568:
216:
580:
733:
604:
401:
592:
62:
393:
425:
556:
2869:
49:
647:
794:
837:(body lice) emphasize the attendant hazards of lice copulation. A single young female confined with six or more males will die in a few days, having laid very few eggs. Similarly, death of a virgin female was reported after admitting a male to her confinement. The female laid only one egg after mating, and her entire body was tinged with red—a condition attributed to rupture of the
448:". Between its claw and thumb, the louse grasps the hair of its host. With their short legs and large claws, lice are well adapted to clinging to the hair of their host. These adaptations leave them incapable of jumping, or even walking efficiently on flat surfaces. Lice can climb up strands of hair very quickly, allowing them to move quickly and reach another host.
490:
416:. Eyes are present in all species within the Pediculidae family, but are reduced or absent in most other members of the Anoplura suborder. Like other members of the Anoplura, head louse mouthparts are highly adapted for piercing the skin and sucking blood. These mouth parts are retracted into the insect's head except during feeding.
895:
Lice have no wings or powerful legs for jumping, so they move using the claws on their legs to move from hair to hair. Normally, head lice infest a new host only by close contact between individuals, making social contacts among children and parent-child interactions more likely routes of infestation
780:
during head louse development is subtle. The only visible differences between different instars and the adult, other than size, is the relative length of the abdomen, which increases with each molt, as well as the existence of reproductive organs in the adults. Aside from reproduction, nymph behavior
841:
during the sexual act. Old females frequently die following, if not during, copulation. During its lifespan of 4 weeks a female louse lays 50-150 eggs. Eggs hatch within 6–9 days, each nymphal stage last for 4–5 days and accordingly the period from egg to adults lasts for 18–24 days. Adult lice live
655:
In many languages, the terms used for the hatched eggs, which were obvious for all to see, have subsequently become applied to the embryonated eggs that are difficult to detect. Thus, the term "nit" in
English is often used for both. However, in recent years, my colleagues and I have felt the need
805:
is similar), female is on top, with the male below. Dilation of the female's vagina has already occurred, and the male's dilator rests against his back (dorsal surface), out of the way. The male vesica, which contains the penis proper (not seen), is fully inserted into the vagina. Note the male's
784:
Nymph mortality in captivity is about 38%, especially within the first two days of life. In the wild, mortality may instead be highest in the third instar. Nymph hazards are numerous. Failure to completely hatch from the egg is invariably fatal. Death during molting can also occur, although it is
308:
are morphologically almost identical, but do not normally interbreed. From genetic studies, they are thought to have diverged as subspecies about 30,000–110,000 years ago, when many humans began to wear a significant amount of clothing. However, the degree of separation is contentious as they can
345:
480:
In male lice, the front two legs are slightly larger than the other four. This specialized pair of legs are used for holding the female during copulation. Males are slightly smaller than females and are characterized by a pointed end of the abdomen and a well-developed genital apparatus visible
908:
About 6–12 million people, mainly children, are treated annually for head lice in the United States alone. In the UK, it is estimated that two thirds of children will experience at least one case of head lice before leaving primary school. High levels of louse infestations have also been
781:
is similar to the adult. Like adults, nymphs feed also only on human blood (hematophagia), and cannot survive long away from a host. Outside their hosts lice cannot survive more than 24 hrs. The time required for head lice to complete their nymph development to the imago lasts for 12–15 days.
856:
The number of children per family, the sharing of beds and closets, hair washing habits, local customs and social contacts, healthcare in a particular area (e.g. school), and socioeconomic status were found to be significant factors in head louse infestation. Girls are two to four times more
785:
reportedly uncommon. During feeding, the nymph gut can rupture, dispersing the host's blood throughout the insect body. This results in death within a day or two. Whether the high mortality recorded under experimental conditions is representative of conditions in the wild is unclear.
512:
To attach an egg, the adult female secretes a glue from her reproductive organ. This glue quickly hardens into a "nit sheath" that covers the hair shaft and large parts of the egg except for the operculum, a cap through which the embryo breathes. The glue was previously thought to be
567:
944:
The sequencing of the genome of the body louse was first proposed in the mid-2000s and the annotated genome was published in 2010. An analysis of the body and head louse transcriptomes revealed these two organisms are extremely similar genetically.
509:), are attached near the base of a host hair shaft. Eggs are usually laid on the base of the hair, 3–5 mm off the scalp surface. In warm climates, and especially the tropics, eggs may be laid 6 inches (15 cm) or more down the hair shaft.
886:
Although any part of the scalp may be colonized, lice favor the nape of the neck and the area behind the ears, where the eggs are usually laid. Head lice are repelled by light and move towards shadows or dark-coloured objects in their vicinity.
656:
for some simple means of distinguishing between the two without laborious qualification. We have, therefore, come to reserve the term "nit" for the hatched and empty egg shell and refer to the developing embryonated egg as an "egg".
528:
Each egg is oval-shaped and about 0.8 mm in length. They are bright, transparent, and tan to coffee-colored so long as they contain an embryo, but appear white after hatching. Head lice hatch typically six to nine days after
351:
350:
347:
346:
540:
leaves behind its egg shell, still attached to the hair shaft. The empty egg shell remains in place until physically removed by abrasion or the host, or until it slowly disintegrates, which may take six or more months.
352:
968:
Human lice are divided into three deeply divergent mitochondrial clades known as A, B, and C. Three subclades have been identified, D (a sister clade of A), E (a sister clade of C), and F (a sister clade of B).
2999:
1844:
2298:
Pittendrigh BR, Clark JM, Johnston JS, Lee SH, Romero-Severson J, Dasch GA (November 2006). "Sequencing of a new target genome: the
Pediculus humanus humanus (Phthiraptera: Pediculidae) genome project".
384:. Head lice are grey in general, but their precise color varies according to the environment in which they were raised. After feeding, consumed blood causes the louse body to take on a reddish color.
349:
320:), also infests humans. It is morphologically different from the other two species and is much closer in appearance to the lice which infest other primates. Louse infestation of the body is known as
960:
but extensively fragmented. For the head louse, and the body louse, they are on 20 minichromosomes, for the pubic louse 14 minichromosomes and the chimpanzee louse,18 minichromosomes.
2992:
1258:
Tovar-Corona, Jaime M.; Castillo-Morales, Atahualpa; Chen, Lu; Olds, Brett P.; Clark, John M.; Reynolds, Stuart E.; Pittendrigh, Barry R.; Feil, Edward J.; Urrutia, Araxi O. (2015).
293:
in spending their entire lifecycle on a host. Head lice cannot fly, and their short, stumpy legs render them incapable of jumping, or even walking efficiently on flat surfaces.
2446:"The mitochondrial genome of the chimpanzee louse, Pediculus schaeffi: insights into the process of mitochondrial genome fragmentation in the blood-sucking lice of great apes"
1874:
Mumcuoglu KY, Pollack RJ, Reed DL, Barker SC, Gordon S, Toloza AC, Picollo MI, Taylan-Ozkan A, Chosidow O, Habedank B, Ibarra J, Meinking TL, Vander
Stichele RH (March 2020).
