217:, and the line is also moving. In the year 1900, the agonic line passed roughly through Detroit and then was east of Florida. It currently passes roughly west of Chicago, IL, and through New Orleans, LA. If a navigator is located on the agonic line, then variation is zero: the Magnetic North Pole and the Geographic North Pole appear to be directly in line with each other. If a navigator is east of the agonic line, then the variation is westward; magnetic north appears slightly west of the Geographic North Pole. If a navigator is west of the agonic line, then the variation is eastward; the Magnetic North Pole appears to the east of the Geographic North Pole. The farther the navigator is from the agonic line, the greater the variation. The local magnetic variation is indicated on
242:
error can be corrected using a deviation table. Deviation tables are very difficult to create. Once a deviation table is established, it is only good for that particular vessel, with that particular configuration. If electrical wires are moved or anything else magnetic (speakers, electric motors, etc.) are moved, the deviation table will change. All deviations in the deviation table are indicated west or east. If the compass is pointing west of the
Magnetic North Pole, then the deviation is westward. If the compass is pointing east of the Magnetic North Pole, then the deviation is eastward.
124:
20:
213:) is different depending on the geographic position on the globe. The Magnetic North Pole is currently in Northern Canada and is moving generally south. A straight line can be drawn from the Geographic North Pole, down to the Magnetic North Pole and then continued straight down to the equator. This line is known as the
270:
The formula is always added moving down, and subtracted when moving up. The most complicated part is determining if the values are positive or negative. The True, Magnetic, and
Compass values are directions on the compass, they must always be a positive number between 0–360. Variation and Deviation
241:
recreational vessel will generally have much less compass deviation than a steel-hulled vessel. Electrical wires carrying current have a small magnetic field around them and can cause deviation. Any type of magnet, such as found in a speaker can also cause large magnitudes of compass deviation. The
182:. From any position on the globe, a direction can be determined to either the Geographic North Pole or to the Magnetic North Pole. These directions are expressed in degrees from 0–360°, and also fractions of a degree. The differences between these two directions at any point on the globe is
190:, but for the purposes of the mnemonic, the term 'variation' is preferred). When a compass is installed in a vehicle or vessel, local anomalies of the vessel can introduce error into the direction that the compass points. The difference between the local
271:
can be positive or negative. If either
Variation or Deviation is westward, then the values are entered into the equation as positive. If the Variation or Deviation is eastward, then the values are entered into the formula as a negative. Some use the
402:
Aviation: CDMVT Can Dead Man Vote Twice: Mnemonic. Easy way to calculate compass magnetic or true north is maintaining the original signs for variation and deviation (+ for east and -for west): C+(Var)= M+(Dev)= T / T-(Dev)= M-(Var)= C
225:. The magnetic variation is indicated along with the year of that variation. The annual increase or decrease of the variation is also usually indicated, so that the variation for the current year can be calculated.
162:. The most common use of the TVMDC method is deriving compass courses during nautical navigation from maps. The inverse correction from compass heading to true heading is "CDMVTAE", with
59:
in which the craft's bow or nose is pointed. Note that the heading may not necessarily be the direction that the vehicle actually travels, which is known as its
275:: True Virgins Make Dull Companions - Going downward Add Whiskey (or West). An alternative, working the opposite direction: Can Dead Men Vote Twice.
143:
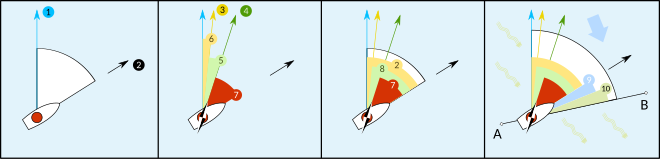
8 - Magnetic heading, the compass heading corrected for magnetic deviation but not magnetic variation; thus, the heading reliative to magnetic north.
