31:
225:, they were able to show that the mouse and human proteins remained segregated to separate halves of the heterokaryon a short time after cell fusion. However, the proteins eventually diffused and over time the border between the two halves was lost. Lowering the temperature slowed the rate of this diffusion by causing the membrane phospholipids to transition from a fluid to a gel phase. Singer and Nicolson rationalized the results of these experiments using their fluid mosaic model.
206:
375:
390:
are a family of GTP-binding proteins highly conserved among eukaryotes. Prokaryotes have similar proteins called paraseptins. They form compartmentalizing ring-like structures strongly associated with the cell membranes. Septins are involved in the formation of structures such as, cilia and flagella,
370:
When integral proteins of the lipid bilayer are tethered to the extracellular matrix, they are unable to diffuse freely. Proteins with a long intracellular domain may collide with a fence formed by cytoskeleton filaments. Both processes restrict the diffusion of proteins and lipids directly involved,
311:
cell, in about 1 second. It has also been observed that individual lipid molecules rotate rapidly around their own axis. Moreover, phospholipid molecules can, although they seldom do, migrate from one side of the lipid bilayer to the other (a process known as flip-flop). However, flip-flop movement
268:
The existence of non-bilayer lipid formations with important biological functions was confirmed subsequent to publication of the fluid mosaic model. These membrane structures may be useful when the cell needs to propagate a non bilayer form, which occurs during cell division and the formation of a
320:
There are restrictions to the lateral mobility of the lipid and protein components in the fluid membrane imposed by zonation. Early attempts to explain the assembly of membrane zones include the formation of lipid rafts and “cytoskeletal fences”, corrals wherein lipid and membrane proteins can
228:
The fluid mosaic model explains changes in structure and behavior of cell membranes under different temperatures, as well as the association of membrane proteins with the membranes. While Singer and
Nicolson had substantial evidence drawn from multiple subfields to support their model, recent
341:
Cell membrane proteins and glycoproteins do not exist as single elements of the lipid membrane, as first proposed by Singer and
Nicolson in 1972. Rather, they occur as diffusing complexes within the membrane. The assembly of single molecules into these macromolecular complexes has important
439:
proposed that lipid membranes are layers composed by proteins and lipids with pore-like structures that allow specific permeability for certain molecules. Then, they suggested a model for the cell membrane, consisting of a lipid layer surrounded by protein layers at both sides of
197:
Tri-Layer model. These models had proteins present as sheets neighboring a lipid layer, rather than incorporated into the phospholipid bilayer. Other models described repeating, regular units of protein and lipid. These models were not well supported by microscopy and
306:
During the 1970s, it was acknowledged that individual lipid molecules undergo free lateral diffusion within each of the layers of the lipid membrane. Diffusion occurs at a high speed, with an average lipid molecule diffusing ~2μm, approximately the length of a large
96:
where embedded proteins are generally randomly distributed. For example, it is stated that "A prediction of the fluid mosaic model is that the two-dimensional long-range distribution of any integral protein in the plane of the membrane is essentially random."
362:
Some proteins embedded in the bilipid layer interact with the extracellular matrix outside the cell, cytoskeleton filaments inside the cell, and septin ring-like structures. These interactions have a strong influence on shape and structure, as well as on
312:
is enhanced by flippase enzymes. The processes described above influence the disordered nature of lipid molecules and interacting proteins in the lipid membranes, with consequences to membrane fluidity, signaling, trafficking and function.
255:
and cholesterol-interacting proteins can concentrate into lipid rafts and constrain cell signaling processes to only these rafts. Another form of asymmetry was shown by the work of
Mouritsen and Bloom in 1984, where they proposed a
332:
are membrane nanometric platforms with a particular lipid and protein composition that laterally diffuse, navigating on the liquid bilipid layer. Sphingolipids and cholesterol are important building blocks of the lipid rafts.
281:
The membrane bilayer is not always flat. Local curvature of the membrane can be caused by the asymmetry and non-bilayer organization of lipids as discussed above. More dramatic and functional curvature is achieved through
250:
Additionally, the two leaflets of biological membranes are asymmetric and divided into subdomains composed of specific proteins or lipids, allowing spatial segregation of biological processes associated with membranes.
