanning electron microscopy study"
3022:
Aström M, Rausing A (July 1995). "Chronic
Achilles tendinopathy. A survey of surgical and histopathologic findings".
2126:"Elasticity in extracellular matrix 'shape modules' of tendon, cartilage, etc. A sliding proteoglycan-filament model"
4138:
1223:
1308:
194:
4609:
4546:
4438:
3977:
144:
120:
248:. The collagen fibers run parallel to each other and are grouped into fascicles. Each fascicle is bound by an
1881:"The "other" 15-40%: The Role of Non-Collagenous Extracellular Matrix Proteins and Minor Collagens in Tendon"
1600:
4482:
4447:
2753:
269:
33:
1529:
168:
132:
2253:
1711:
1222:
negative
Poisson's ratio in the fibres of the tendon. More recently, tests carried out in vivo (through
450:
1489:, in which the tendon is marinated in garlic. It is also sometimes found in the Vietnamese noodle dish
149:
4604:
4470:
4465:
4349:
4320:
4243:
3786:
3748:
3428:
3384:
1405:
241:
372:
4148:
4058:
3761:
3644:
2281:
1449:
1400:
446:
407:
273:
249:
2811:(2nd ed.). Nicolais & Borzacchiello.Pub. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. pp. 2928–2939.
2543:
Proceedings of the
Institution of Mechanical Engineers. Part H, Journal of Engineering in Medicine
1293:: inflammation of the paratenon, or paratendinous sheet located between the tendon and its sheath.
359:
fibres of the vascular walls, type IX collagen, type IV collagen in the basement membranes of the
205:. It sends the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system, while withstanding
4339:
4041:
3958:
3400:
3357:
3314:
3265:
3097:
3047:
2916:
2857:
2566:
2175:"Tendon cells in vivo form a three dimensional network of cell processes linked by gap junctions"
2016:
1409:
1188:
2586:"Viscoelastic properties of collagen: synchrotron radiation investigations and structural model"
1501:
265:
4561:
4538:
4202:
4115:
3756:
3725:
3546:
3349:
3306:
3257:
3222:
3187:
3141:
3089:
3039:
3004:
2959:
2908:
2849:
2812:
2776:
2734:
2699:
2650:
2615:
2558:
2523:
2482:
2447:
2412:
2377:
2241:
2196:
2155:
2106:
2057:
2008:
1945:
1910:
1861:
1826:
1762:
1699:
1655:
1546:
399:
206:
70:
2987:
Maffulli N, Wong J, Almekinders LC (October 2003). "Types and epidemiology of tendinopathy".
2752:
Gatt R, Vella Wood M, Gatt A, Zarb F, Formosa C, Azzopardi KM, et al. (September 2015).
4614:
4331:
4160:
4143:
4120:
3392:
3341:
3296:
3249:
3214:
3179:
3131:
3081:
3031:
2996:
2898:
2888:
2841:
2768:
2726:
2689:
2681:
2642:
2605:
2597:
2584:
Puxkandl R, Zizak I, Paris O, Keckes J, Tesch W, Bernstorff S, et al. (February 2002).
2550:
2513:
2474:
2439:
2404:
2367:
2359:
2233:
2186:
2145:
2137:
2096:
2088:
2047:
2000:
1972:
1937:
1900:
1892:
1853:
1818:
1752:
1744:
1691:
1645:
1637:
1575:
1441:
1178:
403:
3072:
Sharma P, Maffulli N (January 2005). "Tendon injury and tendinopathy: healing and repair".
457:
potential for muscle mass than a man with a longer tendon and a shorter muscle. Successful
4362:
4105:
4051:
4024:
4000:
3948:
3771:
3733:
3526:
3421:
1809:
Lin TW, Cardenas L, Soslowsky LJ (June 2004). "Biomechanics of tendon injury and repair".
1242:
462:
348:
245:
198:
61:
2670:"Specialization of tendon mechanical properties results from interfascicular differences"
2395:
Hulmes DJ (2002). "Building collagen molecules, fibrils, and suprafibrillar structures".
3388:
2590:
Philosophical
Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences
1733:"Elastic fibres are broadly distributed in tendon and highly localized around tenocytes"
81:
4460:
4293:
4268:
4110:
4019:
3819:
3479:
2807:
Screen HR, Tanner KE (2012). "Structure & Biomechanics of
Biological Composites.".
2694:
2669:
2610:
2585:
2518:
2501:
2467:
Comparative
Biochemistry and Physiology. Part A, Molecular & Integrative Physiology
2372:
2347:
2191:
2174:
2150:
2125:
2101:
2076:
1905:
1880:
1757:
1732:
1650:
1625:
1429:
1268:
3332:
Berge JC, Storer RW (October 1995). "Intratendinous ossification in birds: A review".
3301:
3284:
3218:
3000:
2478:
2443:
2318:
1976:
1941:
4598:
4374:
4029:
4014:
3837:
3809:
3796:
3694:
3609:
3452:
3035:
1556:
1468:
1453:
1290:
474:
424:
323:
3404:
3361:
3318:
3269:
3051:
2921:
2893:
2876:
2861:
2793:
Batson EL, Paramour RJ, Smith TJ, Birch HL, Patterson-Kane JC, Goodship AE. (2003).
2570:
2020:
3894:
3884:
3814:
3589:
3581:
3183:
3101:
2944:
2343:
1822:
1514:
1348:
1332:
1320:
1264:
1218:
1199:
1105:
twist and turn your body, maintain your posture, or bend and straighten your trunk
1094:
twist and turn your body, maintain your posture, or bend and straighten your trunk
1083:
twist and turn your body, maintain your posture, or bend and straighten your trunk
1072:
twist and turn your body, maintain your posture, or bend and straighten your trunk
1061:
twist and turn your body, maintain your posture, or bend and straighten your trunk
458:
387:
40:
3136:
3119:
90:
2772:
2730:
2141:
284:
The dry mass of normal tendons, which is 30–45% of their total mass, is made of:
125:
4522:
4273:
4216:
4089:
4046:
3804:
3669:
3654:
3594:
3551:
3484:
1536:
1352:
1344:
1328:
1316:
1212:
466:
439:
376:
360:
237:
2554:
1857:
4551:
4306:
4283:
4258:
3874:
3869:
3776:
3738:
3604:
3571:
3536:
3461:
3283:
Boyer MI, Watson JT, Lou J, Manske PR, Gelberman RH, Cai SR (September 2001).
2646:
1641:
1417:
1340:
1287:: degeneration with inflammation of the tendon as well as vascular disruption.
1284:
1278:
1247:
233:
86:
65:
55:
3375:
Organ CL (2006). "Biomechanics of ossified tendons in ornithopod dinosaurs".
485:
There are about 4000 tendons in the human body, of which 55 are listed here:
137:
4569:
4495:
4399:
4394:
4384:
4301:
4278:
4263:
3889:
3684:
3619:
3345:
1541:
1413:
1361:
1324:
419:
356:
352:
334:
213:
3679:
3353:
3310:
3261:
3226:
3191:
3145:
3093:
3008:
2963:
2912:
2780:
2738:
2703:
2685:
2654:
2619:
2601:
2562:
2486:
2451:
2416:
2408:
2381:
2159:
2061:
2012:
1914:
1865:
1830:
1766:
1659:
1505:
Ossified tendon from an
Edmontosaurus bone bed in Wyoming (Lance Formation)
786:
cross the ankle joint and help move your foot up and down, or side to side
775:
cross the ankle joint and help move your foot up and down, or side to side
764:
cross the ankle joint and help move your foot up and down, or side to side
3043:
2853:
2527:
2245:
2200:
2110:
1949:
1703:
1263:
Tendons are subject to many types of injuries. There are various forms of
753:
Cross the ankle joint and help move the foot up and down, or side to side
742:
Cross the ankle joint and help move the foot up and down, or side to side
4512:
4357:
4221:
3857:
3702:
3469:
3085:
2754:"Negative Poisson's ratios in tendons: An unexpected mechanical response"
2304:"A review on postural realignment and its muscular and neural components"
1517:
1336:
1227:
395:
380:
253:
217:
2237:
1490:
264:. The space between the fascia and the tendon tissue is filled with the
17:
4411:
4406:
4379:
3916:
3911:
3906:
3766:
3624:
3541:
3474:
2903:
2845:
2052:
2035:
1482:
1478:
391:
338:
316:
2363:
2092:
2004:
1896:
1748:
1695:
174:
4500:
4036:
3921:
3852:
3847:
3842:
3649:
3639:
3614:
3599:
3561:
3494:
3253:
698:
Bend backwards and forwards, and when swinging the leg while walking
687:
Bend backwards and forwards, and when swinging the leg while walking
676:
Bend backwards and forwards, and when swinging the leg while walking
665:
Bend backwards and forwards, and when swinging the leg while walking
654:
Bend backwards and forwards, and when swinging the leg while walking
330:
261:
4171:
3396:
2668:
Thorpe CT, Udeze CP, Birch HL, Clegg PD, Screen HR (November 2012).
