413:
235:
40:
404:. The normal triglyceride level is less than 150 mg/dL (1.7 mmol/L). Once diagnosed, other blood tests are usually required to determine whether the raised triglyceride level is caused by other underlying disorders ("secondary hypertriglyceridemia") or whether no such underlying cause exists ("primary hypertriglyceridaemia"). There is a hereditary predisposition to both primary and secondary hypertriglyceridemia.
231:. Once diagnosed, other blood tests are usually required to determine whether the raised triglyceride level is caused by other underlying disorders ("secondary hypertriglyceridemia") or whether no such underlying cause exists ("primary hypertriglyceridemia"). There is a hereditary predisposition to both primary and secondary hypertriglyceridemia.
1247:
European
Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation; Reiner, Zeljko; Catapano, Alberico L.; De Backer, Guy; Graham, Ian; Taskinen, Marja-Riitta; Wiklund, Olov; Agewall, Stefan; Alegria, Eduardo; Chapman, M. John; Durrington, Paul; Erdine, Serap; Halcox, Julian; Hobbs, Richard;
577:
class may be used in conjunction, with statins being the main drug treatment for moderate hypertriglyceridemia where reduction of cardiovascular risk is required. Medications are recommended in those with high levels of triglycerides that are not corrected with lifestyle modifications, with
248:
may occur in people whose triglyceride levels are above 1000 mg/dL (11.3 mmol/L). Hypertriglyceridemia is associated with 1–4% of all cases of pancreatitis. The symptoms are similar to pancreatitis secondary to other causes, although the presence of xanthomas or risk factors for
216:), and neurological symptoms. Some experience attacks of abdominal pain that may be mild episodes of pancreatitis. Eruptive xanthomas are 2–5 mm papules, often with a red ring around them, that occur in clusters on the skin of the trunk, buttocks and extremities.
560:
The decision to treat hypertriglyceridemia with medication depends on the levels and on the presence of other risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Very high levels that would increase the risk of pancreatitis is treated with a drug from the
1627:
1604:
1250:"ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: the Task Force for the management of dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS)"
545:
Lifestyle changes including weight loss, exercise and dietary modification may improve hypertriglyceridemia. This may include dietary changes such as restriction of fat and carbohydrates (specifically
168:
1025:
Chou R, Dana T, Blazina I, Daeges M, Bougatsos C, Jeanne TL (October 2016). "Screening for
Dyslipidemia in Younger Adults: A Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force".
1426:
Abourbih S, Filion KB, Joseph L, Schiffrin EL, Rinfret S, Poirier P, et al. (October 2009). "Effect of fibrates on lipid profiles and cardiovascular outcomes: a systematic review".
85:
1547:
Thorp JG, Campos AI, Grotzinger AD, Gerring ZF, An J, Ong JS, et al. (October 2021). "Symptom-level modelling unravels the shared genetic architecture of anxiety and depression".
196:
Most people with elevated triglycerides experience no symptoms. Some forms of primary hypertriglyceridemia can lead to specific symptoms: both familial chylomicronemia and primary
831:
Garg A, Grundy SM, Unger RH (October 1992). "Comparison of effects of high and low carbohydrate diets on plasma lipoproteins and insulin sensitivity in patients with mild NIDDM".
1754:
961:
1295:
Berglund, Lars; Brunzell, John D.; Goldberg, Anne C.; Goldberg, Ira J.; Sacks, Frank; Murad, Mohammad Hassan; Stalenhoef, Anton F. H.; Endocrine society (September 2012).
1461:
Jun M, Foote C, Lv J, Neal B, Patel A, Nicholls SJ, et al. (May 2010). "Effects of fibrates on cardiovascular outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis".
