40:
347:, may also stimulate Kupffer cell proliferation. A time frame of 14 to 21 days for complete replenishment of Kupffer cell populations has been demonstrated in animal studies. Despite high monocyte influx and maturation rates, hepatic Kupffer cell populations are tightly maintained. Evidently, there is a high rate of turnover, with the average lifespan of a Kupffer cell estimated at 3.8 days. However, the ultimate fate of Kupffer cells
67:
382:. Cells in the periportal zone are directly exposed to bloodflow, and express greater lysosomal activity to more efficiently process incoming foreign substances. In contrast, cells in the centrilobular zone experience less perfusion, and are equipped with greater stores of superoxide to combat deeply-penetrating injuries and infections.
482:
in response to ethanol-induced liver injury, common in chronic alcoholics. Chronic alcoholism and liver injury deal with a two-hit system. While the first hit is direct, mediated by the direct toxicity of ethanol and its metabolic byproducts, the second hit is indirect, mediated by increased uptake
374:
The amount of
Kupffer cells in the liver is held constant. Kupffer cells have a proliferative capacity, allowing for cell populations to replenish themselves: this is in complete contrast to monocyte-derived macrophages that have no proliferative potential. Old or defective cells are removed through
371:. Kupffer cells are integral in the innate responses of the immune system. They are important for host defense and play a role in the metabolism of many different compounds including, lipids, protein complexes and small particles. They are also useful in removing apoptotic cells from circulation.
199:
will first come in contact with
Kupffer cells, the first immune cells in the liver. It is because of this that any change to Kupffer cell functions can be connected to various liver diseases such as alcoholic liver disease, viral hepatitis, intrahepatic cholestasis, steatohepatitis, activation or
331:
in the bone marrow and transported through blood circulation to the liver can also fully differentiate into true
Kupffer cells. Unlike other tissue macrophages, which must be continually renewed by circulating monocytes, these monocyte-derived Kupffer cells are capable of self-renewal once a
458:
Kupffer cells are incredibly plastic cells that have the capability to polarize specific activation states and can perform different functions in different microenvironments. M1 (classical activation) and M2 (alternative activation) designate the two extremes of
220:. Kupffer cell function and structures are specialized depending on their location. Periportal Kupffer cells tend to be larger and have more lysosomal enzyme and phagocytic activity, whereas centrilobular Kupffer cells create more superoxide radical.
466:
Kupffer cells play a role in the pathogenesis of a damaged liver in response to sepsis. The macrophages in the liver activate and release both IL-1 and TNF-alpha. In turn, this activates leukocytes and sinusoidal endothelial cells to express
502:. The presence of endotoxin induces a strong M1 polarization of Kupffer cells. A large amount of reactive oxygen species, pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines are produced by the activated Kupffer cells which lead to liver injury.
463:. M1-polarized Kupffer cells produce a large amount of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-alpha. On the other hand, M2-polarized Kupffer cells produce a large quantity of anti-inflammatory mediators, for example, IL-10.
187:
within the lumen of the liver sinusoids and are adhesive to their endothelial cells which make up the blood vessel walls. Kupffer cells comprise the largest population of tissue-resident
1263:
1852:
324:
where they stay. There they complete their differentiation into
Kupffer cells. Under normal conditions, these Kupffer cell populations are long-lived and self-renewing.
443:
1229:
148:
1256:
1770:
1383:
300:.) Because of this detection system, Kupffer cells play a critical role in initiating and mediating immune responses to bacterial infection of the liver.
39:
1845:
1249:
591:"Stellate Cells, Hepatocytes, and Endothelial Cells Imprint the Kupffer Cell Identity on Monocytes Colonizing the Liver Macrophage Niche"
1838:
798:
1975:
155:
281:
143:
513:, receptors on the Kupffer cell that internalize endotoxin. This in turn activates the transcription of pro-inflammatory
2125:
1653:
1461:
335:
Development of mature
Kupffer cells is regulated by numerous growth factors, with macrophage colony-stimulating factor (
201:
989:"Critical Roles of Kupffer Cells in the Pathogenesis of Alcoholic Liver Disease: From Basic Science to Clinical Trials"
518:
262:
213:
883:
Chen, Jiajia; Deng, Xiaoyi; Liu, Yongjian; Tan, Qiuhua; Huang, Guidong; Che, Qishi; Guo, Jiao; Su, Zhengquan (2020).