1963:
Fratzl P (2009). "Cellulose and collagen: from fibres to tissues".
305:
15–40% non-collagenous extracellular matrix components, including:
4579:
3969:
3926:
3879:
3862:
3829:
3781:
3716:
3634:
3566:
3556:
3531:
3509:
3499:
3444:
2834:
European
Journal of Applied Physiology and Occupational Physiology
2274:"Having a short Achilles tendon may be an athlete's Achilles heel"
1500:
1477:
tendon) is used as a food in some Asian cuisines (often served at
1445:
1433:
108:
4574:
4389:
4226:
3674:
3659:
3629:
3521:
3516:
3504:
3489:
1510:
1474:
1437:
1238:
432:
428:
202:
4175:
3973:
3417:
2173:
McNeilly CM, Banes AJ, Benjamin M, Ralphs JR (December 1996).
2945:"Biology of tendon injury: healing, modeling and remodeling"
2875:
Reeves ND, Maganaris CN, Ferretti G, Narici MV (June 2005).
431:, present where the cells processes meet and in cell bodies
3120:"The pathogenesis of tendinopathy. A molecular perspective"
2348:"The role of the non-collagenous matrix in tendon function"
1339:
materials at the injury site occurs. After the release of
3413:
39:"Sinew" redirects here. For the song by Purity Ring, see
1164:
An overview of the materials that the tendon is made of
874:
thumbs can move toward and away from your other fingers
863:
thumbs can move toward and away from your other fingers
852:
thumbs can move toward and away from your other fingers
841:
thumbs can move toward and away from your other fingers
3165:
3163:
3161:
3159:
3157:
3155:
3074:
The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume
2952:
Journal of Musculoskeletal & Neuronal Interactions
4560:
4537:
4481:
4446:
4437:
4430:
4348:
4330:
4319:
4292:
4251:
4242:
4235:
4209:
4131:
4098:
4007:
3828:
3795:
3747:
3724:
3715:
3693:
3580:
3460:
3451:
1241:. In particular, a study showed that disuse of the
155:
143:
131:
119:
107:
102:
97:
48:
3067:
3065:
3063:
3061:
1965:Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science
1879:Taye N, Karoulias SZ, Hubmacher D (January 2020).
1731:Grant TM, Thompson MS, Urban J, Yu J (June 2013).
240:(tenocytes). Tendon cells synthesize the tendon's
3113:
3111:
1796:Human Tendons: Anatomy, Physiology, and Pathology
272:. Normal healthy tendons are anchored to bone by
2982:
2980:
2212:
2210:
2034:Raspanti M, Congiu T, Guizzardi S (March 2002).
1789:
1787:
1785:
2352:International Journal of Experimental Pathology
386:The collagen in tendons are held together with
2938:
2936:
2934:
2932:
2258:: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of August 2024 (
1716:: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of August 2024 (
1624:Harvey T, Flamenco S, Fan CM (December 2019).
1440:for sewing, attaching feathers to arrows (see
1191:, allowing the muscle to generate more force.
423:The cells communicate with each other through
4187:
3985:
3429:
1331:are recruited within the first 24 hours, and
1319:are recruited to the injury site, along with
703:Quadriceps tendons(patellar tendon/ patella)
232:, whose main cellular components are special
8:
3170:Wang JH (2006). "Mechanobiology of tendon".
2075:Scott JE, Orford CR, Hughes EW (June 1981).
1605:Southern Hills Hospital & Medical Center
1436:. Some specific uses include using sinew as
489:Sortable table of tendons in the human body
375:. After secretion from the cell, cleaved by
300:small amounts of collagens V, VI, and others
670:Adductor longus, brevis and magnus tendons
27:Type of tissue that connects muscle to bone
4443:
4434:
4327:
4248:
4239:
4194:
4180:
4172:
3992:
3978:
3970:
3721:
3457:
3436:
3422:
3414:
3024:Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research
1779:Dorlands Medical Dictionary 2012.Page 1382
1113:
599:Help bend the elbow or rotate the forearm
588:Help bend the elbow or rotate the forearm
577:Help bend the elbow or rotate the forearm
566:Help bend the elbow or rotate the forearm
555:Help bend the elbow or rotate the forearm
487:
80:
54:
3300:
3135:
2920:
2902:
2892:
2693:
2609:
2517:
2371:
2190:
2149:
2100:
2051:
1904:
1756:
1649:
435:, present only where the processes meet.
1177:
1142:Where it can be found in the human body
347:Although most of a tendon's collagen is
2674:Journal of the Royal Society, Interface
1567:
637:Extensor carpi radialis brevis tendons
2251:
2217:Benjamin M, Ralphs JR (October 1997).
1709:
1134:include/exclude Tendon in the name???
394:and, in compressed regions of tendon,
172:
45:
1672:Dorlands Medical Dictionary, page 602
544:Rotator cuff tendons at the shoulder
533:Rotator cuff tendons at the shoulder
522:Rotator cuff tendons at the shoulder
511:Rotator cuff tendons at the shoulder
367:Ultrastructure and collagen synthesis
7:
3954:
2219:"Tendons and ligaments--an overview"
830:help you move your fingers and toes
819:help you move your fingers and toes
808:help you move your fingers and toes
797:help you move your fingers and toes
731:Bend or straighten the knee include
720:Bend or straighten the knee include
709:Bend or straighten the knee include
260:. The whole tendon is enclosed by a
244:, which abounds with densely-packed
2500:Cribb AM, Scott JE (October 1995).
813:Flexor digitorum profundus tendons
310:cartilage oligomeric matrix protein
2311:British Journal of Sports Medicine
2040:Archives of Histology and Cytology
1485:restaurants). One popular dish is
1377:vascular endothelial growth factor
329:0.2% inorganic components such as
25:
4491:Dense irregular connective tissue
4156:List of muscles of the human body
2973:from the original on Jan 5, 2024.
1552:List of muscles of the human body
1428:Sinew was widely used throughout
1111:Naming convention for the table:
258:dense irregular connective tissue
3953:
3944:
3943:
3036:10.1097/00003086-199507000-00021
1993:Journal of Cellular Biochemistry
1798:. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics.
