111:
199:. He placed several signs around the island which read: "Property of the Norwegian Meteorological Institute". By this action the foundation was laid for the acknowledgment of Norway's right to the island of Jan Mayen in 1928. The island came under the sovereignty of Norway by royal decree of 8 May 1929 and finally became officially part of the Norwegian Kingdom on 27 February 1930.
119:
214:
that tried to bring large swathes of East
Greenland under Norwegian sovereignty. With Hallvard's inspiration, based on his experiences in Svalbard and Jan Mayen, the movement began to build a network of Norwegian trapping stations, combined with surveys and explorations of the almost uninhabited
235:
Station, where he was a meteorology assistant, radio telegraphist and leader of expeditions that were undertaken with the station as a base. By 1932 about 80 cabins manned by
Norwegian trappers and fishermen were built in different areas of
221:(NSIU) —"Norwegian Svalbard and Arctic Ocean Survey", established by Hoel in 1928, sent well-organized research expeditions to East Greenland. Expedition vessels also supplied the trapping stations with equipment financed by the
268:. Following the 1933 resolution of the court awarding Greenland to the Danish government, Norway's claims in Greenland were given up and most Norwegian outposts were closed. However some of the stations, such as Myggbukta and
252:. In 1932 Norway staked sovereignty claims in areas of Northeast and Southeast Greenland where Norwegian stations had been built. The Norwegian flag was raised at Myggbukta and Finnsbu by Devold and his men, and
291:. The venture, however, was a failure and ended dramatically when all their supplies and sled dogs were unloaded on an ice floe that broke up almost immediately and began to drift.
423:
168:
On the following winter he took a radio telegraphy course, and in the spring of 1923 he was hired as a meteorology assistant and radio telegraphist at the
396:
217:
261:
469:
33:
249:
550:
196:
118:
545:
540:
306:
in French uniform, but partly under
Norwegian command. For this he received The French Second World War Commemorative Medal.
309:
Between 1951 and 1957 he was involved in
Norwegian fisheries, as head of the herring smoking plant at Gofarnes, north of
535:
510:
122:
Territories of
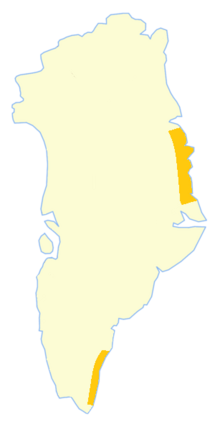
Eastern Greenland claimed by Norway until the 1933 Permanent Court of International Justice resolution.
180:. Hallvard Devold remained on Kvadehuken until October 1924, when the station was wrapped up for financial reasons.
275:
After leaving
Greenland, Hallvard travelled to Antarctica in 1933, where he took part in the expedition of Captain
482:“A cursed affair”—how a Norwegian expedition to Greenland became the USA’s first maritime capture in World War II.
283:, who had formerly shared East Greenland experiences with him. The expedition attempted the exploration of the
284:
241:
195:
had given Norway jurisdiction over the island. Hallvard decided to call for its annexation on behalf of the
363:
161:
until 1922. He went for the first time to the Arctic in the summer of 1922 as a coal mining technician in
134:
76:
303:
276:
53:
231:
In the period between 1926 and 1933 Hallvard wintered in
Northeast Greenland for six years, mostly in
530:
525:
313:, exporting Norwegian smoked herring to a number of countries. He died in 1957 and was buried in the
173:
358:
222:
154:
465:
245:
192:
158:
299:
188:
314:
183:
Between 1925 and 1926 Hallvard was the head of the
Norwegian radio and weather station at
130:
385:
519:
298:
Hallvard volunteered for military service in the spring of 1940 and took part in the
280:
253:
207:
187:, which was manned by three Norwegians, not including him. The island was considered
110:
345:
295:
32:
341:
272:
continued operation for a few years under Danish jurisdiction and restrictions.
177:
138:
203:
169:
157:
in 1920. He worked as a meteorological assistant at the Haldde
Observatory in
412:
Report on the
Activities of Norges Svalbard- og Ishavsundersøkelser 1936-1944
256:
was named governor and Devold had Police jurisdiction until Ingstad arrived.
141:(1902–1977) shared his vision and helped to establish a Norwegian station at
133:, trapper and meteorologist. He was instrumental in the attempt to establish
335:
269:
265:
232:
184:
318:
310:
288:
162:
257:
142:
176:
by the director of the Geophysical Institute, along with his brother
228:, a company that Hallvard had helped to set up and was the CEO of.
210:, Hallvard became one of the main leaders of the "Greenland case"
117:
109:
237:
449:
Lands That Hold One Spellbound: A Story of East Greenland,
436:
Lands That Hold One Spellbound: A Story of East Greenland,
386:
Hallvard Devold - Polarhistorie.no - Norsk Polarinstitutt
104:
Vision to expand Norwegian sovereignty to East Greenland
114:
One of the signs placed by Hallvard Devold in Jan Mayen
129:(8 November 1898 – 10 September 1957) was a Norwegian
16:
Norwegian Arctic explorer, trapper and meteorologist
100:
92:
84:
61:
39:
23:
424:Norwegian Expedition to South-East Greenland, 1932
511:Eirik the Red’s Land: the land that never was
8:
397:Einar-Arne Drivenes & Harald Dag Jølle,
330:Hallvard Devold is the author of the book
31:
20:
262:Permanent Court of International Justice
375:
260:protested and brought the case to the
218:Norges Svalbard og Ishavsundersøkelser
96:Polar explorer, trapper, meteorologist
7:
381:
379:
348:in Antarctica are named after him.