1920:
785:
Naito M, Hasegawa G, Takahashi K (November 1997). "Development, differentiation, and maturation of
Kupffer cells".
2141:
528:
Cytokines and superoxides go on to cause inflammation and oxidizing damage respectively, while TNFα triggers the
450:-coated pathogens. CRIg is conserved in mice and humans and is a critical component of the innate immune system.
235:, which project in every direction. The microvilli and pseudopodia play a role in the endocytosis of particles.
2161:
1715:
553:
131:
119:
1149:
Stachura J, Gałązka K (December 2003). "History and current status of Polish gastroenterological pathology".
2019:
2004:
1898:
1817:
1736:
1605:
479:
328:
313:
359:
The primary function of the
Kupffer cell is to remove foreign debris and particles that have come from the
2184:
1913:
1878:
1862:
297:
293:
192:
191:
in the body. Gut bacteria, bacterial endotoxins, and microbial debris transported to the liver from the
1965:
1908:
557:
386:
360:
564:
of the liver blood vessels and that they originated from it. In 1898, after several years of research,
136:
2194:
2189:
1925:
1812:
837:
490:
Ethanol increases permeability of the intestinal epithelium, resulting in endotoxin produced by the
2036:
1600:
1575:
363:
when passing through the liver. It is possible for the
Kupffer cells to take in large particles by
340:
44:
1830:
589:
Bonnardel J, T'Jonck W, Gaublomme D, Browaeys R, Scott CL, Martens L, et al. (October 2019).
2031:
1888:
1746:
969:
830:"Bone marrow-derived monocytes give rise to self-renewing and fully differentiated Kupffer cells"
810:
484:
285:
2156:
2151:
2069:
2026:
1610:
1208:
1181:
1154:
1131:
1104:
1069:
1028:
1010:
961:
938:
Helmy KY, Katschke KJ, Gorgani NN, Kljavin NM, Elliott JM, Diehl L, et al. (March 2006).
914:
865:
802:
762:
726:
708:
687:
Dixon, Laura J.; Barnes, Mark; Tang, Hui; Pritchard, Michele T.; Nagy, Laura E. (April 2013).
664:
620:
447:
289:
200:
rejection of the liver during liver transplantation and liver fibrosis. They form part of the
419:
through phagocytic action. The globin chains are re-used, while the iron-containing portion,
2121:
2116:
2111:
2106:
2064:
2059:
2014:
2009:
1947:
1935:
1687:
1590:
1405:
1235:
1096:
1059:
1018:
1000:
951:
904:
896:
855:
845:
794:
716:
700:
654:
610:
602:
495:
491:
270:
266:
940:"CRIg: a macrophage complement receptor required for phagocytosis of circulating pathogens"
2136:
1636:
1425:
1357:
565:
471:. This results in tissue damage to the endothelium because of proteases, oxygen radicals,
428:
841:
401:. Excessive production of these mediators is linked to the development of liver injury.
2079:
1930:
1903:
1702:
1682:
1631:
1475:
1420:
1400:
1395:
1317:
1281:
1232:- Comparative Organology at University of California, Davis - "Mammal, liver (EM, Low)"
1064:
1047:
1023:
988:
909:
860:
829:
721:
688:
659:
642:
615:
590:
416:
394:
217:
378:
Kupffer cells are heterogeneous in their function, dependent on their location in the
2178:
1987:
1952:
1893:
1782:
1692:
1337:
460:
379:
344:
292:. (Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is a bacterial endotoxin which is found in the cell wall
258:
246:
973:
814:
1942:
1883:
1807:
1741:
1710:
1435:
1327:
1290:
1273:
505:
The cascade begins with endotoxin-mediated activation of the Toll-like receptor 4 (
405:
364:
327:
However, if resident
Kupffer cell populations are depleted, monocytes derived from
232:
66:
1241:
1100:
606:
124:
2054:
2046:
1484:
1367:
561:
499:
432:
375:
apoptosis, as well as through being phagocytized by neighbouring
Kupffer cells.
