321:
164:
544:
452:
358:
260:
39:
142:
and microscopic blood vessels that form on the surfaces of a wound during the healing process. Granulation tissue typically grows from the base of a wound and is able to fill wounds of almost any size. Examples of granulation tissue can be seen in
438:, and protect the healing tissue from pathogenic infection. This is necessary both to aid the healing process and to protect against invading pathogens, as the wound often does not have an effective skin barrier to act as a first line of defense.
512:
It is necessary for a network of blood vessels to be established as soon as possible to provide the growing tissue with nutrients, to take away cellular wastes, and transport new leukocytes to the area.
630:
211:
Granulation tissue is composed of tissue matrix supporting a variety of cell types, most of which can be associated with one of the following functions:
682:
320:
770:
473:
379:
281:
56:
612:
499:
405:
307:
122:
103:
336:, a weaker form of the structural protein that can be produced rapidly. This is later replaced by the stronger, long-stranded
75:
477:
383:
285:
60:
765:
651:
82:
737:
27:
581:
675:
151:. Its histological appearance is characterized by proliferation of fibroblasts and thin-walled, delicate capillaries (
462:
368:
270:
627:
89:
481:
466:
387:
372:
289:
274:
49:
71:
324:
Histopathology of granulation tissue at 11 days after injury, showing fibroblasts, hemorrhage and lymphocytes.
668:
517:, the main cells that deposit granulation tissue, depend on oxygen to proliferate and lay down the new
518:
249:
216:
638:
189:
163:
144:
96:
608:
333:
139:
435:
634:
337:
744:
707:
759:
717:
691:
548:
223:
172:
543:
732:
533:
525:
229:
152:
537:
529:
451:
431:
423:
419:
357:
329:
259:
38:
514:
427:
148:
551:, with substantial variation depending on wound size and healing conditions.
727:
573:
196:
20:
328:
The extracellular matrix of granulation tissue is created and modified by
179:
light red or dark pink, being perfused with new capillary loops or "buds";
702:
167:
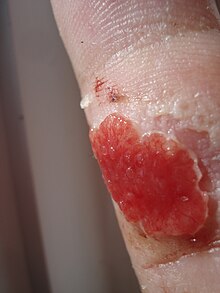
Example of granulation tissue from a cut on a finger with "proud flesh".
155:), and infiltrated inflammatory cells in a loose extracellular matrix.
542:
319:
162:
722:
660:
341:
664:
445:
351:
253:
32:
637:Chapter 9 from an "Introduction to Pathology" on a
63:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
26:"Proud flesh" redirects here. For other uses, see
536:. These branch out in a systematic way, forming
532:quickly grow into the tissue from older, intact
418:The main immune cells active in the tissue are
240:) is informally referred to as "proud flesh".
676:
547:Approximate times of the different phases of
8:
480:. Unsourced material may be challenged and
386:. Unsourced material may be challenged and
288:. Unsourced material may be challenged and
683:
669:
661:
607:. Jaypee Brother Medical Pub. p. 18.
332:. Initially, it consists of a network of
16:New tissue that forms on a wound's surface
500:Learn how and when to remove this message
406:Learn how and when to remove this message
308:Learn how and when to remove this message
123:Learn how and when to remove this message
565:
188:bumpy (granular) in appearance, due to
555:is seen in green box at days to weeks.
584:from the original on 16 November 2018
7:
478:adding citations to reliable sources
384:adding citations to reliable sources
286:adding citations to reliable sources
61:adding citations to reliable sources
14:
430:are also present. These work to
236:An excess of granulation tissue (
524:In vascularisation, also called
450:
356:
258:
37:
574:"Granulation Tissue Definition"
48:needs additional citations for
171:During the migratory phase of
1:
553:Granulation tissue formation
28:Proud Flesh (disambiguation)
650:Reference list is found on
605:Srb's Manual of Surgery, 4e
789:
771:Connective tissue diseases
247:
25:
18:
698:
175:, granulation tissue is:
19:Not to be confused with
556:
325:
202:painless when healthy;
168:
603:Bhat, Sriram (2013).
546:
323:
166:
766:Anatomical pathology
540:with other vessels.
