750:
738:
2085:
2070:
2100:
717:
for dimerization of the enzyme monomers. However, this was shown to be incorrect. On the other hand, it was shown that the presence of NADP at the structural site promotes the dimerization of dimers to form enzyme tetramers. It was also thought that the tetramer state was necessary for catalytic activity; however, this too was shown to be false. The NADP structural site is quite different from the NADP catalytic coenzyme binding site, and contains the nucleotide-binding fingerprint.
882:
629:
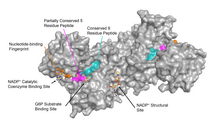
636:. Phosphorus is shown in orange. Oxygen atoms of crystallographic waters are shown as red spheres. The conserved 9-peptide sequence of G6PD, and the partially conserved 5-residue sequence of G6PD are shown in cyan and magenta respectively. All other amino acids from G6PD are shown in black. Hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions are shown by green dashed lines. All green dashes represent distances of less than 3.7 Å.
36:
2960:
660:. For some higher organisms, such as humans, G6PD contains an additional NADP binding site, called the NADP structural site, that does not seem to participate directly in the reaction catalyzed by G6PD. The evolutionary purpose of the NADP structural site is unknown. As for size, each monomer is approximately 500 amino acids long (514 amino acids for humans).
567:
of a single gene coding for G6PD. Moreover, at least 168 disease-causing mutations in this gene have been discovered. These mutations are mainly missense mutations that result in amino acid substitutions, and while some of them result in G6PD deficiency, others do not seem to result in any noticeable
808:
on lysine 403 (Lys403), an evolutionarily conserved residue. The K403 acetylated G6PD is incapable of forming active dimers and displays a complete loss of activity. Mechanistically, acetylating Lys403 sterically hinders the NADP from entering the NADP structural site, which reduces the stability of
671:
on the enzyme: a 9 residue peptide in the substrate binding site, RIDHYLGKE (residues 198-206 on human G6PD), a nucleotide-binding fingerprint, GxxGDLA (residues 38-44 on human G6PD), and a partially conserved sequence EKPxG near the substrate binding site (residues 170-174 on human G6PD), where we
716:
The NADP structural site is located greater than 20Å away from the substrate binding site and the catalytic coenzyme NADP binding site. Its purpose in the enzyme catalyzed reaction has been unclear for many years. For some time, it was thought that NADP binding to the structural site was necessary
707:
due to G6PD deficiency is rare, mutation sites on G6PD have been shown to lie near the NADP binding site, the G6P binding site, and near the interface between the two monomers. Thus, mutations in these critical areas are possible without completely disrupting the function of G6PD. In fact, it has
800:
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase is stimulated by its substrate G6P. The usual ratio of NADPH/NADP in the cytosol of tissues engaged in biosyntheses is about 100/1. Increased utilization of NADPH for fatty acid biosynthesis will dramatically increase the level of NADP, thus stimulating G6PD to
772:
mutations involve mutations near the structural site, thus affecting the long term stability of these enzymes in the body, ultimately resulting in G6PD deficiency. For example, two severe class I mutations, G488S and G488V, drastically increase the dissociation constant between NADP and the
889:
Cell growth and proliferation are affected by G6PD. Pharmacologically ablating G6PD has been shown to overcome cross-tolerance of breast cancer cells to anthracyclines. G6PD inhibitors are under investigation to treat cancers and other conditions.
720:
The structural site bound to NADP possesses favorable interactions that keep it tightly bound. In particular, there is a strong network of hydrogen bonding with electrostatic charges being diffused across multiple atoms through
761:
NADP structural site of G6PD. NADP is shown in cream. Phosphorus is shown in orange. The oxygen atoms of crystallographic water molecules are shown as red spheres. The conserved 9-peptide sequence of G6PD is show in
773:
structural site by a factor of 7 to 13. With the proximity of residue 488 to Arg487, it is thought that a mutation at position 488 could affect the positioning of Arg487 relative to NADP, and thus disrupt binding.
2084:
1705:
695:
at position 172 is thought to play a crucial role in positioning Lys171 correctly with respect to the substrate, G6P. In the two crystal structures of normal human G6P, Pro172 is seen exclusively in the
2069:
1393:"Crystal structures of F420-dependent glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase FGD1 involved in the activation of the anti-tuberculosis drug candidate PA-824 reveal the basis of coenzyme and substrate binding"
2099:
2438:
2140:
672:
have use "x" to denote a variable amino acid. The crystal structure of G6PD reveals an extensive network of electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonding involving G6P, 3 water molecules, 3
801:
produce more NADPH. Yeast G6PD is inhibited by long chain fatty acids according to two older publications and might be product inhibition in fatty acid synthesis which requires NADPH.
2433:
2594:
828:
Regulation can also occur through genetic pathways. The isoform, G6PDH, is regulated by transcription and posttranscription factors. Moreover, G6PD is one of a number of
2248:
1709:
360:
165:
2133:
2488:
379:
911:
866:
769:
532:
2282:
937:"Identification of the structural gene for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in yeast. Inactivation leads to a nutritional requirement for organic sulfur"
2523:
2126:
2483:
2368:
700:, while in the crystal structure of one disease causing mutant (variant Canton R459L), Pro172 is seen almost exclusively in the trans conformation.
1115:"Human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: the crystal structure reveals a structural NADP(+) molecule and provides insights into enzyme deficiency"
2311:
2423:
2022:
703:
With access to crystal structures, some scientists have tried to model the structures of other mutants. For example, in German ancestry, where
1535:
Eger-Neufeldt I, Teinzer A, Weiss L, Wieland O (March 1965). "Inhibition of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase by long chain acyl-coenzyme A".
898:(dehydroepiandrosterone) and ANAD (6-aminonicotinamide), effectively decrease the growth of AML cell lines. G6PD is hypomethylated at K403 in
755:
Hydrophobic stacking interactions (green). All green dashes represent distances less than 4.4 Å. Slightly different view than the first panel.