830:
occurring during any period of the night or day. Mating attachment frequently lasts more than an hour. Young males can successfully pair with older females, and vice versa.
643:
is a common public health measure to prevent transmission of lice. Some authors have therefore restricted the definition of nit to describe only a hatched or nonviable egg:
2985:
1979:
Mumcuoglu KY, Miller J, Gofin R, et al. (September 1990). "Epidemiological studies on head lice infestation in Israel. I. Parasitological examination of children".
2663:
Liao, Chien-Wei; Cheng, Po-Ching; Chuang, Ting-Wu; Chiu, Kuan-Chih; Chiang, I-Chen; Kuo, Juo-Han; Tu, Yun-Hung; Fan, Yu-Min; Jiang, Hai-Tao; Fan, Chia-Kwung (2017).
1852:
573:
The female reproductive organ secretes a glue that quickly hardens into a "nit sheath" to cover the hair shaft and large parts of the egg, except for the operculum.
3380:
3240:
348:
2157:
2794:
2712:
Amanzougaghene, Nadia; Fenollar, Florence; Davoust, Bernard; Djossou, Félix; Ashfaq, Muhammad; Bitam, Idir; Raoult, Didier; Mediannikov, Oleg (June 2019).
3341:
2596:
Gao, Feng; Amanzougaghene, Nadia; Mumcuoglu, Kosta Y.; Fenollar, Florence; Alfi, Shir; Yesilyurt, Gonca; Raoult, Didier; Mediannikov, Oleg (2016).
3461:
3367:
1796:
1501:
Burkhart CN, Burkhart CG (July 2005). "Head lice: scientific assessment of the nit sheath with clinical ramifications and therapeutic options".
3476:
579:
1620:
Pollack RJ, Kiszewski AE, Spielman A (August 2000). "Overdiagnosis and consequent mismanagement of head louse infestations in North
America".
603:
2506:
1596:
2182:
Mumcuoglu KY, Barker SC, Burgess IE, et al. (April 2007). "International guidelines for effective control of head louse infestations".
1770:
2827:
1701:
Mumcuoglu KY, Meinking TA, Burkhart CN, Burkhart CG (August 2006). "Head louse infestations: the 'no nit' policy and its consequences".
3456:
2776:
768:
three times before reaching the sexually mature adult stage. Thus, mobile head lice populations may contain eggs, nits, three nymphal
591:
2598:"High Ancient Genetic Diversity of Human Lice, Pediculus humanus, from Israel Reveals New Insights into the Origin of Clade B Lice"
2241:"High Ancient Genetic Diversity of Human Lice, Pediculus humanus, from Israel Reveals New Insights into the Origin of Clade B Lice"
2132:
555:
870:
All stages except eggs are blood-feeders and bite the skin four to five times daily to feed. They inject saliva which contains an
2344:"Genome sequences of the human body louse and its primary endosymbiont provide insights into the permanent parasitic lifestyle"
2401:
Olds BP, Coates BS, Steele LD, et al. (April 2012). "Comparison of the transcriptional profiles of head and body lice".
3372:
724:
In
British and Irish slang the term "nit" is often used, across different age groups, to refer to the head lice themselves.
1415:
2903:
1074:
703:
Because nits are simply egg casings that can contain a developing embryo or be empty shells, not all nits are infective.
365:
3289:
1059:
806:
attachment with his specialized claws on the first leg pair to the specialized notch on the female's third leg pair.
688:
Others have retained the broad definition, while simultaneously attempting to clarify its relevance to infestation:
3385:
61:
826:. Pairing can begin within the first 10 hours of adult life. After 24 hours, adult lice copulate frequently, with
215:
3012:
639:
Of these three, only eggs containing viable embryos have the potential to infest or reinfest a host. However, a
481:
inside the abdomen. Females are characterized by two gonopods in the shape of a W at the end of their abdomens.
3113:
2820:
2312:
2977:
2529:
Knapp, Michael; Boutellis, Amina; Drali, Rezak; Rivera, Mario A.; Mumcuoglu, Kosta Y.; Raoult, Didier (2013).
857:
frequently infested than boys. Children between 4 and 14 years of age are the most frequently infested group.
3418:
2714:"Mitochondrial diversity and phylogeographic analysis of Pediculus humanus reveals a new Amazonian clade "F""
3117:
437:
369:
1447:
Williams LK, Reichert A, MacKenzie WR, Hightower AW, Blake PA (May 2001). "Lice, nits, and school policy".
3466:
3257:
3134:
381:
170:
3214:
3052:
2790:
2065:
851:
461:
31:
2531:"Evidence of Sympatry of Clade A and Clade B Head Lice in a Pre-Columbian Chilean Mummy from Camarones"
3395:
3315:
3208:
3043:
2888:
2609:
2542:
2355:
2252:
909:
reported from all over the world, including
Australia, Denmark, France, Ireland, Israel, and Sweden.
815:
329:
3471:
2813:
2210:
957:
811:
325:
3294:
3194:
3109:
2743:
2426:
2324:
2239:
Amanzougaghene N, Mumcuoglu KY, Fenollar F, Alfi S, Yesilyurt G, Raoult D, Mediannikov O (2016).
2114:
2004:
1961:
1726:
1645:
1472:
195:
56:
2786:
2053:
732:
400:
3403:
3302:
2735:
2694:
2686:
2645:
2627:
2578:
2560:
2502:
2496:
2467:
2418:
2383:
2316:
2280:
2191:
2031:
1996:
1907:
1718:
1683:
1637:
1602:
1592:
1518:
1464:
1297:
1279:
1203:
953:
409:
267:
240:
147:
3408:
412:, each with five segments, protrudes from the insect's head. Head lice also have one pair of
2725:
2676:
2635:
2617:
2568:
2550:
2475:
2457:
2410:
2373:
2363:
2308:
2270:
2260:
2106:
1988:
1953:
1897:
1887:
1710:
1675:
1629:
1584:
1554:
1510:
1456:
1287:
1271:
1238:
1193:
838:
392:
3220:
3154:
1679:
819:
761:
537:
424:
186:
17:
3428:
2613:
2546:
2359:
2256:
2136:
1399:
The Louse; an account of the lice which infest man, their medical importance and control
1361:
The Louse; an account of the lice which infest man, their medical importance and control
1334:
1321:
The Louse; an account of the lice which infest man, their medical importance and control
1137:
The Louse; an account of the lice which infest man, their medical importance and control
30:
This article is about the animal. For the infestation known as pediculosis capitis, see
2640:
2597:
2573:
2530:
2480:
2445:
2378:
2343:
2275:
2240:
2086:
1992:
1902:
1875:
1292:
1259:
897:
757:
263:
2868:
2158:"Two thirds of British children will catch head lice during school years, study finds"
1588:
1559:
1542:
1198:
1181:
48:
3451:
3445:
3200:
2961:
2414:
2118:
1714:
1633:
871:
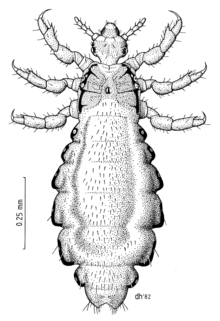
777:
640:
502:
2747:
2328:
2008:
1965:
1744:
1730:
1476:
3307:
3185:
2916:
1876:"International recommendations for an effective control of head louse infestations"
1649:
753:
413:
286:
2430:
692:
In the United States the term "nit" refers to any egg regardless of its viability.
