36:
407:
224:
118:
102:
282:
Innervation to the facet joints vary between segments of the spinal, but they are generally innervated by medial branch nerves that come off the dorsal rami. It is thought that these nerves are for primary sensory input, though there is some evidence that they have some motor input local musculature.
298:
In the thoracic and lumbar spine, the facet joints are innervated by the medial branch nerves from the vertebral segment above the upper segment and the upper segment. For example, the facet joint between T1 and T2 is innervated by C8 and T1 medial branch nerves. Facet joint between L1 and L2; the
878:
10. Zhu Wei Lim, Shih-Chuan Tsai, Yi-Ching Lin, Yuan-Yang Cheng, Shin-Tsu Chang. A worthwhile measurement of early vigilance and therapeutic monitor in axial spondyloarthritis: a literature review of quantitative sacroiliac scintigraphy. European
Medical Journal (EMJ) Rheumatology 2021 July 15;
874:
9. Shin-Tsu Chang, Chuan-Ching Liu, Wan-Hua Yang. Single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography (hybrid imaging) in the diagnosis of unilateral facet joint arthritis after internal fixation for atlas fracture. HSOA Journal of
Medicine: Study & Research 2019; 2: 010.
397:
by specialist physicians such as facet loading (also called Kemps test). However, this test has poor sensitivity (50-70%) and specificity (67.3%) for lumbar facet pain. Often providers perform diagnostic injections to determine if the facet joint is the underlying source of pain.
439:
Corticosteroid injections into the joint space may provide temporary pain relief anywhere from days to several months. With repeated injections, sometimes the patient may experience a more permanent improvement in their symptoms. Steroid injections are typically performed under
327:, and surgery. In the thoracic spine the facet joints function to restrain the amount of flexion and anterior translation of the corresponding vertebral segment and function to facilitate rotation. Cavitation of the
299:
T12 and L1 medial branch nerves. However, the L5 and S1 facet joint is innervated by the L4 medial branch nerve and the L5 dorsal ramus. In this case, there is no L5 medial branch to innervate the facet joint.
384:
Facet joint arthritis may not always have any symptoms, but often manifests as a dull ache across the back. However like many deep organs of the body it can be experienced by the patient in a variety of
315:
shear forces, excessive rotation and flexion. Facet joints appear to have little influence on the range of side bending (lateral flexion). These functions can be disrupted by degeneration,
287:) from the same levels. In other words, the facet joint between C4 and C5 vertebral segments is innervated by the C4 and C5 medial branch nerves. However, there are two exceptions:
920:
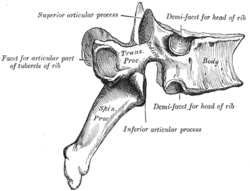
110:. The facet joint is the joint between the inferior articular process (labeled at bottom) and the superior articular process (labeled at top) of the subsequent vertebra.
459:). Current guidelines as per the International Spine Intervention Society require two successful medial branch blocks before progressing to a radiofrequency ablation.
338:
The facet joints, both superior and inferior, are aligned in a way to allow flexion and extension, and to limit rotation. This is especially true in the lumbar spine.
199:
372:, possibly impinging on the spinal nerve roots within. More advanced cases can involve severe inflammatory responses in the Z-joint, not unlike a swollen
863:
704:"Relationship of Physical Examination Findings and Self-Reported Symptom Severity and Physical Function in Patients With Degenerative Lumbar Conditions"
1098:
913:
832:
1226:
456:
1447:
1044:
800:
682:
610:
568:
175:
1457:
1271:
57:
906:
455:
or lesioning, also known as rhizolysis, can be used to give longer lasting relief by destroying the nerves that supply the facet joint (
444:
to ensure accuracy given the complex shape and deep location of the facet. Some patients do not benefit from corticosteriod injections.
272:
1177:
79:
1408:
1172:
1221:
1118:
977:
1276:
1113:
972:
307:
The biomechanical function of each pair of facet joints is to guide and limit movement of the spinal motion segment. In the
1403:
194:
1398:
1082:
517:
312:
820:
1291:
1213:
779:
Lavelle, William F.; Carl, Allen L.; Lavelle, Elizabeth Demers; Furdyna, Aimee (2009-01-01), Smith, HOWARD S. (ed.),
50:
44:
1078:
350:. This is particularly true for joints in the spine, and the facet joint in particular. This is commonly known as
347:
61:
1244:
1164:
1018:
346:
In large part due to the mechanical nature of their function, all joints undergo degenerative changes with the
158:
1380:
1375:
1093:
452:
393:, further complicate the diagnostic approach. Typically facet joint arthritis is diagnosed with specialized
291:
The facet joint between C2 and C3 is innervated by the third occipital nerve and the C3 medial branch nerve.