818:
Rodríguez-García R, Arriaga LR, Mell M, Moleiro LH, López-Montero I, Monroy F (March 2009). "Bimodal spectrum for the curvature fluctuations of bilayer vesicles: pure bending plus hybrid curvature-dilation modes".
209:
The Frye-Edidin experiment showed that when two cells are fused the proteins of both diffuse around the membrane and mingle rather than being locked to their area of the membrane.
460:– SJ Singer and GL Nicolson proposed the fluid mosaic model as an explanation for the data and latest evidence regarding the structure and thermodynamics of cell membranes.
562:"The Fluid-Mosaic Model of Membrane Structure: still relevant to understanding the structure, function and dynamics of biological membranes after more than 40 years"
1425:
321:
diffuse freely, but that they can seldom leave. These ideas remain controversial, and alternative explanations are available such as the proteolipid code.
472:– TA Kervin and M Overduin proposed the proteolipid code to fully explain membrane zonation as the lipid raft theory became increasingly controversial.
367:. Moreover, they impose physical constraints that restrict the free lateral diffusion of proteins and at least some lipids within the bilipid layer.
1854:
868:
186:
of the lipid bilayer in which they were embedded, and demonstrated that the molecules within the cell membrane are dynamic rather than static.
878:
1228:
260:
of lipid-protein interactions to address the biophysical evidence that the membrane can range in thickness and hydrophobicity of proteins.
636:
Silvius JR (December 2005). "Partitioning of membrane molecules between raft and non-raft domains: insights from model-membrane studies".
298:
formation and cell division. Curvature development is in constant flux and contributes to the dynamic nature of biological membranes.
1418:
454:
plasma and organelle membranes, have the same structure: a bilayer of phospholipids with monolayers of proteins at both sides of it.
601:
Frye LD, Edidin M (September 1970). "The rapid intermixing of cell surface antigens after formation of mouse-human heterokaryons".
213:
An important experiment that provided evidence supporting fluid and dynamic biological was performed by Frye and Edidin. They used
450:, based on electron microscopy studies, establishes the "Unit Membrane Hypothesis". This, states that all membranes in the cell,
1487:
945:"Sphingolipids, Membrane Rafts and Caveolae - sphingomyelin and cholesterol - structure, occurrence, biochemistry and function"
291:
944:
1589:
1847:
1411:
1932:
194:
2023:
1923:
730:"Nonbilayer lipids affect peripheral and integral membrane proteins via changes in the lateral pressure profile"
1584:
1840:
230:
85:
1549:
1936:
1918:
1524:
93:
182:, and calorimetry. These studies showed that integral membrane proteins diffuse at rates affected by the
2033:
1972:
1927:
1788:
1574:
1467:
447:
179:
466:– K Simons and E Ikonen proposed the lipid raft theory as an initial explanation of membrane zonation.
418:
30:
1821:
1374:
1276:
1033:
978:
896:"Role of flippases, scramblases and transfer proteins in phosphatidylserine subcellular distribution"
828:
684:
507:
498:
Singer SJ, Nicolson GL (February 1972). "The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes".
364:
287:
257:
73:
2028:
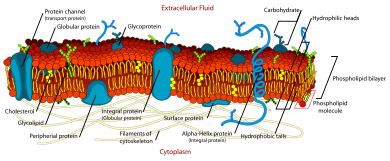
1447:
205:
414:
1239:
1002:
531:
343:
234:
383:
Septin ring-like structures (in green) can pinch cell membranes and split them into subdomains.
1977:
1771:
1609:
1492:
1390:
1362:
1343:
1292:
1182:
1110:
1061:
994:
925:
874:
844:
800:
751:
710:
653:
618:
583:
523:
89:
69:
1992:
1910:
1382:
1333:
1323:
1284:
1209:
1172:
1164:
1100:
1092:
1051:
1041:
986:
915:
907:
836:
790:
782:
741:
700:
692:
645:
610:
573:
515:
50:
1200:
Danielli J, Davson H (1935). "A contribution to the theory of permeability of thin films".