440:. As is typical in the Anoplura, these legs are short and terminate with a single
2730:
2622:
2555:
2265:
2022:
Mumcuoglu KY (May 2006). "Effective treatment of head louse with pediculicides".
3354:
3063:
2893:
2883:
2498:
Parasite
Diversity and Diversification: Evolutionary Ecology Meets Phylogenetics
2495:
Morand, Serge; Krasnov, Boris R.; Littlewood, D. Timothy J. (26 February 2015).
1069:
714:
Head lice eggs (nits) are brown or white (empty shells) and attached to the hair
646:
530:
364:, adult head lice are small (2.5–3 mm long), dorsoventrally flattened (see
333:
321:
223:
2681:
2664:
2348:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
1514:
793:
489:
3176:
3058:
3038:
2937:
2931:
2926:
2911:
2858:
2853:
2462:
2110:
1957:
1243:
1222:
1064:
1049:
1044:
433:
313:
305:
304:) in preferring to attach eggs to scalp hair rather than to clothing. The two
297:
296:
The non-disease-carrying head louse differs from the related disease-carrying
243:
2805:
2690:
2631:
2564:
2471:
1283:
3328:
3160:
3088:
3075:
3008:
2713:
2368:
1460:
1275:
949:
933:
929:
741:
498:
469:
133:
123:
93:
73:
3280:
2739:
2698:
2665:"Prevalence of Pediculus capitis in schoolchildren in Battambang, Cambodia"
2649:
2582:
2422:
2387:
2320:
2284:
2195:
2035:
1911:
1722:
1687:
1641:
1522:
1468:
1301:
1207:
312:
A much more distantly related species of hair-clinging louse, the pubic or
2772:
Centers for
Disease Control and Prevention: Division of Parasitic Diseases
2000:
1606:
822:, the production of viable offspring by virgin females, does not occur in
3274:
3130:
765:
361:
113:
1822:
3346:
3123:
3083:
2956:
2921:
1054:
769:
522:
518:
457:
377:
3359:
2781:
1892:
896:
than shared combs, hats, brushes, towels, clothing, beds, or closets.
3021:
1335:"pediculosis – Definition from the Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary"
1182:"Molecular evolution of Pediculus humanus and the origin of clothing"
1140:
925:
827:
632:
514:
271:
251:
103:
83:
3251:
2090:
3333:
3030:
2966:
921:
875:
792:
773:
731:
645:
488:
445:
423:
399:
391:
343:
259:
255:
247:
214:
2133:"NJ Head Lice | Philadelphia and South New Jersey Hair Lice"
464:
through which the insect breathes. The last segment contains the
3320:
3145:
918:
465:
441:
373:
290:
279:
3255:
2981:
2809:
1771:"Head lice: How to spot nits in hair and what to do about them"
617:
Empty shells are matte, collapsed and white in color. The term
3100:
2777:
James Cook
University, Australia: Head Lice Information Sheet
2234:
2232:
1004:
found in ancient Roman Judea and 4,000-year-old Chilean mummy
2771:
1797:"Nit treatments are like diets. The truth is, nothing works"
517:-based, but more recent studies have shown it to be made of
1359:
Buxton, Patrick A. (1947). "The Anoplura or Sucking Lice".
874:
and suck blood. The digested blood is excreted as dark red
2800:
2313:
10.1603/0022-2585(2006)43[1103:SOANTG]2.0.CO;2
1579:
Burgess, I. F. (1995). "Human lice and their management".
2782:
University of Nebraska: Head Lice Resources You Can Trust
2062:
De Geer (Insecta: Phthiraptera (=Anoplura): Pediculidae)"
1323:(2nd ed.). London: Edward Arnold. pp. 136–141.
460:
are visible. The first six segments each have a pair of
2444:
Herd, Kate E.; Barker, Stephen C.; Shao, Renfu (2015).
1666:
Burgess, I. F. (2004). "Human lice and their control".
356:
Head louse crawling on hairbrush showing how tiny it is
282:
infest most orders of mammals and all orders of birds.
2342:
Kirkness EF, Haas BJ, Sun W, et al. (July 2013).
1845:"Back to school herbalism — natural ways to nuke nits"
991:
head and body: Central Africa, Ethiopia, United States
900:
is by far the most common route of lice transmission.
501:. Females lay about three or four eggs per day. Louse
1936:
Bacot, A. (1917). "Contributions to the bionomics of
1401:(2nd ed.). London: Edward Arnold. pp. 5–23.
1163:
Proceedings of the Royal Institution of Great Britain
818:
is necessary for the female to produce fertile eggs.
1363:(2nd ed.). London: Edward Arnold. pp. 1–4.
372:
segments are fused, but otherwise distinct from the
3264:
3184:
3175:
3144:
3099:
3074:
3029:
3020:
2949:
2902:
2876:
2841:
1161:Maunder, J. W. (1983). "The Appreciation of Lice".
493:
Head louse egg (nit) attached to hair shaft of host
1422:. Whitehouse Station, NJ USA: Merck & Co. 2008
2669:Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection
609:A first-stage nymph hatching from an egg (detail)
1180:Kittler R, Kayser M, Stoneking M (August 2003).
1661:
1659:
1536:
1534:
1532:
1496:
1494:
1492:
1490:
1488:
1486:
1442:
1440:
1438:
1436:
712:
701:
690:
676:
665:
653:
2211:"DNA from Peruvian Mummy Lice Reveals History"
1574:
1572:
1570:
1503:Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology
561:Louse egg attached to a hair shaft of its host
3241:Template:Tick-borne diseases and infestations
2993:
2821:
2068:, Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences
2052:Weems, H. V. Jr.; Fasulo, T. R. (June 2007).
380:, the latter being composed of seven visible
8:
2501:. Cambridge University Press. p. 208.
2251:(2016 Oct 14, 11(10):e01646595): e0164659.
1410:
1408:
1393:Buxton, Patrick A. (1947). "The Anatomy of
1315:Buxton, Patrick A. (1947). "The crab louse
1131:Buxton, Patrick A. (1947). "The biology of
752:Head lice, like other insects of the order
585:The operculum allows the embryo to breathe.
309:produce fertile offspring in a laboratory.
254:that spend their entire lives on the human
3252:
3181:
3026:
3000:
2986:
2978:
2828:
2814:
2806:
1126:
1124:
1122:
1120:
1118:
1116:
1114:
1112:
1110:
744:), which is similar to that of head lice (
47:
38:
2729:
2680:
2639:
2621:
2572:
2554:
2479:
2461:
2377:
2367:
2274:
2264:
2135:. Lice Lifters New Jersey. Archived from
1901:
1891:
1558:
1388:
1386:
1384:
1382:
1380:
1378:
1376:
1374:
1372:
1370:
1354:
1352:
1350:
1291:
1242:
1197:
1156:
1154:
1152:
1150:
1108:
1106:
1104:
1102:
1100:
1098:
1096:
1094:
1092:
1090:
924:may indicate that some diseases (such as
678:...nits (dead eggs or empty egg cases)...