2241:
2049:
1654:"Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: a "housekeeping" enzyme subject to tissue-specific regulation by hormones, nutrients, and oxidant stress"
993:
113:
2518:
2478:
1603:
Wang YP, Zhou LS, Zhao YZ, Wang SW, Chen LL, Liu LX, Ling ZQ, Hu FJ, Sun YP, Zhang JY, Yang C, Yang Y, Xiong Y, Guan KL, Ye D (June 2014).
2990:
2528:
2495:
559:
of over 100 known G6PDs from different organisms reveal sequence identity ranging from 30% to 94%. Human G6PD has over 30% identity in
2995:
2622:
2383:
2296:
2679:
2278:
482:
2985:
2234:
1730:
372:
2291:
2093:: X-RAY STRUCTURE OF A DELETION VARIANT OF HUMAN GLUCOSE 6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEXED WITH STRUCTURAL AND COENZYME NADP
768:
The structural site has been shown to be important for maintaining the long term stability of the enzyme. More than 40 severe
2617:
2443:
2184:
1903:"Variants of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase are due to missense mutations spread throughout the coding region of the gene"
323:
299:
2835:
185:
2428:
1434:"Inactivation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase by 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Selective modification of an active-site lysine"
2118:
916:
782:
2950:
1178:"Refinement of evolutionary medicine predictions based on clinical evidence for the manifestations of Mendelian diseases"
522:
2456:
1605:"Regulation of G6PD acetylation by SIRT2 and KAT9 modulates NADPH homeostasis and cell survival during oxidative stress"
501:. Of greater quantitative importance is the production of NADPH for tissues involved in biosynthesis of fatty acids or
2589:
2353:
743:
Hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interaction network (green). All green dashes represent distances less than 3.8 Å
2358:
2078:: X-RAY STRUCTURE OF HUMAN GLUCOSE 6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE (VARIANT CANTON R459L) COMPLEXED WITH STRUCTURAL NADP+
604:
2820:
2108:: X-RAY STRUCTURE OF HUMAN GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE (DELETION VARIANT) COMPLEXED WITH GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE
2936:
2923:
2910:
2897:
2884:
2871:
2858:
2632:
2604:
2576:
2538:
2505:
2408:
2274:
2179:
2157:
2042:
814:
467:
42:
2830:
1154:
317:
2784:
2727:
2398:
2265:
2205:
2200:
408:
210:
173:
304:
2732:
2556:
2363:
2153:
1488:"What is the role of the second "structural" NADP+-binding site in human glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase?"
451:
2448:
2261:
899:
1242:"Three-dimensional modeling of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-deficient variants from German ancestry"
384:
2753:
2672:
2641:
2403:
2301:
1066:"Structural studies of glucose-6-phosphate and NADP+ binding to human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase"
786:
292:
20:
2825:
169:
588:
2418:
2413:
2373:
2035:
1853:
1253:
1189:
833:
726:
227:
126:
2226:
749:
2789:
2306:
805:
560:
518:
432:
320:
222:
244:
2722:
1969:
1932:
1790:"Targeting tumor phenotypic plasticity and metabolic remodeling in adaptive cross-drug tolerance"
1683:
1342:
Corpas FJ, Barroso JB, Sandalio LM, Distefano S, Palma JM, Lupiáñez JA, Del Río LA (March 1998).
1324:
1065:
1037:
649:
556:
737:
881:
725:
with 4 water molecules (see figure). Moreover, there is an extremely strong set of hydrophobic
2980:
2393:
2388:
1998:
1961:
1924:
1879:
1819:
1770:
1675:
1634:
1585:
1517:
1455:
1414:
1373:
1316:
1281:
1215:
1136:
1090:
1029:
989:
966:
848:
569:
498:
471:
426:
311:
160:
1788:
Goldman A, Khiste S, Freinkman E, Dhawan A, Majumder B, Mondal J, et al. (August 2019).
708:
been shown that most disease causing mutations of G6PD occur near the NADP structural site.
2768:
2763:
2737:
2665:
2561:
2348:
1990:
1953:
1914:
1869:
1861:
1809:
1801:
1760:
1665:
1624:
1616:
1575:
1544:
1507:
1499:
1445:
1404:
1363:
1355:
1308:
1271:
1261:
1205:
1197:
1126:
1080:
1021:
956:
948:
902:, SIRT2 activates G6PD to enhance NADPH production and promote leukemia cell proliferation.
870:
856:
668:
656:
that binds to G6P, and a catalytic coenzyme binding site that binds to NADP/NADPH using the
628:
617:
536:
1842:"SIRT2 activates G6PD to enhance NADPH production and promote leukaemia cell proliferation"
793:. Thus, regulation of G6PD has downstream consequences for the activity of the rest of the
280:
152:
2815:
2799:
2712:
2566:
2551:
1012:
Cappellini MD, Fiorelli G (January 2008). "Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency".
852:
847:
G6PD is remarkable for its genetic diversity. Many variants of G6PD, mostly produced from
809:
the enzyme. Cells sense extracellular oxidative stimuli to decrease G6PD acetylation in a
256:
1857:
1257:
1193:
215:
2964:
2853:
2794:
2257:
1957:
1874:
1841:
1814:
1789:
1747:
Tian WN, Braunstein LD, Pang J, Stuhlmeier KM, Xi QC, Tian X, Stanton RC (April 1998).
1629:
1604:
1512:
1487:
1368:
1343:
1276:
1241:
1210:
1177:
952:
510:
490:
355:
1580:
1563:
1450:
1433:
1312:
1131:
1114:
1025:
961:
936:
813:-dependent manner. The SIRT2-mediated deacetylation and activation of G6PD stimulates
633:
335:
2974:
2758:
2717:
2215:
2210:
1973:
1548:
722:
685:
657:
641:
596:
514:
506:
330:
118:
1936:
1687:
1328:
1041:
877:, or reaction with certain medicines, antibiotics, antipyretics, and antimalarials.
