2002:
78:
1630:
1642:
1682:, was often described as being not as cultured by people in the Central plains. However, this image originated with the later development of Chu relative to the Central plains, and the stereotype was retrospectively cultivated by Confucian scholars in the Qin dynasty, to indirectly criticise the ruling regime, and the Han dynasty as a means of curbing their ideological opponents who were associated with such cultural practices. As the founder of the Han dynasty was from the state, Chu culture would later become a basis of the culture of the later Han dynasty, along with that of the Qin dynasty's and other preceding states' from the Warring States period.
1813:
1488:
1409:, secretly followed Li Xin's army for three days and three nights, before launching a surprise offensive and destroying Li Xin army. Upon learning of Li's defeat, Ying Zheng replaced Li with Wang Jian, putting Wang in command of the 600,000-strong army he had requested earlier and placing Meng Wu beneath him as a deputy. Worried that the Qin tyrant might fear the power he now possessed and order him executed upon some pretense, Wang Jian constantly sent messengers back to the king in order to remain in contact and reduce the king's suspicion.
1000:
339:
1203:
1172:. Wu's reforms began to transform Chu into an efficient and powerful state in 389 BC, as he lowered the salaries of officials and removed useless officials. He also enacted building codes to make the capital Ying seem less barbaric. Despite Wu Qi's unpopularity among Chu's ruling class, his reforms strengthened the king and left the state very powerful until the late 4th century BC, when
1295:
2001:
1622:
1156:
to the north in 447 BC. By the end of the 5th century BC, the Chu government had become very corrupt and inefficient, with much of the state's treasury used primarily to pay for the royal entourage. Many officials had no meaningful task except taking money and Chu's army, while large, was of low
1422:
in Henan) and made camp at Pingyu. The Chu armies under Xiang Yan used their full strength against the camp but failed. Wang Jian ordered his troops to defend their positions firmly but avoid advancing further into Chu territory. After failing to lure the Qin army into an attack, Xiang Yan ordered a
1215:
The Chu people are soft and weak. Their lands stretch far and wide, and the government cannot effectively administer the expanse. Their troops are weary and although their formations are well-ordered, they do not have the resources to maintain their positions for long. To defeat them, we must strike
1192:
in either 334 or 333 BC. However, the officials of Chu wasted no time in their revenge and Wu Qi was assassinated at King Dao's funeral in 381 BC. Prior to Wu's service in the state of Chu, Wu lived in the state of Wei, where his military analysis of the six opposing states was recorded in
1824:
woodworks. Red and black pigmented lacquer were most used. Silk-weaving also attained a high level of craftsmanship, creating lightweight robes with flowing designs. These examples (as at
Mawangdui) were preserved in waterlogged tombs where the lacquer did not peel off over time and in tombs sealed
1673:
period, the difference between the culture of Chu and the
Central Plains states to the north was negligible. Only in the late Spring and Autumn period does Chu culture begin to diverge, preserving some older aspects of the culture and developing new phenomena. It also absorbed some elements from
1689:
in the Zhou style. The bronze wares of the state of Chu also have their own characteristics. For example, the bronze Jin (altar table) unearthed from the Chu tomb in
Xichuan, Henan Province are complex in shape. Dated to the mid sixth century BC, it was one of the early confirmed lost-wax cast
1761:, and other artifacts reveal heavy Taoist and native folk influence in Chu culture. The disposition to a spiritual, often pleasurable and decadent lifestyle, and the confidence in the size of the Chu realm led to the inefficiency and eventual destruction of the Chu state by the ruthless
3673:《左傳·僖公十二年》: "黃人恃諸侯之睦于齊也,不共楚職,曰,自郢及我,九百里,焉能害我。夏,楚滅黃。 'The people of Huang, relying on the friendship of the States with Qi, did not render the tribute which was due from them to Chu, saying "From Ying to us is 900 li; what harm can Chu do to us?" This summer, Chu extinguished Huang."
1829:, which was borrowed by the Wu and Yue states. It has a design that embellishes the characters with motifs of animals, snakes, birds, and insects. This is another representation of the natural world and its liveliness. Chu produced broad bronze swords that were similar to
1239:. In 241 BC, five of the seven major warring states–Chu, Zhao, Wei, Yan and Han–formed an alliance to fight the rising power of Qin. King Kaolie of Chu was named the leader of the alliance and Lord Chunshen the military commander. According to historian
1036:
of the era. After a number of battles with neighboring states, sometime between 695 and 689 BC, the Chu capital moved south-east from
Danyang to Ying. Chu first consolidated its power by absorbing other states in its original area (modern
1505:
of a Qin administrator in Hubei. Chu aspired to overthrow the painful yoke of Qin rule and re-establishing a separate state. The attitude was captured in a
Chinese expression about implacable hostility: "Though Chu has but three
3644:
2084:
indicated their role as oracles. Other Yins recorded by history were: Yuyin, Lianyin, Jiaoyin, Gongjiyin, Lingyin, Huanlie Zhi Yin (Commander of Palace guards) and Yueyin (Minister of Music). In counties and commanderies, Gong
4447:
1076:
as its representative in the central plain area, through the means of intimidation and threats, Chu forced Zheng to ally with itself. On the other hand, Jin had to balance out Chu's influence by repeatedly allying with
5323:
1836:
Chu created a riverine transport system of boats augmented by wagons. These are detailed in bronze tallies with gold inlay regarding trade along the river systems connecting with those of the Chu capital at Ying.
5313:
1216:
swiftly, unexpectedly and retreat quickly before they can counter-attack. This will create unease in their weary soldiers and reduce their fighting spirit. Thus, with persistence, their army can be defeated.
77:
1772:
Archaeological evidence shows that Chu music was annotated differently from Zhou. Chu music also showed an inclination for using different performance ensembles, as well as unique instruments. In Chu, the
1276:
in 223 BC. By the late 4th century BC, however, Chu's prominent status had fallen into decay. As a result of several invasions headed by Zhao and Qin, Chu was eventually completely wiped out by Qin.
1523:) and reigned briefly, the people of Chu and its former ruling house organized the first violent insurrections against the new Qin administration. They were especially resentful of the Qin
1332:
from the powerless Zhou king would be wise. Sima Cuo, however, considered that the primary difficulty was not legitimacy but the strength of Qin's opponents; he argued that "conquering
994:
1562:, Xiang Liang's nephew, proclaimed himself the "Hegemon-King of Western Chu" and promoted King Huai II to "Emperor Yi". He subsequently had Yi assassinated. Xiang Yu then engaged with
2425:
969:. After this death, Zhou ceased to expand to the south, allowing the southern tribes and Chu to cement their own autonomy much earlier than the states to the north. The Chu viscount
4455:
1479:), tell of a protracted campaign in Huaiyang under Wang Jian. Both soldiers wrote letters requesting supplies of clothing and money from home to sustain the long waiting campaign.
1629:
2930:) (Xiong Wei 熊圍, changed to Xiong Qian 熊虔) ruled 540–529 BC: uncle of Jia'ao and younger brother of King Kang, overthrown by his younger brothers and committed suicide.
1386:. Chu had recovered sufficiently to mount serious resistance. Despite its size, resources, and manpower, though, Chu's corrupt government worked against it. In 224 BC,
1798:. Numerous burials and burial objects in the Ba and Yue styles have been discovered throughout the territory of Chu, co-existing with Chu-style burials and burial objects.
5328:
2789:) (Xiong Da 熊達), ruled 740–690 BC: either younger brother or younger son of Fenmao, murdered son of Fenmao and usurped the throne. Declared himself first king of Chu.
2005:
Pair of shamans or attendants, Chu culture, Jiangling, Hubei province, China, Warring States period, 4th-3rd century BC, wood, cinnabar, black lacquer. Portland Art Museum
5308:
1120:". King Zhao eventually returned to Ying but, after another attack from Wu in 504 BC, he temporarily moved the capital into the territory of the former state of
1765:
state of Qin. Even though the Qin realm lacked the vast natural resources and waterways of Chu, the Qin government maximized its output under the efficient minister
5303:
2140:. Rulers of Chu systematically migrated states annexed by Chu to the Jing mountains in order to control them more efficiently. East of Jing mountains are the Tu (
4743:
4089:
5298:
4484:
Anhui
Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology and Bengbu Museum (June 2015). "The Excavation of the tomb of Bai, Lord of the Zhongli State".
1609:, the southern folk culture and aesthetics were mixed with the Han-sponsored Confucian tradition and Qin-influenced central governance to create a distinct "
1589:
intermarriages, rewarded his allies with large fiefdoms, and allowed the population to rest from centuries of warfare. The core Chu territories centered in
1558:, a scion of Chu's traditional royal family, on the throne of Chu under the regnal name King Huai II. In 206 BC, after the fall of the Qin Empire,
1714:, tigers, and free-flowing clouds and serpent-like beings. Some archaeologists speculate that Chu may have had cultural connections to the previous
1809:, some Confucian scholars considered Chu culture with distaste, criticizing the "lewd" music and shamanistic rituals associated with Chu culture.
1699:
1363:
finally conquered Chu's capital at Ying. Following the fall of Ying, the Chu government moved to various locations in the east until settling in
3979:
4380:
1845:
Although bronze inscriptions from the ancient state of Chu show little linguistic differences from the "Elegant Speech" (yǎyán 雅言) during the
4548:
4525:
3502:
3484:
2196:
was an immense freshwater lake that historically existed in Chu's realm, It was crossed by Yanzi river, the northern
Yunmeng was named Meng (
4393:
1268:
As Qin expanded into Chu's territory, Chu was forced to expand southwards and eastwards, absorbing local cultural influences along the way.
1231:
During the late
Warring States period, Chu was increasingly pressured by Qin to its west, especially after Qin enacted and preserved the
3436:
1566:, another prominent anti-Qin rebel, in a long struggle for supremacy over the lands of the former Qin Empire, which became known as the
966:
2029:) were the top government officials of Chu. Sima was the military commander of Chu's army. Lingyin, Mo'ao and Sima were the San Gong (
4736:
4659:
4622:
4586:
4189:
4164:
3962:
3906:
3703:
1641:
1375:
in 260 BC. The Qin army massacred their prisoners, removing the last major obstacle to Qin dominance over the
Chinese states.
4206:
2954:) (Xiong Qiji 熊弃疾, changed to Xiong Ju 熊居) ruled 528–516 BC: younger brother of Zi'ao, tricked Zi'ao into committing suicide.
3284:
2074:). For example: Lingyin (Prime minister), Gongyin (Minister of works), and Zhenyin were all suffixed by the word "Yin". Shenyin (
1423:
retreat; Wang Jian seized this opportunity to launch a swift assault. The Qin forces pursued the retreating Chu forces to Qinan (
3565:
3118:) (Xiong Heng 熊橫) ruled 298–263 BC: son of King Huai. As a prince, one of his elderly tutors was buried at the site of the
5293:
1581:
Liu Bang immediately enacted a more traditional and less intrusive administration than the Qin before him, made peace with the
309:
4881:
4636:
4422:
4360:
3879:
3854:
3829:
3800:
3570:
853:
618:
601:
488:
1826:
4294:
4946:
2094:
In many cases, positions in Chu's bureaucracy were hereditarily held by members of a cadet branch of Chu's royal house of
1806:
1762:
1308:
1232:
1089:. The tension between Chu and Jin did not loosen until the year of 579 BC when a truce was signed between the two states.
557:
2065:) respectively. Mo'ao's status was gradually lowered while Lingyin and Sima became more powerful posts in the Chu court.
