209:, by drinking the blood of animals which fed on venomous snakes. He is thought to have assumed that those animals acquired some detoxifying property, so that their blood would contain transformed components of the snake venom that could induce resistance to it instead of exerting a toxic effect. Mithridates reasoned that, by drinking the blood of these animals, he could acquire a similar resistance. Fearing assassination by poison, he took daily sub-lethal doses of venom to build tolerance. He is also said to have sought to create a 'universal antidote' to protect him from all poisons. For nearly 2000 years, poisons were thought to be the
906:(CDC) concluded that "Multiple studies in different settings have consistently shown that infection with SARS-CoV-2 and vaccination each result in a low risk of subsequent infection with antigenically similar variants for at least 6 months. Numerous immunologic studies and a growing number of epidemiologic studies have shown that vaccinating previously infected individuals significantly enhances their immune response and effectively reduces the risk of subsequent infection, including in the setting of increased circulation of more infectious variants. ..."
718:
299:
66:
502:
647:
primary and secondary responses were first described in 1921 by
English immunologist Alexander Glenny although the mechanism involved was not discovered until later. This type of immunity is both active and adaptive because the body's immune system prepares itself for future challenges. Active immunity often involves both the cell-mediated and humoral aspects of immunity as well as input from the
627:
148:
160:
396:, and it became common practice to use this term without regard for chronology. The success and general acceptance of Jenner's procedure would later drive the general nature of vaccination developed by Pasteur and others towards the end of the 19th century. In 1891, Pasteur widened the definition of
268:
as being caused by a miasma, a noxious form of "bad air". If someone was exposed to the miasma in a swamp, in evening air, or breathing air in a sickroom or hospital ward, they could catch a disease. Since the 19th century, communicable diseases came to be viewed as being caused by germs/microbes.
646:
are activated by a pathogen, memory B-cells and T- cells develop, and the primary immune response results. Throughout the lifetime of an animal, these memory cells will "remember" each specific pathogen encountered, and can mount a strong secondary response if the pathogen is detected again. The
136:
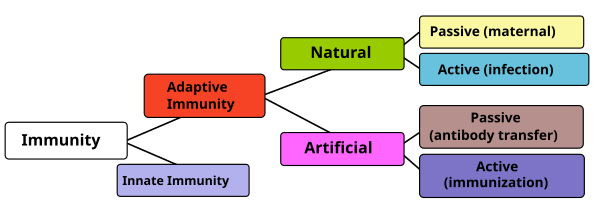
such as vaccination). Adaptive immunity can also be classified as 'active' or 'passive'. Active immunity is acquired through the exposure to a pathogen, which triggers the production of antibodies by the immune system. Passive immunity is acquired through the transfer of antibodies or activated
108:
while the non-reaction to self substances is described as immunity. The two components of the immune system create a dynamic biological environment where "health" can be seen as a physical state where the self is immunologically spared, and what is foreign is inflammatorily and immunologically
713:
for his pioneering work in vaccination. The method
Pasteur used entailed treating the infectious agents for those diseases, so they lost the ability to cause serious disease. Pasteur adopted the name vaccine as a generic term in honor of Jenner's discovery, which Pasteur's work built
2262:
Arias, Andrés A.; Neehus, Anna-Lena; Ogishi, Masato; Meynier, Vincent; Krebs, Adam; Lazarov, Tomi; Lee, Angela M.; Arango-Franco, Carlos A.; Yang, Rui; Orrego, Julio; Corcini Berndt, Melissa; Rojas, Julian; Li, Hailun; Rinchai, Darawan; Erazo-Borrás, Lucia (2024-09-12).
195:: "the sick and the dying were tended by the pitying care of those who had recovered, because they knew the course of the disease and were themselves free from apprehensions. For no one was ever attacked a second time, or not with a fatal result".
829:(OMV) vaccines contain the outer membrane of a bacterium without any of its internal components or genetic material. Thus, ideally, they stimulate an immune response effective against the original bacteria without the risk of an infection.
787:
are inactivated toxic compounds from micro-organisms in cases where these (rather than the micro-organism itself) cause illness, used prior to an encounter with the toxin of the micro-organism. Examples of toxoid-based vaccines include
524:
Artificially acquired passive immunity is a short-term immunization induced by the transfer of antibodies, which can be administered in several forms; as human or animal blood plasma, as pooled human immunoglobulin for intravenous
252:
in the 9th century. In the treatise, Al Razi describes the clinical presentation of smallpox and measles and goes on to indicate that exposure to these specific agents confers lasting immunity (although he does not use this term).
117:
and maintain homeostasis, contributing to the activation of an adaptive immune response. It does not adapt to specific external stimulus or a prior infection, but relies on genetically encoded recognition of particular patterns.
764:
vaccines are composed of micro-organisms that have been cultivated under conditions which disable their ability to induce disease. These responses are more durable, however, they may require booster shots. Examples include
112:
Innate immunity, also known as native immunity, is a semi-specific and widely distributed form of immunity. It is defined as the first line of defense against pathogens, representing a critical systemic response to prevent
729:
became the first group to require their military recruits to be vaccinated against smallpox, as the spread of smallpox was linked to combat. Subsequently, the practice of vaccination would increase with the spread of war.
426:
from one individual to another. Passive immunity can occur naturally, such as when maternal antibodies are transferred to the foetus through the placenta, and can also be induced artificially, when high levels of
174:
For thousands of years mankind has been intrigued with the causes of disease and the concept of immunity. The prehistoric view was that disease was caused by supernatural forces, and that illness was a form of
1548:
705:, a substance that contains antigen. A vaccine stimulates a primary response against the antigen without causing symptoms of the disease. The term vaccination was coined by Richard Dunning, a colleague of
898:
Hybrid immunity is the combination of natural immunity and artificial immunity. Studies of hybrid-immune people found that their blood was better able to neutralize the Beta and other variants of
447:
individuals. Passive immunization is used when there is a high risk of infection and insufficient time for the body to develop its own immune response, or to reduce the symptoms of ongoing or
144:
The diagram below summarizes these divisions of immunity. Adaptive immunity recognizes more diverse patterns. Unlike innate immunity it is associated with memory of the pathogen.
