132:
48:
224:, a deepening of the trochlear sulcus where the patella sits, a realignment of the attachment of the patella tendon on the tibia, and tightening or releasing of the capsule on either side of the patella, according to which side the patella is slipping. Some grade IV conditions may require more involved surgery to realign the femur and/or tibia.
140:
Diagnosis is made through palpation of the knee, to see whether it slips inside the joint more than would normally be expected. Often, a dog owner might be told that his or her pet has "loose knee", but this is not a medical term, and it is not correct to use it interchangeably with luxating patella.
144:
Luxating patella cannot be present without the knee being loose, but a loose knee is not necessarily slipping out of the joint. Even with luxating patella, symptoms such as intermittent limping in the rear leg might be mild or absent. Physical examination and manual manipulation are the preferred
135:
MRI after luxation of the right patella: A bone bruise is at the medial surface of the patella (axial image) and in the corresponding surface of the lateral condyle of the femur (coronal). The medial retinaculum of the patella is at least partially
588:
573:
234:
Additional help can be given with the use of pet ramps, stairs, or steps. These can help the animal travel from one place to another, especially up and down, without adding any pain or damage to the patella.
243:
Most cases of patellar luxation are medial, and this is frequently a congenital problem in toy- and miniature-breed dogs. Breeds showing a predisposition for medial patellar luxation include miniature and
396:"Trochlear wedge sulcoplasty, tibial tuberosity transposition, and lateral imbrication for correction of a traumatic patellar luxation in a miniature companion pig: A case report and visual description"
635:
189:
Grade III - the patella remains luxated most of the time, but can be manually reduced with the stifle joint in extension. Flexion and extension of the stifle results again in luxation of the patella.
628:
538:
303:. Although the specific cause of patellar luxation is unknown in these cases, a defect in hind limb conformation is generally agreed to be the underlying cause.
621:
123:
defect. In congenital cases, it is frequently bilateral. The condition can also be inherited through genetics. This can also be caused by obesity.
199:
Grade IV - the patella is permanently luxated and cannot be manually repositioned, with up to 90° of rotation of the proximal tibial plateau. The
1009:
220:
to correct, if the animal has difficulty walking. The surgery required is governed by the type of abnormality present, but often involves a
231:
can be used as a preliminary treatment to strengthen ligaments and the surrounding tissues of the joint and can delay or prevent surgery.
394:
Høy-Petersen, J.; Smith, J. S.; Merkatoris, P. T.; Black, K. E.; Faivre, C. M.; Miles, K. G.; Tatarniuk, D. M.; Kraus, K. H. (2020).
175:
of the stifle joint. The patella remains luxated until it is manually reduced or when the animal extends the joint and derotates the
96:, particularly small and miniature breeds. The condition usually becomes evident between the ages of 4 and 6 months. It can occur in
788:
454:
378:
107:
There have been several reports of patella luxation in other species such as miniature pigs, alpacas, llamas, cattle and goats.
671:
273:
535:
854:
55:
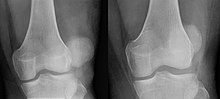
Patellar luxation on radiograph: Left before, right after reduction; after reduction, the patella is still displaced.
86:
450:
101:
829:
483:
289:
161:
Grade I - the patella can be manually luxated but is reduced (returns to the normal position) when released.
806:
645:
1004:
727:
85:, or kneecap, dislocates or moves out of its normal location. It can be associated with damage to the
508:
341:
681:
253:
783:
737:
592:
959:
811:
292:. Large-breed dogs are also affected, and the Labrador retriever seems particularly predisposed.
116:
983:
676:
427:
374:
257:
60:
1014:
978:
967:
516:
417:
407:
349:
300:
261:
971:
949:
928:
834:
542:
285:
269:
152:
The four recognized diagnostic grades of patellar luxation include, in order of severity:
131:
321:"The Knee and Shoulder Centers - [PRINTABLE] Anterior Cruciate Ligament Surgery"
897:
864:
719:
704:
686:
613:
507:
Engdahl, Karolina; Bergström, Annika; Höglund, Odd; Hanson, Jeanette (September 2023).
422:
395:
340:
Engdahl, Karolina; Bergström, Annika; Höglund, Odd; Hanson, Jeanette (September 2023).
281:
277:
146:
601:
597:
295:
Patellar luxation is less common in cats than in dogs. Predisposed breeds include the
998:
732:
709:
320:
249:
521:
354:
892:
849:
844:
171:
Grade II - the patella can be manually luxated or it can spontaneously luxate with
17:
954:
933:
228:
221:
65:
916:
902:
773:
742:
654:
582:
412:
204:
120:
47:
882:
877:
872:
798:
778:
756:
509:"The epidemiology of patellar luxation in an insured Swedish dog population"
342:"The epidemiology of patellar luxation in an insured Swedish dog population"
296:
265:
431:
663:
145:
methods for diagnosis. More extreme cases can result in severe lameness.