1417:
1281:
390:
369:
268:
206:
182:
170:
839:
1422:
1236:
1204:
1013:
1001:
780:
662:
590:
548:
522:
1249:
424:
394:
888:
703:
406:
1344:
1309:
1263:
1154:
1069:
1040:
512:
260:
283:
Within the cervical spine, most joints are innervated by the medial branch nerve (a branch of the
1352:
1146:
857:
796:
758:
750:
678:
643:
606:
564:
320:
316:
107:
1390:
1049:
964:
945:
788:
740:
670:
598:
556:
420:
127:
123:
661:
Hou, David D.; Carrino, John A. (2007-01-01), Waldman, Steven D.; Bloch, Joseph I. (eds.),
335:) associated with manual spinal manipulation, commonly referred to as "cracking the back."
1452:
1367:
1357:
1006:
996:
389:
patterns. The location of facet joints, deep in the back and covered with large tracts of
893:
1060:
988:
792:
674:
560:
527:
373:
352:
328:
324:
252:
368:
due to the degenerative process. Even small changes to the facet joint can narrow the
294:
The facet joint between C7 and T1 is innervated by the C7 and C8 medial branch nerves.
1441:
1088:
602:
428:
386:
1331:
471:, can be performed in certain cases, particularly when the nerve root is affected.
365:
308:
163:
1340:
954:
898:
745:
635:
547:
Lowe, Whitney; Chaitow, Leon (2009-01-01), Lowe, Whitney; Chaitow, Leon (eds.),
468:
441:
284:
256:
729:"The inability of the clinical picture to characterize pain from facet joints"
754:
187:
1032:
728:
361:
311:, for example, the facet joints function to protect the motion segment from
17:
762:
647:
223:
933:
332:
264:
227:
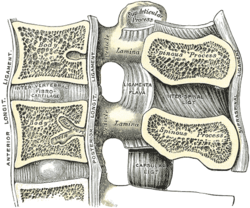
Illustration highlighting facet joint articulation between two vertebrae
212:
1195:
727:
Manchikanti, L.; Pampati, V.; Fellows, B.; Baha, A. G. (April 2000).
117:
937:
929:
405:
222:
146:
101:
902:
331:
within the facet joints is responsible for the popping sound (
29:
497:
489:
481:
419:
Conservative treatment of facet joint arthritis involves
1389:
1366:
1339:
1330:
1308:
1290:
1262:
1235:
1212:
1203:
1194:
1163:
1145:
1127:
1068:
1059:
1031:
986:
962:
953:
944:
193:
181:
169:
157:
145:
140:
135:
94:
629:
627:
787:, Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, pp. 167–176,
589:Lowe, Whitney (2003-01-01), Lowe, Whitney (ed.),
894:Emedicine article on Lumbosacral Facet Syndrome
669:, Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, pp. 85–92,
634:Mann, S. J.; Viswanath, O.; Singh, P. (2022).
914:
8:
1414:ligaments connecting the sacrum and ischium
427:, with muscle strengthening, correction of
1336:
1209:
1200:
1065:
959:
950:
921:
907:
899:
271:and each facet joint is innervated by the
116:
100:
1099:Tectorial membrane of atlanto-axial joint
744:
663:"chapter 8 - Nuclear Medicine Techniques"
80:Learn how and when to remove this message
410:Illustration depicting facet joint block
43:This article includes a list of general
591:"Chapter 9 - Lumbar and thoracic spine"
549:"Chapter 9 - Lumbar and thoracic spine"
539:
862:: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (
855:
597:, Edinburgh: Mosby, pp. 129–143,
555:, Edinburgh: Mosby, pp. 175–198,
267:. There are two facet joints in each
210:
91:
7:
1272:intraarticular sternocostal ligament
774:
772:
27:Joint between two adjacent vertebrae
553:Orthopedic Massage (Second Edition)
793:10.1016/b978-1-4160-4836-7.00022-5
675:10.1016/b978-0-7216-0334-6.50012-1
561:10.1016/b978-0-443-06812-6.00009-x
431:, and biomechanics being the key.
