339:
199:
372:
64:
364:
207:
48:
380:
71:
293:. Den Helder and the base would be protected by a string of fortifications, costing 6 million Francs. Soon the construction of Fort Kijkduin and Fort Erfprins started, and Erfprins was connected to the Kaaphoofd battery. Somewhat later, the construction of Fort Dirksz Admiraal began, and het Nieuwe Werk was changed to a fortress.
198:
491:
Post World War II, fortifications like those of Den Helder were completely obsolete. It meant that they were disarmed, but that did not mean that the buildings were immediately abandoned. While the army retreated from the fortresses, the Dutch navy expanded and could use some buildings. In 1950 the
478:
the Dutch government severely economized on defense spending. Some new light caliber guns were put into service in the area, but with regard to big guns, nothing was done. In about 1930, the big guns of Fort
Harssens were decommissioned. Just before World War II the fortifications and their guns no
395:
For Den Helder, the commission proposed to build four brick towers at: One at the shoal De Laan, One at De Hors, one at
Harssens (at the end of the east dam of Nieuwediep) and one at the Zuidwal (the shoal stretching from the east dam of the Nieuwediep towards the east). These were to be armed each
391:
showed the power and near impregnability of armored ships. It sparked a wide interest in updating coastal defences. On 3 June 1864, a new commission for coastal defense was appointed. It opted for the principle that harbors and roadsteads would be defended by fixed fortifications. These would be
253:
visited the north of
Holland and Texel and Nieuwediep. By then there were about a dozen warships in the harbor. Napoleon wanted to fortify the place, and transfer the Amsterdam navy base to Den Helder. The finances were the only problem. Indeed, King Louis regularly talked about the subject with
470:
During World War I the
Fortifications of Den Helder were manned by the mobilized Dutch army. By then, the fortresses and their heavy artillery might still have seemed impressive. In reality most of it was already obsolete in 1906. By then, guns like 24 cm ijzer and the 24 cm L/25 were
237:
called 'Het Nieuwe Werk'. On the north side there was an old field fortification near the coast. There were 61 24-pdr guns and 22 lighter guns. However, these elements did not form a cohesive defensive position and so the two battalions were ordered to retreat. Without a possibility to use the
482:
During World War II, the German army garrisoned the
Fortifications of Den Helder. For Germany the base was important for the small craft of its navy and to protect coastal shipping. The Germans built a number of bunkers and anti-aircraft emplacements to protect their position.
500:
would lead to less work for the Dutch military, which the municipality tried to compensate by developing tourism. In 1992 the foundation became the owner of the fortress and in 1993 it got a subsidy of 7.2 million guilders to restore the fort. Fort
Westoever would be next.
174:. During the nineteenth century the fortifications were improved and expanded. During World War II, the fortifications were garrisoned by the German army. Post war, the fortifications were decommissioned between 1951 and 1957. They are now getting re-developed for tourism.
448:
Apart from building Fort
Harssens there were also some other modernizations. Between 1875 and 1878 Fort Erfprins was modernized. It got an underground barracks for about 1,000 men, protected against grenade fire. Erfprins also got emplacements for 24 cm guns.
495:
In 1989 the foundaton "Stichting
Stelling Den Helder" was founded. It aimed to preserve the fortifications of Den Helder. The first activities were guided tours at Fort Kijkduin, which also aimed to raise public awareness of the fortress. The end of the
195:, as a canal and deep harbor. The harbor was important for the republic's navy as well as its commercial ships. However, further development was barred by the cities on the Zuiderzee fearing that their commerce might move to Nieuwediep.
420:
muzzle loader, the army looked to France and
Germany. In 1870 the Dutch army got the 24 cm ijzer, an iron rifled breech loader based on a French model. Other guns that showed up in Den Helder were the 24 cm L/25 and the
399:
In 1870 the fortress law asked for money for a fort on the
Zuidwal. A decision that was described as grabbing something from the plan. However, the decision was overturned when the next minister opted for the fortress on De Laan.
392:
supported by supported by shallow draught armored vessels like rams and monitors. The commission clearly advised to buy some of the new heavy guns that were in use or development abroad. These were to be placed on turntables.
