216:
236:
31:
401:
strategy for the detection of DNA copy-number changes on a genome-wide scale. The resolution of detection could be as high as >30,000 "bands" and the size of chromosomal deletion detected could as small as 5–20 kb in length. Other computation methods were selected to discover DNA sequencing deletion errors such as
400:
The introduction of molecular techniques in conjunction with classical cytogenetic methods has in recent years greatly improved the diagnostic potential for chromosomal abnormalities. In particular, microarray-comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) based on the use of BAC clones promises a sensitive
361:
Microdeletions are associated with many different conditions, including
Angelman Syndrome, Prader-Willi Syndrome, and DiGeorge Syndrome. Some syndromes, including Angelman syndrome and Prader-Willi syndrome, are associated with both microdeletions and genomic imprinting, meaning that same
443:. Loss of these proteins decreases the rate of spontaneous DNA deletion events in mitochondria. This finding implies that the repair of DNA double-strand breaks by homologous recombination is a step in the formation of mitochondrial DNA deletions.
365:
Recent work suggests that some deletions of highly conserved sequences (CONDELs) may be responsible for the evolutionary differences present among closely related species. Such deletions in humans, referred to as
1213:
Ivanetich, K. M.; Lucas, S.; Marsh, J. A.; Ziman, M. R.; Katz, I. D.; Bradshaw, J. J. (1978). "Organic compounds. Their interaction with and degradation of hepatic microsomal drug-metabolizing enzymes in vitro".
299:
Small deletions are less likely to be fatal; large deletions are usually fatal – there are always variations based on which genes are lost. Some medium-sized deletions lead to recognizable human disorders, e.g.
287:, which includes band names, symbols and abbreviated terms used in the description of human chromosome and chromosome abnormalities. Abbreviations include a minus sign (−) for chromosome deletions, and
1493:
1151:
Volik, S.; Zhao, S.; Chin, K.; Brebner, J. H.; Herndon, D. R.; Tao, Q.; Kowbel, D.; Huang, G.; Lapuk, A.; Kuo, W.-L.; Magrane, G.; de Jong, P.; Gray, J. W.; Collins, C. (4 June 2003).
101:
to occur between a chromosome with a large intercalary deficiency and a normal complete homolog, the unpaired region of the normal homolog must loop out of the linear structure into a
277:
1451:
759:
577:
938:
McLean CY, Reno PL, Pollen AA, Bassan AI, Capellini TD, Guenther C, Indjeian VB, Lim X, Menke DB, Schaar BT, Wenger AM, Bejerano G, Kingsley DM (March 2011).
2264:
2020:
207:
Micro-deletion is usually found in children with physical abnormalities. A large amount of deletion would result in immediate abortion (miscarriage).
1444:
860:
831:
553:
2133:
243:
with annotated bands and sub-bands as used for the nomenclature of chromosome abnormalities. It shows dark and white regions as seen on
1437:
1259:
805:
526:
2123:
626:
Banavali, Nilesh K. (2013). "Analyzing the
Relationship between Single Base Flipping and Strand Slippage near DNA Duplex Termini".
215:
1706:
436:
2105:
2048:
1638:
2099:
2038:
1976:
1593:
1096:
482:
94:
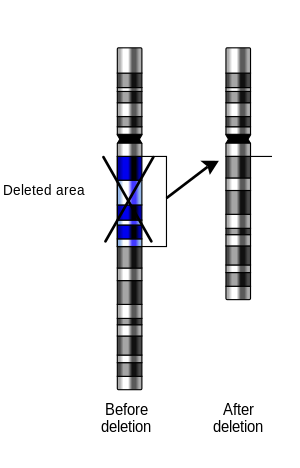
breaks, if a part of it is deleted or lost, the missing piece of chromosome is referred to as a deletion or a deficiency.
1622:
663:"Cytosine Unstacking and Strand Slippage at an Insertion–Deletion Mutation Sequence in an Overhang-Containing DNA Duplex"
2042:
2034:
1990:
1682:
1557:
1535:
263:
2233:
2221:
1601:
1488:
335:
1678:
1674:
1980:
1418:
1743:
1048:"BAC-based PCR fragment microarray: high-resolution detection of chromosomal deletion and duplication breakpoints"
90:
of a part of the chromosome. The breaks can be induced by heat, viruses, radiation, or chemical reactions. When a
2147:
2109:
1908:
1368:
467:
156:
1597:
591:
Banavali, Nilesh K. (2013). "Partial Base
Flipping is Sufficient for Strand Slippage near DNA Duplex Termini".
