444:
tubules. The C-Fibres typically terminate in the pulp tissue proper, either as free nerve endings or as branches around blood vessels. Sensory nerve fibers that originate from inferior and superior alveolar nerves innervate the odontoblastic layer of the pulp cavity. These nerves enter the tooth through the apical foramen as myelinated nerve bundles. They branch to form the subodontoblastic nerve plexus of
Raschkow, which is separated from the odontoblasts by a cell-free zone of Weil. This plexus lies between the cell-free and cell-rich zones of the pulp.
40:
1011:. The pulp becomes more fibrotic, reducing the regenerative capacity of the pulp due to the loss of these cells. The overall pulp cavity may become smaller by the addition of secondary or tertiary dentin and cause pulp recession. The lack of sensitivity associated with older teeth is due to receded pulp horns, pulp fibrosis, the addition of dentin, or all these changes. Restorative treatment can be performed without local anaesthesia on older dentitions.
328:
935:
tissue) or adherent (attached to pulp wall continuous with dentine, but not fully enclosed). Depending on the structure, they are either true (dentine lined by odontoblasts), false (formed from degenerating cells that mineralise) or diffuse (more irregular in shape to false stones). The aetiology of pulp stones is little understood. It has been recorded that pulpal calcifications can occur due to:
448:
251:
138:
934:
Pulp stones are calcified masses that occur in the pulp, either in the apical or coronal portions. They are classified according to their structure or location. According to their location, pulp stones can be classed either as free (completely surrounded by pulp), embedded (surrounded by dentine
899:
After a pulp exposure, pulp cells are recruited and differentiate into odontoblast-like cells, contributing to the formation of a dentine bridge, increasing dentin thickness. The odontoblast-like cell is a mineralized structure formed by a new population of pulp-derived cells that can be expressed as
754:
Irreversible puplitis may be symptomatic or asymptomatic. Asymptomatic irreversible pulpitis results from transition of symptomatic irreversible pulpitis into an inactive/quiescent state. This is due to its aetiology; inflammatory exudate can be quickly removed, e.g. through a large carious cavity or
484:
The dental pulp is also innervated by the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. These sympathetic axons project into the radicular pulp, where they form a plexus along the blood vessels. Their function is mainly related to blood vessel constriction within the dental pulp. A sharp fall
829:
Necrosis may be symptomatic or asymptomatic. Symptomatic necrosis involves lingering pain response to hot and cold stimuli, spontaneous pain that may cause a patient to awaken during sleep, difficulty eating and sensitivity to percussion. Asymptomatic necrosis is non-responsive to thermal stimuli or
750:
Irreversible and reversible pulpitis are distinguished by the pain responses to thermal stimulation. If the condition is reversible, the pulp's pain response lasts a few seconds upon exposure to cold or hot. If the pain lingers from minutes to hours, the condition is classified as irreversible. This
746:
Pulpitis is established when the pulp chamber is compromised by bacterial infection. Irreversible pulpitis is diagnosed when the pulp is inflamed and infected beyond healing. Removal of the aetiological agent does not permit healing, and a root canal is often indicated. Irreversible pulpitis follows
438:
The plexus of
Raschkow monitors painful sensations. By virtue of their peptide content, they also play important functions in inflammatory events and subsequent tissue repair. There are two types of nerve fibers that mediate the sensation of pain: A-Fibres conduct rapid and sharp pain sensations and
891:
bacteria and activate T cells, triggering the adaptive immune response that occurs in association with DCs. In the pulp, DCs secrete a range of cytokines that influence immune responses, and are key regulators of the infection defence. A comparatively small number of B cells are present in healthy
863:
Pulpal response to caries can be divided into two stages – pre- and post-infection. In caries-affected human teeth, odontoblast-like cells appear at the dentine-pulp interface along with specialized pulp immune cells to combat caries. Once they identify specific bacterial components, these cells
838:
Asymptomatic necrosis is may go unnoticed by the patient and so a diagnosis may not be attempted. Diagnosis may involve X-rays and sensitivity testing with. hot or cold stimuli (using warm gutta-percha or ethyl chloride), or an electric pulp tester. Tooth vitality (blood supply) may be assessed
443:
group, whereas C-Fibres are involved in dull aching pain and are thinner and unmyelinated. The A-Fibres, mainly of the A-delta type, are preferentially located in the periphery of the pulp, where they are in close association with the odontoblasts and extend fibers to many but not all dentinal
636:
Reversible pulpitis is a mild to moderate inflammation caused by any momentary irritation or stimulant whereby no pain is felt upon the stimulants' removal. The pulp swells when the protective layers of enamel and dentine are compromised. Unlike irreversible pulpitis, the pulp gives a regular
959:
Pulp stones can reach as high as 50% in surveyed samples. Pulp stones are estimated to typically range from 8–9%. Pulpal calcifications are more common in females and more frequent in maxillary teeth compared to mandibular teeth. The reason is uncertain. They are more common in molar teeth,
820:
is when the pulp has died/dying. Causes include untreated caries, trauma or bacterial infection. It is often subsequent to chronic pulpitis. Teeth with pulp necrosis undergo a root canal or extraction to prevent further spread of the infection, which may lead to an abscess.
481:. The neurons enter the pulp cavity through the apical foramen and branch off to form the nerve plexus of Raschkow. Nerves from the plexus of Raschkow provide branches to form a marginal plexus around the odontoblasts, with some nerves penetrating the dentinal tubules.
960:
especially first molars compared to second molars and premolars. A review suggested this was because the first molars are the first teeth to be located in the mandible (lower jaw) and have longer exposure to degenerative changes. They also have a larger blood supply.
980:
to the pulp's odontoblastic layer, triggering the response. This mainly responds to cold. At this stage, simple restoration can be performed. As the decay progresses near the pulp, the response magnifies. Sensation to heat and cold increases. At this stage, indirect
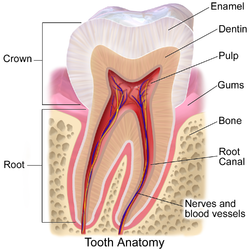
205:. It is composed of a central pulp chamber, pulp horns, and radicular canals. The large mass of the pulp is contained within the pulp chamber, which is contained in and mimics the overall shape of the crown of the tooth. Because of the continuous deposition of the
637:
response to sensibility tests and inflammation resolves with management of the cause. No significant radiographic changes are present in the periapical region. Further examination is required to ensure that the dental pulp has returned to its normal state.
