433:
335:
359:
137:
347:
383:
371:
421:
227:, especially the eighth (T8). Neurologic signs result from severe angulation of the spine, narrowing of the spinal canal, instability of the spine, and luxation or fracture of the vertebrae. Signs include rear limb weakness or paralysis, urinary or fecal incontinence, and spinal pain. Most cases of hemivertebrae have no or mild symptoms, so treatment is usually conservative. Severe cases may respond to surgical spinal cord decompression and vertebral stabilization.
79:
456:
282:
nerve roots from that segment. It may lead to certain neurological problems depending on the severity of the block. It can increase stress on the inferior and the superior intervertebral joints. It can lead to an abnormal angle in the spine, there are certain syndromes associated with block vertebrae; for example,
281:
Block vertebrae occur when there is improper segmentation of the vertebrae, leading to parts of or the entire vertebrae being fused. The adjacent vertebrae fuse through their intervertebral discs and also through other intervertebral joints so that it can lead to blocking or stretching of the exiting
199:
pseudoarticulation instead. Additionally, if L6 fuses to another vertebra this is increasingly likely to cause lower back pain. The presence of a sixth vertebra in the space where five vertebrae normally reside also decreases the flexibility of the spine and increases the likelihood of injury.
198:
Sacralization of L6 means L6 attaches to S1 via a rudimentary joint. This L6-S1 joint creates additional motion, increasing the potential for motion-related stress and lower back pain/conditions. This condition can usually be treated without surgery, injecting steroid medication at the
1110:
432:
1103:
414:) during vertebrae formation. There are usually no symptoms. There are also coronal clefts mainly in skeletal dysplasias such as chondrodysplasia punctata. In dogs, butterfly vertebrae occur most often in Bulldogs, Pugs, and Boston Terriers.
1067:
1047:
1096:
358:
334:
125:. Conversely the sacrum appears to have only four segments instead of its designated five segments. Lumbosacral transitional vertebrae consist of the process of the last lumbar vertebra fusing with the first
490:
The significance of transitional vertebrae has been questioned by one study finding similar prevalence in the general population as those with low back pain, but more recent study found a large difference.
346:
1797:
506:
cats. In Manx it accompanies a condition known as sacrocaudal dysgenesis that gives these cats their characteristic tailless or stumpy tail appearance. It is inherited in Manx as an
790:
Molnar, R. E., 2001, Theropod paleopathology: a literature survey: In: Mesozoic
Vertebrate Life, edited by Tanke, D. H., and Carpenter, K., Indiana University Press, p. 337-363.
66:
by deforming the vertebral canal or causing instability. This condition occurs in the womb. Congenital vertebral anomalies include alterations of the shape and number of
382:
370:
420:
825:
Flückiger M, Damur-Djuric N, Hässig M, Morgan J, Steffen F (2006). "A lumbosacral transitional vertebra in the dog predisposes to cauda equina syndrome".
1690:
1183:
1088:
459:
Short ribs at the first lumbar vertebra, which is thus a transitional vertebra, since lumbar vertebrae normally do not have ribs attached to them.
1792:
665:
1631:
502:
is characterized by a midline cleft in the vertebral arch. It usually causes no symptoms in dogs. It is seen most commonly in
Bulldogs and
398:
Butterfly vertebrae have a sagittal cleft through the body of the vertebrae and a funnel shape at the ends. This gives the appearance of a
171:, or both. These anomalies are observed in about 3.5 percent of people, and it is usually bilateral but can be unilateral or incomplete (
809:
640:
860:
Apazidis A, Ricart PA, Diefenbach CM, Spivak JM (September 2011). "The prevalence of transitional vertebrae in the lumbar spine".