457:
415:
235:
2163:
2155:
2141:
2127:
2085:
2006:
1718:
1413:
997:"Comprehensive patient-level classification and quantification of driver events in TCGA PanCanAtlas cohorts"
779:
385:
355:
135:
by changing the 3-nucleotide protein reading frame of the genetic sequence. Deletions are representative of
765:- "This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (
1609:
1460:
1252:
477:
402:
316:
848:
2237:
1373:
1337:
1300:
753:
389:
351:
252:
170:
165:
161:
120:
2217:
2213:
822:
Mitchell, Richard
Sheppard; Kumar, Vinay; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson (2007).
116:
in the template DNA, followed by template DNA strand slippage, within the DNA polymerase active site.
1964:
1889:
1828:
1634:
1282:
1164:
951:
487:
388:
cohorts revealed that there are on average 12 driver events per tumor, of which 2.1 are deletions of
2137:
1950:
1347:
995:
Vyatkin, Alexey D.; Otnyukov, Danila V.; Leonov, Sergey V.; Belikov, Aleksey V. (14 January 2022).
548:. Michael R. Cummings, Charlotte A. Spencer, Michael Angelo Palladino (Eleventh ed.). Boston.
308:
132:
362:
microdeletion can cause two different syndromes depending on which parent the deletion came from.
30:
2241:
2229:
2225:
2189:
2184:
2119:
1733:
1513:
1119:
1077:
571:
435:
encode proteins that are necessary for recombinational repair and are employed in the repair of
853:
Rosenberg's
Molecular and Genetic Basis of Neurological and Psychiatric Disease (Fifth Edition)
2269:
2203:
1820:
1739:
1694:
1662:
1650:
1332:
1327:
1245:
1223:
1192:
1069:
1028:
977:
920:
902:
856:
827:
741:
692:
643:
608:
559:
549:
522:
440:
371:
301:
113:
2198:
2194:
2091:
1968:
1936:
1567:
1403:
1352:
1182:
1172:
1111:
1059:
1018:
1008:
967:
959:
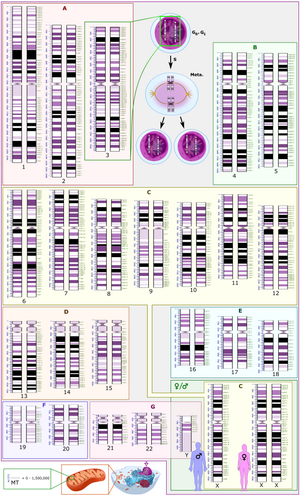
910:
894:
847:
Srour, Myriam; Shevell, Michael (2015-01-01), Rosenberg, Roger N.; Pascual, Juan M. (eds.),
731:
723:
682:
674:
635:
600:
472:
281:
802:
2208:
1797:
1342:
809:
339:
330:
Deletions are responsible for an array of genetic disorders, including some cases of male
128:
384:
Recent comprehensive patient-level classification and quantification of driver events in
1168:
955:
231:
an arbitrary karyotype that involves a variety of autosomal and allosomal abnormalities.
1882:
1848:
1843:
1518:
1319:
1023:
996:
972:
939:
915:
882:
736:
711:
687:
662:
492:
259:
59:
1187:
1152:
2258:
2077:
1877:
1838:
1833:
1761:
1747:
1723:
1711:
1699:
1687:
1667:
1572:
1550:
1545:
1523:
203:– a relatively small amount of deletion (up to 5Mb that could include a dozen genes).