1931:
1929:
1927:
1925:
1923:
1921:
1622:The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal
1260:"Alternative Splice in Alternative Lice"
597:A first-stage nymph hatching from an egg
1086:
628:Remnants of already-hatched eggs (nits)
551:
436:project from the fused segments of the
1541:Meinking, Terri Lynn (May–June 1999).
625:Viable eggs that will eventually hatch
2209:Anderson, Andrea (February 8, 2008).
2047:
2045:
1680:10.1146/annurev.ento.49.061802.123253
917:Analysis of the DNA of lice found on
7:
3396:a1b802af-3667-4d9b-89a2-b86a0d4e44c8
1981:International Journal of Dermatology
1880:International Journal of Dermatology
1703:International Journal of Dermatology
1221:Stoneking, Mark (29 December 2004).
1024:head only: Ethiopia, Nepal, Thailand
772:, and the adults (male and female) (
683:Kosta Y. Mumcuoglu and others (2006)
936:, instead of the other way around.
708:L. Keoki Williams and others (2001)
667:The empty eggshell, termed a nit...
360:Like other insects of the suborder
1993:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1990.tb04845.x
1851:. 1 September 2018. Archived from
1583:. Vol. 36. pp. 271–342.
1581:Advances in Parasitology Volume 36
956:of human lice are not on a single
621:may include any of the following:
25:
2718:Infection, Genetics and Evolution
1223:"Erratum: Molecular Evolution of
497:Like most insects, head lice are
266:of this specific parasite, while
3015:-borne diseases and infestations
2867:
2415:10.1111/j.1365-2583.2012.01132.x
1715:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2006.02827.x
1634:10.1097/00006454-200008000-00003
1143:: Edward Arnold. pp. 24–72.
602:
590:
578:
566:
554:
428:Head louse gripping a human hair
274:host a closely related species,
60:
2184:Journal of Drugs in Dermatology
2024:Journal of Drugs in Dermatology
1547:Current Problems in Dermatology
1264:Molecular Biology and Evolution
3462:Parasitic arthropods of humans
1938:Pediculus humanus (vestimenti)
546:SEM images of a head louse egg
258:and feed exclusively on human
1:
3477:Taxa named by Charles De Geer
3426:Psocodea Species File (new):
3416:Psocodea Species File (old):
2301:Journal of Medical Entomology
1823:"How to get rid of head lice"
1628:(8): 689–93, discussion 694.
1589:10.1016/S0065-308X(08)60493-5
1560:10.1016/S1040-0486(99)90005-4
1199:10.1016/S0960-9822(03)00507-4
846:Factors affecting infestation
842:for an additional 3–4 weeks.
2731:10.1016/j.meegid.2019.02.006
2623:10.1371/journal.pone.0164659
2556:10.1371/journal.pone.0076818
2266:10.1371/journal.pone.0164659
1075:Treatment of human head lice
1014:head and body: South America
981:found in ancient Roman Judea
456:Seven segments of the louse
366:anatomical terms of location
262:. Humans are the only known
2797:Featured Creatures Web site
1420:The Merck Veterinary Manual
1227:and the Origin of Clothing"
1060:List of parasites of humans
1029:Clade E (sister of clade C)
1009:Clade F (sister of clade B)
986:Clade D (sister of clade A)
928:) may have passed from the
3493:
2836:Human lice and pediculosis
2682:10.1016/j.jmii.2017.09.003
1515:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.01.134
849:
697:Terri Lynn Meinking (1999)
536:After hatching, the louse
29:
3457:Insects described in 1767
3295:Pediculus_humanus_capitis
3266:Pediculus humanus capitis
3239:For ticks and mites, see
3235:
2865:
2463:10.1186/s12864-015-1843-3
2111:10.1017/s0031182000004194
2060:Pediculus humanus capitis
2058:Linnaeus and Head Louse,
2056:Pediculus humanus humanus
2054:"Human Lice: Body Louse,
1958:10.1017/S0031182000006065
1244:10.1016/j.cub.2004.12.024
803:Pediculus humanus capitis
799:Pediculus humanus humanus
789:Reproduction and lifespan
746:Pediculus humanus capitis
738:Pediculus humanus humanus
302:Pediculus humanus humanus
250:. Head lice are wingless
236:Pediculus humanus capitis
220:Pediculus humanus capitis
201:
194:
180:Pediculus humanus capitis
176:
169:
57:Scientific classification
55:
46:
41:
27:Insect parasite of humans
18:Pediculus humanus capitis
3114:Cordylobia anthropophaga
2403:Insect Molecular Biology
978:head and body: worldwide
404:Female head louse, adult
3118:Cochliomyia hominivorax
2950:Other terms of interest
2801:Head Louse infestations
2369:10.1073/pnas.1003379107
1461:10.1542/peds.107.5.1011
635:) that will never hatch
285:Lice differ from other
3135:mosquito-borne disease
2095:, Supplementary notes"
1034:head only: West Africa
807:
749:
728:Development and nymphs
722:
711:
700:
686:
675:
664:
651:
494:
429:
405:
397:
396:Male head louse, adult
357:
289:ectoparasites such as
226:
3215:Armillifer armillatus
3053:head lice infestation
2087:Nuttall, George H. F.
2066:University of Florida
1276:10.1093/molbev/msv151
852:Head lice infestation
796:
735:
661:Ian F. Burgess (1995)
649:
631:Nonviable eggs (dead
492:
468:and (separately) the
427:
403:
395:
368:), and wingless. The
355:
218:
32:Head lice infestation
3209:Porocephalus crotali
3044:pediculosis corporis
2889:Pediculosis corporis
2215:GenomeWeb Daily News
1745:"Head lice and nits"
1416:"Lice (Pediculosis)"
1001:head only: worldwide
964:Mitochondrial clades
898:Head-to-head contact
672:J. W. Maunder (1983)
330:pediculosis corporis
2614:2016PLoSO..1164659A
2547:2013PLoSO...876818B
2360:2010PNAS..10712168K
2257:2016PLoSO..1164659A
2162:instituteofmums.com
1855:on 23 December 2018
1777:. 13 September 2018
958:circular chromosome
954:mitochondrial genes
332:for body lice, and
326:pediculosis capitis
278:. Other species of
3195:Linguatula serrata
3110:Dermatobia hominis
2787:body and head lice
1825:. 25 December 2021
1668:Annu. Rev. Entomol
812:reproduce sexually
808:
750:
652:
495:
430:
406:
398:
358:
276:Pediculus schaeffi
227:
162:P. h. capitis
3439:
3438:
3404:Open Tree of Life
3258:Taxon identifiers
3249:
3248:
3231:
3230:
3171:
3170:
2975:
2974:
2508:978-1-316-23993-3
2093:Pediculus humanus
1942:Pediculus capitis
1893:10.1111/ijd.15096
1598:978-0-12-031736-3
1395:Pediculus humanus
1270:(10): 2749–2759.