536:
Patellar
Luxation, canine and feline (cat and dog) veterinary factsheets
217:
172:
82:
565:
458:
41:
Trick knee, subluxation of patella, floating patella, floating kneecap
887:
577:
245:
696:
200:
176:
130:
920:
821:
617:
765:
97:
93:
203:
groove is shallow or absent, with displacement of the
555:
942:
915:
863:
820:
797:
764:
755:
718:
695:
662:
653:
559:
59:
37:
32:
369:Ettinger, Stephen J.; Feldman, Edward C. (1995).
119:, but most frequently, it is a developmental,
629:
8:
445:
443:
441:
92:Patellar luxation is a common condition in
761:
659:
636:
622:
614:
556:
207:muscle group in the direction of luxation.
46:
29:
520:
421:
411:
353:
115:Rarely, it can be caused by some form of
371:Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine
373:(4th ed.). W.B. Saunders Company.
312:
179:in the opposite direction of luxation.
7:
484:"Cruciate Ligament Rupture in Dogs"
25:
789:Slipped capital femoral epiphysis
455:Orthopedic Foundation for Animals
149:typically develops secondarily.
522:10.1016/j.prevetmed.2023.106034
400:Frontiers in Veterinary Science
355:10.1016/j.prevetmed.2023.106034
216:Grades II, III, and IV require
513:Preventive Veterinary Medicine
346:Preventive Veterinary Medicine
274:Cavalier King Charles Spaniels
81:, is a condition in which the
1:
1010:Dog musculoskeletal disorders
855:Patellofemoral pain syndrome
1031:
102:domestic short-haired cats
87:anterior cruciate ligament
413:10.3389/fvets.2020.567886
54:
45:
290:Teddy Roosevelt Terriers
227:A therapeutic dosage of
830:Chondromalacia patellae
268:, Patterdale Terriers,
807:Angular limb deformity
137:
100:, as well, especially
728:Boutonniere deformity
254:Jack Russell Terriers
134:
77:, sometimes called a
964:Abnormal angulation
888:Bunion/hallux valgus
682:Subacromial bursitis
784:Protrusio acetabuli
738:Swan neck deformity
672:Adhesive capsulitis
482:Ward, DVM, Ernest.
451:"Patellar Luxation"
960:Ligamentous laxity
812:Unequal leg length
541:2008-04-27 at the
258:Yorkshire Terriers
138:
992:
991:
984:Joint dislocation
911:
910:
751:
750:
677:Rotator cuff tear
611:
610:
201:femoral trochlear
71:
70:
27:Medical condition
18:Luxating patellas
16:(Redirected from
1022:
979:Bone malrotation
968:Valgus deformity
840:Luxating patella
762:
660:
638:
631:
624:
615:
557:
545:
533:
527:
526:
524:
504:
498:
497:
495:
494:
479:
473:
472:
470:
469:
463:
457:. Archived from
447:
436:
435:
425:
415:
391:
385:
384:
366:
360:
359:
357:
337:
331:
330:
328:
327:
317:
286:Plummer Terriers
239:In animal breeds
75:luxating patella
50:
33:Luxating patella
30:
21:
1030:
1029:
1025:
1024:
1023:
1021:
1020:
1019:
995:
994:
993:
988:
972:Varus deformity
950:Joint stiffness
938:
929:Cauliflower ear
907:
859:
835:Genu recurvatum
816:
793:
747:
714:
691:
649:
646:musculoskeletal
642:
612:
607:
606:
568:
554:
549:
548:
543:Wayback Machine
534:
530:
506:
505:
501:
492:
490:
481:
480:
476:
467:
465:
461:
449:
448:
439:
393:
392:
388:
381:
368:
367:
363:
339:
338:
334:
325:
323:
319:
318:
314:
309:
282:Boston Terriers
241:
214:
196:
186:
168:
158:
129:
113:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1028:
1026:
1018:
1017:
1012:
1007:
997:
996:
990:
989:
987:
986:
981:
976:
975:
974:
962:
957:
952:
946:
944:
940:
939:
937:
936:
931:
925:
923:
913:
912:
909:
908:
906:
905:
900:
898:Hallux rigidus
895:
890:
885:
880:
875:
869:
867:
861:
860:
858:
857:
852:
847:
842:
837:
832:
826:
824:
818:
817:
815:
814:
809:
803:
801:
795:
794:
792:
791:
786:
781:
776:
770:
768:
759:
753:
752:
749:
748:
746:
745:
740:
735:
730:
724:
722:
716:
715:
713:
712:
707:
705:Cubitus valgus
701:
699:
693:
692:
690:
689:
687:Winged scapula
684:
679:
674:
668:
666:
657:
651:
650:
643:
641:
640:
633:
626:
618:
609:
608:
605:
604:
585:
569:
564:
563:
561:
560:Classification
553:
552:External links
550:
547:
546:
528:
499:
474:
437:
386:
379:
361:
332:
311:
310:
308:
305:
240:
237:
213:
210:
209:
208:
195:
192:
191:
190:
185:
182:
181:
180:
167:
164:
163:
162:
157:
154:
147:Osteoarthritis
128:
125:
112:
109:
69:
68:
63:
57:
56:
52:
51:
43:
42:
39:
35:
34:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1027:
1016:
1013:
1011:
1008:
1006:
1003:
1002:
1000:
985:
982:
980:
977:
973:
969:
966:
965:
963:
961:
958:
956:
953:
951:
948:
947:
945:
943:General terms
941:
935:
932:
930:
927:
926:
924:
922:
918:
914:
904:
901:
899:
896:
894:
891:
889:
886:
884:
881:
879:
876:
874:
871:
870:
868:
866:
862:
856:
853:
851:
848:
846:
843:
841:
838:
836:
833:
831:
828:
827:
825:
823:
819:
813:
810:
808:
805:
804:
802:
800:
796:
790:
787:
785:
782:
780:
777:
775:
772:
771:
769:
767:
763:
760:
758:
754:
744:
741:
739:
736:
734:
733:Mallet finger
731:
729:
726:
725:
723:
721:
717:
711:
710:Cubitus varus
708:
706:
703:
702:
700:
698:
694:
688:
685:
683:
680:
678:
675:
673:
670:
669:
667:
665:
661:
658:
656:
652:
647:
639:
634:
632:
627:
625:
620:
619:
616:
603:
599:
595:
594:
590:
586:
584:
580:
579:
575:
571:
570:
567:
562:
558:
551:
544:
540:
537:
532:
529:
523:
518:
514:
510:
503:
500:
489:
485:
478:
475:
464:on 2007-08-26
460:
456:
452:
446:
444:
442:
438:
433:
429:
424:
419:
414:
409:
405:
401:
397:
390:
387:
382:
380:0-7216-6795-3
376:
372:
365:
362:
356:
351:
347:
343:
336:
333:
322:
316:
313:
306:
304:
302:
298:
293:
291:
287:
283:
279:
275:
271:
267:
263:
259:
255:
251:
247:
238:
236:
232:
230:
225:
223:
219:
211:
206:
202:
198:
197:
193:
188:
187:
183:
178:
174:
170:
169:
165:
160:
159:
155:
153:
150:
148:
142:
133:
126:
124:
122:
118:
110:
108:
105:
103:
99:
95:
90:
88:
84:
80:
76:
67:
64:
62:
58:
53:
49:
44:
40:
36:
31:
19:
1005:Cat diseases
893:Hallux varus
850:Patella baja
845:Patella alta
839:
587:
572:
531:
512:
502:
491:. Retrieved
487:
477:
466:. Retrieved
459:the original
403:
399:
389:
370:
364:
345:
335:
324:. Retrieved
315:
294:
242:
233:
226:
215:
151:
143:
139:
117:blunt trauma
114:
106:
91:
78:
74:
72:
955:Contracture
934:Torticollis
648:deformities
462:(text/html)
262:Pomeranians
246:toy Poodles
229:glucosamine
222:sulcoplasty
66:Orthopedics
38:Other names
999:Categories
903:Hammer toe
774:Coxa valga
757:Lower limb
743:Wrist drop
655:Upper limb
515:: 106034.
493:2020-01-23
468:2007-09-04
406:: 567886.
348:: 106034.
326:2007-11-27
307:References
301:Abyssinian
270:Chihuahuas
205:quadriceps
136:disrupted.
121:congenital
79:trick knee
883:Foot drop
878:Flat feet
873:Club foot
779:Coxa vara
644:Acquired
297:Devon Rex
278:Papillons
266:Pekingese
212:Treatment
184:Grade III
127:Diagnosis
61:Specialty
664:shoulder
539:Archived
432:33521073
299:and the
194:Grade IV
166:Grade II
1015:Patella
423:7838352
250:Maltese
218:surgery
173:flexion
156:Grade I
83:patella
430:
420:
377:
111:Causes
697:elbow
602:836.4
598:836.3
583:M22.1
177:tibia
921:neck
919:and
917:Head
865:foot
822:knee
720:hand
593:9-CM
428:PMID
375:ISBN
288:and
98:cats
94:dogs
799:leg
766:hip
589:ICD
574:ICD
517:doi
488:VCA
418:PMC
408:doi
350:doi
1001::
600:,
596::
581::
578:10
511:.
486:.
453:.
440:^
426:.
416:.
402:.
398:.
344:.
284:,
280:,
276:,
272:,
264:,
260:,
256:,
252:,
248:,
104:.
89:.
73:A
970:/
637:e
630:t
623:v
591:-
576:-
566:D
525:.
519::
496:.
471:.
434:.
410::
404:7
383:.
358:.
352::
329:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.