69:
2707:
822:
653:
609:
148:
82:
35:
1266:
644:
of two identical monomers (see main thumbnail). Depending on conditions, such as
94:
2931:
2866:
2702:
704:
592:
579:
Other species experience a variation in G6PD as well. In higher plants, several
486:
475:
339:
2959:
1994:
1670:
1653:
1201:
2509:
2461:
2149:
1805:
1085:
874:
829:
502:
1765:
1748:
2905:
2879:
2580:
1919:
1902:
1064:
Kotaka M, Gover S, Vandeputte-Rutten L, Au SW, Lam VM, Adams MJ (May 2005).
681:
494:
479:
422:
415:
2466:
2002:
1883:
1823:
1638:
1620:
1521:
1418:
1409:
1392:
1285:
1219:
1140:
1094:
1033:
2017:
1965:
1928:
1774:
1749:"Importance of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity for cell growth"
1679:
1589:
1503:
1459:
1377:
970:
122:
1564:"Inhibition of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase by palmitoyl coenzyme A"
1344:"A dehydrogenase-mediated recycling system of NADPH in plant peroxisomes"
1155:"G6PD glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase [ Homo sapiens (human) ]"
677:
580:
573:
564:
548:
529:
89:
1320:
411:
268:
2608:
2321:
1299:
Luzzatto L, Bienzle U (June 1979). "The malaria/G.-6-P.D. hypothesis".
860:
697:
692:
584:
568:
functional differences. Some scientists have proposed that some of the
287:
106:
101:
1865:
1359:
2918:
2688:
2646:
2542:
2341:
2336:
2331:
2326:
2316:
2160:
673:
552:
418:
367:
263:
251:
239:
180:
984:
Aster J, Kumar V, Robbins SL, Abbas AK, Fausto N, Cotran RS (2010).
632:
Substrate binding site of G6PD bound to G6P (shown in cream), from
2892:
2471:
836:
818:
810:
627:
459:
1944:
Mason PJ (September 1996). "New insights into G6PD deficiency".
895:
439:
275:
142:
76:
64:
2661:
2230:
2122:
2031:
1706:"Cancer Research Moves Beyond the Original Hallmarks of Cancer"
2027:
663:
Functional and structural conservation between human G6PD and
521:. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase is also an enzyme in the
988:. Saunders/Elsevier. pp. Kindle Locations 33340–33341.
880:
2439:
Malate dehydrogenase (oxaloacetate-decarboxylating) (NADP+)
645:
602:-dependent (as opposed to NADP-dependent) G6PD is found in
563:
to G6PD sequences from other species. Humans also have two
2657:
1432:
Szweda LI, Uchida K, Tsai L, Stadtman ER (February 1993).
1391:
Bashiri G, Squire CJ, Moreland NJ, Baker EN (June 2008).
894:
cell proliferation assay indicates that G6PD inhibitors,
572:
in human G6PD resulted from generations of adaptation to
583:
of G6PDH have been reported, which are localized in the
1240:
Kiani F, Schwarzl S, Fischer S, Efferth T (July 2007).
729:interactions that result in overlapping π systems.
478:) by maintaining the level of the reduced form of the
2948:
1731:"Entrez Gene: G6PD glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase"
29:
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, NAD binding domain
1652:
Kletzien RF, Harris PK, Foellmi LA (February 1994).
16:
Enzyme involved in the production of energy by cells
2844:
2808:
2777:
2746:
2695:
2631:
2603:
2575:
2537:
2504:
2434:
Malate dehydrogenase (oxaloacetate-decarboxylating)
2273:
2193:
2167:
1537:
935:Thomas D, Cherest H, Surdin-Kerjan Y (March 1991).
378:
366:
354:
349:
329:
310:
298:
286:
274:
262:
250:
238:
233:
221:
209:
204:
199:
179:
159:
141:
136:
112:
100:
88:
75:
63:
55:
50:
28:
2595:Vitamin-K-epoxide reductase (warfarin-insensitive)
1486:Wang XT, Chan TF, Lam VM, Engel PC (August 2008).
873:in the presence of simple infection, ingestion of
851:, have been described with wide-ranging levels of
485:(NADPH). The NADPH in turn maintains the level of
821:to counteract oxidative damage and protect mouse
1840:Xu SN, Wang TS, Li X, Wang YP (September 2016).
547:G6PD is widely distributed in many species from
474:that supplies reducing energy to cells (such as
1113:Au SW, Gover S, Lam VM, Adams MJ (March 2000).
648:, these dimers can themselves dimerize to form
1007:
1005:
986:Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease
652:. Each monomer in the complex has a substrate
2673:
2242:
2134:
2043:
1699:
1697:
859:. Two transcript variants encoding different
517:. G6PD reduces NADP to NADPH while oxidizing
8:
1742:
1740:
912:Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
867:Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
1981:Wajcman H, Galactéros F (August 2004). "".
869:is very common worldwide, and causes acute
483:nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
2680:
2666:
2658:
2524:D-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome c-553)
2249:
2235:
2227:
2141:
2127:
2119:
2050:
2036:
2028:
1901:Vulliamy T, Beutler E, Luzzatto L (1993).
1835:
1833:
346:
133:
34:
1918:
1873:
1813:
1764:
1669:
1628:
1579:
1511:
1449:
1408:
1367:
1275:
1265:
1209:
1176:Šimčíková D, Heneberg P (December 2019).
1130:
1084:
960:
2369:D-malate dehydrogenase (decarboxylating)
445:
2955:
2065:
1562:Kawaguchi A, Bloch K (September 1974).