606:
A healthy tooth is expected to respond to sensitivity testing with a short, sharp burst of pain which subsides when the stimulus is removed. An exaggerated or prolonged response to sensitivity testing indicates that the tooth has some degree of symptomatic
295:. Together the epithelial enamel organ and ectomesenchymal dental papilla and follicle form the tooth germ. The dental papilla is the origin of dental pulp. Cells at the periphery of the dental papilla undergo cell division and differentiation to become
807:
Treatments include root canal or tooth extraction. In endodontic therapy, removal of the inflamed pulp relieves the pain. The empty root canal system is then obturated with gutta-percha (rubber material that acts as a pressure/pain reliever).
955:
Pulp stones usually consist of circular layers of mineralised tissues. These layers are made up of blood clots, dead cells and collagen fibres. Occasionally, pulp stones appear surrounded by odontoblast-like cells that contain tubules.
770:) and others. Thermal tests are subjective, and are therefore performed the compromised tooth and the adjacent and contralateral teeth, allowing the patient to compare them. Normal healthy teeth are used as a baseline for diagnoses.
476:
As the dental pulp is a highly vascularised and innervated region of the tooth, it is the site of origin for most pain-related sensations. The dental pulp nerve is innervated by one of the trigeminal nerves, otherwise known as the
488:
There are two main types of sensory nerve fibres in the pulp, each densely placed at different locations. The differing structural features of the two sensory nerve fibres also result in different types of sensory stimulation.
230:
Accessory canals are pathways from the radicular pulp. These canals, which extend laterally through the dentin to the periodontal tissue, are seen especially in the apical third of the root. Accessory canals are also called
971:
Pulp acts as a security and alarm system. Slight decay in tooth structure not extending to the dentin may not alarm the pulp, but as the dentin gets exposed, due either to dental caries or trauma, sensitivity starts. The
1835:
895:
When bacteria get closer to the pulp but are still confined to primary or secondary dentine, acid demineralization of dentine occurs, producing tertiary dentine to help protect the pulp from further injury.
603:). Although less accurate, sensitivity tests, such as Electric Pulp Tests or Thermal Tests, are more routinely used in clinical practice than vitality testing, which requires specialised equipment.
517:. Stimuli that displaces the fluid within the dentinal tubules will trigger the intradental myelinated A-Fibres, leading to the sharp pain sensation commonly associated with dentine hypersensitivity
2420:
Pulp is also a famous
Sustainable Clothing Brand born in India. They aim to create an environment friendly ecosystem and an option for the consumer to adopt Conscious & Sustainable lifestyle.
1803:
2157:
Gabardo MC, Wambier LM, Rocha JS, Küchler EC, de Lara RM, Leonardi DP, et al. (September 2019). "Association between Pulp Stones and Kidney Stones: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis".
533:
They are heavily influenced by modulating interneurons before they reach the thalamus. C-Fibre stimulation often results in a "slow pain", normally characterised as a dull and aching pain.
758:
As the names imply, these diseases are largely characterised by their symptoms: pain duration and location, and exacerbating and relieving factors. Inputs include clinical tests (cold
855:
Untreated necrotic pulp may result in further complications, such as infection, fever, swelling, abscesses and bone loss. Two treatment options are available for pulpal necrosis.
985:
may be advisable. At this stage it may be impossible to clinically diagnose the extent of decay. Carious dentin by dental decay progressing to the pulp may get fractured during
755:
previous trauma that caused painless pulp exposure. The build-up of pressure in a confined pulp space initiates pain reflexes. When this pressure is relieved, pain subsides.
1827:
1621:
1164:
385:
Pulpal core, which is in the center of the pulp chamber, with many cells and an extensive vascular supply; except for its location, it is very similar to the cell-rich zone.
291:
is the origin of the tooth bud. The bud stage progresses to the cap stage when the epithelium forms the enamel organ. The ectomesenchyme cells condense further and become
1246:
302:
The development of dental pulp can also be split into two stages: coronal pulp development (near the crown of the tooth) and root pulp development (apex of the tooth).
996:
or endodontic therapy. Traumatized pulp starts an inflammatory response. The hard and closed surroundings builds pressure inside the pulp chamber, compressing the
209:, the pulp chamber becomes smaller with the age. This is not uniform throughout the coronal pulp but progresses faster on the floor than on the roof or sidewalls.
1399:
1341:
963:
In general, pulp stones do not require treatment. Depending on the stones' size and location, they may interfere with endodontic treatment and should be removed.
498:
The A-Fibres present in the pulp can be further classified into 2 different types. A-Delta Fibres make up 90% of the A-Fibres, while the rest are A-Beta Fibres.
113:
2240:
Jannati R, Afshari M, Moosazadeh M, Allahgholipour SZ, Eidy M, Hajihoseini M (May 2019). "Prevalence of pulp stones: A systematic review and meta-analysis".
1795:
2471:
513:
Able to respond to stimuli through a shell of calcified tissue due to the stimulus-induced fluid flow in dentinal tubules. This is known as the
299:. Pulpoblasts form in the middle of the pulp. This completes the formation of the pulp. The dental pulp is essentially a mature dental papilla.
2292:
2130:
1598:
1567:
1375:
1317:
279:
The first sign of tooth development is known to be as early as the 6th week of intrauterine life. The oral epithelium begins to multiply and
89:
1107:
Iqbal M, Kim S, Yoon F (May 2007). "An investigation into differential diagnosis of pulp and periapical pain: a PennEndo database study".
2320:
912:(BDs). BDs kill microorganisms by forming micropores that destroy membrane integrity and cause leakage of the cell content. Another is
2399:
2004:
920:
that stimulates chemokine production to attract immune cells to the affected areas and neutralize bacterial by-products in pulp cells
747:
reversible pulpitis absent early intervention. While the pulp is still vital and vascularised, it is not classified as 'dead pulp'.
2757:
1153:
1614:
883:. This sampling process is part of the normal immune response, as it triggers leukocytes from the circulatory system to adhere to
485:
in pulpal blood flow may be caused by stimulation of these nerves. There is no evidence for a parasympathetic pulpal innervation.
595:
The health of the dental pulp can be established by a variety of diagnostic aids which test either the blood supply to a tooth (
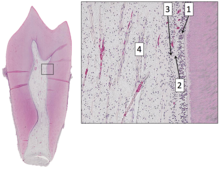
216:. They are not always straight but vary in shape, size, and number. They are continuous with the periapical tissues through the
1472:
1238:
243:
The pulp has a background similar to that of dentin because both are derived from the dental papilla of the tooth germ. During
1000:
and eliciting pain. At this stage, the pulp starts to die, progressing to periapical abscess formation (chronic pulpitis).
2089:
767:
108:
1045:
1003:
Pulp horns recede with age. The pulp undergoes a decrease in intercellular substance, water, and cells as it fills with
381:
This area is lined peripherally by a specialized odontogenic area which has four layers (from innermost to outermost):
2464:
504:
Mainly located at the pulp-dentine border at the top of the pulp, and more specifically concentrated in the pulp horn.