588:" of cell-mediated immunity, is conferred by the transfer of "sensitized" or activated T-cells from one individual into another. It is rarely used in humans because it requires
451:
diseases. Passive immunity provides immediate protection, but the body does not develop memory, therefore the patient is at risk of being infected by the same pathogen later.
2343:
926:
and numerous other immune response genes. While many of these genes are generally required for active and passive immune responses (see sections above), there are also many
1349:
Janeway CA Jr, Travers P, Walport M, et al. Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and
Disease. 5th edition. New York: Garland Science; 2001. Glossary. Available from:
352:. Immunization has existed in various forms for at least a thousand years, without the terminology. The earliest use of immunization is unknown, but, about 1000 AD, the
634:, reinfection at later time points leads to a rapid increase in antibody production and effector T cell activity. These later infections can be mild or even unapparent.
741:
Inactivated vaccines are composed of micro-organisms that have been killed with chemicals and/or heat and are no longer infectious. Examples are vaccines against
104:
cells that can distinguish between specific "non-self" substances in the presence of "self". The reaction to foreign substances is etymologically described as
2240:
903:
1860:
568:, was often the only specific treatment for certain infections. Immunoglobulin therapy continued to be a first line therapy in the treatment of severe
1187:
Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, et al. Molecular
Biology of the Cell. 4th edition. New York: Garland Science; 2002. Innate Immunity. Available from:
372:(poking the skin with powdered material derived from smallpox crusts) was quite common. This practice was first introduced into the west in 1721 by
2336:
972:
966:
814:
are composed of small fragments or pieces from a pathogenic (disease-causing) organism. A characteristic example is the subunit vaccine against
494:
that are transferred to the gut of a nursing infant, protecting against bacterial infections, until the newborn can synthesize its antibodies.
356:
began practicing a form of immunization by drying and inhaling powders derived from the crusts of smallpox lesions. Around the 15th century in
839:
that codes for an antigen into host cells, which then produce that antigen, stimulating an immune response. This category of vaccine includes
1661:
665:
Naturally acquired active immunity occurs as the result of an infection. When a person is exposed to a live pathogen and develops a primary
1906:
Acevedo, R; Fernandez, S; Zayas, C; Acosta, D; Sarmiento, ME; Ferro, VA; Rosenquvist, E; Campa, C; Cardoso, D; Garcia, L; Perez, JL (2014).
1384:
295:
began to explain how bacteria caused disease, and how, following infection, the human body gained the ability to resist further infections.
1450:
187:(blood, phlegm, yellow bile or black bile). The first written descriptions of the concept of immunity may have been made by the Athenian
2329:
1523:
1490:
1172:
996:
944:) but are otherwise healthy. They also seem to respond to other infections more or less normally. The condition is therefore called
826:
669:, this leads to immunological memory. Many disorders of immune system function can affect the formation of active immunity, such as
564:
The artificial induction of passive immunity has been used for over a century to treat infectious disease, and before the advent of
2675:
2235:
938:
in humans. Individuals with genetic defects in TNF may get recurrent and life-threatening infections with tuberculosis bacteria (
686:
519:
133:
1651:
179:
punishment for "bad deeds" or "evil thoughts" visited upon the soul by the gods or by one's enemies. In
Classical Greek times,
129:. Like the innate system, the acquired system includes both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components.
125:. Unlike the innate immunity, the acquired immunity is highly specific to a particular pathogen, including the development of
2670:
549:. Immunity derived from passive immunization lasts for only a short period of time, and there is also a potential risk for
2613:
1846:
249:
592:(matched) donors, which are often difficult to find. In unmatched donors this type of transfer carries severe risks of
1032:
1026:
960:
2499:
940:
388:), which caused a mild infection that also induced immunity to smallpox. By 1800, the procedure was referred to as
183:, who is regarded as the Father of Medicine, diseases were attributed to an alteration or imbalance in one of the
593:
373:
121:
Adaptive or acquired immunity is the active component of the host immune response, mediated by antigen-specific
257:
199:
1868:
717:
137:
T-cells derived from an immune host either artificially or through the placenta; it is short-lived, requiring
1591:
2003 The
Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia, Sixth Edition. Columbia University Press (from Answers.com, 2006.)
2679:
2437:
1100:
978:
609:
298:
240:
The first clinical description of immunity which arose from a specific disease-causing organism is probably
31:
2701:
2419:
2355:
1601:
1090:
605:
573:
322:
288:
230:
85:
750:
202:(120-63 BC) who, to induce active immunity for snake venom, recommended using a method similar to modern
109:
eliminated. "Disease" can arise when what is foreign cannot be eliminated or what is self is not spared.
2648:
2504:
2482:
931:
761:
542:
530:
2665:
2598:
2509:
2433:
2184:
2076:
1135:
848:
648:
631:
621:
480:
326:
222:
126:
81:
2321:
2772:
2725:
2660:
2643:
2477:
2395:
696:
569:
463:
naturally acquires passive immunity from its mother during pregnancy. Maternal passive immunity is
210:
1838:
2545:
2216:
1529:
1392:
1332:
589:
50:
132:
Adaptive immunity can be acquired either 'naturally' (by infection) or 'artificially' (through
2593:
2359:
2286:
2208:
2200:
2153:
2104:
2045:
2027:
1988:
1939:
1820:
1802:
1761:
1712:
1657:
1519:
1486:
1458:
1324:
1280:
1231:
1168:
1008:
815:
811:
742:
674:
585:
448:
45:
is the state of being insusceptible or resistant to a noxious agent or process, especially a
2713:
2653:
2625:
2620:
2588:
2575:
2565:
2294:
2276:
2192:
2143:
2135:
2094:
2084:
2035:
2019:
1978:
1970:
1929:
1919:
1810:
1792:
1751:
1743:
1702:
1694:
1511:
1314:
1270:
1262:
1221:
1213:
1160:
1110:
954:
851:, which differ in the chemical form of nucleic acid and how it is delivered into host cells.
