221:
43:
275:
343:
As each state's territory gradually took shape in the 5th- to 3rd-century BCE Warring States period, the commanderies at the borders flourished. This gave rise to a two-tier administrative system, with counties subordinate to commanderies. Each of the states' territories was by now comparatively
467:(581–618) in 589. As there were already over 100 provinces, the province and commandery levels of the administration were merged into one level, typically rendered in English as prefecture, marking the end of the commandery. Some Emperors to referred to this level of administration as a
451:. Although the legacy three-tier system was still in formal effect, rulers of various kingdoms had defined and re-defined provinces until they became increasingly sub-divided, blurring the distinction between provinces and commanderies and reflecting the chaos of China at the time.
446:
period. The number of administrative units drastically increased due to intense warfare, fluid political boundaries, forced migrations, widespread population loss, and the loss of central government control in many areas particularly during the
344:
larger, hence there was no need for the military might of a commandery in the inner regions where counties were established. The border commanderies' military and strategic significance became more important than those of counties.
369:
356:, the Qin government still had to engage in military activity because there were rebels from among the six former states who were unwilling to submit to Qin rule. As a result,
735:
340:. Despite having smaller populations and ranking lower on the official hierarchies, the commanderies were larger and boasted greater military strength than the counties.
740:
415:
325:
360:
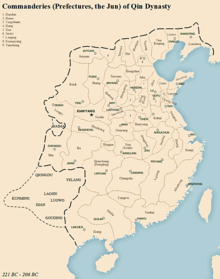
set up 36 commanderies in the Qin Empire, each subdivided into counties. This established the first two-tier administrative system known to exist in China.
266:(c. 7th century CE). Several neighboring countries adopted Chinese commanderies as the basis for their own administrative divisions.
730:
60:
647:
480:
126:
401:). Parallel to these, some Qin commanderies were continued, placed under a governor appointed directly by the central government.
541:; 'grand defender'). Both terms are also translated as "governor". A grand administrator drew an annual salary of 2,000
443:
107:
393:
and granting large territories to his relatives. These two sets of kingdoms were placed under hereditary rulers assisted by a
709:
410:
79:
64:
611:
496:
430:
which were geographic rather than formal political areas, there were initially 13 provinces and roughly 100 commanderies.
405:
237:
594:
86:
580:
439:
93:
53:
297:
75:
676:
31:
475:("province") and the political function was the same, regardless. By the end of the Tang dynasty the term
427:
564:
492:
337:
390:
386:
563:) system of administrative rank. Many former grand administrators were promoted to the posts of the
313:
460:
394:
378:
643:
382:
305:
100:
17:
448:
320:—began annexing their smaller rivals. These new lands were not part of their original
176:
153:
495:, the chief administrative officers of the areas were known as commandery administrators (
357:
197:
568:
423:
419:
220:
724:
414:). — establishing a three-tier system composed of provinces, commanderies, and
606:
602:
588:
301:
293:
263:
259:
183:
635:
524:
464:
375:
353:
317:
309:
225:
42:
704:
479:
saw no more use in China (and a new higher tier of administrative unit, the
333:
438:
China was greatly divided during the following five centuries, during the
274:
300:
from the 8th to 5th centuries BCE, the larger and more powerful of the
504:
245:
677:"The government and geography of the northern frontier of Late Han"
273:
255:
681:
The government and geography of the northern frontier of Late Han
321:
36:
483:
had been introduced, bringing back a three-tier system).
352:
Following the unification of China in 221 BCE under the
642:(in Chinese). China: Zhonghua Publishing House (中华书局).
370:
List of provinces and commanderies of the Han dynasty
202:
188:
434:
Jin dynasty and the
Southern and Northern dynasties
196:
182:
175:
170:
152:
143:
67:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
404:By the Eastern Han dynasty, the commanderies were
262:(c. 7th century BCE) until the early
638:(2009). "Geography of the Later Han (后汉的地理)".
332:). Eventually, commanderies were developed as
254:) was a historical administrative division of
158:
8:
514:
27:Historical administrative division of China
736:Administrative divisions of Imperial China
167:
127:Learn how and when to remove this message
741:Former administrative divisions of China
591:, alluding to its historical equivalents
219:
627:
140:
364:Han dynasty and Three Kingdoms period
7:
640:History of the Three Kingdoms (三国史话)
65:adding citations to reliable sources
224:Commanderies and provinces of the
25:
531:was renamed grand administrator (
683:. Australian National University
324:and were instead organized into
278:Commanderies of the Qin dynasty.
41:
459:China was finally re-united by
444:Northern and Southern dynasties
389:recognizing nearly independent
385:was initially reinstated, with
52:needs additional citations for
710:Records of the Grand Historian
559:
554:
546:
537:
532:
509:
500:
471:("commandery"), but most used
406:subordinated to a new division
250:
241:
203:
189:
159:
1:
612:Government of the Han dynasty
18:Jun (administrative division)
731:Former commanderies of China
597:, poetically referred to as
583:, poetically referred to as
549:) of grain according to the
675:de Crespigny, Rafe (2004).
757:
367:
29:
258:that was in use from the
214:
166:
148:
571:later in their careers.