398:
Odontoblastic layer, the outermost layer which contains odontoblasts and lies next to the predentin and mature dentin.
700:
Tooth tap test (lightweight, blunt instrument gently tapped onto affected tooth to determine extent of inflammation)
507:
Have a relatively small diameter with a relatively slow conduction velocity. They are is still faster than C-Fibres.
2871:
2688:
2662:
2657:
2499:
697:
Sensitivity tests to see if pain/discomfort is experienced when tooth is in contact with hot, cold or sweet stimuli
2683:
2601:
2575:
2570:
1415:"Potential Novel Strategies for the Treatment of Dental Pulp-Derived Pain: Pharmacological Approaches and Beyond"
1500:"Scaffold-free microtissues: differences from monolayer cultures and their potential in bone tissue engineering"
2596:
72:
1891:
Nusstein JM, Reader A, Drum M (April 2010). "Local anesthesia strategies for the patient with a "hot" tooth".
780:
Patient may complain of sharp lingering pains that last longer than 30 seconds, even after removal of stimulus
904:. They are responsible for the upregulation of innate immunity effectors, including antimicrobial agents and
566:
Protective/sensory: extremes in temperature, pressure, or trauma to the dentin or pulp are perceived as pain;
2866:
2709:
1074:
Illustrated Dental
Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy, Bath-Balogh and Fehrenbach, Elsevier, 2011, page 164.
259:
244:
2805:
2795:
2704:
2622:
2457:
1020:
120:
96:
84:
2617:
2494:
2429:
1008:
977:
2346:
Yu C, Abbott PV (March 2007). "An overview of the dental pulp: its functions and responses to injury".
2317:"Root canal treatment (endodontic therapy) explained: What is it? Why is it needed? What does it do?"
840:
194:
1287:
378:
The central region of the coronal and radicular pulp contains large nerve trunks and blood vessels.
2828:
887:
cells lining blood vessels and then migrates to the site of infection for defence. Macrophages can
713:
Treatment should resolve reversible pulpitis; early treating may help prevent irreversible pulpitis
560:
2371:
2265:
2182:
2136:
1996:
1393:
1335:
993:
901:
213:
777:
Spontaneous and unpredictable pain at any time, and specific causal factors cannot be identified
716:
Follow-up required to determine whether the reversible pulpitis has returned to a normal status
39:
27:
Part in the center of a tooth made up of living connective tissue and cells called odontoblasts
2750:
2667:
2363:
2316:
2298:
2288:
2257:
2217:
2174:
2126:
2062:
1988:
1949:
1908:
1873:
1777:
1759:
1720:
1669:
1594:
1563:
1529:
1446:
1381:
1371:
1323:
1313:
1212:
1124:
973:
527:
They are mainly located at the core of the pulp and extend underneath the odontoblastic layer.
166:
1498:
Langenbach F, Naujoks C, Smeets R, Berr K, Depprich R, Kübler N, Handschel J (January 2013).
2580:
2355:
2249:
2209:
2166:
2118:
2052:
2042:
1980:
1939:
1900:
1865:
1796:"Differential Diagnosis of Toothache Pain: Part 1, Odontogenic Etiologies | Dentistry Today"
1767:
1751:
1738:
Yoo, Hugo Hb; Nunes-Nogueira, Vania Santos; Fortes Villas Boas, Paulo J. (7 February 2020).
1710:
1700:
1659:
1555:
1519:
1511:
1436:
1426:
1204:
1116:
1025:
590:
247:, when the dentin forms around the dental papilla, the innermost tissue is considered pulp.
2384:
1968:
1192:
2841:
2544:
2517:
2442:
570:
224:
198:
2815:
2780:
2745:
2480:
2359:
2057:
2030:
1772:
1739:
1715:
1688:
1524:
1499:
1441:
1414:
872:
844:
759:
327:
292:
284:
217:
1091:
Problem
Solving in the Diagnosis of Odontogenic Pain in problem solving in endodontics
2860:
2737:
2537:
2213:
2186:
2029:
Farges JC, Alliot-Licht B, Renard E, Ducret M, Gaudin A, Smith AJ, Cooper PR (2015).
1869:
1664:
1647:
909:
792:
No pain on percussion because the bacteria are not present in the peri-apical region.
530:
C-Fibres have higher pain thresholds, responsible for detecting inflammatory threats.
288:
202:
174:
2375:
2269:
2140:
2000:
1464:
2800:
2714:
2627:
2527:
1755:
1191:
Rôças IN, Lima KC, Assunção IV, Gomes PN, Bracks IV, Siqueira JF (September 2015).
982:
917:
913:
763:
599:) or the sensory response of the nerves within the root canal to specific stimuli (
427:
419:
407:
395:
Cell-free zone (zone of Weil, which is rich in both capillaries and nerve networks.
280:
235:
because they are usually located on the lateral surface of the roots of the teeth.
510:
A-Fibres transmit signals to the brainstem and then to the contralateral thalamus.
447:
77:
2728:
2509:
1559:
986:
888:
884:
549:
415:
411:
403:
296:
250:
178:
2170:
2081:
1904:
1208:
1120:
1049:
212:
Radicular pulp canals extend down from the cervical region of the crown to the
2775:
2122:
1856:
Jafarzadeh H (June 2009). "Laser
Doppler flowmetry in endodontics: a review".
1515:
1007:. This decrease in cells is evident in the reduced number of undifferentiated
868:
734:
628:
In a healthy tooth, enamel and dentin layers protect the pulp from infection.
611:. A tooth that does not respond at all to sensitivity testing may have become
423:
389:
227:
organs is 0.38cc, and the mean volume of a single adult human pulp is 0.02cc.
137:
2302:
1992:
1763:
1431:
1385:
1327:
905:
786:
Pain may increase with changes of posture, e.g. from lying down to standing.
101:
17:
2367:
2261:
2221:
2178:
2066:
1953:
1912:
1877:
1781:
1724:
1673:
1533:
1465:"Dental Pulp Neurophysiology: Part 1. Clinical and Diagnostic Implications"
1450:
1216:
1128:
2047:
1705:
305:
The pulp develops in four regions from the periphery to the central pulp:
2641:
2532:
1004:
922:
892:
pulp tissue, and pulpitis and caries progression increase their numbers.
817:
612:
608:
430:. The nerve plexus of Raschkow is located central to the cell-rich zone.
2554:
2522:
2253:
1550:
Fried K, Gibbs JL (2014), Goldberg M (ed.), "Dental Pulp
Innervation",
730:
662:
206:
185:. The pulp's activity and signalling processes regulate its behaviour.