1153:What is its purpose in the body
1131:the name of the Tendon in Latin
923:Flexor digitorum longus tendons
890:Flexor digitorum brevis tendons
791:Flexor digitorum longus tendons
626:Extensor carpi radialis tendons
355:zones, type III collagen in the
4508:Dense regular connective tissue
3289:Journal of Orthopaedic Research
2894:10.1152/japplphysiol.01266.2004
2342:Thorpe CT, Birch HL, Clegg PD,
1885:Journal of Orthopaedic Research
1385:transforming growth factor beta
1274:Types of tendinopathy include:
934:Abductor digiti minimi tendons
879:Flexor hallucis longus tendons
846:Flexor pollicis longus tendons
824:Abductor digiti minimi tendons
230:dense regular connective tissue
195:dense fibrous connective tissue
3242:Journal of Cellular Physiology
3184:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2005.05.011
1823:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2003.11.005
1391:Effects of activity on healing
1381:basic fibroblast growth factor
1373:platelet-derived growth factor
1077:Transversus abdominis tendons
940:bend and straighten your toes
929:bend and straighten your toes
918:bend and straighten your toes
907:bend and straighten your toes
896:bend and straighten your toes
885:bend and straighten your toes
604:Flexor carpi radialis tendons
371:Collagen fibres coalesce into
1:
3302:10.1016/S0736-0266(01)00017-1
3219:10.1016/S0945-053X(01)00196-2
3001:10.1016/s0278-5919(03)00004-8
2943:Sharma P, Maffulli N (2006).
2881:Journal of Applied Physiology
2635:Journal of Structural Biology
2479:10.1016/S1095-6433(02)00171-X
2444:10.1016/S0021-9290(03)00135-0
2397:Journal of Structural Biology
1977:10.1016/S1359-0294(03)00011-6
1942:10.1016/S0945-053X(98)90125-1
615:Flexor carpi ulnaris tendons
2773:10.1016/j.actbio.2015.06.018
2731:10.1016/j.actbio.2013.05.004
2226:Histology and Histopathology
2142:10.1113/jphysiol.2003.050179
1369:insulin-like growth factor 1
1000:Sternocleidomastoid tendons
64:, one of the tendons in the
3137:10.1093/rheumatology/keg448
2809:Encyclopaedia of Composites
2317:(12): 51–76. Archived from
1601:"Framing Within Our Bodies"
1509:In some organisms, notably
659:Obturator internus tendons
453:between tendon and muscle.
4631:
4139:Anatomical terms of muscle
2989:Clinics in Sports Medicine
2555:10.1243/095441104322984004
2124:Scott JE (December 2003).
1858:10.1152/physrev.00031.2003
1794:Jozsa L, Kannus P (1997).
1527:
1466:
1210:
1182:Magnified view of a tendon
956:Levator palpebrae tendons
912:Abductor hallucis tendons
868:abductor pollicis tendons
857:Extensor pollicis tendons
835:Opponens pollicis tendons
769:Tibialis anterior tendons
38:
31:
3939:
3118:Riley G (February 2004).
2647:10.1016/j.jsb.2009.10.002
2130:The Journal of Physiology
1642:10.1038/s41556-019-0417-z
1432:eras as a tough, durable
1309:matrix metalloproteinases
1167:Ideally given in %?
1088:Latissimus dorsi tendons
1066:External oblique tendons
1055:Rectus abdominis tendons
1022:splenius capitis tendons
167:
79:
53:
1050:move your head and neck
1039:move your head and neck
1028:move your head and neck
1017:move your head and neck
1006:move your head and neck
995:move your head and neck
780:Peroneus longus tendons
582:Brachioradialis tendons
3346:10.1002/jmor.1052260105
3172:Journal of Biomechanics
2432:Journal of Biomechanics
2240:(inactive 2024-08-20).
2081:The Biochemical Journal
1811:Journal of Biomechanics
1698:(inactive 2024-08-20).
1473:Tendon (in particular,
1454:composite recurved bows
1408:, which can affect the
1139:part of the human body
1099:Erector spinae tendons
692:Gluteus medius tendons
256:, which is a sheath of
34:Tendon (disambiguation)
2686:10.1098/rsif.2012.0362
2602:10.1098/rstb.2001.1033
2409:10.1006/jsbi.2002.4450
2278:Sports Injury Bulletin
1576:"Protect Your Tendons"
1530:anatomical terminology
1506:
1183:
984:eyes, eyelids and jaw
973:eyes, eyelids and jaw
962:eyes, eyelids and jaw
951:eyes, eyelids and jaw
736:Gastrocnemius tendons
538:Subscapularis tendons
527:Supraspinatus tendons
516:Infraspinatus tendons
169:Anatomical terminology
89:of a piece of tendon;
3334:Journal of Morphology
1846:Physiological Reviews
1504:
1254:Clinical significance
1181:
1102:Head, Neck and Torso
1091:Head, Neck and Torso
1080:Head, Neck and Torso
1069:Head, Neck and Torso
1058:Head, Neck and Torso
1047:Head, Neck and Torso
1036:Head, Neck and Torso
1025:Head, Neck and Torso
1014:Head, Neck and Torso
1011:Semispinalis capitis
1003:Head, Neck and Torso
992:Head, Neck and Torso
981:Head, Neck and Torso
970:Head, Neck and Torso
959:Head, Neck and Torso
948:Head, Neck and Torso
451:myotendinous junction
3086:10.2106/JBJS.D.01850
1406:extracellular matrix
802:Interosseus tendons
643:Help bend the wrist
632:Help bend the wrist
621:Help bend the wrist
610:Help bend the wrist
505:Teres minor tendons
280:Extracellular matrix
242:extracellular matrix
228:A tendon is made of
32:For other uses, see
4059:Fascial compartment
3389:2006Pbio...32..652O
2238:10.14670/HH-12.1135
1630:Nature Cell Biology
1424:Society and culture
1401:mechanotransduction
1189:no change in length
1044:thyrohyoid tendons
978:Temporalis tendons
640:Shoulders and arms
629:Shoulders and arms
618:Shoulders and arms
607:Shoulders and arms
596:Shoulders and arms
585:Shoulders and arms
574:Shoulders and arms
563:Shoulders and arms
552:Shoulders and arms
541:Shoulders and arms
530:Shoulders and arms
519:Shoulders and arms
508:Shoulders and arms
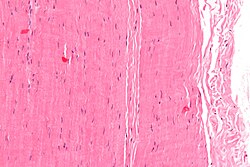
490:
449:are present at the
447:Golgi tendon organs
408:chondroitin sulfate
193:is a tough band of
2846:10.1007/bf02386194
2761:Acta Biomaterialia
2719:Acta Biomaterialia
2506:Journal of Anatomy
2179:Journal of Anatomy
2053:10.1679/aohc.65.37
1737:Journal of Anatomy
1580:NIH News in Health
1528:This article uses
1507:
1450:circumpolar people
1410:actin cytoskeleton
1184:
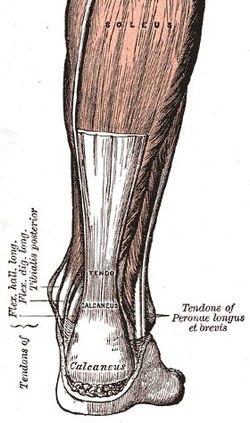
989:Trapezius tendons
901:Lumbrical tendons
725:Sartorius tendons
714:Hamstring tendons
648:Iliopsoas tendons
593:Supinator tendons
488:
294:0–10% collagen III
150:H3.03.00.0.00020
4592:
4591:
4588:
4587:
4533:
4532:
4426:
4425:
4422:
4421:
4315:
4314:
4203:Connective tissue
4169:
4168:
3967:
3966:
3935:
3934:
3711:
3710:
2818:978-0-470-12828-2
2680:(76): 3108–3117.
2596:(1418): 191–197.
2438:(10): 1529–1553.
2364:10.1111/iep.12027
2185:(Pt 3): 593–600.
2136:(Pt 2): 335–343.
2093:10.1042/bj1950573
2005:10.1002/jcb.20776
1897:10.1002/jor.24440
1749:10.1111/joa.12048
1696:10.1159/000147022
1636:(12): 1490–1503.