670:
601:
550:
538:
417:
385:
318:
314:
279:
The first scientist who developed a full theory of immunity was Ilya
Mechnikov who revealed
65:
2608:
1647:
1362:
832:
803:
799:
666:
405:
303:
225:, was used well into the 19th century. The term "immunes" is also found in the epic poem "
276:
immunis, meaning exemption from military service, tax payments or other public services.
2299:
2188:
2080:
2635:
2580:
2521:
2441:
2414:
2148:
2123:
2099:
2064:
2040:
2007:
1983:
1958:
1934:
1907:
1815:
1780:
1756:
1731:
1628:
1515:
1275:
1250:
1226:
1201:
1164:
1105:
1020:
807:
558:
554:
361:
353:
2006:
Pardi, Norbert; Hogan, Michael J.; Porter, Frederick W.; Weissman, Drew (April 2018).
400:
in honour of Jenner, and it then became essential to qualify the term by referring to
2766:
2603:
2492:
2264:
2220:
2172:
1707:
1682:
1533:
1130:
1095:
867:
710:
706:
660:
545:. It is also used in the treatment of several types of acute infection, and to treat
444:
401:
377:
284:
77:
1336:
501:
2570:
2555:
2550:
2487:
2385:
935:
836:
766:
534:
280:
265:
138:
105:
97:
93:
54:
1698:
17:
2089:
1573:
1120:
844:
840:
754:
690:
565:
491:
393:
389:
369:
365:
234:
218:
184:
180:
122:
70:
2281:
2196:
1350:
1319:
1302:
1217:
1188:
626:
596:. It has, however, been used to treat certain diseases including some types of
2693:
2446:
2352:
1747:
1420:
1115:
949:
899:
863:
793:
506:
423:
330:
310:
292:
214:
188:
101:
2290:
2204:
2031:
1959:"DNA immunization as a technology platform for monoclonal antibody induction"
1924:
1806:
930:
that appear to be required for very specific immune responses. For instance,
870:
injection as they are not absorbed reliably through the gut. Live attenuated
2751:
2456:
1506:
Mayor, Adrienne (2019). "Mithridates of Pontus and His
Universal Antidote".
1125:
1085:
1080:
495:
476:
338:
226:
114:
89:
2212:
2157:
2108:
2049:
1992:
1943:
1824:
1765:
1716:
1328:
1284:
1235:
467:-mediated immunity. The mother's antibodies (MatAb) are passed through the
392:. To avoid confusion, smallpox inoculation was increasingly referred to as
2236:"Science Brief: SARS-CoV-2 Infection-induced and Vaccine-induced Immunity"
902:
than never-infected, vaccinated people. Moreover, on 29 October 2021, the
721:
Poster from before the 1979 eradication of smallpox, promoting vaccination
244:("Kitab fi al-jadari wa-al-hasbah″, translated 1848) written by the
2741:
2526:
2514:
2472:
2426:
2390:
2139:
2023:
923:
468:
464:
436:
349:
167:
46:
2265:"Tuberculosis in otherwise healthy adults with inherited TNF deficiency"
1974:
1882:
422:
Passive immunity is the immunity acquired by the transfer of ready-made
159:
2746:
2560:
2409:
2380:
1588:
879:
875:
856:
789:
774:
770:
746:
734:
726:
702:
643:
639:
397:
334:
261:
245:
206:
176:
164:
38:
27:
State of being insusceptible or resistant to a noxious agent or process
1797:
1266:
2718:
2706:
2451:
2402:
1683:"Passive immunity in prevention and treatment of infectious diseases"
1066:
919:
915:
784:
597:
546:
381:
345:
203:
192:
2122:
Lauer KB, Borrow R, Blanchard TJ (January 2017). Papasian CJ (ed.).
1369:. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 2 November 2021.
348:, the induction of active immunity emerged in an attempt to contain
147:
100:. The adaptive component, on the other hand, involves more advanced
2316:
475:
receptor on placental cells. This occurs around the third month of
53:. Immunity may occur naturally or be produced by prior exposure or
1044:
1038:
1002:
990:
984:
948:(MSMD) and variants of it can be caused by other genes related to
887:
883:
871:
778:
500:
460:
440:
432:
428:
357:
297:
273:
158:
64:
1867:. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Archived from
757:. Most vaccines of this type are likely to require booster shots.
341:
became the first major success of modern therapeutic immunology.
1249:
Riera Romo, M.; Pérez-Martínez, D.; Castillo Ferrer, C. (2016).
1056:
1050:
1014:
927:
526:
472:
2325:
630:
The time course of an immune response. Due to the formation of
487:
380:
introduced the far safer method of deliberate infection with
260:
was also widely accepted. The theory viewed diseases such as
213:
of disease, and a complicated mixture of ingredients, called
2317:
The Center for
Modeling Immunity to Enteric Pathogens (MIEP)
1908:"Bacterial outer membrane vesicles and vaccine applications"
822:
In addition, there are some newer types of vaccines in use:
146:
2173:"COVID super-immunity: one of the pandemic's great puzzles"
498:
present in mothers milk is an example of passive immunity.
701:
Artificially acquired active immunity can be induced by a
486:
Passive immunity is also provided through the transfer of
1732:"Notes on the Production of Immunity to Diphtheria Toxin"
697:
Pandemic prevention § CRISPR-based immune subsystems
1656:(Fifth ed.). New York and London: Garland Science.
952:
production or signaling (e.g. by mutations in the genes
1957:
Liu, Shuying; Wang, Shixia; Lu, Shan (April 27, 2016).
855:
A variety of vaccine types are under development; see
2124:"Multivalent and Multipathogen Viral Vector Vaccines"
2734:
2692:
2634:
2535:
2465:
2373:
2366:
1451:"The Concept of Immunity. History and Applications"
191:who, in 430 BC, described that when the plague hit
233:to describe a North African tribe's resistance to
946:Mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial disease
1602:"The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1908"
1301:Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O (February 2006).