4941:
4729:
3336:
1962:
1286:
708:
189:
2178:. In Chu's northern border lies the Fangcheng mountain. Strategically, Fangcheng is an ideal defense against states of
5203:
4760:
1703:
4343:
also says he was the younger brother of Xiong Kang, but historians generally agree that he was the son of Xiong Kang.
1658:
Based on the archaeological finds, Chu's culture was initially quite similar to that of the other Zhou states of the
4104:
1501:
The Chu populace in areas conquered by Qin openly ignored the stringent Qin laws and governance, as recorded in the
3939:
3597:
3402:
2542:
2129:
2020:
1875:, further demonstrated substrate influences, but there are competing hypotheses on their genealogical affiliation.
1299:
914:
225:
4991:
4971:
3412:
3364:
2307:
1690:
artifacts discovered in China proper. Later Chu burials, especially during the
Warring States, featured distinct
1602:
1546:). This uprising was crushed by the Qin army but it inspired a new wave of other rebellions. One of the leaders,
1502:
1888:
1866:
1812:
1487:
2183:
1861:, which the Chu may have acquired as a result of its southern migration into what Tian Jizhou believed to be a
1634:
1527:; folk poems record the mournful sadness of Chu families whose men worked in the frigid north to construct the
696:
1721:
Another common Chu idea was the worship of gibbons and other animals perceived to have auspicious amounts of
1666:
lands that it conquered to the south and east, developing a blended culture compared to the northern plains.
2234:
was an important outpost in the mountainous western border of Chu. It was located in today's Wuguan town of
1904:
1882:
276:
3297:
2822:) (Xiong Jian 熊艱), ruled 676–672 BC: son of King Wen, killed by younger brother, the future King Cheng
1567:
1496:
4752:
4327:
calls him Xiong Zhihong (熊摯紅), and says his younger Xiong Yan killed him and usurped the throne. However,
3322:
1686:
1674:
annexed areas. The culture of Chu had significant internal diversity from locality to locality. Chu, like
1467:
between Qin and Zhao 35 years before. The excavated personal letters of two regular Qin soldiers, Hei Fu (
684:
626:
609:
585:
3747:
1894:
1862:
1702:. A common Chu motif was the vivid depiction of wildlife, mystical animals, and natural imagery, such as
1440:
The next year, in 223 BC, Qin launched another campaign and captured the Chu capital Shouchun. King
5130:
4277:
3598:"Yu Ding: Evidence of the Extermination of the State of E during the Western Zhou Dynasty (禹鼎:西周灭鄂国的见证)"
3109:
2647:
2179:
1858:
1317:
1061:
700:
184:
53:
2942:) (Xiong Bi 熊比) ruled 529 BC (less than 20 days): younger brother of King Ling, committed suicide.
2918:) (Xiong Yuan 熊員) ruled 544–541 BC: son of King Kang, murdered by his uncle, the future King Ling.
1444:
was captured and his state annexed. The following year, Wang Jian and Meng Wu led the Qin army against
999:
30:
This article is about the state of Chu during the Zhou dynasty. For other states of the same name, see
3454:
1748:
in Chinese mythology. For this reason, fire worshiping and red coloring were practiced by Chu people.
695:
in the early 8th century BC. Chu was located in the south of the Zhou heartland and lasted during the
5288:
5233:
5208:
5152:
5139:
4140:
3934:
3348:
3332:
3302:
1898:
1691:
1563:
1325:
31:
2242:. Any forces that marched from the west, mainly from Qin, to Chu's realm would have to pass Shaoxi.
1910:
Mixture of Austroasiatic, Hmong-Mien and Tibeto-Burman (Pullyblank 1983, Schuessler 2004 & 2007)
1060:
in 632 BC. During the 6th century BC, Jin and Chu fought numerous battles over the hegemony of
5041:
4921:
4916:
4795:
4003:. The Harmony of Civilization and Prosperity for All: Selected Papers of Beijing Forum(2004-2008).
3407:
2835:
2689:
2105:
1528:
1464:
1372:
1324:
led to two conclusions concerning the unification of China. Zhang Yi argued in favor of conquering
1313:
1137:
1053:
3926:
3506:
3488:
3178:) (熊負芻 Xiong Fuchu) ruled 227–223 BC: brother of King Ai. Captured by Qin troops and deposed
1550:
of Chu, proclaimed himself the new king of Chu. Jing Ju was defeated by another rebel force under
543:
4986:
4951:
4578:
3129:
2861:
2552:
1535:
1348:
1273:
1169:
1029:
910:
524:
516:
2189:
4574:
Ancient China and the Yue: Perceptions and Identities on the Southern Frontier, c, 400 BC–50 AD
3246:) (originally King Huai II 楚後懷王) ruled 208–206 BC: grandson or great-grandson of King Huai
2010:
1406:
1244:
5258:
5106:
4655:
4618:
4582:
4544:
4521:
4513:
4497:
4185:
4160:
4018:
3958:
3902:
3875:
3850:
3825:
3699:
3328:
3237:
3119:
3102:) (Xiong Huai 熊槐) ruled 328–299 BC: son of King Wei, was tricked and held hostage by the
3017:
2891:
2839:
2825:
2665:
2574:
1869:
area in southern China. Recent excavated texts, corroborated by dialect words recorded in the
1758:
1606:
1598:
1555:
1457:
1329:
1321:
1113:
1057:
1056:. These alliances kept Chu in check, and the Chu kingdom lost their first major battle at the
1042:
962:
886:
779:
451:
443:
4560:"Dialects, diachrony, diglossia or all three? Tomb text glimpses into the language(s) of Chǔ"
3722:
3440:
2446:
1718:, since many motifs used by Chu appeared earlier at Shang sites such as serpent-tailed gods.
958:
5091:
4501:
4008:
3360:
3093:
3057:
3005:
2995:
2957:
2945:
2921:
2897:
2881:
2494:
2328:
2300:
1109:
1007:
painting from the Jingmen Tomb (Chinese: 荊門楚墓; Pinyin: Jīngmén chǔ mù, about 316 BC) of the
938:
902:
648:
380:
357:
1437:) and Xiang Yan was either killed in the action or committed suicide following his defeat.
1072:, causing Jin's temporary inability to counter Chu's expansion. Chu strategically used the
5318:
5101:
4426:
4364:
3190:) ruled 223 BC (Chu conquered by Qin): brother of Fuchu, killed in battle against Qin
3145:
3073:
3066:) (Xiong Liangfu 熊良夫) ruled 369–340 BC: brother of King Su. Defeated and annexed the
3029:
2977:
2792:
2590:
2341:
2165:
2147:
1946:
1775:
1711:
1419:
1391:
1180:
were ascendant. Chu's powerful army once again became successful, defeating the states of
1161:
825:
795:
429:
338:
5026:
4339:
both say that Xiong Zhi abdicated due to illness and was succeeded by brother Xiong Yan.
3082:) (Xiong Shang 熊商) ruled 339–329 BC: son of King Xuan. Defeated and partitioned the
1463:
At their peak, Chu and Qin together fielded over 1,000,000 troops, more than the massive
666:
415:
3527:
3166:) (Xiong You 熊猶 or Xiong Hao 熊郝) ruled 228 BC: brother of King You, killed by Fuchu
2870:) (Xiong Lü 熊侶) ruled 613–591 BC: son of King Mu. Defeated the State of Jin at the
4443:
4252:
4214:
3389:
3352:
3344:
3293:
3181:
3157:
3045:
2986:) (Xiong Zhang 熊章) ruled 488–432 BC: son of King Zhao. He conquered the states of
2849:
2780:
2235:
2193:
2137:
2133:
1958:
1871:
1707:
1207:
1105:
982:
946:
858:
787:
692:
578:
571:
244:
4036:
Tian, Jizhou (1989). "Chuguo ji qi minzu (The country of Chu and its nationalities)".
2080:) was the minister of religious duties or the high priest of Chu, multiple entries in
1398:
thought that less than 200,000 men would be sufficient. Ying Zheng ordered Li Xin and
1202:
5282:
5253:
5218:
5071:
4976:
4966:
4931:
4845:
4815:
3670:
3575:
3356:
3280:
2875:
2456:
2288:
2258:
2209:
2155:
1954:
1715:
1646:
1430:
1390:
called for a meeting with his subjects to discuss his plans for the invasion of Chu.
1387:
1371:
force of 400,000 men onto the field, surrounding them and forcing their surrender at
1344:
1340:
1258:
1073:
1046:
1033:
942:
922:
906:
775:
126:
2890:) (Xiong Shen 熊審) ruled 590–560 BC: son of King Zhuang. Defeated by Jin at the
1140:, who took revenge for his former captivity by crushing and completely annexing Wu.
1052:
The threat from Chu resulted in multiple northern alliances under the leadership of
5228:
5223:
5177:
5096:
5081:
5076:
5061:
5056:
5046:
5021:
5006:
4886:
4871:
4820:
4785:
4335:
3103:
2991:
2971:
2871:
2701:
2371:
2282:
2270:
2095:
1846:
1741:
1670:
1659:
1507:
1395:
1368:
1253:) was the actual commander in the battle. The allies attacked Qin at the strategic
1173:
1149:
1086:
1069:
1008:
918:
894:
815:
805:
688:
533:
387:
212:
4415:
4353:
1261:
for the loss and began to mistrust him. Afterwards, Chu moved its capital east to
4572:
4013:
3996:
3138:) (Xiong Yuan 熊元) ruled 262–238 BC: son of King Qingxiang. Moved capital to
1786:
Chu came into frequent contact with other peoples in the south, most notably the
5263:
5248:
5238:
5198:
5172:
5167:
5162:
5116:
5036:
5031:
5016:
5011:
4981:
4961:
4936:
4926:
4901:
4896:
4876:
4866:
4840:
4835:
4825:
4810:
4780:
4775:
4711:
4685:
4300:
3652:
3631:
3340:
3310:
3306:
3083:
3067:
2987:
2967:
2595:
2523:
2407:
2401:
2383:
2347:
2322:
2294:
2264:
1926:
1850:
1791:
1737:
1729:
1679:
1675:
1610:
1575:
1571:
1551:
1520:
1453:
1445:
1379:
1359:, expanding downriver in the following decades. In 278 BC, the Qin general
1352:
1343:
was its great agricultural output and its control over the upper reaches of the
1333:
1185:
1181:
1177:
1153:
1133:
1125:
1121:
1117:
1082:
1004:
704:
676:
594:
344:
302:
258:
162:
4654:, Freer Gallery of Art and Arthur M. Sackler Gallery, Smithsonian Institution,
3896:
5213:
5193:
5157:
5066:
5051:
5001:
4996:
4956:
4861:
4830:
4805:
4800:
4541:
Kinship: Studies of Recently Discovered Bronze Inscritpions from Ancient China
3997:"Language Contact and Language Change in the History of the Sinitic Languages"
3622:
Lothar von Falkenahausen in Cambridge History of Ancient China, 1999, page 516
3601:
3383:
3200:
3087:
2802:
2749:
2677:
2631:
2607:
2413:
2395:
2389:
2377:
2365:
2276:
2151:
2098:. Mo'ao, one of the three chancellors of Chu, was exclusively chosen from Qu (
1787:
1769:, installing a meritocracy focused solely on agricultural and military might.
1766:
1744:
glosses on Zhou ritual. Chu people affiliated themselves with the god of fire
1539:
1383:
1356:
1336:
is conquering Chu" and, "once Chu is eliminated, the country will be united".
1269:
1254:
1236:
1189:
1101:
1093:
1078:
1032:, Chu reached the height of its power and its ruler was considered one of the
872:
791:
467:
460:
146:
4022:
2801:) (Xiong Zi 熊貲), ruled 689–677 BC: son of King Wu, moved the capital to
1783:, while both instruments were equally preferred in the northern Zhou states.