1984:
1944:
1927:
2810:
2285:
Ten Cate's oral histology : development, structure, and function
2200:
Goga R, Chandler NP, Oginni AO (June 2008). "Pulp stones: a review".
1368:
The dental pulp : biology, pathology, and regenerative therapies
880:
876:
751:
is a common presenting complaint that facilitates initial diagnosis.
577:
545:
440:
170:
2385:"Guideline on pulp therapy for primary and immature permanent teeth"
559:
Nutritive: the pulp keeps the organic components of the surrounding
126:
2086:
Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and
Disease. 5th Edition
839:
using doppler flowmetry. Sequelae of a necrotic pulp include acute
830:
electric pulp tests, leaving the patient unaware of the pathology.
796:
Key characteristics of asymptomatic irreversible pulpitis include:
871:
can sample and respond to the environment, involving macrophages,
773:
Key characteristics of symptomatic irreversible pulpitis include:
446:
326:
249:
182:
136:
60:
2449:
1269:
Antonio Nanci, Ten Cate's Oral
Histology, Elsevier, 2007, page 91
681:
Non-spontaneous and milder pain compared to irreversible pulpitis
2080:
Charles A Janeway J, Travers P, Walport M, Shlomchik MJ (2001).
1193:"Advanced Caries Microbiota in Teeth with Irreversible Pulpitis"
997:
908:. One important antimicrobial agent produced by odontoblasts is
803:
Pulp will respond to sensitiviity tests as a healthy pulp would.
388:
Cell-rich zone, which contains fibroblasts and undifferentiated
2453:
2421:
1740:"Anticoagulant treatment for subsegmental pulmonary embolism"
2031:"Dental Pulp Defence and Repair Mechanisms in Dental Caries"
1593:. India: Reed Elsevier India Private Limited. p. 29.
1312:. Frank, Marion E. (Marion Elizabeth), 1940-. Ames, Iowa.
1279:
766:, palpation), radiographic analysis (peri-apical and/or
1822:
1820:
569:
Defensive/reparative: the formation of reparative or
254:
SDEO: Dental pulp of a stained and decalcified tooth.
694:
X-rays to determine extent of decay and inflammation
655:
Excessive dehydration of a cavity during restoration
2736:
2727:
2697:
2676:
2650:
2640:
2610:
2589:
2563:
2553:
2508:
2487:
1969:"Tooth trauma: pathology and the treatment options"
729:When preparing cavities, dehydrate with sufficient
544:The primary function of the dental pulp is to form
107:
95:
83:
71:
59:
54:
49:
32:
2117:. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
1926:Eramo S, Natali A, Pinna R, Milia E (April 2018).
1239:"universal classification in endodontic diagnosis"
501:Have a relatively low-threshold sensory apparatus.
2383:American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. (2009).
2108:
2106:
2024:
2022:
1545:
1543:
1828:"Endodontic diagnosis: If it looks like a horse"
989:, traumatizing the pulp, resulting in pulpitis.
737:and apply sufficient varnish to protect the pulp
580:which surrounds and protects the pulpal tissue.
1554:, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp. 75–95,
2465:
1310:Fundamentals of oral histology and physiology
8:
2082:"Principles of innate and adaptive immunity"
1744:The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
1591:Prep Manual for Undergraduates: Endodontics
2733:
2647:
2560:
2472:
2458:
2450:
1928:"Dental pulp regeneration via cell homing"
1646:Michaelson PL, Holland GR (October 2002).
1413:Schuh CM, Benso B, Aguayo S (2019-09-18).
1398:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
1340:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
38:
2056:
2046:
1943:
1771:
1714:
1704:
1663:
1523:
1440:
1430:
992:Pulpitis can be painful and may call for
312:Cell-free zone – likely to be an artefact
287:, which gives rise to dental lamina. The
1620:. American Association of Endodontics.
1037:
864:activate innate and adaptive immunity.
402:Cells found in the dental pulp include
181:that comprise the innermost layer of a
2438:
2427:
2235:
2233:
2231:
2152:
2150:
1584:
1582:
1580:
1578:
1493:
1491:
1489:
1391:
1361:
1359:
1357:
1355:
1353:
1351:
1333:
684:Short sharp pain caused by a stimulant
678:Temporary post-restoration sensitivity
124:
29:
2007:from the original on 22 November 2018
576:Formative: cells of the pulp produce
563:supplied with moisture and nutrients;
7:
1627:from the original on 27 January 2021
1265:
1263:
1232:
1230:
1228:
1226:
1186:
1184:
1148:
1146:
1144:
1142:
1140:
1138:
1102:
1100:
1084:
1082:
1080:
1070:
1068:
1066:
1161:American Association of Endodontics
2360:10.1111/j.1834-7819.2007.tb00525.x
2242:Journal of Evidence-Based Medicine
1693:International Journal of Dentistry
789:Analgesics tend to be ineffective.
25:
1243:Journal of Multidisciplinary Care
1237:Glickman G, Schweitzer J (2016).
2214:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2008.01374.x
2202:International Endodontic Journal
1932:International Endodontic Journal
1870:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2009.01548.x
1858:International Endodontic Journal
1665:10.1046/j.1365-2591.2002.00579.x
1652:International Endodontic Journal
2405:from the original on 2018-08-26
2323:from the original on 2006-09-02
2092:from the original on 2019-05-12
1893:Dental Clinics of North America
1838:from the original on 2018-11-22
1806:from the original on 2018-11-10
1689:"Dental pulp testing: a review"
1475:from the original on 2020-02-18
1290:from the original on 2020-02-21
1249:from the original on 2019-04-16
1170:from the original on 2021-01-27
1089:Gutmann JL, Lovdahl PE (2011).
646:Bacterial infection from caries
141:Diagram showing pulp histology:
1756:10.1002/14651858.CD010222.pub4
1:
768:cone-beam computed tomography
668:Fractured tooth exposing pulp
658:Irritation of exposed dentine
1504:Clinical Oral Investigations
661:Repetitive trauma caused by
223:The total volume of all the
1967:Oxford M (1 January 2014).
1560:10.1007/978-3-642-55160-4_6
258:There are 4 main stages of
2888:
2500:Universal Numbering System
2171:10.1016/j.joen.2019.06.006
1905:10.1016/j.cden.2009.12.003
1687:Chen E, Abbott PV (2009).
1209:10.1016/j.joen.2015.05.013
1121:10.1016/j.joen.2007.01.006
916:(NO), a highly diffusible
847:and tooth discolouration.
588:
2837:
2824:
2791:
2766:
2348:Australian Dental Journal
2123:10.1007/978-3-642-55160-4
2035:Mediators of Inflammation
1516:10.1007/s00784-012-0887-x
1419:Frontiers in Pharmacology
1366:Goldberg M (2014-07-30).
