1529:
26:
332:
as well as being traversed by nerve fibers involved in eye movements that elsewhere; dysfunction of horizontal saccades will additionally also indirectly disrupt (slow and misdirect) vertical saccades (though slowing of all saccades may also be accounted for by destruction of adjacent omnipause neurons of the interposited raphe nucleus).
331:
Destructive lesions of the PPRF cause ipsilateral horizontal conjugate gaze palsy and mostly impair ipsilateral horizontal saccades, however, other horizontal and vertical eye movements may also be affected as the PPRF contains multiple distinct populations of neurons important in saccade generation,
322:
The PPRF generates excitatory bursts that are delivered to the ipsilateral abduecens nucleus to drive ipsilateral saccades (inhibitory saccadic stimuli are meanwhile delivered to the abducens nucleus from the contralateral medulla oblongata).
339:
characterised by quick twitches directed contralaterally whereas ipsilateral twitches are slow and do not move beyond the midline. More extensive lesions will also affect inhibition of antagonists, abolishing ipsilateral saccades.
410:
202:
The PPRF (and adjacent regions of the pons) are traversed by fibers projecting to the abducens nucleus that mediate smooth pursuit, vestibular reflexes, and gaze holding.
351:
of the medial pontine regions are relatively common. Due to the small size of the arteries in the area, the most common cause of a local lesion is an infarction due to
942:
785:
1275:
335:
In the short-term, unilateral lesions of the PPRF may be characterised clinically by contralateral deviation of the eyes; looking contralaterally induces
463:, respectively - their silmuntaneous contraction will thus cause both eyes to move ipsilaterally (i.e. towards the side of the PPRF in question).
699:
674:
646:
606:
576:
536:
504:
1223:
1503:
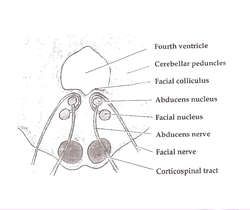
1213:
1023:
824:
148:
114:
1268:
1014:
934:
1218:
884:
846:
733:
280:
192:
144:
899:
1082:
894:
872:
416:
188:
1077:
978:
851:
1261:
1163:
1458:
1288:
1032:
1027:
1000:
966:
947:
877:
1572:
1564:
1089:
1052:
1004:
775:
1428:
1343:
1072:
961:
841:
819:
638:
421:
379:
Loss of horizontal saccades directed towards the side of the lesion, no matter the current position of gaze
1528:
1378:
1168:
770:
368:
1158:
915:
889:
456:
312:
273:
1338:
25:
1598:
1463:
1438:
1403:
1240:
1111:
1009:
814:
460:
390:
288:
227:
219:
107:
556:
1518:
1508:
1368:
1363:
1328:
1208:
1153:
1067:
239:
1398:
1373:
1353:
1062:
726:
284:
215:
196:
160:
1549:
1603:
1423:
1358:
973:
836:
790:
754:
695:
670:
642:
602:
601:(10th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 156.
572:
532:
500:
244:
164:
35:
1613:
1483:
1453:
1443:
1408:
1284:
1148:
1057:
1018:
956:
831:
564:
426:
397:
269:
184:
156:
68:
39:
1618:
1498:
1493:
1478:
1393:
1313:
1094:
780:
295:
The pararaphal nucleus - one of distinct neuron population in the PPRF - projects to the
159:. It projects to the ipsilateral abducens (cranial nerve VI) nucleus, and contralateral
1513:
1488:
1468:
1448:
1348:
1323:
1186:
1129:
809:
568:
352:
316:
259:
1639:
1633:
1388:
1333:
719:
360:
231:
1413:
1383:
1235:
1139:
863:
800:
356:
311:
The PPRF mediates horizontal conjugate eye movements. It is important in mediating
223:
1433:
1121:
911:
375:, respectively. Unilateral lesions of the PPRF produce characteristic findings:
1556:
1473:
1418:
1303:
431:
372:
364:
300:
102:
56:
287:(specifically the population of its neurons that innervate the contralateral
1580:
1318:
336:
296:
1253:
262:(i.e. simultaneous horizontal movement of both eyes) by projecting to both:
359:. Like other small arteries of the brain, these vessels are vulnerable to
1608:
1308:
120:
436:
168:
711:
1543:
383:
348:
63:
499:(2nd ed.). Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell. p. 310.
90:
743:
694:(3rd ed.). New York: Oxford University Press. p. 661.