1081:
727:
219:
Three chromosomal abnormalities with ISCN nomenclature, with increasing complexity:
1872:
1779:
1775:
1655:
1643:
1627:
1615:
1605:
1508:
1295:
1123:
370:, may be responsible for the anatomical and behavioral differences between humans,
307:
Deletion of a number of pairs that is not evenly divisible by three will lead to a
284:
940:"Human-specific loss of regulatory DNA and the evolution of human-specific traits"
1013:
1894:
1865:
1860:
1757:
1097:"Using a VOM Model for Reconstructing Potential Coding Regions in EST Sequences"
462:
347:
331:
140:
75:
17:
1127:
2014:
2010:
1816:
1562:
1540:
1530:
1115:
898:
766:
248:
136:
91:
83:
79:
67:
906:
563:
1855:
1811:
1503:
1498:
1177:
269:
255:
244:
240:
1429:
1196:
1073:
1032:
981:
924:
745:
696:
647:
612:
543:
1971:
1921:
1917:
1789:
1468:
1408:
1398:
1393:
1268:
367:
343:
323:. In contrast, a deletion that is evenly divisible by three is called an
258:
chromosome pairs, both the female (XX) and male (XY) versions of the two
98:
63:
39:
1227:
963:
2024:
1807:
1480:
1064:
1047:
320:
124:
678:
639:
604:
131:. Deletions that do not occur in multiples of three bases can cause a
1153:"End-sequence profiling: Sequence-based analysis of aberrant genomes"
849:"Chapter 14 - Global Developmental Delay and Intellectual Disability"
379:
712:"A fully computational and reasonable representation for karyotypes"
2113:
2052:
2028:
1958:
452:
427:
421:
312:
29:
1216:
Drug
Metabolism and Disposition: The Biological Fate of Chemicals
2159:
2151:
2095:
2081:
2056:
1984:
1954:
1944:
661:
Manjari, Swati R.; Pata, Janice D.; Banavali, Nilesh K. (2014).
346:). Deletion of part of the short arm of chromosome 5 results in
227:
Prader–Willi
Syndrome i.e. deletion in the 15q11-q12 region and
1433:
1241:
1940:
375:
112:
The smallest single base deletion mutations occur by a single
71:
883:"Prader-Willi, Angelman, and 15q11-q13 duplication syndromes"
319:, producing a severely altered and potentially nonfunctional
223:
A tumour karyotype in a male with loss of the Y chromosome,
1237:
315:
occurring after the deletion to be read incorrectly during
197:– a deletion that occurs from the interior of a chromosome.
86:
have fragile spots where breaks occur, which result in the
881:
Kalsner, Louisa; Chamberlain, Stormy J. (April 22, 2015).
812:
at The GEN2PHEN Knowledge Centre. Posted Fri, 08/01/2010.
191:– a deletion that occurs towards the end of a chromosome.
278:
International System for Human
Cytogenomic Nomenclature
2177:
2070:
1999:
1929:
1916:
1907:
1806:
1788:
1774:
1583:
1476:
1467:
1386:
1361:
1318:
1311:
1275:
74:is left out during DNA replication. Any number of
358:, the most common genetic cause of infant death.
1157:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
27:Mutation that removes a part of a DNA sequence
2199:46,XX testicular disorders of sex development
1445:
1253:
8:
1208:
1206:
855:, Boston: Academic Press, pp. 151–161,
758:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
66:(a genetic aberration) in which a part of a
2021:Acute myeloblastic leukemia with maturation
767:http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
1926:
1913:
1785:
1473:
1452:
1438:
1430:
1315:
1260:
1246:
1238:
576:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
1186:
1176:
1063:
1022:
1012:
971:
914:
735:
710:Warrender JD, Moorman AV, Lord P (2019).
686:
519:Human Genetics: Concepts and Applications
184:Types of deletion include the following:
1387:Mutation with respect to overall fitness
593:Journal of the American Chemical Society
291:for deletions of parts of a chromosome.
280:(ISCN) is an international standard for
234:
214:
512:
510:
508:
504:
139:organisms, including humans and not in
82:to an entire piece of chromosome. Some
784:Coriell Institute for Medical Research
751:
569:
119:Deletions can be caused by errors in
7:
1095:Shmilovici, A.; Ben-Gal, I. (2007).
780:"ISCN Symbols and Abbreviated Terms"
374:and other varieties of mammals like
247:. Each row is vertically aligned at
2265:Modification of genetic information
2134:Desmoplastic small-round-cell tumor
1104:Journal of Computational Statistics
628:The Journal of Physical Chemistry B
1312:Mutation with respect to structure
887:Pediatric Clinics of North America
803:LSDB — Controlled vocabulary terms
25:
195:Intercalary/interstitial deletion
1707:22q11.2 distal deletion syndrome
2106:Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
2049:Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia
1977:Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma
1639:Chromosome 5q deletion syndrome
127:, which causes several serious
151:Causes include the following:
78:can be deleted, from a single
1:
1829:Klinefelter syndrome (47,XXY)
1594:1q21.1 copy number variations
728:10.1093/bioinformatics/btz440
521:(6th ed.). McGraw Hill.
483:Chromosomal deletion syndrome
338:, and two thirds of cases of
143:organisms, such as bacteria.