368:
321:
254:
228:
196:
956:
939:
754:
1960:
1595:
1585:
1565:
1557:
1519:
1502:
1492:
1430:
1322:
569:
522:
478:
Kupffer cell activation contributes to pathogenesis of both chronic and acute
472:
413:
409:
317:
308:
Development of an initial population of Kupffer cells begins in the embryonic
274:
224:
188:
95:
1014:
1005:
712:
284:. This receptor is involved in recognising and binding the lipid A domain of
17:
1996:
1802:
1648:
1580:
1531:
1497:
1362:
1342:
1332:
1172:Śródka A, Gryglewski RW, Szczepański W (2006). "Browicz or Kupffer cells?".
541:
424:
390:
250:
1212:
1185:
1158:
1108:
1073:
1032:
965:
918:
869:
799:
10.1002/(SICI)1097-0029(19971115)39:4<350::AID-JEMT5>3.0.CO;2-L
766:
730:
668:
624:
806:
2095:
1775:
1669:
1548:
1536:
1512:
1507:
1295:
1135:
704:
537:
533:
529:
514:
398:
309:
242:
223:
Kupffer cells are amoeboid in character, with surface features including
850:
1677:
1524:
900:
161:
1765:
1641:
1305:
468:
885:"Kupffer Cells in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Friend or Foe?"
884:
560:) but thought, inaccurately, that they were an integral part of the
987:
Zeng, Tao; Zhang, Cui-Li; Xiao, Mo; Yang, Rui; Xie, Ke-Qin (2016).
47:
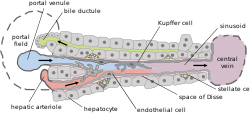
picture showing the steady-state location and interactions between
1870:
1720:
1048:"Endotoxin and Kupffer cell activation in alcoholic liver disease"
828:
Scott C, Zheng F, De Baetselier P, et al. (27 January 2016).
385:
In response to infection or irritation, Kupffer cells can produce
184:
107:
85:
442:
Helmy et al. identified a receptor present in Kupffer cells, the
556:
in 1876. The scientist called them "Sternzellen" (star cells or
510:
506:
436:
420:
336:
1834:
1245:
544:, a loss of function of the liver due to extensive scarring.
753:
Basit, Hajira; Tan, Michael L.; Webster, Daniel R. (2020),
540:, or scarring of the liver. Fibrosis will eventually cause
408:
bacteria, Kupffer cells are also responsible for recycling
423:, is further broken down into iron, which is re-used, and
238:
The nucleus is indented and ovoid, and can be lobulated.
320:. Once they enter the blood stream, they migrate to the
216:
in both the centrilobular and periportal regions of the
1238: – Histology Learning System at Boston University
1087:
Haubrich WS (July 2004). "Kupffer of Kupffer cells".
641:
Nguyen-Lefebvre, Anh Thu; Horuzsko, Anatolij (2015).
2094:
2045:
1995:
1986:
1869:
1795:
1755:
1729:
1701:
1668:
1621:
1556:
1547:
1483:
1474:
1454:
1382:
1304:
1289:
1280:
142:
130:
118:
106:
101:
91:
81:
76:
32:
444:complement receptor of the immunoglobulin family
280:Importantly, Kupffer cells express the SR-AI/II
761:, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing,
1846:
1257:
1230:Anatomy photo: digestive/mammal/liver5/liver4
8:
889:International Journal of Biological Sciences
339:) playing a key role. Cytokines involved in
1122:Szymańska R, Schmidt-Pospuła M (1979). "".
1992:
1853:
1839:
1831:
1553:
1480:
1388:
1310:
1301:
1286:
1264:
1250:
1242:
446:(CRIg). Mice without CRIg could not clear
296:, whereas lipoteichoic acid is present in
65:
38:
1063:
1022:
1004:
955:
908:
859:
849:
720:
658:
614:
183:, are specialized cells localized in the
1771:Megakaryocyte–erythroid progenitor cell
581:
212:Kupffer cells can be found attached to
1151:Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology
643:"Kupffer Cell Metabolism and Function"
521:(TNFα), with concurrent production of
475:and other substances from leukocytes.
159:
29:
536:synthesis. These processes result in
241:Notable cytoplasmic elements include
7:
748:
746:
744:
742:
740:
682:
680:
678:
647:Journal of Enzymology and Metabolism
636:
634:
57:liver sinusoidal endothelial cells
25:
1976:Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell
787:Microscopy Research and Technique
552:The cells were first observed by
1863:liver, pancreas and biliary tree
487:(endotoxin) from the intestine.
