103:
91:
38:. While its architecture is very similar to a conventional transmission electron microscope, it has a few key differences that enable it to take advantage of a 5 keV electron source, but trading off many advantages of higher voltage operations, including higher resolution, the possibility of X-ray microanalysis and
125:
step for TEM imaging of light elements (H, C, N, O, S, P). While staining is beneficial for experiments aimed at high resolution structure determination, it is highly undesirable in certain protein sample preparations, because it could destabilize the protein sample due to its acid pH and relatively
67:
Further, a relatively low mean free path (15 nm) for organic samples at 5 kV means that for samples with constant thickness, high contrast will be obtained from small variations in density. For example, for 5% contrast in the LVEM bright field image, we only need a difference in density between
154:
Currently available low voltage microscopes are only able to obtain resolutions of 1–3 nanometers (nm). While this is well beyond resolutions possible from optical (light) microscopes, they are not yet able to compete with the atomic resolution obtainable from conventional (higher voltage) electron
129:
LVEM experiments carried out on an extracted membrane protein sample that was analyzed with and without the staining procedure show a marked improvement in the appearance of the sample when standard staining is omitted. Results show that LVEM could be even more useful than conventional EM for this
145:
The first low-voltage electron microscopes were capable of spatial resolutions of about 2.5 nm in TEM, 2.0 nm in STEM, and 3.0 nm in SEM modes. The SEM resolution has been improved to ~1.2 nm at 800 eV by 2010, while a 0.14 nm TEM resolution at 15 keV has been reported in
158:
Low voltage limits the maximum thickness of samples which can be studied in the TEM or STEM mode. Whereas it is about 50–90 nm in conventional TEM, it decreases to around 20–65 nm for LVEM at 5 kV. However, thicknesses of the order of 20 nm or less are required to attain the maximal
59:
of light elements. The comparison images below show that decreasing the acceleration voltage from 80 kV to 5 kV significantly enhances the contrast of test samples. The improved contrast is a direct result of increased electron scattering associated with a reduced accelerating voltage.
63:
LVEM brings an enhancement of imaging contrast nearly twenty times higher than for 100 kV. This is very promising for biological specimens which are composed of light elements and do not exhibit sufficient contrast in classical TEMs.
440:
Asmar, G.A.; Hanson, M.A.; Ward, A.B.; Lasalde, J.A.; Stevens, R.C.; Potter, C.; Kuhn, P. M. (2004). "Low-Voltage
Electron Microscopy (LVEM) as a probe for solubilized membrane protein aggregation states".
166:
in 2015 these limitations were overcome with a 25 kV low voltage electron microscope that can produce high quality results with thin sectioned samples up to around 100 nm+.
426:
186:
372:
130:
particular application because it avoids the potentially disrupting staining step, thus providing an undisturbed image of the protein's aggregation state.
126:
high heavy metal concentration. The addition of stain to sectioned samples such as biological materials or polymers can also introduce imaging artifacts.
198:
42:, etc. Recently a new low voltage transmission electron microscope has been introduced that operates at variable voltage ranges between 6–25 kV.
485:
391:
Drummy, Lawrence, F.; Yang, Junyan; Martin, David C. (2004). "Low-voltage electron microscopy of polymer and organic molecular thin films".
133:
Additionally, The ability to eliminate the staining step could aid to improve safety in the lab, as common heavy metal stains, such as
90:
180:
35:
501:
Van Aken, R. H.; Maas, D. J.; Hagen, C. W.; Barth, J. E.; Kruit, P (2010). "Design of an aberration corrected low-voltage SEM".
68:
the phases of 0.07 g/cm. This means that the usual need to stain polymers for enhanced contrast in the TEM (typically done with
215:
612:
204:
607:
345:
Nebesářová1, Jana; Vancová, Marie (2007). "How to
Observe Small Biological Objects in Low Voltage Electron Microscope".
192:
538:"Atomic Resolution Imaging at an Ultralow Accelerating Voltage by a Monochromatic Transmission Electron Microscope"
102:
587:
420:
366:
159:
resolution in the TEM and STEM modes 5 kV. These thickness are sometimes achievable with the use of an
28:(keV) or less. Traditional electron microscopes use accelerating voltages in the range of 10-1000 keV.
549:
450:
210:
175:
73:
21:
31:
Low voltage imaging in transmitted electrons is possible in many new scanning electron detectors.
121:
The improved contrast allows for the significant reduction, or elimination, of the heavy metal
567:
518:
481:
408:
257:
56:
557:
510:
458:
400:
354:
272:
553:
454:
242:
160:
134:
122:
601:
267:
562:
537:
514:
404:
262:
237:
25:
55:
A substantial decrease in electron energy allows for a significant improvement of
462:
358:
295:
232:
536:
Morishita, Shigeyuki; Mukai, Masaki; Suenaga, Kazu; Sawada, Hidetaka (2016).
277:
252:
247:
571:
522:
412:
76:) may not be necessary with the low voltage electron microscopy technique.
287:
282:
300:
69:
39:
81:
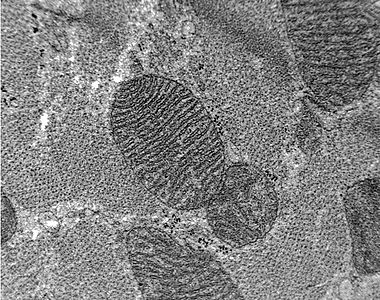
Comparison – TEM images of unstained thin section of rat heart
227:
LVEM is especially efficient for the following applications.