4891:
4690:
4631:
4329:
3927:"Indigenous or Foreign? A Look at the Origins of the Monkey Hero Sun Wukong"
3795:
3666:
3561:
2998:
died, so he made a commemorative bell and attended the Marquis's funeral at
2843:
2713:
2653:
2579:
2252:
2221:
2081:
1802:
1590:
1240:
974:
848:
743:
481:
103:
4505:
3532:
ChinaKnowledge.de - An Encyclopaedia on Chinese History, Literature and Art
2909:
2834:) (Xiong Yun 熊惲), ruled 671–626 BC: brother of Du'ao, defeated by the
2737:
2091:), also known as Xianyin (minister of county) was the chief administrator.
1524:
2068:
Ministers whose functions vary according to their titles were called Yin (
4721:
3289:
3249:
3139:
2933:
2807:
2619:
2557:
2499:
2175:
1854:
1559:
1394:
said that the invasion force needed to be at least 600,000 strong, while
1367:
in 241 BC. After a massive two-year struggle, Bai Qi lured the main
1364:
1262:
1129:
970:
783:
771:
767:
502:
401:
202:
109:
4394:"Richard Hinckley Allen: Star Names – Their Lore and Meaning: Ophiuchus"
1662:
basin. However, subsequently, Chu absorbed indigenous elements from the
1092:
At the beginning of the sixth century BC, Jin strengthened the state of
5111:
3274:
3218:
2999:
2725:
2478:
2460:
2239:
2231:
2217:
2213:
2174:), one of the later capitals of Chu, is known by its contemporary name
1821:
1745:
1695:
1621:
1594:
1582:
1547:
1449:
1399:
1097:
1022:
898:
876:
862:
763:
759:
747:
540:
17:
3984:(2 ed.). Journal of Chuxiong Teacher's College. pp. 105–109.
2508:), ruled 11th century BC: son of Yuxiong, first use of clan name Yan (
1294:
928:
4493:
2761:
2472:
2436:
1795:
1753:
1733:
1663:
1360:
1351:
opted to support Sima Cuo. In 316 BC, Qin invaded and conquered
1065:
890:
656:
348:
168:
4715:
4597:
4559:
4536:
3898:
Metalworking in Bronze Age China: The Lost-Wax Process By Peng Peng
4911:
4906:
4323:
3379:
3376:
3169:
3123:
3039:
3038:) (Xiong Yi 熊疑) ruled 401–381 BC: son of King Sheng. He made
2642:
2000:
1930:
1830:
1811:
1780:
1640:
1628:
1620:
1586:
1486:
1441:
1434:
1293:
1165:
1038:
1013:
998:
978:
755:
751:
739:
735:
3698:. Zhonghua Book Company. pp. 940–945, 972, 1140, 2055–2066.
2646:
says Xiong Kang died early without ascending the throne, but the
2104:) clan. During the early spring and autumn period and before the
2047:) were added as the undersecretaries of Lingyin. Likewise, Sima (
1891:(Erkes 1930, Long & Ma 1983, Brooks 2001, Sagart et al. 2005)
1825:
with coal or white clay. Chu used the calligraphic script called
583:
5243:
5086:
4446:; Maes, Piet; Dolja, Valerian; Koonin, Eugene V.; Kuhn, Jens H.
2858:) (Xiong Shangchen 熊商臣) ruled 625–614 BC: son of King Cheng
2225:
1570:. The conflict ended in victory for Liu Bang: he proclaimed the
1223:
1195:
1018:
4725:
2966:) (Xiong Zhen 熊珍) ruled 515–489 BC: son of King Ping. The
1538:
occurred in 209 BC under the leadership of a Chu peasant,
1132:
to serve as allies against Wu. Yue was initially subjugated by
4090:"上古楚语中的南亚语成分 (Austroasiatic elements in ancient Chu dialect)"
3227:) as King Jia of Chu 楚假王 (Jia for fake) ruled 209–208 BC
1757:, historical records, excavated bamboo documents such as the
562:
548:
4543:. The Chinese University Press of Hong Kong. pp. 9–32.
1933:), Schuessler (2007) proposes two Austroasiatic comparanda:
5324:
States and territories disestablished in the 3rd century BC
3154:) (Xiong Han 熊悍) ruled 237–228 BC: son of King Kaolie.
2628:), son of Xiong Yang, gave the title king to his three sons
2551:), ruled 11th century BC: son of Xiong Kuang, enfeoffed by
1953:"thorn, thorny bamboo (added to names of thorny plants)",
1722:
1291:
The Chu state was completely eradicated by the Qin dynasty.
4598:"Kra-Dai and the Proto-History of South China and Vietnam"
4264:
3849:. University of Hawaii Press. pp. 1–4, 149, 151–165.
3824:. University of Hawaii Press. pp. 3, 21–22, 32, 168.
3292:, the Hegemon-King of Western Chu who defeated the Qin at
2722:), ruled 821–800 BC: youngest brother of Xiong Shuang
913:(r. 1042–1021 BC) enfeoffed Yuxiong's great-grandson
5314:
States and territories established in the 11th century BC
3733:
3731:
3126:. The Chu capital of Ying was captured and sacked by Qin.
3026:) (Xiong Dang 熊當) ruled 407–402 BC: son of King Jian
3014:) (Xiong Zhong 熊中) ruled 431–408 BC: son of King Hui
2906:) (Xiong Zhao 熊招) ruled 559–545 BC: son of King Gong
2674:), ruled ?–848 BC: younger brother of Xiong Zhi
1879:
Aberrant early Chinese dialect, originally from the North
1100:
delta to act as a counterweight against Chu. Wu defeated
623:
606:
521:
507:
493:
3054:) (Xiong Zang 熊臧) ruled 380–370 BC: son of King Dao
995:
Interstate relations during the Spring and Autumn period
472:
4184:. Beijing: National Library of China publishing house.
3649:
The Institute for Advanced Technology in the Humanities
3351:. Opinions differ, however, as to whether that star is
2770:) (Xiong Xuan 熊眴) ruled 757–741 BC: son of Xiao'ao
1378:
By 225 BC, only four kingdoms remained: Qin, Chu,
4613:
Cook, Constance A.; et al., eds. (January 2004),
4352:
Activities of Exhibition and Education in Astronomy. "
3872:
Defining Chu : Image and Reality in Ancient China
3822:
Defining Chu : Image and Reality in Ancient China
3331:, Chu is represented by a star in the "Twelve States"
2758:) (Xiong Kan 熊坎), ruled 763–758 BC: son of Ruo'ao
2746:) (Xiong Yi 熊儀), ruled 790–764 BC: son of Xiong E
2108:, Lingyin was a position held by Ruo'aos, namely Dou (
4452:
International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV)
3634:
in Cambridge History of Ancient China, 1999, page 556
2208:). The lake's body covers parts of today's Zhijiang,
1647:
1519:
After Ying Zheng declared himself the First Emperor (
981:
one of his capitals. In either 703 or 706, the ruler
941:"). Then the first capital of Chu was established at
905:(r. 1099–1050 BC). After the Zhou overthrew the
824:
OC: /*qlamʔ/, /*qʰɯːm/) which would later be written
734:), Chu included most of the present-day provinces of
448:
434:
420:
406:
392:
3042:
chancellor and reformed the Chu government and army.
5186:
5138:
5129:
4854:
4768:
4759:
2146:) mountains. In the north-east part of Chu are the
2035:) of Chu. In the Spring and Autumn period, Zuoyin (
1578:Gaozu, while Xiang Yu committed suicide in defeat.
1452:, capturing the descendants of the royal family of
1104:and then invaded Chu in 506 BC. Following the
617:
600:
593:
577:
570:
556:
539:
532:
515:
501:
487:
480:
466:
459:
442:
428:
414:
400:
386:
379:
374:
356:
327:
272:
255:
241:
222:
208:
198:
177:
119:
96:
39:
3546:Honolulu: Enrich Professional Publishing. p. 46-47
1685:Early Chu burial offerings consisted primarily of
1801:Some archaeological records of the Chu appear at
1728:Later Chu culture was known for its affinity for
1148:Freed from its difficulties with Wu, Chu annexed
977:in 863 BC but subsequently made its capital
4680:(in Chinese), Fuzhou: Fujian People's Publishing
4615:Defining Chu: Image and Reality in Ancient China
4381:Star Names – Their Lore and Meaning: Capricornus
3874:. University of Hawaii Press. pp. 140–150.
3847:Defining Chu: Image and Reality in Ancient China
2846:. He was murdered by his son, the future King Mu
2487:), ruled 11th century BC: also called Xuexiong (
1698:, iron, and silk, accompanied by a reduction in
1287:Qin's wars of unification § Conquest of Chu
4255:, Duke Wen, 6th year of, Duke Xuan, 8th year of
2698:), ruled 837–828 BC: brother of Xiong Yong
1857:and syntactical interferences from non-Sinitic
1853:spoken in Chu has long been assumed to reflect
1820:Chu artisanship includes color, especially the
1633:Drum with and Bird and Tiger Frame, Chu-state,
1542:, who proclaimed himself "King of Rising Chu" (
1412:Wang Jian's army passed through southern Chen (
1213:
1041:), then it expanded into the north towards the
27:Chinese Zhou dynasty state (c.1030 BC – 223 BC)
2662:), son of Xiong Kang, abdicated due to illness
857:, the ruling family of Chu descended from the
4737:
4695:
4673:
4641:
4416:
4354:
3981:Liăng-Zhōu jīnwén yùnwén he xiān-Qín 'Chŭ-yīn
3805:
3781:
3775:
3769:
3259:
3253:
3241:
3231:
3222:
3210:
3204:
3185:
3173:
3161:
3149:
3133:
3113:
3097:
3077:
3061:
3049:
3033:
3021:
3009:
2981:
2970:captured the capital Ying and he fled to the
2961:
2949:
2937:
2925:
2913:
2901:
2885:
2865:
2853:
2829:
2817:
2811:
2796:
2784:
2765:
2753:
2741:
2729:
2717:
2705:
2693:
2681:
2669:
2657:
2635:
2623:
2611:
2599:
2561:
2546:
2527:
2515:
2509:
2503:
2488:
2482:
2464:
2450:
2440:
2356:
2313:
2203:
2197:
2169:
2159:
2141:
2115:
2109:
2099:
2086:
2075:
2069:
2060:
2054:
2048:
2042:
2036:
2030:
2024:
2014:
1511:
1474:
1468:
1424:
1413:
1248:
1108:, it occupied Chu's capital at Ying, forcing
926:
880:
866:
829:
819:
809:
799:
729:
719:
362:
45:
8:
4671:Investigation of the Pre-Qin Surname System
4564:TTW-3, Zürich, 26.-29.VI.2009, "Genius Loci"
4448:"Megataxonomy of negative-sense RNA viruses"
3471:
4131:. University of Hawaii Press. p. 193, 316-7
4066:
1732:. The Chu culture and government supported
1347:, leading directly into the Chu heartland.
804:OC: /*rneːlʔ/) which was later written as
774:. For more than 400 years, the Chu capital
5135:
4765:
4744:
4730:
4722:
2734:), ruled 799–791 BC: son of Xiong Xun
2710:), ruled 827–822 BC: son of Xiong Yan
2686:), ruled 847–838 BC: son of Xiong Yan
2650:recorded him as the successor of Xiong Qu.
2202:), the southern Yunmeng was known as Yun (
2136:; a chain of mountains located in today's
371:
337:
76:
36:
5329:3rd-century BC disestablishments in China
4537:"The language of the bronze inscriptions"
4288:
4286:
4129:An Etymological Dictionary of Old Chinese
4012:
4001:Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences
2573:BC: son of Xiong Yi, defeated and killed
2532:), ruled 11th century BC: son of Xiong Li
1456:. These conquered territories became the
4299:(in Chinese). jianbo.org. Archived from
3718:
1201:
5309:11th-century BC establishments in China
4159:. Zhishufang Press. 2003. p. 372.