2035:Acute promyelocytic leukemia
1991:Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
1683:17q12 microdeletion syndrome
1558:22q11.2 duplication syndrome
1536:16p11.2 duplication syndrome
1014:10.1371/journal.pgen.1009996
1602:1q21.1 duplication syndrome
1489:1q21.1 duplication syndrome
409:Mitochondrial DNA deletions
350:syndrome. Deletions in the
336:Duchenne muscular dystrophy
2286:
1369:Chromosomal translocations
267:
175:Breaking without rejoining
2148:Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma
1883:XYYYY syndrome (49,XYYYY)
1849:XXXXY syndrome (49,XXXXY)
1844:XXXYY syndrome (49,XXXYY)
1116:10.1007/s00180-007-0021-8
899:10.1016/j.pcl.2015.03.004
542:Klug, William S. (2015).
468:List of genetic disorders
334:, two thirds of cases of
1623:Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome
1598:1q21.1 deletion syndrome
1461:Chromosome abnormalities
458:Chromosome abnormalities
416:Saccharomyces cerevisiae
34:Deletion on a chromosome
2007:Philadelphia chromosome
1878:XYYY syndrome (48,XYYY)
1839:XXXY syndrome (48,XXXY)
1834:XXYY syndrome (48,XXYY)
1719:22q13 deletion syndrome
1494:2q31.1 microduplication
1409:Nearly neutral mutation
1178:10.1073/pnas.1232418100
824:Robbins basic pathology
356:spinal muscular atrophy
1866:Pentasomy X (49,XXXXX)
1798:Turner syndrome (45,X)
1679:Smith–Magenis syndrome
1675:Miller–Dieker syndrome
1610:1p36 deletion syndrome
1419:Nonsynonymous mutation
1374:Chromosomal inversions
1276:Mechanisms of mutation
478:Microdeletion syndrome
403:end-sequence profiling
273:
232:
162:Chromosomal crossovers
35:
1873:XYY syndrome (47,XYY)
1861:Tetrasomy X (48,XXXX)
1744:Prader–Willi syndrome
1399:Advantageous mutation
1338:Conservative mutation
826:. Saunders/Elsevier.
354:-encoding gene cause
311:, causing all of the
268:Further information:
238:
218:
171:Unequal crossing over
166:chromosomal inversion
121:chromosomal crossover
33:
1965:Mantle cell lymphoma
1635:Cri du chat syndrome
1394:Deleterious mutation
1362:Large-scale mutation
545:Concepts of genetics
488:Insertion (genetics)
437:double strand breaks
419:, the nuclear genes
264:mitochondrial genome
1951:Follicular lymphoma
1414:Synonymous mutation
1348:Frameshift mutation
1169:2003PNAS..100.7696V
1046:Ren, H (May 2005).
964:10.1038/nature09774
956:2011Natur.471..216M
634:(46): 14320–14328.
309:frameshift mutation
251:level. It shows 22
2190:Uniparental disomy
2185:Fragile X syndrome
2120:Myxoid liposarcoma
1972:t(11 CCND1:14 IGH)
1856:Trisomy X (47,XXX)
1734:genomic imprinting
1514:Distal trisomy 10q
1065:10.1002/humu.20164
808:2011-10-06 at the
517:Lewis, R. (2004).
274:
266:(at bottom left).
233:
36:
2252:
2251:
2204:Marker chromosome
2173:
2172:
2066:
2065:
1903:
1902:
1770:
1769:
1740:Angelman syndrome
1695:DiGeorge syndrome
1663:Jacobsen syndrome
1651:Williams syndrome
1427:
1426:
1382:
1381:
1333:Missense mutation
1328:Nonsense mutation
1163:(13): 7696–7701.
862:978-0-12-410529-4
833:978-1-4160-2973-1
722:(24): 5264–5270.
679:10.1021/bi500189g
673:(23): 3807–3816.
640:10.1021/jp408957c
605:10.1021/ja401573j
599:(22): 8274–8282.