1547:Chordae tendineae
1171:
1170:
1109:
1108:
967:Masseter tendons
400:glycosaminoglycan
291:60–80% collagen I
183:
182:
178:
16:(Redirected from
4622:
4444:
4435:
4363:Reticular fibers
4332:Ground substance
4328:
4249:
4240:
4196:
4189:
4182:
4173:
4161:Composite muscle
3994:
3987:
3980:
3971:
3957:
3956:
3947:
3946:
3722:
3458:
3438:
3431:
3424:
3415:
3409:
3408:
3372:
3366:
3365:
3329:
3323:
3322:
3304:
3280:
3274:
3273:
3254:10.1002/jcp.1110
3237:
3231:
3230:
3202:
3196:
3195:
3178:(9): 1563–1582.
3167:
3150:
3149:
3139:
3115:
3106:
3105:
3069:
3056:
3055:
3030:(316): 151–164.
3019:
3013:
3012:
2984:
2975:
2974:
2972:
2949:
2940:
2927:
2926:
2924:
2906:
2896:
2887:(6): 2278–2286.
2872:
2866:
2865:
2829:
2823:
2822:
2804:
2798:
2791:
2785:
2784:
2758:
2749:
2743:
2742:
2725:(8): 7948–7956.
2714:
2708:
2707:
2697:
2665:
2659:
2658:
2630:
2624:
2623:
2613:
2581:
2575:
2574:
2538:
2532:
2531:
2521:
2497:
2491:
2490:
2462:
2456:
2455:
2427:
2421:
2420:
2392:
2386:
2385:
2375:
2339:
2333:
2332:
2330:
2329:
2323:
2308:
2302:Young M (2002).
2299:
2293:
2292:
2290:
2289:
2280:. Archived from
2270:
2264:
2263:
2257:
2249:
2232:(4): 1135–1144.
2223:
2214:
2205:
2204:
2194:
2170:
2164:
2163:
2153:
2121:
2115:
2114:
2104:
2072:
2066:
2065:
2055:
2031:
2025:
2024:
1999:(6): 1436–1449.
1987:
1981:
1980:
1960:
1954:
1953:
1925:
1919:
1918:
1908:
1876:
1870:
1869:
1841:
1835:
1834:
1806:
1800:
1799:
1791:
1780:
1777:
1771:
1770:
1760:
1728:
1722:
1721:
1715:
1707:
1679:
1673:
1670:
1664:
1663:
1653:
1621:
1615:
1614:
1612:
1611:
1597:
1591:
1590:
1588:
1587:
1572:
1487:suan bao niu jin
1114:
747:Achilles tendon
681:Gluteus maximus
571:Triceps tendons
549:Deltoid tendons
497:Human body part
491:
404:dermatan sulfate
288:60–85% collagen
274:Sharpey's fibres
175:edit on Wikidata
84:
74:, 1st ed., 1858)
58:
46:
21:
4630:
4629:
4625:
4624:
4623:
4621:
4620:
4619:
4610:Skeletal system
4595:
4594:
4593:
4584:
4556:
4529:
4477:
4418:
4358:Collagen fibers
4344:
4322:
4311:
4294:Wandering cells
4288:
4231:
4205:
4200:
4170:
4165:
4127:
4094:
4025:Skeletal muscle
4003:
4001:Muscular system
3998:
3968:
3963:
3931:
3824:
3791:
3743:
3734:Artificial silk
3707:
3689:
3576:
3447:
3442:
3412:
3397:10.1666/05039.1
3374:
3373:
3369:
3331:
3330:
3326:
3282:
3281:
3277:
3239:
3238:
3234:
3204:
3203:
3199:
3169:
3168:
3153:
3117:
3116:
3109:
3071:
3070:
3059:
3021:
3020:
3016:
2986:
2985:
2978:
2970:
2947:
2942:
2941:
2930:
2874:
2873:
2869:
2831:
2830:
2826:
2819:
2806:
2805:
2801:
2792:
2788:
2756:
2751:
2750:
2746:
2716:
2715:
2711:
2667:
2666:
2662:
2632:
2631:
2627:
2583:
2582:
2578:
2540:
2539:
2535:
2512:(Pt 2): 423–8.
2499:
2498:
2494:
2473:(4): 987–1000.
2464:
2463:
2459:
2429:
2428:
2424:
2394:
2393:
2389:
2346:(August 2013).
2341:
2340:
2336:
2327:
2325:
2321:
2306:
2301:
2300:
2296:
2287:
2285:
2272:
2271:
2267:
2250:
2221:
2216:
2215:
2208:
2172:
2171:
2167:
2123:
2122:
2118:
2074:
2073:
2069:
2033:
2032:
2028:
1989:
1988:
1984:
1962:
1961:
1957:
1927:
1926:
1922:
1878:
1877:
1873:
1843:
1842:
1838:
1808:
1807:
1803:
1793:
1792:
1783:
1778:
1774:
1730:
1729:
1725:
1708:
1681:
1680:
1676:
1671:
1667:
1623:
1622:
1618:
1609:
1607:
1599:
1598:
1594:
1585:
1583:
1574:
1573:
1569:
1565:
1533:
1526:
1499:
1471:
1465:
1426:
1393:
1304:
1261:
1256:
1243:Achilles tendon
1215:
1209:
1176:
945:Ocular tendons
937:Hands and Feet
926:Hands and Feet
915:Hands and Feet
904:Hands and Feet
893:Hands and Feet
882:Hands and Feet
871:Hands and Feet
860:Hands and Feet
849:Hands and Feet
838:Hands and Feet
827:Hands and Feet
816:Hands and Feet
805:Hands and Feet
794:Hands and Feet
758:Soleus tendons
560:Biceps tendons
483:
481:List of tendons
463:Achilles tendon
416:
373:macroaggregates
369:
349:type I collagen
282:
246:collagen fibers
226:
179:
93:
75:
62:Achilles tendon
44:
37:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
4628:
4626:
4618:
4617:
4612:
4607:
4597:
4596:
4590:
4589:
4586:
4585:
4583:
4582:
4577:
4572:
4566:
4564:
4558:
4557:
4555:
4554:
4549:
4543:
4541:
4535:
4534:
4531:
4530:
4528:
4527:
4526:
4525:
4520:
4515:
4505:
4504:
4503:
4498:
4487:
4485:
4479:
4478:
4476:
4475:
4474:
4473:
4468:
4458:
4452:
4450:
4441:
4432:
4428:
4427:
4424:
4423:
4420:
4419:
4417:
4416:
4415:
4414:
4409:
4404:
4403:
4402:
4397:
4387:
4382:
4375:Elastic fibers
4372:
4371:
4370:
4360:
4354:
4352:
4346:
4345:
4343:
4342:
4336:
4334:
4325:
4321:Extracellular
4317:
4316:
4313:
4312:
4310:
4309:
4304:
4298:
4296:
4290:
4289:
4287:
4286:
4281:
4276:
4271:
4269:Reticular cell
4266:
4261:
4255:
4253:
4246:
4237:
4233:
4232:
4230:
4229:
4224:
4219:
4213:
4211:
4207:
4206:
4201:
4199:
4198:
4191:
4184:
4176:
4167:
4166:
4164:
4163:
4158:
4153:
4152:
4151:
4146:
4135:
4133:
4129:
4128:
4126:
4125:
4124:
4123:
4118:
4111:Pennate muscle
4108:
4102:
4100:
4096:
4095:
4093:
4092:
4083:
4082:
4081:
4076:
4071:
4066:
4056:
4055:
4054:
4049:
4044:
4034:
4033:
4032:
4027:
4022:
4020:Cardiac muscle
4011:
4009:
4005:
4004:
3999:
3997:
3996:
3989:
3982:
3974:
3965:
3964:
3962:
3961:
3951:
3940:
3937:
3936:
3933:
3932:
3930:
3929:
3924:
3919:
3914:
3909:
3904:
3903:
3902:
3892:
3887:
3882:
3877:
3872:
3867:
3866:
3865:
3860:
3855:
3850:
3840:
3834:
3832:
3826:
3825:
3823:
3822:
3817:
3812:
3807:
3801:
3799:
3793:
3792:
3790:
3789:
3784:
3779:
3774:
3769:
3764:
3759:
3753:
3751:
3749:Semi-synthetic
3745:
3744:
3742:
3741:
3736:
3730:
3728:
3719:
3713:
3712:
3709:
3708:
3706:
3705:
3699:
3697:
3691:
3690:
3688:
3687:
3682:
3677:
3672:
3667:
3662:
3657:
3652:
3647:
3642:
3637:
3632:
3627:
3622:
3617:
3612:
3607:
3602:
3597:
3592:
3586:
3584:
3578:
3577:
3575:
3574:
3569:
3564:
3559:
3554:
3549:
3544:
3539:
3534:
3529:
3524:
3519:
3514:
3513:
3512:
3502:
3497:
3492:
3487:
3482:
3477:
3472:
3466:
3464:
3455:
3449:
3448:
3443:
3441:
3440:
3433:
3426:
3418:
3411:
3410:
3383:(4): 652–665.