3655:(with modifications from Andrew Miller)
3556:
3554:
3552:
3428:
2182:. Due to its strategic value, numerous
1265:, farther away from the threat of Qin.
794:. The house of Chu originally bore the
671:
5304:States of the Spring and Autumn period
4146:, Ed. Paul Sidwell, 2006. #205. p. 115
3920:
3918:
2186:were built on the Fangcheng mountain.
1751:The naturalistic and flowing art, the
1257:but were defeated. King Kaolie blamed
1188:. Yue was partitioned between Chu and
1011:, depicting men wearing precursors to
523:
450:
324:
4248:
4246:
3689:
3687:
3685:
3683:
3681:
3359:. It is also represented by the star
2158:. The first capital of Chu, Danyang (
1992:possibly being a noun-forming prefix.
254:
240:
221:
217:
7:
4054:
3363:in the "Right Wall" asterism in the
2340:Sometime in the 6th century BC
2128:Progenitors of Chu such as viscount
1907:(Zhang Yongyan 1992, Zhou Jixu 2001)
5299:States of the Warring States period
4539:. In Shaughnessy, Edward L. (ed.).
1885:(Norman & Mei 1976, Boltz 1999)
1136:of Wu until he released their king
965:'s boat sank and he drowned in the
778:was located at the junction of the
4144:A Mon-Khmer Comparative Dictionary
4078:You Rujie 1992, Dong Kun 2006 etc.
3925:Walker, Hera S. (September 1998).
3768:Traditionally taken to be the Qu (
3487:. 合肥晚报. 2011-01-25. Archived from
3258:) as Hegemon-King of Western Chu (
1816:Bronze ladle from the state of Chu
1302:, dated 433 BC, State of Chu.
1021:dress) and riding in a two-horsed
865:. Zhuanxu's great-grandson Wuhui (
847:According to legends recounted in
25:
4518:Old Chinese: A New Reconstruction
4265:Anhui Provincial Institute (2015)
3505:. 凤凰网. 2011-01-25. Archived from
2616:), younger brother of Xiong Sheng
2475:(𦀚伯) or Fuju (附沮), son of Jilian
1988:“bristle”, with Chinese initial *
1510:, Qin shall fall by Chu's hand" (
1068:, Jin was defeated by Chu in the
1049:was annexed by the state of Chu.
3995:LaPolla, Randy J. (2010-01-01).
3285:Four Lords of the Warring States
2132:were said to originate from the
893:, adopted the ancestral surname
814:OC: /*meʔ/). They also bore the
307:
4205:Tian, Chengfang (Autumn 2008).
1961:/jǝrlaaʔ/, all descending from
1597:and then to Liu Bang's brother
1574:and was later honored with the
1491:Spearhead from the state of Chu
1206:Bronze from the Tomb of Chu in
1045:. In the summer of 648 BC, the
871:) was put in charge of fire by
861:and his grandson and successor
624:
607:
584:
563:
549:
522:
508:
494:
473:
4637:Records of the Grand Historian
4617:, University of Hawaii Press,
4596:Chamberlain, James R. (2016).
4581:: Cambridge University Press,
3801:Records of the Grand Historian
3571:Records of the Grand Historian
3296:and vied with Liu Bang in the
2589:BC: son of Xiong Ai, defeated
1980:is comparable to Khmer ជ្រាំង
1402:to lead the army against Chu.
854:Records of the Grand Historian
661:
449:
435:
421:
407:
393:
363:
1:
4652:Music in the Age of Confucius
3528:"The Regional State of Chu 楚"
2583:
2567:
2246:List of states annexed by Chu
1833:swords but not as intricate.
1593:was granted first to general
1339:The importance of Shu in the
1309:Records of the Warring States
231:
150:
137:
130:
88:
65:
4571:Brindley, Erica Fox (2015),
4442:Wolf, Yuri; Krupovic, Mart;
4014:10.1016/j.sbspro.2010.05.036
3651:(in Chinese). Translated by
3600:(in Chinese). Archived from
3574:(in Chinese). Archived from
3277:, poet who committed suicide
925:and the hereditary title of
885:) had six sons, all born by
790:, Henan, but later moved to
4602:Journal of the Siam Society
4520:, Oxford University Press,
3870:Constance A., Cook (1999).
3845:Constance A., Cook (1999).
3820:Constance A., Cook (1999).
3804:, "Biography of Xiang Yu" (
3544:A History Of Chu (Volume 1)
3365:"Heavenly Market" enclosure
2994:. The year before he died,
2514:), later written as Xiong (
2053:) was assisted by Zuosima (
1648:
1429:; northwest of present-day
1152:in 479 BC and overran
351:(bottom) Chinese characters
5345:
3940:University of Pennsylvania
3472:Baxter & Sagart (2014)
3320:
3106:until death in 296 BC
2874:, and was recognized as a
2423:
1494:
1300:Tomb of Marquis Yi of Zeng
1284:
1124:. Chu began to strengthen
992:
159:Chen (陳) (278–241 BC)
71:BC – 223 BC
29:
4696:
4674:
4642:
4417:
4355:
3806:
3782:
3776:
3770:
3542:Zhang, Zhengming. (2019)
3526:Theobald, Ulrich. (2018)
3413:Chu Kingdom (Han dynasty)
3260:
3254:
3242:
3232:
3223:
3211:
3205:
3186:
3174:
3162:
3150:
3134:
3114:
3098:
3078:
3062:
3050:
3034:
3022:
3010:
2982:
2962:
2950:
2938:
2926:
2914:
2902:
2886:
2866:
2854:
2830:
2818:
2812:
2797:
2785:
2766:
2754:
2742:
2730:
2718:
2706:
2694:
2682:
2670:
2658:
2636:
2624:
2612:
2600:
2562:
2547:
2528:
2516:
2510:
2504:
2489:
2483:
2465:
2451:
2441:
2426:Rulers of Chu family tree
2357:
2314:
2204:
2198:
2170:
2164:) was located in today's
2160:
2150:; the drainage divide of
2142:
2116:
2110:
2100:
2087:
2076:
2070:
2061:
2055:
2049:
2043:
2037:
2031:
2025:
2015:
1512:
1475:
1469:
1425:
1414:
1249:
1112:to flee to his allies in
985:became the ruler of Chu.
927:
881:
867:
830:
820:
810:
800:
730:
720:
709:Qin's wars of unification
652:
638:
370:
336:
332:
282:
268:
218:
75:
64:
46:
4295:
4127:Schuessler, Axel. 2007.
4038:Zhongguo Minzushi Yanjiu
3955:中國學術思想研究輯刊: 二編, Volume 6
3485:"河南库区发掘工作圆满结束,出土文物已通过验收"
3309:and then founder of the
2168:, Hubei province. Ying (
1635:Spring and Autumn period
1448:around the mouth of the
989:Spring and Autumn period
959:his campaign against Chu
796:ancestral temple surname
703:it was destroyed by the
697:Spring and Autumn period
691:. Their first ruler was
4558:Behr, Wolfgang (2009).
4535:Behr, Wolfgang (2017).
4396:. penelope.uchicago.edu
4103:: 28–36. Archived from
3953:Lin, Qingzhang (2008).
3459:Encyclopedia Britannica
3305:, later citizen of the
3264:) ruled 206–202 BC
3215:) ruled 210–209 BC
1984:“to bristle” and ប្រែង
1827:"Birds and Worms" style
1779:was preferred over the
1740:supplemented with some
1700:bronze vessel offerings
1312:, a debate between the
957:In 977 BC, during
879:. Wuhui's son Luzhong (
277:Ancient Chinese coinage
5294:Ancient Chinese states
4753:Ancient Chinese states
4516:; et al. (2014),
4506:10.1515/char-2014-0008
4180:Song, Zhiying (2012).
3737:Li and Zheng, page 188
3645:"5.僖公 BOOK V. DUKE XI"
3323:Chinese constellations
3209:) as King Yin of Chu (
2006:
1817:
1655:
1638:
1626:
1503:excavated bamboo slips
1492:
1303:
1298:Bronze bells from the
1229:
1211:
1025:
897:. Jilian's descendant
742:, along with parts of
165:(壽春) (241–224 BC)
4650:So, Jenny F. (2000),
4278:Tsinghua Bamboo Slips
4088:Ye, Xiaofeng (2014).
3978:Yù, Suíshēng (1993).
3403:Prime Minister of Chu
3393:are named after Chǔ.
3110:King Qingxiang of Chu
2648:Tsinghua Bamboo Slips
2004:
1917:Noticing that both 荆
1841:Linguistic influences
1815:
1644:
1632:
1624:
1490:
1483:Qin and Han dynasties
1405:The Chu army, led by
1297:
1205:
1196:The Book of Master Wu
1160:In the late 390s BC,
1144:Warring States period
1002:
707:in 223 BC during the
701:Warring States period
685:ancient Chinese state
185:Chinese folk religion
4669:Zhang Shuyi (2008),
3935:Sino-Platonic Papers
3748:"The Warring States"
3694:Gu, Donggao (1993).
3566:"楚世家 (House of Chu)"
2640:), son of Xiong Qu.
2455:), granddaughter of
1925:refer to the thorny
1899:Zhengzhang Shangfang
1320:and the Qin general
875:and given the title
699:. At the end of the
619:Baxter–Sagart (2014)
257:• Conquered by
4486:Chinese Archaeology
4235:Hong, Gang (2012).
4207:"從新出文字材料論楚沈尹氏之族屬源流"
3895:Peng, Peng (2020).
3408:Chu Silk Manuscript
3070:around 348 BC.
2690:Xiong Yan (younger)
2604:), son of Xiong Dan
2469:) as ancestral name
1847:Eastern Zhou period
1694:, such as colorful
1529:Great Wall of China
1465:Battle of Changping
1460:of the Qin Empire.
1243:, the Zhao general
1199:. Of Chu, he said:
1028:Under the reign of
901:was the teacher of
190:Ancestor veneration
4514:Baxter, William H.
4461:on 13 January 2019
4425:2011-05-22 at the
4363:2011-05-22 at the
4303:on 2 December 2013
3669:, twelfth year of
3461:. 3 November 2023.
3298:Chu–Han Contention
3130:King Kaolie of Chu
2996:Marquis Yi of Zeng
2862:King Zhuang of Chu
2553:King Cheng of Zhou
2400:About 348 BC
2394:after 418 BC
2346:after 506 BC
2321:after 622 BC
2293:after 643 BC
2007:
1976:< Old Chinese *
1941:< Old Chinese *
1897:(Liu Xingge 1988,
1855:lexical borrowings
1818:
1656:
1639:
1627:
1568:Chu–Han Contention
1554:. Xiang installed
1536:Dazexiang Uprising
1497:Chu–Han Contention
1493:
1349:King Huiwen of Qin
1304:
1212:
1026:
1017:(i.e. traditional
251:706 or 703 BC
224:• Founded by
5276:
5275:
5272:
5271:
5125:
5124:
4550:978-9-629-96639-3
4527:978-0-19-994537-5
4498:Walter de Gruyter
4379:Allen, Richard. "
4182:《左传》研究文献辑刊(全二十二册)
3942:. pp. 53–54.
3901:. cambria Press.