555:978-0-321-94891-5
441:mitochondrial DNA
390:tumor suppressors
342:(those caused by
302:Williams syndrome
262:, as well as the
189:Terminal deletion
107:compensation loop
70:or a sequence of
56:deletion mutation
16:(Redirected from
2277:
2195:XX male syndrome
2092:Synovial sarcoma
1969:Multiple myeloma
1937:Burkitt lymphoma
1927:
1914:
1817:other karyotypes
1786:
1568:Cat-eye syndrome
1474:
1454:
1447:
1440:
1431:
1404:Neutral mutation
1353:Dynamic mutation
1316:
1262:
1255:
1248:
1239:
1232:
1231:
1210:
1201:
1200:
1190:
1180:
1148:
1142:
1141:
1139:
1138:
1132:
1126:. Archived from
1101:
1092:
1086:
1085:
1067:
1043:
1037:
1036:
1026:
1016:
992:
986:
985:
975:
935:
929:
928:
918:
878:
872:
871:
870:
869:
844:
838:
837:
819:
813:
800:
794:
793:
791:
790:
776:
770:
763:
757:
749:
739:
707:
701:
700:
690:
658:
652:
651:
623:
617:
616:
588:
582:
581:
575:
567:
539:
533:
532:
514:
473:Medical genetics
282:human chromosome
129:genetic diseases
21:
18:Genetic deletion
2285:
2284:
2280:
2279:
2278:
2276:
2275:
2274:
2255:
2254:
2253:
2248:
2209:Ring chromosome
2169:
2062:
1995:
1899:
1815:
1802:
1766:
1579:
1478:
1463:
1458:
1428:
1423:
1378:
1357:
1343:Silent mutation
1307:
1271:
1266:
1236:
1235:
1212:
1211:
1204:
1150:
1149:
1145:
1136:
1134:
1130:
1099:
1094:
1093:
1089:
1045:
1044:
1040:
1007:(1): e1009996.
994:
993:
989:
950:(7337): 216–9.
937:
936:
932:
880:
879:
875:
867:
865:
863:
846:
845:
841:
834:
821:
820:
816:
810:Wayback Machine
801:
797:
788:
786:
778:
777:
773:
764:
750:
709:
708:
704:
660:
659:
655:
625:
624:
620:
590:
589:
585:
568:
556:
541:
540:
536:
529:
516:
515:
506:
501:
449:
411:
398:
340:cystic fibrosis
297:
272:
260:sex chromosomes
213:
182:
149:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2283:
2281:
2273:
2272:
2267:
2257:
2256:
2250:
2249:
2247:
2246:
2245:
2244:
2206:
2201:
2192:
2187:
2181:
2179:
2175:
2174:
2171:
2170:
2168:
2167:
2145:
2131:
2117:
2103:
2089:
2074:
2072:
2068:
2067:
2064:
2063:
2061:
2060:
2046:
2032:
2018:
2003:
2001:
1997:
1996:
1994:
1993:
1988:
1974:
1962:
1948:
1933:
1931:
1924:
1911:
1909:Translocations
1905:
1904:
1901:
1900:
1898:
1897:
1892:
1886:
1885:
1880:
1875:
1869:
1868:
1863:
1858:
1852:
1851:
1846:
1841:
1836:
1831:
1825:
1823:
1804:
1803:
1801:
1800:
1794:
1792:
1783:
1772:
1771:
1768:
1767:
1765:
1764:
1754:
1753:
1752:
1751:
1729:
1728:
1727:
1726:
1716:
1715:
1714:
1704:
1703:
1702:
1692:
1691:
1690:
1672:
1671:
1670:
1660:
1659:
1658:
1648:
1647:
1646:
1632:
1631:
1630:
1620:
1619:
1618:
1589:
1587:
1581:
1580:
1578:
1577:
1576:
1575:
1565:
1560:
1555:
1554:
1553:
1543:
1538:
1533:
1528:
1527:
1526:
1519:Patau syndrome
1516:
1511:
1506:
1501:
1496:
1491:
1485:
1483:
1471:
1465:
1464:
1459:
1457:
1456:
1449:
1442:
1434:
1425:
1424:
1422:
1421:
1416:
1411:
1406:
1401:
1396:
1390:
1388:
1384:
1383:
1380:
1379:
1377:
1376:
1371:
1365:
1363:
1359:
1358:
1356:
1355:
1350:
1345:
1340:
1335:
1330:
1324:
1322:
1320:Point mutation
1313:
1309:
1308:
1306:
1305:
1304:
1303:
1298:
1290:
1285:
1279:
1277:
1273:
1272:
1267:
1265:
1264:
1257:
1250:
1242:
1234:
1233:
1222:(3): 218–225.
1202:
1143:
1087:
1058:(5): 476–482.
1052:Human Mutation
1038:
987:
930:
893:(3): 587–606.