555:Other functions include:
119:
37:
2113:Goldberg M, ed. (2014).
1432:10.3389/fphar.2019.01068
44:Section of a human molar
1832:www.dentaleconomics.com
859:Pulp response to caries
851:Prognosis and treatment
458:Cell-free zone of Weil;
331:Pulpal dentin junction.
197:central to each tooth,
148:Cell-free zone of Weil;
2806:Dental-enamel junction
2796:Cementoenamel junction
2758:Zuckerkandl's tubercle
2437:Cite journal requires
2283:Nanci A (2017-10-13).
2159:Journal of Endodontics
1800:www.dentistrytoday.com
1648:"Is pulpitis painful?"
1615:"Endodontic Diagnosis"
1308:Hand AR (2014-11-21).
1197:Journal of Endodontics
1154:"Endodontic diagnosis"
1109:Journal of Endodontics
1021:Dental pulp stem cells
783:Possible referred pain
689:Differential diagnosis
573:(by the odontoblasts);
523:Unmyelinated C-Fibres:
468:
434:The plexus of Raschkow
406:(the principal cell),
375:
255:
158:
121:Anatomical terminology
2495:Glossary of dentistry
945:Orthodontic treatment
843:, dental abscess, or
800:No clinical symptoms.
742:Irreversible pulpitis
450:
410:, defence cells like
344:odontoblastic process
330:
253:
140:
867:In uninfected pulp,
841:apical periodontitis
494:Myelinated A-Fibres:
335:outside tooth/enamel
285:ectomesenchyme cells
195:neurovascular bundle
2422:"The Pulp Official"
2165:(9): 1099–1105.e2.
2048:10.1155/2015/230251
1706:10.1155/2009/365785
948:Traumatic occlusion
902:Toll-like receptors
665:or jaw misalignment
632:Reversible pulpitis
515:hydrodynamic theory
479:fifth cranial nerve
451:Plexus of Raschkow:
2354:(1 Suppl): S4–16.
2254:10.1111/jebm.12331
994:root canal therapy
703:Electric pulp test
561:mineralized tissue
469:
455:Odontoblast layer;
376:
323:Internal structure
256:
159:
145:Odontoblast layer;
2872:Tissues (biology)
2854:
2853:
2850:
2849:
2751:Cusp of Carabelli
2723:
2722:
2636:
2635:
2294:978-0-323-48524-1
2132:978-3-642-55159-8
1985:10.1136/inp.f7208
1945:10.1111/iej.12868
1834:. December 2007.
1600:978-81-312-1056-7
1569:978-3-642-55159-8
1377:978-3-642-55160-4
1319:978-1-118-93831-7
1093:(Fifth ed.).
1009:mesenchymal cells
939:Pulp degeneration
726:Regular check-ups
309:Odontoblast layer
260:tooth development
167:connective tissue
135:
134:
130:
16:(Redirected from
2879:
2734:
2648:
2561:
2474:
2467:
2460:
2451:
2446:
2440:
2435:
2433:
2425:
2413:
2411:
2410:
2404:
2389:
2379:
2332:
2331:
2329:
2328:
2313:
2307:
2306:
2280:
2274:
2273:
2237:
2226:
2225:
2197:
2191:
2190:
2154:
2145:
2144:
2110:
2101:
2100:
2098:
2097:
2077:
2071:
2070:
2060:
2050:
2026:
2017:
2016:
2014:
2012:
1964:
1958:
1957:
1947:
1923:
1917:
1916:
1888:
1882:
1881:
1853:
1847:
1846:
1844:
1843:
1824:
1815:
1814:
1812:
1811:
1792:
1786:
1785:
1775:
1735:
1729:
1728:
1718:
1708:
1684:
1678:
1677:
1667:
1643:
1637:
1636:
1634:
1632:
1626:
1619:
1611:
1605:
1604:
1589:Hedge J (2008).
1586:
1573:
1572:
1547:
1538:
1537:
1527:
1495:
1484:
1483:
1481:
1480:
1461:
1455:
1454:
1444:
1434:
1410:
1404:
1403:
1397:
1389:
1363:
1346:
1345:
1339:
1331:
1305:
1299:
1298:
1296:
1295:
1276:
1270:
1267:
1258:
1257:
1255:
1254:
1234:
1221:
1220:
1188:
1179:
1178:
1176:
1175:
1169:
1158:
1150:
1133:
1132:
1104:
1095:
1094:
1086:
1075:
1072:
1061:
1060:
1058:
1057:
1048:. Archived from
1042:
1026:Dental pulp test
974:dentinal tubules
601:Sensitivity Test
591:Dental pulp test
472:Pulp innervation
193:The pulp is the
127:edit on Wikidata
42:
30:
21:
2887:
2886:
2882:
2881:
2880:
2878:
2877:
2876:
2857:
2856:
2855:
2846:
2842:Dental alveolus
2833:
2820:
2787:
2762:
2719:
2693:
2689:Second premolar
2672:
2663:Lateral incisor
2658:Central incisor
2632:
2606:
2602:Second premolar
2585:
2576:Lateral incisor
2571:Central incisor
2549:
2504:
2483:
2478:
2436:
2426:
2419:
2416:
2408:
2406:
2402:
2387:
2382:
2345:
2341:
2339:Further reading
2336:
2335:
2326:
2324:
2315:
2314:
2310:
2295:
2282:
2281:
2277:
2239:
2238:
2229:
2199:
2198:
2194:
2156:
2155:
2148:
2133:
2115:The Dental Pulp
2112:
2111:
2104:
2095:
2093:
2079:
2078:
2074:
2028:
2027:
2020:
2010:
2008:
1966:
1965:
1961:
1925:
1924:
1920:
1890:
1889:
1885:
1855:
1854:
1850:
1841:
1839:
1826:
1825:
1818:
1809:
1807:
1794:
1793:
1789:
1750:(2): CD010222.