529:) or intramuscular (IG) use, and in the form of
1779:Zhang, Jielin; Crumpacker, Clyde (2022-05-18).
1629:"Microbiology and Immunology On-Line Textbook"
1206:The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology
88:components. Innate immunity is present in all
2337:
1572:Rāzī, Abū Bakr Muḥammad ibn Zakarīyā (1848).
1414:
1412:
1410:
1408:
1406:
1404:
1402:
1251:"Innate immunity in vertebrates: an overview"
1155:"Molecules, cells, and tissues of immunity".
30:"Immune" redirects here. For other uses, see
8:
1650:, Travers P, Walport M, Shlomchik M (2001).
1472:
1470:
1468:
1351:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK10759/
1189:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26846/
272:The modern word "immunity" derives from the
1485:] (in French). Paris: Francois Bourin.
2370:
2344:
2330:
2322:
2241:Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
2063:Bull JJ, Nuismer SL, Antia R (July 2019).
2008:"mRNA vaccines — a new era in vaccinology"
1642:
1640:
1638:
1444:
1442:
1440:
1438:
1436:
1434:
1432:
1303:"Pathogen recognition and innate immunity"
904:Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
886:in order to produce immunity based in the
302:Louis Pasteur in his laboratory, 1885, by
2298:
2280:
2147:
2098:
2088:
2039:
1982:
1933:
1923:
1814:
1796:
1755:
1706:
1676:
1674:
1318:
1274:
1225:
673:(both acquired and congenital forms) and
198:Active immunotherapy may have begun with
1730:Glenny AT, Südmersen HJ (October 1921).
1547:Chambers, Ephraim (1728). "Mithridate".
1425:. Academic Press – via Amazon.com.
1385:"Introduction to the History of disease"
1378:
1376:
716:
625:
217:, was used to cure poisoning during the
1843:Smallpox – A Great and Terrible Scourge
1781:"HIV UTR, LTR, and Epigenetic Immunity"
1575:A Treatise on the Small-pox and Measles
1147:
604:. This type of transfer differs from a
2065:"Recombinant vector vaccine evolution"
1623:
1621:
1619:
1617:
1615:
1200:Turvey SE, Broide DH (February 2010).
514:Artificially acquired passive immunity
321:, and following the 1890 discovery by
1681:Keller MA, Stiehm ER (October 2000).
1457:. University of Pavia. Archived from
7:
1296:
1294:
914:Immunity is determined genetically.
733:There are four types of traditional
483:that can pass through the placenta.
455:Naturally acquired passive immunity
229:" written around 60 BC by the poet
221:. An updated version of this cure,
1963:Emerging Microbes & Infections
1861:"Immunization: You call the shots"
1516:10.1016/B978-0-12-815339-0.00011-1
1477:Jean Tardieu de Maleissye (1991).
242:A Treatise on Smallpox and Measles
25:
1865:The National Immunization Program
1422:History of Immunology (Hardcover)
934:(TNF) is required for defense of
576:lot antibiotics were introduced.
1455:Immunology Course Medical School
1391:. Rhodes College. Archived from
1165:10.1016/B978-012198382-6/50025-X
687:artificial induction of immunity
533:(MAb). Passive transfer is used
2128:Clinical and Vaccine Immunology
509:antitoxin produced (dated 1895)
329:of antitoxin based immunity to
2671:Immunoglobulin class switching
1550:History of Science: Cyclopædia
1383:Lindquester GJ (Spring 2006).
608:, in which (undifferentiated)
1:
2171:Callaway, Ewen (2021-10-14).
2012:Nature Reviews Drug Discovery
1847:National Institutes of Health
1699:10.1128/CMR.13.4.602-614.2000
1687:Clinical Microbiology Reviews
580:Transfer of activated T-cells
2090:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006857
572:until the 1930s, even after
520:Temporarily induced immunity
505:One of the first bottles of
435:) antibodies specific for a
256:Until the 19th century, the
2134:(1): e00298–16, e00298–16.
862:Most vaccines are given by
479:. IgG is the only antibody
291:, the fledgling science of
2789:
2500:Polyclonal B cell response
2282:10.1038/s41586-024-07866-3
2197:10.1038/d41586-021-02795-x
2069:PLOS Computational Biology
1320:10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.015
1218:10.1016/j.jaci.2009.07.016
941:Mycobacterium tuberculosis
857:Experimental Vaccine Types
694:
684:
658:
619:
517:
415:
29:
2234:Staff (29 October 2021).
1748:10.1017/S0022172400033945
1631:. USC School of Medicine.
594:graft versus host disease
374:Lady Mary Wortley Montagu
1925:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00121
1159:: 1–15. 1 January 2004.
610:hematopoietic stem cells
200:Mithridates VI of Pontus
163:A representation of the
141:for continued immunity.
1912:Frontiers in Immunology
1508:Toxicology in Antiquity
1419:Silverstein AM (1989).
1101:Heterosubtypic immunity
443:are transferred to non-
32:Immune (disambiguation)
2614:Tolerance in pregnancy
2356:adaptive immune system
1736:The Journal of Hygiene
1091:Cell-mediated immunity
827:Outer Membrane Vesicle
722:
635:
606:bone marrow transplant
510:
306:
289:germ theory of disease
231:Marcus Annaeus Lucanus
171:
151:
94:inflammatory responses
73:
2649:Somatic hypermutation
2483:Polyclonal antibodies
2478:Monoclonal antibodies
1553:. London. p. 561
1212:(2 Suppl 2): S24-32.
932:Tumor Necrosis Factor
849:viral vector vaccines
720:
681:Artificially acquired
659:Further information:
629:
620:Further information:
561:of non-human origin.