156:Anatomical terms of microanatomy
59:(blue). Cell nuclei are in grey.
27:Macrophages located in the liver
568:identified them, correctly, as
1:
1052:Alcohol Research & Health
351:is not yet fully understood.
261:. Kupffer cells also contain
1462:Extramedullary hematopoiesis
1101:10.1053/j.gastro.2004.05.041
689:"Kupffer Cells in the Liver"
607:10.1016/j.immuni.2019.08.017
214:sinusoidal endothelial cells
202:mononuclear phagocyte system
1174:Polish Journal of Pathology
519:tumor necrosis factor-alpha
332:population is established.
273:, all of which demonstrate
263:rough endoplasmic reticulum
2211:
1921:Fibrous capsule of Glisson
1124:Archiwum Historii Medycyny
957:10.1016/j.cell.2005.12.039
836:. 7, 10321 (2016): 10321.
367:and smaller particles via
1628:Antigen-presenting cells
1416:
1391:
1353:
1313:
1236:Histology image: 15508loa
755:"Histology, Kupffer Cell"
532:in the liver to initiate
427:, which is conjugated to
316:differentiate into fetal
154:
113:macrophagocytus stellatus
64:
37:
1716:Nucleated red blood cell
1272:Myeloid blood cells and
1006:10.3389/fimmu.2016.00538
693:Comprehensive Physiology
554:Karl Wilhelm von Kupffer
329:hematopoietic stem cells
2005:Intrahepatic bile ducts
1818:Hematopoietic stem cell
1737:Leukocyte extravasation
1606:Foreign-body giant cell
993:Frontiers in Immunology
498:into the liver via the
480:alcoholic liver disease
461:macrophage polarization
1153:. 54 Suppl 3: 183–92.
435:and secreted into the
387:inflammatory cytokines
298:gram-positive bacteria
294:gram-negative bacteria
208:Location and structure
193:gastrointestinal tract
53:hepatic stellate cells
1966:Hepatic stellate cell
834:Nature Communications
558:hepatic stellate cell
454:Clinical significance
361:hepatic portal system
181:Kupffer–Browicz cells
71:Basic liver structure
1926:Perisinusoidal space
1813:Hematopoietic system
1601:Langhans giant cells
705:10.1002/cphy.c120026
177:stellate macrophages
2037:Common hepatic duct
1576:Alveolar macrophage
1199:Wake K (2009). "".
1046:Wheeler MD (2003).
851:10.1038/ncomms10321
842:2016NatCo...710321S
341:type 2 inflammation
45:Confocal microscopy
2032:Right hepatic duct
1889:Ligamentum venosum
1747:Intrinsic immunity
1611:Touton giant cells
901:10.7150/ijbs.47143
485:lipopolysaccharide
286:lipopolysaccharide
282:scavenger receptor
137:H3.04.05.0.00016
2172:
2171:
2157:Centroacinar cell
2152:Pancreatic islets
2090:
2089:
2070:Sphincter of Oddi
2027:Left hepatic duct
1828:
1827:
1791:
1790:
1664:
1663:
1591:Epithelioid cells
1470:
1469:
1450:
1449:
1446:
1445:
1378:
1377:
895:(13): 2367–2378.
601:(4): 638–654.e9.