1225:Pediculus humanus
1133:Pediculus humanus
950:bilateral animals
833:Experiments with
824:Pediculus humanus
353:
213:
212:
208:
204:Pediculus capitis
16:(Redirected from
3484:
3432:
3431:
3422:
3421:
3412:
3411:
3399:
3398:
3389:
3388:
3376:
3375:
3363:
3362:
3350:
3349:
3337:
3336:
3324:
3323:
3311:
3310:
3298:
3297:
3285:
3284:
3283:
3253:
3182:
3027:
3002:
2995:
2988:
2979:
2871:
2830:
2823:
2816:
2807:
2759:
2758:
2756:
2754:
2733:
2709:
2703:
2702:
2684:
2660:
2654:
2653:
2643:
2625:
2608:(10): e0164659.
2593:
2587:
2586:
2576:
2558:
2526:
2520:
2519:
2517:
2515:
2492:
2486:
2485:
2483:
2465:
2441:
2435:
2434:
2398:
2392:
2391:
2381:
2371:
2354:(27): 12168–73.
2339:
2333:
2332:
2295:
2289:
2288:
2278:
2268:
2236:
2227:
2226:
2224:
2222:
2206:
2200:
2199:
2179:
2173:
2172:
2170:
2169:
2154:
2148:
2147:
2145:
2144:
2129:
2123:
2122:
2091:"The biology of
2083:
2077:
2076:
2074:
2073:
2049:
2040:
2039:
2019:
2013:
2012:
1976:
1970:
1969:
1933:
1916:
1915:
1905:
1895:
1871:
1865:
1864:
1862:
1860:
1841:
1835:
1834:
1832:
1830:
1819:
1813:
1812:
1810:
1808:
1793:
1787:
1786:
1784:
1782:
1767:
1761:
1760:
1758:
1756:
1741:
1735:
1734:
1698:
1692:
1691:
1663:
1654:
1653:
1617:
1611:
1610:
1576:
1565:
1564:
1562:
1538:
1527:
1526:
1498:
1481:
1480:
1444:
1431:
1430:
1428:
1427:
1412:
1403:
1402:
1390:
1365:
1364:
1356:
1345:
1344:
1342:
1341:
1331:
1325:
1324:
1312:
1306:
1305:
1295:
1255:
1249:
1248:
1246:
1218:
1212:
1211:
1201:
1177:
1171:
1170:
1158:
1145:
1144:
1139:(2nd ed.).
1128:
882:Position on host
839:alimentary canal
760:. Newly hatched
720:
709:
698:
684:
673:
662:
606:
594:
582:
570:
558:
521:similar to hair
354:
340:Adult morphology
336:for pubic lice.
206:
182:
65:
64:
51:
39:
21:
3492:
3491:
3487:
3486:
3485:
3483:
3482:
3481:
3442:
3441:
3440:
3435:
3427:
3425:
3417:
3415:
3407:
3402:
3394:
3392:
3384:
3379:
3371:
3366:
3358:
3353:
3345:
3340:
3332:
3327:
3319:
3314:
3306:
3301:
3293:
3288:
3279:
3278:
3273:
3260:
3250:
3245:
3227:
3221:porocephaliasis
3167:
3155:Tunga penetrans
3140:
3095:
3070:
3016:
3006:
2976:
2971:
2945:
2898:
2872:
2863:
2837:
2834:
2768:
2763:
2762:
2752:
2750:
2711:
2710:
2706:
2662:
2661:
2657:
2595:
2594:
2590:
2528:
2527:
2523:
2513:
2511:
2509:
2494:
2493:
2489:
2443:
2442:
2438:
2400:
2399:
2395:
2341:
2340:
2336:
2297:
2296:
2292:
2238:
2237:
2230:
2220:
2218:
2217:. GenomeWeb LLC
2208:
2207:
2203:
2181:
2180:
2176:
2167:
2165:
2156:
2155:
2151:
2142:
2140:
2131:
2130:
2126:
2085:
2084:
2080:
2071:
2069:
2051:
2050:
2043:
2021:
2020:
2016:
1978:
1977:
1973:
1935:
1934:
1919:
1873:
1872:
1868:
1858:
1856:
1843:
1842:
1838:
1828:
1826:
1821:
1820:
1816:
1806:
1804:
1795:
1794:
1790:
1780:
1778:
1769:
1768:
1764:
1754:
1752:
1743:
1742:
1738:
1700:
1699:
1695:
1665:
1664:
1657:
1619:
1618:
1614:
1599:
1578:
1577:
1568:
1540:
1539:
1530:
1500:
1499:
1484:
1446:
1445:
1434:
1425:
1423:
1414:
1413:
1406:
1392:
1391:
1368:
1358:
1357:
1348:
1339:
1337:
1333:
1332:
1328:
1314:
1313:
1309:
1257:
1256:
1252:
1231:Current Biology
1220:
1219:
1215:
1186:Current Biology
1179:
1178:
1174:
1160:
1159:
1148:
1130:
1129:
1088:
1083:
1041:
1031:
1021:
1011:
998:
988:
975:
966:
942:
915:
913:Archaeogenetics
906:
893:
884:
868:
863:
854:
848:
820:Parthenogenesis
791:
736:Development of
730:
721:
718:
710:
707:
699:
696:
685:
682:
674:
671:
663:
660:
615:
614:
613:
610:
607:
598:
595:
586:
583:
574:
571:
562:
559:
548:
547:
505:(also known as
487:
478:
476:Sex differences
454:
422:
390:
344:
342:
328:for head lice,
207:(De Geer, 1767)
190:
184:
178:
165:
151:
148:P. humanus
59:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
3490:
3488:
3480:
3479:
3474:
3469:
3464:
3459:
3454:
3444:
3443:
3437:
3436:
3434:
3433:
3423:
3413:
3400:
3390:
3377:
3364:
3351:
3338:
3325:
3312:
3299:
3286:
3270:
3268:
3262:
3261:
3256:
3247:
3246:
3244:
3243:
3236:
3233:
3232:
3229:
3228:
3226:
3225:
3205:
3190:
3188:
3179:
3173:
3172:
3169:
3168:
3166:
3165:
3150:
3148:
3142:
3141:
3139:
3138:
3128:
3105:
3103:
3097:
3096:
3094:
3093:
3080:
3078:
3072:
3071:
3069:
3068:
3056:
3035:
3033:
3024:
3018:
3017:
3007:
3005:
3004:
2997:
2990:
2982:
2973:
2972:
2970:
2969:
2964:
2959:
2953:
2951:
2947:
2946:
2944:
2943:
2942:
2941:
2934:
2929:
2924:
2914:
2908:
2906:
2900:
2899:
2897:
2896:
2891:
2886:
2880:
2878:
2874:
2873:
2866:
2864:
2862:
2861:
2856:
2851:
2845:
2843:
2839:
2838:
2835:
2833:
2832:
2825:
2818:
2810:
2804:
2803:
2798:
2784:
2779:
2774:
2767:
2766:External links
2764:
2761:
2760:
2704:
2675:(4): 585–591.
2655:
2588:
2541:(10): e76818.
2521:
2507:
2487:
2436:
2393:
2334:
2307:(6): 1103–11.
2290:
2228:
2201:
2174:
2149:
2124:
2105:(2): 201–221.