518:
Vertebral anomalies is associated with an increased incidence of some other specific anomalies as well, together being called the
1585:
312:. This suggests that the basic development pattern of vertebrae goes at least as far back as the most recent common ancestor of
1304:
463:
Transitional vertebrae have the characteristics of two types of vertebra. The condition usually involves the vertebral arch or
697:
467:. It occurs at the cervicothoracic, thoracolumbar, or lumbosacral junction. For instance, the transverse process of the last
475:, disk changes, or thecal sac compression. Back pain associated with lumbosacral transitional vertebrae (LSTV) is known as
265:
The probable cause of hemivertebrae is a lack of blood supply causing part of the vertebrae not to form. Hemivertebrae in
1420:
1123:
183:, it is asymptomatic in many cases (especially bilateral type). Low back pain in these cases most likely occurs due to
1590:
1309:
1139:
1127:
364:
Congenital block vertebra in the lumbar spine (partial vertebrae 3 and 4). The rear portion of the disc still exists.
1621:
1675:
340:
Block vertebrae of the cervical spine (vertebrae 4 and 5). Probably based on degenerative or inflammatory changes.
283:
136:
1595:
542:
897:"Role of the Lumbosacral Transition Vertebra and Vertebral Lamina in the Pathogenesis of Lumbar Disc Herniation"
1530:
1173:
536:
235:
476:
352:
Several congenital block vertebrae in the transition from the thoracic to the lumbar spine and hemivertebrae.
1567:
1201:
1178:
102:
1470:
1135:
484:
251:
122:
944:
1685:
464:
445:
of the lumbar vertebral column, showing butterfly vertebrae at several levels, most typically in L1.
321:
1503:
1119:
1071:
519:
480:
411:
259:
188:
669:
1365:
548:
507:
224:
156:
152:
98:
207:
Hemivertebrae are wedge-shaped vertebrae and therefore can cause an angle in the spine (such as
1700:
1680:
1010:
992:
926:
877:
842:
805:
747:
613:
468:
305:
247:
38:
1747:
1742:
1663:
1655:
1575:
1539:
1347:
1299:
1256:
1000:
982:
916:
908:
869:
834:
737:
603:
595:
438:
231:
59:
43:
1763:
1498:
1328:
1294:
1247:
243:
160:
118:
62:. Most, around 85%, are not clinically significant, but they can cause compression of the
219:). Among the congenital vertebral anomalies, hemivertebrae are the most likely to cause
1626:
1557:
1521:
1493:
1415:
1319:
1193:
1005:
970:
921:
896:
608:
583:
299:
126:
1076:
1786:
1636:
1580:
1547:
1430:
1251:
838:
558:
308:, specialists in ancient disease and injury. A block vertebra has been documented in
239:
180:
176:
895:
Jin L, Yin Y, Chen W, Zhang R, Guo J, Tao S, Guo Z, Hou Z, Zhang Y (December 2021).
1718:
1611:
1453:
1425:
1211:
1206:
584:"A Review of Symptomatic Lumbosacral Transitional Vertebrae: Bertolotti's Syndrome"
530:
499:
255:
184:
168:
110:
78:
471:
may resemble a rib. A transitional vertebra at the lumbosacral junction can cause
873:
1641:
1408:
1399:
1284:
1216:
766:
455:
172:
63:
47:
1616:
1552:
1465:
1459:
1435:
1403:
1370:
1339:
1289:
1261:
1056:
503:
325:
313:
996:
17:
1723:
1668:
1475:
1360:
1353:
1334:
1266:
1230:
1060:
742:
725:
472:
407:
399:
320:. The tyrannosaur's block vertebra was probably caused by a "failure of the
220:
212:
114:
1014:
987:
930:
881:
846:
751:
617:
129:. While only around 10 percent of adults have a spinal abnormality due to
702:
Clinical
Neurology in Small Animals: Localization, Diagnosis and Treatment
1165:
1161:
1143:
945:"Congenital and Inherited Anomalies of the Nervous System: Small Animals"
216:
208:
140:
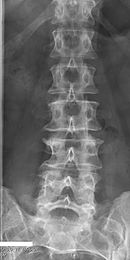
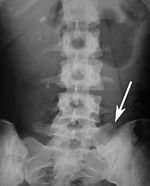
Sacralization of the L5 vertebra is seen at the lower right of the image.