144:
molecule in most organisms. Hypertriglyceridemia occurs in various physiologic conditions and in various diseases, and high triglyceride levels are associated with
1855:
1967:
534:
175:
and contribute significantly to cardiovascular mortality in industrialised countries as of 2021. Extreme triglyceride levels also increase the risk of
1747:
1352:
Davidson MH, Cannon CP, Armani AM (28 January 2008). "Pharmacological
Therapy for Cardiovascular Disease". In Davidson MH, Toth PP, Maki KC (eds.).
1212:
Gill JM, Herd SL, Tsetsonis NV, Hardman AE (February 2002). "Are the reductions in triacylglycerol and insulin levels after exercise related?".
424:
1369:
1504:
Blair HA, Dhillon S (October 2014). "Omega-3 carboxylic acids (Epanova): a review of its use in patients with severe hypertriglyceridemia".
1003:
1962:
1740:
1642:
788:
Tsuang W, Navaneethan U, Ruiz L, Palascak JB, Gelrud A (April 2009). "Hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis: presentation and management".
1801:
583:
220:
causes larger, tuberous xanthomas; these are red or orange and occur on the elbows and knees. Palmar crease xanthomas may also occur.
343:
602:
Analysis of the genes in depression and anxiety showed those linked solely to depression were also linked to hypertriglyceridemia.
1767:
416:
339:
1816:
217:
412:
1910:
1888:
1821:
1806:
1796:
1726:
321:
1070:"Screening for Lipid Disorders in Children and Adolescents: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement"
1883:
182:
Hypertriglyceridemia itself is usually symptomless, although high levels may be associated with skin lesions known as
1941:
1763:
1936:
550:
1847:
1653:
1870:
1811:
315:
197:
64:
636:, thus corresponding to "high triglyceride levels in the blood" or "too many triglycerides in the blood".
537:
concluded that testing the general population under the age of 40 without symptoms is of unclear benefit.
157:
104:
1068:
Bibbins-Domingo K, Grossman DC, Curry SJ, Davidson KW, Epling JW, García FA, et al. (August 2016).
234:
682:
Berglund L, Brunzell JD, Goldberg AC, Goldberg IJ, Sacks F, Murad MH, Stalenhoef AF (September 2012).
1878:
1787:
401:
228:
149:
117:
1297:"Evaluation and treatment of hypertriglyceridemia: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline"
684:"Evaluation and treatment of hypertriglyceridemia: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline"
1838:
1631:
645:
361:
353:
296:
1732:
1572:
1529:
1486:
1194:
1050:
813:
615:
570:
566:
554:
305:
277:
273:
245:
205:
176:
164:
97:
1361:
1931:
1693:
1664:
1564:
1521:
1478:
1443:
1408:
1365:
1334:
1316:
1277:
1269:
1229:
1186:
1148:
1130:
1091:
1042:
969:
943:
894:
848:
805:
767:
713:
269:
52:
1556:
1513:
1470:
1435:
1398:
1353:
1324:
1308:
1261:
1221:
1178:
1138:
1122:
1081:
1034:
933:
925:
884:
840:
797:
757:
749:
703:
695:
39:
1860:
281:
145:
89:
1707:
1387:"Dietary management of dyslipidaemias. Is there any evidence for cardiovascular benefit?"
514:
8 to 12 hours. Triglyceride levels remain temporarily higher for a period after eating.
1779:
1329:
1143:
1110:
938:
913:
912:
Beigneux AP, Miyashita K, Ploug M, Blom DJ, Ai M, Linton MF, et al. (April 2017).
762:
737:
708:
683:
366:
311:
301:
109:
1636:
1474:
1182:
1956:
1902:
1576:
1354:
357:
289:
121:
69:
57:
1533:
1490:
1403:
1386:
1198:
1169:
Nordestgaard BG, Varbo A (August 2014). "Triglycerides and cardiovascular disease".
1054:
817:
586:
is another prescription drug used to treat very high levels of blood triglycerides.
1771:
1704:
626:
349:
329:
285:
238:
133:
73:
419:, showing usual ranges for triglycerides (increasing with age) in orange at right.