927:
40:glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase from
2424:Malate dehydrogenase (decarboxylating)
489:in these cells that helps protect the
196:
25:
1481:
1479:
1477:
1475:
1473:
1471:
1469:
7:
2519:D-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome)
1235:
1233:
1231:
1229:
1108:
1106:
1104:
1059:
1057:
1055:
1053:
1051:
2529:Mannitol dehydrogenase (cytochrome)
1753:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
1568:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
1438:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
1397:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
2623:Quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase
2384:Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
2297:3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase
1958:10.1111/j.1365-2141.1996.tb00001.x
953:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07981.x
608:, and is of interest for treating
535:makes a human prone to non-immune
14:
2379:Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
2175:Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
397:Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
200:Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
2958:
2098:
2083:
2068:
804:G6PD is negatively regulated by
748:
736:
616:was shown to be reactive toward
466:This enzyme participates in the
2292:3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase
863:have been found for this gene.
688:, and other polar amino acids.
2618:Malate dehydrogenase (quinone)
2444:Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase
2185:Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase
1946:British Journal of Haematology
612:. The bacterial G6PD found in
1:
1581:10.1016/S0021-9258(20)79887-X
1451:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)53699-1
1313:10.1016/S0140-6736(79)91857-9
1132:10.1016/S0969-2126(00)00104-0
1026:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60073-2
917:Genetic resistance to malaria
640:G6PD is generally found as a
137:Available protein structures:
2457:Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
2429:Malate dehydrogenase (NADP+)
1704:de Lartigue J (2012-06-12).
1549:10.1016/0006-291X(65)90116-6
1267:10.1371/journal.pone.0000625
2590:Vitamin K epoxide reductase
2359:Carbohydrate dehydrogenases
2354:Beta-Ketoacyl ACP reductase
497:damage from compounds like
3012:
2991:Enzymes of known structure
1995:10.1016/j.crvi.2004.07.010
1671:10.1096/fasebj.8.2.8119488
1202:10.1038/s41598-019-54976-4
837:hypoxia-inducible factor 1
783:6-phosphoglucono-δ-lactone
605:Mycobacterium tuberculosis
533:genetic deficiency of G6PD
18:
2996:Pentose phosphate pathway
2836:Michaelis–Menten kinetics
2409:L-threonine dehydrogenase
2180:6-phosphogluconolactonase
2158:pentose phosphate pathway
2063:
2018:- G6PD Deficiency Website
1806:10.1126/scisignal.aas8779
1708:. OncLive. Archived from
1086:10.1107/S0907444905002350
815:pentose phosphate pathway
795:pentose phosphate pathway
791:pentose phosphate pathway
665:Leuconostoc mesenteroides
614:Leuconostoc mesenteroides
468:pentose phosphate pathway
345:
132:
43:Leuconostoc mesenteroides
33:
2728:Diffusion-limited enzyme
2399:Isocitrate dehydrogenase
2206:Phosphopentose epimerase
2201:Phosphopentose isomerase
1983:Comptes Rendus Biologies
1766:10.1074/jbc.273.17.10609
1073:Acta Crystallographica D
667:G6PD points to 3 widely
525:, a type of glycolysis.
523:Entner–Doudoroff pathway
19:Not to be confused with
2986:NADPH-dependent enzymes
2557:L-gulonolactone oxidase
2364:Carnitine dehydrogenase
2262:alcohol oxidoreductases
2154:carbohydrate metabolism
2023:ATSDR - G6PD Deficiency
1920:10.1002/humu.1380020302
1348:The Biochemical Journal
781:G6PD converts G6P into
2449:Sorbitol dehydrogenase
1621:10.1002/embj.201387224
1410:10.1074/jbc.M801854200
900:acute myeloid leukemia
887:
885:
637:
620:, in addition to G6P.
2821:Eadie–Hofstee diagram
2754:Allosteric regulation
2642:Choline dehydrogenase
2404:Lactate dehydrogenase
2302:Alcohol dehydrogenase
1504:10.1110/ps.035352.108
884:
879:
843:Clinical significance
631:
505:, such as the liver,
21:Glucose 6-phosphatase
2831:Lineweaver–Burk plot
2419:Malate dehydrogenase
2414:L-xylulose reductase
2374:DXP reductoisomerase
834:transcription factor
817:to supply cytosolic
712:NADP structural site
543:Species distribution
456:-glucono-1,5-lactone
436:-glucose 6-phosphate
2307:Aldo-keto reductase
1858:2016NatSR...632734X
1258:2007PLoSO...2..625K
1194:2019NatSR...918577S
561:amino acid sequence
519:glucose-6-phosphate
2790:Enzyme superfamily
2723:Enzyme promiscuity
1846:Scientific Reports
1182:Scientific Reports
886:
849:missense mutations
830:glycolytic enzymes
638:
557:sequence alignment
2946:
2945:
2655:
2654:
2635:: other acceptors
2611:/similar acceptor
2394:IMP dehydrogenase
2389:HMG-CoA reductase
2224:
2223:
2116:
2115:
1866:10.1038/srep32734
1794:Science Signaling
1360:10.1042/bj3300777
1079:(Pt 5): 495–504.
995:978-1-4160-3121-5
857:clinical symptoms
832:activated by the
669:conserved regions
570:genetic variation
499:hydrogen peroxide
472:metabolic pathway
455:
435:
427:chemical reaction
394:
393:
390:
389:
293:metabolic pathway
195:
194:
191:
190:
186:structure summary
3003:
2963:
2962:
2954:
2826:Hanes–Woolf plot
2769:Enzyme activator
2764:Enzyme inhibitor
2738:Enzyme catalysis
2682:
2675:
2668:
2659:
2562:Xanthine oxidase
2349:Aldose reductase
2251:
2244:
2237:
2228:
2143:
2136:
2129:
2120:
2102:
2087:
2072:
2052:
2045:
2038:
2029:
2006:
1977:
1940:
1922:
1888:
1887:
1877:
1837:
1828:
1827:
1817:
1785:
1779:
1778:
1768:
1759:(17): 10609–17.