487:Administrative hierarchy
298:Spring and Autumn period
270:History and development
76:"Commandery" China
455:Sui and Tang dynasties
279:
229:
565:Three Ducal Ministers
519:'defender of the
493:Warring States period
277:
223:
61:improve this article
30:For other uses, see
527:, the position of
420:legendary accounts
383:Zhou feudal system
379:triumphed over Chu
280:
230:
32:郡 (disambiguation)
517:
308:—including
218:
217:
210:
209:
177:Standard Mandarin
137:
136:
129:
111:
16:(Redirected from
748:
693:
692:
690:
688:
672:
666:
660:
654:
653:
632:
561:
556:
548:
539:
534:
518:
515:
511:
502:
449:Sixteen Kingdoms
408:, the province (
381:in 206 BCE, the
252:
243:
206:
205:
192:
191:
168:
162:
161:
141:
132:
125:
121:
118:
112:
110:
69:
45:
37:
21:
756:
755:
751:
750:
749:
747:
746:
745:
721:
720:
701:
696:
686:
684:
674:
673:
669:
661:
657:
650:
634:
633:
629:
625:
620:
577:
523:'). In the
489:
457:
436:
372:
366:
358:Qin Shi Huangdi
350:
290:
285:
272:
133:
122:
116:
113:
70:
68:
58:
46:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
754:
752:
744:
743:
738:
733:
723:
722:
719:
718:
700:
697:
695:
694:
667:
655:
648:
626:
624:
621:
619:
616:
615:
614:
609:
592:
576:
573:
569:Nine Ministers
488:
485:
456:
453:
435:
432:
428:Nine Provinces
424:Yellow Emperor
368:Main article:
365:
362:
349:
346:
289:
286:
284:
281:
271:
268:
216:
215:
212:
211:
208:
207:
200:
194:
193:
186:
180:
179:
173:
172:
171:Transcriptions
164:
163:
156:
150:
149:
146:
145:
135:
134:
49:
47:
40:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
753:
742:
739:
737:
734:
732:
729:
728:
726:
716:
712:
711:
706:
703:
702:
698:
682:
678:
671:
668:
664:
659:
656:
651:
649:9787101066890
645:
641:
637:
631:
628:
622:
617:
613:
610:
608:
604:
600:
596:
593:
590:
586:
582:
579:
578:
574:
572:
570:
566:
562:
552:
544:
540:
530:
526:
522:
512:
506:
498:
494:
486:
484:
482:
478:
474:
470:
466:
462:
454:
452:
450:
445:
441:
433:
431:
429:
425:
421:
418:. Based upon
417:
413:
412:
407:
402:
400:
396:
392:
388:
387:Emperor Gaozu
384:
380:
377:
371:
363:
361:
359:
355:
347:
345:
341:
339:
335:
331:
327:
323:
319:
315:
311:
307:
306:vassal states
303:
299:
295:
287:
282:
276:
269:
267:
265:
261:
257:
253:
247:
239:
235:
227:
222:
213:
201:
199:
195:
187:
185:
181:
178:
174:
169:
165:
157:
155:
151:
147:
142:
139:
131:
128:
120:
109:
106:
102:
99:
95:
92:
88:
85:
81:
78: –
77:
73:
72:Find sources:
66:
62:
56:
55:
50:This article
48:
44:
39:
38:
33:
19:
714:
708:
699:Bibliography
685:. Retrieved
680:
670:
662:
658:
639:
630:
607:Qing dynasty
603:Ming dynasty
598:
589:Tang dynasty
584:
558:
550:
542:
536:
528:
520:
508:
490:
476:
472:
468:
458:
437:
409:
403:
398:
373:
351:
342:
338:major realms
336:between the
329:
294:Eastern Zhou
291:
288:Eastern Zhou
264:Tang dynasty
260:Eastern Zhou
249:
233:
231:
184:Hanyu Pinyin
138:
123:
114:
104:
97:
90:
83:
71:
59:Please help
54:verification
51:
687:18 February
525:Han dynasty
461:Emperor Wen
376:Han dynasty
348:Qin dynasty
292:During the
226:Han dynasty
725:Categories
636:Lü, Simian
618:References
587:after the
395:chancellor
354:Qin Empire
334:marchlands
234:commandery
198:Wade–Giles
144:Commandery
117:March 2016
87:newspapers
705:Sima Qian
623:Citations
374:When the
665:vol. 71.
575:See also
416:counties
326:counties
228:, 219 CE
601:in the
538:tàishǒu
529:junshou
510:jùnshǒu
497:Chinese
491:In the
481:circuit
463:of the
422:of the
238:Chinese
154:Chinese
101:scholar
715:Shi Ji
663:Shi Ji
646:
560:pǐnzhì
551:pinzhi
507::
505:pinyin
499::
248::
246:pinyin
240::
103:
96:
89:
82:
74:
399:xiàng
391:kings
322:fiefs
283:China
256:China
108:JSTOR
94:books
689:2016
644:ISBN
605:and
581:Zhou
516:lit.
473:zhou
442:and
411:zhōu
330:xiàn
316:and
302:Zhou
204:chün
80:news
599:jun
585:jun
567:or
543:dan
521:jun
477:jun
469:jun
465:Sui
440:Jin
426:'s
318:Wei
314:Jin
310:Qin
304:'s
296:'s
251:jùn
190:jùn
63:by
727::
717:).
707:.
679:.
595:Fu
557:;
555:品秩
535:;
533:太守
513:;
503:;
501:郡守
312:,
244:;
232:A
713:(
691:.
652:.
553:(
547:石
545:(
397:(
328:(
242:郡
236:(
160:郡
130:)
124:(
119:)
115:(
105:·
98:·
91:·
84:·
57:.
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.