197:Norwegian Meteorological Institute
14:
497:Gyldendal Norsk Forlag, Oslo 1940
414:, Norsk Polarinstitutt, Oslo 1945
240:, including some in the distant
279:, together with renowned skier
462:Encyclopedia of the Antarctic,
1:
302:as an Allied soldier of the
153:Hallvard graduated from the
464:Taylor & Francis, 2007
334:(Polar Life), published in
567:
484:Norwegian Polar Institute.
551:University of Oslo alumni
30:
399:Norwegian Polar History,
202:Together with geologist
546:Explorers of the Arctic
541:Explorers of Antarctica
285:Princess Ragnhild Coast
242:King Frederick VI Coast
226:(Arktisk Næringsdrift)
127:Hallvard Ophuus Devold
123:
115:
317:graveyard in Karmøy,
277:Hjalmar Riiser-Larsen
137:in 1931. His brother
121:
113:
460:Beau Riffenburgh ,
191:at the time and the
536:Norwegian explorers
447:Spencer Apollonio,
434:Spencer Apollonio,
364:Erik the Red's Land
250:Kangerlussuaq Fjord
135:Eric the Red's Land
493:Devold, Hallvard.
401:vol. 2, Oslo, 2004
359:Arctic Trading Co.
223:Arctic Trading Co.
215:area. By 1929 the
155:University of Oslo
124:
116:
480:Frode Skarstein,
470:978-0-415-97024-2
438:2008, pp. 188-189
325:Works and honours
246:Storfjord Station
193:League of Nations
108:
107:
65:10 September 1957
558:
498:
491:
485:
478:
472:
458:
452:
445:
439:
432:
426:
421:
415:
409:
403:
394:
388:
383:
300:Battle of Narvik
212:(Grønlandssaken)
145:, SE Greenland.
72:
70:
50:
48:
35:
21:
566:
565:
561:
560:
559:
557:
556:
555:
516:
515:
507:
502:
501:
492:
488:
479:
475:
459:
455:
446:
442:
433:
429:
422:
418:
410:
406:
395:
391:
384:
377:
372:
355:
327:
315:Kopervik Church
294:At the time of
151:
131:Arctic explorer
80:
74:
68:
66:
57:
51:
46:
44:
43:8 November 1898
26:
25:Hallvard Devold
17:
12:
11:
5:
564:
562:
554:
553:
548:
543:
538:
533:
528:
518:
517:
514:
513:
506:
505:External links
503:
500:
499:
486:
473:
453:
440:
427:
416:
404:
389:
374:
373:
371:
368:
367:
366:
361:
354:
351:
350:
349:
339:
326:
323:
304:Foreign Legion
238:East Greenland
174:Brøggerhalvøya
150:
147:
106:
105:
102:
101:Known for
98:
97:
94:
90:
89:
86:
82:
81:
75:
73:(aged 58)
63:
59:
58:
52:
41:
37:
36:
28:
27:
24:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
563:
552:
549:
547:
544:
542:
539:
537:
534:
532:
529:
527:
524:
523:
521:
512:
509:
508:
504:
496:
490:
487:
483:
477:
474:
471:
467:
463:
457:
454:
450:
444:
441:
437:
431:
428:
425:
420:
417:
413:
408:
405:
402:
400:
393:
390:
387:
382:
380:
376:
369:
365:
362:
360:
357:
356:
352:
347:
343:
340:
337:
333:
329:
328:
324:
322:
320:
316:
312:
307:
305:
301:
297:
292:
290:
286:
282:
281:Olav Kjelbotn
278:
273:
271:
267:
263:
259:
255:
254:Helge Ingstad
251:
247:
243:
239:
234:
229:
227:
224:
220:
219:
213:
209:
208:Gustav Smedal
205:
200:
198:
194:
190:
189:no man's land
186:
181:
179:
175:
171:
166:
164:
160:
156:
148:
146:
144:
140:
136:
132:
128:
120:
112:
103:
99:
95:
93:Occupation(s)
91:
87:
83:
78:
64:
60:
55:
42:
38:
34:
29:
22:
19:
494:
489:
481:
476:
461:
456:
451:2008, p. 192
448:
443:
435:
430:
419:
411:
407:
398:
392:
346:Devoldkalven
331:
308:
296:World War II
293:
274:
230:
225:
216:
211:
201:
182:
167:
152:
126:
125:
18:
531:1957 deaths
526:1898 births
342:Devold Peak
206:and jurist
178:Finn Devold
172:station in
139:Finn Devold
85:Nationality
520:Categories
370:References
204:Adolf Hoel
170:Kvadehuken
69:1957-09-11
47:1898-11-08
495:Polarliv.
336:Gyldendal
270:Torgilsbu
266:The Hague
233:Myggbukta
185:Jan Mayen
149:Biography
88:Norwegian
353:See also
338:in 1940.
332:Polarliv
319:Rogaland
311:Kopervik
289:dog sled
163:Svalbard
79:, Norway
56:, Norway
54:Tysfjord
258:Denmark
248:in the
143:Finnsbu
67: (
45: (
468:
77:Karmøy
466:ISBN
344:and
244:and
159:Alta
62:Died
40:Born
287:by
264:in
522::
378:^
321:.
165:.
71:)
49:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.