3367:
3324:
3295:(5): 869–872.
3275:
3248:(2): 211–222.
3232:
3213:(2): 185–195.
3207:Matrix Biology
3197:
3151:
3130:(2): 131–142.
3107:
3080:(1): 187–202.
3057:
3014:
2995:(4): 675–692.
2976:
2958:(2): 181–190.
2928:
2867:
2840:(3): 239–242.
2824:
2817:
2799:
2786:
2744:
2709:
2660:
2625:
2576:
2549:(2): 109–119.
2533:
2492:
2457:
2422:
2387:
2358:(4): 248–259.
2334:
2294:
2265:
2206:
2165:
2116:
2087:(3): 573–581.
2067:
2026:
1982:
1955:
1930:Matrix Biology
1920:
1871:
1852:(2): 649–698.
1836:
1817:(6): 865–877.
1801:
1781:
1772:
1743:(6): 573–579.
1723:
1690:(4): 341–348.
1684:Acta Anatomica
1674:
1665:
1616:
1592:
1566:
1564:
1561:
1560:
1559:
1554:
1549:
1544:
1539:
1525:
1522:
1498:
1495:
1467:Main article:
1464:
1461:
1430:pre-industrial
1425:
1422:
1392:
1389:
1303:
1300:
1295:
1294:
1288:
1282:
1269:tendon rupture
1265:tendinopathies
1260:
1257:
1255:
1252:
1211:Main article:
1208:
1205:
1175:
1172:
1169:
1168:
1165:
1162:
1158:
1157:
1154:
1151:
1147:
1146:
1143:
1140:
1136:
1135:
1132:
1129:
1125:
1124:
1121:
1118:
1107:
1106:
1103:
1100:
1096:
1095:
1092:
1089:
1085:
1084:
1081:
1078:
1074:
1073:
1070:
1067:
1063:
1062:
1059:
1056:
1052:
1051:
1048:
1045:
1041:
1040:
1037:
1034:
1030:
1029:
1026:
1023:
1019:
1018:
1015:
1012:
1008:
1007:
1004:
1001:
997:
996:
993:
990:
986:
985:
982:
979:
975:
974:
971:
968:
964:
963:
960:
957:
953:
952:
949:
946:
942:
941:
938:
935:
931:
930:
927:
924:
920:
919:
916:
913:
909:
908:
905:
902:
898:
897:
894:
891:
887:
886:
883:
880:
876:
875:
872:
869:
865:
864:
861:
858:
854:
853:
850:
847:
843:
842:
839:
836:
832:
831:
828:
825:
821:
820:
817:
814:
810:
809:
806:
803:
799:
798:
795:
792:
788:
787:
784:
783:Hips and Legs
781:
777:
776:
773:
772:Hips and Legs
770:
766:
765:
762:
761:Hips and Legs
759:
755:
754:
751:
750:Hips and legs
748:
744:
743:
740:
739:Hips and legs
737:
733:
732:
729:
728:Hips and legs
726:
722:
721:
718:
717:Hips and legs
715:
711:
710:
707:
706:Hips and legs
704:
700:
699:
696:
695:Hips and legs
693:
689:
688:
685:
684:Hips and legs
682:
678:
677:
674:
673:Hips and legs
671:
667:
666:
663:
662:Hips and legs
660:
656:
655:
652:
651:Hips and legs
649:
645:
644:
641:
638:
634:
633:
630:
627:
623:
622:
619:
616:
612:
611:
608:
605:
601:
600:
597:
594:
590:
589:
586:
583:
579:
578:
575:
572:
568:
567:
564:
561:
557:
556:
553:
550:
546:
545:
542:
539:
535:
534:
531:
528:
524:
523:
520:
517:
513:
512:
509:
506:
502:
501:
498:
495:
482:
479:
465:and a shorter
415:
412:
368:
365:
345:
344:
343:
342:
327:
320:
313:
303:
302:
301:
298:
297:2% collagen IV
295:
292:
281:
278:
270:areolar tissue
225:
222:
216:, are made of
212:Tendons, like
197:that connects
181:
180:
171:
165:
164:
159:
153:
152:
147:
141:
140:
135:
129:
128:
123:
117:
116:
111:
105:
104:
100:
99:
95:
94:
85:
77:
76:
71:Gray's Anatomy
59:
51:
50:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4627:
4616:
4613:
4611:
4608:
4606:
4603:
4602:
4600:
4581:
4578:
4576:
4573:
4571:
4568:
4567:
4565:
4563:
4559:
4553:
4550:
4548:
4545:
4544:
4542:
4540:
4536:
4524:
4521:
4519:
4516:
4514:
4511:
4510:
4509:
4506:
4502:
4499:
4497:
4494:
4493:
4492:
4489:
4488:
4486:
4484:
4480:
4472:
4469:
4467:
4464:
4463:
4462:
4459:
4457:
4454:
4453:
4451:
4449:
4445:
4442:
4440:
4436:
4433:
4429:
4413:
4410:
4408:
4405:
4401:
4398:
4396:
4393:
4392:
4391:
4388:
4386:
4383:
4381:
4378:
4377:
4376:
4373:
4369:
4366:
4365:
4364:
4361:
4359:
4356:
4355:
4353:
4351:
4347:
4341:
4338:
4337:
4335:
4333:
4329:
4326:
4324:
4318:
4308:
4305:
4303:
4300:
4299:
4297:
4295:
4291:
4285:
4282:
4280:
4277:
4275:
4272:
4270:
4267:
4265:
4262:
4260:
4257:
4256:
4254:
4250:
4247:
4245:
4241:
4238:
4234:
4228:
4225:
4223:
4220:
4218:
4215:
4214:
4212:
4208:
4204:
4197:
4192:
4190:
4185:
4183:
4178:
4177:
4174:
4162:
4159:
4157:
4154:
4150:
4147:
4145:
4142:
4141:
4140:
4137:
4136:
4134:
4130:
4122:
4119:
4117:
4114:
4113:
4112:
4109:
4107:
4104:
4103:
4101:
4097:
4091:
4087:
4084:
4080:
4077:
4075:
4072:
4070:
4067:
4065:
4062:
4061:
4060:
4057:
4053:
4050:
4048:
4045:
4043:
4040:
4039:
4038:
4035:
4031:
4030:Smooth muscle
4028:
4026:
4023:
4021:
4018:
4017:
4016:
4015:Muscle tissue
4013:
4012:
4010:
4006:
4002:
3995:
3990:
3988:
3983:
3981:
3976:
3975:
3972:
3960:
3952:
3950:
3942:
3941:
3938:
3928:
3925:
3923:
3920:
3918:
3915:
3913:
3910:
3908:
3905:
3901:
3898:
3897:
3896:
3893:
3891:
3888:
3886:
3883:
3881:
3878:
3876:
3873:
3871:
3868:
3864:
3861:
3859:
3856:
3854:
3851:
3849:
3846:
3845:
3844:
3841:
3839:
3836:
3835:
3833:
3831:
3827:
3821:
3818:
3816:
3813:
3811:
3808:
3806:
3803:
3802:
3800:
3798:
3794:
3788:
3785:
3783:
3780:
3778:
3775:
3773:
3770:
3768:
3765:
3763:
3760:
3758:
3755:
3754:
3752:
3750:
3746:
3740:
3737:
3735:
3732:
3731:
3729:
3727:
3723:
3720:
3718:
3714:
3704:
3701:
3700:
3698:
3696:
3692:
3686:
3683:
3681:
3678:
3676:
3673:
3671:
3668:
3666:
3663:
3661:
3658:
3656:
3653:
3651:
3648:
3646:
3643:
3641:
3638:
3636:
3633:
3631:
3628:
3626:
3623:
3621:
3618:
3616:
3613:
3611:
3608:
3606:
3603:
3601:
3598:
3596:
3593:
3591:
3588:
3587:
3585:
3583:
3579:
3573:
3570:
3568:
3565:
3563:
3560:
3558:
3555:
3553:
3550:
3548:
3545:
3543:
3540:
3538:
3535:
3533:
3530:
3528:
3525:
3523:
3520:
3518:
3515:
3511:
3508:
3507:
3506:
3503:
3501:
3498:
3496:
3493:
3491:
3488:
3486:
3483:
3481:
3478:
3476:
3473:
3471:
3468:
3467:
3465:
3463:
3459:
3456:
3454:
3450:
3446:
3439:
3434:
3432:
3427:
3425:
3420:
3419:
3416:
3406:
3402:
3398:
3394:
3390:
3386:
3382:
3378:
3371:
3368:
3363:
3359:
3355:
3351:
3347:
3343:
3339:
3335:
3328:
3325:
3320:
3316:
3312:
3308:
3303:
3298:
3294:
3290:
3286:
3279:
3276:
3271:
3267:
3263:
3259:
3255:
3251:
3247:
3243:
3236:
3233:
3228:
3224:
3220:
3216:
3212:
3208:
3201:
3198:
3193:
3189:
3185:
3181:
3177:
3173:
3166:
3164:
3162:
3160:
3158:
3156:
3152:
3147:
3143:
3138:
3133:
3129:
3125:
3121:
3114:
3112:
3108:
3103:
3099:
3095:
3091:
3087:
3083:
3079:
3075:
3068:
3066:
3064:
3062:
3058:
3053:
3049:
3045:
3041:
3037:
3033:
3029:
3025:
3018:
3015:
3010:
3006:
3002:
2998:
2994:
2990:
2983:
2981:
2977:
2969:
2965:
2961:
2957:
2953:
2946:
2939:
2937:
2935:
2933:
2929:
2923:
2918:
2914:
2910:
2905:
2900:
2895:
2890:
2886:
2882:
2878:
2871:
2868:
2863:
2859:
2855:
2851:
2847:
2843:
2839:
2835:
2828:
2825:
2820:
2814:
2810:
2803:
2800:
2796:
2795:Equine Vet J.
2790:
2787:
2782:
2778:
2774:
2770:
2766:
2762:
2755:
2748:
2745:
2740:
2736:
2732:
2728:
2724:
2720:
2713:
2710:
2705:
2701:
2696:
2691:
2687:
2683:
2679:
2675:
2671:
2664:
2661:
2656:
2652:
2648:
2644:
2641:(2): 183–91.
2640:
2636:
2629:
2626:
2621:
2617:
2612:
2607:
2603:
2599:
2595:
2591:
2587:
2580:
2577:
2572:
2568:
2564:
2560:
2556:
2552:
2548:
2544:
2537:
2534:
2529:
2525:
2520:
2515:
2511:
2507:
2503:
2496:
2493:
2488:
2484:
2480:
2476:
2472:
2468:
2461:
2458:
2453:
2449:
2445:
2441:
2437:
2433:
2426:
2423:
2418:
2414:
2410:
2406:
2403:(1–2): 2–10.
2402:
2398:
2391:
2388:
2383:
2379:
2374:
2369:
2365:
2361:
2357:
2353:
2349:
2345:
2338:
2335:
2324:on 2019-04-06
2320:
2316:
2312:
2305:
2298:
2295:
2284:on 2007-10-21
2283:
2279:
2275:
2269:
2266:
2261:
2255:
2247:
2243:
2239:
2235:
2231:
2227:
2220:
2213:
2211:
2207:
2202:
2198:
2193:
2188:
2184:
2180:
2176:
2169:
2166:
2161:
2157:
2152:
2147:
2143:
2139:
2135:
2131:
2127:
2120:
2117:
2112:
2108:
2103:
2098:
2094:
2090:
2086:
2082:
2078:
2071:
2068:
2063:
2059:
2054:
2049:
2045:
2041:
2037:
2030:
2027:
2022:
2018:
2014:
2010:
2006:
2002:
1998:
1994:
1986:
1983:
1978:
1974:
1970:
1966:
1959:
1956:
1951:
1947:
1943:
1939:
1935:
1931:
1924:
1921:
1916:
1912:
1907:
1902:
1898:
1894:
1890:
1886:
1882:
1875:
1872:
1867:
1863:
1859:
1855:
1851:
1847:
1840:
1837:
1832:
1828:
1824:
1820:
1816:
1812:
1805:
1802:
1797:
1790:
1788:
1786:
1782:
1776:
1773:
1768:
1764:
1759:
1754:
1750:
1746:
1742:
1738:
1734:
1727:
1724:
1719:
1713:
1705:
1701:
1697:
1693:
1689:
1685:
1678:
1675:
1669:
1666:
1661:
1657:
1652:
1647:
1643:
1639:
1635:
1631:
1627:
1620:
1617:
1606:
1602:
1596:
1593:
1581:
1577:
1571:
1568:
1562:
1558:
1557:Tendon sheath
1555:
1553:
1550:
1548:
1545:
1543:
1540:
1538:
1535:
1534:
1531:
1523:
1521:
1519:
1516:
1515:ornithischian
1512:
1503:
1497:Other animals
1496:
1494:
1492:
1488:
1484:
1480:
1476:
1470:
1469:Tendon (meal)
1463:Culinary uses
1462:
1460:
1457:
1455:
1451:
1447:
1443:
1439:
1435:
1431:
1423:
1421:
1419:
1415:
1411:
1407:
1402:
1397:
1390:
1388:
1386:
1382:
1378:
1374:
1370:
1365:
1363:
1357:
1354:
1353:proliferation
1350:
1346:
1342:
1338:
1334:
1330:
1326:
1322:
1318:
1312:
1310:
1301:
1299:
1292:
1291:Paratenonitis
1289:
1286:
1283:
1280:
1277:
1276:
1275:
1272:
1270:
1266:
1258:
1253:
1251:
1249:
1244:
1240:
1235:
1233:
1229:
1225:
1220:
1214:
1206:
1204:
1201:
1196:
1192:
1190:
1180:
1173:
1166:
1163:
1160:
1159:
1155:
1152:
1149:
1148:
1144:
1141:
1138:
1137:
1133:
1130:
1127:
1126:
1122:
1119:
1116:
1115:
1112:
1104:
1101:
1098:
1097:
1093:
1090:
1087:
1086:
1082:
1079:
1076:
1075:
1071:
1068:
1065:
1064:
1060:
1057:
1054:
1053:
1049:
1046:
1043:
1042:
1038:
1035:
1032:
1031:
1027:
1024:
1021:
1020:
1016:
1013:
1010:
1009:
1005:
1002:
999:
998:
994:
991:
988:
987:
983:
980:
977:
976:
972:
969:
966:
965:
961:
958:
955:
954:
950:
947:
944:
943:
939:
936:
933:
932:
928:
925:
922:
921:
917:
914:
911:
910:
906:
903:
900:
899:
895:
892:
889:
888:
884:
881:
878:
877:
873:
870:
867:
866:
862:
859:
856:
855:
851:
848:
845:
844:
840:
837:
834:
833:
829:
826:
823:
822:
818:
815:
812:
811:
807:
804:
801:
800:
796:
793:
790:
789:
785:
782:
779:
778:
774:
771:
768:
767:
763:
760:
757:
756:
752:
749:
746:
745:
741:
738:
735:
734:
730:
727:
724:
723:
719:
716:
713:
712:
708:
705:
702:
701:
697:
694:
691:
690:
686:
683:
680:
679:
675:
672:
669:
668:
664:
661:
658:
657:
653:
650:
647:
646:
642:
639:
636:
635:
631:
628:
625:
624:
620:
617:
614:
613:
609:
606:
603:
602:
598:
595:
592:
591:
587:
584:
581:
580:
576:
573:
570:
569:
565:
562:
559:
558:
554:
551:
548:
547:
543:
540:
537:
536:
532:
529:
526:
525:
521:
518:
515:
514:
510:
507:
504:
503:
499:
496:
493:
492:
486:
480:
478:
476:
475:carpal tunnel
470:
468:
464:
460:
454:
452:
448:
443:
441:
436:
434:
430:
426:
425:gap junctions
421:
413:
411:
409:
405:
401:
397:
393:
389:
384:
382:
378:
374:
366:
364:
362:
358:
354:
353:cartilaginous
350:
340:
336:
332:
328:
325:
324:proteoglycans
321:
318:
314:
311:
307:
306:
304:
299:
296:
293:
290:
289:
287:
286:
285:
279:
277:
275:
271:
267:
263:
259:
255:
251:
250:endotendineum
247:
243:
239:
235:
231:
223:
221:
219:
215:
210:
208:
204:
200:
196:
192:
188:
176:
170:
166:
163:
160:
158:
154:
151:
148:
146:
142:
139:
136:
134:
130:
127:
124:
122:
118:
115:
112:
110:
106:
101:
96:
92:
91:H&E stain
88:
83:
78:
73:
72:
67:
63:
57:
52:
47:
42:
35:
30:
19:
4517:
4340:Tissue fluid
4085:
3895:Polyethylene
3664:
3380:
3377:Paleobiology
3376:
3370:
3340:(1): 47–77.