1987:
1472:
1022:"Dynamic, yet structured: The cell membrane three decades after the Singer-Nicolson model"
1378:
1338:
1311:
1280:
1129:
1037:
982:
832:
688:
511:
1872:
1435:
1177:
1152:
1105:
1080:
969:
Lingwood D, Simons K (January 2010). "Lipid rafts as a membrane-organizing principle".
920:
895:
795:
770:
705:
672:
436:
404:
351:
222:
46:
1403:
1056:
1021:
696:
2017:
1997:
1957:
1880:
1864:
1718:
1678:
1653:
1569:
1482:
1457:
421:
found that red blood cell membranes are formed by a fatty layer two molecules thick,
347:
199:
81:
54:
35:
1386:
1006:
535:
374:
1895:
1885:
1698:
1670:
1648:
1641:
1621:
1561:
1477:
1462:
840:
270:
218:
214:
190:
1832:
174:
The fluid property of functional biological membranes had been determined through
17:
1020:
Vereb G, Szöllosi J, Matkó J, Nagy P, Farkas T, Vigh L, et al. (July 2003).
746:
729:
649:
578:
561:
519:
1890:
1800:
1766:
1693:
1688:
1579:
432:
252:
84:
are also found in the cell membrane. The biological model, which was devised by
1328:
1026:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
786:
1967:
1962:
1795:
1735:
1728:
1713:
1708:
1703:
1658:
1604:
1594:
1544:
1539:
1529:
329:
283:
175:
58:
1816:
1778:
1751:
1723:
1631:
1616:
1599:
1534:
1507:
1439:
1046:
990:
295:
183:
65:
1394:
1347:
1213:
1186:
1114:
1096:
1065:
998:
929:
848:
804:
755:
657:
587:
1296:
714:
622:
527:
2002:
1952:
1761:
1517:
1502:
1497:
1168:
308:
77:
1264:
728:
van den Brink-van der Laan E, Killian JA, de
Kruijff B (November 2004).
614:
202:
data, and did not accommodate evidence for dynamic membrane properties.
1783:
1683:
1636:
1512:
387:
62:
45:
explains various characteristics regarding the structure of functional
1130:"Uberdie osmotischen Eigenshafter der Lebenden Pflanzen und tierzelle"
911:
129:
The hydrophilic phosphate side is outwards and hydrophobic inwards.
1982:
1900:
1626:
358:
Cytoskeletal fences (corrals) and binding to the extracellular matrix
1288:
1153:"On Bimolecular Layers of Lipoids on the Chromocytes of the Blood"
373:
371:
as well as of other interacting components of the cell membranes.
204:
1836:
1407:
1756:
873:(5th ed.). New York: Garland Science. pp. 621–622.
771:"The BAR domain superfamily: membrane-molding macromolecules"
638:
Biochimica et
Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research
673:"Mattress model of lipid-protein interactions in membranes"
894:
Hankins HM, Baldridge RD, Xu P, Graham TR (January 2015).
237:
have validated the fluid mosaic nature of cell membranes.
160:
Embedded within or on the surface of phospholipid layers
127:
It provides selective permeability to the cell membrane.
407:
hypothesized that cell membranes are made out of lipids.
163:
These form channels to allow the movement of molecules.
1310:
Kervin, Troy A.; Overduin, Michael (27 February 2024).
425:
they described the bilipid nature of the cell membrane.
189:
Previous models of biological membranes included the
152:
It helps the plasma membrane to retain its fluidity.
1312:"Membranes are functionalized by a proteolipid code"
1945:
1909:
1871:
1809:
1744:
1669:
1560:
1446:
867:Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, et al. (2008).
57:(two molecules thick layer consisting primarily of
1236:Newsletter of the American Society of Cell Biology
734:Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes
566:Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes
217:to force human and mouse cells to fuse and form a
27:Describe the fluid mosaic model of plasma membrane
1081:"The emerging functions of septins in metazoans"
149:Between phospholipids and phospholipid bilayers
138:Attached to proteins on outside membrane layers
1202:Journal of Cellular and Comparative Physiology
769:Frost A, Unger VM, De Camilli P (April 2009).