34:
A low cost alternative is a dedicated tabletop low voltage
593:
LVEM5 low voltage electron microscope from Delong
America
592:
330:
319:
24:
which operates at accelerating voltages of a few kilo
386:
384:
382:
187:High-resolution transmission electron microscopy
96:Low voltage (5 kV) image showing higher contrast
8:
425:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
371:: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (
561:
199:Scanning transmission electron microscope
478:Structural genomics on membrane proteins
340:
338:
312:
86:
418:
364:
18:Low-voltage electron microscope (LVEM)
7:
14:
137:do have associated health risks.
181:Transmission electron microscope
101:
89:
36:transmission electron microscope
588:WENDMANs VIEWS on NANOTECH Blog
480:. CRC Press. pp. 271–274.
216:Low-energy electron diffraction
563:10.1103/PhysRevLett.117.153004
515:10.1016/j.ultramic.2010.07.012
405:10.1016/j.ultramic.2004.01.011
205:Low-energy electron microscopy
108:Conventional TEM (80 kV) image
1:
443:Microscopy and Microanalysis
347:Microscopy and Microanalysis
193:Scanning electron microscope
476:Lundstrom, Kenneth (2006).
629:
331:LVEM25 from Delong America
463:10.1017/S1431927604886069
359:10.1017/S143192760708124X
320:LVEM5 from Delong America
542:Physical Review Letters
613:Scientific techniques
211:Electron diffraction
608:Electron microscopy
554:2016PhRvL.117o3004M
455:2004MiMic..10S1492A
176:Electron microscope
74:ruthenium tetroxide
22:electron microscope
117:Stain not required
487:978-1-57444-526-8
258:Materials science
223:Application areas
123:negative staining
620:
576:
575:
565:
533:
527:
526:
498:
492:
491:
473:
467:
466:
449:(2): 1492–1493.
437:
431:
430:
424:
416:
388:
377:
376:
370:
362:
342:
333:
328:
322:
317:
105:
93:
628:
627:
623:
622:
621:
619:
618:
617:
598:
597:
584:
579:
535:
534:
530:
503:Ultramicroscopy
500:
499:
495:
488:
475:
474:
470:
439:
438:
434:
417:
393:Ultramicroscopy
390:
389:
380:
363:
344:
343:
336:
329:
325:
318:
314:
310:
305:
225:
172:
152:
143:
119:
114:
113:
112:
109:
106:
97:
94:
83:
82:
53:
51:Higher contrast
48:
12:
11:
5:
626:
624:
616:
615:
610:
600:
599:
596:
595:
590:
583:
582:External links
580:
578:
577:
548:(15): 153004.
528:
509:(11): 1411–9.
493:
486:
468:
432:
399:(4): 247–256.
378:
353:(3): 248–249.
334:
323:
311:
309:
306:
304:
303:
298:
293:
292:Tissue samples
290:
285:
280:
275:
270:
265:
260:
255:
250:
245:
243:Drug discovery
240:
235:
229:
224:
221:
220:
219:
213:
208:
202:
196:
190:
184:
178:
171:
168:
161:ultramicrotome
151:
148:
142:
139:
135:uranyl acetate
118:
115:
111:
110:
107:
100:
98:
95:
88:
85:
84:
80:
79:
78:
52:
49:
47:
44:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
625:
614:
611:
609:
606:
605:
603:
594:
591:
589:
586:
585:
581:
573:
569:
564:
559:
555:
551:
547:
543:
539:
532:
529:
524:
520:
516:
512:
508:
504:
497:
494:
489:
483:
479:
472:
469:
464:
460:
456:
452:
448:
444:
436:
433:
428:
422:
414:
410:
406:
402:
398:
394:
387:
385:
383:
379:
374:
368:
360:
356:
352:
348:
341:
339:
335:
332:
327:
324:
321:
316:
313:
307:
302:
299:
297:
294:
291:
289:
286:
284:
281:
279:
276:
274:
271:
269:
268:Nanoparticles
266:
264:
261:
259:
256:
254:
251:
249:
246:
244:
241:
239:
236:
234:
231:
230:
228:
222:
217:
214:
212:
209:
206:
203:
200:
197:
194:
191:
188:
185:
182:
179:
177:
174:
173:
169:
167:
164:
162:
156:
155:microscopes.
149:
147:
140:
138:
136:
131:
127:
124:
116:
104:
99:
92:
87:
77:
75:
71:
65:
61:
58:
50:
45:
43:
41:
37:
32:
29:
27:
26:electronvolts
23:
19:
545:
541:
531:
506:
502:
496:
477:
471:
446:
442:
435:
421:cite journal
396:
392:
367:cite journal
350:
346:
326:
315:
263:Nanomedicine
238:Cell biology
226:
165:
157:
153:
144:
132:
128:
120:
66:
62:
54:
33:
30:
17:
15:
150:Limitations
602:Categories
308:References
296:Toxicology
233:Antibodies
141:Resolution
46:Advantages
278:Pathology
273:Nanotubes
253:Histology
248:Education
572:27768334
523:20728276
413:15149719
288:Proteins
283:Polymers
170:See also
57:contrast
550:Bibcode
451:Bibcode
301:Viruses
189:(HRTEM)
570:
521:
484:
411:
218:(LEED)
207:(LEEM)
201:(STEM)
146:2016.
70:osmium
20:is an
195:(SEM)
183:(TEM)
568:PMID
519:PMID
482:ISBN
427:link
409:PMID
373:link
40:EELS
558:doi
546:117
511:doi
507:110
459:doi
401:doi
355:doi
72:or
604::
566:.
556:.
544:.
540:.
517:.
505:.
457:.
447:10
445:.
423:}}
419:{{
407:.
397:99
395:.
381:^
369:}}
365:{{
351:13
349:.
337:^
163:.
16:A
574:.
560::
552::
525:.
513::
490:.
465:.
461::
453::
429:)
415:.
403::
375:)
361:.
357::
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.