130:
105:. It is defined by the nonfusion of the first and second segments of the
67:
726:"Imaging findings and surgical treatment of hemivertebrae in three dogs"
1733:
1391:
442:
317:
1039:
304:
Evidence for block vertebrae found in the fossil record is studied by
179:
rudimentary facets) as well. Although sacralization may be a cause of
1051:
912:
554:
287:
164:
106:
83:
133:, a sixth lumbar vertebra is one of the more common abnormalities.
388:
Congenital block vertebra of the lumbar spine. CT volume rendering.
376:
Congenital block vertebra of the lumbar spine. CT volume rendering.
599:
454:
403:
270:
192:
135:
483:
with a lumbosacral transitional vertebra are at greater risk for
1276:
426:
Butterfly vertebra (red). Normal vertebra for comparison (blue).
87:
1092:
1709:
1239:
1152:
266:
487:, which can cause rear limb weakness and incontinence.
191:
may be thin and narrow. This abnormality is found by
1029:
1756:
1732:
1708:
1699:
1654:
1604:
1566:
1538:
1529:
1520:
1486:
1446:
1390:
1383:
1318:
1275:
1238:
1229:
1192:
1160:
1151:
1134:
1033:
37:
32:
981:(1). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 56.
800:Ettinger, Stephen J.; Feldman, Edward C. (1995).
767:"Hemivertebra | Radiology Reference Article"
410:(which usually only remains as the center of the
1798:Congenital disorders of musculoskeletal system
230:Recognised associations are many and include:
1104:
223:problems. The most common location is the mid
86:, seen as 6 vertebrae that do not connect to
8:
582:Jancuska, JM; Spivak, JM; Bendo, JA (2015).
269:are most common in the tail, resulting in a
1705:
1535:
1526:
1387:
1235:
1157:
1148:
1111:
1097:
1089:
1030:
145:Sacralization of the fifth lumbar vertebra
29:
1004:
986:
920:
741:
719:
717:
607:
58:are a collection of malformations of the
802:Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine
691:
689:
687:
77:
804:(4th ed.). W.B. Saunders Company.
574:
416:
330:
724:Jeffery N, Smith P, Talbot C (2007).
406:. It is caused by persistence of the
7:
1632:Greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome
1122:malformations and deformations of
117:or segments, not five. This sixth
25:
975:Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases
113:subsequently appears to have six
839:10.1111/j.1740-8261.2005.00103.x
431:
419:
381:
369:
357:
345:
333:
1305:Congenital patellar dislocation
1184:Wallis–Zieff–Goldblatt syndrome
74:Lumbarization and sacralization
187:. In sacralization, the L5-S1
56:Congenital vertebral anomalies
1:
1793:Dog musculoskeletal disorders
33:Congenital anomalies of spine
969:Solomon, Benjamin D (2011).
874:10.1016/j.spinee.2011.08.005
630:Dorland's Medical Dictionary
479:. One study found that male
290:is a normal block vertebra.
1591:Oto-palato-digital syndrome
1586:Hallermann–Streiff syndrome
1310:Congenital knee dislocation
1128:musculoskeletal abnormality
971:"VACTERL/VATER Association"
949:The Merck Veterinary Manual
167:on one side or both, or to
1814:
1622:Craniodiaphyseal dysplasia
297:
1596:Treacher Collins syndrome
1447:reduction deficits / limb
698:"Developmental Disorders"
543:Tracheoesophageal fistula
1421:Cenani–Lenz syndactylism
1174:Cleidocranial dysostosis
537:Cardiovascular anomalies
236:cleidocranial dysostosis
1568:Craniofacial dysostosis
743:10.2460/javma.230.4.532
666:"Laser Spine Institute"
526:V – Vertebral anomalies
1124:musculoskeletal system
988:10.1186/1750-1172-6-56
460:
451:Transitional vertebrae
141:
91:
1676:Klippel–Feil syndrome
827:Vet Radiol Ultrasound
765:Weerakkody, Yuranga.