494:leaking from the
448:complement system
290:lipoteichoic acid
271:annulate lamellae
170:
169:
165:
16:(Redirected from
2202:
2126:Uncinate process
2065:Ampulla of Vater
2060:Common bile duct
2015:Canals of Hering
2010:Bile canaliculus
1993:
1948:Lobules of liver
1936:Periportal space
1855:
1848:
1841:
1832:
1762:Precursor cells
1688:Promegakaryocyte
1554:
1481:
1406:Promegakaryocyte
1389:
1311:
1302:
1287:
1266:
1259:
1252:
1243:
1217:
1216:
1201:Kaibogaku Zasshi
1196:
1190:
1189:
1169:
1163:
1162:
1146:
1140:
1139:
1119:
1113:
1112:
1089:Gastroenterology
1084:
1078:
1077:
1067:
1043:
1037:
1036:
1026:
1008:
984:
978:
977:
959:
935:
929:
928:
926:
925:
912:
880:
874:
873:
863:
853:
825:
819:
818:
782:
776:
775:
774:
773:
750:
735:
734:
724:
684:
673:
672:
662:
638:
629:
628:
618:
586:
496:intestinal lumen
492:intestinal flora
267:nuclear envelope
175:, also known as
162:edit on Wikidata
69:
42:
30:
21:
2210:
2209:
2205:
2204:
2203:
2201:
2200:
2199:
2175:
2174:
2173:
2168:
2086:
2041:
1982:
1865:
1861:Anatomy of the
1859:
1829:
1824:
1787:
1751:
1730:Immune response
1725:
1703:Red blood cells
1697:
1660:
1637:Langerhans cell
1632:Dendritic cells
1617:
1543:
1466:
1442:
1426:Proerythroblast
1412:
1374:
1358:Monocytopoiesis
1349:
1293:
1276:
1270:
1226:
1221:
1220:
1198:
1197:
1193:
1171:
1170:
1166:
1148:
1147:
1143:
1121:
1120:
1116:
1086:
1085:
1081:
1045:
1044:
1040:
986:
985:
981:
937:
936:
932:
923:
921:
882:
881:
877:
827:
826:
822:
784:
783:
779:
771:
769:
752:
751:
738:
686:
685:
676:
640:
639:
632:
588:
587:
583:
578:
566:Tadeusz Browicz
550:
456:
429:glucuronic acid
417:red blood cells
395:oxygen radicals
357:
314:precursor cells
306:
247:Golgi complexes
218:hepatic lobules
210:
166:
72:
60:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2208:
2206:
2198:
2197:
2192:
2187:
2177:
2176:
2170:
2169:
2167:
2166:
2165:
2164:
2159:
2154:
2146:
2145:
2144:
2139:
2131:
2130:
2129:
2119:
2114:
2109:
2100:
2098:
2092:
2091:
2088:
2087:
2085:
2084:
2083:
2082:
2080:Cholecystocyte
2074:
2073:
2072:
2062:
2057:
2051:
2049:
2043:
2042:
2040:
2039:
2034:
2029:
2024:
2023:
2022:
2017:
2012:
2001:
1999:
1990:
1984:
1983:
1981:
1980:
1979:
1978:
1973:
1968:
1963:
1955:
1950:
1945:
1940:
1939:
1938:
1931:Liver sinusoid
1928:
1923:
1918:
1917:
1916:
1911:
1904:Lobes of liver
1901:
1899:Round ligament
1896:
1891:
1886:
1881:
1875:
1873:
1867:
1866:
1860:
1858:
1857:
1850:
1843:
1835:
1826:
1825:
1823:
1822:
1821:
1820:
1810:
1805:
1799:
1797:
1793:
1792:
1789:
1788:
1786:
1785:
1780:
1779:
1778:
1773:
1768:
1759:
1757:
1753:
1752:
1750:
1749:
1744:
1739:
1733:
1731:
1727:
1726:
1724:
1723:
1718:
1713:
1707:
1705:
1699:
1698:
1696:
1695:
1690:
1685:
1683:Megakaryoblast
1680:
1674:
1672:
1666:
1665:
1662:
1661:
1659:
1658:
1657:
1656:
1646:
1645:
1644:
1639:
1634:
1625:
1623:
1619:
1618:
1616:
1615:
1614:
1613:
1608:
1603:
1593:
1588:
1583:
1578:
1573:
1568:
1562:
1560:
1551:
1545:
1544:
1542:
1541:
1540:
1539:
1529:
1528:
1527:
1517:
1516:
1515:
1505:
1500:
1495:
1489:
1487:
1478:
1476:Myeloid tissue
1472:
1471:
1468:
1467:
1465:
1464:
1458:
1456:
1452:
1451:
1448:
1447:
1444:
1443:
1441:
1440:
1439:
1438:
1433:
1428:
1421:Erythropoiesis
1417:
1414:
1413:
1411:
1410:
1409:
1408:
1403:
1401:Megakaryoblast
1396:Thrombopoiesis
1392:
1386:
1380:
1379:
1376:
1375:
1373:
1372:
1371:
1370:
1365:
1354:
1351:
1350:
1348:
1347:
1346:
1345:
1340:
1335:
1330:
1325:
1318:Granulopoiesis
1314:
1308:
1299:
1284:
1278:
1277:
1271:
1269:
1268:
1261:
1254:
1246:
1240:
1239:
1233:
1225:
1224:External links
1222:
1219:
1218:
1191:
1164:
1141:
1114:
1079:
1038:
979:
930:
875:
820:
777:
736:
699:(2): 785–797.