519:extracellular matrix
474:improve this section
380:improve this section
282:improve this section
250:Extracellular matrix
244:Extracellular matrix
217:extracellular matrix
190:punctate hemorrhages
72:"Granulation tissue"
57:improve this article
639:Tuskegee University
145:pyogenic granulomas
713:Granulation tissue
633:2010-09-27 at the
628:Healing and Repair
557:
340:, as evidenced in
326:
182:soft to the touch;
169:
136:Granulation tissue
753:
752:
530:endothelial cells
510:
509:
502:
426:, although other
416:
415:
408:
334:type-III collagen
318:
317:
310:
222:operation of the
140:connective tissue
133:
132:
125:
107:
778:
685:
678:
671:
662:
655:
648:
642:
625:
619:
618:
600:
594:
593:
591:
589:
570:
505:
498:
494:
491:
485:
454:
446:
411:
404:
400:
397:
391:
360:
352:
313:
306:
302:
299:
293:
262:
254:
128:
121:
117:
114:
108:
106:
65:
41:
33:
788:
787:
781:
780:
779:
777:
776:
775:
756:
755:
754:
749:
738:Intussusception
694:
689:
659:
658:
652:image main page
649:
645:
635:Wayback Machine
626:
622:
615:
602:
601:
597:
587:
585:
572:
571:
567:
562:
506:
495:
489:
486:
471:
455:
444:
442:Vascularization
434:old or damaged
412:
401:
395:
392:
377:
361:
350:
338:type-I collagen
314:
303:
297:
294:
279:
263:
252:
246:
230:vascularisation
209:
161:
129:
118:
112:
109:
66:
64:
54:
42:
31:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
786:
785:
782:
774:
773:
768:
758:
757:
751:
750:
748:
747:
745:Vasculogenesis
742:
741:
740:
730:
725:
720:
715:
710:
708:Maggot therapy
705:
699:
696:
695:
690:
688:
687:
680:
673:
665:
657:
656:
643:
620:
613:
595:
564:
563:
561:
558:
508:
507:
458:
456:
449:
443:
440:
414:
413:
364:
362:
355:
349:
346:
316:
315:
266:
264:
257:
248:Main article:
245:
242:
238:caro luxurians
234:
233:
227:
220:
208:
205:
204:
203:
200:
193:
186:
183:
180:
160:
157:
131:
130:
45:
43:
36:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
784:
783:
772:
769:
767:
764:
763:
761:
746:
743:
739:
736:
735:
734:
731:
729:
726:
724:
721:
719:
718:Growth factor
716:
714:
711:
709:
706:
704:
701:
700:
697:
693:
692:Wound healing
686:
681:
679:
674:
672:
667:
666:
663:
653:
647:
644:
640:
636:
632:
629:
624:
621:
616:
614:9789350259443
610:
606:
599:
596:
583:
579:
575:
569:
566:
559:
554:
550:
549:wound healing
545:
541:
539:
535:
534:blood vessels
531:
527:
522:
520:
516:
504:
501:
493:
490:February 2024
483:
479:
475:
469:
468:
464:
459:This section
457:
453:
448:
447:
441:
439:
437:
433:
429:
425:
421:
410:
407:
399:
396:February 2024
389:
385:
381:
375:
374:
370:
365:This section
363:
359:
354:
353:
347:
345:
343:
339:
335:
331:
322:
312:
309:
301:
298:February 2024
291:
287:
283:
277:
276:
272:
267:This section
265:
261:
256:
255:
251:
243:
241:
239:
231:
228:
225:
224:immune system
221:
218:
215:formation of
214:
213:
212:
206:
201:
198:
195:pulsatile on
194:
191:
187:
184:
181:
178:
177:
176:
174:
173:wound healing
165:
158:
156:
154:
150:
146:
141:
137:
127:
124:
116:
105:
102:
98:
95:
91:
88:
84:
81:
77:
74: –
73:
69:
68:Find sources:
62:
58:
52:
51:
46:This article
44:
40:
35:
34:
29:
22:
733:Angiogenesis
712:
646:
623:
604:
598:
586:. Retrieved
577:
568:
552:
526:angiogenesis
523:
511:
496:
487:
472:Please help
460:
417:
402:
393:
378:Please help
366:
327:
304:
295:
280:Please help
268:
237:
235:
210:
170:
153:angiogenesis
135:
134:
119:
110:
100:
93:
86:
79:
67:
55:Please help
50:verification
47:
538:anastomoses
515:Fibroblasts
432:phagocytize
424:neutrophils
420:macrophages
330:fibroblasts
149:pulp polyps
760:Categories
588:25 October
560:References
428:leukocytes
159:Appearance
83:newspapers
728:Stem cell
461:does not
367:does not
269:does not
207:Structure
197:palpation
21:Granuloma
703:Fibrosis
631:Archived
582:Archived
348:Immunity
344:tissue.
113:May 2020
641:website
578:Memidex
482:removed
467:sources
388:removed
373:sources
290:removed
275:sources
138:is new
97:scholar
611:
436:tissue
185:moist;
99:
92:
85:
78:
70:
104:JSTOR
90:books
723:Scar
609:ISBN
590:2014
465:any
463:cite
422:and
371:any
369:cite
342:scar
273:any
271:cite
147:and
76:news
476:by
382:by
284:by
59:by
762::
580:.
576:.
528:,
521:.
684:e
677:t
670:v
654:.
617:.
592:.
503:)
497:(
492:)
488:(
484:.
470:.
409:)
403:(
398:)
394:(
390:.
376:.
311:)
305:(
300:)
296:(
292:.
278:.
232:;
226:;
219:;
199:;
192:;
126:)
120:(
115:)
111:(
101:·
94:·
87:·
80:·
53:.
30:.
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.