233:
A compass installed in a vehicle or vessel has a certain amount of error caused by the magnetic properties of the vessel. This error is known as
516:
69:. Any difference between the heading and course is due to the motion of the underlying medium, the air or water, or other effects like
455:
237:. The magnitude of the compass deviation varies greatly depending upon the local anomalies created by the vessel. A
464:
135:
4 - Compass north, including a two-part error; the magnetic variation (6) and the ship's own magnetic field (5)
447:
175:
56:
158:
for converting from true heading, to magnetic and compass headings. TVMDC is a mnemonic initialism for
145:
9, 10 - Effects of crosswind and tidal current, causing the vessel's track to differ from its heading.
141:
7 - Compass heading or compass course, before correction for magnetic deviation or magnetic variation.
412:
210:
187:
535:
179:
61:
476:
234:
206:
195:
183:
96:
78:
74:
70:
508:
502:
512:
417:
468:
39:
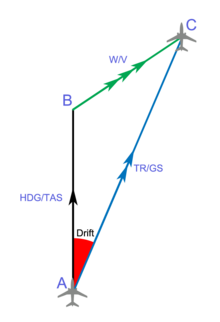
towards C (TR, track, in blue; GS=Ground Speed). The drift angle (shaded red) is due to the
497:
Sea School (1977) True
Virgins Make Dull Companions. Add Whiskey Going downward: Mnemonic
303:
Therefore, to achieve a true course of 120°, one should follow a compass heading of 126°.
166:
The most common use of the CDMVTAE rule is to convert compass headings to map headings.
371:
The formula can also be calculated in reverse. The formula is subtracted when moving up.
250:
Calculating TVMDC is done with simple arithmetic. First arrange the values vertically:
191:
529:
83:
24:
480:
423:
222:
164:
compass heading, deviation, magnetic heading, variation, true heading, add easterly
160:
true heading, variation, magnetic heading, deviation, compass heading, add westerly
123:
28:
214:
374:
Compass course is 093°, the
Deviation is 4° West and the Variation is 3° West.
87:. At least seven ways to measure the heading of a vehicle have been described.
472:
238:
100:
48:
40:
346:
True course is 306°, the
Variation is 4° East and the Deviation is 11° West.
283:
True course is 120°, the
Variation is 5° West, and the Deviation is 1° West.
133:
3 - Magnetic north, which differs from true north by the magnetic variation.
326:
True course is 035°, the
Variation is 4° West and the Deviation is 1° East.
306:
True course is 120°, the
Variation is 5° East and the Deviation is 1° East.
178:
around which the Earth rotates is not in exactly the same position as the
272:
155:
394:
Thus, when following a compass course of 093°, the true course is 086°.
139:
6 - Magnetic variation, caused by variations in Earth's magnetic field.
19:
504:
The
Weekend Navigator: Simple Boat Navigation With GPS and Electronics
194:
and the direction that the compass indicates as north is known as
122:
108:
18:
218:
112:
104:
131:
2 - Heading, the direction the vessel is "pointing towards"
35:
towards point B (HDG, in black; TAS=True Air Speed) and its
137:
5 - Magnetic deviation, caused by vessel's magnetic field.
507:(Illustrated ed.). McGraw-Hill Professional. p.
441:
439:
99:, so 0° (or 360°) indicates a direction toward
8:
435:
221:nautical charts at the center of the
7:
202:Determine variation in North America
14:
77:. The difference is known as the
448:"The Seven Ways to Find Heading"
81:, and can be determined by the
55:of a vessel or aircraft is the
95:Heading is typically based on
1:
552:
465:Cambridge University Press
127:Heading and track (A to B)
501:Sweet, Robert J. (2004).
473:10.1017/S0373463316000096
446:Gade, Kenneth (2016).
148:
147:A, B - Vessel's track.
44:
456:Journal of Navigation
176:Geographic North Pole
126:
22:
413:Bearing (navigation)
211:magnetic declination
188:magnetic declination
420:- Flight instrument
229:Determine deviation
180:Magnetic North Pole
97:cardinal directions
207:Magnetic variation
196:magnetic deviation
184:magnetic variation
149:
45:
518:978-0-07-143035-7
418:Heading indicator
235:compass deviation
57:compass direction
16:Compass direction
543:
522:
485:
484:
452:
443:
111:, and 270° true
43:(W/V, in green).