3329:Chinese astronomy
3238:Emperor Yi of Chu
3120:Guodian Chu Slips
3018:King Sheng of Chu
2892:Battle of Yanling
2840:Battle of Chengpu
2826:King Cheng of Chu
2666:Xiong Yan (elder)
2575:King Zhao of Zhou
1945:is comparable to
1849:, the variety of
1607:Emperor Wu of Han
1605:. By the time of
1458:Kuaiji Prefecture
1330:Mandate of Heaven
1306:According to the
1272:was conquered by
1193:his magnum opus,
1043:North China Plain
963:King Zhao of Zhou
887:Caesarian section
786:near present-day
642:
641:
634:
633:
489:Yale Romanization
381:Standard Mandarin
323:
322:
319:
318:
315:
314:
264: 223 BC
59:
16:(Redirected from
5336:
5136:
4766:
4746:
4739:
4732:
4723:
4699:
4698:
4681:
4677:
4676:
4664:
4645:
4644:
4627:
4609:
4591:
4567:
4554:
4530:
4509:
4471:
4470:
4468:
4466:
4460:
4454:. Archived from
4444:Zhang, Yong Zhen
4439:
4433:
4432:
4429:". 24 Jun 2006.
4420:
4419:
4412:
4406:
4405:
4403:
4401:
4390:
4384:
4377:
4371:
4370:
4358:
4357:
4350:
4344:
4319:
4313:
4312:
4310:
4308:
4290:
4281:
4274:
4268:
4262:
4256:
4250:
4241:
4240:
4232:
4226:
4225:
4224:– via 简帛网.
4223:
4222:
4213:. Archived from
4202:
4196:
4195:
4177:
4171:
4170:
4153:
4147:
4138:
4132:
4125:
4119:
4118:
4116:
4115:
4109:
4094:
4085:
4079:
4076:
4070:
4067:Chamberlain 2016
4064:
4058:
4052:
4046:
4045:
4033:
4027:
4026:
4016:
4007:(5): 6858–6868.
3992:
3986:
3985:
3975:
3969:
3968:
3950:
3944:
3943:
3931:
3922:
3913:
3912:
3892:
3886:
3885:
3867:
3861:
3860:
3842:
3836:
3835:
3817:
3811:
3809:
3808:
3793:
3787:
3785:
3784:
3779:
3778:
3773:
3772:
3766:
3760:
3759:
3757:
3755:
3744:
3738:
3735:
3726:
3716:
3710:
3709:
3691:
3676:
3675:
3662:
3660:
3641:
3635:
3629:
3623:
3620:
3614:
3613:
3611:
3609:
3604:on 4 August 2012
3594:
3588:
3587:
3585:
3583:
3578:on 10 March 2012
3558:
3547:
3540:
3534:
3524:
3518:
3517:
3515:
3514:
3499:
3493:
3492:
3481:
3475:
3469:
3463:
3462:
3451:
3445:
3444:
3439:. Archived from
3433:
3361:Epsilon Ophiuchi
3263:
3262:
3257:
3256:
3245:
3244:
3235:
3234:
3226:
3225:
3214:
3213:
3208:
3207:
3189:
3188:
3177:
3176:
3165:
3164:
3153:
3152:
3137:
3136:
3117:
3116:
3101:
3100:
3094:King Huai of Chu
3081:
3080:
3065:
3064:
3058:King Xuan of Chu
3053:
3052:
3037:
3036:
3025:
3024:
3013:
3012:
3006:King Jian of Chu
2985:
2984:
2965:
2964:
2958:King Zhao of Chu
2953:
2952:
2946:King Ping of Chu
2941:
2940:
2929:
2928:
2922:King Ling of Chu
2917:
2916:
2905:
2904:
2898:King Kang of Chu
2889:
2888:
2882:King Gong of Chu
2869:
2868:
2857:
2856:
2833:
2832:
2821:
2820:
2816:) or Zhuang'ao (
2815:
2814:
2800:
2799:
2788:
2787:
2769:
2768:
2757:
2756:
2745:
2744:
2733:
2732:
2721:
2720:
2709:
2708:
2697:
2696:
2685:
2684:
2673:
2672:
2661:
2660:
2639:
2638:
2627:
2626:
2615:
2614:
2603:
2602:
2588:
2585:
2572:
2569:
2565:
2564:
2550:
2549:
2531:
2530:
2519:
2518:
2513:
2512:
2507:
2506:
2495:King Wen of Zhou
2492:
2491:
2486:
2485:
2468:
2467:
2454:
2453:
2444:
2443:
2360:
2359:
2334:611 BC Yong
2317:
2316:
2312:622 BC Lù (
2275:684–680 BC
2269:688–680 BC
2207:
2206:
2201:
2200:
2173:
2172:
2163:
2162:
2145:
2144:
2119:
2118:
2113:
2112:
2106:Ruo'ao rebellion
2103:
2102:
2090:
2089:
2079:
2078:
2073:
2072:
2064:
2063:
2058:
2057:
2052:
2051:
2046:
2045:
2040:
2039:
2034:
2033:
2028:
2027:
2018:
2017:
1651:
1515:
1514:
1478:
1477:
1472:
1471:
1428:
1427:
1417:
1416:
1328:and seizing the
1252:
1251:
1227:
932:
931:
903:King Wen of Zhou
889:. The youngest,
884:
883:
870:
869:
833:
832:
823:
822:
813:
812:
803:
802:
733:
732:
723:
722:
673:
663:
654:
630:
629:
628:
613:
612:
611:
589:
588:
587:
566:
565:
552:
551:
528:
527:
526:
511:
510:
497:
496:
476:
475:
455:
454:
453:
438:
437:
424:
423:
410:
409:
396:
395:
372:
366:
365:
341:
325:
311:
310:
299:
298:
284:
283:
247:proclaimed king
236:
233:
155:
152:
142:
139:
135:
132:
90:
85:
80:
70:
67:
52:
49:
48:
37:
21:
5344:
5343:
5339:
5338:
5337:
5335:
5334:
5333:
5279:
5278:
5277:
5268:
5182:
5121:
4850:
4755:
4750:
4716:Chu and Kra-Dai
4708:
4706:Further reading
4703:
4668:
4662:
4649:
4625:
4612:
4595:
4589:
4570:
4557:
4551:
4534:
4528:
4512:
4483:
4479:
4474:
4464:
4462:
4458:
4441:
4440:
4436:
4430:
4427:Wayback Machine
4413:
4409:
4399:
4397:
4392:
4391:
4387:
4378:
4374:
4368:
4367:". 4 Jul 2006.
4365:Wayback Machine
4351:
4347:
4320:
4316:
4306:
4304:
4297:
4292:
4291:
4284:
4275:
4271:
4263:
4259:
4251:
4244:
4234:
4233:
4229:
4220:
4218:
4204:
4203:
4199:
4192:
4179:
4178:
4174:
4167:
4155:
4154:
4150:
4139:
4135:
4126:
4122:
4113:
4111:
4107:
4092:
4087:
4086:
4082:
4077:
4073:
4065:
4061:
4053:
4049:
4035:
4034:
4030:
3994:
3993:
3989:
3977:
3976:
3972:
3965:
3957:. p. 176.
3952:
3951:
3947:
3929:
3924:
3923:
3916:
3909:
3894:
3893:
3889:
3882:
3869:
3868:
3864:
3857:
3844:
3843:
3839:
3832:
3819:
3818:
3814:
3794:
3790:
3767:
3763:
3753:
3751:
3746:
3745:
3741:
3736:
3729:
3719:Brindley (2015)
3717:
3713:
3706:
3693:
3692:
3679:
3658:
3656:
3643:
3642:
3638:
3630:
3626:
3621:
3617:
3607:
3605:
3596:
3595:
3591:
3581:
3579:
3560:
3559:
3550:
3541:
3537:
3525:
3521:
3512:
3510:
3501:
3500:
3496:
3483:
3482:
3478:
3470:
3466:
3453:
3452:
3448:
3435:
3434:
3430:
3426:
3421:
3399:
3373:
3335:, part of the "
3327:In traditional
3325:
3319:
3271:
3146:King You of Chu
3074:King Wei of Chu
3030:King Dao of Chu
2978:King Hui of Chu
2793:King Wen of Chu
2591:King Mu of Zhou
2586:
2570:
2428:
2422:
2248:
2148:Dabie mountains
2126:
2059:) and Yousima (
1999:
1963:Proto-Mon-Khmer
1843:
1654:on a toad stand
1619:
1499:
1485:
1289:
1283:
1228:
1220:
1162:King Dao of Chu
1146:
997:
991:
955:
845:
840:
834:OC: /*ɢʷlɯm/).
430:Tongyong Pinyin
352:
308:
261:
248:
234:
228:
194:
173:
153:
140:
133:
115:
106:(before 704 BC)
92:
87:
83:
68:
60:
51:
50:
42:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
5342:
5340:
5332:
5331:
5326:
5321:
5316:
5311:
5306:
5301:
5296:
5291:
5281:
5280:
5274:
5273:
5270:
5269:
5267:
5266:
5261:
5256:
5251:
5246:
5241:
5236:
5231:
5226:
5221:
5216:
5211:
5206:
5201:
5196:
5190:
5188:
5184:
5183:
5181:
5180:
5175:
5170:
5165:
5160:
5155:
5150:
5144:
5142:
5133:
5131:Warring States
5127:
5126:
5123:
5122:
5120:
5119:
5114:
5109:
5104:
5099:
5094:
5089:
5084:
5079:
5074:
5069:
5064:
5059:
5054:
5049:
5044:
5039:
5034:
5029:
5024:
5019:
5014:
5009:
5004:
4999:
4994:
4989:
4984:
4979:
4974:
4969:
4964:
4959:
4954:
4949:
4944:
4939:
4934:
4929:
4924:
4919:
4914:
4909:
4904:
4899:
4894:
4889:
4884:
4879:
4874:
4869:
4864:
4858:
4856:
4852:
4851:
4849:
4848:
4843:
4838:
4833:
4828:
4823:
4818:
4813:
4808:
4803:
4798:
4793:
4788:
4783:
4778:
4772:
4770:
4763:
4757:
4756:
4751:
4749:
4748:
4741:
4734:
4726:
4720:
4719:
4707:
4704:
4702:
4701:
4683:
4666:
4660:
4647:
4629:
4623:
4610:
4593:
4587:
4568:
4555:
4549:
4532:
4526:
4510:
4480:
4478:
4475:
4473:
4472:
4434:
4407:
4385:
4372:
4345:
4314:
4282:
4276:See also, the
4269:
4257:
4253:Gongyang Zhuan
4242:
4227:
4197:
4190:
4172:
4165:
4148:
4133:
4120:
4080:
4071:
4059:
4047:
4028:
3987:
3970:
3963:
3945:
3914:
3907:
3887:
3880:
3862:
3855:
3837:
3830:
3812:
3788:
3761:
3739:
3727:
3711:
3704:
3677:
3636:
3624:
3615:
3589:
3548:
3535:
3519:
3494:
3491:on 2011-07-11.
3476:
3474:, p. 332.
3464:
3446:
3443:on 2011-07-07.