555:
553:
551:
549:
547:
545:
342:functional consequences for the cell; such as
1848:
1419:
68:are embedded. The phospholipid bilayer gives
8:
493:
491:
489:
487:
485:
1855:
1841:
1833:
1426:
1412:
1404:
92:in 1972, describes the cell membrane as a
1337:
1327:
1176:
1104:
1055:
1045:
919:
862:
860:
858:
794:
745:
704:
577:
1263:Simons, Kai; Ikonen, Elina (June 1997).
1079:Saarikangas J, Barral Y (October 2011).
104:
29:
481:
290:on the membrane surface, assisting in
141:It helps in cell-to-cell recognition.
671:Mouritsen OG, Bloom M (August 1984).
7:
1265:"Functional rafts in cell membranes"
1157:The Journal of Experimental Medicine
124:The main fabric of plasma membrane
1361:Leslie, Mitch (25 November 2011).
1151:Gorter E, Grendel F (March 1925).
391:dendritic spines, and yeast buds.
302:Lipid movement within the membrane
25:
1229:"In Memory of J. David Robertson"
316:Restrictions to lateral diffusion
1387:10.1126/science.334.6059.1046-b
841:10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.128101
1:
1590:Microtubule organizing center
870:Molecular Biology of the Cell
697:10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84007-2
191:Robertson Unit Membrane Model
943:Christie, William (Bill) W.
747:10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.06.010
650:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2005.09.003
579:10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.10.019
520:10.1126/science.175.4023.720
344:ion and metabolite transport
1933:Peripheral membrane protein
2050:
1924:Integral membrane proteins
1329:10.1186/s12915-024-01849-6
787:10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.010
560:Nicolson GL (June 2014).
1585:Prokaryotic cytoskeleton
1134:VJSCHR Naturf Ges Zurich
61:phospholipids) in which
34:Fluid mosaic model of a
1968:Lipid raft/microdomains
1363:"Do Lipid Rafts Exist?"
1047:10.1073/pnas.1332550100
991:10.1126/science.1174621
821:Physical Review Letters
603:Journal of Cell Science
241:Subsequent developments
231:fluorescence microscopy
86:Seymour Jonathan Singer
1973:Membrane contact sites
1937:Lipid-anchored protein
1919:Membrane glycoproteins
1214:10.1002/jcp.1030050409
1097:10.1038/embor.2011.193
384:
210:
94:two-dimensional liquid
38:
1928:transmembrane protein
1575:Intermediate filament
1468:Endoplasmic reticulum
377:
264:Non-bilayer membranes
208:
170:Experimental evidence
33:
1953:Caveolae/Coated pits
1822:Extracellular matrix
1169:10.1084/jem.41.4.439
477:Notes and references
365:compartmentalization
288:phosphatidylinositol
49:. According to this
1525:Cytoplasmic granule
1379:2011Sci...334.1046L
1373:(6059): 1046–1047.
1281:1997Natur.387..569S
1038:2003PNAS..100.8053V
983:2010Sci...327...46L
833:2009PhRvL.102l8101R
689:1984BpJ....46..141M
677:Biophysical Journal
615:10.1242/jcs.7.2.319
512:1972Sci...175..720S
395:Historical timeline
106:
80:. Small amounts of
1978:Membrane nanotubes
1863:Structures of the
1550:Weibel–Palade body
1434:Structures of the
1227:Heuser JE (1995).
1128:Overton E (1895).
448:J. David Robertson
385:
277:Membrane curvature
246:Membrane asymmetry
235:structural biology
211:
105:
43:fluid mosaic model
39:
18:Fluid Mosaic Model
2011:
2010:
1911:Membrane proteins
1830:
1829:
1610:Spindle pole body
1275:(6633): 569–572.
1091:(11): 1118–1126.
1032:(14): 8053–8058.
912:10.1111/tra.12233
880:978-0-8153-4105-5
506:(4023): 720–731.