396:
with 8-12 heavy guns in armored iron cupolas. The commission also advised to re-arm some of the existing works with heavy caliber guns. Most of these should be able to penetrate armor at a distance of 2,000 m.
461:
gun. This was a modern powerful gun. However, critics warned that doing the minimum of what was required, would lead to a quick obsolescence of the fortress. Due to World War I, the plan was not executed.
273:
behind the Kaaphoofd battery; another such tower at the southern end of Den Helder village; one more tower on the Sluisdijk; changing the Nieuwe Werk to a fortress; Building a fortress on top of the
338:
350:
navy base, not much seems to have happened at the Fortifications of Den Helder during these years. Het Nieuwe Werk was changed to become Fort Oostoever. In 1825 Fort Westoever was built.
441:. That same year construction began. While there were some doubts about the plan it was deemed to be realistic and effective. With its two armored cupolas with two Krupp
297:
492:
army transferred Fort Erfprins to the navy to use as a training facility. It also transferred other facilities. For some time it held on to Fort Dirks Admiraal.
94:
346:
In February 1818, a commission was appointed to investigate the defense of Den Helder and the Naval base Willemsoord. While these were busy years for the
1065:
63:
434:
330:
declared Den Helder to be in a state of siege. Though not much was done in terms of besieging Den Helder, the siege lasted till 21 April 1814.
233:
After the defeat, Den Helder, or rather the harbor of Nieuwediep, was defended by two battalions. On its southern side Nieuwediep had an earth
471:
completely useless against modern battleships. The only guns that were still dangerous to enemy capital ships were those of Fort Harssens.
289:
visited Den Helder and Texel. He decided to create a base for building, repairing and equipping warships near Den Helder, which became
215:
457:
Just before World War I, the Dutch government decided to modernize Fort Kijkduin. It was planned to get armored cupolas with the
1070:
156:
in the Netherlands from the end of the 18th century till the end of World War II. They are now getting repurposed for tourism.
903:"Rapport der Gecommitteerden tot het maaken van een haven voor 's lands scheepen van oorlog in het Nieuwe Diep bij Den Helder"
1018:
168:
was an important harbor. Starting in 1810, it was fortified, creating the Fortifications of Den Helder known in Dutch as
371:
219:
300:, the naval base of Den Helder was held by the French side. By then, the Fortifications of Den Helder consisted of:
191:
became ever shallower while ships became bigger. At the end of the 18th century, this led to the development of the
238:
coastal batteries to prevent the British fleet from appearing before Nieuwediep, the Dutch fleet retreated to the
417:
347:
388:
327:
290:
270:
523:
543:
227:
409:
976:
538:
533:
1075:
964:
889:
518:
513:
255:
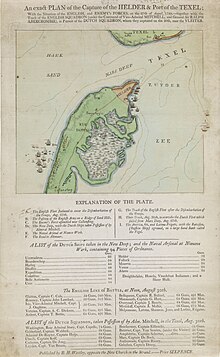
242:. Cut off from its base, the Dutch fleet surrendered on 30 August 1799 in what became known as the
548:
363:
266:
192:
165:
206:
952:
458:
509:
These are some parts of the Fortifications of Den Helder that are still more or less intact.
239:
1031:
442:
243:
1032:"Wijziging der wet van 21 januari 1879 ... Voltooiing van het Vestingstelsel, Dienst 1879"
942:
475:
408:
The advancements in armor led to a speedy development of more powerful guns. This was the
250:
47:
929:
445:
each, Fort Harssens was something very different from the existing 19th century forts.
1059:
528:
438:
422:
413:
269:, and allow mortars to cover the approaches to Nieuwediep; A brick fortress tower,
258:, then director of fortifications in the department where Den Helder was located.
1044:
1009:
998:
989:
919:
902:
223:
38:
379:
153:
34:
109:
96:
1045:"Geschiedkundige gedenkstukken en aanmerkingen over het bestuur van Holland"
991:
Geschiedkundige beschouwing van den oorlog op het grondgebied der Bataafsche
188:
1011:
Geschiedkundige gedenkstukken en aanmerkingen over het bestuur van Holland
921:
Neerlands heldendaden te land: van de vroegste tijden af tot op onze dagen
1051:. Koninklijke Vereniging ter Beoefening van de Krijgswetenschap: 495–567.