543:hypogammaglobulinemia
531:monoclonal antibodies
504:
301:
162:
150:
68:
2666:Junctional diversity
2434:Antigen presentation
2140:10.1128/CVI.00298-16
2024:10.1038/nrd.2017.243
1479:{Histoire du poison}
1389:Disease and Immunity
1157:Immunology Guidebook
1136:Virgin soil epidemic
649:innate immune system
632:immunological memory
622:immunological memory
570:respiratory diseases
490:antibodies found in
223:Theriacum Andromachi
127:immunological memory
92:, immune responses:
2661:V(D)J recombination
2644:Affinity maturation
2396:Antigenic variation
2189:2021Natur.598..393C
2081:2019PLSCB..15E6857B
1975:10.1038/emi.2016.27
1578:. Sydenham Society.
882:vaccines are given
471:to the fetus by an
170:of the 19th century
155:History of theories
61:Innate and adaptive
812:conjugate vaccines
723:
655:Naturally acquired
636:
557:, especially from
541:diseases, such as
511:
368:, the practice of
307:
172:
152:
134:deliberate actions
74:
51:infectious disease
18:Immunity (medical)
2760:
2759:
2688:
2687:
2438:professional APCs
2275:(8029): 417–425.
2183:(7881): 393–394.
1798:10.3390/v14051084
1663:978-0-8153-4101-7
1483:History of Poison
1267:10.1111/imm.12597
1202:"Innate immunity"
816:Hepatitis B virus
709:, and adapted by
675:immunosuppression
612:are transferred.
586:adoptive transfer
449:immunosuppressive
16:(Redirected from
2780:
2654:Clonal selection
2626:Immune privilege
2621:Immunodeficiency
2576:Cross-reactivity
2566:Hypersensitivity
2371:
2346:
2339:
2332:
2323:
2305:
2304:
2302:
2284:
2259:
2253:
2252:
2250:
2248:
2231:
2225:
2224:
2168:
2162:
2161:
2151:
2119:
2113:
2112:
2102:
2092:
2060:
2054:
2053:
2043:
2003:
1997:
1996:
1986:
1954:
1948:
1947:
1937:
1927:
1903:
1897:
1896:
1894:
1893:
1887:www.vaccines.gov
1879:
1873:
1872:
1857:
1851:
1850:
1835:
1829:
1828:
1818:
1800:
1776:
1770:
1769:
1759:
1727:
1721:
1720:
1710:
1678:
1669:
1667:
1644:
1633:
1632:
1625:
1610:
1609:
1598:
1592:
1586:
1580:
1579:
1569:
1563:
1562:
1560:
1558:
1544:
1538:
1537:
1503:
1497:
1496:
1474:
1463:
1462:
1446:
1427:
1426:
1416:
1397:
1396:
1380:
1371:
1370:
1363:"Immunity types"
1359:
1353:
1347:
1341:
1340:
1322:
1298:
1289:
1288:
1278:
1246:
1240:
1239:
1229:
1197:
1191:
1185:
1179:
1178:
1152:
1111:Humoral immunity
833:Genetic vaccines
671:immunodeficiency
602:immunodeficiency
551:hypersensitivity
539:immunodeficiency
535:prophylactically
418:Passive immunity
412:Passive immunity
386:smallpox vaccine
319:diphtheria toxin
315:Alexandre Yersin
21:
2788:
2787:
2783:
2782:
2781:
2779:
2778:
2777:
2763:
2762:
2761:
2756:
2730:
2684:
2630:
2609:Clonal deletion
2537:
2531:
2461:
2362:
2350:
2313:
2308:
2261:
2260:
2256:
2246:
2244:
2233:
2232:
2228:
2170:
2169:
2165:
2121:
2120:
2116:
2075:(7): e1006857.
2062:
2061:
2057:
2005:
2004:
2000:
1956:
1955:
1951:
1905:
1904:
1900:
1891:
1889:
1883:"Vaccine Types"
1881:
1880:
1876:
1859:
1858:
1854:
1837:
1836:
1832:
1778:
1777:
1773:
1729:
1728:
1724:
1680:
1679:
1672:
1664:
1646:
1645:
1636:
1627:
1626:
1613:
1600:
1599:
1595:
1587:
1583:
1571:
1570:
1566:
1556:
1554:
1546:
1545:
1541:
1526:
1505:
1504:
1500:
1493:
1476:
1475:
1466:
1448:
1447:
1430:
1418:
1417:
1400:
1382:
1381:
1374:
1361:
1360:
1356:
1348:
1344:
1300:
1299:
1292:
1248:
1247:
1243:
1199:
1198:
1194:
1186:
1182:
1175:
1154:
1153:
1149:
1145:
1140:
1076:
912:
896:
894:Hybrid immunity
699:
693:
685:Main articles:
683:
667:immune response
663:
657:
624:
618:
616:Active immunity
590:histocompatible
582:
553:reactions, and
537:in the case of
522:
516:
457:
420:
414:
406:measles vaccine
304:Albert Edelfelt
211:proximate cause
157:
63:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2786:
2784:
2776:
2775:
2765:
2764:
2758:
2757:
2755:
2754:
2749:
2744:
2738:
2736:
2732:
2731:
2729:
2728:
2723:
2722:
2721:
2711:
2710:
2709:
2698:
2696:
2690:
2689:
2686:
2685:
2683:
2682:
2673:
2668:
2663:
2658:
2657:
2656:
2651:
2640:
2638:
2636:Immunogenetics
2632:
2631:
2629:
2628:
2623:
2618:
2617:
2616:
2611:
2606:
2601:
2596:
2584:
2583:
2581:Co-stimulation
2578:
2573:
2568:
2563:
2558:
2553:
2548:
2541:
2539:
2533:
2532:
2530:
2529:
2524:
2522:Immune complex
2518:
2517:
2512:
2507:
2502:
2497:
2496:
2495:
2490:
2485:
2480:
2469:
2467:
2463:
2462:
2460:
2459:
2454:
2449:
2444:
2442:Dendritic cell
2430:
2429:
2424:
2423:
2422:
2420:Conformational
2417:
2406:
2405:
2400:
2399:
2398:
2393:
2388:
2377:
2375:
2368:
2364:
2363:
2351:
2349:
2348:
2341:
2334:
2326:
2320:
2319:
2312:
2311:External links
2309:
2307:
2306:
2254:
2226:
2163:
2114:
2055:
2018:(4): 261–279.