873:
861:
839:
832:
814:
795:
771:
716:Bioinformatics
702:
653:
618:
583:
554:
534:
528:978-0072951745
527:
503:
502:
500:
497:
496:
495:
493:10q26 deletion
490:
485:
480:
475:
470:
465:
460:
455:
448:
445:
410:
407:
397:
394:
296:
293:
212:
209:
205:
204:
198:
192:
181:
178:
177:
176:
173:
168:
159:
148:
145:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2282:
2271:
2268:
2266:
2263:
2262:
2260:
2243:
2239:
2235:
2231:
2227:
2223:
2219:
2215:
2212:
2211:
2210:
2207:
2205:
2202:
2200:
2196:
2193:
2191:
2188:
2186:
2183:
2182:
2180:
2176:
2165:
2161:
2157:
2153:
2149:
2146:
2143:
2139:
2135:
2132:
2129:
2125:
2121:
2118:
2115:
2111:
2107:
2104:
2101:
2097:
2093:
2090:
2087:
2083:
2079:
2078:Ewing sarcoma
2076:
2075:
2073:
2069:
2058:
2054:
2050:
2047:
2044:
2040:
2036:
2033:
2030:
2026:
2022:
2019:
2016:
2012:
2008:
2005:
2004:
2002:
1998:
1992:
1989:
1986:
1982:
1978:
1975:
1973:
1970:
1966:
1963:
1960:
1956:
1952:
1949:
1946:
1942:
1938:
1935:
1934:
1932:
1928:
1925:
1923:
1919:
1915:
1912:
1910:
1906:
1896:
1893:
1891:
1888:
1887:
1884:
1881:
1879:
1876:
1874:
1871:
1870:
1867:
1864:
1862:
1859:
1857:
1854:
1853:
1850:
1847:
1845:
1842:
1840:
1837:
1835:
1832:
1830:
1827:
1826:
1824:
1822:
1818:
1813:
1809:
1805:
1799:
1796:
1795:
1793:
1791:
1787:
1784:
1781:
1777:
1773:
1763:
1762:Proximal 18q-
1759:
1756:
1755:
1749:
1745:
1741:
1738:
1737:
1736:
1735:
1731:
1730:
1725:
1722:
1721:
1720:
1717:
1713:
1710:
1709:
1708:
1705:
1701:
1698:
1697:
1696:
1693:
1689:
1686:
1685:
1684:
1680:
1676:
1673:
1669:
1666:
1665:
1664:
1661:
1657:
1654:
1653:
1652:
1649:
1645:
1642:
1641:
1640:
1636:
1633:
1629:
1626:
1625:
1624:
1621:
1617:
1614:
1613:
1611:
1607:
1603:
1599:
1595:
1591:
1590:
1588:
1586:
1582:
1574:
1571:
1570:
1569:
1566:
1564:
1561:
1559:
1556:
1552:
1549:
1548:
1547:
1546:Down syndrome
1544:
1542:
1539:
1537:
1534:
1532:
1529:
1525:
1522:
1521:
1520:
1517:
1515:
1512:
1510:
1507:
1505:
1502:
1500:
1497:
1495:
1492:
1490:
1487:
1486:
1484:
1482:
1477:Duplications,
1475:
1472:
1470:
1466:
1462:
1455:
1450:
1448:
1443:
1441:
1436:
1435:
1432:
1420:
1417:
1415:
1412:
1410:
1407:
1405:
1402:
1400:
1397:
1395:
1392:
1391:
1389:
1385:
1375:
1372:
1370:
1367:
1366:
1364:
1360:
1354:
1351:
1349:
1346:
1344:
1341:
1339:
1336:
1334:
1331:
1329:
1326:
1325:
1323:
1321:
1317:
1314:
1310:
1302:
1299:
1297:
1294:
1293:
1292:Substitution
1291:
1289:
1286:
1284:
1281:
1280:
1278:
1274:
1270:
1263:
1258:
1256:
1251:
1249:
1244:
1243:
1240:
1229:
1225:
1221:
1217:
1209:
1207:
1203:
1198:
1194:
1189:
1184:
1179:
1174:
1170:
1166:
1162:
1158:
1154:
1147:
1144:
1133:on 2020-05-31
1129:
1125:
1121:
1117:
1113:
1109:
1105:
1098:
1091:
1088:
1083:
1079:
1075:
1071:
1066:
1061:
1057:
1053:
1049:
1042:
1039:
1034:
1030:
1025:
1020:
1015:
1010:
1006:
1002:
1001:PLOS Genetics
998:
991:
988:
983:
979:
974:
969:
965:
961:
957:
953:
949:
945:
941:
934:
931:
926:
922:
917:
912:
908:
904:
900:
896:
892:
888:
884:
877:
874:
864:
858:
854:
850:
843:
840:
835:
829:
825:
818:
815:
811:
807:
804:
799:
796:
785:
781:
775:
772:
768:
761:
755:
747:
743:
738:
733:
729:
725:
721:
717:
713:
706:
703:
698:
694:
689:
684:
680:
676:
672:
668:
664:
657:
654:
649:
645:
641:
637:
633:
629:
622:
619:
614:
610:
606:
602:
598:
594:
587:
584:
579:
573:
565:
561:
557:
551:
547:
546:
538:
535:
530:
524:
520:
513:
511:
509:
505:
498:
494:
491:
489:
486:
484:
481:
479:
476:
474:
471:
469:
466:
464:
461:
459:
456:
454:
451:
450:
446:
444:
442:
438:
434:
430:
429:
424:
423:
418:
417:
413:In the yeast
408:
406:
404:
395:
393:
391:
387:
382:
381:
377:
373:
369:
363:
359:
357:
353:
349:
345:
341:
337:
333:
328:
326:
322:
318:
314:
310:
305:
303:
294:
292:
290:
286:
283:
279:
271:
265:
261:
257:
254:
250:
246:
242:
237:
230:
226:
222:
217:
210:
208:
202:
201:Microdeletion
199:
196:
193:
190:
187:
186:
185:
179:
174:
172:
169:
167:
163:
160:
158:
157:translocation
154:
153:
152:
146:
144:
142:
138:
134:
130:
126:
122:
117:
115:
114:base flipping
110:
108:
104:
100:
95:
93:
89:
85:
81:
77:
73:
69:
65:
61:
57:
53:
49:
48:gene deletion
46:(also called
45:
41:
32:
19:
1732:
1606:TAR syndrome
1584:
1509:Tetrasomy 9p
1296:Transversion
1287:
1219:
1215:
1160:
1156:
1146:
1135:. Retrieved
1128:the original
1110:(1): 49–69.
1107:
1103:
1090:
1055:
1051:
1041:
1004:
1000:
990:
947:
943:
933:
890:
886:
876:
866:, retrieved
852:
842:
823:
817:
798:
787:. Retrieved
783:
774:
754:cite journal
719:
715:
705:
670:
667:Biochemistry
666:
656:
631:
627:
621:
596:
592:
586:
544:
537:
518:
432:
426:
420:
414:
412:
399:
383:
364:
360:
329:
324:
306:
298:
288:
285:nomenclature
275:
228:
224:
220:
211:Nomenclature
206:
200:
194:
188:
183:
155:Losses from
150:
118:
111:
106:
102:
96:
87:
55:
51:
47:
43:
37:
1895:46,XX/46,XY
1812:tetrasomies
1758:Distal 18q-
463:Null allele
372:chimpanzees
348:Cri du chat
332:infertility
317:translation
141:prokaryotic
84:chromosomes
76:nucleotides
2259:Categories
1890:45,X/46,XY
1790:Monosomies
1563:Trisomy 22
1541:Trisomy 18
1531:Trisomy 16
1479:including
1301:Transition
1137:2014-01-10
868:2022-01-07
789:2022-10-27
499:References
327:deletion.
253:homologous
249:centromere
137:eukaryotic
133:frameshift
92:chromosome
68:chromosome
52:deficiency
1808:Trisomies
1585:Deletions
1504:Trisomy 9
1499:Trisomy 8
1481:trisomies
1469:Autosomal
1283:Insertion
907:0031-3955
572:cite book
564:880404074
396:Detection
270:Karyotype
256:autosomal
245:G banding
241:karyotype
164:within a
58:) (sign:
2270:Mutation
1930:Lymphoid
1922:lymphoma
1918:Leukemia
1288:Deletion
1269:Mutation
1197:12788976
1082:28030180
1074:15832308
1033:35030162
982:21390129
925:26022164
806:Archived
746:31228194
697:24854722
648:24206351
613:23692220
447:See also
380:monkeys.
