188:
Base
Protocol. If there are several HSS in the network, BSF must first know which one to use. This can be done by either setting up a pre-defined HSS to BSF, or by querying the Subscriber Locator Function (SLF). NAFs recover the key session of BSF during the Zn interface, which also uses the
209:. The NAF was developed on SimpleSAMLPhP and a Firefox extension was developed to process the GBA digest authencation request from the BSF. Bluetooth SIM Access Profile was used between the Firefox browser and the mobile phone. Later a partner developed a "zero installation" concept.
149:
In the shared secret cases, the customer and the operator are first mutually authenticated through 3G and
Authentication Key (AKA) and they agree on session keys which can then be used between the client and services that the customer wants to use. This is called
157:
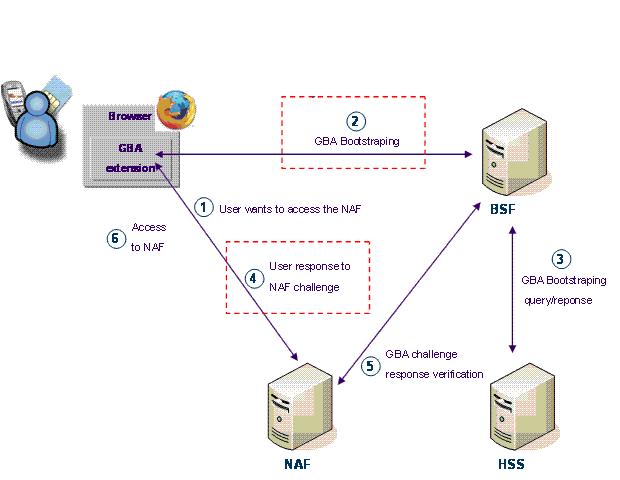
Figure above shows the network GAA entities and interfaces between them. Optional entities are drawn with lines network and borders dotted the scoreboard. The User
Equipment (UE) is, for example, the user's mobile phone. The UE and
230:
Sadly, despite many advantages and potential uses of GBA, its implementation in handsets has been limited since GBA standardization in 2006. Most notably, GBA was implemented in
Symbian-based handsets.
126:
A means to dialog with a smartcard and signed the challenge sent by the BSF, either
Bluetooth SAP or a Java or native application could be used to serve the request coming from the browser.
213:
154:. After that, the services can retrieve the session keys from the operator, and they can be used in some application specific protocol between the client and services.
279:
73:
116:
with 500 PHP lines of code and only a few tens of lines of code are
Service Provider specific making it really easy to port it to another Web site.
248:
93:- Another advantage is the ease with which the authentication method may be integrated into terminals and service providers, as it is based on
123:
A Web browser (in fact an HTTP client) implementing digest authentication and the special case designed by a "3gpp" string in the HTTP header.
23:) is a technology that enables the authentication of a user. This authentication is possible if the user owns a valid identity on an HLR (
53:
GBA authenticates by making a network component challenge the smartcard and verify that the answer is the one predicted by the HLR/HSS.
198:
The SPICE project developed an extended Use Case named "split terminal" where a user on a PC can authenticate with their mobile phone:
86:- There is no need for user enrollment phase nor secure deployment of keys, making this solution a very low cost one when compared to
217:
105:
and the effort to implement GBA on top of digest authentication is minimal. For example, it could be implemented on SimpleSAMLPhP
310:
181:), which are the implementation servers, over the Ua interface, which can use any specific application protocol necessary.
61:
57:
283:
167:
98:
202:
184:
BSF retrieves data from the subscriber from the Home
Subscriber Server (HSS) during the Zh interface, which uses the
315:
87:
83:
This solution has some strong points of certificate and shared secrets without having some of their weaknesses:
109:
189:
diameter at the base
Protocol. If NAF is not in the home network, it must use a Zn-proxy to contact BSF .
28:
226:
references GBA in its
Advanced Trusted Environment: OMTP TR1 recommendation, first released in May 2008.