2078:
2041:
2014:
1971:
1952:(2): 228–258.
1917:
1866:
1849:Irish Examiner
1836:
1814:
1803:. 21 June 2018
1788:
1762:
1736:
1693:
1655:
1612:
1597:
1566:
1543:"Infestations"
1528:
1482:
1432:
1404:
1366:
1346:
1326:
1317:Phthirus pubis
1307:
1250:
1213:
1192:(16): 1414–7.
1172:
1146:
1085:
1084:
1082:
1079:
1078:
1077:
1072:
1067:
1062:
1057:
1052:
1047:
1040:
1037:
1036:
1035:
1030:
1027:
1026:
1025:
1020:
1017:
1016:
1015:
1010:
1007:
1006:
1005:
1002:
997:
994:
993:
992:
987:
984:
983:
982:
979:
974:
971:
965:
962:
941:
938:
914:
911:
905:
902:
892:
889:
883:
880:
867:
864:
862:
859:
850:Main article:
847:
844:
797:Copulation in
790:
787:
758:hemimetabolous
729:
726:
716:
705:
694:
680:
669:
658:
650:Louse hatching
637:
636:
629:
626:
612:
611:
608:
601:
599:
596:
589:
587:
584:
577:
575:
572:
565:
563:
560:
553:
550:
549:
545:
544:
543:
486:
483:
477:
474:
453:
450:
444:and opposing "
421:
418:
389:
386:
341:
338:
211:
210:
199:
198:
192:
191:
185:
174:
173:
171:Trinomial name
167:
166:
159:
157:
153:
152:
145:
143:
139:
138:
131:
127:
126:
121:
117:
116:
111:
107:
106:
101:
97:
96:
91:
87:
86:
81:
77:
76:
71:
67:
66:
53:
52:
44:
43:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3489:
3478:
3475:
3473:
3470:
3468:
3467:Ectoparasites
3465:
3463:
3460:
3458:
3455:
3453:
3450:
3449:
3447:
3430:
3424:
3420:
3414:
3410:
3405:
3401:
3397:
3391:
3387:
3382:
3378:
3374:
3369:
3365:
3361:
3356:
3352:
3348:
3343:
3339:
3335:
3330:
3326:
3322:
3317:
3313:
3309:
3304:
3300:
3296:
3291:
3287:
3282:
3276:
3272:
3271:
3269:
3267:
3263:
3259:
3254:
3242:
3238:
3237:
3234:
3223:
3222:
3217:
3216:
3211:
3210:
3206:
3203:
3202:
3201:linguatulosis
3197:
3196:
3192:
3191:
3189:
3187:
3183:
3180:
3178:
3174:
3163:
3162:
3157:
3156:
3152:
3151:
3149:
3147:
3143:
3136:
3132:
3129:
3126:
3125:
3120:
3119:
3115:
3111:
3107:
3106:
3104:
3102:
3098:
3091:
3090:
3085:
3082:
3081:
3079:
3077:
3073:
3066:
3065:
3060:
3057:
3054:
3050:
3046:
3045:
3040:
3037:
3036:
3034:
3032:
3028:
3025:
3023:
3019:
3014:
3010:
3003:
2998:
2996:
2991:
2989:
2984:
2983:
2980:
2968:
2965:
2963:
2962:Sucking louse
2960:
2958:
2955:
2954:
2952:
2948:
2940:
2939:
2935:
2933:
2930:
2928:
2925:
2923:
2920:
2919:
2918:
2915:
2913:
2910:
2909:
2907:
2905:
2901:
2895:
2892:
2890:
2887:
2885:
2882:
2881:
2879:
2875:
2870:
2860:
2857:
2855:
2852:
2850:
2847:
2846:
2844:
2840:
2831:
2826:
2824:
2819:
2817:
2812:
2811:
2808:
2802:
2799:
2796:
2792:
2788:
2785:
2783:
2780:
2778:
2775:
2773:
2770:
2769:
2765:
2749:
2745:
2741:
2737:
2732:
2727:
2723:
2719:
2715:
2708:
2705:
2700:
2696:
2692:
2688:
2683:
2678:
2674:
2670:
2666:
2659:
2656:
2651:
2647:
2642:
2637:
2633:
2629:
2624:
2619:
2615:
2611:
2607:
2603:
2599:
2592:
2589:
2584:
2580:
2575:
2570:
2566:
2562:
2557:
2552:
2548:
2544:
2540:
2536:
2532:
2525:
2522:
2510:
2504:
2500:
2499:
2491:
2488:
2482:
2477:
2473:
2469:
2464:
2459:
2455:
2451:
2447:
2440:
2437:
2432:
2428:
2424:
2420:
2416:
2412:
2409:(2): 257–68.
2408:
2404:
2397:
2394:
2389:
2385:
2380:
2375:
2370:
2365:
2361:
2357:
2353:
2349:
2345:
2338:
2335:
2330:
2326:
2322:
2318:
2314:
2310:
2306:
2302:
2294:
2291:
2286:
2282:
2277:
2272:
2267:
2262:
2258:
2254:
2250:
2246:
2242:
2235:
2233:
2229:
2216:
2212:
2205:
2202:
2197:
2193:
2190:(4): 409–14.
2189:
2185:
2178:
2175:
2163:
2159:
2153:
2150:
2139:on 2013-01-12
2138:
2134:
2128:
2125:
2120:
2116:
2112:
2108:
2104:
2100:
2096:
2094:
2088:
2082:
2079:
2067:
2063:
2061:
2057:
2048:
2046:
2042:
2037:
2033:
2029:
2025:
2018:
2015:
2010:
2006:
2002:
1998:
1994:
1990:
1986:
1982:
1975:
1972:
1967:
1963:
1959:
1955:
1951:
1947:
1943:
1939:
1932:
1930:
1928:
1926:
1924:
1922:
1918:
1913:
1909:
1904:
1899:
1894:
1889:
1886:(3): 272–80.
1885:
1881:
1877:
1870:
1867:
1854:
1850:
1846:
1840:
1837:
1824:
1818:
1815:
1802:
1798:
1792:
1789:
1776:
1772:
1766:
1763:
1750:
1746:
1740:
1737:
1732:
1728:
1724:
1720:
1716:
1712:
1708:
1704:
1697:
1694:
1689:
1685:
1681:
1677:
1673:
1669:
1662:
1660:
1656:
1651:
1647:
1643:
1639:
1635:
1631:
1627:
1623:
1616:
1613:
1608:
1604:
1600:
1594:
1590:
1586:
1582:
1575:
1573:
1571:
1567:
1561:
1556:
1553:(3): 75–118.
1552:
1548:
1544:
1537:
1535:
1533:
1529:
1524:
1520:
1516:
1512:
1509:(1): 129–33.
1508:
1504:
1497:
1495:
1493:
1491:
1489:
1487:
1483:
1478:
1474:
1470:
1466:
1462:
1458:
1455:(5): 1011–5.