674:
630:
580:
579:
577:
574:
549:
546:
530:stellate cells
455:
452:
412:by destroying
356:
353:
305:
302:
259:microfilaments
209:
206:
168:
167:
158:
152:
151:
146:
140:
139:
134:
128:
127:
122:
116:
115:
110:
104:
103:
99:
98:
93:
89:
88:
83:
79:
78:
74:
73:
70:
62:
61:
43:
35:
34:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2207:
2196:
2193:
2191:
2188:
2186:
2185:Liver anatomy
2183:
2182:
2180:
2163:
2162:Stellate cell
2160:
2158:
2155:
2153:
2150:
2149:
2148:Microanatomy
2147:
2143:
2140:
2138:
2135:
2134:
2132:
2127:
2123:
2120:
2118:
2115:
2113:
2110:
2108:
2105:
2104:
2102:
2101:
2099:
2097:
2093:
2081:
2078:
2077:
2075:
2071:
2068:
2067:
2066:
2063:
2061:
2058:
2056:
2053:
2052:
2050:
2048:
2044:
2038:
2035:
2033:
2030:
2028:
2025:
2021:
2018:
2016:
2013:
2011:
2008:
2007:
2006:
2003:
2002:
2000:
1998:
1994:
1991:
1989:
1988:Biliary tract
1985:
1977:
1974:
1972:
1969:
1967:
1964:
1962:
1959:
1958:
1957:Microanatomy
1956:
1954:
1953:Liver segment
1951:
1949:
1946:
1944:
1941:
1937:
1934:
1933:
1932:
1929:
1927:
1924:
1922:
1919:
1915:
1912:
1910:
1907:
1906:
1905:
1902:
1900:
1897:
1895:
1894:Porta hepatis
1892:
1890:
1887:
1885:
1882:
1880:
1877:
1876:
1874:
1872:
1868:
1864:
1856:
1851:
1849:
1844:
1842:
1837:
1836:
1833:
1819:
1816:
1815:
1814:
1811:
1809:
1806:
1804:
1801:
1800:
1798:
1794:
1784:
1783:Myelomonocyte
1781:
1777:
1774:
1772:
1769:
1767:
1764:
1763:
1761:
1760:
1758:
1754:
1748:
1745:
1743:
1740:
1738:
1735:
1734:
1732:
1728:
1722:
1719:
1717:
1714:
1712:
1709:
1708:
1706:
1704:
1700:
1694:
1693:Megakaryocyte
1691:
1689:
1686:
1684:
1681:
1679:
1676:
1675:
1673:
1671:
1667:
1655:
1652:
1651:
1650:
1647:
1643:
1640:
1638:
1635:
1633:
1630:
1629:
1627:
1626:
1624:
1620:
1612:
1609:
1607:
1604:
1602:
1599:
1598:
1597:
1594:
1592:
1589:
1587:
1584:
1582:
1579:
1577:
1574:
1572:
1571:Kupffer cells
1569:
1567:
1564:
1563:
1561:
1559:
1555:
1552:
1550:
1546:
1538:
1535:
1534:
1533:
1530:
1526:
1523:
1522:
1521:
1518:
1514:
1511:
1510:
1509:
1506:
1504:
1501:
1499:
1496:
1494:
1491:
1490:
1488:
1486:
1482:
1479:
1477:
1473:
1463:
1460:
1459:
1457:
1453:
1437:
1434:
1432:
1429:
1427:
1424:
1423:
1422:
1419:
1418:
1415:
1407:
1404:
1402:
1399:
1398:
1397:
1394:
1393:
1390:
1387:
1385:
1381:
1369:
1366:
1364:
1361:
1360:
1359:
1356:
1355:
1352:
1344:
1341:
1339:
1338:Metamyelocyte
1336:
1334:
1331:
1329:
1326:
1324:
1321:
1320:
1319:
1316:
1315:
1312:
1309:
1307:
1303:
1300:
1297:
1292:
1288:
1285:
1283:
1282:Hematopoiesis
1279:
1275:
1267:
1262:
1260:
1255:
1253:
1248:
1247:
1244:
1237:
1234:
1231:
1228:
1227:
1223:
1214:
1210:
1206:
1202:
1195:
1192:
1187:
1183:
1179:
1175:
1168:
1165:
1160:
1156:
1152:
1145:
1142:
1137:
1133:
1129:
1125:
1118:
1115:
1110:
1106:
1102:
1098:
1094:
1090:
1083:
1080:
1075:
1071:
1066:
1061:
1057:
1053:
1049:
1042:
1039:
1034:
1030:
1025:
1020:
1016:
1012:
1007:
1002:
998:
994:
990:
983:
980:
975:
971:
967:
963:
958:
953:
950:(5): 915–27.