1744:
1735:
1734:
1727:
1721:
1720:
1718:
1717:
1701:
1692:
1691:
1673:
1649:
1643:
1642:
1632:
1609:The EMBO Journal
1600:
1594:
1593:
1583:
1574:(18): 5793–800.
1559:
1553:
1552:
1532:
1526:
1525:
1515:
1483:
1464:
1463:
1453:
1429:
1423:
1422:
1412:
1403:(25): 17531–41.
1388:
1382:
1381:
1371:
1354:(Pt 2): 777–84.
1339:
1333:
1332:
1307:(8127): 1183–4.
1296:
1290:
1289:
1279:
1269:
1237:
1224:
1223:
1213:
1173:
1167:
1166:
1164:
1162:
1151:
1145:
1144:
1134:
1110:
1099:
1098:
1088:
1070:
1061:
1046:
1045:
1009:
1000:
999:
981:
975:
974:
964:
941:The EMBO Journal
932:
871:hemolytic anemia
752:
740:
723:hydrogen bonding
698:cis conformation
624:Enzyme structure
618:4-hydroxynonenal
589:plastidic stroma
537:hemolytic anemia
453:
449:
433:
347:
197:
134:
38:
26:
3011:
3010:
3006:
3005:
3004:
3002:
3001:
3000:
2971:
2970:
2969:
2957:
2949:
2947:
2942:
2854:Oxidoreductases
2840:
2816:Enzyme kinetics
2804:
2800:List of enzymes
2773:
2742:
2713:Catalytic triad
2691:
2686:
2656:
2651:
2627:
2599:
2571:
2567:Alcohol oxidase
2552:Glucose oxidase
2533:
2500:
2269:
2258:Oxidoreductases
2255:
2225:
2220:
2189:
2163:
2147:
2117:
2112:
2109:
2103:
2094:
2088:
2079:
2073:
2059:
2056:
2014:
2009:
1980:
1943:
1900:
1896:
1894:Further reading
1891:
1839:
1838:
1831:
1787:
1786:
1782:
1746:
1745:
1738:
1729:
1728:
1724:
1715:
1713:
1703:
1702:
1695:
1651:
1650:
1646:
1615:(12): 1304–20.
1602:
1601:
1597:
1561:
1560:
1556:
1534:
1533:
1529:
1492:Protein Science
1485:
1484:
1467:
1431:
1430:
1426:
1390:
1389:
1385:
1341:
1340:
1336:
1298:
1297:
1293:
1239:
1238:
1227:
1175:
1174:
1170:
1160:
1158:
1153:
1152:
1148:
1112:
1111:
1102:
1068:
1063:
1062:
1049:
1020:(9606): 64–74.
1011:
1010:
1003:
996:
983:
982:
978:
934:
933:
929:
925:
908:
855:and associated
853:enzyme activity
845:
779:
766:
765:
764:
763:
758:
757:
756:
753:
745:
744:
741:
714:
626:
600:
545:
528:Clinically, an
491:red blood cells
470:(see image), a
447:
443:
46:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
3009:
3007:
2999:
2998:
2993:
2988:
2983:
2973:
2972:
2968:
2967:
2944:
2943:
2941:
2940:
2927:
2914:
2901:
2888:
2875:
2862:
2848:
2846:
2842:
2841:
2839:
2838:
2833:
2828:
2823:
2818:
2812:
2810:
2806:
2805:
2803:
2802:
2797:
2792:
2787:
2781:
2779:
2778:Classification
2775:
2774:
2772:
2771:
2766:
2761:
2756:
2750:
2748:
2744:
2743:
2741:
2740:
2735:
2730:
2725:
2720:
2715:
2710:
2705:
2699:
2697:
2693:
2692:
2687:
2685:
2684:
2677:
2670:
2662:
2653:
2652:
2650:
2649:
2644:
2638:
2636:
2629:
2628:
2626:
2625:
2620:
2614:
2612:
2601:
2600:
2598:
2597:
2592:
2586:
2584:
2573:
2572:
2570:
2569:
2564:
2559:
2554:
2548:
2546:
2535:
2534:
2532:
2531:
2526:
2521:
2515:
2513:
2502:
2501:
2499:
2498:
2493:
2492:
2491:
2486:
2476:
2475:
2474:
2469:
2452:
2451:
2446:
2441:
2436:
2431:
2426:
2421:
2416:
2411:
2406:
2401:
2396:
2391:
2386:
2381:
2376:
2371:
2366:
2361:
2356:
2351:
2346:
2345:
2344:
2339:
2334:
2329:
2324:
2319:
2314:
2304:
2299:
2294:
2288:
2286:
2271:
2270:
2256:
2254:
2253:
2246:
2239:
2231:
2222:
2221:
2219:
2218:
2213:
2208:
2203:
2197:
2195:
2191:
2190:
2188:
2187:
2182:
2177:
2171:
2169:
2165:
2164:
2148:
2146:
2145:
2138:
2131:
2123:
2114:
2113:
2111:
2110:
2104:
2097:
2095:
2089:
2082:
2080:
2074:
2067:
2064:
2061:
2060:
2057:
2055:
2054:
2047:
2040:
2032:
2026:
2025:
2020:
2013:
2012:External links
2010:
2008:
2007:
1978:
1941:
1907:Human Mutation
1897:
1895:
1892:
1890:
1889:
1829:
1780:
1736:
1722:
1693:
1644:
1595:
1554:
1527:
1498:(8): 1403–11.
1465:
1424:
1383:
1334:
1291:
1225:
1168:
1146:
1125:(3): 293–303.