551:
550:
546:
545:
544:
542:
541:
540:
526:
525:
519:
500:
494:
489:
488:
450:
445:
444:
437:
432:
409:
400:
369:
281:
248:
231:
209:(also known as
204:
186:(also known as
172:
146:
144:
142:
140:
138:
136:
134:
132:
130:
129:1 - True North
128:
121:
93:
17:
12:
11:
5:
549:
547:
539:
538:
528:
527:
524:
523:
517:
498:
493:
490:
487:
486:
434:
433:
431:
428:
427:
426:
421:
415:
408:
405:
399:
396:
392:
391:
388:
385:
382:
379:
368:
365:
364:
363:
360:
357:
354:
351:
344:
343:
340:
337:
334:
331:
324:
323:
320:
317:
314:
311:
301:
300:
297:
294:
291:
288:
280:
277:
268:
267:
264:
261:
258:
255:
247:
244:
230:
227:
203:
200:
192:Magnetic North
171:
168:
120:
117:
92:
89:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
548:
537:
534:
533:
531:
520:
514:
510:
506:
505:
499:
496:
495:
491:
482:
478:
474:
470:
466:
462:
458:
457:
449:
442:
440:
436:
429:
425:
422:
419:
416:
414:
411:
410:
406:
404:
397:
395:
389:
386:
383:
380:
377:
376:
375:
372:
366:
361:
358:
355:
352:
349:
348:
347:
341:
338:
335:
332:
329:
328:
327:
321:
318:
315:
312:
309:
308:
307:
304:
298:
295:
292:
289:
286:
285:
284:
278:
276:
274:
265:
262:
259:
256:
253:
252:
251:
245:
243:
240:
236:
228:
226:
224:
220:
216:
212:
208:
201:
199:
197:
193:
189:
185:
181:
177:
169:
167:
165:
161:
157:
153:
125:
118:
116:
114:
110:
106:
102:
98:
90:
88:
86:
85:
84:wind triangle
80:
76:
72:
68:
64:
63:
58:
54:
50:
42:
41:wind velocity
38:
34:
30:
26:
25:wind triangle
21:
503:
492:Bibliography
460:
454:
424:Ship motions
401:
393:
373:
370:
345:
325:
305:
302:
282:
269:
249:
232:
223:compass rose
205:
173:
163:
159:
151:
150:
107:, 180° true
94:
82:
66:
60:
52:
46:
36:
32:
29:jet airliner
215:agonic line
103:, 90° true
536:Navigation
467:: 955–70.
430:References
239:fiberglass
170:Background
101:true north
49:navigation
263:Deviation
257:Variation
530:Category
481:53587934
407:See also
279:Examples
273:mnemonic
260:Magnetic
156:mnemonic
152:TVMDC,AW
91:Notation
75:slipping
71:skidding
27:shows a
390:C: 093°
384:M: 089°
378:T: 086°
367:Reverse
362:C: 313°
359:D: +11°
356:M: 302°
350:T: 306°
342:C: 038°
336:M: 039°
330:T: 035°
322:C: 114°
316:M: 115°
310:T: 120°
299:C: 126°
293:M: 125°
287:T: 120°
266:Compass
246:Formula
53:heading
33:heading
515:
479:
387:D: -4°
381:V: -3°
353:V: −4°
339:D: −1°
333:V: +4°
319:D: −1°
313:V: −5°
296:D: +1°
290:V: +5°
62:course
51:, the
37:course
477:S2CID
463:(5).
451:(PDF)
398:CDMVT
154:is a
119:TVMDC
109:south
79:drift
67:track
23:This
513:ISBN
254:True
219:NOAA
174:The
113:west
105:east
469:doi
73:or
65:or
47:In
31:'s
532::
511:.
509:66
475:.
461:69
459:.
453:.
438:^
198:.
115:.
521:.
483:.
471::
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.