497:
286:
234:
875:
378:
370:
362:
337:
274:
205:
197:
930:"Instelling van een fonds ter verbetering van de kustverdediging"
907:
Resolutien van de Heeren Staten van Hollandt Ende Westvrieslandt
262:
944:
Geschiedenis onzer Zeemacht tijdens de Fransche Overheersching
261:
Kraijenhoff came with a plan to build: A fort at the Kijkduin
1049:
Orgaan der Vereniging Ter Beoefening van de Krijgswetenschap
613:
611:
152:
form a circle of fortresses and other works that defended
1020:
Rapport der Commissie tot het herzien der kustverdediging
226:, just south of Den Helder on 27 August. This became the
296:
During the revolt which led to the establishment of the
652:
650:
319:
Battery La Révolution or l'Imperiale, later Kaap Hoofd
187:
During the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, the
566:
70:
164:By the late 18th century, Den Helder or better the
138:
130:
125:
88:
18:
988:Kraijenhoff, Cornelis Rudolphus Theodorus (1832),
479:longer posed a serious threat to enemy warships.
416:. While the Dutch navy first standardized on the
383:Emplacement for a 24 cm gun at Fort Erfprins
277:De Laan. The estimated cost was about 2,000,000.
298:Sovereign Principality of the United Netherlands
977:"Opleiding kanonniers voor handelsbescherming"
848:
322:Battery l'Indivisibilité, later Oost-Batterij
8:
890:"Straks gezellig dagje uit in Fort Kijkduin"
680:
641:
617:
169:
824:
15:
965:"Geheimzinnig fort vervult jongensdromen"
788:
776:
437:took the lead and secured money to build
860:
836:
602:
953:"Fort Kijkduin volop in belangstelling"
901:Van Boetzelaer, D.; Ouwens, P. (1785),
888:Abcouwer, Caroline (23 November 1993).
740:
728:
716:
704:
692:
590:
578:
559:
668:
656:
629:
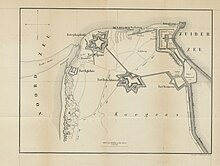
52:The Den Helder Fortifications in 1869.
812:
800:
764:
304:Fort La Salle, later renamed Erfprins
7:
752:
334:The time of wooden ships (1815-1862)
310:Fort L'Ecluse, later Dirksz Admiraal
281:Construction of the fortifications
14:
1066:Fortifications in the Netherlands
313:Fort Du Gonnier, later Oost-Oever
222:. It started with a landing near
216:Anglo-Russian invasion of Holland
567:Van Boetzelaer & Ouwens 1785
69:
62:
46:
505:Elements of Stelling Den Helder
326:On 16 November 1813 commander
1:
951:Hoogland, Wim (8 July 1989).
876:Stichting Stelling Den Helder
1038:. Militaire spectator. 1879.
307:Fort Morland, later Kijkduin
150:Fortifications of Den Helder
77:Fortifications of Den Helder
19:Fortifications of Den Helder
1008:Napoleon, Lodewijk (1820),
220:War of the Second Coalition
1092:
918:Bosscha, Johannes (1873),
354:Armor and modern artillery
57:
45:
32:
23:
433:In 1879 Minister of War
230:, which the Dutch lost.
487:Disarmament and tourism
453:1913 plans for Kijkduin
389:Battle of Hampton Roads
328:Carel Hendrik Ver Huell
291:Willemsoord, Den Helder
265:, this would cover the
1071:Coastal fortifications
1043:Evers, F.J.H. (1906).
384:
376:
368:
343:
211:
203:
202:Anglo-Russian invasion
170:
110:52.958353°N 4.757987°E
382:
374:
366:
341:
316:The work on the Falga
228:Battle of Callantsoog
209:
201:
983:. 20 September 1950.