3427:
3425:
3422:
3420:
3417:
3416:
3415:
3410:
3405:
3398:
3395:
3390:Jingchuvirales
3372:
3369:
3321:Main article:
3318:
3315:
3314:
3313:
3300:
3287:
3278:
3270:
3267:
3266:
3265:
3247:
3228:
3216:
3197:
3196:
3192:
3191:
3182:Lord Changping
3179:
3167:
3158:King Ai of Chu
3155:
3143:
3127:
3107:
3091:
3071:
3055:
3046:King Su of Chu
3043:
3027:
3015:
3003:
2975:
2955:
2943:
2931:
2919:
2907:
2895:
2879:
2859:
2850:King Mu of Chu
2847:
2823:
2805:
2790:
2781:King Wu of Chu
2777:
2776:
2772:
2771:
2759:
2747:
2735:
2723:
2711:
2699:
2687:
2675:
2663:
2651:
2629:
2617:
2605:
2593:
2577:
2555:
2539:
2538:
2534:
2533:
2521:
2497:
2493:), teacher of
2476:
2470:
2463:; adopted Mi (
2433:
2432:
2421:
2418:
2417:
2416:
2410:
2404:
2398:
2392:
2386:
2380:
2374:
2368:
2362:
2353:
2352:574 BC Shuyong
2350:
2344:
2338:
2337:601 BC Shuliao
2335:
2332:
2325:
2319:
2310:
2304:
2297:
2291:
2285:
2279:
2273:
2267:
2261:
2255:
2247:
2244:
2236:Danfeng County
2194:Jianghan Plain
2138:Hubei province
2134:Jing Mountains
2125:
2122:
2041:) and Youyin (
1998:
1995:
1994:
1993:
1970:
1915:
1914:
1911:
1908:
1902:
1892:
1886:
1880:
1842:
1839:
1692:burial objects
1687:bronze vessels
1625:Tomb guardian.
1618:
1615:
1603:Kingdom of Chu
1495:Main article:
1484:
1481:
1418:; present-day
1285:Main article:
1282:
1279:
1218:
1208:Xichuan County
1145:
1142:
1106:Battle of Boju
1074:state of Zheng
1047:State of Huang
993:Main article:
990:
987:
954:
951:
921:of Chu in the
859:Yellow Emperor
844:
841:
839:
836:
788:Xichuan County
714:Also known as
693:King Wu of Chu
640:
639:
636:
635:
632:
631:
621:
615:
614:
604:
598:
597:
591:
590:
581:
579:Middle Chinese
575:
574:
572:Middle Chinese
568:
567:
560:
554:
553:
546:
537:
536:
530:
529:
519:
513:
512:
505:
499:
498:
491:
485:
484:
482:Yue: Cantonese
478:
477:
470:
464:
463:
457:
456:
446:
440:
439:
432:
426:
425:
418:
412:
411:
404:
398:
397:
390:
384:
383:
377:
376:
375:Transcriptions
368:
367:
360:
354:
353:
342:
334:
333:
330:
329:
321:
320:
317:
316:
313:
312:
305:
296:
293:
292:
287:
280:
279:
274:
270:
269:
266:
265:
262:
256:
253:
252:
249:
242:
239:
238:
229:
223:
220:
219:
216:
215:
210:
209:Historical era
206:
205:
200:
196:
195:
193:
192:
187:
181:
179:
175:
174:
172:
171:
166:
160:
157:
156:– 278 BC)
144:
123:
121:
117:
116:
114:
113:
107:
100:
98:
94:
93:
82:
81:
73:
72:
62:
61:
44:
43:
40:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
5341:
5330:
5327:
5325:
5322:
5320:
5317:
5315:
5312:
5310:
5307:
5305:
5302:
5300:
5297:
5295:
5292:
5290:
5287:
5286:
5284:
5265:
5262:
5260:
5257:
5255:
5252:
5250:
5247:
5245:
5242:
5240:
5237:
5235:
5232:
5230:
5227:
5225:
5222:
5220:
5217:
5215:
5212:
5210:
5207:
5205:
5202:
5200:
5197:
5195:
5192:
5191:
5189:
5185:
5179:
5176:
5174:
5171:
5169:
5166:
5164:
5161:
5159:
5156:
5154:
5151:
5149:
5146:
5145:
5143:
5141:
5137:
5134:
5132:
5128:
5118:
5115:
5113:
5110:
5108:
5105:
5103:
5100:
5098:
5095:
5093:
5090:
5088:
5085:
5083:
5080:
5078:
5075:
5073:
5070:
5068:
5065:
5063:
5060:
5058:
5055:
5053:
5050:
5048:
5045:
5043:
5040:
5038:
5035:
5033:
5030:
5028:
5025:
5023:
5020:
5018:
5015:
5013:
5010:
5008:
5005:
5003:
5000:
4998:
4995:
4993:
4990:
4988:
4985:
4983:
4980:
4978:
4975:
4973:
4970:
4968:
4965:
4963:
4960:
4958:
4955:
4953:
4950:
4948:
4945:
4943:
4940:
4938:
4935:
4933:
4930:
4928:
4925:
4923:
4920:
4918:
4915:
4913:
4910:
4908:
4905:
4903:
4900:
4898:
4895:
4893:
4890:
4888:
4885:
4883:
4880:
4878:
4875:
4873:
4870:
4868:
4865:
4863:
4860:
4859:
4857:
4853:
4847:
4844:
4842:
4839:
4837:
4834:
4832:
4829:
4827:
4824:
4822:
4819:
4817:
4814:
4812:
4809:
4807:
4804:
4802:
4799:
4797:
4794:
4792:
4789:
4787:
4784:
4782:
4779:
4777:
4774:
4773:
4771:
4767:
4764:
4762:
4758:
4754:
4747:
4742:
4740:
4735:
4733:
4728:
4727:
4724:
4717:
4713:
4710:
4709:
4705:
4693:
4692:
4687:
4684:
4679:
4672:
4667:
4663:
4661:0-295-97953-4
4657:
4653:
4648:
4639:
4638:
4633:
4630:
4626:
4624:0-8248-2905-0
4620:
4616:
4611:
4607:
4603:
4599:
4594:
4590:
4588:9781107084780
4584:
4580:
4576:
4575:
4569:
4565:
4561:
4556:
4552:
4546:
4542:
4538:
4533:
4529:
4523:
4519:
4515:
4511:
4507:
4503:
4499:
4495:
4491:
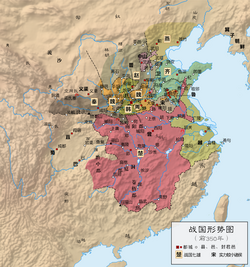
4487:
4482:
4481:
4476:
4457:
4453:
4449:
4445:
4438:
4435:
4428:
4424:
4421:
4411:
4408:
4395:
4389:
4386:
4382:
4376:
4373:
4366:
4362:
4359:
4349:
4346:
4342:
4338:
4337:
4332:
4331:
4326:
4325:
4318:
4315:
4302:
4298:
4289:
4287:
4283:
4279:
4273:
4270:
4267:, p. 83.
4266:
4261:
4258:
4254:
4249:
4247:
4243:
4238:
4231:
4228:
4217:on 2015-02-06
4216:
4212:
4208:
4201:
4198:
4193:
4191:9787501346158
4187:
4183:
4176:
4173:
4168:
4166:9789867938176
4162:
4158:
4152:
4149:
4145:
4142:
4137:
4134:
4130:
4124:
4121:
4110:on 2021-01-14
4106:
4102:
4098:
4091:
4084:
4081:
4075:
4072:
4069:, p. 67.
4068:
4063:
4060:
4056:
4051:
4048:
4043:
4039:
4032:
4029:
4024:
4020:
4015:
4010:
4006:
4002:
3998:
3991:
3988:
3983:
3982:
3974:
3971:
3966:
3964:9789866528071
3960:
3956:
3949:
3946:
3941:
3937:
3936:
3928:
3921:
3919:
3915:
3910:
3908:9781604979626
3904:
3900:
3899:
3891:
3888:
3883:
3877:
3873:
3866:
3863:
3858:
3852:
3848:
3841:
3838:
3833:
3827:
3823:
3816:
3813:
3803:
3802:
3797:
3792:
3789:
3780:), and Zhao (
3765:
3762:
3749:
3743:
3740:
3734:
3732:
3728:
3724:
3720:
3715:
3712:
3707:
3705:9787101012187
3701:
3697:
3690:
3688:
3686:
3684:
3682:
3678:
3674:
3672:
3671:Duke Xi of Lu
3668:
3654:
3650:
3646:
3640:
3637:
3633:
3628:
3625:
3619:
3616:
3603:
3599:
3593:
3590:
3577:
3573:
3572:
3567:
3563:
3557:
3555:
3553:
3549:
3545:
3539:
3536:
3533:
3529:
3523:
3520:
3509:on 2018-09-30
3508:
3504:
3498:
3495:
3490:
3486:
3480:
3477:
3473:
3468:
3465:
3460:
3456:
3450:
3447:
3442:
3438:
3432:
3429:
3423:
3418:
3414:
3411:
3409:
3406:
3404:
3401:
3400:
3396:
3394:
3392:
3391:
3386:
3385:
3381:
3378:
3370:
3368:
3366:
3362:
3358:
3357:24 Capricorni
3354:
3350:
3346:
3342:
3341:lunar mansion
3338:
3334:
3330:
3324:
3316:
3312:
3308:
3304:
3301:
3299:
3295:
3291:
3288:
3286:
3283:, one of the
3282:
3281:Lord Chunshen
3279:
3276:
3273:
3272:
3268:
3251:
3248:
3239:
3229:
3220:
3217:
3202:
3199:
3198:
3194:
3193:
3183:
3180:
3171:
3168:
3159:
3156:
3147:
3144:
3141:
3131:
3128:
3125:
3121:
3111:
3108:
3105:
3095:
3092:
3089:
3085:
3075:
3072:
3069:
3059:
3056:
3047:
3044:
3041:
3031:
3028:
3019:
3016:
3007:
3004:
3001:
2997:
2993:
2989:
2979:
2976:
2973:
2969:
2959:
2956:
2947:
2944:
2935:
2932:
2923:
2920:
2911:
2908:
2899:
2896:
2893:
2883:
2880:
2877:
2873:
2863:
2860:
2851:
2848:
2845:
2842:. Husband to
2841:
2837:
2827:
2824:
2809:
2806:
2804:
2794:
2791:
2782:
2779:
2778:
2774:
2773:
2763:
2760:
2751:
2748:
2739:
2736:
2727:
2724:
2715:
2712:
2703:
2700:
2691:
2688:
2679:
2676:
2667:
2664:
2655:
2652:
2649:
2645:
2644:
2633:
2630:
2621:
2618:
2609:
2606:
2597:
2594:
2592:
2581:
2578:
2576:
2559:
2556:
2554:
2544:
2541:
2540:
2536:
2535:
2525:
2522:
2501:
2498:
2496:
2480:
2477:
2474:
2471:
2462:
2458:
2457:Shang dynasty
2448:
2438:
2435:
2434:
2430:
2429:
2427:
2419:
2415:
2411:
2409:
2405:
2403:
2399:
2397:
2393:
2391:
2387:
2385:
2381:
2379:
2375:
2373:
2369:
2367:
2363:
2355:538 BC Lai (
2354:
2351:
2349:
2345:
2343:
2339:
2336:
2333:
2330:
2326:
2324:
2320:
2311:
2309:
2305:
2302:
2298:
2296:
2292:
2290:
2286:
2284:
2280:
2278:
2274:
2272:
2268:
2266:
2262:
2260:
2256:
2254:
2250:
2249:
2245:
2243:
2241:
2237:
2233:
2229:
2227:
2223:
2219:
2215:
2211:
2195:
2191:
2187:
2185:
2181:
2180:central plain
2177:
2167:
2157:
2156:Yangtse river
2153:
2149:
2139:
2135:
2131:
2123:
2121:
2114:) and Cheng (
2107:
2097:
2092:
2083:
2066:
2022:
2012:
2003:
1996:
1991:
1987:
1983:
1979:
1975:
1971:
1968:
1964:
1960:
1956:
1952:
1948:
1944:
1940:
1936:
1935:
1934:
1932:
1928:
1924:
1920:
1912:
1909:
1906:
1905:Tibeto-Burman