1737:
1736:
1732:
1686:
1685:
1681:
1645:
1644:
1640:
1630:
1628:
1624:
1617:
1613:
1612:
1608:
1601:
1588:
1587:
1576:
1570:
1552:The Dental Pulp
1549:
1548:
1541:
1497:
1496:
1487:
1478:
1476:
1463:
1462:
1458:
1412:
1411:
1407:
1390:
1378:
1365:
1364:
1349:
1332:
1320:
1307:
1306:
1302:
1293:
1291:
1278:
1277:
1273:
1268:
1261:
1252:
1250:
1236:
1235:
1224:
1190:
1189:
1182:
1173:
1171:
1167:
1156:
1152:
1151:
1136:
1106:
1105:
1098:
1088:
1087:
1078:
1073:
1064:
1055:
1053:
1044:
1043:
1039:
1034:
1017:
1005:collagen fibers
969:
932:
873:dendritic cells
861:
853:
836:
827:
814:
744:
723:
710:
691:
675:
643:
634:
626:
621:
593:
587:
571:tertiary dentin
542:
474:
467:
461:Cell-rich zone;
436:
374:
325:
241:
225:permanent teeth
191:
157:
151:Cell-rich zone;
131:
45:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2885:
2883:
2875:
2874:
2869:
2867:Parts of tooth
2859:
2858:
2852:
2851:
2848:
2847:
2845:
2844:
2838:
2835:
2834:
2832:
2831:
2825:
2822:
2821:
2819:
2818:
2816:Dental papilla
2813:
2808:
2803:
2798:
2792:
2789:
2788:
2786:
2785:
2784:
2783:
2781:Apical foramen
2773:
2767:
2764:
2763:
2761:
2760:
2755:
2754:
2753:
2742:
2740:
2731:
2725:
2724:
2721:
2720:
2718:
2717:
2712:
2707:
2701:
2699:
2695:
2694:
2692:
2691:
2686:
2684:First premolar
2680:
2678:
2674:
2673:
2671:
2670:
2665:
2660:
2654:
2652:
2645:
2638:
2637:
2634:
2633:
2631:
2630:
2625:
2620:
2614:
2612:
2608:
2607:
2605:
2604:
2599:
2597:First premolar
2593:
2591:
2587:
2586:
2584:
2583:
2578:
2573:
2567:
2565:
2558:
2551:
2550:
2548:
2547:
2542:
2541:
2540:
2535:
2530:
2525:
2514:
2512:
2506:
2505:
2503:
2502:
2497:
2491:
2489:
2485:
2484:
2481:Dental anatomy
2479:
2477:
2476:
2469:
2462:
2454:
2448:
2447:
2439:|journal=
2415:
2414:
2380:
2342:
2340:
2337:
2334:
2333:
2308:
2293:
2275:
2248:(2): 133–139.
2227:
2192:
2146:
2131:
2102:
2072:
2018:
1959:
1938:(4): 405–419.
1918:
1883:
1848:
1816:
1787:
1730:
1679:
1658:(10): 829–32.
1638:
1606:
1599:
1574:
1568:
1539:
1485:
1469:www.cda-adc.ca
1456:
1405:
1376:
1370:. Heidelberg.
1347:
1318:
1300:
1284:www.sdeo.ac.uk
1271:
1259:
1222:
1180:
1134:
1096:
1076:
1062:
1036:
1035:
1033:
1030:
1029:
1028:
1023:
1016:
1013:
968:
965:
953:
952:
949:
946:
943:
942:Increasing age
940:
931:
928:
910:beta-defensins
860:
857:
852:
849:
845:radicular cyst
835:
832:
826:
823:
813:
810:
805:
804:
801:
794:
793:
790:
787:
784:
781:
778:
760:ethyl chloride
743:
740:
739:
738:
727:
722:
719:
718:
717:
714:
709:
706:
705:
704:
701:
698:
695:
690:
687:
686:
685:
682:
679:
674:
671:
670:
669:
666:
659:
656:
653:
650:
647:
642:
639:
633:
630:
625:
622:
620:
619:Pulp diagnoses
617:
589:Main article:
586:
583:
582:
581:
574:
567:
564:
541:
538:
537:
536:
535:
534:
531:
528:
520:
519:
518:
511:
508:
505:
502:
499:
473:
470:
466:
465:
462:
459:
456:
452:
439:belong to the
435:
432:
400:
399:
396:
393:
386:
373:
372:
369:
368:cell-poor zone
366:
365:cell-rich zone
363:
360:
357:
354:
351:
348:
345:
342:
339:
336:
332:
324:
321:
320:
319:
316:
315:Cell-rich zone
313:
310:
293:dental papilla
277:
276:
273:
270:
267:
240:
237:
233:lateral canals
218:apical foramen
190:
187:
156:
155:
152:
149:
146:
142:
133:
132:
123:
117:
116:
111:
105:
104:
99:
93:
92:
87:
81:
80:
75:
69:
68:
63:
57:
56:
52:
51:
47:
46:
43:
35:
34:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2884:
2873:
2870:
2868:
2865:
2864:
2862:
2843:
2840:
2839:
2836:
2830:
2827:
2826:
2823:
2817:
2814:
2812:
2809:
2807:
2804:
2802:
2799:
2797:
2794:
2793:
2790:
2782:
2779:
2778:
2777:
2774:
2772:
2769:
2768:
2765:
2759:
2756:
2752:
2749:
2748:
2747:
2744:
2743:
2741:
2739:
2735:
2732:
2730:
2726:
2716:
2713:
2711:
2708:
2706:
2703:
2702:
2700:
2696:
2690:
2687:
2685:
2682:
2681:
2679:
2675:
2669:
2666:
2664:
2661:
2659:
2656:
2655:
2653:
2649:
2646:
2643:
2639:
2629:
2626:
2624:
2621:
2619:
2616:
2615:
2613:
2609:
2603:
2600:
2598:
2595:
2594:
2592:
2588:
2582:
2579:
2577:
2574:
2572:
2569:
2568:
2566:
2562:
2559:
2556:
2552:
2546:
2543:
2539:
2536:
2534:
2531:
2529:
2526:
2524:
2521:
2520:
2519:
2516:
2515:
2513:
2511:
2507:
2501:
2498:
2496:
2493:
2492:
2490:
2486:
2482:
2475:
2470:
2468:
2463:
2461:
2456:
2455:
2452:
2444:
2431:
2423:
2418:
2417:
2401:
2398:(6): 179–86.
2397:
2393:
2386:
2381:
2377:
2373:
2369:
2365:
2361:
2357:
2353:
2349:
2344:
2343:
2338:
2322:
2318:
2312:
2309:
2304:
2300:
2296:
2290:
2286:
2279:
2276:
2271:
2267:
2263:
2259:
2255:
2251:
2247:
2243:
2236:
2234:
2232:
2228:
2223:
2219:
2215:
2211:
2208:(6): 457–68.
2207:
2203:
2196:
2193:
2188:
2184:
2180:
2176:
2172:
2168:
2164:
2160:
2153:
2151:
2147:
2142:
2138:
2134:
2128:
2124:
2120:
2116:
2109:
2107:
2103:
2091:
2087:
2083:
2076:
2073:
2068:
2064:
2059:
2054:
2049:
2044:
2040:
2036:
2032:
2025:
2023:
2019:
2006:
2002:
1998:
1994:
1990:
1986:
1982:
1978:
1974:
1970:
1963:
1960:
1955:
1951:
1946:
1941:
1937:
1933:
1929:
1922:
1919:
1914:
1910:
1906:
1902:
1899:(2): 237–47.