410:rifled breech loader
1036:Militaire spectator
941:Herman, H. (1923),
524:Fort Dirks Admiraal
435:Den Beer Poortugael
256:Cornelis Krayenhoff
171:Stelling Den Helder
115:52.958353; 4.757987
106: /
26:Stelling Den Helder
849:Jongensdromen 1990
544:Batterij Kaaphoofd
429:1886 Fort Harssens
385:
377:
369:
344:
218:was a part of the
212:
210:Den Helder in 1799
204:
981:Bredasche courant
924:, vol. III-1
459:28 cm SK L/45 gun
412:constructed as a
183:Lessons and plans
146:
145:
1083:
1052:
1039:
1027:
1025:
1014:
1004:
1000:Laan of Zuidwal?
994:
984:
972:
971:. 6 August 1990.
960:
947:
937:
936:: 295–307. 1913.
925:
914:
897:
864:
858:
852:
846:
840:
834:
828:
822:
816:
810:
804:
798:
792:
786:
780:
774:
768:
762:
756:
750:
744:
738:
732:
726:
720:
714:
708:
702:
696:
690:
684:
681:Kraijenhoff 1832
678:
672:
666:
660:
654:
645:
642:Kraijenhoff 1832
639:
633:
627:
621:
618:Kraijenhoff 1832
615:
606:
600:
594:
588:
582:
576:
570:
569:, p. 20-40.
564:
443:30.5 cm MRK L/25
418:9-inch Armstrong
404:Modern artillery
367:Harssens in 1925
285:In October 1811
244:Vlieter incident
173:
121:
120:
118:
117:
116:
111:
107:
104:
103:
102:
99:
73:
72:
66:
50:
41:
16:
1091:
1090:
1086:
1085:
1084:
1082:
1081:
1080:
1056:
1055:
1042:
1030:
1023:
1017:
1007:
997:
987:
975:
963:
950:
940:
928:
917:
900:
887:
884:
872:
867:
859:
855:
847:
843:
835:
831:
825:Kanonniers 1950
823:
819:
811:
807:
799:
795:
787:
783:
775:
771:
763:
759:
751:
747:
739:
735:
727:
723:
715:
711:
703:
699:
691:
687:
679:
675:
667:
663:
655:
648:
640:
636:
628:
624:
616:
609:
601:
597:
589:
585:
577:
573:
565:
561:
557:
507:
489:
476:Interwar period
468:
455:
431:
406:
361:
356:
336:
283:
251:Louis Bonaparte
185:
180:
162:
114:
112:
108:
105:
100:
97:
95:
93:
92:
84:
83:
82:
81:
80:
79:
78:
74:
53:
33:
28:
12:
11:
5:
1089:
1087:
1079:
1078:
1073:
1068:
1058:
1057:
1054:
1053:
1040:
1028:
1015:
1005:
995:
985:
973:
961:
948:
938:
926:
915:
898:
883:
880:
879:
878:
871:
870:External links
868:
866:
865:
853:
841:
829:
817:
815:, p. 516.
805:
803:, p. 301.
793:
791:, p. 137.
789:Wijziging 1879
781:
777:Wijziging 1879
769:
767:, p. 517.
757:
745:
743:, p. 341.
733:
731:, p. 339.
721:
719:, p. 338.
709:
707:, p. 337.
697:
695:, p. 335.
685:
683:, p. 319.
673:
671:, p. 116.
661:
646:
644:, p. 317.
634:
622:
620:, p. 315.
607:
595:
593:, p. 120.
583:
581:, p. 114.
571:
558:
556:
553:
552:
551:
546:
541:
539:Fort Oostoever
536:
534:Fort Westoever
531:
526:
521:
516:
506:
503:
488:
485:
467:
466:The World Wars
464:
454:
451:
430:
427:
405:
402:
360:
357:
355:
352:
335:
332:
324:
323:
320:
317:
314:
311:
308:
305:
282:
279:
184:
181:
179:
176:
161:
158:
144:
143:
140:
136:
135:
132:
128:
127:
123:
122:
90:
86:
85:
76:
75:
68:
67:
61:
60:
59:
58:
55:
54:
51:
43:
42:
30:
29:
24:
21:
20:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1088:
1077:
1074:
1072:
1069:
1067:
1064:
1063:
1061:
1050:
1046:
1041:
1037:
1033:
1029:
1022:
1021:
1016:
1013:
1012:
1006:
1002:
1001:
996:
993:
992:
986:
982:
978:
974:
970:
969:De Volkskrant
966:
962:
958:
954:
949:
946:
945:
939:
935:
931:
927:
923:
922:
916:
912:
908:
904:
899:
895:
891:
886:
885:
881:
877:
874:
873:
869:
862:
861:Abcouwer 1993
857:
854:
850:
845:
842:
838:
837:Hoogland 1989
833:
830:
826:
821:
818:
814:
809:
806:
802:
797:
794:
790:
785:
782:
779:, p. 38.