102:
72:
255:
185:
68:
card and the service provider. This shared secret is limited in time and for a specific domain.
24:
206:
113:
249:"Generic Authentication Architecture by Timo Olkkonen, Helsinki University of Technology"
170:
166:) mutually authenticate themselves during the Ub (number above) interface, using the
304:
39:
145:
The second, SSC, is based on public-private key pairs and digital certificates.
43:
199:
42:). The user authentication is instantiated by a shared secret, one in the
142:
The first, GBA, is based on a shared secret between the client and server
47:
216:
developed an OpenID extension for
Firefox which uses GBA authentication.
65:
138:
There are two ways to use GAA (Generic Authentication Architecture).
106:
135:
Actually, contents in this section are from external literature.
94:
35:
50:
inside the mobile phone and the other is on the HLR/HSS.
60:
and relying on it for every authentication request, the
223:
56:
Instead of asking the service provider to trust the
40:http://www.3gpp.org/ftp/Specs/html-info/33220.htm
280:"OMTP Advanced Trusted Environment: OMTP TR1"
8:
173:protocol. The UE also communicates with the
101:". Every Web server already implement HTTP
200:http://www.ist-spice.org/demos/demo3.htm
64:establishes a shared secret between the
240:
218:Presentation at ICIN 2008 by Peter Weik
7:
222:The Open Mobile Terminal Platform
17:Generic Bootstrapping Architecture
14:
107:http://rnd.feide.no/simplesamlphp
71:
1:
175:Network Application Functions
160:Bootstrapping Server Function
119:- On device side is needed:
168:Digest access authentication
99:Digest access authentication
34:GBA is standardized at the
332:
311:Cryptographic protocols
212:The research institute
29:Home Subscriber Server
25:Home Location Register
103:digest authentication
224:http://www.omtp.org
205:2009-03-24 at the
131:Technical overview
112:2008-12-19 at the
316:Mobile technology
323:
295:
294:
292:
291:
282:. Archived from
276:
270:
269:
267:
266:
260:
254:. Archived from
253:
245:
214:Fraunhofer FOKUS
75:
46:, for example a
27:) or on an HSS (
331:
330:
326:
325:
324:
322:
321:
320:
301:
300:
299:
298:
289:
287:
278:
277:
273:
264:
262:
258:
251:
247:
246:
242:
237:
207:Wayback Machine
195:
133:
114:Wayback Machine
97:'s well known "
81:
12:
11:
5:
329:
327:
319:
318:
313:
303:
302:
297:
296:
271:
239:
238:
236:
233:
228:
227:
220:
210:
194:
191:
147:
146:
143:
132:
129:
128:
127:
124:
80:
77:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
328:
317:
314:
312:
309:
308:
306:
286:on 2008-10-21
285:
281:
275:
272:
261:on 2016-07-05
257:
250:
244:
241:
234:
232:
225:
221:
219:
215:
211:
208:
204:
201:
197:
196:
192:
190:
187:
182:
180:
176:
172:
169:
165:
161:
155:
153:
152:bootstrapping
144:
141:
140:
139:
136:
130:
125:
122:
121:
120:
117:
115:
111:
108:
104:
100:
96:
91:
89:
84:
79:Strong points
78:
76:
74:
69:
67:
63:
59:
54:
51:
49:
45:
41:
37:
32:
30:
26:
22:
18:
288:. Retrieved
284:the original
274:
263:. Retrieved
256:the original
243:
229:
183:
178:
174:
163:
159:
156:
151:
148:
137:
134:
118:
92:
85:
82:
70:
55:
52:
33:
20:
16:
15:
305:Categories
290:2009-01-04
265:2010-07-05
235:References
44:smartcard
203:Archived
186:Diameter
110:Archived
48:SIM card
66:simcard
259:(PDF)
252:(PDF)
193:Uses
95:HTTP
36:3GPP
179:NAF
171:AKA
164:BSF
88:PKI
62:BSF
58:BSF
31:).
21:GBA
307::
90:.
293:.
268:.
177:(
162:(
38:(
19:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.