1100:
1047:
1001:
994:
976:
926:
924:
921:
920:
919:
914:
907:
904:
844:
841:
789:enzyme of the
778:
775:
760:
759:
754:
747:
746:
742:
735:
734:
733:
732:
731:
713:
710:
686:glutamic acids
625:
622:
598:
544:
541:
515:adrenal glands
511:adipose tissue
507:mammary glands
464:
463:
392:
391:
388:
387:
382:
376:
375:
370:
364:
363:
358:
352:
351:
343:
342:
333:
327:
326:
315:
308:
307:
302:
296:
295:
290:
284:
283:
278:
272:
271:
266:
260:
259:
254:
248:
247:
242:
236:
235:
231:
230:
225:
219:
218:
213:
207:
206:
202:
201:
193:
192:
189:
188:
183:
177:
176:
163:
157:
156:
146:
139:
138:
130:
129:
116:
110:
109:
104:
98:
97:
92:
86:
85:
80:
73:
72:
67:
61:
60:
57:
53:
52:
48:
47:
39:
31:
30:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3008:
2997:
2994:
2992:
2989:
2987:
2984:
2982:
2979:
2978:
2976:
2966:
2961:
2956:
2952:
2938:
2934:
2933:
2928:
2925:
2921:
2920:
2915:
2912:
2908:
2907:
2902:
2899:
2895:
2894:
2889:
2886:
2882:
2881:
2876:
2873:
2869:
2868:
2863:
2860:
2856:
2855:
2850:
2849:
2847:
2843:
2837:
2834:
2832:
2829:
2827:
2824:
2822:
2819:
2817:
2814:
2813:
2811:
2807:
2801:
2798:
2796:
2795:Enzyme family
2793:
2791:
2788:
2786:
2783:
2782:
2780:
2776:
2770:
2767:
2765:
2762:
2760:
2759:Cooperativity
2757:
2755:
2752:
2751:
2749:
2745:
2739:
2736:
2734:
2731:
2729:
2726:
2724:
2721:
2719:
2718:Oxyanion hole
2716:
2714:
2711:
2709:
2706:
2704:
2701:
2700:
2698:
2694:
2690:
2683:
2678:
2676:
2671:
2669:
2664:
2663:
2660:
2648:
2645:
2643:
2640:
2639:
2637:
2634:
2630:
2624:
2621:
2619:
2616:
2615:
2613:
2610:
2606:
2602:
2596:
2593:
2591:
2588:
2587:
2585:
2582:
2578:
2574:
2568:
2565:
2563:
2560:
2558:
2555:
2553:
2550:
2549:
2547:
2544:
2540:
2536:
2530:
2527:
2525:
2522:
2520:
2517:
2516:
2514:
2511:
2507:
2503:
2497:
2494:
2490:
2487:
2485:
2482:
2481:
2480:
2477:
2473:
2470:
2468:
2465:
2464:
2463:
2460:
2458:
2454:
2453:
2450:
2447:
2445:
2442:
2440:
2437:
2435:
2432:
2430:
2427:
2425:
2422:
2420:
2417:
2415:
2412:
2410:
2407:
2405:
2402:
2400:
2397:
2395:
2392:
2390:
2387:
2385:
2382:
2380:
2377:
2375:
2372:
2370:
2367:
2365:
2362:
2360:
2357:
2355:
2352:
2350:
2347:
2343:
2340:
2338:
2335:
2333:
2330:
2328:
2325:
2323:
2320:
2318:
2315:
2313:
2310:
2309:
2308:
2305:
2303:
2300:
2298:
2295:
2293:
2290:
2289:
2287:
2284:
2280:
2276:
2272:
2267:
2263:
2259:
2252:
2247:
2245:
2240:
2238:
2233:
2232:
2229:
2217:
2216:Transaldolase
2214:
2212:
2211:Transketolase
2209:
2207:
2204:
2202:
2199:
2198:
2196:
2192:
2186:
2183:
2181:
2178:
2176:
2173:
2172:
2170:
2166:
2162:
2159:
2155:
2151:
2144:
2139:
2137:
2132:
2130:
2125:
2124:
2121:
2107:
2101:
2096:
2092:
2086:
2081:
2077:
2071:
2066:
2062:
2053:
2048:
2046:
2041:
2039:
2034:
2033:
2030:
2024:
2021:
2019:
2016:
2015:
2011:
2004:
2000:
1996:
1992:
1989:(8): 711–20.
1988:
1985:(in French).
1984:
1979:
1975:
1971:
1967:
1963:
1959:
1955:
1952:(4): 585–91.
1951:
1947:
1942:
1938:
1934:
1930:
1926:
1921:
1916:
1913:(3): 159–67.
1912:
1908:
1904:
1899:
1898:
1893:
1885:
1881:
1876:
1871:
1867:
1863:
1859:
1855:
1851:
1847:
1843:
1836:
1834:
1830:
1825:
1821:
1816:
1811:
1807:
1803:
1799:
1795:
1791:
1784:
1781:
1776:
1772:
1767:
1762:
1758:
1754:
1750:
1743:
1741:
1737:
1732:
1726:
1723:
1712:on 2018-01-02
1711:
1707:
1700:
1698:
1694:
1689:
1685:
1681:
1677:
1672:
1667:
1664:(2): 174–81.
1663:
1659:
1658:FASEB Journal
1655:
1648:
1645:
1640:
1636:
1631:
1626:
1622:
1618:
1614:
1610:
1606:
1599:
1596:
1591:
1587:
1582:
1577:
1573:
1569:
1565:
1558:
1555:
1550:
1546:
1542:
1538:
1531:
1528:
1523:
1519:
1514:
1509:
1505:
1501:
1497:
1493:
1489:
1482:
1480:
1478:
1476:
1474:
1472:
1470:
1466:
1461:
1457:
1452:
1447:
1444:(5): 3342–7.