1454:
1450:
1443:
1441:
1439:
1437:
1433:
1421:
1417:
1411:
1409:
1405:
1400:
1396:
1389:
1387:
1385:
1383:
1381:
1379:
1377:
1375:
1373:
1371:
1367:
1362:
1355:
1353:
1351:
1347:
1336:
1330:
1327:
1322:
1318:
1311:
1308:
1303:
1299:
1294:
1289:
1285:
1281:
1277:
1273:
1269:
1265:
1261:
1254:
1251:
1245:
1240:
1236:
1232:
1228:
1226:
1217:
1214:
1209:
1205:
1200:
1195:
1191:
1187:
1183:
1176:
1173:
1168:
1164:
1157:
1155:
1153:
1151:
1147:
1142:
1138:
1134:
1127:
1125:
1123:
1121:
1119:
1117:
1115:
1113:
1111:
1109:
1107:
1105:
1103:
1101:
1099:
1097:
1095:
1093:
1091:
1087:
1080:
1076:
1073:
1071:
1068:
1066:
1063:
1061:
1058:
1056:
1053:
1051:
1048:
1046:
1043:
1042:
1038:
1033:
1032:
1028:
1023:
1022:
1018:
1013:
1012:
1008:
1003:
1000:
999:
995:
990:
989:
985:
980:
977:
976:
972:
970:
963:
961:
959:
955:
951:
948:Unlike other
946:
939:
937:
935:
931:
927:
923:
920:
912:
910:
903:
901:
899:
890:
888:
881:
879:
877:
873:
872:anticoagulant
865:
860:
858:
853:
845:
843:
840:
836:
835:P. h. humanus
831:
829:
825:
821:
817:
813:
804:
800:
795:
788:
786:
782:
779:
778:Metamorphosis
775:
771:
767:
763:
759:
755:
747:
743:
739:
734:
727:
725:
715:
704:
693:
689:
679:
668:
657:
648:
644:
642:
641:no nit policy
634:
630:
627:
624:
623:
622:
620:
605:
600:
593:
588:
581:
576:
569:
564:
557:
552:
542:
539:
534:
532:
526:
524:
520:
516:
510:
508:
504:
500:
491:
485:Eggs and nits
484:
482:
475:
473:
471:
467:
463:
459:
451:
449:
447:
443:
439:
435:
426:
419:
417:
415:
411:
402:
394:
387:
385:
383:
379:
375:
371:
367:
363:
339:
337:
335:
331:
327:
323:
319:
318:Pthirus pubis
315:
310:
307:
303:
299:
294:
292:
288:
283:
281:
277:
273:
269:
265:
261:
257:
253:
249:
245:
242:
238:
237:
232:
225:
221:
217:
209:
205:
200:
197:
193:
188:
183:
181:
175:
172:
168:
164:
163:
158:
155:
154:
150:
149:
144:
141:
140:
137:
136:
132:
129:
128:
125:
122:
119:
118:
115:
112:
109:
108:
105:
102:
99:
98:
95:
92:
89:
88:
85:
82:
79:
78:
75:
72:
69:
68:
63:
58:
54:
50:
45:
40:
37:
33:
19:
3265:
3219:
3213:
3207:
3199:
3193:
3186:Pentastomida
3159:
3153:
3122:
3108:
3087:
3062:
3048:
3042:
3013:ectoparasite
2936:
2917:Pediculicide
2848:
2751:. Retrieved
2721:
2717:
2707:
2672:
2668:
2658:
2605:
2601:
2591:
2538:
2534:
2524:
2512:. Retrieved
2497:
2490:
2453:
2450:BMC Genomics
2449:
2439:
2406:
2402:
2396:
2351:
2347:
2337:
2304:
2300:
2293:
2248:
2244:
2219:. Retrieved
2214:
2204:
2187:
2183:
2177:
2166:. Retrieved
2164:. 2017-04-20
2161:
2152:
2141:. Retrieved
2137:the original
2127:
2102:
2099:Parasitology
2098:
2092:
2081:
2070:. Retrieved
2059:
2055:
2030:(5): 451–2.
2027:
2023:
2017:
1987:(7): 502–6.
1984:
1980:
1974:
1949:
1946:Parasitology
1945:
1941:
1937:
1883:
1879:
1869:
1857:. Retrieved
1853:the original
1848:
1839:
1827:. Retrieved
1817:
1805:. Retrieved
1801:The Guardian
1800:
1791:
1779:. Retrieved
1775:News Shopper
1774:
1765:
1753:. Retrieved
1751:. 2017-10-19
1748:
1739:
1709:(8): 891–6.
1706:
1702:
1696:
1671:
1667:
1625:
1621:
1615:
1580:
1550:
1546:
1506:
1502:
1452:
1448:
1424:. Retrieved
1419:
1398:
1394:
1360:
1338:. Retrieved
1329:
1320:
1316:
1310:
1267:
1263:
1253:
1237:(24): 2309.
1234:
1230:
1224:
1216:
1189:
1185:
1175:
1166:
1162:
1136:
1132:
967:
947:
943:
916:
907:
904:Distribution
894:
891:Transmission
885:
869:
855:
834:
832:
823:
809:
802:
798:
783:
754:Phthiraptera
751:
745:
737:
723:
713:
702:
691:
687:
677:
666:
654:
638:
618:
616:
535:
527:
511:
506:
496:
479:
455:
431:
408:One pair of
407:
359:
317:
311:
301:
295:
287:hematophagic
284:
275:
244:ectoparasite
235:
234:
230:
228:
219:
203:
202:
179:
177:
161:
160:
156:Subspecies:
146:
134:
36:
3355:iNaturalist
3064:phthiriasis
2894:Phthiriasis
2884:Pediculosis
2877:Infestation
2514:30 December
1859:23 December
1807:23 December
1781:23 December
1755:23 December
1070:Pediculosis
531:oviposition
334:phthiriasis
322:pediculosis
268:chimpanzees
224:Des Helmore
124:Pediculidae
42:Head louse
3472:Subspecies
3446:Categories
3059:Crab louse
3049:Head louse
3039:Body louse
3009:Arthropods
2938:Delphinium
2932:Phenothrin
2927:Permethrin
2912:Nitpicking
2859:Body louse
2854:Crab louse
2849:Head louse
2753:26 January
2221:August 31,
2168:2017-09-28
2143:2012-11-22
2072:2008-02-21
1674:: 457–81.
1449:Pediatrics
1426:2008-10-08
1340:2008-04-23
1081:References
1065:Nitpicking
1050:Crab louse
1045:Body louse
816:copulation
810:Head lice
719:NHS (2018)
314:crab louse
306:subspecies
298:body louse
231:head louse
94:Arthropoda
3177:Crustacea
3161:tungiasis
3089:cimicosis
3076:Hemiptera
2904:Treatment
2691:1684-1182
2632:1932-6203
2565:1932-6203
2472:1471-2164
2119:251061971
1284:0737-4038
952:, the 37
934:Old World
930:New World
861:Behaviour
742:body lice
499:oviparous
470:genitalia
462:spiracles
142:Species:
135:Pediculus
80:Kingdom:
74:Eukaryota
3275:Wikidata
3131:Mosquito
2748:73476298
2740:30769089
2699:29150362
2650:27741281
2602:PLOS ONE
2583:24204678
2535:PLOS ONE
2423:22404397
2388:20566863
2329:25046936
2321:17162941
2285:27741281
2245:PLOS ONE
2196:17668538
2089:(1919).