368:hCONDELs
325:in-frame
103:deletion
99:synapsis
88:deletion
64:mutation
44:deletion
40:genetics
2158:) t (1
2025:RUNX1T1
2000:Myeloid
1821:mosaics
1165:Bibcode
1124:2737235
1024:8759692
973:3071156
952:Bibcode
916:4449422
737:6954653
688:4063443
321:protein
295:Effects
125:meiosis
123:during
62:) is a
2110:COL1A1
1782:linked
1226:
1195:
1188:164650
1185:
1122:
1080:
1072:
1031:
1021:
980:
970:
944:Nature
923:
913:
905:
859:
830:
744:
734:
695:
685:
646:
611:
562:
552:
525:
433:Rad59p
431:p and
313:codons
239:Human
147:Causes
2178:Other
2164:FOXO1
2162:; 13
2156:FOXO1
2154:; 13
2140:; 22
2136:t(11
2126:; 16
2124:DDIT3
2122:t(12
2114:PDGFB
2108:t(17
2084:; 22
2080:t(11
2071:Other
2053:RBM15
2037:t(15
2029:RUNX1
2013:; 22
1953:t(14
1228:26540
1131:(PDF)
1120:S2CID
1100:(PDF)
1078:S2CID
453:Indel
428:Rad52
422:Rad51
344:ΔF508
180:Types
54:, or
2160:PAX7
2152:PAX3
2150:t(2
2112:;22
2098:;18
2094:t(x
2082:FLI1
2057:MKL1
2055:;22
2051:t(1
2043:RARA
2041:,17
2027:;21
2023:t(8
2009:t(9
1985:NPM1
1979:t(2
1959:BCL2
1957:;18
1943:;14
1939:t(8
1224:PMID
1193:PMID
1070:PMID
1029:PMID
978:PMID
921:PMID
903:ISSN
857:ISBN
828:ISBN
760:link
742:PMID
693:PMID
644:PMID
609:PMID
578:link
560:OCLC
550:ISBN
523:ISBN
386:TCGA
276:The
97:For
80:base
42:, a
2142:EWS
2138:WT1
2128:FUS
2100:SSX
2096:SYT
2086:EWS
2039:PML
2015:BCR
2011:ABL
1983:;5
1981:ALK
1955:IGH
1945:IGH
1941:MYC
1183:PMC
1173:doi
1161:100
1112:doi
1060:doi
1019:PMC
1009:doi
968:PMC
960:doi
948:471
911:PMC
895:doi
732:PMC
724:doi
683:PMC
675:doi
636:doi
632:117
601:doi
597:135
439:in
425:p,
378:or
376:ape
352:SMN
289:del
229:(C)
225:(B)
221:(A)
105:or
72:DNA
38:In
2261::
2242:22
2240:,
2238:21
2236:;
2234:20
2232:;
2230:18
2228:;
2226:15
2224:;
2222:14
2220:;
2216:;
1748:15
1724:22
1712:22
1700:22
1688:17
1668:11
1612:)
1573:22
1551:21
1524:13
1218:.
1205:^
1191:.
1181:.
1171:.
1159:.
1155:.
1118:.
1108:22
1106:.
1102:.
1076:.
1068:.
1056:25
1054:.
1050:.
1027:.
1017:.
1005:18
1003:.
999:.
976:.
966:.
958:.
946:.
942:.
919:.
909:.
901:.
891:62
889:.
885:.
851:,
782:.
769:)"
756:}}
752:{{
740:.
730:.
720:35
718:.
714:.
691:.
681:.
671:53
669:.
665:.
642:.
630:.
607:.
595:.
574:}}
570:{{
558:.
507:^
405:.
392:.
304:.
109:.
50:,
2218:9
2214:6
2197:/
2166:)
2144:)
2130:)
2116:)
2102:)
2088:)
2059:)
2045:)
2031:)
2017:)
1987:)
1967:/
1961:)
1947:)
1920:/
1819:/
1814:,
1810:/
1780:Y
1778:/
1776:X
1760:/
1750:)
1746:(
1742:/
1681:/
1677:/
1656:7
1644:5
1637:/
1628:4
1616:1
1608:/
1604:/
1600:/
1596:/
1592:(
1453:e
1446:t
1439:v
1261:e
1254:t
1247:v
1230:.
1220:6
1199:.
1175::
1167::
1140:.
1114::
1084:.
1062::
1035:.
1011::
984:.
962::
954::
927:.
897::
836:.
792:.
762:)
748:.
726::
699:.
677::
650:.
638::
615:.
603::
580:)
566:.
531:.
60:Δ
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.