1443:
1439:
1435:
1428:
1425:
1420:
1416:
1411:
1406:
1402:
1398:
1394:
1387:
1384:
1379:
1375:
1370:
1365:
1361:
1357:
1353:
1349:
1345:
1338:
1335:
1330:
1326:
1322:
1318:
1314:
1310:
1306:
1302:
1295:
1292:
1287:
1283:
1278:
1273:
1268:
1263:
1259:
1255:
1251:
1247:
1243:
1236:
1234:
1232:
1230:
1226:
1221:
1217:
1212:
1207:
1203:
1199:
1195:
1191:
1187:
1183:
1179:
1172:
1169:
1156:
1150:
1147:
1142:
1138:
1133:
1128:
1124:
1120:
1116:
1109:
1107:
1105:
1101:
1096:
1092:
1087:
1082:
1078:
1074:
1067:
1060:
1058:
1056:
1054:
1052:
1048:
1043:
1039:
1035:
1031:
1027:
1023:
1019:
1015:
1008:
1006:
1002:
997:
991:
987:
980:
977:
972:
968:
963:
958:
954:
950:
947:(3): 547–53.
946:
942:
938:
931:
928:
922:
918:
915:
913:
910:
909:
905:
903:
901:
897:
893:
883:
878:
876:
872:
868:
864:
862:
858:
854:
850:
842:
840:
838:
835:
831:
826:
824:
820:
816:
812:
807:
802:
798:
796:
792:
788:
787:rate-limiting
784:
776:
774:
771:
751:
739:
730:
728:
724:
718:
711:
709:
706:
701:
699:
694:
689:
687:
683:
679:
675:
670:
666:
661:
659:
655:
651:
647:
643:
635:
630:
623:
621:
619:
615:
611:
607:
606:
601:
595:. A modified
594:
590:
586:
582:
577:
575:
571:
566:
562:
558:
554:
550:
542:
540:
538:
534:
531:
526:
524:
520:
516:
512:
508:
504:
500:
496:
492:
488:
484:
481:
477:
473:
469:
461:
457:
441:
437:
431:
430:
429:
428:
424:
420:
417:
413:
410:
406:
402:
398:
386:
383:
381:
377:
374:
371:
369:
365:
362:
359:
357:
353:
348:
344:
341:
337:
334:
332:
331:Gene Ontology
328:
325:
322:
319:
316:
313:
309:
306:
303:
301:
297:
294:
291:
289:
285:
282:
279:
277:
273:
270:
269:NiceZyme view
267:
265:
261:
258:
255:
253:
249:
246:
243:
241:
237:
232:
229:
226:
224:
220:
217:
214:
212:
208:
203:
198:
187:
184:
182:
178:
175:
171:
167:
164:
162:
158:
154:
150:
147:
144:
140:
135:
131:
128:
124:
120:
117:
115:
111:
108:
105:
103:
99:
96:
93:
91:
87:
84:
81:
78:
74:
71:
68:
66:
62:
58:
54:
49:
45:
44:
37:
32:
27:
22:
2932:Translocases
2929:
2916:
2903:
2890:
2877:
2867:Transferases
2864:
2851:
2708:Binding site
2455:
2378:
2194:nonoxidative
2174:
2105:
2090:
2075:
1986:
1982:
1949:
1945:
1910:
1906:
1849:
1845:
1797:
1793:
1783:
1756:
1752:
1725:
1714:. Retrieved
1710:the original
1661:
1657:
1647:
1612:
1608:
1598:
1571:
1567:
1557:
1543:(1): 43–48.
1540:
1536:
1530:
1495:
1491:
1441:
1437:
1427:
1400:
1396:
1386:
1351:
1347:
1337:
1304:
1300:
1294:
1249:
1245:
1188:(1): 18577.
1185:
1181:
1171:
1159:. Retrieved
1149:
1122:
1118:
1076:
1072:
1017:
1013:
985:
979:
944:
940:
930:
891:
888:
865:
846:
827:
823:erythrocytes
803:
799:
794:
790:
780:
767:
719:
715:
702:
690:
664:
662:
658:Rossman fold
654:binding site
639:
613:
610:tuberculosis
603:
578:
546:
527:
476:erythrocytes
465:
404:
400:
396:
395:
257:BRENDA entry
41:
2703:Active site
2583:as acceptor
2058:PDB gallery
1252:(7): e625.
1161:13 December
806:acetylation
785:and is the
705:enzymopathy
593:peroxisomes
576:infection.
555:. Multiple
503:isoprenoids
487:glutathione
245:IntEnz view
205:Identifiers
51:Identifiers
2975:Categories
2906:Isomerases
2880:Hydrolases
2747:Regulation
2510:cytochrome
2150:Metabolism
1716:2012-06-26
923:References
875:fava beans
777:Regulation
682:histidines
513:, and the
452:6-phospho-
314:structures
281:KEGG entry
228:9001-40-5
149:structures
2785:EC number
2581:disulfide
2168:oxidative
1974:221484452
1852:: 32734.
1119:Structure
650:tetramers
495:oxidative
480:co-enzyme
423:catalyzes
416:cytosolic
234:Databases
107:PDOC00067
95:IPR022674
2981:EC 1.1.1
2809:Kinetics
2733:Cofactor
2696:Activity
2545:acceptor
2512:acceptor
2489:11β-HSD2
2484:11β-HSD1
2285:acceptor
2003:15506519
1937:46431236
1884:27586085
1824:31431543
1688:38768580
1639:24769394
1522:18493020
1419:18434308
1329:31214682
1286:17637841
1246:PLOS ONE
1220:31819097
1141:10745013
1095:15858258
1042:29165746
1034:18177777
906:See also
892:In vitro
861:isoforms
839:(HIF1).
727:stacking
678:arginine
581:isoforms
574:malarial
565:isoforms
549:bacteria
530:X-linked
493:against
412:1.1.1.49
385:proteins
373:articles
361:articles
318:RCSB PDB
216:1.1.1.49
166:RCSB PDB
90:InterPro
2965:Biology
2919:Ligases
2689:Enzymes
2609:quinone
2161:enzymes
2156:·
1966:8826878
1929:8364584
1875:5009355
1854:Bibcode
1815:7261372
1800:(595).