180:
152:
75:
31:
1257:
715:
455:
These two cranial nerve nuclei in turn control the ipsilateral
230:). The frontal eye field meanwhile receives afferents from the
555:
Loftus, Brian D.; Athni, Sudhir S.; Cherches, Igor M. (2010),
411:
Rostral interstitial nucleus of medial longitudinal fasciculus
382:
Contralateral gaze deviation (acute lesions, such as early
637:. Contemporary Neurology Series (3rd ed.). New York:
527:
Brazis, Paul W.; Masdeu, Joseph C.; Biller, José (2022).
599:
Barr's The Human
Nervous System: An Anatomical Viewpoint
531:(8th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health.
1591:
1536:
1296:
1199:
1179:
1138:
1120:
1107:
1045:
989:
923:
910:
862:
799:
763:
750:
101:
89:
84:
74:
62:
52:
47:
18:
151:mediating horizontal gaze. It is situated in the
597:Kiernan, John A.; Rajakumar, Nagalingam (2013).
495:Patestas, Maria A.; Gartner, Leslie P. (2016).
38:(PPRF not labeled, but region is visible, near
1269:
727:
8:
393:on looking away from the side of the lesion
1276:
1262:
1254:
1117:
920:
760:
734:
720:
712:
24:
476:
448:
249:other parts of the reticular formation.
96:formatio reticularis pontis paramediana
660:
658:
633:Leigh, R. John; Zee, David S. (1999).
161:oculomotor (cranial nerve III) nucleus
133:paramedian pontine reticular formation
118:
19:Paramedian pontine reticular formation
15:
195:. It is continuous caudally with the
7:
628:
626:
624:
622:
620:
618:
550:
548:
522:
520:
518:
516:
490:
488:
486:
484:
482:
480:
363:, especially those generated due to
80:Transverse and lateral pontine veins
692:Neuroanatomy through Clinical Cases
569:10.1016/b978-0-323-05712-7.00002-7
529:Localization in Clinical Neurology
210:The PPRF receives afferents from:
165:conjugate horizontal eye movements
14:
367:or low-flow states in those with
315:. It is probably not involved in
1527:
400:and slowing of vertical saccades
272:(which controls the ipsilateral
143:) is a subset of neurons of the
115:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
149:caudal pontine reticular nuclei
885:Medial longitudinal fasciculus
847:Medial longitudinal fasciculus
669:(12th ed.). p. 404.
665:Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011).
635:The Neurology of Eye Movements
281:medial longitudinal fasciculus
193:medial longitudinal fasciculus
1:
900:Lateral vestibulospinal tract
197:nucleus prepositus hypoglossi
1083:Lateral parabrachial nucleus
895:Medial vestibulospinal tract
873:Inferior cerebellar peduncle
417:Internuclear ophthalmoplegia
179:The PPRF is situated in the
1078:Medial parabrachial nucleus
852:Vestibulo-oculomotor fibers
285:oculomotor (CN III) nucleus
1656:
497:A Textbook of Neuroanatomy
396:Bilateral lesions produce
183:just ventralmedial to the
1525:
1033:Inferior salivary nucleus
1028:Superior salivary nucleus
878:Vestibulocerebellar tract
260:horizontal conjugate gaze
113:
23:
1565:Ascending and Descending
1090:Superior olivary nucleus
1053:Pedunculopontine nucleus
1005:Trigeminal motor nucleus
825:Ventral trigeminal tract
776:Superior medullary velum
690:Blumenfeld, Hal (2021).
563:, Elsevier, p. 42,
270:abducens (CN VI) nucleus
1073:Subparabrachial nucleus
842:Central tegmental tract
820:Dorsal trigeminal tract
639:Oxford University Press
557:"Clinical Neuroanatomy"
422:One and a half syndrome
413:- vertical gaze center.