1658:
1439:
594:
As of 2006, the prevalence of hypertriglyceridemia in the United States was 30%.
1926:
1688:
1385:
Anagnostis P, Paschou SA, Goulis DG, Athyros VG, Karagiannis A (February 2018).
1011:
844:
453:
333:
153:
80:
1560:
1265:
1126:
620:
1669:
1621:
1617:
1613:
1517:
397:
259:
224:
93:
1320:
1273:
1134:
632:
1699:
1296:
1249:
446:
442:
1568:
1525:
1482:
1447:
1412:
1360:. Contemporary Cardiology. Totowa, New Jersey: Humana Press, Inc. pp.
1338:
1281:
1233:
1190:
1152:
1111:"Fellow's voice: Hypertriglyceridemia: Understanding the current guideline"
1095:
1086:
1069:
1046:
947:
898:
889:
872:
809:
771:
717:
929:
852:
1828:
1312:
699:
546:
381:
201:
184:
113:
1596:
801:
753:
1225:
579:
562:
511:
264:
172:
1608:
1038:
574:
325:
213:
914:"Autoantibodies against GPIHBP1 as a Cause of Hypertriglyceridemia"
457:
372:
233:
209:
163:
Chronically elevated serum triglyceride levels are a component of
137:
47:
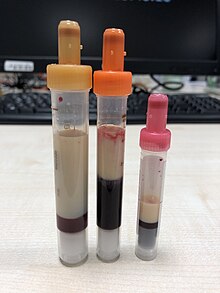
Blood samples of a young patient with extreme hypertriglyceridemia
1647:
1736:
141:
738:"Hypertriglyceridemia: its etiology, effects and treatment"
336:, leads to elevated levels of triglycerides in the blood.
169:
metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
86:
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
517:
The AHA recommends an optimal triglyceride level of 100
1586:
1301:
The
Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism
688:
The
Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism
1919:
1901:
1869:
1846:
1837:
1778:
1679:
1590:
1164:
1162:
103:
79:
63:
51:
29:
24:
877:Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine
241:, which cause hypertriglyceridemia at high level
1856:Lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency
310:Genetic predisposition; some forms of familial
1748:
736:Yuan G, Al-Shali KZ, Hegele RA (April 2007).
8:
991:Current Diagnosis & Treatment Cardiology
783:
781:
535:United States Preventive Services Task Force
427:has set guidelines for triglyceride levels:
1843:
1802:Familial apoprotein CII deficiency/Type Ib
1755:
1741:
1733:
1587:
731:
729:
727:
525:mmol/L) or lower to improve heart health.
204:), eye abnormalities (lipemia retinalis),
38:
21:
1402:
1328:
1142:
1115:American Journal of Preventive Cardiology
1085:
937:
888:
866:
864:
862:
761:
707:
677:
675:
673:
671:
669:
667:
665:
663:
661:
276:- it is one of the defined components of
1817:Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia/Type III
1506:American Journal of Cardiovascular Drugs
993:. 3rd ed. McGraw-Hill Medical, 2009. p19
790:The American Journal of Gastroenterology
429:
411:
657:
1807:Familial hypercholesterolemia/Type IIa
425:National Cholesterol Education Program
249:hypertriglyceridemia may offer clues.
140:. Triglycerides are the most abundant
1968:Medical conditions related to obesity
1822:Familial hypertriglyceridemia/Type IV
1797:Lipoprotein lipase deficiency/Type Ia
7:
375:and associated autoimmune responses
1729:(EMedicineHealth.com; October 2020)
918:The New England Journal of Medicine
324:- Deficiency of this water-soluble
132:is the presence of high amounts of
1008:Triglycerides: Why do they matter?
584:Epanova (omega-3-carboxylic acids)
171:, both of which typically involve
14:
871:Pejic RN, Lee DT (May–Jun 2006).
