304:
172:
487:, which are different from French consonants. Nevertheless, the breadth of contact has some importance; it influences the shape of the tongue farther back and so the shape of the resonant cavity. Also, if the release of a denti-alveolar consonant is not abrupt, the tongue may peel off from the roof of the mouth from back to front and so shift from an alveolar to a dental pronunciation.
77:
36:
336:, produced by creating an obstruction with the tongue apex (tongue tip) only. Sometimes laminal is used exclusively for an articulation that involves only the blade of the tongue with the tip being lowered and apicolaminal for an articulation that involves both the blade of the tongue and the raised tongue tip. The distinction applies only to
442:
Because laminal consonants use the flat of the tongue, they cover a broader area of contact than apical consonants. Laminal consonants in some languages have been recorded with a broad occlusion (closure) that covers all the front of the mouth from the hard palate to the teeth, which makes it
331:
of the tongue, the flat top front surface just behind the tip of the tongue, in contact with upper lip, teeth, alveolar ridge, to possibly, as far back as the prepalatal arch, although in the last contact may involve parts behind the blade as well. It is distinct from an
450:. It spans the alveolar ridge to the teeth but is a little farther forward than other alveolar laminal consonants, which cover more of the alveolar ridge and might be considered postalveolar. This occurs in
480:, which produces the harmonics of the vowels. Thus, French coronals are alveolar and differ from English alveolars primarily in being laminal rather than apical (in French, the tongue is flatter).
476:, however, the important element is the place of the rearmost occlusion, which is the point that the resonant chamber in the mouth terminates. That determines the size, shape and acoustics of the
751:
466:
or denti-alveolar, the tip of the tongue can be seen touching the back of the teeth or even protruding between the teeth, which gives them the common name of
462:
Part of the confusion in naming laminal consonants is quite literally a matter of point of view. When one looks at a person pronouncing a laminal
87:
710:
589:
49:
744:
720:
233:
215:
193:
63:
391:
has a three-way distinction between laminal dental, apical alveolar and true subapical retroflex in nasal and voiceless oral stops.
1001:
145:
775:
491:
353:
974:
117:
102:
969:
981:
964:
124:
956:
737:
996:
991:
303:
1408:
986:
1261:
131:
908:
853:
1019:
838:
771:
447:
186:
180:
113:
1222:
1217:
1128:
533:
1239:
1049:
848:
823:
767:
422:
255:
197:
55:
828:
805:
783:
1266:
1229:
941:
484:
372:
1337:
1207:
1184:
933:
886:
858:
523:
357:
307:
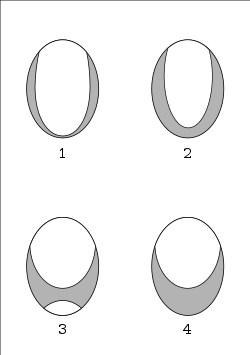
Schematic linguograms of 1) apical, 2) upper apical, 3) laminal and 4) apicolaminal stops based on
1202:
1035:
843:
800:
690:
682:
463:
406:
398:
388:
380:
138:
1324:
1281:
1158:
1123:
946:
913:
815:
716:
528:
337:
324:
443:
difficult to compare the two. Alveolar laminals and apicals are two different articulations.
1349:
1342:
1197:
1153:
1148:
1011:
923:
900:
876:
833:
792:
674:
518:
467:
410:
333:
596:
1314:
1212:
1192:
1133:
1101:
918:
702:
451:
435:
418:
394:
17:
1286:
414:
368:
483:
There are true laminal dentals in some languages with no alveolar contact, such as in
1402:
1372:
1332:
1309:
1276:
1249:
706:
694:
634:
1382:
1301:
1291:
1271:
384:
328:
1387:
1377:
1367:
1254:
1111:
477:
76:
1170:
678:
429:
364:
263:
1359:
1165:
1116:
1076:
1071:
1058:
651:
473:
376:
94:
1093:
1081:
402:
686:
662:
653:
Articulatory and
Acoustic Properties of Apical and Laminal Articulations
1066:
312:
1106:
302:
327:(speech sound) produced by obstructing the air passage with the
733:
729:
311::16), illustrating the areas of the tongue in contact with the
590:"The Articulation of the Coronal Sounds in the Peking Dialect"
165:
70:
29:
663:"The articulation of Malayalam coronal stops and nasals"
446:
A very common laminal articulation is sometimes called
98:
1358:
1323:
1300:
1238:
1183:
1092:
1057:
1048:
1028:
1010:
955:
932:
899:
869:
814:
791:
782:
348:Some languages contrast laminal and apical sounds:
290:
277:
272:
262:
253:
248:
432:have the distinction in both stops and fricatives.