1903:
1900:
1896:
1893:
1890:
1887:
1884:
1883:Austroasiatic
1881:
1878:
1877:
1876:
1874:
1873:
1868:
1864:
1860:
1856:
1852:
1848:
1840:
1838:
1834:
1832:
1828:
1823:
1814:
1810:
1808:
1804:
1799:
1797:
1793:
1789:
1784:
1782:
1778:
1777:
1770:
1768:
1764:
1760:
1759:Guodian slips
1756:
1755:
1749:
1747:
1743:
1739:
1735:
1731:
1726:
1724:
1719:
1717:
1716:Shang dynasty
1713:
1709:
1705:
1701:
1697:
1693:
1688:
1683:
1681:
1677:
1672:
1667:
1665:
1661:
1653:
1650:
1643:
1636:
1631:
1623:
1616:
1614:
1612:
1608:
1604:
1600:
1596:
1592:
1588:
1584:
1579:
1577:
1573:
1569:
1565:
1561:
1557:
1553:
1549:
1545:
1541:
1537:
1532:
1530:
1526:
1522:
1517:
1509:
1504:
1498:
1489:
1482:
1480:
1466:
1461:
1459:
1455:
1451:
1447:
1443:
1438:
1436:
1432:
1421:
1410:
1408:
1403:
1401:
1397:
1393:
1389:
1385:
1381:
1376:
1374:
1370:
1366:
1362:
1358:
1354:
1350:
1346:
1345:Yangtze River
1342:
1341:Sichuan Basin
1337:
1335:
1331:
1327:
1323:
1319:
1315:
1311:
1310:
1301:
1296:
1292:
1288:
1280:
1278:
1275:
1271:
1266:
1264:
1260:
1259:Lord Chunshen
1256:
1246:
1242:
1238:
1234:
1226:
1225:
1217:
1209:
1204:
1200:
1198:
1197:
1191:
1187:
1183:
1179:
1175:
1171:
1167:
1163:
1158:
1155:
1151:
1143:
1141:
1139:
1135:
1131:
1127:
1123:
1119:
1115:
1111:
1107:
1103:
1099:
1095:
1090:
1088:
1084:
1080:
1075:
1071:
1067:
1063:
1062:central plain
1059:
1055:
1050:
1048:
1044:
1040:
1035:
1034:five Hegemons
1031:
1024:
1020:
1016:
1015:
1010:
1006:
1001:
996:
988:
986:
984:
980:
976:
972:
968:
964:
960:
952:
950:
948:
945:(present-day
944:
940:
936:
930:
924:
923:Nanyang Basin
920:
916:
912:
908:
907:Shang dynasty
904:
900:
896:
892:
888:
878:
874:
864:
860:
856:
855:
850:
842:
837:
835:
827:
817:
807:
797:
793:
789:
785:
781:
777:
773:
769:
765:
761:
757:
753:
749:
745:
741:
737:
727:
717:
712:
710:
706:
702:
698:
694:
690:
686:
682:
678:
674:
668:
664:
658:
650:
646:
637:
622:
620:
616:
605:
603:
602:Baxter (1992)
599:
596:
592:
582:
580:
576:
573:
569:
561:
559:
555:
547:
545:
542:
538:
535:
531:
525:
520:
518:
514:
506:
504:
500:
492:
490:
486:
483:
479:
471:
469:
465:
462:
458:
452:
447:
445:
441:
433:
431:
427:
419:
417:
413:
405:
403:
399:
391:
389:
385:
382:
378:
373:
369:
361:
359:
355:
350:
346:
340:
335:
331:
326:
306:
304:
301:
300:
297:
295:
294:
291:
288:
286:
285:
281:
278:
275:
271:
267:
263:
260:
250:
246:
230:
227:
214:
211:
207:
204:
201:
197:
191:
188:
186:
183:
182:
180:
176:
170:
167:
164:
161:
158:
148:
145:
128:
125:
124:
122:
118:
111:
108:
105:
102:
101:
99:
95:
86: Chu (楚)
79:
74:
63:
58:
55:
38:
33:
19:
5234:Western Zhou
5209:Eastern Zhou
5187:Minor states
5147:
5140:Seven states
4855:Minor states
4790:
4769:Major states
4761:Zhou dynasty
4712:Miyake, Marc
4689:
4678:
4675:(《先秦姓氏制度考察》)
4670:
4651:
4635:
4614:
4605:
4601:
4573:
4563:
4540:
4517:
4489:
4485:
4463:. Retrieved
4456:the original
4451:
4437:
4431:(in Chinese)
4410:
4398:. Retrieved
4388:
4375:
4369:(in Chinese)
4348:
4340:
4334:
4328:
4322:
4317:
4305:. Retrieved
4301:the original
4272:
4260:
4239:. 中国财政经济出版社.
4236:
4230:
4219:. Retrieved
4215:the original
4210:
4200:
4181:
4175:
4156:
4151:
4143:
4136:
4128:
4123:
4112:. Retrieved
4105:the original
4100:
4096:
4083:
4074:
4062:
4050:
4041:
4037:
4031:
4004:
4000:
3990:
3980:
3973:
3954:
3948:
3933:
3897:
3890:
3871:
3865:
3846:
3840:
3821:
3815:
3799:
3791:
3764:
3752:. Retrieved
3750:(in Chinese)
3742:
3714:
3695:
3664:
3657:. Retrieved
3648:
3639:
3627:
3618:
3606:. Retrieved
3602:the original
3592:
3580:. Retrieved
3576:the original
3569:
3543:
3538:
3531:
3522:
3511:. Retrieved
3507:the original
3503:"科大考古队觅宝千余件"
3497:
3489:the original
3479:
3467:
3458:
3449:
3441:the original
3431:
3388:
3382:
3374:
3345:Black Turtle
3326:
3104:State of Qin
2972:State of Sui
2872:Battle of Bi
2836:state of Jin
2702:Xiong Shuang
2641:
2582:(熊䵣), ruled
2431:Early rulers
2412:249 BC
2406:334 BC
2388:431 BC
2382:447 BC
2376:445 BC
2370:479 BC
2364:512 BC
2306:622 BC
2299:623 BC
2281:678 BC
2263:690 BC
2257:704 BC
2251:863 BC
2230:
2188:
2127:
2093:
2067:
2008:
1989:
1985:
1981:
1977:
1973:
1966:
1950:
1942:
1938:
1922:
1918:
1916:
1870:
1844:
1835:
1819:
1805:. After the
1800:
1785:
1774:
1771:
1754:Songs of Chu
1752:
1750:
1727:
1720:
1684:
1671:Western Zhou
1668:
1660:Yellow River
1657:
1580:
1543:
1533:
1518:
1500:
1473:) and Jing (
1462:
1439:
1411:
1404:
1377:
1338:
1307:
1305:
1290:
1267:
1230:
1222:
1214:
1194:
1159:
1147:
1091:
1070:battle of Bi
1051:
1027:
1012:
1009:State of Chu
956:
953:Western Zhou
934:
852:
846:
816:lineage name
725:
715:
713:
689:Zhou dynasty
680:
670:
660:
644:
643:
534:Southern Min
388:Hanyu Pinyin
290:Succeeded by
289:
213:Zhou dynasty
112:(704–223 BC)
56:
5289:Chu (state)
4902:Western Guo
4897:Eastern Guo
4686:Zuo Qiuming
4293:Ziju (子居).
4097:Minzu Yuwen
3653:James Legge
3632:Cho-Yun Hsu
3311:Han dynasty
3307:Qin dynasty
3230:Xiong Xin (
2968:State of Wu
2596:Xiong Sheng
2524:Xiong Kuang
2445:), married
2232:Shaoxi Pass
1997:Bureaucracy
1947:Proto-Monic
1927:chaste tree
1865:or (para-)
1851:Old Chinese
1807:Han dynasty
1736:and native
1696:lacquerware
1669:During the
1652:(羽人) figure
1613:" culture.
1576:temple name
1572:Han dynasty
1552:Xiang Liang
1521:Shi Huangdi
1355:and nearby
1316:strategist
1274:King Kaolie
1235:reforms of
1134:King Fuchai
1030:King Zhuang
1005:lacquerware
949:in Henan).
687:during the
681:*s-r̥aʔ
677:Old Chinese
595:Old Chinese
345:seal script
303:Qin dynasty
235: 1030
134: 1030
69: 1030
5283:Categories
4465:12 January
4400:23 October
4221:2017-09-28
4211:Jianbo(简帛)
4141:Shorto, H.
4114:2020-09-09
3881:0824818857
3856:0824818857
3831:0824818857
3721:, p.
3608:23 October
3582:3 December
3513:2011-02-17
3419:References
3384:Chuviridae
3201:Chen Sheng
2678:Xiong Yong
2632:Xiong Kang
2608:Xiong Yang
2587: 941
2571: 977
2424:See also:
2190:Yunmeng Ze
2152:Huai river
2019:) and the
1957:/cǝrlaʔ/,
1889:Hmong–Mien
1867:Hmong–Mien
1859:substrates
1794:, and the
1767:Shang Yang
1645:Lacquered
1540:Chen Sheng
1513:楚雖三戶, 亡秦必楚
1388:Ying Zheng
1255:Hangu Pass
1237:Shang Yang
1233:Legalistic
1170:chancellor
1128:in modern
983:Xiong Tong
973:overthrew
911:King Cheng
873:Emperor Ku
667:Wade–Giles
468:Suzhounese
416:Wade–Giles
347:(top) and
245:Xiong Tong
199:Government
154: 680
141: 680
5259:Zhongshan
5107:Zhongshan
4691:Zuo Zhuan
4632:Sima Qian
4579:Cambridge
4500:: 62–85.
4330:Zuo Zhuan
4296:清华简《楚居》解析
4055:Behr 2009
4023:1877-0428
3796:Sima Qian
3774:), Jing (
3754:4 October
3667:Zuo zhuan
3562:Sima Qian
3424:Citations
3317:Astronomy
3084:Yue state
3068:Zuo state
2844:Zheng Mao
2714:Xiong Xun
2654:Xiong Zhi
2580:Xiong Dan
2566:), ruled
2537:Viscounts
2222:Huanggang
2124:Geography
2082:Zuo Zhuan
1803:Mawangdui
1742:Confucian
1738:shamanism
1712:phoenixes
1591:Pengcheng
1556:Xiong Xin
1407:Xiang Yan
1392:Wang Jian
1373:Changping
1245:Pang Nuan
1241:Yang Kuan
1157:quality.
1110:King Zhao
1096:near the
967:Han River
917:with the
849:Sima Qian
784:Xi Rivers
744:Chongqing
683:) was an
343:"Chu" in
178:Religion
169:Pengcheng
104:Viscounty
4922:Han (SE)
4917:Han (NW)
4714:. 2018.
4608:: 27–77.
4423:Archived
4361:Archived
4307:10 April
4157:中國早期國家性質
3659:28 March
3397:See also
3343:in the "
3333:asterism
3303:Liu Bang
3290:Xiang Yu
3250:Xiang Yu
3140:Shouchun
3088:Qi state
2620:Xiong Qu
2558:Xiong Ai
2543:Xiong Yi
2500:Xiong Li
2176:Jingzhou
2166:Zhijiang
2130:Xiong Yi
1969:"thorn";
1763:Legalist
1599:Liu Jiao
1585:through
1564:Liu Bang
1560:Xiang Yu
1544:Zhangchu
1420:Huaiyang
1365:Shouchun
1322:Sima Cuo
1318:Zhang Yi
1314:Diplomat
1263:Shouchun
1219:—
1130:Zhejiang
971:Xiong Qu
939:viscount
915:Xiong Yi
843:Founding
772:Shanghai
768:Zhejiang
503:Jyutping
402:Bopomofo
273:Currency
237:BC
226:Xiong Yi
203:Monarchy
163:Shouchun
5112:Zhoulai
5102:Zhongli
4566:: 1–48.