337:Protein complexes
223:antibody staining
180:x-ray diffraction
167:
166:
90:Garth L. Nicolson
16:(Redirected from
2041:
2024:Membrane biology
1993:Nuclear envelope
1988:Nodes of Ranvier
1857:
1850:
1843:
1834:
1428:
1421:
1414:
1405:
1399:
1398:
1358:
1352:
1351:
1341:
1331:
1307:
1301:
1300:
1260:
1254:
1253:
1251:
1250:
1244:
1238:. Archived from
1233:
1224:
1218:
1217:
1197:
1191:
1190:
1180:
1148:
1142:
1141:
1125:
1119:
1118:
1108:
1076:
1070:
1069:
1059:
1049:
1017:
1011:
1010:
966:
960:
959:
957:
955:
940:
934:
933:
923:
891:
885:
884:
864:
853:
852:
815:
809:
808:
798:
766:
760:
759:
749:
740:(1–2): 275–288.
725:
719:
718:
708:
668:
662:
661:
633:
627:
626:
598:
592:
591:
581:
572:(6): 1451–1466.
557:
540:
539:
495:
419:François Grendel
286:, which bind to
107:
51:biological model
21:
2049:
2048:
2044:
2043:
2042:
2040:
2039:
2038:
2014:
2013:
2012:
2007:
1941:
1905:
1873:Membrane lipids
1867:
1861:
1831:
1826:
1805:
1740:
1665:
1556:
1473:Golgi apparatus
1449:
1442:
1432:
1402:
1360:
1359:
1355:
1309:
1308:
1304:
1262:
1261:
1257:
1248:
1246:
1242:
1231:
1226:
1225:
1221:
1199:
1198:
1194:
1150:
1149:
1145:
1127:
1126:
1122:
1078:
1077:
1073:
1019:
1018:
1014:
977:(5961): 46–50.
968:
967:
963:
953:
951:
942:
941:
937:
893:
892:
888:
881:
866:
865:
856:
817:
816:
812:
768:
767:
763:
727:
726:
722:
670:
669:
665:
635:
634:
630:
600:
599:
595:
559:
558:
543:
497:
496:
483:
479:
397:
382:
360:
339:
327:
318:
304:
279:
266:
248:
243:
195:Davson-Danielli
172:
103:
101:Chemical makeup
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2047:
2045:
2037:
2036:
2031:
2026:
2016:
2015:
2009:
2008:
2006:
2005:
2000:
1998:Phycobilisomes
1995:
1990:
1985:
1980:
1975:
1970:
1965:
1960:
1958:Cell junctions
1955:
1949:
1947:
1943:
1942:
1940:
1939:
1930:
1921:
1915:
1913:
1907:
1906:
1904:
1903:
1898:
1893:
1888:
1883:
1877:
1875:
1869:
1868:
1862:
1860:
1859:
1852:
1845:
1837:
1828:
1827:
1825:
1824:
1819:
1813:
1811:
1807:
1806:
1804:
1803:
1798:
1793:
1792:
1791:
1786:
1776:
1775:
1774:
1769:
1764:
1754:
1748:
1746:
1745:Other internal
1742:
1741:
1739:
1738:
1733:
1732:
1731:
1726:
1721:
1716:
1711:
1706:
1701:
1696:
1691:
1681:
1675:
1673:
1667:
1666:
1664:
1663:
1662:
1661:
1656:
1646:
1645:
1644:
1639:
1634:
1629:
1619:
1614:
1613:
1612:
1607:
1602:
1597:
1587:
1582:
1577:
1572:
1566:
1564:
1558:
1557:
1555:
1554:
1553:
1552:
1547:
1542:
1537:
1532:
1522:
1521:
1520:
1515:
1510:
1505:
1500:
1495:
1485:
1480:
1475:
1470:
1465:
1460:
1454:
1452:
1444:
1443:
1433:
1431:
1430:
1423:
1416:
1408:
1401:
1400:
1353:
1302:
1255:
1219:
1208:(4): 495–508.
1192:
1163:(4): 439–443.
1143:
1120:
1071:
1012:
961:
935:
886:
879:
854:
827:(12): 128101.
810:
781:(2): 191–196.
761:
720:
683:(2): 141–153.
663:
644:(3): 193–202.
628:
609:(2): 319–335.