949:
945:
941:
934:
931:
920:
916:
911:
906:
902:
898:
894:
890:
886:
879:
876:
871:
867:
862:
857:
852:
847:
843:
839:
835:
831:
824:
821:
816:
812:
808:
804:
800:
796:
793:(4): 350–64.
792:
788:
781:
778:
768:
764:
760:
756:
749:
747:
745:
743:
741:
737:
732:
728:
723:
718:
714:
710:
706:
702:
698:
694:
690:
683:
681:
679:
675:
670:
666:
661:
656:
652:
648:
644:
637:
635:
631:
626:
622:
617:
612:
608:
604:
600:
596:
592:
585:
582:
575:
573:
571:
567:
563:
559:
555:
547:
545:
543:
539:
535:
531:
526:
524:
520:
516:
512:
508:
503:
501:
497:
493:
488:
486:
481:
476:
474:
470:
464:
462:
453:
451:
449:
445:
440:
438:
434:
430:
426:
422:
418:
415:
411:
407:
402:
400:
396:
392:
388:
383:
381:
380:liver lobules
376:
372:
370:
366:
362:
354:
352:
350:
346:
342:
338:
333:
330:
325:
323:
319:
315:
311:
303:
301:
299:
295:
291:
287:
283:
278:
276:
272:
268:
264:
260:
256:
252:
248:
244:
239:
236:
234:
230:
226:
221:
219:
215:
207:
205:
203:
198:
194:
190:
186:
182:
178:
174:
173:Kupffer cells
163:
157:
153:
150:
147:
145:
141:
138:
135:
133:
129:
126:
123:
121:
117:
114:
111:
109:
105:
100:
97:
94:
90:
87:
84:
80:
75:
68:
63:
58:
54:
50:
49:Kupffer cells
46:
41:
36:
31:
19:
18:Kupffer cells
2020:Interlobular
1971:Kupffer cell
1970:
1943:Portal triad
1884:Cantlie line
1742:Phagocytosis
1711:Reticulocyte
1570:
1485:Granulocytes
1436:Reticulocyte
1328:Promyelocyte
1291:Myelopoiesis
1207:(1): 17–21.
1204:
1200:
1194:
1180:(4): 183–5.
1177:
1173:
1167:
1150:
1144:
1130:(3): 331–6.
1127:
1123:
1117:
1092:
1088:
1082:
1058:(4): 300–6.
1055:
1051:
1041:
996:
992:
982:
947:
943:
933:
922:. Retrieved
892:
888:
878:
833:
823:
790:
786:
780:
770:, retrieved
758:
696:
692:
650:
646:
598:
594:
584:
551:
527:
504:
489:
477:
465:
457:
441:
403:
384:
377:
373:
365:phagocytosis
358:
348:
334:
326:
307:
279:
255:microtubules
240:
237:
233:lamellipodia
222:
211:
180:
176:
172:
171:
112:
56:
55:(green) and
52:
48:
33:Kupffer cell
2195:Macrophages
2190:Human cells
2055:Cystic duct
2047:Gallbladder
1596:giant cells
1586:Osteoclasts
1566:Histiocytes
1558:Macrophages
1368:Promonocyte
570:macrophages
562:endothelium
523:superoxides
500:portal vein
473:prostanoids
433:hepatocytes
404:Apart from
369:pinocytosis
322:fetal liver
318:macrophages
304:Development
277:activity.