369:artificial heart valves
1169:Pontocerebellar fibers
771:Cerebellopontine angle
313:saccadic eye movements
1159:Corticopontine fibers
890:Vestibulospinal tract
457:lateral rectus muscle
398:horizontal gaze palsy
344:Clinical significance
274:lateral rectus muscle
30:Axial section of the
1599:Accidental viewpoint
1010:Facial motor nucleus
815:Trigeminal lemniscus
461:medial rectus muscle
459:, and contralateral
389:Gaze-evoked lateral
289:medial rectus muscle
283:) the contralateral
228:frontopontine fibers
220:middle frontal gyrus
141:paraabducens nucleus
34:at the level of the
1504:Vertical–horizontal
1209:Reticular formation
1154:Corticobulbar tract
1149:Corticospinal tract
1068:Parabrachial nuclei
240:superior colliculus
191:and lateral to the
1604:Auditory illusions
1399:Impossible trident
1200:Other grey: Raphe/
1142:: Motor/descending
1063:Pneumotaxic center
1046:Grey: Other nuclei
258:The PPRF mediates
1627:
1626:
1619:Temporal illusion
1614:Tactile illusions
1584:(2015 photograph)
1285:Optical illusions
1251:
1250:
1195:
1194:
1103:
1102:
1041:
1040:
974:Vestibular nuclei
837:Lateral lemniscus
791:Facial colliculus
701:978-1-60535-962-5
676:978-0-7295-3752-0
648:978-0-19-512972-4
608:978-1-4511-7327-7
578:978-0-323-05712-7
561:Neurology Secrets
538:978-1-9751-6024-1
506:978-1-118-67746-9
245:vestibular nuclei
216:frontal eye field
139:) (also known as
129:
128:
124:
36:facial colliculus
1647:
1531:
1484:Schroeder stairs
1459:Peripheral drift
1454:Penrose triangle
1278:
1271:
1264:
1255:
1118:
1058:Apneustic center
1019:Abducens nucleus
994:
957:Cochlear nucleus
928:
921:
832:Medial lemniscus
761:
736:
729:
722:
713:
706:
705:
687:
681:
680:
662:
653:
652:
630:
613:
612:
594:
588:
587:
586:
585:
552:
543:
542:
524:
511:
510:
492:
464:
453:
427:Ophthalmoparesis
268:the ipsilateral
187:. It is located
185:abducens nucleus
157:abducens nucleus
155:adjacent to the
121:edit on Wikidata
69:Pontine arteries
40:abducens nucleus
28:
16:
1655:
1654:
1650:
1649:
1648:
1646:
1645:
1644:
1630:
1629:
1628:
1623:
1587:
1537:Popular culture
1532:
1523:
1494:Spinning dancer
1314:Ambiguous image
1292:
1282:
1252:
1247:
1201:
1191:
1175:
1134:
1109:
1099:
1095:Locus coeruleus
1037:
990:
985:
924:
906:
858:
795:
786:Medial eminence
781:Sulcus limitans
752:
746:
742:Anatomy of the
740:
710:
709:
702:
689:
688:
684:
677:
664:
663:
656:
649:
632:
631:
616:
609:
596:
595:
591:
583:
581:
579:
554:
553:
546:
539:
526:
525:
514:
507:
494:
493:
478:
473:
468:
467:
454:
450:
445:
407:
346:
329:
327:Pathophysiology
309:
256:
208:
177:
125:
43:
12:
11:
5:
1653:
1651:
1643:
1642:
1632:
1631:
1625:
1624:
1622:
1621:
1616:
1611:
1606:
1601:
1595:
1593:
1589:
1588:
1586:
1585:
1577:
1576:(1961 drawing)
1569:
1568:(1960 drawing)
1561:
1553:
1546:
1540:
1538:
1534:
1533:
1526:
1524:
1522:
1521:
1516:
1511:
1506:
1501:
1496:
1491:
1489:Shepard tables
1486:
1481:
1476:
1471:
1466:
1461:
1456:
1451:
1449:Penrose stairs
1446:
1441:
1436:
1431:
1426:
1421:
1416:
1411:
1406:
1401:
1396:
1391:
1386:
1381:
1376:
1371:
1366:
1361:
1356:
1351:
1346:
1344:Checker shadow
1341:
1336:
1331:
1326:
1324:Autostereogram
1321:
1316:
1311:
1306:
1300:
1298:
1294:
1293:
1283:
1281:
1280:
1273:
1266:
1258:
1249:
1248:
1246:
1245:
1244:
1243:
1233:
1232:
1231:
1226:
1221:
1216:
1205:
1203:
1197:
1196:
1193:
1192:
1190:
1189:
1187:Basilar sulcus
1183:
1181:
1177:
1176:
1174:
1173:
1172:
1171:
1161:
1156:
1151:
1145:
1143:
1136:
1135:
1133:
1132:
1130:Pontine nuclei
1126:
1124:
1115:
1105:
1104:
1101:
1100:
1098:
1097:
1092:
1087:
1086:
1085:
1080:
1075:
1065:
1060:
1055:
1049:
1047:
1043:
1042:
1039:
1038:
1036:
1035:
1030:
1021:
1012:
1007:
997:
995:
987:
986:
984:
983:
982:
981:
971:
970:
969:
964:
954:
953:
952:
951:
950:
945:
931:
929:
918:
916:Cranial nuclei
908:
907:
905:
904:
903:
902:
897:
892:
882:
881:
880:
869:
867:
860:
859:
857:
856:
855:
854:
844:
839:
834:
829:
828:
827:
822:
812:
810:Trapezoid body
806:
804:
797:
796:
794:
793:
788:
783:
778:
773:
767:
765:
758:
748:
747:
741:
739:
738:
731:
724:
716:
708:
707:
700:
682:
675:
667:Last's Anatomy
654:
647:
614:
607:
589:
577:
544:
537:
512:
505:
475:
474:
472:
469:
466:
465:
447:
446:
444:
441:
440:
439:
434:
429:
424:
419:
414:
406:
403:
402:
401:
394:
387:
380:
353:lipohyalinosis
345:
342:
328:
325:
317:smooth pursuit
308:
305:
293:
292:
277:
255:
252:
251:
250:
247:
242:
237:
214:contralateral
207:
204:
176:
173:
127:
126:
117:
111:
110:
105:
99:
98:
93:
87:
86:
82:
81:
78:
72:
71:
66:
60:
59:
54:
50:
49:
45:
44:
29:
21:
20:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1652:
1641:
1638:
1637:
1635:
1620:
1617:
1615:
1612:
1610:
1607:
1605:
1602:
1600:
1597:
1596:
1594:
1590:
1583:
1582:
1578:
1575:
1574:
1570:
1567:
1566:
1562:
1559:
1558:
1554:
1552:
1551:
1547:
1545:
1542:
1541:
1539:
1535:
1530:
1520:
1517:
1515:
1512:
1510:
1507:
1505:
1502:
1500:
1497:
1495:
1492:
1490:
1487:
1485:
1482:
1480:
1477:
1475:
1472:
1470:
1467:
1465:
1462:
1460:
1457:
1455:
1452:
1450:
1447:
1445:
1442:
1440:
1437:
1435:
1432:
1430:
1427:
1425:
1422:
1420:
1417:
1415:
1412:
1410:
1407:
1405:
1402:
1400:
1397:
1395:
1392:
1390:
1387:
1385:
1382:
1380:
1379:Fraser spiral
1377:
1375:
1372:
1370:
1367:
1365:
1362:
1360:
1357:
1355:
1352:
1350:
1347:
1345:
1342:
1340:
1337:
1335:
1332:
1330:
1327:
1325:
1322:
1320:
1317:
1315:
1312:
1310:
1307:
1305:
1302:
1301:
1299:
1295:
1290:
1286:
1279:
1274:
1272:
1267:
1265:
1260:
1259:
1256:
1242:
1239:
1238:
1237:
1234:
1230:
1227:
1225:
1222:
1220:
1217:
1215:
1212:
1211:
1210:
1207:
1206:
1204:
1198:
1188:
1185:
1184:
1182:
1178:
1170:
1167:
1166:
1165:
1162:
1160:
1157:
1155:
1152:
1150:
1147:
1146:
1144:
1141:
1137:
1131:
1128:
1127:
1125:
1123:
1119:
1116:
1113:
1106:
1096:
1093:
1091:
1088:
1084:
1081:
1079:
1076:
1074:
1071:
1070:
1069:
1066:
1064:
1061:
1059:
1056:
1054:
1051:
1050:
1048:
1044:
1034:
1031:
1029:
1025:
1022:
1020:
1016:
1013:
1011:
1008:
1006:
1002:
999:
998:
996:
993:
988:
980:
977:
976:
975:
972:
968:
965:
963:
960:
959:
958:
955:
949:
946:
944:
941:
940:
938:
937:
936:
933:
932:
930:
927:
922:
919:
917:
913:
909:
901:
898:
896:
893:
891:
888:
887:
886:
883:
879:
876:
875:
874:
871:
870:
868:
865:
861:
853:
850:
849:
848:
845:
843:
840:
838:
835:
833:
830:
826:
823:
821:
818:
817:
816:
813:
811:
808:
807:
805:
802:
798:
792:
789:
787:
784:
782:
779:
777:
774:
772:
769:
768:
766:
762:
759:
756:
749:
745:
737:
732:
730:
725:
723:
718:
717:
714:
703:
697:
693:
686:
683:
678:
672:
668:
661:
659:
655:
650:
644:
640:
636:
629:
627:
625:
623:
621:
619:
615:
610:
604:
600:
593:
590:
580:
574:
570:
566:
562:
558:
551:
549:
545:
540:
534:
530:
523:
521:
519:
517:
513:
508:
502:
498:
491:
489:
487:
485:
483:
481:
477:
470:
462:
458:
452:
449:
442:
438:
435:
433:
430:
428:
425:
423:
420:
418:
415:
412:
409:
408:
404:
399:
395:
392:
388:
385:
381:
378:
377:
376:
374:
370:
366:
362:
358:
354:
350:
343:
341:
338:
333:
326:
324:
320:
318:
314:
306:
304:
302:
298:
290:
286:
282:
279:(through the
278:
275:
271:
267:
266:
265:
264:
261:
253:
248:
246:
243:
241:
238:
236:
233:
232:visual cortex
229:
225:
221:
217:
213:
212:
211:
205:
203:
200:
198:
194:
190:
186:
182:
174:
172:
170:
166:
162:
158:
154:
150:
146:
142:
138:
134:
122:
116:
112:
109:
106:
104:
100:
97:
94:
92:
88:
83:
79:
77:
73:
70:
67:
65:
61:
58:
55:
51:
46:
41:
37:
33:
27:
22:
17:
1579:
1571:
1563:
1555:
1550:Trompe-l'œil
1548:
1414:Lilac chaser
1384:Gravity hill
1236:Raphe nuclei
1228:
991:
925:
691:
685:
666:
634:
598:
592:
582:, retrieved
560:
528:
496:
451:
357:hypertension
347:
334:
330:
321:
310:
294:
263:
257:
235:
224:frontal lobe
209:
201:
178:
140:
136:
132:
130:
95:
1560:(1864 book)
1464:Poggendorff
1439:Oppel-Kundt
1434:Necker cube
1429:Müller-Lyer
1404:Irradiation
939:Trigeminal
373:arrhythmias
361:microemboli
163:to mediate
85:Identifiers
1557:Spectropia
1474:Rubin vase
1424:McCollough
1419:Mach bands
1369:Ehrenstein
1364:Ebbinghaus
1329:Barberpole
1304:Afterimage
1229:Paramedian
584:2024-07-17
471:References
432:Opsoclonus
365:turbulence
301:cerebellum
103:NeuroNames
57:Brain stem
1609:Illusions
1581:The dress
1573:Waterfall
1374:Flash lag
1354:Cornsweet
1339:Café wall
1319:Ames room
1297:Illusions
1224:Tegmental
1202:reticular
992:efferent:
943:Principal
926:afferent:
803:: Sensory
755:tegmentum
391:nystagmus
337:nystagmus
297:flocculus
254:Efferents
206:Afferents
1634:Category
1359:Delboeuf
1309:Ambigram
1108:Ventral/
979:Superior
967:Anterior
866:: Motor
405:See also
307:Function
189:anterior
169:saccades
1592:Related
1519:Zöllner
1509:White's
1444:Orbison
1409:Jastrow
1180:Surface
764:Surface
751:Dorsal/
437:Saccade
386:, only)
349:Lesions
299:of the
222:of the
218:of the
175:Anatomy
53:Part of
48:Details
1544:Op art
1499:Ternus
1479:Sander
1394:Hering
1334:Bezold
1241:Median
1214:Caudal
962:Dorsal
948:Spinal
698:
673:
645:
605:
575:
535:
503:
384:stroke
64:Artery
1514:Wundt
1469:Ponzo
1349:Chubb
1140:White
864:White
801:White
226:(via
119:[
91:Latin
1640:Pons
1389:Grid
1289:list
1219:Oral
1122:Grey
1112:base
912:Grey
744:pons
696:ISBN
671:ISBN
643:ISBN
603:ISBN
573:ISBN
533:ISBN
501:ISBN
443:Note
355:and
181:pons
167:and
153:pons
147:and
145:oral
137:PPRF
131:The
108:1399
76:Vein
32:pons
1164:MCP
1024:GVE
1015:GSE
1001:SVE
935:GSA
565:doi
371:or
1636::
1026::
1017::
1003::
914::
657:^
641:.
617:^
571:,
559:,
547:^
515:^
479:^
319:.
303:.
291:).
276:),
199:.
171:.
1291:)
1287:(
1277:e
1270:t
1263:v
1114:)
1110:(
757:)
753:(
735:e
728:t
721:v
704:.
679:.
651:.
611:.
567::
541:.
509:.
234:.
135:(
123:]
42:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.