667:Journal of the International Phonetic Association
639:Proceedings of the North East Linguistics Society
745:
8:
656:. Working Papers in Phonetics. Vol. 79.
576:
103:introducing citations to additional sources
64:Learn how and when to remove these messages
1054:
866:
788:
752:
738:
730:
673:(2). Cambridge University Press: 129–142.
494:, the diacritic for laminal consonants is
401:differentiate between laminal and apical
234:Learn how and when to remove this message
216:Learn how and when to remove this message
661:Dart, Sarah N.; Nihalani, Paroo (1999).
628:. Bloomington: Indiana University Press.
438:makes the distinction only in its stops.
375:, the apical stops are normally called "
179:This article includes a list of general
93:Relevant discussion may be found on the
552:
545:
245:
564:
340:, which use the front of the tongue.
7:
315:during articulation (shown in grey).
308:
712:The Sounds of the World's Languages
635:"A Cross-Sectional View of s, ʃ, θ"
185:it lacks sufficient corresponding
25:
626:Fundamental problems in phonetics
45:This article has multiple issues.
170:
86:relies largely or entirely on a
75:
34:
776:International Phonetic Alphabet
354:Australian Aboriginal languages
53:or discuss these issues on the
1:
421:make such a distinction with
367:contrast apical and laminal
1425:
577:Dart & Nihalani (1999)
352:The contrast is common in
1144:
765:
679:10.1017/S0025100300006502
633:Gafos, Diamandis (1997).
428:Some native languages of
18:Lamino-alveolar consonant
356:, which usually have no
650:Dart, Sarah N. (1991).
534:List of phonetic topics
423:postalveolar consonants
200:more precise citations.
768:Articulatory phonetics
624:Catford, J.C. (1977).
507:COMBINING SQUARE BELOW
316:
942:Pharyngeal/epiglottal
715:. Oxford: Blackwell.
306:
1267:Labio-palatalization
458:Compared to alveolar
99:improve this article
27:Phone (speech sound)
957:Double articulation
524:Subapical consonant
114:"Laminal consonant"
1409:Coronal consonants
363:Some languages in
344:Compared to apical
338:coronal consonants
317:
1396:
1395:
1282:Pharyngealization
1179:
1178:
1044:
1043:
1002:Uvular–epiglottal
895:
894:
529:Coronal consonant
379:" but are really
321:laminal consonant
301:
300:
244:
243:
236:
226:
225:
218:
164:
163:
149:
68:
16:(Redirected from
1416:
1350:Voice onset time
1055:
975:Labial–retroflex
867:
789:
754:
747:
740:
731:
726:
703:Ladefoged, Peter
698:
657:
646:
629:
611:
610:
608:
607:
601:
595:. Archived from
594:
586:
580:
574:
568:
562:
556:
550:
519:Apical consonant
508:
505:
504:
500:
498:
411:Mandarin Chinese
334:apical consonant
294:
286:
281:
258:
257:
246:
239:
232:
221:
214:
210:
207:
201:
196:this article by
187:inline citations
174:
173:
166:
159:
156:
150:
148:
107:
79:
71:
60:
38:
37:
30:
21:
1424:
1423:
1419:
1418:
1417:
1415:
1414:
1413:
1399:
1398:
1397:
1392:
1354:
1319:
1296:
1241:
1234:
1175:
1140:
1088:
1040:
1024:
1006:
970:Labial–alveolar
951:
928:
909:Alveolo-palatal
891:
865:
854:Palato-alveolar
810:
778:
772:Co-articulation
761:
758:
723:
701:
660:
649:
632:
623:
620:
615:
614:
605:
603:
599:
592:
588:
587:
583:
575:
571:
563:
559:
551:
547:
542:
515:
506:
502:
501:
496:
495:
460:
346:
292:
284:
279:
254:
240:
229:
228:
227:
222:
211:
205:
202:
192:Please help to
191:
175:
171:
160:
154:
151:
108:
106:
92:
80:
39:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1422:
1420:
1412:
1411:
1401:
1400:
1394:
1393:
1391:
1390:
1385:
1380:
1375:
1370:
1364:
1362:
1356:
1355:
1353:
1352:
1347:
1346:
1345:
1340:
1329:
1327:
1321:
1320:
1318:
1317:
1312:
1306:
1304:
1298:
1297:
1295:
1294:
1289:
1287:Glottalization
1284:
1279:
1274:
1269:
1264:
1262:Palatalization
1259:
1258:
1257:
1246:
1244:
1236:
1235:
1233:
1232:
1227:
1226:
1225:
1220:
1210:
1205:
1200:
1195:
1189:
1187:
1181:
1180:
1177:
1176:
1174:
1173:
1168:
1163:
1162:
1161:
1156:
1145:
1142:
1141:
1139:
1138:
1137:
1136:
1131:
1121:
1120:
1119:
1109:
1104:
1098:
1096:
1090:
1089:
1087:
1086:
1085:
1084:
1074:
1069:
1063:
1061:
1052:
1046:
1045:
1042:
1041:
1039:
1038:
1032:
1030:
1026:
1025:
1023:
1022:
1020:Velopharyngeal
1016:
1014:
1008:
1007:
1005:
1004:
999:
994:
989:
984:
982:Labial–palatal
979:
978:
977:
972:
965:Labial–coronal
961:
959:
953:
952:
950:
949:
944:
938:
936:
930:
929:
927:
926:
921:
916:
911:
905:
903:
897:
896:
893:
892:
890:
889:
884:
879:
873:
871:
864:
863:
862:
861:
856:
846:
841:
839:Denti-alveolar
836:
831:
826:
820:
818:
812:
811:
809:
808:
803:
797:
795:
786:
780:
779:
766:
763:
762:
759:
757:
756:
749:
742:
734:
728:
727:
721:
707:Maddieson, Ian
699:
658:
647:
630:
619:
616:
613:
612:
581:
579:, p. 133.
569:
567:, p. 129.
557:
555:, p. 152.
553:Catford (1977)
544:
543:
541:
538:
537:
536:
531:
526:
521:
514:
511:
459:
456:
448:denti-alveolar
440:
439:
433:
426:
415:Serbo-Croatian
392:
361:
345:
342:
299:
298:
295:
288:
287:
282:
275:
274:
270:
269:
266:
260:
259:
251:
250:
242:
241:
224:
223:
178:
176:
169:
162:
161:
97:. Please help
83:
81:
74:
69:
43:
42:
40:
33:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1421:
1410:
1407:
1406:
1404:
1389:
1386:
1384:
1381:
1379:
1376:
1374:
1371:
1369:
1366:
1365:
1363:
1361:
1357:
1351:
1348:
1344:
1341:
1339:
1336:
1335:
1334:
1331:
1330:
1328:
1326:
1322:
1316:
1313:
1311:
1308:
1307:
1305:
1303:
1299:
1293:
1290:
1288:
1285:
1283:
1280:
1278:
1277:Uvularization
1275:
1273:
1270:
1268:
1265:
1263:
1260:
1256:
1253:
1252:
1251:
1250:Labialization
1248:
1247:
1245:
1243:
1237:
1231:
1228:
1224:
1221:
1219:
1216:
1215:
1214:
1211:
1209:
1206:
1204:
1201:
1199:
1196:
1194:
1191:
1190:
1188:
1186:
1182:
1172:
1169:
1167:
1164:
1160:
1157:
1155:
1152:
1151:
1150:
1147:
1146:
1143:
1135:
1132:
1130:
1127:
1126:
1125:
1122:
1118:
1115:
1114:
1113:
1110:
1108:
1105:
1103:
1100:
1099:
1097:
1095:
1091:
1083:
1080:
1079:
1078:
1075:
1073:
1070:
1068:
1065:
1064:
1062:
1060:
1056:
1053:
1051:
1047:
1037:
1034:
1033:
1031:
1027:
1021:
1018:
1017:
1015:
1013:
1009:
1003:
1000:
998:
997:Coronal–velar
995:
993:
992:Labial–uvular
990:
988:
985:
983:
980:
976:
973:
971:
968:
967:
966:
963:
962:
960:
958:
954:
948:
945:
943:
940:
939:
937:
935:
931:
925:
922:
920:
917:
915:
912:
910:
907:
906:
904:
902:
898:
888:
885:
883:
880:
878:
875:
874:
872:
868:
860:
857:
855:
852:
851:
850:
847:
845:
842:
840:
837:
835:
832:
830:
827:
825:
822:
821:
819:
817:
813:
807:
804:
802:
799:
798:
796:
794:
790:
787:
785:
781:
777:
773:
769:
764:
755:
750:
748:
743:
741:
736:
735:
732:
724:
722:0-631-19815-6
718:
714:
713:
708:
704:
700:
696:
692:
688:
684:
680:
676:
672:
668:
664:
659:
655:
654:
648:
644:
640:
636:
631:
627:
622:
621:
617:
602:on 2021-07-24
598:
591:
585:
582:
578:
573:
570:
566:
561:
558:
554:
549:
546:
539:
535:
532:
530:
527:
525:
522:
520:
517:
516:
512:
510:
493:
488:
486:
481:
479:
475:
471:
469:
465:
457:
455:
453:
449:
444:
437:
434:
431:
427:
424:
420:
416:
412:
408:
404:
400:
396:
393:
390:
386:
382:
378:
374:
370:
366:
362:
359:
355:
351:
350:
349:
343:
341:
339:
335:
330:
326:
322:
314:
310:
305:
296:
289:
283:
276:
271:
267:
265:
261:
252:
247:
238:
235:
220:
217:
209:
199:
195:
189:
188:
182:
177:
168:
167:
158:
147:
144:
140:
137:
133:
130:
126:
123:
119:
116: –
115:
111:
110:Find sources:
104:
100:
96:
90:
89:
88:single source
84:This article
82:
78:
73:
72:
67:
65:
58:
57:
52:
51:
46:
41:
32:
31:
19:
1302:Tongue shape
1292:Nasalization
1272:Velarization
1242:articulation
1012:Pathological
987:Labial–velar
881:
870:Active place
849:Postalveolar
824:Linguolabial
760:Articulation
711:
670:
666:
652:
642:
638:
625:
618:Bibliography
604:. Retrieved
597:the original
584:
572:
565:Gafos (1997)
560:
548:
489:
482:
474:Acoustically
472:
461:
445:
441:
385:postalveolar
347:
320:
318:
230:
212:
206:October 2019
203:
184:
155:October 2019
152:
142:
135:
128:
121:
109:
85:
61:
54:
48:
47:Please help
44:
1112:Approximant
829:Interdental
806:Labiodental
478:oral cavity
198:introducing
1240:Secondary
1230:Percussive
1198:Ingressive
1171:Continuant
606:2014-08-26
540:References
485:Hindustani
430:California
373:Hindustani
365:South Asia
358:fricatives
309:Dart (1991
285:̻
264:IPA Number
181:references
125:newspapers
50:improve it
1360:Phonation
1338:Aspirated
1333:Voiceless
1208:Implosive
1193:Egressive
1185:Airstream
1166:Occlusive
1117:Semivowel
1077:Fricative
1072:Affricate
1059:Obstruent
934:Laryngeal
887:Subapical
859:Retroflex
695:145638382
403:sibilants
399:Mirandese
389:Malayalam
377:retroflex
280:(decimal)
95:talk page
56:talk page
1403:Category
1255:Rounding
1223:Ejective
1218:Pulmonic
1203:Ejective
1129:Tap/flap
1094:Sonorant
1082:Sibilant
1036:Bidental
844:Alveolar
801:Bilabial
709:(1996).
687:44526241
513:See also
503:◌̻
464:alveolar
409:region;
407:alveolar
381:alveolar
291:Unicode
273:Encoding
1373:Breathy
1159:Lateral
1124:Vibrant
1067:Plosive
947:Glottal
914:Palatal
882:Laminal
816:Coronal
490:In the
405:in the
278:Entity
249:Laminal
194:improve
139:scholar
1383:Creaky
1343:Tenuis
1310:Sulcal
1154:Rhotic
1149:Liquid
1050:Manner
924:Uvular
901:Dorsal
877:Apical
834:Dental
793:Labial
719:
693:
685:
499:
497:U+033B
468:dental
452:French
436:Dahalo
419:Polish
417:, and
395:Basque
313:palate
297:U+033B
183:, but
141:
134:
127:
120:
112:
1388:Stiff
1378:Slack
1368:Modal
1325:Voice
1315:Domed
1213:Click
1134:Trill
1107:Vowel
1102:Nasal
1029:Other
919:Velar
784:Place
691:S2CID
683:JSTOR
600:(PDF)
593:(PDF)
371:. In
369:stops
329:blade
325:phone
323:is a
293:(hex)
146:JSTOR
132:books
717:ISBN
397:and
118:news
675:doi
492:IPA
383:or
268:410
101:by
1405::
774:–
770:–
705:;
689:.
681:.
671:29
669:.
665:.
643:27
641:.
637:.
509:.
470:.
454:.
413:,
387:.
319:A
256:◌̻
59:.
753:e
746:t
739:v
725:.
697:.
677::
645:.
609:.
425:.
360:.
237:)
231:(
219:)
213:(
208:)
204:(
190:.
157:)
153:(
143:·
136:·
129:·
122:·
105:.
91:.
66:)
62:(
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.