1898:
1894:
1887:
1884:
1879:
1875:
1871:
1867:
1864:(6): 476–90.
1863:
1859:
1852:
1849:
1837:
1833:
1829:
1823:
1821:
1817:
1805:
1801:
1797:
1791:
1788:
1783:
1779:
1774:
1769:
1765:
1761:
1757:
1753:
1749:
1745:
1741:
1734:
1731:
1726:
1722:
1717:
1712:
1707:
1702:
1698:
1694:
1690:
1683:
1680:
1675:
1671:
1666:
1661:
1657:
1653:
1649:
1642:
1639:
1623:
1616:
1610:
1607:
1602:
1596:
1592:
1585:
1583:
1581:
1579:
1575:
1571:
1565:
1561:
1557:
1553:
1546:
1544:
1540:
1535:
1531:
1526:
1521:
1517:
1513:
1509:
1505:
1501:
1494:
1492:
1490:
1486:
1474:
1470:
1466:
1460:
1457:
1452:
1448:
1443:
1438:
1433:
1428:
1424:
1420:
1416:
1409:
1406:
1401:
1395:
1387:
1383:
1379:
1373:
1369:
1362:
1360:
1358:
1356:
1354:
1352:
1348:
1343:
1337:
1329:
1325:
1321:
1315:
1311:
1304:
1301:
1289:
1285:
1281:
1275:
1272:
1266:
1264:
1260:
1248:
1244:
1240:
1233:
1231:
1229:
1227:
1223:
1218:
1214:
1210:
1206:
1203:(9): 1450–5.
1202:
1198:
1194:
1187:
1185:
1181:
1166:
1162:
1155:
1149:
1147:
1145:
1143:
1141:
1139:
1135:
1130:
1126:
1122:
1118:
1115:(5): 548–51.
1114:
1110:
1103:
1101:
1097:
1092:
1085:
1083:
1081:
1077:
1071:
1069:
1067:
1063:
1052:on 2017-02-20
1051:
1047:
1046:"Endodontium"
1041:
1038:
1031:
1027:
1024:
1022:
1019:
1018:
1014:
1012:
1010:
1006:
1001:
999:
995:
990:
988:
984:
979:
975:
967:Complications
966:
964:
961:
957:
951:Dental caries
950:
947:
944:
941:
938:
937:
936:
929:
927:
925:
924:
919:
915:
911:
907:
903:
897:
893:
890:
886:
882:
878:
874:
870:
865:
858:
856:
850:
848:
846:
842:
833:
831:
824:
822:
819:
812:Pulp necrosis
811:
809:
802:
799:
798:
797:
791:
788:
785:
782:
779:
776:
775:
774:
771:
769:
765:
761:
756:
752:
748:
741:
736:
732:
728:
725:
724:
720:
715:
712:
711:
707:
702:
699:
696:
693:
692:
688:
683:
680:
677:
676:
672:
667:
664:
660:
657:
654:
651:
649:Thermal shock
648:
645:
644:
641:Common causes
640:
638:
631:
629:
623:
618:
616:
614:
610:
604:
602:
598:
597:Vitality Test
592:
584:
579:
575:
572:
568:
565:
562:
558:
557:
556:
553:
551:
547:
539:
532:
529:
526:
525:
524:
521:
516:
512:
509:
506:
503:
500:
497:
496:
495:
492:
491:
490:
486:
482:
480:
471:
463:
460:
457:
454:
453:
449:
445:
442:
433:
431:
429:
425:
421:
417:
413:
409:
405:
397:
394:
391:
387:
384:
383:
382:
379:
370:
367:
364:
361:
358:
355:
352:
349:
346:
343:
340:
338:dentin tubule
337:
334:
333:
329:
322:
317:
314:
311:
308:
307:
306:
303:
300:
298:
294:
290:
289:dental lamina
286:
282:
274:
271:
268:
265:
264:
263:
261:
252:
248:
246:
245:odontogenesis
238:
236:
234:
228:
226:
221:
220:or foramina.
219:
215:
210:
208:
204:
200:
196:
188:
186:
184:
180:
176:
175:blood vessels
172:
168:
164:
153:
150:
147:
144:
143:
139:
128:
122:
118:
115:
112:
110:
106:
103:
100:
98:
94:
91:
88:
86:
82:
79:
76:
74:
70:
67:
64:
62:
58:
53:
48:
41:
36:
31:
19:
2770:
2710:Second molar
2623:Second molar
2488:Nomenclature
2430:cite journal
2407:. Retrieved
2395:
2392:Pediatr Dent
2391:
2351:
2347:
2325:. Retrieved
2311:
2287:. Elsevier.
2284:
2278:
2245:
2241:
2205:
2201:
2195:
2162:
2158:
2114:
2094:. Retrieved
2085:
2075:
2038:
2034:
2009:. Retrieved
1976:
1972:
1962:
1935:
1931:
1921:
1896:
1892:
1886:
1861:
1857:
1851:
1840:. Retrieved
1831:
1808:. Retrieved
1799:
1790:
1747:
1743:
1733:
1696:
1692:
1682:
1655:
1651:
1641:
1629:. Retrieved
1609:
1590:
1551:
1507:
1503:
1477:. Retrieved
1468:
1459:
1422:
1418:
1408:
1367:
1309:
1303:
1292:. Retrieved
1283:
1274:
1251:. Retrieved
1242:
1200:
1196:
1172:. Retrieved
1160:
1112:
1108:
1090:
1054:. Retrieved
1050:the original
1040:
1002:
998:nerve fibres
991:
983:pulp capping
970:
962:
958:
954:
933:
921:
918:free radical
914:nitric oxide
898:
894:
866:
862:
854:
837:
828:
815:
806:
795:
772:
764:gutta percha
757:
753:
749:
745:
635:
627:
605:
600:
596:
594:
585:Pulp testing
554:
550:odontoblasts
543:
522:
514:
493:
487:
483:
478:
475:
437:
428:plasma cells
420:granulocytes
408:odontoblasts
401:
380:
377:
371:pulp chamber
304:
301:
297:odontoblasts
278:
257:
242:
232:
229:
222:
211:
192:
179:odontoblasts
162:
160:
90:A05.1.03.051
66:pulpa dentis
65:
18:Pulp chamber
2715:Third molar
2705:First molar
2628:Third molar
2618:First molar
2011:22 November
1979:(1): 2–14.
1973:In Practice
1510:(1): 9–17.