3337:
3333:
3327:
3292:
3288:
3278:
3245:
3241:
3235:
3210:
3206:
3200:
3175:
3171:
3127:
3124:Rheumatology
3123:
3077:
3073:
3027:
3023:
3017:
2992:
2988:
2955:
2951:
2884:
2880:
2870:
2837:
2833:
2827:
2808:
2802:
2794:
2789:
2764:
2760:
2747:
2722:
2718:
2712:
2677:
2673:
2663:
2638:
2634:
2628:
2593:
2589:
2579:
2546:
2542:
2536:
2509:
2505:
2495:
2470:
2466:
2460:
2435:
2431:
2425:
2400:
2396:
2390:
2355:
2351:
2337:
2326:. Retrieved
2319:the original
2314:
2310:
2297:
2286:. Retrieved
2282:the original
2277:
2268:
2254:cite journal
2229:
2225:
2182:
2178:
2168:
2133:
2129:
2119:
2084:
2080:
2070:
2046:(1): 37–43.
2043:
2039:
2029:
1996:
1992:
1985:
1971:(1): 32–39.
1968:
1964:
1958:
1936:(1): 65–73.
1933:
1929:
1923:
1891:(1): 23–35.
1888:
1884:
1874:
1849:
1845:
1839:
1814:
1810:
1804:
1795:
1775:
1740:
1736:
1726:
1712:cite journal
1687:
1683:
1677:
1668:
1633:
1629:
1619:
1608:. Retrieved
1604:
1595:
1584:. Retrieved
1582:. 2017-05-15
1579:
1570:
1508:
1486:
1472:
1458:
1427:
1398:
1394:
1383:(bFGF), and
1366:
1358:
1349:angiogenesis
1333:phagocytosis
1321:erythrocytes
1313:
1305:
1296:
1273:
1262:
1236:
1219:viscoelastic
1217:Tendons are
1216:
1200:proteoglycan
1197:
1193:
1185:
1161:Composition
1120:Explanation
1110:
484:
471:
459:bodybuilders
455:
444:
437:
417:
388:proteoglycan
385:
370:
346:
283:
238:tendon cells
227:
211:
190:
186:
184:
113:
69:
41:Womb (album)
29:
4605:Soft tissue
4562:Specialized
4552:Mesenchymal
4523:Aponeurosis
4274:Tendon cell
4236:Composition
4217:Soft tissue
4090:Aponeurosis
4042:Superficial
3726:Regenerated
3670:Spider silk
2904:11379/25397
2767:: 201–208.
1537:Aponeurosis
1345:chemotactic
1329:macrophages
1317:neutrophils
1213:Soft tissue
1123:Formatting
467:calf muscle
440:anastomoses
433:connexin 32
429:connexin 43
377:procollagen
361:capillaries
234:fibroblasts
103:Identifiers
4599:Categories
4307:Macrophage
4284:Melanocyte
4259:Fibroblast
4210:Physiology
4116:Unipennate
3875:Modacrylic
3870:Microfiber
3787:Triacetate
3739:Milk fiber
3605:Camel hair
3537:Lotus silk
2328:2010-06-23
2288:2007-10-26
1610:2023-09-11
1586:2023-09-11
1563:References
1448:and other
1418:G-proteins
1341:vasoactive
1285:Tendinitis
1279:Tendinosis
1248:astronauts
1033:Mylohyoid
268:, a fatty
87:Micrograph
66:human body
4570:Cartilage
4539:Embryonic
4496:Submucosa
4456:Reticular
4385:Fibrillin
4302:Mast cell
4279:Adipocyte
4264:Fibrocyte
4149:Insertion
4121:Bipennate
3890:Polyester
3762:Diacetate
3717:Synthetic
3620:Chiengora
2344:Screen HR
1542:Cartilage
1518:dinosaurs
1414:integrins
1371:(IGF-I),
1362:cytokines
1347:factors,
1325:Monocytes
1207:Mechanics
1174:Functions
1150:Function
500:Function
420:tenocytes
414:Tenocytes
381:proteases
379:N- and C-
357:reticulin
335:manganese
266:paratenon
224:Structure
214:ligaments
4513:Ligament
4252:Resident
4227:Scarring
4222:Fibrosis
4106:Fusiform
4052:Visceral
3949:Category
3858:Technora
3820:Metallic
3703:Asbestos
3645:Pashmina
3610:Cashmere
3405:86568665
3362:46926646
3354:29865323
3319:20903366
3311:11562135
3270:22026692
3262:11424088
3227:11852234
3192:16000201
3146:12867575
3094:15634833
3052:25486134
3009:14560540
2968:Archived
2964:16849830
2922:10508646
2913:15705722
2862:20626078
2781:26102335
2739:23669621
2704:22764132
2655:19822213
2620:11911776
2571:46256718
2563:15116898
2487:12485688
2452:14499302
2417:12064927
2382:23718692
2160:12923209
2062:12002609
2021:39384363
2013:16518859
1915:31410892
1866:15044685
1831:15111074
1767:23587025
1660:31768046
1524:See also
1399:Several
1379:(VEGF),
1375:(PDGF),
1351:and the
1337:necrotic
396:aggrecan
254:epitenon
218:collagen
18:Epitenon
4615:Tendons
4461:Adipose
4412:Elaunin
4407:EMILIN1
4380:Elastin
4069:Forearm
3959:Commons
3917:Vinylon
3912:Vectran
3907:Spandex
3838:Acrylic
3830:Polymer
3797:Mineral
3777:Piñatex
3767:Lyocell
3757:Acetate
3695:Mineral
3625:Guanaco
3475:Bagasse
3453:Natural
3385:Bibcode
3102:1111422
3044:7634699
2854:2583169
2695:3479922
2611:1692933
2528:7592005
2519:1167437
2373:3721456
2246:9302572
2201:8982835
2192:1167702
2151:2343561
2111:6459082
2102:1162928
1950:9628253
1906:6917864
1758:3666236
1704:1706129
1651:6895435
1483:dim sum
1479:yum cha
1302:Healing
1228:auxetic
1117:Column
392:decorin
339:calcium
317:elastin
236:called
207:tension
126:D013710
98:Details
4547:Mucoid
4518:Tendon
4501:Dermis
4439:Proper
4368:COL3A1
4350:Fibers
4323:matrix
4144:Origin
4086:Tendon
4037:Fascia
4008:Tissue
3922:Vinyon
3900:UHMWPE
3885:Olefin
3853:Kevlar