1998:
1949:
1898:
1874:
1871:on 2006-09-29.
1852:
1830:
1771:
1742:(2): 176–220.
1722:
1670:
1662:
1634:
1611:
1606:NobelPrize.org
1593:
1581:
1564:
1539:
1524:
1498:
1491:
1464:
1461:on 2007-01-02.
1428:
1398:
1395:on 2006-07-21.
1372:
1354:
1342:
1313:(4): 783–801.
1290:
1261:(2): 125–139.
1241:
1192:
1180:
1173:
1146:
1144:
1141:
1139:
1138:
1133:
1128:
1123:
1118:
1113:
1108:
1106:Hoskins effect
1103:
1098:
1093:
1088:
1083:
1077:
1075:
1072:
918:in humans and
911:
908:
895:
892:
853:
852:
830:
820:
819:
808:polysaccharide
797:
782:
758:
682:
679:
656:
653:
617:
614:
581:
578:
559:gamma globulin
555:serum sickness
515:
512:
456:
453:
416:Main article:
413:
410:
362:Ottoman Empire
283:in 1882. With
156:
153:
62:
59:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2785:
2774:
2771:
2770:
2768:
2753:
2750:
2748:
2745:
2743:
2740:
2739:
2737:
2733:
2727:
2724:
2720:
2717:
2716:
2715:
2712:
2708:
2705:
2704:
2703:
2700:
2699:
2697:
2695:
2691:
2681:
2677:
2674:
2672:
2669:
2667:
2664:
2662:
2659:
2655:
2652:
2650:
2647:
2646:
2645:
2642:
2641:
2639:
2637:
2633:
2627:
2624:
2622:
2619:
2615:
2612:
2610:
2607:
2605:
2604:Clonal anergy
2602:
2600:
2597:
2595:
2592:
2591:
2590:
2586:
2585:
2582:
2579:
2577:
2574:
2572:
2569:
2567:
2564:
2562:
2559:
2557:
2554:
2552:
2549:
2547:
2543:
2542:
2540:
2534:
2528:
2525:
2523:
2520:
2519:
2516:
2513:
2511:
2508:
2506:
2503:
2501:
2498:
2494:
2493:Microantibody
2491:
2489:
2486:
2484:
2481:
2479:
2476:
2475:
2474:
2471:
2470:
2468:
2464:
2458:
2455:
2453:
2450:
2448:
2445:
2443:
2439:
2435:
2432:
2431:
2428:
2425:
2421:
2418:
2416:
2413:
2412:
2411:
2408:
2407:
2404:
2401:
2397:
2394:
2392:
2389:
2387:
2384:
2383:
2382:
2379:
2378:
2376:
2372:
2369:
2365:
2361:
2357:
2354:
2347:
2342:
2340:
2335:
2333:
2328:
2327:
2324:
2318:
2315:
2314:
2310:
2301:
2296:
2292:
2288:
2283:
2278:
2274:
2270:
2266:
2258:
2255:
2243:
2242:
2237:
2230:
2227:
2222:
2218:
2214:
2210:
2206:
2202:
2198:
2194:
2190:
2186:
2182:
2178:
2174:
2167:
2164:
2159:
2155:
2150:
2145:
2141:
2137:
2133:
2129:
2125:
2118:
2115:
2110:
2106:
2101:
2096:
2091:
2086:
2082:
2078:
2074:
2070:
2066:
2059:
2056:
2051:
2047:
2042:
2037:
2033:
2029:
2025:
2021:
2017:
2013:
2009:
2002:
1999:
1994:
1990:
1985:
1980:
1976:
1972:
1968:
1964:
1960:
1953:
1950:
1945:
1941:
1936:
1931:
1926:
1921:
1917:
1913:
1909:
1902:
1899:
1888:
1884:
1878:
1875:
1870:
1866:
1862:
1856:
1853:
1848:
1844:
1840:
1839:"Variolation"
1834:
1831:
1826:
1822:
1817:
1812:
1808:
1804:
1799:
1794:
1790:
1786:
1782:
1775:
1772:
1767:
1763:
1758:
1753:
1749:
1745:
1741:
1737:
1733:
1726:
1723:
1718:
1714:
1709:
1704:
1700:
1696:
1693:(4): 602–14.