344:Cholesteryl ester storage disease
1942:APOA1 familial renal amyloidosis
1812:Combined hyperlipidemia/Type IIb
1428:The American Journal of Medicine
417:Reference ranges for blood tests
378:Glycogen storage disease type 1.
340:Lysosomal acid lipase deficiency
200:include skin symptoms (eruptive
33:Elevated levels of triglycerides
1404:10.1016/j.maturitas.2017.11.011
553:) and increased consumption of
218:Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia
510:These levels are tested after
16:High triglyceride blood levels
1:
1889:Chylomicron retention disease
1475:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60656-3
1183:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61177-6
557:from algae, nuts, and seeds.
471:Normal range – low risk
400:, often performed as part of
322:Lipoprotein lipase deficiency
227:, often performed as part of
1848:Hypoalphalipoproteinemia/HDL
1440:10.1016/j.amjmed.2009.03.030
1248:Kjekshus, John (July 2011).
1884:Apolipoprotein B deficiency
1871:Hypobetalipoproteinemia/LDL
1027:Annals of Internal Medicine
1004:"What's considered normal?"
845:10.2337/diabetes.41.10.1278
504:Very high – high risk
318:i.e. Type II hyperlipidemia
1984:
1963:Lipid metabolism disorders
1561:10.1038/s41562-021-01094-9
1127:10.1016/j.ajpc.2022.100322
573:as well as drugs from the
156:levels) and predispose to
1911:Barraquer–Simons syndrome
1518:10.1007/s40256-014-0090-3
582:being recommended first.
551:sugar-sweetened beverages
435:
432:
396:The diagnosis is made on
348:Certain medications e.g.
223:The diagnosis is made on
148:, even in the absence of
46:
37:
1266:10.1093/eurheartj/ehr158
1109:Koneru SC (2022-03-01).
989:Crawford, H., Micheal.
316:combined hyperlipidemia
1829:Xanthoma/Xanthomatosis
1727:Lowering Triglycerides
1549:Nature Human Behaviour
1356:Therapeutic Lipidology
1254:European Heart Journal
1087:10.1001/jama.2016.9852
890:10.3122/jabfm.19.3.310
873:"Hypertriglyceridemia"
482:Slightly above normal
420:
242:
158:cardiovascular disease
105:Differential diagnosis
1434:(10): 962.e1–962.e8.
930:10.1056/NEJMoa1611930
415:
369:(underactive thyroid)
237:
1879:Abetalipoproteinemia
1792:Hypertriglyceridemia
1788:Hypercholesterolemia
1313:10.1210/jc.2011-3213
1014:. 28 September 2012.
700:10.1210/jc.2011-3213
612:hypertriglyceridemia
208:(enlargement of the
198:mixed hyperlipidemia
150:hypercholesterolemia
130:Hypertriglyceridemia
118:hypercholesterolemia
25:Hypertriglyceridemia
1839:Hypolipoproteinemia
1469:(9729): 1875–1884.
972:on 28 February 2014
802:10.1038/ajg.2009.27
754:10.1503/cmaj.060963
646:Remnant cholesterol
571:omega-3 fatty acids
555:omega-3 fatty acids
362:protease inhibitors
354:hydrochlorothiazide
297:alcohol consumption
1937:Lipoid proteinosis
1680:External resources
1226:10.1042/cs20010204
421:
328:, that hydrolyzes
306:nephrotic syndrome
278:metabolic syndrome
274:insulin resistance
246:Acute pancreatitis
243:
206:hepatosplenomegaly
192:Signs and symptoms
177:acute pancreatitis
165:metabolic syndrome
98:metabolic syndrome
1950:
1949:
1932:Adiposis dolorosa
1897:
1896:
1717:
1716:
1555:(10): 1432–1442.
1371:978-1-58829-551-4
1260:(14): 1769–1818.
1177:(9943): 626–635.
924:(17): 1647–1658.