696:Braund, K.G. (2003).
485:cauda equina syndrome
477:Bertolotti's syndrome
458:
284:Klippel–Feil syndrome
252:Jarcho-Levin syndrome
139:
123:transitional vertebra
81:
1686:Spina bifida occulta
1202:Madelung's deformity
1179:Sprengel's deformity
672:on November 28, 2016
481:German Shepherd Dogs
465:transverse processes
1504:RAPADILINO syndrome
520:VACTERL association
412:intervertebral disc
394:Butterfly vertebrae
260:VACTERL association
189:intervertebral disc
1366:Rocker bottom foot
730:J Am Vet Med Assoc
641:"Spinal Cord, Inc"
549:Esophageal atresia
508:autosomal dominant
461:
225:thoracic vertebrae
163:(L5) fuses to the
157:transverse process
153:congenital anomaly
142:
92:
1780:
1779:
1776:
1775:
1772:
1771:
1701:Thoracic skeleton
1681:Spondylolisthesis
1650:
1649:
1516:
1515:
1512:
1511:
1379:
1378:
1225:
1224:
1086:
1085:
469:cervical vertebra
306:paleopathologists
248:fetal pyelectasis
84:sacral vertebra 1
82:Lumbarization of
53:
52:
27:Medical condition
16:(Redirected from
1805:
1748:Pectus carinatum
1743:Pectus excavatum
1706:
1664:Spinal curvature
1656:Vertebral column
1576:Crouzon syndrome
1540:Craniosynostosis
1536:
1527:
1392:fingers and toes
1388:
1300:Discoid meniscus
1257:Upington disease
1236:
1158:
1149:
1113:
1106:
1099:
1090:
1031:
1019:
1018:
1008:
990:
966:
960:
959:
957:
956:
941:
935:
934:
924:
913:10.1111/os.13122
907:(8): 2355–2362.
892:
886:
885:
857:
851:
850:
822:
816:
815:
797:
791:
788:
782:
781:
779:
777:
762:
756:
755:
745:
721:
712:
711:
709:
708:
693:
682:
681:
679:
677:
668:. Archived from
662:
656:
655:
653:
651:
637:
631:
628:
622:
621:
611:
588:Int J Spine Surg
579:
564:L – Limb defects
439:Volume rendering
435:
423:
385:
373:
361:
349:
337:
232:Aicardi syndrome
44:Medical genetics
30:
21:
1813:
1812:
1808:
1807:
1806:
1804:
1803:
1802:
1783:
1782:
1781:
1768:
1764:Poland syndrome
1752:
1728:
1695:
1646:
1600:
1562:
1508:
1499:Larsen syndrome
1487:multiple joints
1482:
1442:
1375:
1314:
1295:Genu recurvatum
1271:
1248:Hip dislocation
1221:
1188:
1138:
1130:
1117:
1087:
1082:
1081:
1042:
1028:
1023:
1022:
968:
967:
963:
954:
952:
943:
942:
938:
894:
893:
889:
859:
858:
854:
824:
823:
819:
812:
799:
798:
794:
789:
785:
775:
773:
771:Radiopaedia.org
764:
763:
759:
723:
722:
715:
706:
704:
695:
694:
685:
675:
673:
664:
663:
659:
649:
647:
639:
638:
634:
629:
625:
581:
580:
576:
571:
516:
497:
453:
446:
436:
427:
424:
396:
389:
386:
377:
374:
365:
362:
353:
350:
341:
338:
302:
296:
279:
277:Block vertebrae
244:Gorlin syndrome
205:
161:lumbar vertebra
155:, in which the
119:lumbar vertebra
76:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1811:
1809:
1801:
1800:
1795:
1785:
1784:
1778:
1777:
1774:
1773:
1770:
1769:
1767:
1766:
1760:
1758:
1754:
1753:
1751:
1750:
1745:
1739:
1737:
1730:
1729:
1727:
1726:
1721:
1715:
1713:
1703:
1697:
1696:
1694:
1693:
1688:
1683:
1678:
1673:
1672:
1671:
1660:
1658:
1652:
1651:
1648:
1647:
1645:
1644:
1639:
1634:
1629:
1627:Dolichocephaly
1624:
1619:
1614:
1608:
1606:
1602:
1601:
1599:
1598:
1593:
1588:
1583:
1578:
1572:
1570:
1564:
1563:
1561:
1560:
1558:Trigonocephaly
1555:
1550:
1544:
1542:
1533:
1531:Skull and face
1524:
1518:
1517:
1514:
1513:
1510:
1509:
1507:
1506:
1501:
1496:
1494:Arthrogryposis
1490:
1488:
1484:
1483:
1481:
1480:
1479:
1478:
1473:
1468:
1456:
1450:
1448:
1444:
1443:
1441:
1440:
1439:
1438:
1428:
1423:
1418:
1416:Arachnodactyly
1413:
1412:
1411:
1396:
1394:
1385:
1381:
1380:
1377:
1376:
1374:
1373:
1368:
1363:
1358:
1357:
1356:
1344:
1343:
1342:
1337:
1324:
1322:
1320:foot deformity
1316:
1315:
1313:
1312:
1307:
1302:
1297:
1292:
1287:
1281:
1279:
1273:
1272:
1270:
1269:
1264:
1259:
1254:
1244:
1242:
1233:
1227:
1226:
1223:
1222:
1220:
1219:
1214:
1209:
1204:
1198:
1196:
1194:hand deformity
1190:
1189:
1187:
1186:
1181:
1176:
1170:
1168:
1155:
1146:
1132:
1131:
1118:
1116:
1115:
1108:
1101:
1093:
1084:
1083:
1080:
1079:
1064:
1043:
1038:
1037:
1035:
1034:Classification
1027:
1026:External links
1024:
1021:
1020:
961:
936:
887:
852:
817:
810:
792:
783:
757:
713:
683:
657:
645:Spinalcord.com
632:
623:
573:
572:
570:
567:
566:
565:
562:
555:Renal (kidney)
551:
545:
539:
533:
527:
515:
512:
496:
493:
452:
449:
448:
447:
437:
430:
428:
425:
418:
395:
392:
391:
390:
387:
380:
378:
375:
368:
366:
363:
356:
354:
351:
344:
342:
339:
332:
322:resegmentation
300:Paleopathology
298:Main article:
295:
292:
278:
275:
204:
201:
127:sacral segment
121:is known as a
75:
72:
51:
50:
41:
35:
34:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1810:
1799:
1796:
1794:
1791:
1790:
1788:
1765:
1762:
1761:
1759:
1755:
1749:
1746:
1744:
1741:
1740:
1738:
1735:
1731:
1725:
1722:
1720:
1717:
1716:
1714:
1711:
1707:
1704:
1702:
1698:
1692:
1691:Sacralization
1689:
1687:
1684:
1682:
1679:
1677:
1674:
1670:
1667:
1666:
1665:
1662:
1661:
1659:
1657:
1653:
1643:
1640:
1638:
1637:Plagiocephaly
1635:
1633:
1630:
1628:
1625:
1623:
1620:
1618:
1615:
1613:
1610:
1609:
1607:
1603:
1597:
1594:
1592:
1589:
1587:
1584:
1582:
1581:Hypertelorism
1579:
1577:
1574:
1573:
1571:
1569:
1565:
1559:
1556:
1554:
1551:
1549:
1548:Scaphocephaly
1546:
1545:
1543:
1541:
1537:
1534:
1532:
1528:
1525:
1523:
1519:
1505:
1502:
1500:
1497:
1495:
1492:
1491:
1489:
1485:
1477:
1474:
1472:
1469:
1467:
1464:
1463:
1462:
1461:
1457:
1455:
1452:
1451:
1449:
1445:
1437:
1434:
1433:
1432:
1431:Brachydactyly
1429:
1427:
1424:
1422:
1419:
1417:
1414:
1410:
1407:
1406:
1405:
1401:
1398:
1397:
1395:
1393:
1389:
1386:
1384:Either / both
1382:
1372:
1369:
1367:
1364:
1362:
1359:
1355:
1352:
1351:
1350:
1349:
1345:
1341:
1338:
1336:
1333:
1332:
1331:
1330:
1326:
1325:
1323:
1321:
1317:
1311:
1308:
1306:
1303:
1301:
1298:
1296:
1293:
1291:
1288:
1286:
1283:
1282:
1280:
1278:
1274:
1268:
1265:
1263:
1260:
1258:
1255:
1253:
1252:Hip dysplasia
1249:
1246:
1245:
1243:
1241:
1237:
1234:
1232:
1228:
1218:
1215:
1213:
1210:
1208:
1205:
1203:
1200:
1199:
1197:
1195:
1191:
1185:
1182:
1180:
1177:
1175:
1172:
1171:
1169:
1167:
1163:
1159:
1156:
1154:
1150:
1147:
1145:
1141:
1137:
1133:
1129:
1125:
1121:
1114:
1109:
1107:
1102:
1100:
1095:
1094:
1091:
1078:
1074:
1073:
1069:
1065:
1062:
1058:
1054:
1053:
1049:
1045:
1044:
1041:
1036:
1032:
1025:
1016:
1012:
1007:
1002:
998:
994:
989:
984:
980:
976:
972:
965:
962:
950:
946:
940:
937:
932:
928:
923:
918:
914:
910:
906:
902:
898:
891:
888:
883:
879:
875:
871:
868:(9): 858–62.
867:
863:
856:
853:
848:
844:
840:
836:
832:
828:
821:
818:
813:
811:0-7216-6795-3
807:
803:
796:
793:
787:
784:
772:
768:
761:
758:
753:
749:
744:
739:
735:
731:
727:
720:
718:
714:
703:
699:
692:
690:
688:
684:
671:
667:
661:
658:
646:
642:
636:
633:
627:
624:
619:
615:
610:
605:
601:
600:10.14444/2042
597:
593:
589:
585:
578:
575:
568:
563:
560:
556:
552:
550:
546:
544:
540:
538:
534:
532:
528:
525:
524:
523:
521:
513:
511:
509:
505:
501:
494:
492:
488:
486:
482:
478:
474:
470:
466:
457:
450:
444:
440:
434:
429:
422:
417:
415:
413:
409:
405:
401:
393:
384:
379:
372:
367:
360:
355:
348:
343:
336:
331:
329:
327:
323:
319:
315:
311:
307:
301:
294:Fossil record
293:
291:
289:
285:
276:
274:
272:
268:
263:
261:
257:
253:
249:
245:
241:
240:gastroschisis
237:
233:
228:
226:
222:
218:
214:
210:
203:Hemivertebrae
202:
200:
196:
194:
190:
186:
182:
181:low back pain
178:
177:contralateral
174:
170:
166:
162:
158:
154:
150:
149:sacralization
146:
138:
134:
132:
128:
124:
120:
116:
112:
108:
104:
100:
96:
95:Lumbarization
89:
85:
80:
73:
71:
69:
65:
61:
57:
49:
45:
42:
40:
36:
31:
19:
18:Hemivertebrae
1612:Macrocephaly
1458:
1454:Acheiropodia
1426:Ectrodactyly
1346:
1327:
1212:Oligodactyly
1207:Clinodactyly
1136:Appendicular
1066:
1046:
978:
974:
964:
953:. Retrieved
948:
939:
904:
900:
890:
865:
861:
855:
833:(1): 39–44.
830:
826:
820:
801:
795:
786:
774:. Retrieved
770:
760:
736:(4): 532–6.