593:
541:
480:
478:
475:
474:
473:
467:
461:
455:
441:
437:James Danielli
426:
408:
405:Ernest Overton
396:
393:
359:
356:
338:
335:
326:
323:
317:
314:
303:
300:
278:
275:
265:
262:
258:Mattress Model
247:
244:
242:
239:
171:
168:
165:
164:
161:
158:
154:
153:
150:
147:
143:
142:
139:
136:
135:Carbohydrates
132:
131:
125:
122:
118:
117:
114:
111:
102:
99:
47:cell membranes
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2046:
2035:
2032:
2030:
2027:
2025:
2022:
2021:
2019:
2004:
2001:
1999:
1996:
1994:
1991:
1989:
1986:
1984:
1983:Myelin sheath
1981:
1979:
1976:
1974:
1971:
1969:
1966:
1964:
1961:
1959:
1956:
1954:
1951:
1950:
1948:
1944:
1938:
1934:
1931:
1929:
1925:
1922:
1920:
1917:
1916:
1914:
1912:
1908:
1902:
1899:
1897:
1896:Sphingolipids
1894:
1892:
1889:
1887:
1886:Phospholipids
1884:
1882:
1881:Lipid bilayer
1879:
1878:
1876:
1874:
1870:
1866:
1865:cell membrane
1858:
1853:
1851:
1846:
1844:
1839:
1838:
1835:
1823:
1820:
1818:
1815:
1814:
1812:
1808:
1802:
1799:
1797:
1794:
1790:
1787:
1785:
1782:
1781:
1780:
1777:
1773:
1770:
1768:
1765:
1763:
1760:
1759:
1758:
1755:
1753:
1750:
1749:
1747:
1743:
1737:
1734:
1730:
1727:
1725:
1722:
1720:
1719:Proteinoplast
1717:
1715:
1712:
1710:
1707:
1705:
1702:
1700:
1697:
1695:
1692:
1690:
1687:
1686:
1685:
1682:
1680:
1679:Mitochondrion
1677:
1676:
1674:
1672:
1671:Endosymbionts
1668:
1660:
1657:
1655:
1654:Lamellipodium
1652:
1651:
1650:
1647:
1643:
1640:
1638:
1635:
1633:
1630:
1628:
1625:
1624:
1623:
1620:
1618:
1615:
1611:
1608:
1606:
1603:
1601:
1598:
1596:
1593:
1592:
1591:
1588:
1586:
1583:
1581:
1578:
1576:
1573:
1571:
1570:Microfilament
1568:
1567:
1565:
1563:
1559:
1551:
1548:
1546:
1543:
1541:
1538:
1536:
1533:
1531:
1528:
1527:
1526:
1523:
1519:
1516:
1514:
1511:
1509:
1506:
1504:
1501:
1499:
1496:
1494:
1491:
1490:
1489:
1486:
1484:
1483:Autophagosome
1481:
1479:
1476:
1474:
1471:
1469:
1466:
1464:
1461:
1459:
1458:Cell membrane
1456:
1455:
1453:
1451:
1448:Endomembrane
1445:
1441:
1437:
1429:
1424:
1422:
1417:
1415:
1410:
1409:
1406:
1396:
1392:
1388:
1384:
1380:
1376:
1372:
1368:
1364:
1357:
1354:
1349:
1345:
1340:
1335:
1330:
1325:
1321:
1317:
1313:
1306:
1303:
1298:
1294:
1290:
1289:10.1038/42408
1286:
1282:
1278:
1274:
1270:
1266:
1259:
1256:
1245:on 2018-10-08
1241:
1237:
1230:
1223:
1220:
1215:
1211:
1207:
1203:
1196:
1193:
1188:
1184:
1179:
1174:
1170:
1166:
1162:
1158:
1154:
1147:
1144:
1139:
1135:
1131:
1124:
1121:
1116:
1112:
1107:
1102:
1098:
1094:
1090:
1086:
1082:
1075:
1072:
1067:
1063:
1058:
1053:
1048:
1043:
1039:
1035:
1031:
1027:
1023:
1016:
1013:
1008:
1004:
1000:
996:
992:
988:
984:
980:
976:
972:
965:
962:
950:
949:lipidmaps.org
946:
939:
936:
931:
927:
922:
917:
913:
909:
905:
901:
897:
890:
887:
882:
876:
872:
871:
863:
861:
859:
855:
850:
846:
842:
838:
834:
830:
826:
822:
814:
811:
806:
802:
797:
792:
788:
784:
780:
776:
772:
765:
762:
757:
753:
748:
743:
739:
735:
731:
724:
721:
716:
712:
707:
702:
698:
694:
690:
686:
682:
678:
674:
667:
664:
659:
655:
651:
647:
643:
639:
632:
629:
624:
620:
616:
612:
608:
604:
597:
594:
589:
585:
580:
575:
571:
567:
563:
556:
554:
552:
550:
548:
546:
542:
537:
533:
529:
525:
521:
517:
513:
509:
505:
501:
494:
492:
490:
488:
486:
482:
476:
471:
468:
465:
462:
459:
456:
453:
449:
445:
442:
438:
434:
430:
427:
424:
420:
416:
412:
409:
406:
402:
399:
398:
394:
392:
389:
380:
376:
372:
368:
366:
357:
355:
353:
349:
348:cell adhesion
346:, signaling,
345:
336:
334:
331:
324:
322:
315:
313:
310:
301:
299:
297:
293:
289:
285:
276:
274:
272:
263:
261:
259:
254:
245:
240:
238:
236:
232:
226:
224:
220:
216:
207:
203:
201:
200:thermodynamic
196:
192:
187:
185:
181:
178:experiments,
177:
169:
162:
159:
156:
155:
151:
148:
145:
144:
140:
137:
134:
133:
130:
126:
123:
121:Phospholipid
120:
119:
115:
112:
109:
108:
100:
98:
95:
91:
87:
83:
82:carbohydrates
79:
75:
71:
67:
64:
60:
56:
55:lipid bilayer
53:, there is a
52:
48:
44:
37:
36:cell membrane
32:
19:
2034:Cell anatomy
1891:Lipoproteins
1699:Gerontoplast
1649:Pseudopodium
1642:Radial spoke
1622:Undulipodium
1562:Cytoskeleton
1478:Parenthesome
1370:
1366:
1356:
1319:
1315:
1305:
1272:
1268:
1258:
1247:. Retrieved
1240:the original
1235:
1222:
1205:
1201:
1195:
1160:
1156:
1146:
1137:
1133:
1123:
1088:
1085:EMBO Reports
1084:
1074:
1029:
1025:
1015:
974:
970:
964:
954:14 September
952:. Retrieved
948:
938:
906:(1): 35–47.
903:
899:
889:
869:
824:
820:
813:
778:
774:
764:
737:
733:
723:
680:
676:
666:
641:
637:
631:
606:
602:
596:
569:
565:
503:
499:
469:
463:
457:
451:
443:
428:
422:
415:Evert Gorter
410:
400:
386:
379:S.cerevisiae
378:
369:
361:
340:
328:
319:
305:
280:
271:gap junction
267:
249:
229:advances in
227:
219:heterokaryon
215:Sendai virus
212:
188:
173:
146:Cholesterol
128:
42:
40:
1801:Magnetosome
1767:Spliceosome
1694:Chromoplast
1689:Chloroplast
1580:Microtubule
1316:BMC Biology
433:Hugh Davson
330:Lipid rafts
325:Lipid rafts
294:formation,
284:BAR domains
253:Cholesterol
110:Components
59:amphipathic
2029:Organelles
2018:Categories
1963:Glycocalyx
1796:Proteasome
1789:Inclusions
1736:Nitroplast
1729:Apicoplast
1714:Elaioplast
1709:Amyloplast
1704:Leucoplast
1659:Filopodium
1605:Basal body
1595:Centrosome
1545:Peroxisome
1540:Glyoxysome
1530:Melanosome
1440:organelles
1249:2014-12-05
1140:: 159–201.
116:Functions
74:elasticity
2003:Porosomes
1817:Cell wall
1779:Cytoplasm
1752:Nucleolus
1724:Tannosome
1632:Flagellum
1617:Myofibril
1600:Centriole
1535:Microbody
1508:Phagosome
1322:(1): 46.