839:(10): 1278–1285.
508:
507:
314:such as familial
270:Diabetes mellitus
127:
126:
19:Medical condition
1975:
1844:
1768:lipid metabolism
1757:
1750:
1743:
1734:
1588:
1581:
1580:
1544:
1538:
1537:
1501:
1495:
1494:
1458:
1452:
1451:
1423:
1417:
1416:
1406:
1382:
1376:
1375:
1359:
1349:
1343:
1342:
1332:
1307:(9): 2969–2989.
1292:
1286:
1285:
1244:
1238:
1237:
1214:Clinical Science
1209:
1203:
1202:
1166:
1157:
1156:
1146:
1106:
1100:
1099:
1089:
1065:
1059:
1058:
1039:10.7326/M16-0946
1022:
1016:
1015:
1000:
994:
987:
981:
980:
978:
977:
968:. Archived from
958:
952:
951:
941:
909:
903:
902:
892:
868:
857:
856:
828:
822:
821:
785:
776:
775:
765:
748:(8): 1113–1120.
733:
722:
721:
711:
694:(9): 2969–2989.
679:
524:
520:
430:
42:
22:
1983:
1982:
1978:
1977:
1976:
1974:
1973:
1972:
1953:
1952:
1951:
1946:
1915:
1893:
1865:
1861:Tangier disease
1833:
1774:
1761:
1723:
1718:
1713:
1712:
1675:
1674:
1599:
1585:
1584:
1546:
1545:
1541:
1503:
1502:
1498:
1460:
1459:
1455:
1425:
1424:
1420:
1384:
1383:
1379:
1372:
1351:
1350:
1346:
1294:
1293:
1289:
1246:
1245:
1241:
1211:
1210:
1206:
1168:
1167:
1160:
1108:
1107:
1103:
1067:
1066:
1062:
1024:
1023:
1019:
1002:
1001:
997:
988:
984:
975:
973:
962:"Triglycerides"
960:
959:
955:
911:
910:
906:
870:
869:
860:
830:
829:
825:
787:
786:
779:
735:
734:
725:
681:
680:
659:
654:
642:
616:combining forms
608:
600:
592:
543:
531:
522:
518:
501:> 5.65
468:< 1.70
436:Interpretation
410:
394:
389:
386:HIV medications
282:central obesity
255:
194:
146:atherosclerosis
90:atherosclerosis
20:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1981:
1979:
1971:
1970:
1965:
1955:
1954:
1948:
1947:
1945:
1944:
1939:
1934:
1929:
1923:
1921:
1917:
1916:
1914:
1913:
1907:
1905:
1899:
1898:
1895:
1894:
1892:
1891:
1886:
1881:
1875:
1873:
1867:
1866:
1864:
1863:
1858:
1852:
1850:
1841:
1835:
1834:
1832:
1831:
1826:
1825:
1824:
1819:
1814:
1809:
1804:
1799:
1784:
1782:
1780:Hyperlipidemia
1776:
1775:
1762:
1760:
1759:
1752:
1745:
1737:
1731:
1730:
1722:
1721:External links
1719:
1715:
1714:
1711:
1710:
1708:article/126568
1696:
1684:
1683:
1681:
1677:
1676:
1673:
1672:
1661:
1650:
1639:
1624:
1600:
1595:
1594:
1592:
1591:Classification
1583:
1582:
1539:
1512:(5): 393–400.
1496:
1453:
1418:
1377:
1370:
1344:
1287:
1239:
1220:(2): 223–231.
1204:
1158:
1101:
1080:(6): 625–633.
1060:
1033:(8): 560–564.
1017:
995:
982:
953:
904:
883:(3): 310–316.
858:
823:
796:(4): 984–991.