733:
729:
705:. Retrieved
701:
676:November 27,
674:. Retrieved
670:the original
660:
650:November 27,
648:. Retrieved
644:
635:
626:
591:
587:
577:
531:Anal atresia
517:
514:Associations
500:Spina bifida
498:
495:Spina bifida
489:
462:
397:
309:
303:
280:
264:
256:OEIS complex
229:
206:
197:
185:biomechanics
159:of the last
148:
144:
143:
111:lumbar spine
94:
93:
55:
54:
1642:Saddle nose
1409:Webbed toes
1400:Polydactyly
1285:Genu valgum
1217:Polydactyly
901:Orthop Surg
326:sclerotomes
173:ipsilateral
64:spinal cord
48:orthopedics
1787:Categories
1617:Platybasia
1553:Oxycephaly
1466:Phocomelia
1460:Ectromelia
1436:Stub thumb
1404:Syndactyly
1371:Hammer toe
1340:Pigeon toe
1290:Genu varum
1262:Coxa valga
1120:Congenital
955:2007-02-04
707:2007-02-04
569:References
314:archosaurs
221:neurologic
1669:Scoliosis
1476:Hemimelia
1361:Pes cavus
1354:Flat feet
1335:Club foot
1267:Coxa vara
997:1750-1172
561:anomalies
473:arthritis
408:notochord
400:butterfly
213:scoliosis
115:vertebrae
68:vertebrae
39:Specialty
1719:Cervical
1166:shoulder
1162:clavicle
1144:dysmelia
1015:21846383
931:34791784
882:21951610
847:16429983
776:26 April
752:17302550
618:26484005
217:lordosis
209:kyphosis
131:genetics
1734:sternum
1006:3169446
922:8654657
862:Spine J
609:4603258
557:and/or
510:trait.
443:CT scan
324:of the
318:mammals
273:shape.
151:) is a
101:in the
99:anomaly
1757:other:
1471:Amelia
1348:valgus
1013:
1003:
995:
951:. 2006
929:
919:
880:
845:
808:
750:
616:
606:
594:: 42.
559:radial
402:on an
310:T. rex
288:sacrum
286:. The
215:, and
165:sacrum
109:. The
107:sacrum
97:is an
1724:Bifid
1605:other
1522:Axial
1329:varus
1077:756.1
1063:.0-.4
1057:Q67.5
441:of a
404:x-ray
271:screw
193:X-ray
169:ilium
103:spine
60:spine
1710:ribs
1277:knee
1153:Arms
1140:limb
1072:9-CM
1011:PMID
993:ISSN
927:PMID
878:PMID
843:PMID
806:ISBN
778:2022
748:PMID
678:2016
652:2016
614:PMID
553:R –
547:E –
541:T –
535:C –
529:A –
504:Manx
316:and
267:dogs
147:(or
88:ribs
1240:hip
1231:Leg
1068:ICD
1061:Q76
1048:ICD
1001:PMC
983:doi
917:PMC
909:doi
870:doi
835:doi
738:doi
734:230
604:PMC
596:doi
328:".
250:3,
242:3,
195:.
175:or
1789::
1402:/
1250:/
1164:/
1142:/
1126:/
1075::
1059:,
1055::
1052:10
1009:.
999:.
991:.
977:.
973:.
947:.
925:.
915:.
905:13
903:.
899:.
876:.
866:11
864:.
841:.
831:47
829:.
769:.
746:.
732:.
728:.
716:^
700:.
686:^
643:.
612:.
602:.
590:.
586:.
522::
262:.
258:,
254:,
246:,
238:,
234:,
211:,
70:.
46:,
1736::
1712::
1112:e
1105:t
1098:v
1070:-
1050:-
1040:D
1017:.
985::
979:6
958:.
933:.
911::
884:.
872::
849:.
837::
814:.
780:.
754:.
740::
710:.
680:.
654:.
620:.
598::
592:9
90:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.