49:it lacks sufficient corresponding
25:
1178:posterior sacrococcygeal ligament
1409:interosseous sacroiliac ligament
1173:anterior sacrococcygeal ligament
603:10.1016/b978-072343226-5.50014-9
34:
1119:posterior atlantoaxial ligament
978:posterior longitudinal ligament
1277:radiate sternocostal ligaments
1114:anterior atlantoaxial ligament
973:anterior longitudinal ligament
821:NASS on facet joint injections
152:articulationes zygapophysiales
1:
1448:Bones of the vertebral column
1404:posterior sacroiliac ligament
1399:anterior sacroiliac ligament
1083:Transverse ligament of atlas
889:Diagram at spineuniverse.com
518:Artificial facet replacement
498:
490:
482:
1458:Joints of the head and neck
273:recurrent meningeal nerves.
1474:
1079:Cruciate ligament of atlas
636:"Lumbar Facet Arthropathy"
467:Surgery, in the form of a
435:Corticosteroid injections
205:
115:
99:
1245:Costotransverse ligament
1227:Intra-articular ligament
1019:intertransverse ligament
781:"Chapter 22 - BACK PAIN"
1381:inferior pubic ligament
1376:superior pubic ligament
1094:Apical ligament of dens
785:Current Therapy in Pain
746:10.36076/ppj.2000/3/158
453:Radiofrequency ablation
364:, the joint can become
64:more precise citations.
1418:sacrotuberous ligament
1282:costoxiphoid ligaments
415:Conservative treatment
411:
370:intervertebral foramen
228:
207:Anatomical terminology
1423:sacrospinous ligament
1014:interspinous ligament
1002:supraspinous ligament
523:Facet joint injection
409:
353:facet joint arthritis
342:Facet joint arthritis
269:spinal motion segment
226:
1250:Lumbocostal ligament
457:medial branch nerves
425:osteopathic medicine
395:physical examination
348:wear and tear of age
319:, fracture, injury,
237:zygapophysial joints
1155:iliolumbar ligament
1041:intervertebral disc
513:Articular processes
261:articular processes
130:and their ligaments
1353:Obturator membrane
595:Orthopedic Massage
412:
391:paraspinal muscles
229:
1435:
1434:
1431:
1430:
1326:
1325:
1258:
1257:
1190:
1189:
1186:
1185:
1027:
1026:
802:978-1-4160-4836-7
684:978-0-7216-0334-6
612:978-0-7234-3226-5
570:978-0-443-06812-6
358:facet arthropathy
221:
220:
216:
108:thoracic vertebra
90:
89:
82:
16:(Redirected from
1465:
1337:
1222:Radiate ligament
1210:
1201:
1066:
1050:nucleus pulposus
989:vertebral arches
965:vertebral bodies
960:
951:
923:
916:
909:
900:
868:
867:
861:
853:
851:
850:
844:
838:. Archived from
837:
829:
823:
818:
812:
811:
810:
809:
776:
767:
766:
748:
724:
718:
717:
715:
714:
708:academic.oup.com
700:
694:
693:
692:
691:
658:
652:
651:
631:
622:
621:
620:
619:
586:
580:
579:
578:
577:
544:
501:
493:
485:
421:physical therapy
263:of two adjacent
213:edit on Wikidata
128:lumbar vertebrae
124:sagittal section
120:
104:
92:
85:
78:
74:
71:
65:
60:this article by
51:inline citations
38:
37:
30:
21:
1473:
1472:
1468:
1467:
1466:
1464:
1463:
1462:
1438:
1437:
1436:
1427:
1385:
1368:Pubic symphysis
1362:
1358:Obturator canal
1322:
1304:
1286:
1254:
1237:Costotransverse
1231:
1182:
1159:
1141:
1123:
1055:
1045:anulus fibrosus
1023:
1007:nuchal ligament
997:ligamenta flava
982:
940:
927:
885:
872:
871:
854:
848:
846:
842:
835:
833:"Archived copy"
831:
830:
826:
819:
815:
807:
805:
803:
778:
777:
770:
726:
725:
721:
712:
710:
702:
701:
697:
689:
687:
685:
667:Pain Management
660:
659:
655:
633:
632:
625:
617:
615:
613:
588:
587:
583:
575:
573:
571:
546:
545:
541:
536:
509:
495:("out/from") +
479:Ancient Greek:
477:
465:
450:
437:
417:
404:
382:
344:
305:
280:
251:) are a set of
217:
131:
111:
86:
75:
69:
66:
56:Please help to
55:
39:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1471:
1469:
1461:
1460:
1455:
1450:
1440:
1439:
1433:
1432:
1429:
1428:
1426:
1425:
1420:
1411:
1406:
1401:
1395:
1393:
1387:
1386:
1384:
1383:
1378:
1372:
1370:
1364:
1363:
1361:
1360:
1355:
1349:
1347:
1334:
1328:
1327:
1324:
1323:
1321:
1320:
1314:
1312:
1306:
1305:
1303:
1302:
1296:
1294:
1288:
1287:
1285:
1284:
1279:
1274:
1268:
1266:
1260:
1259:
1256:
1255:
1253:
1252:
1247:
1241:
1239:
1233:
1232:
1230:
1229:
1224:
1218:
1216:
1207:
1205:Costovertebral
1198:
1192:
1191:
1188:
1187:
1184:
1183:
1181:
1180:
1175:
1169:
1167:
1165:Sacrococcygeal
1161:
1160:
1158:
1157:
1151:
1149:
1143:
1142:
1140:
1139:
1133:
1131:
1125:
1124:
1122:
1121:
1116:
1110:
1109:
1102:
1101:
1096:
1091:
1086:
1074:
1072:
1063:
1061:Synovial joint
1057:
1056:
1054:
1053:
1047:
1037:
1035:
1029:
1028:
1025:
1024:
1022:
1021:
1016:
1011:
1010:
1009:
999:
993:
991:
984:
983:
981:
980:
975:
969:
967:
957:
948:
942:
941:
928:
926:
925:
918:
911:
903:
897:
896:
891:
884:
883:External links
881:
870:
869:
824:
813:
801:
768:
739:(2): 158–166.
733:Pain Physician
719:
695:
683:
653:
642:. StatPearls.
623:
611:
581:
569:
538:
537:
535:
532:
531:
530:
528:Facet syndrome
525:
520:
515:
508:
505:
476:
473:
464:
461:
449:
446:
442:image guidance
436:
433:
416:
413:
403:
400:
381:
378:
374:arthritic knee
360:. As with any
343:
340:
329:synovial fluid
325:osteoarthritis
304:
301:
296:
295:
292:
279:
276:
219:
218:
209:
203:
202:
197:
191:
190:
185:
179:
178:
173:
167:
166:
161:
155:
154:
149:
143:
142:
138:
137:
133:
132:
121:
113:
112:
105:
97:
96:
88:
87:
42:
40:
33:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1470:
1459:
1456:
1454:
1451:
1449:
1446:
1445:
1443:
1424:
1421:
1419:
1415:
1412:
1410:
1407:
1405:
1402:
1400:
1397:
1396:
1394:
1392:
1388:
1382:
1379:
1377:
1374:
1373:
1371:
1369:
1365:
1359:
1356:
1354:
1351:
1350:
1348:
1346:
1345:pelvic girdle
1342:
1338:
1335:
1333:
1329:
1319:
1316:
1315:
1313:
1311:
1310:Costochondral
1307:
1301:
1298:
1297:
1295:
1293:
1292:Interchondral
1289:
1283:
1280:
1278:
1275:
1273:
1270:
1269:
1267:
1265:
1261:
1251:
1248:
1246:
1243:
1242:
1240:
1238:
1234:
1228:
1225:
1223:
1220:
1219:
1217:
1215:
1211:
1208:
1206:
1202:
1199:
1197:
1193:
1179:
1176:
1174:
1171:
1170:
1168:
1166:
1162:
1156:
1153:
1152:
1150:
1148:
1144:
1138:
1135:
1134:
1132:
1130:
1129:Zygapophysial
1126:
1120:
1117:
1115:
1112:
1111:
1108:
1104:
1103:
1100:
1097:
1095:
1092:
1090:
1089:Alar ligament
1087:
1084:
1080:
1076:
1075:
1073:
1071:
1070:Atlanto-axial
1067:
1064:
1062:
1058:
1051:
1048:
1046:
1042:
1039:
1038:
1036:
1034:
1030:
1020:
1017:
1015:
1012:
1008:
1005:
1004:
1003:
1000:
998:
995:
994:
992:
990:
985:
979:
976:
974:
971:
970:
968:
966:
961:
958:
956:
952:
949:
947:
943:
939:
935:
931:
924:
919:
917:
912:
910:
905:
904:
901:
895:
892:
890:
887:
886:
882:
880:
876:
865:
859:
845:on 2020-04-06
841:
834:
828:
825:
822:
817:
814:
804:
798:
794:
790:
786:
782:
775:
773:
769:
764:
760:
756:
752:
747:
742:
738:
734:
730:
723:
720:
709:
705:
699:
696:
686:
680:
676:
672:
668:
664:
657:
654:
649:
645:
641:
637:
630:
628:
624:
614:
608:
604:
600:
596:
592:
585:
582:
572:
566:
562:
558:
554:
550:
543:
540:
533:
529:
526:
524:
521:
519:
516:
514:
511:
510:
506:
504:
502:
500:
494:
492:
486:
484:
474:
472:
470:
462:
460:
458:
454:
447:
445:
443:
434:
432:
430:
426:
422:
414:
408:
401:
399:
396:
392:
388:
387:referral pain
379:
377:
375:
371:
367:
363:
359:
355:
354:
349:
341:
339:
336:
334:
330:
326:
323:from trauma,
322:
318:
314:
310:
302:
300:
293:
290:
289:
288:
286:
277:
275:
274:
270:
266:
262:
258:
254:
250:
246:
242:
241:zygapophyseal
238:
234:
225:
214:
208:
204:
201:
198:
196:
192:
189:
186:
184:
180:
177:
174:
172:
168:
165:
162:
160:
156:
153:
150:
148:
144:
139:
134:
129:
125:
119:
114:
109:
103:
98:
93:
84:
81:
73:
63:
59:
53:
52:
46:
41:
32:
31:
19:
1413:
1318:no ligaments
1317:
1300:no ligaments
1299:
1264:Sternocostal
1137:no ligaments
1136:
1128:
1107:no ligaments
1106:
877:
873:
847:. Retrieved
840:the original
827:
816:
806:, retrieved
784:
736:
732:
722:
711:. Retrieved
707:
698:
688:, retrieved
666:
656:
639:
616:, retrieved
594:
584:
574:, retrieved
552:
542:
496:
488:
480:
478:
466:
451:
438:
418:
383:
357:
351:
345:
337:
309:lumbar spine
306:
297:
281:
259:between the
257:plane joints
248:
244:
240:
236:
233:facet joints
232:
230:
176:A03.2.06.001
151:
76:
67:
48:
18:Facet joints
1341:Syndesmoses
1214:Head of rib
1147:Lumbosacral
955:Syndesmosis
879:8:129-139.
487:("yoke") +
469:facetectomy
321:instability
317:dislocation
285:dorsal rami
278:Innervation
141:Identifiers
95:Facet joint
62:introducing
1442:Categories
1391:Sacroiliac
849:2019-11-13
808:2020-11-03
713:2023-01-26
690:2020-11-03
640:StatPearls
618:2020-11-03
576:2020-11-03
534:References
245:apophyseal
70:March 2016
45:references
1105:Lateral:
1033:Symphysis
946:Vertebral
934:ligaments
755:1533-3159
503:("grow")
475:Etymology
402:Treatment
380:Diagnosis
362:arthritis
265:vertebrae
1077:Medial:
858:cite web
763:16906195
648:30855816
507:See also
448:Ablation
366:enlarged
333:crepitus
313:anterior
303:Function
253:synovial
249:Z-joints
463:Surgery
429:posture
164:D021801
136:Details
126:of two
122:Median
58:improve
1453:Joints
1332:Pelvis
1196:Thorax
930:Joints
799:
761:
753:
681:
646:
609:
567:
499:phyein
235:(also
47:, but
938:torso
843:(PDF)
836:(PDF)
483:zygon
247:, or
211:[
200:10447
147:Latin
932:and
864:link
797:ISBN
759:PMID
751:ISSN
679:ISBN
644:PMID
607:ISBN
565:ISBN
231:The
188:1707
171:TA98
159:MeSH
1343:of
987:Of
963:Of
936:of
789:doi
741:doi
671:doi
599:doi
557:doi
491:apo
423:or
356:or
195:FMA
183:TA2
1444::
1416::
860:}}
856:{{
795:,
783:,
771:^
757:.
749:.
735:.
731:.
706:.
677:,
665:,
638:.
626:^
605:,
593:,
563:,
551:,
376:.
255:,
243:,
239:,
106:A
1085:)
1081:(
1052:)
1043:(
922:e
915:t
908:v
866:)
852:.
791::
765:.
743::
737:3
716:.
673::
650:.
601::
559::
215:]
83:)
77:(
72:)
68:(
54:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.