2036:16703782
2009:39798857
1966:86846228
1912:32767380
1829:5 August
1731:38910169
1723:16911370
1688:14651472
1642:10959734
1523:15965432
1477:26076461
1469:11331679
1302:26169943
1208:12932325
1039:See also
919:Peruvian
717:—
706:—
695:—
681:—
670:—
659:—
519:proteins
410:antennae
382:segments
370:thoracic
362:Anoplura
241:obligate
239:) is an
196:Synonyms
120:Family:
114:Psocodea
90:Phylum:
84:Animalia
70:Domain:
3419:1234992
3409:1034010
3347:4987992
3321:3574591
3124:myiasis
3084:Bed bug
3022:Insecta
2957:Cooties
2922:Lindane
2842:Species
2789:on the
2724:: 1–8.
2641:5065229
2610:Bibcode
2574:3813697
2543:Bibcode
2481:4557858
2379:2901460
2356:Bibcode
2276:5065229
2253:Bibcode
2001:2228380
1903:7984059
1650:2557006
1607:7484466
1293:4576711
1169:: 1–31.
1055:Lindane
1019:Clade C
996:Clade B
973:Clade A
932:to the
922:mummies
866:Feeding
770:instars
523:keratin
458:abdomen
452:Abdomen
378:abdomen
272:bonobos
252:insects
187:De Geer
130:Genus:
110:Order:
104:Insecta
100:Class:
3429:879262
3393:NZOR:
3386:121226
3373:186076
3360:413842
3334:PEDIHA
3281:Q27358
2746:
2738:
2697:
2689:
2648:
2638:
2630:
2581:
2571:
2563:
2505:
2478:
2470:
2431:175421
2429:
2421:
2386:
2376:
2327:
2319:
2283:
2273:
2194:
2117:
2034:
2007:
1999:
1964:
1910:
1900:
1749:nhs.uk
1729:
1721:
1686:
1648:
1640:
1605:
1595:
1521:
1475:
1467:
1300:
1290:
1282:
1206:
1141:London
940:Genome
926:typhus
828:mating
814:, and
762:nymphs
756:, are
633:embryo
515:chitin
438:thorax
420:Thorax
248:humans
189:, 1767
3308:5K9BF
3031:Louse
2967:Louse
2744:S2CID
2456:(1).
2427:S2CID
2325:S2CID
2115:S2CID
2005:S2CID
1962:S2CID
1727:S2CID
1646:S2CID
1473:S2CID
876:frass
774:imago
766:moult
764:will
538:nymph
446:thumb
291:fleas
264:hosts
260:blood
256:scalp
3452:Lice
3381:NCBI
3368:ITIS
3342:GBIF
3329:EPPO
3146:Flea
3047:) /
3011:and
2795:IFAS
2755:2022
2736:PMID
2695:PMID
2687:ISSN
2646:PMID
2628:ISSN
2579:PMID
2561:ISSN
2516:2017
2503:ISBN
2468:ISSN
2419:PMID
2384:PMID
2317:PMID
2281:PMID
2223:2014
2192:PMID
2032:PMID
1997:PMID
1940:and
1908:PMID
1861:2018
1831:2021
1809:2018
1783:2018
1757:2018
1719:PMID
1684:PMID
1638:PMID
1603:PMID
1593:ISBN
1519:PMID
1465:PMID
1298:PMID
1280:ISSN
1204:PMID
507:nits
503:eggs
466:anus
442:claw
434:legs
432:Six
414:eyes
388:Head
376:and
374:head
280:lice
270:and
229:The
3316:EoL
3303:CoL
3290:AFD
3101:Fly
2726:doi
2677:doi
2636:PMC
2618:doi
2569:PMC
2551:doi
2476:PMC
2458:doi
2411:doi
2374:PMC
2364:doi
2352:107
2309:doi
2271:PMC
2261:doi
2107:doi
1989:doi
1954:doi
1944:".
1898:PMC
1888:doi
1711:doi
1676:doi
1630:doi
1585:doi
1555:doi
1511:doi
1457:doi
1453:107
1397:".
1319:".
1288:PMC
1272:doi
1239:doi
1194:doi
1135:".
776:).
619:nit
246:of
222:by
3448::
3406::
3383::
3370::
3357::
3344::
3331::
3318::
3305::
3292::
3277::
3212:/
3116:/
3112:/
2793:/
2791:UF
2742:.
2734:.
2722:70
2720:.
2716:.
2693:.
2685:.
2673:52
2671:.
2667:.
2644:.
2634:.
2626:.
2616:.
2606:11
2604:.
2600:.
2577:.
2567:.
2559:.
2549:.
2537:.
2533:.
2474:.
2466:.
2454:16
2452:.
2448:.
2425:.
2417:.
2407:21
2405:.
2382:.
2372:.
2362:.
2350:.
2346:.
2323:.
2315:.
2305:43
2303:.
2279:.
2269:.
2259:.
2249:14
2247:.
2243:.
2231:^
2213:.
2186:.
2160:.
2113:.
2103:11
2101:.
2097:.
2064:.
2044:^
2026:.
2003:.
1995:.
1985:29
1983:.
1960:.
1948:.
1920:^
1906:.
1896:.
1884:60
1882:.
1878:.
1847:.
1799:.
1773:.
1747:.
1725:.
1717:.
1707:45
1705:.
1682:.
1672:49
1670:.
1658:^
1644:.
1636:.
1626:19
1624:.
1601:.
1591:.
1569:^
1551:11
1549:.
1545:.
1531:^
1517:.
1507:53
1505:.
1485:^
1471:.
1463:.
1451:.
1435:^
1418:.
1407:^
1369:^
1349:^
1296:.
1286:.
1278:.
1268:32
1266:.
1262:.
1235:14
1233:.
1229:.
1202:.
1190:13
1188:.
1184:.
1167:55
1165:.
1149:^
1089:^
878:.
533:.
525:.
472:.
324:,
3224:)
3218:(
3204:)
3198:(
3164:)
3158:(
3137:)
3133:(
3127:)
3121:(
3092:)
3086:(
3067:)
3061:(
3055:)
3051:(
3041:(
3001:e
2994:t
2987:v
2829:e
2822:t
2815:v
2757:.
2728::
2701:.
2679::
2652:.
2620::
2612::
2585:.
2553::
2545::
2539:8
2518:.
2484:.
2460::
2433:.
2413::
2390:.
2366::
2358::
2331:.
2311::
2287:.
2263::
2255::
2225:.
2198:.
2188:6
2171:.
2146:.
2121:.
2109::
2075:.
2038:.
2028:5
2011:.
1991::
1968:.
1956::
1950:9
1914:.
1890::
1863:.
1833:.
1811:.
1785:.
1759:.
1733:.
1713::
1690:.
1678::
1652:.
1632::
1609:.
1587::
1563:.
1557::
1525:.
1513::
1479:.
1459::
1429:.
1343:.
1304:.
1274::
1247:.
1241::
1210:.
1196::
801:(
748:)
740:(
316:(
300:(
233:(
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.