352:migration
309:bacterial
296:organelle
184:viscosity
157:Proteins
113:Location
66:molecules
1810:External
1762:Ribosome
1518:Acrosome
1503:Endosome
1498:Lysosome
1395:22116853
1348:38414038
1339:10898092
1187:19868999
1115:21997296
1066:12832616
1007:35095032
999:20044567
930:25284293
849:19392326
805:19379681
756:15519321
658:16271405
588:24189436
536:83851531
221:. Using
193:and the
176:labeling
78:membrane
70:fluidity
1901:Sterols
1784:Cytosol
1684:Plastid
1637:Axoneme
1513:Vacuole
1493:Exosome
1488:Vesicle
1463:Nucleus
1375:Bibcode
1367:Science
1297:9177342
1277:Bibcode
1178:2130960
1106:3207108
1034:Bibcode
979:Bibcode
971:Science
921:4275391
900:Traffic
829:Bibcode
796:4832598
715:6478029
706:1435039
685:Bibcode
623:4098863
528:4333397
508:Bibcode
500:Science
388:Septins
381:septins
292:vesicle
76:to the
63:protein
1627:Cilium
1450:system
1393:
1346:
1336:
1295:
1269:Nature
1185:
1175:
1113:
1103:
1064:
1057:166180
1054:
1005:
997:
928:
918:
877:
847:
803:
793:
754:
713:
703:
656:
621:
586:
534:
526:
350:, and
1946:Other
1772:Vault
1243:(PDF)
1232:(PDF)
1003:S2CID
532:S2CID
1436:cell
1391:PMID
1344:PMID
1293:PMID
1183:PMID
1111:PMID
1062:PMID
995:PMID
956:2024
926:PMID
875:ISBN
845:PMID
801:PMID
775:Cell
752:PMID
738:1666
711:PMID
654:PMID
642:1746
619:PMID
584:PMID
570:1838
524:PMID
470:2024
464:1997
458:1972
452:i.e.
444:1957
435:and
429:1935
423:i.e.
417:and
411:1925
401:1895
233:and
88:and
72:and
41:The
1757:RNA
1383:doi
1371:334
1334:PMC
1324:doi
1285:doi
1273:387
1210:doi
1173:PMC
1165:doi
1101:PMC
1093:doi
1052:PMC
1042:doi
1030:100
987:doi
975:327
916:PMC
908:doi
837:doi
825:102
791:PMC
783:doi
779:137
742:doi
701:PMC
693:doi
646:doi
611:doi
574:doi
516:doi
504:175
440:it.
2020::
1438:/
1389:.
1381:.
1369:.
1365:.
1342:.
1332:.
1320:22
1318:.
1314:.
1291:.
1283:.
1271:.
1267:.
1234:.
1204:.
1181:.
1171:.
1161:41
1159:.
1155:.
1138:40
1136:.
1132:.
1109:.
1099:.
1089:12
1087:.
1083:.
1060:.
1050:.
1040:.
1028:.
1024:.
1001:.
993:.
985:.
973:.
947:.
924:.
914:.
904:16
902:.
898:.
857:^
843:.
835:.
823:.
799:.
789:.
777:.
773:.
750:.
736:.
732:.
709:.
699:.
691:.
681:46
679:.
675:.
652:.
640:.
617:.
605:.
582:.
568:.
564:.
544:^
530:.
522:.
514:.
502:.
484:^
446:–
431:–
413:–
403:–
354:.
273:.
1935:/
1926:/
1856:e
1849:t
1842:v
1427:e
1420:t
1413:v
1397:.
1385::
1377::
1350:.
1326::
1299:.
1287::
1279::
1252:.
1216:.
1212::
1206:5
1189:.
1167::
1117:.
1095::
1068:.
1044::
1036::
1009:.
989::
981::
958:.
932:.
910::
883:.
851:.
839::
831::
807:.
785::
758:.
744::
717:.
695::
687::
660:.
648::
625:.
613::
607:7
590:.
576::
538:.
518::
510::
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.