3848:Twaron
3843:Aramid
3815:Basalt
3810:Carbon
3680:Vicuña
3665:Tendon
3655:Rabbit
3650:Qiviut
3640:Mohair
3615:Catgut
3600:Byssus
3595:Angora
3590:Alpaca
3582:Animal
3562:Rattan
3552:Raffia
3495:Cotton
3480:Bamboo
3445:Fibers
3403:
3360:
3352:
3317:
3309:
3268:
3260:
3225:
3190:
3144:
3100:
3092:
3050:
3042:
3007:
2962:
2919:
2911:
2860:
2852:
2815:
2779:
2737:
2702:
2692:
2653:
2618:
2608:
2569:
2561:
2526:
2516:
2485:
2450:
2415:
2380:
2370:
2244:
2199:
2189:
2158:
2148:
2109:
2099:
2060:
2019:
2011:
1948:
1913:
1903:
1864:
1829:
1765:
1755:
1702:
1658:
1648:
1513:, and
1442:fletch
1438:thread
1259:Injury
337:, and
331:copper
262:fascia
199:muscle
187:tendon
68:(from
49:Tendon
4580:Blood
4483:Dense
4471:White
4466:Brown
4448:Loose
4431:Types
4244:Cells
4132:Other
4099:Shape
4074:Thigh
3927:Zylon
3880:Nylon
3863:Nomex
3805:Glass
3782:Rayon
3772:Modal
3635:Llama
3567:Sisal
3557:Ramie
3532:Kenaf
3527:Kapok
3510:Linen
3500:Fique
3485:Bashō
3470:Abacá
3462:Plant
3401:S2CID
3358:S2CID
3315:S2CID
3266:S2CID
3098:S2CID
3048:S2CID
2971:(PDF)
2948:(PDF)
2917:S2CID
2858:S2CID
2757:(PDF)
2567:S2CID
2322:(PDF)
2307:(PDF)
2222:(PDF)
2017:S2CID
1511:birds
1446:Inuit
1434:fiber
1239:bones
1232:horse
1145:????
1128:Name
494:Name
322:1–5%
315:1–2%
191:sinew
173:[
114:tendo
109:Latin
4575:Bone
4400:FBN3
4395:FBN2
4390:FBN1
4047:Deep
3675:Wool
3660:Silk
3630:Hair
3572:Wood
3547:Pine
3542:Piña
3522:Jute
3517:Hemp
3505:Flax
3490:Coir
3350:PMID
3307:PMID
3258:PMID
3223:PMID
3188:PMID
3142:PMID
3090:PMID
3040:PMID
3005:PMID
2960:PMID
2909:PMID
2850:PMID
2813:ISBN
2777:PMID
2735:PMID
2700:PMID
2651:PMID
2616:PMID
2559:PMID
2524:PMID
2483:PMID
2448:PMID
2413:PMID
2378:PMID
2260:link
2242:PMID
2197:PMID
2156:PMID
2107:PMID
2058:PMID
2009:PMID
1946:PMID
1911:PMID
1862:PMID
1827:PMID
1763:PMID
1718:link
1700:PMID
1656:PMID
1475:beef
1343:and
1327:and
1198:The
1156:???
418:The
406:and
203:bone
162:9721
138:2010
121:MeSH
60:The
4079:Leg
4064:Arm
3685:Yak
3393:doi
3342:doi
3338:226
3297:doi
3250:doi
3246:188
3215:doi
3180:doi
3132:doi
3082:doi
3032:doi
3028:316
2997:doi
2899:hdl
2889:doi
2842:doi
2769:doi
2727:doi
2690:PMC
2682:doi
2643:doi
2639:169
2606:PMC
2598:doi
2594:357
2551:doi
2547:218
2514:PMC
2510:187
2475:doi
2471:133
2440:doi
2405:doi
2401:137
2368:PMC
2360:doi
2234:doi
2187:PMC
2183:189
2146:PMC
2138:doi
2134:553
2097:PMC
2089:doi
2085:195
2048:doi
2001:doi
1973:doi
1938:doi
1901:PMC
1893:doi
1854:doi
1819:doi
1753:PMC
1745:doi
1741:222
1692:doi
1688:139
1646:PMC
1638:doi
1491:phở
1481:or
1335:of
1224:MRI
308:3%
201:to
189:or
157:FMA
133:TA2
4601::
3399:.
3391:.
3381:32
3379:.
3356:.
3348:.
3336:.
3313:.
3305:.
3293:19
3291:.
3287:.
3264:.
3256:.
3244:.
3221:.
3211:21
3209:.
3186:.
3176:39
3174:.
3154:^
3140:.
3128:43
3126:.
3122:.
3110:^
3096:.
3088:.
3078:87
3076:.
3060:^
3046:.
3038:.
3026:.
3003:.
2993:22
2991:.
2979:^
2966:.
2954:.
2950:.
2931:^
2915:.
2907:.
2897:.
2885:98
2883:.
2879:.
2856:.
2848:.
2838:59
2836:.
2775:.
2765:24
2763:.
2759:.
2733:.
2721:.
2698:.
2688:.
2676:.
2672:.
2649:.
2637:.
2614:.
2604:.
2592:.
2588:.
2565:.
2557:.
2545:.
2522:.
2508:.
2504:.
2481:.
2469:.
2446:.
2436:36
2434:.
2411:.
2399:.
2376:.
2366:.
2356:94
2354:.
2350:.
2313:.
2309:.
2276:.
2256:}}
2252:{{
2230:12
2228:.
2224:.
2209:^
2195:.
2181:.
2177:.
2154:.
2144:.
2132:.
2128:.
2105:.
2095:.
2083:.
2079:.
2056:.
2044:65
2042:.
2038:.
2015:.
2007:.
1997:98
1995:.
1967:.
1944:.
1934:17
1932:.
1909:.
1899:.
1889:38
1887:.
1883:.
1860:.
1850:84
1848:.
1825:.
1815:37
1813:.
1784:^
1761:.
1751:.
1739:.
1735:.
1714:}}
1710:{{
1686:.
1654:.
1644:.
1634:21
1632:.
1628:.
1603:.
1578:.
1493:.
1323:.
1250:.
477:.
469:.
442:.
333:,
276:.
209:.
185:A
145:TH
4195:e
4188:t
4181:v
4088:/
3993:e
3986:t
3979:v
3437:e
3430:t
3423:v
3407:.
3395::
3387::
3364:.
3344::
3321:.
3299::
3272:.
3252::
3229:.
3217::
3194:.
3182::
3148:.
3134::
3104:.
3084::
3054:.
3034::
3011:.
2999::
2956:6
2925:.
2901::
2891::
2864:.
2844::
2821:.
2783:.
2771::
2741:.
2729::
2723:9
2706:.
2684::
2678:9
2657:.
2645::
2622:.
2600::
2573:.
2553::
2530:.
2489:.
2477::
2454:.
2442::
2419:.
2407::
2384:.
2362::
2331:.
2315:9
2291:.
2262:)
2248:.
2236::
2203:.
2162:.
2140::
2113:.
2091::
2064:.
2050::
2023:.
2003::
1979:.
1975::
1969:8
1952:.
1940::
1917:.
1895::
1868:.
1856::
1833:.
1821::
1769:.
1747::
1720:)
1706:.
1694::
1662:.
1640::
1613:.
1589:.
1532:.
341:.
326:,
319:,
312:,
177:]
43:.
36:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.