1692:
1688:
1684:
1677:
1675:
1671:
1665:
1659:
1655:
1654:
1653:Immunobiology
1649:
1643:
1641:
1639:
1635:
1630:
1624:
1622:
1620:
1618:
1616:
1612:
1607:
1603:
1597:
1594:
1590:
1585:
1582:
1577:
1576:
1568:
1565:
1552:
1551:
1543:
1540:
1535:
1531:
1527:
1525:9780128153390
1521:
1517:
1513:
1509:
1502:
1499:
1494:
1492:2-87686-082-1
1488:
1484:
1480:
1473:
1471:
1469:
1465:
1460:
1456:
1452:
1445:
1443:
1441:
1439:
1437:
1435:
1433:
1429:
1424:
1423:
1415:
1413:
1411:
1409:
1407:
1405:
1403:
1399:
1394:
1390:
1386:
1379:
1377:
1373:
1368:
1364:
1358:
1355:
1352:
1346:
1343:
1338:
1334:
1330:
1326:
1321:
1316:
1312:
1308:
1304:
1297:
1295:
1291:
1286:
1282:
1277:
1272:
1268:
1264:
1260:
1256:
1252:
1245:
1242:
1237:
1233:
1228:
1223:
1219:
1215:
1211:
1207:
1203:
1196:
1193:
1190:
1184:
1181:
1176:
1174:9780121983826
1170:
1166:
1162:
1158:
1151:
1148:
1142:
1137:
1134:
1132:
1131:Vaccine-naive
1129:
1127:
1124:
1122:
1119:
1117:
1114:
1112:
1109:
1107:
1104:
1102:
1099:
1097:
1096:Herd immunity
1094:
1092:
1089:
1087:
1084:
1082:
1079:
1078:
1073:
1071:
1069:
1068:
1063:
1059:
1058:
1053:
1052:
1048:
1046:
1041:
1040:
1035:
1034:
1029:
1028:
1023:
1022:
1017:
1016:
1011:
1010:
1005:
1004:
999:
998:
993:
992:
987:
986:
981:
980:
975:
974:
969:
968:
963:
962:
957:
956:
951:
947:
943:
942:
937:
933:
929:
925:
921:
917:
909:
907:
905:
901:
893:
891:
889:
885:
881:
877:
873:
869:
868:intramuscular
865:
860:
858:
850:
846:
842:
838:
834:
831:
828:
825:
824:
823:
817:
813:
809:
805:
801:
798:
795:
791:
786:
783:
780:
776:
772:
768:
763:
759:
756:
752:
748:
744:
740:
739:
738:
736:
731:
728:
719:
715:
712:
711:Louis Pasteur
708:
707:Edward Jenner
704:
698:
692:
688:
680:
678:
676:
672:
668:
662:
661:Immune system
654:
652:
650:
645:
641:
633:
628:
623:
615:
613:
611:
607:
603:
599:
595:
591:
587:
579:
577:
575:
571:
567:
562:
560:
556:
552:
548:
544:
540:
536:
532:
528:
521:
513:
508:
503:
499:
497:
493:
489:
484:
482:
478:
474:
470:
466:
462:
454:
452:
450:
446:
442:
438:
434:
430:
425:
419:
411:
409:
407:
403:
402:polio vaccine
399:
395:
391:
387:
383:
379:
378:Edward Jenner
375:
371:
367:
363:
359:
355:
351:
347:
342:
340:
336:
332:
328:
324:
320:
316:
312:
305:
300:
296:
294:
290:
286:
285:Louis Pasteur
282:
277:
275:
270:
267:
263:
259:
258:miasma theory
254:
251:
247:
243:
238:
236:
232:
228:
224:
220:
216:
212:
208:
207:serum therapy
205:
201:
196:
194:
190:
186:
182:
178:
169:
166:
161:
154:
149:
145:
142:
140:
139:booster doses
135:
130:
128:
124:
119:
116:
110:
107:
103:
99:
95:
91:
87:
83:
79:
78:immune system
72:
67:
60:
58:
56:
52:
48:
44:
40:
33:
19:
2571:Inflammation
2556:Alloimmunity
2551:Autoimmunity
2536:Immunity vs.
2488:Autoantibody
2386:Superantigen
2272:
2268:
2257:
2245:. Retrieved
2239:
2229:
2180:
2176:
2166:
2131:
2127:
2117:
2072:
2068:
2058:
2015:
2011:
2001:
1966:
1962:
1952:
1915:
1911:
1901:
1890:. Retrieved
1886:
1877:
1869:the original
1864:
1855:
1842:
1833:
1788:
1784:
1774:
1739:
1735:
1725:
1690:
1686:
1652:
1605:
1596:
1589:A "al-Razi".
1584:
1574:
1567:
1555:. Retrieved
1549:
1542:
1507:
1501:
1482:
1478:
1459:the original
1454:
1449:Gherardi E.
1421:
1393:the original
1388:
1366:
1357:
1345:
1310:
1306:
1258:
1254:
1244:
1209:
1205:
1195:
1183:
1156:
1150:
1065:
1061:
1055:
1049:
1043:
1037:
1031:
1025:
1019:
1013:
1007:
1001:
995:
989:
983:
977:
971:
965:
959:
953:
945:
939:
936:tuberculosis
913:
897:
861:
854:
845:RNA vaccines
841:DNA vaccines
837:nucleic acid
821:
767:yellow fever
732:
724:
700:
664:
637:
584:Passive or "
583:
563:
523:
485:
458:
421:
343:
308:
281:phagocytosis
278:
271:
266:Black Plague
255:
241:
239:
197:
173:
143:
131:
120:
111:
106:inflammation
98:phagocytosis
75:
69:Scheme of a
55:immunization
42:
36:
2694:Lymphocytes
2353:Lymphocytic
2247:12 November
1791:(5): 1084.
1510:: 161–174.
1121:Inoculation
922:encode the
804:recombinant
755:hepatitis A
691:vaccination
574:sulfonamide
566:antibiotics
492:breast milk
394:variolation
390:vaccination
376:. In 1798,
370:inoculation
366:east Africa
235:snake venom
219:Renaissance
185:four humors
181:Hippocrates
123:lymphocytes
71:Fc receptor
2773:Immunology
2735:Substances
2599:Peripheral
2587:Inaction:
2466:Antibodies
2447:Macrophage
2360:complement
1969:(4): e33.
1892:2020-08-07
1255:Immunology
1143:References
1116:Immunology
950:interferon
924:antibodies
900:SARS-CoV-2
864:hypodermic
794:diphtheria
762:attenuated
695:See also:
518:See also:
507:diphtheria
424:antibodies
331:diphtheria
311:Emile Roux
293:immunology
248:physician
215:Mithridate
189:Thucydides
2752:Cytolysin
2742:Cytokines
2589:Tolerance
2538:tolerance
2457:Immunogen
2291:0028-0836
2221:238991466
2205:0028-0836
2032:1474-1784
1807:1999-4915
1648:Janeway C
1557:4 October
1534:239289426
1126:Premunity
1086:Antivenin
1081:Antiserum
874:and some
725:In 1807,
547:poisoning
496:Colostrum
477:gestation
339:antitoxin
317:isolated
227:Pharsalia
115:infection
102:lymphatic
90:metazoans
2767:Category
2702:Cellular
2546:Immunity
2544:Action:
2527:Paratope
2515:Idiotype
2505:Allotype
2473:Antibody
2427:Mimotope
2391:Allergen
2374:Antigens
2367:Lymphoid
2300:11390478
2213:34650244
2158:27535837
2109:31323032
2050:29326426
1993:27048742
1944:24715891
1825:35632825
1766:20474734
1717:11023960
1337:14357403
1329:16497588
1285:26878338
1236:19932920
1074:See also
910:Genetics
835:deliver
735:vaccines
469:placenta
465:antibody
437:pathogen
384:virus, (
350:smallpox
327:Kitasato
309:In 1888
177:theurgic
168:epidemic
86:adaptive
47:pathogen
43:immunity
2747:Opsonin
2726:NK cell
2714:Humoral
2594:Central
2561:Allergy
2510:Isotype
2410:Epitope
2381:Antigen
2185:Bibcode
2149:5216423
2100:6668849
2077:Bibcode
2041:5906799
1984:4855071
1935:3970029
1918:: 121.