987:mastication
930:Pulp stones
889:phagocytose
885:endothelial
762:, EPT, hot-
624:Normal pulp
416:macrophages
412:histiocytes
404:fibroblasts
390:mesenchymal
362:artery/vein
356:fibroblasts
353:capillaries
350:odontoblast
281:invaginates
275:Crown stage
239:Development
55:Identifiers
2861:Categories
2776:Root canal
2642:Mandibular
2409:2013-07-30
2327:2022-04-16
2096:2020-02-21
2041:: 230251.
1842:2018-11-22
1810:2018-11-22
1699:: 365785.
1479:2020-02-21
1294:2020-02-21
1253:2018-11-22
1174:2018-11-22
1056:2013-07-23
1032:References
906:chemokines
869:leukocytes
735:chloroform
721:Prevention
441:myelinated
424:mast cells
272:Bell stage
2555:Maxillary
2545:Deciduous
2518:Permanent
2303:990257609
2187:198966934
1993:0263-841X
1764:1469-493X
1394:cite book
1386:885561103
1336:cite book
1328:891186059
976:pass the
834:Diagnosis
708:Treatment
540:Functions
464:Pulp core
347:predentin
318:Pulp core
269:Cap stage
266:Bud stage
214:root apex
199:permanent
154:Pulp core
2677:Premolar
2590:Premolar
2533:premolar
2400:Archived
2376:11342369
2368:17546858
2321:Archived
2270:53945208
2262:30461204
2222:18422587
2179:31351581
2141:78890480
2090:Archived
2067:26538821
2005:Archived
2001:76350641
1954:29047120
1913:20433976
1878:19459999
1836:Archived
1804:Archived
1782:32030721
1725:20339575
1674:12406376
1631:14 March
1622:Archived
1534:22695872
1473:Archived
1451:31620000
1425:: 1068.
1288:Archived
1247:Archived
1217:26187422
1165:Archived
1163:. 2013.
1129:17437869
1015:See also
978:stimulus
923:in vitro
825:Symptoms
818:necrosis
673:Symptoms
613:necrotic
609:pulpitis
548:(by the
2829:Mamelon
2651:Incisor
2564:Incisor
2523:incisor
2058:4619960
1773:7004894
1716:2837315
1525:3585766
1442:6759635
881:B cells
877:T cells
875:(DCs),
731:alcohol
663:bruxism
207:dentine
203:primary
189:Anatomy
165:is the
78:D003782
50:Details
2811:Dentin
2801:Enamel
2668:Canine
2581:Canine
2528:canine
2374:
2366:
2301:
2291:
2268:
2260:
2220:
2185:
2177:
2139:
2129:
2065:
2055:
1999:
1991:
1952:
1911:
1876:
1780:
1770:
1762:
1723:
1713:
1672:
1597:
1566:
1532:
1522:
1449:
1439:
1384:
1374:
1326:
1316:
1280:"SDEO"
1215:
1127:
652:Trauma
578:dentin
546:dentin
426:, and
392:cells.
341:dentin
177:, and
171:nerves
2738:Crown
2729:Parts
2698:Molar
2644:teeth
2611:Molar
2557:teeth
2538:molar
2510:Teeth
2403:(PDF)
2388:(PDF)
2372:S2CID
2266:S2CID
2183:S2CID
2137:S2CID
1997:S2CID
1625:(PDF)
1618:(PDF)
1168:(PDF)
1157:(PDF)
816:Pulp
359:nerve
283:into
183:tooth
125:[
114:55631
61:Latin
2771:Pulp
2746:Cusp
2443:help
2364:PMID
2299:OCLC
2289:ISBN
2258:PMID
2218:PMID
2175:PMID
2127:ISBN
2063:PMID
2039:2015
2013:2018
1989:ISSN
1950:PMID
1909:PMID
1874:PMID
1778:PMID
1760:ISSN
1748:2020
1721:PMID
1697:2009
1670:PMID
1633:2018
1595:ISBN
1564:ISBN
1530:PMID
1447:PMID
1400:link
1382:OCLC
1372:ISBN
1342:link
1324:OCLC
1314:ISBN
1213:PMID
1125:PMID
879:and
163:pulp
161:The
85:TA98
73:MeSH
33:Pulp
2356:doi
2250:doi
2210:doi
2167:doi
2119:doi
2053:PMC
2043:doi
1981:doi
1940:doi
1901:doi
1866:doi
1768:PMC
1752:doi
1711:PMC
1701:doi
1660:doi
1556:doi
1520:PMC
1512:doi
1437:PMC
1427:doi
1205:doi
1117:doi
552:).
201:or
109:FMA
102:934
97:TA2
2863::
2434::
2432:}}
2428:{{
2396:31
2394:.
2390:.
2370:.
2362:.
2352:52
2350:.
2319:.
2297:.
2264:.
2256:.
2246:12
2244:.
2230:^
2216:.
2206:41
2204:.
2181:.
2173:.
2163:45
2161:.
2149:^
2135:.
2125:.
2105:^
2088:.
2084:.
2061:.
2051:.
2037:.
2033:.
2021:^
2003:.
1995:.
1987:.
1977:36
1975:.
1971:.
1948:.
1936:51
1934:.
1930:.
1907:.
1897:54
1895:.
1872:.
1862:42
1860:.
1830:.
1819:^
1802:.
1798:.
1776:.
1766:.
1758:.
1746:.
1742:.
1719:.
1709:.
1695:.
1691:.
1668:.
1656:35
1654:.
1650:.
1577:^
1562:,
1542:^
1528:.
1518:.
1508:17
1506:.
1502:.
1488:^
1471:.
1467:.
1445:.
1435:.
1423:10
1421:.
1417:.
1396:}}
1392:{{
1380:.
1350:^
1338:}}
1334:{{
1322:.
1286:.
1282:.
1262:^
1245:.
1241:.
1225:^
1211:.
1201:41
1199:.
1195:.
1183:^
1159:.
1137:^
1123:.
1113:33
1111:.
1099:^
1079:^
1065:^
926:.
615:.
422:,
418:,
414:,
262::
173:,
169:,
2473:e
2466:t
2459:v
2445:)
2441:(
2424:.
2412:.
2378:.
2358::
2330:.
2305:.
2272:.
2252::
2224:.
2212::
2189:.
2169::
2143:.
2121::
2099:.
2069:.
2045::
2015:.
1983::
1956:.
1942::
1915:.
1903::
1880:.
1868::
1845:.
1813:.
1784:.
1754::
1727:.
1703::
1676:.
1662::
1635:.
1603:.
1558::
1536:.
1514::
1482:.
1453:.
1429::
1402:)
1388:.
1344:)
1330:.
1297:.
1256:.
1219:.
1207::
1177:.
1131:.
1119::
1059:.
733:/
129:]
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.