229:pseudopodia
197:portal vein
189:macrophages
102:Identifiers
2179:Categories
1997:Bile ducts
1961:Hepatocyte
1520:Eosinophil
1503:Neutrophil
1493:Myeloblast
1431:Normoblast
1323:Myeloblast
924:2020-08-31
772:2020-08-25
759:StatPearls
576:References
410:hemoglobin
343:, such as
288:(LPS) and
275:peroxidase
251:centrioles
225:microvilli
96:Macrophage
2142:accessory
1879:Bare area
1803:Phagocyte
1670:Platelets
1649:Monoblast
1581:Microglia
1549:Monocytes
1532:Mast cell
1498:Band cell
1363:Monoblast
1343:Band cell
1333:Myelocyte
1095:(1): 16.
1015:1664-3224
713:2040-4603
542:cirrhosis
515:cytokines
425:bilirubin
414:senescent
399:proteases
391:TNF-alpha
243:ribosomes
2096:Pancreas
1914:Quadrate
1776:CFU-GEMM
1537:CFU-Mast
1513:CFU-Baso
1508:Basophil
1296:CFU-GEMM
1213:19413196
1186:17285760
1159:15075472
1109:15236167
1074:15540801
1033:27965666
974:15525209
966:16530040
919:32760204
870:26813785
815:21193303
767:29630278
731:23720329
669:26937490
625:31561945
595:Immunity
538:fibrosis
534:collagen
406:clearing
355:Function
349:in vivo
310:yolk sac
195:via the
92:Function
82:Location
1909:Caudate
1678:CFU-Meg
1525:CFU-Eos
1455:General
1065:6668869
1024:5126119
999:: 538.
910:7378652
861:4737801
838:Bibcode
807:9407545
722:4748178
660:4771376
616:6876284
548:History
431:within
125:D007728
77:Details
51:(Red),
2133:Ducts
2103:Gross
2076:Cells
1808:Plasma
1766:CFU-GM
1642:CFU-DL
1306:CFU-GM
1274:plasma
1211:
1184:
1157:
1136:386989
1134:
1107:
1072:
1062:
1031:
1021:
1013:
972:
964:
917:
907:
868:
858:
813:
805:
765:
729:
719:
711:
667:
657:
623:
613:
509:) and
469:ICAM-1
397:, and
312:where
269:, and
1871:Liver
1796:Other
1756:Other
1721:CFU-E
1622:Other
970:S2CID
811:S2CID
653:(1).
185:liver
160:[
149:14656
108:Latin
86:Liver
2137:main
2122:Head
2117:Neck
2112:Body
2107:Tail
1209:PMID
1182:PMID
1155:PMID
1132:PMID
1105:PMID
1070:PMID
1029:PMID
1011:ISSN
962:PMID
944:Cell
915:PMID
866:PMID
803:PMID
763:PMID
727:PMID
709:ISSN
665:PMID
621:PMID
517:and
511:CD14
507:TLR4
437:bile
421:heme
345:IL-4
337:CSF1
265:, a
257:and
231:and
179:and
120:MeSH
1654:MPS
1384:MEP
1097:doi
1093:127
1060:PMC
1019:PMC
1001:doi
952:doi
948:124
905:PMC
897:doi
856:PMC
846:doi
795:doi
717:PMC
701:doi
655:PMC
611:PMC
603:doi
525:.
483:of
144:FMA
2181::
1205:84
1203:.
1178:57
1176:.
1128:42
1126:.
1103:.
1091:.
1068:.
1056:27
1054:.
1050:.
1027:.
1017:.
1009:.
995:.
991:.
968:.
960:.
946:.
942:.
913:.
903:.
893:16
891:.
887:.
864:.
854:.
844:.
832:.
809:.
801:.
791:39
789:.
757:,
739:^
725:.
715:.
707:.
695:.
691:.
677:^
663:.
649:.
645:.
633:^
619:.
609:.
599:51
597:.
593:.
572:.
439:.
393:,
389:,
253:,
249:,
245:,
227:,
204:.
132:TH
2128:)
2124:(
1854:e
1847:t
1840:v
1298:)
1294:(
1265:e
1258:t
1251:v
1215:.
1188:.
1161:.
1138:.
1111:.
1099::
1076:.
1035:.
1003::
997:7
976:.
954::
927:.
899::
872:.
848::
840::
817:.
797::
733:.
703::
697:3
671:.
651:1
627:.
605::
164:]
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.