1816:9146425
1785:Viruses
1757:2207044
1367:cdc.gov
1276:4863567
1227:2832725
973:IL12RB2
967:IL12RB1
920:animals
916:Genomes
880:cholera
876:typhoid
800:Subunit
790:tetanus
785:Toxoids
775:rubella
771:measles
747:cholera
727:Bavaria
703:vaccine
644:T cells
640:B cells
481:isotype
398:vaccine
354:Chinese
335:tetanus
323:Behring
264:or the
262:cholera
250:Al-Razi
246:Islamic
165:cholera
39:biology
2719:B cell
2707:T cell
2452:B cell
2415:Linear
2403:Hapten
2297:
2289:
2269:Nature
2219:
2211:
2203:
2177:Nature
2156:
2146:
2107:
2097:
2048:
2038:
2030:
1991:
1981:
1942:
1932:
1823:
1813:
1805:
1764:
1754:
1715:
1705:
1660:
1532:
1522:
1489:
1335:
1327:
1283:
1273:
1234:
1224:
1171:
1067:SPPL2A
1033:IFNGR2
1027:IFNGR1
884:orally
847:, and
810:, and
777:, and
760:Live,
753:, and
751:plague
598:cancer
445:immune
382:cowpox
364:, and
360:, the
346:Europe
337:, the
204:toxoid
193:Athens
82:innate
2217:S2CID
1708:88952
1530:S2CID
1481:[
1333:S2CID
1045:USP18
1039:STAT1
1003:TBX21
991:MCTS1
985:ISG15
979:IL23R
961:IL12B
928:genes
888:bowel
872:polio
779:mumps
714:upon.
638:When
461:fetus
441:toxin
433:horse
429:human
408:etc.
358:India
274:Latin
2358:and
2287:ISSN
2249:2021
2209:PMID
2201:ISSN
2154:PMID
2105:PMID
2046:PMID
2028:ISSN
1989:PMID
1940:PMID
1821:PMID
1803:ISSN
1762:PMID
1713:PMID
1658:ISBN
1559:2020
1520:ISBN
1487:ISBN
1325:PMID
1307:Cell
1281:PMID
1232:PMID
1169:ISBN
1062:NEMO
1057:IRF8
1051:IRF1
1021:JAK1
1015:CYBB
1009:TYK2
997:RORC
955:IFNG
878:and
792:and
689:and
642:and
600:and
527:IVIG
473:FcRn
431:(or
333:and
325:and
313:and
96:and
84:and
80:has
76:The
2680:HLA
2676:MHC
2295:PMC
2277:doi
2273:633
2193:doi
2181:598
2144:PMC
2136:doi
2095:PMC
2085:doi
2036:PMC
2020:doi
1979:PMC
1971:doi
1930:PMC
1920:doi
1811:PMC
1793:doi
1752:PMC
1744:doi
1703:PMC
1695:doi
1512:doi
1315:doi
1311:124
1271:PMC
1263:doi
1259:146
1222:PMC
1214:doi
1210:125
1161:doi
1070:).
866:or
743:flu
488:IgA
439:or
344:In
287:'s
49:or
37:In
2769::
2440::
2293:.
2285:.
2271:.
2267:.
2238:.
2215:.
2207:.
2199:.
2191:.
2179:.
2175:.
2152:.
2142:.
2132:24
2130:.
2126:.
2103:.
2093:.
2083:.
2073:15
2071:.
2067:.
2044:.
2034:.
2026:.
2016:17
2014:.
2010:.
1987:.
1977:.
1965:.
1961:.
1938:.
1928:.
1914:.
1910:.
1885:.
1863:.
1845:.
1841:.
1819:.
1809:.
1801:.
1789:14
1787:.
1783:.
1760:.
1750:.
1740:20
1738:.
1734:.
1711:.
1701:.
1691:13
1689:.
1685:.
1673:^
1637:^
1614:^
1604:.
1528:.
1518:.
1467:^
1453:.
1431:^
1401:^
1387:.
1375:^
1365:.
1331:.
1323:.
1309:.
1305:.
1293:^
1279:.
1269:.
1257:.
1253:.
1230:.
1220:.
1208:.
1204:.
1167:.
1064:,
1060:,
1054:,
1042:,
1036:,
1030:,
1024:,
1018:,
1012:,
1006:,
1000:,
994:,
988:,
982:,
976:,
970:,
964:,
958:,
890:.
859:.
843:,
806:,
802:,
773:,
769:,
749:,
745:,
737::
677:.
651:.
459:A
404:,
237:.
57:.
41:,
2678:/
2436:/
2345:e
2338:t
2331:v
2303:.
2279::
2251:.
2223:.
2195::
2187::
2160:.
2138::
2111:.
2087::
2079::
2052:.
2022::
1995:.
1973::
1967:5
1946:.
1922::
1916:5
1895:.
1849:.
1827:.
1795::
1768:.
1746::
1719:.
1697::
1668:.
1666:.
1608:.
1561:.
1536:.
1514::
1495:.
1339:.
1317::
1287:.
1265::
1238:.
1216::
1177:.
1163::
1047:,
818:.
796:.
781:.
525:(
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.