777:
723:
656:
655:
653:
650:
649:
648:
641:
638:
607:
604:
599:
596:
591:
588:
542:
539:
530:
527:
506:
505:
502:
499:
498:500 or higher
495:
494:
491:
488:
484:
483:
480:
477:
473:
472:
469:
466:
465:< 150
462:
461:
450:
438:
437:
434:
409:
406:
393:
390:
388:
387:
384:
379:
376:
370:
367:Hypothyroidism
364:
346:
337:
319:
312:hyperlipidemia
308:
302:Kidney failure
299:
293:
267:
262:
256:
254:
251:
193:
190:
125:
124:
110:Hyperlipidemia
107:
101:
100:
83:
77:
76:
67:
61:
60:
55:
49:
48:
44:
43:
35:
34:
31:
27:
26:
18:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1980:
1969:
1966:
1964:
1961:
1960:
1958:
1943:
1940:
1938:
1935:
1933:
1930:
1928:
1925:
1924:
1922:
1918:
1912:
1909:
1908:
1906:
1904:
1903:Lipodystrophy
1900:
1890:
1887:
1885:
1882:
1880:
1877:
1876:
1874:
1872:
1868:
1862:
1859:
1857:
1854:
1853:
1851:
1849:
1845:
1842:
1840:
1836:
1830:
1827:
1823:
1820:
1818:
1815:
1813:
1810:
1808:
1805:
1803:
1800:
1798:
1795:
1794:
1793:
1789:
1786:
1785:
1783:
1781:
1777:
1773:
1769:
1765:
1758:
1753:
1751:
1746:
1744:
1739:
1738:
1735:
1728:
1725:
1724:
1720:
1709:
1706:
1702:
1701:
1697:
1695:
1691:
1690:
1686:
1685:
1682:
1678:
1671:
1667:
1666:
1662:
1660:
1656:
1655:
1651:
1649:
1645:
1644:
1640:
1638:
1634:
1633:
1629:
1625:
1623:
1619:
1615:
1611:
1610:
1606:
1602:
1601:
1598:
1593:
1589:
1578:
1574:
1570:
1566:
1562:
1558:
1554:
1550:
1543:
1540:
1535:
1531:
1527:
1523:
1519:
1515:
1511:
1507:
1500:
1497:
1492:
1488:
1484:
1480:
1476:
1472:
1468:
1464:
1457:
1454:
1449:
1445:
1441:
1437:
1433:
1429:
1422:
1419:
1414:
1410:
1405:
1400:
1396:
1392:
1388:
1381:
1378:
1373:
1367:
1363:
1358:
1357:
1348:
1345:
1340:
1336:
1331:
1326:
1322:
1318:
1314:
1310:
1306:
1302:
1298:
1291:
1288:
1283:
1279:
1275:
1271:
1267:
1263:
1259:
1255:
1251:
1243:
1240:
1235:
1231:
1227:
1223:
1219:
1215:
1208:
1205:
1200:
1196:
1192:
1188:
1184:
1180:
1176:
1172:
1165:
1163:
1159:
1154:
1150:
1145:
1140:
1136:
1132:
1128:
1124:
1120:
1116:
1112:
1105:
1102:
1097:
1093:
1088:
1083:
1079:
1075:
1071:
1064:
1061:
1056:
1052:
1048:
1044:
1040:
1036:
1032:
1028:
1021:
1018:
1013:
1009:
1005:
999:
996:
992:
986:
983:
971:
967:
963:
957:
954:
949:
945:
940:
935:
931:
927:
923:
919:
915:
908:
905:
900:
896:
891:
886:
882:
878:
874:
867:
865:
863:
859:
854:
850:
846:
842:
838:
834:
827:
824:
819:
815:
811:
807:
803:
799:
795:
791:
784:
782:
778:
773:
769:
764:
759:
755:
751:
747:
743:
739:
732:
730:
728:
724:
719:
715:
710:
705:
701:
697:
693:
689:
685:
678:
676:
674:
672:
670:
668:
666:
664:
662:
658:
651:
647:
644:
643:
639:
637:
635:
634:
629:
628:
623:
622:
617:
613:
605:
603:
597:
595:
589:
587:
585:
581:
576:
572:
568:
564:
558:
556:
552:
548:
540:
538:
536:
533:In 2016, the
528:
526:
515:
513:
503:
500:
497:
496:
492:
489:
486:
485:
481:
478:
475:
474:
470:
467:
464:
463:
459:
455:
451:
448:
444:
440:
439:
431:
428:
426:
418:
414:
407:
405:
403:
399:
391:
385:
383:
380:
377:
374:
371:
368:
365:
363:
359:
358:beta blockers
355:
351:
347:
345:
341:
338:
335:
331:
330:triglycerides
327:
323:
320:
317:
313:
309:
307:
303:
300:
298:
294:
291:
290:hyperglycemia
287:
283:
279:
275:
271:
268:
266:
263:
261:
258:
257:
252:
250:
247:
240:
236:
232:
230:
226:
221:
219:
215:
211:
207:
203:
199:
191:
189:
187:
186:
180:
178:
174:
170:
166:
161:
159:
155:
151:
147:
143:
139:
135:
134:triglycerides
131:
123:
122:hypercalcemia
119:
115:
111:
108:
106:
102:
99:
95:
91:
87:
84:
82:
78:
75:
71:
70:Heart disease
68:
66:
65:Complications
62:
59:
58:Endocrinology
56:
54:
50:
45:
41:
36:
32:
28:
23:
1791:
1772:dyslipidemia
1764:Inborn error
1698:
1687:
1663:
1652:
1641:
1626:
1603:
1552:
1548:
1542:
1509:
1505:
1499:
1466:
1462:
1456:
1431:
1427:
1421:
1394:
1390:
1380:
1355:
1347:
1304:
1300:
1290:
1257:
1253:
1242:
1217:
1213:
1207:
1174:
1170:
1118:
1114:
1104:
1077:
1073:
1063:
1030:
1026:
1020:
1007:
998:
990:
985:
974:. Retrieved
970:the original
965:
956:
921:
917:
907:
880:
876:
836:
832:
826:
793:
789:
745:
741:
691:
687:
631:
627:triglyceride
625:
619:
611:
609:
601:
593:
590:Epidemiology
559:
544:
532:
516:
509:
422:
395:
350:isotretinoin
334:lipoproteins
286:hypertension
280:(along with
244:
239:Triglyceride
222:
195:
183:
181:
162:
129:
128:
81:Risk factors
74:pancreatitis
1927:Lipomatosis
1689:MedlinePlus
1012:Mayo Clinic
966:MedlinePlus
398:blood tests
356:diuretics,
225:blood tests
154:cholesterol
30:Other names
1957:Categories
1665:DiseasesDB
1121:: 100322.
976:2015-04-23
652:References
521:mg/dL (1.1
493:Some risk
490:2.26–5.65
479:1.70–2.25
408:Guidelines
260:Overeating
94:alcoholism
1700:eMedicine
1577:233259875
1397:: 45–52.
1391:Maturitas
1321:1945-7197
1274:1522-9645
1135:2666-6677
610:The word
606:Etymology
541:Treatment
529:Screening
402:screening
392:Diagnosis
229:screening
185:xanthomas
53:Specialty
1705:med/2921
1569:33859377
1534:23706094
1526:25234378
1491:15570639
1483:20462635
1448:19698935
1413:29290214
1339:22962670
1282:21712404
1234:11834142
1199:33149001
1191:25131982
1153:35243465
1096:27532917
1055:20592431
1047:27538032
948:28402248
899:16672684
833:Diabetes
818:24193233
810:19293788
772:17420495
718:22962670
640:See also
598:Research
580:fibrates
547:fructose
487:200–499
476:150–199
382:Propofol
202:xanthoma
114:atheroma
1659:D015228
1330:3431581
1144:8885448
939:5555413
853:1397701
763:1839776
709:3431581
565:class.