4477:Sources
4418:天文教育資訊網
4414:AEEA. "
4356:天文教育資訊網
4044:: 1–17.
3371:Biology
3275:Qu Yuan
3219:Jing Ju
3000:Suizhou
2876:Hegemon
2838:at the
2750:Xiao'ao
2726:Xiong E
2479:Yuxiong
2461:Pangeng
2447:Bi Zhui
2342:Zhongli
2327:617 BC
2287:648 BC
2240:Shaanxi
2218:Macheng
2214:Shishou
2184:castles
2021:Lingyin
1929:(genus
1913:Unknown
1895:Kra–Dai
1872:Fangyan
1863:Kra–Dai
1822:lacquer
1746:Zhurong
1730:shamans
1708:dragons
1617:Culture
1611:Chinese
1601:as the
1595:Han Xin
1583:Xiongnu
1548:Jing Ju
1450:Yangtze
1400:Meng Wu
1221:Wu Qi,
1138:Goujian
1098:Yangtze
1058:Chengpu
1023:chariot
947:Xichuan
943:Danyang
919:fiefdom
899:Yuxiong
877:Zhurong
863:Zhuanxu
838:History
776:Danyang
764:Jiangsu
760:Jiangxi
748:Guizhou
726:Jingchu
649:Chinese
610:tsrhjaʔ
541:Hokkien
358:Chinese
349:regular
243:•
127:Danyang
120:Capital
110:Kingdom
18:Jingchu
5319:223 BC
4658:
4621:
4585:
4547:
4524:
4494:Berlin
4459:(docx)
4321:Note:
4188:
4163:
4021:
3961:
3905:
3878:
3853:
3828:
3702:
3437:"楚都丹陽"
3349:symbol
3269:People
3195:Others
2910:Jia'ao
2762:Fenmao
2738:Ruo'ao
2473:Yingbo
2437:Jilian
2420:Rulers
2224:, and
2210:Jianli
1986:praeng
1982:crĕəng
1951:jrlaaʔ
1943:tshraʔ
1921:and 楚
1796:Baiyue
1781:zither
1734:Taoism
1704:snakes
1664:Baiyue
1525:corvée
1431:Qichun
1396:Li Xin
1382:, and
1361:Bai Qi
1281:Defeat
1085:, and
1066:597 BC
891:Jilian
770:, and
724:) and
669::
659::
657:pinyin
651::
627:s-r̥aʔ
558:Tâi-lô
97:Status
91:350 BC
84:
57:s-r̥aʔ
5254:Zheng
4967:Liang
4932:Huang
4912:Guzhu
4907:Gumie
4846:Zheng
4492:(1).
4341:Shiji
4336:Guoyu
4324:Shiji
4237:财政史研究
4108:(PDF)
4093:(PDF)
3930:(PDF)
3696:春秋大事表
3665:from
3455:"Chu"
3377:virus
3236:) as
3170:Fuchu
3124:Hubei
3086:with
3040:Wu Qi
2934:Zi'ao
2808:Du'ao
2775:Kings
2643:Shiji
2459:king
2329:Jiang
2301:Jiang
2289:Huang
2011:Mo'ao
1959:Semai
1931:Vitex
1901:2005)
1831:Wuyue
1649:yuren
1587:heqin
1508:clans
1446:Wuyue
1442:Fuchu
1435:Hubei
1166:Wu Qi
1164:made
1116:and "
1064:. In
1039:Hubei
1014:Hanfu
979:Ezhou
826:Xiong
818:Yan (
798:Nai (
756:Anhui
752:Henan
740:Hunan
736:Hubei
625:*
608:*
586:tʂʰjó
564:Tshóo
550:Chhó͘
474:Tshòu
149:(郢) (
129:(丹陽)(
5244:Yiqu
5229:Teng
5224:Song
5178:Zhao
5097:Zeng
5087:Yiqu
5082:Ying
5077:Yang
5062:Xing
5057:Xian
5047:Teng
5042:Tang
5027:Shěn
5022:Shēn
5007:Quan
4992:Peng
4972:Liao
4887:Deng
4872:Chao
4821:Song
4786:Chen
4697:《左传》
4656:ISBN
4643:《史記》
4619:ISBN
4583:ISBN
4545:ISBN
4522:ISBN
4467:2019
4402:2015
4333:and
4309:2012
4186:ISBN
4161:ISBN
4019:ISSN
3959:ISBN
3903:ISBN
3876:ISBN
3851:ISBN
3826:ISBN
3807:項羽本紀
3756:2010
3700:ISBN
3661:2018
3610:2010
3584:2011
3387:and
3380:taxa
3375:The
3337:Girl
3294:Julu
3261:西楚霸王
3175:楚王負芻
3135:楚考烈王
3115:楚頃襄王
2992:Chen
2990:and
2803:Ying
2372:Chen
2308:Liao
2283:Deng
2271:Shen
2259:Quan
2226:Anlu
2154:and
2009:The
1978:kreŋ
1974:Jīng
1967:ɟlaʔ
1955:Khmu
1919:Jīng
1678:and
1534:The
1369:Zhao
1224:Wuzi
1184:and
1176:and
1174:Zhao
1168:his
1150:Chen
1087:Song
1019:silk
792:Ying
782:and
738:and
716:Jing
672:Ch'u
422:Ch'u
147:Ying
5264:Zou
5249:Yue
5239:Wey
5219:Shu
5204:Dai
5199:Cai
5173:Yan
5168:Wei
5163:Qin
5153:Han
5148:Chu
5117:Zou
5037:Tan
5032:Sui
5017:Ruo
5012:Rui
4982:Luo
4962:Lai
4952:Jia
4937:Huo
4927:Hua
4882:Dai
4877:Dao
4867:Bei
4841:Yue
4836:Yan
4826:Wey
4816:Shu
4811:Qin
4796:Jin
4791:Chu
4781:Cao
4776:Cai
4606:104
4502:doi
4009:doi
3530:in
3355:or
3353:Phi
3243:楚義帝
3212:楚隱王
3187:昌平君
3163:楚哀王
3151:楚幽王
3122:in
3099:楚懷王
3079:楚威王
3063:楚宣王
3051:楚肅王
3035:楚悼王
3023:楚聲王
3011:楚簡王
2988:Cai
2983:楚惠王
2963:楚昭王
2951:楚平王
2927:楚靈王
2903:楚康王
2887:楚共王
2867:楚莊王
2855:楚穆王
2831:楚成王
2798:楚文王
2786:楚武王
2408:Yue
2402:Zou
2384:Cai
2348:Sui
2331:(蔣)
2323:Ruo
2303:(江)
2295:Dao
2265:Luo
2192:in
2120:).
2062:右司馬
2056:左司馬
1939:Chǔ
1923:Chǔ
1792:Yue
1680:Yan
1676:Qin
1516:).
1454:Yue
1433:in
1380:Yan
1353:Shu
1334:Shu
1326:Han
1186:Yue
1182:Wei
1178:Qin
1154:Cai
1126:Yue
1122:Ruo
1118:Sui
1114:Yun
1083:Wey
1054:Jin
937:, "
851:'s
780:Dan
705:Qin
662:Chǔ
645:Chu
544:POJ
517:IPA
495:Chó
444:IPA
436:Chǔ
408:ㄔㄨˇ
394:Chǔ
328:Chu
259:Qin
143:BC)
41:Chu
32:Chu
5285::
5214:Lu
5194:Ba
5158:Qi
5092:Yu
5072:Xǔ
5067:Xu
5052:Xi
5002:Qǐ
4997:Pi
4987:Na
4977:Lü
4957:Ju
4947:Ji
4942:Ji
4862:Ba
4831:Wu
4806:Qi
4801:Lu
4700:).
4688:,
4646:).
4634:,
4604:.
4600:.
4577:,
4562:.
4496::
4490:14
4488:.
4450:.
4383:".
4285:^
4245:^
4209:.
4099:.
4095:.
4040:.
4017:.
3999:.
3938:.
3932:.
3917:^
3810:).
3798:.
3786:).
3730:^
3723:86
3680:^
3663:.
3647:.
3568:.
3564:.
3551:^
3457:.
3367:.
3347:"
3339:"
3255:項羽
3233:熊心
3224:景駒
3206:陳勝
2939:訾敖
2915:郟敖
2819:莊敖
2813:堵敖
2767:蚡冒
2755:霄敖
2743:若敖
2731:熊咢
2719:熊徇
2707:熊霜
2695:熊嚴
2683:熊勇
2671:熊延
2659:熊摯
2637:熊康
2625:熊渠
2613:熊楊
2601:熊勝
2584:c.
2568:c.
2563:熊艾
2548:熊繹
2529:熊狂
2505:熊麗
2490:穴熊
2484:鬻熊
2452:妣隹
2442:季連
2414:Lu
2396:Pi
2390:Ju
2378:Qi
2366:Xu
2358:賴國
2318:).
2277:Xi
2238:,
2228:.
2220:,
2216:,
2212:,
2161:丹陽
2096:Mi
2077:沈尹
2050:司馬
2044:右尹
2038:左尹
2032:三公
2026:令尹
2016:莫敖
1990:k-
1972:荆
1937:楚
1790:,
1788:Ba
1776:se
1725:.
1723:qi
1710:,
1706:,
1637:.
1531:.
1470:黑夫
1426:蕲南
1384:Qi
1357:Ba
1270:Lu
1250:庞煖
1190:Qi
1102:Qi
1094:Wu
1081:,
1079:Lu
1003:A
961:,
935:zǐ
909:,
895:Mi
882:陸終
868:吳回
806:Mi
766:,
762:,
758:,
754:,
750:,
746:,
731:荊楚
711:.
679::
675:,
665:;
655:;
509:Co
461:Wu
232:c.
151:c.
138:c.
136:–
131:c.
89:c.
66:c.
4892:E
4745:e
4738:t
4731:v
4718:.
4694:(
4682:.
4665:.
4640:(
4628:.
4592:.
4553:.
4531:.
4508:.
4504::
4469:.
4404:.
4311:.
4280:.
4194:.
4169:.
4117:.
4101:3
4057:.
4042:2
4025:.
4011::
4005:2
3967:.
3911:.
3884:.
3859:.
3834:.
3783:昭
3777:景
3771:屈
3758:.
3725:.
3708:.
3612:.
3586:.
3516:.
3252:(
3240:(
3221:(
3203:(
3184:(
3172:(
3160:(
3148:(
3142:.
3132:(
3112:(
3096:(
3090:.
3076:(
3060:(
3048:(
3032:(
3020:(
3008:(
3002:.
2980:(
2974:.
2960:(
2948:(
2936:(
2924:(
2912:(
2900:(
2894:.
2884:(
2878:.
2864:(
2852:(
2828:(
2810:(
2795:(
2783:(
2764:(
2752:(
2740:(
2728:(
2716:(
2704:(
2692:(
2680:(
2668:(
2656:(
2634:(
2622:(
2610:(
2598:(
2560:(
2545:(
2526:(
2520:)
2517:熊
2511:酓
2502:(
2481:(
2466:芈
2449:(
2439:(
2361:)
2315:六
2253:E
2205:雲
2199:夢
2171:郢
2143:塗
2117:成
2111:鬭
2101:屈
2088:公
2085:(
2071:尹
2023:(
2013:(
1965:*
1949:*
1476:惊
1415:陳
1247:(
1210:.
975:E
933:(
929:子
831:熊
828:(
821:酓
811:芈
808:(
801:嬭
728:(
721:荊
718:(
653:楚
647:(
364:楚
54:*
47:楚
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.