778:
773:
770:
766:
761:
758:
754:
749:
746:
742:
737:
734:
730:
725:
722:
718:
713:
710:
706:
701:
698:
694:
689:
686:
682:
677:
674:
670:
665:
662:
659:, p. 97.
658:
653:
651:
647:
643:
638:
635:
632:, p. 73.
631:
626:
623:
619:
614:
612:
608:
605:, p. 88.
604:
603:Napoleon 1820
599:
596:
592:
587:
584:
580:
575:
572:
568:
563:
560:
554:
550:
547:
545:
542:
540:
537:
535:
532:
530:
529:Fort Harssens
527:
525:
522:
520:
519:Fort Erfprins
517:
515:
514:Fort Kijkduin
512:
511:
510:
504:
502:
499:
493:
486:
484:
480:
477:
472:
465:
463:
460:
452:
450:
446:
444:
440:
439:Fort Harssens
436:
428:
426:
424:
419:
415:
411:
403:
401:
397:
393:
390:
381:
375:A 24 cm ijzer
373:
365:
359:Armored ships
358:
353:
351:
349:
340:
333:
331:
329:
321:
318:
315:
312:
309:
306:
303:
302:
301:
299:
294:
292:
288:
280:
278:
276:
272:
268:
264:
259:
257:
252:
249:In 1807 king
247:
245:
241:
236:
231:
229:
225:
221:
217:
208:
200:
196:
194:
190:
182:
177:
175:
172:
167:
159:
157:
155:
151:
141:
137:
133:
129:
124:
119:
91:
87:
65:
56:
49:
44:
40:
36:
31:
27:
22:
17:
1048:
1035:
1019:
1010:
999:
990:
980:
968:
957:De Telegraaf
956:
943:
933:
920:
910:
906:
893:
856:
844:
832:
820:
808:
796:
784:
772:
760:
755:, p. 5.
748:
741:Rapport 1864
736:
729:Rapport 1864
724:
717:Rapport 1864
712:
705:Rapport 1864
700:
693:Rapport 1864
688:
676:
664:
637:
625:
598:
591:Bosscha 1873
586:
579:Bosscha 1873
574:
562:
549:Oostbatterij
508:
494:
490:
481:
473:
469:
456:
447:
432:
423:24 cm K L/35
414:built-up gun
407:
398:
394:
386:
345:
325:
295:
284:
260:
248:
232:
213:
186:
163:
160:Introduction
149:
147:
126:Site history
25:
669:Herman 1923
657:Herman 1923
630:Herman 1923
474:During the
348:Willemsoord
271:tour-modèle
267:Schulpengat
224:Callantsoog
178:Early years
134:1600 - 1945
113: /
89:Coordinates
39:Netherlands
1076:Den Helder
1060:Categories
934:Marineblad
894:Het Parool
882:References
813:Evers 1906
801:Fonds 1913
765:Evers 1906
193:Nieuwediep
166:Nieuwediep
154:Den Helder
139:Demolished
98:52°57′30″N
35:Den Helder
753:Laan 1874
387:The 1862
214:The 1799
189:Zuiderzee
142:From 1951
101:4°45′29″E
498:Cold War
287:Napoleon
37:in
913:: 20–40
342:In 1847
240:Vlieter
235:redoubt
1026:, 1864
1003:, 1874
1024:(PDF)
555:Notes
275:shoal
131:Built
263:dune
148:The
911:180
1062::
1047:.
1034:.
979:.
967:.
955:.
932:.
909:,
905:,
892:.
649:^
610:^
425:.
246:.
959:.
896:.
863:.
851:.
839:.
827:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.