563:fibrate
512:fasting
295:Excess
265:Obesity
173:obesity
136:in the
1694:000397
1648:145750
1575:
1567:
1532:
1524:
1489:
1481:
1463:Lancet
1446:
1411:
1368:
1364:–142.
1337:
1327:
1319:
1280:
1272:
1232:
1197:
1189:
1171:Lancet
1151:
1141:
1133:
1094:
1053:
1045:
946:
936:
897:
851:
816:
808:
770:
760:
716:
706:
621:hyper-
575:statin
567:Niacin
523:
519:
433:Level
326:enzyme
288:, and
253:Causes
214:spleen
152:(high
1920:Other
1637:272.1
1622:E78.3
1618:E78.2
1614:E78.1
1573:S2CID
1530:S2CID
1487:S2CID
1195:S2CID
1051:S2CID
814:S2CID
633:-emia
614:uses
373:Lupus
210:liver
142:fatty
138:blood
1766:of
1670:6372
1654:MeSH
1643:OMIM
1632:9-CM
1565:PMID
1522:PMID
1479:PMID
1444:PMID
1409:PMID
1366:ISBN
1335:PMID
1317:ISSN
1278:PMID
1270:ISSN
1230:PMID
1187:PMID
1149:PMID
1131:ISSN
1092:PMID
1074:JAMA
1043:PMID
944:PMID
895:PMID
849:PMID
806:PMID
768:PMID
742:CMAJ
714:PMID
569:and
549:and
454:mmol
423:The
272:and
212:and
167:and
1628:ICD
1605:ICD
1557:doi
1514:doi
1471:doi
1467:375
1436:doi
1432:122
1399:doi
1395:108
1362:141
1325:PMC
1309:doi
1262:doi
1222:doi
1218:102
1179:doi
1175:384
1139:PMC
1123:doi
1082:doi
1078:316
1035:doi
1031:165
934:PMC
926:doi
922:376
885:doi
841:doi
798:doi
794:104
758:PMC
750:doi
746:176
704:PMC
696:doi
618:of
342:or
332:in
1959::
1770::
1703::
1692::
1668::
1657::
1646::
1635::
1620:,
1616:,
1612::
1609:10
1571:.
1563:.
1551:.
1528:.
1520:.
1510:14
1508:.
1485:.
1477:.
1465:.
1442:.
1430:.
1407:.
1393:.
1389:.
1333:.
1323:.
1315:.
1305:97
1303:.
1299:.
1276:.
1268:.
1258:32
1256:.
1252:.
1228:.
1216:.
1193:.
1185:.
1173:.
1161:^
1147:.
1137:.
1129:.
1117:.
1113:.
1090:.
1076:.
1072:.
1049:.
1041:.
1029:.
1010:.
1006:.
964:.
942:.
932:.
920:.
916:.
893:.
881:19
879:.
875:.
861:^
847:.
837:41
835:.
812:.
804:.
792:.
780:^
766:.
756:.
744:.
740:.
726:^
712:.
702:.
692:97
690:.
686:.
660:^
630:+
624:+
460:)
449:)
447:dL
443:mg
360:,
352:,
304:,
284:,
188:.
179:.
160:.
120:,
116:,
112:,
96:,
92:,
88:,
72:,
1790:/
1756:e
1749:t
1742:v
1630:-
1607:-
1597:D
1579:.
1559::
1553:5
1536:.
1516::
1493:.
1473::
1450:.
1438::
1415:.
1401::
1374:.
1341:.
1311::
1284:.
1264::
1236:.
1224::
1201:.
1181::
1155:.
1125::
1119:9
1098:.
1084::
1057:.
1037::
979:.
950:.
928::
901:.
887::
855:.
843::
820:.
800::
774:.
752::
720:.
698::
458:L
456:/
452:(
445:/
441:(
292:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.