1775:9553122
1680:8119488
1630:4194121
1590:4153382
1513:2492815
1460:8429010
1378:9480890
1369:1219205
1277:1913203
1254:Bibcode
1211:6901466
1190:Bibcode
971:2001672
770:class I
693:proline
674:lysines
585:cytosol
414:) is a
340:QuickGO
305:profile
288:MetaCyc
223:CAS no.
102:PROSITE
70:PF00479
2951:Portal
2893:Lyases
2647:L2HGDH
2633:1.1.99
2543:oxygen
2467:3β-HSD
2001:
1972:
1964:
1935:
1927:
1882:
1872:
1822:
1812:
1773:
1686:
1678:
1637:
1627:
1588:
1520:
1510:
1458:
1417:
1376:
1366:
1327:
1319:
1301:Lancet
1284:
1274:
1218:
1208:
1157:. NCBI
1139:
1093:
1040:
1032:
1014:Lancet
992:
969:
962:452682
959:
591:, and
587:, the
553:humans
419:enzyme
368:PubMed
350:Search
336:AmiGO
324:PDBsum
264:ExPASy
252:BRENDA
240:IntEnz
211:EC no.
181:PDBsum
155:
145:
127:SUPFAM
83:CL0063
59:G6PD_N
56:Symbol
2845:Types
2605:1.1.5
2577:1.1.4
2539:1.1.3
2506:1.1.2
2472:NSDHL
2275:1.1.1
1970:S2CID
1933:S2CID
1684:S2CID
1325:S2CID
1321:86896
1069:(PDF)
1038:S2CID
819:NADPH
811:SIRT2
762:cyan.
642:dimer
460:NADPH
421:that
405:G6PDH
300:PRIAM
123:SCOPe
114:SCOP2
2937:list
2930:EC7
2924:list
2917:EC6
2911:list
2904:EC5
2898:list
2891:EC4
2885:list
2878:EC3
2872:list
2865:EC2
2859:list
2852:EC1
2322:1B10
2283:NADP
2268:1.1)
2106:2bhl
2091:2bh9
2076:1qki
1999:PMID
1962:PMID
1925:PMID
1880:PMID
1820:PMID
1771:PMID
1676:PMID
1635:PMID
1586:PMID
1518:PMID
1456:PMID
1415:PMID
1374:PMID
1317:PMID
1282:PMID
1216:PMID
1163:2015
1137:PMID
1091:PMID
1030:PMID
990:ISBN
967:PMID
896:DHEA
691:The
684:, 2
680:, 2
676:, 1
634:2BHL
440:NADP
425:the
401:G6PD
380:NCBI
321:PDBe
276:KEGG
174:PDBj
170:PDBe
153:ECOD
143:Pfam
119:1dpg
79:clan
77:Pfam
65:Pfam
2496:17β
2479:11β
2342:7A2
2337:1C4
2332:1C3
2327:1C1
2317:1B1
2312:1A1
2279:NAD
1991:doi
1987:327
1954:doi
1915:doi
1870:PMC
1862:doi
1810:PMC
1802:doi
1761:doi
1757:273
1666:doi
1625:PMC
1617:doi
1576:doi
1572:249
1545:doi
1508:PMC
1500:doi
1446:doi
1442:268
1405:doi
1401:283
1364:PMC
1356:doi
1352:330
1309:doi
1272:PMC
1262:doi
1206:PMC
1198:doi
1127:doi
1081:doi
1022:doi
1018:371
957:PMC
949:doi
599:420
551:to
462:+ H
407:) (
403:or
356:PMC
312:PDB
161:PDB
2977::
2607::
2579::
2541::
2508::
2462:3β
2277::
2266:EC
2260::
2152::
1997:.
1968:.
1960:.
1950:94
1948:.
1931:.
1923:.
1909:.
1905:.
1878:.
1868:.
1860:.
1848:.
1844:.
1832:^
1818:.
1808:.
1798:12
1796:.
1792:.
1769:.
1755:.
1751:.
1739:^
1696:^
1682:.
1674:.
1660:.
1656:.
1633:.
1623:.
1613:33
1611:.
1607:.
1584:.
1570:.
1566:.
1541:19
1539:.
1516:.
1506:.
1496:17
1494:.
1490:.
1468:^
1454:.
1440:.
1436:.
1413:.
1399:.
1395:.
1372:.
1362:.
1350:.
1346:.
1323:.
1315:.
1303:.
1280:.
1270:.
1260:.
1248:.
1244:.
1228:^
1214:.
1204:.
1196:.
1184:.
1180:.
1135:.
1121:.
1117:.
1103:^
1089:.
1077:61
1075:.
1071:.
1050:^
1036:.
1028:.
1016:.
1004:^
965:.
955:.
945:10
943:.
939:.
825:.
797:.
646:pH
539:.
509:,
458:+
450:⇌
442:+
438:+
409:EC
338:/
172:;
168:;
151:/
125:/
121:/
2953::
2939:)
2935:(
2926:)
2922:(
2913:)
2909:(
2900:)
2896:(
2887:)
2883:(
2874:)
2870:(
2861:)
2857:(
2681:e
2674:t
2667:v
2459::
2281:/
2264:(
2250:e
2243:t
2236:v
2142:e
2135:t
2128:v
2051:e
2044:t
2037:v
2005:.
1993::
1976:.
1956::
1939:.
1917::
1911:2
1886:.
1864::
1856::
1850:6
1826:.
1804::
1777:.
1763::
1733:.
1719:.
1690:.
1668::
1662:8
1641:.
1619::
1592:.
1578::
1551:.
1547::
1524:.
1502::
1462:.
1448::
1421:.
1407::
1380:.
1358::
1331:.
1311::
1305:1
1288:.
1264::
1256::
1250:2
1222:.
1200::
1192::
1186:9
1165:.
1143:.
1129::
1123:8
1097:.
1083::
1044:.
1024::
998:.
973:.
951::
597:F
454:D
448:O
446:2
444:H
434:D
399:(
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.