493:. The 3’ region of a transcript contains many polyadenylation signals (PAS). When more proximal (closer towards 5’ end) PAS sites are utilized, this shortens the length of the 3’ untranslated region (3' UTR) of a transcript. Studies in both humans and flies have shown tissue specific APA. With neuronal tissues preferring distal PAS usage, leading to longer 3’ UTRs and testis tissues preferring proximal PAS leading to shorter 3’ UTRs. Studies have shown there is a correlation between a gene's conservation level and its tendency to do alternative polyadenylation, with highly conserved genes exhibiting more APA. Similarly, highly expressed genes follow this same pattern.
589:
477:
691:, two closely related complexes that recycle RNA into nucleotides. This enzyme degrades RNA by attacking the bond between the 3′-most nucleotides with a phosphate, breaking off a diphosphate nucleotide. This reaction is reversible, and so the enzyme can also extend RNA with more nucleotides. The heteropolymeric tail added by polynucleotide phosphorylase is very rich in adenine. The choice of adenine is most likely the result of higher
410:
reduces deadenylation. The rate of deadenylation may also be regulated by RNA-binding proteins. Additionally, RNA triple helix structures and RNA motifs such as the poly(A) tail 3’ end binding pocket retard deadenylation process and inhibit poly(A) tail removal. Once the poly(A) tail is removed, the decapping complex removes the 5′ cap, leading to a degradation of the RNA. Several other proteins are involved in deadenylation in
135:
361:. Poly(A)-binding protein promotes export from the nucleus and translation, and inhibits degradation. This protein binds to the poly(A) tail prior to mRNA export from the nucleus and in yeast also recruits poly(A) nuclease, an enzyme that shortens the poly(A) tail and allows the export of the mRNA. Poly(A)-binding protein is exported to the cytoplasm with the RNA. mRNAs that are not exported are degraded by the
33:
771:
protection of the 3′ end of the RNA from nucleases, but later the specific roles of polyadenylation in nuclear export and translation were identified. The polymerases responsible for polyadenylation were first purified and characterized in the 1960s and 1970s, but the large number of accessory proteins that control this process were discovered only in the early 1990s.
5761:
386:, the poly(A) tails of most mRNAs in the cytoplasm gradually get shorter, and mRNAs with shorter poly(A) tail are translated less and degraded sooner. However, it can take many hours before an mRNA is degraded. This deadenylation and degradation process can be accelerated by microRNAs complementary to the
449:
In the early mouse embryo, cytoplasmic polyadenylation of maternal RNAs from the egg cell allows the cell to survive and grow even though transcription does not start until the middle of the 2-cell stage (4-cell stage in human). In the brain, cytoplasmic polyadenylation is active during learning and
340:
long the enzyme can no longer bind to CPSF and polyadenylation stops, thus determining the length of the poly(A) tail. CPSF is in contact with RNA polymerase II, allowing it to signal the polymerase to terminate transcription. When RNA polymerase II reaches a "termination sequence" (⁵'TTTATT' on the
508:
in the 3′ UTR. MicroRNAs tend to repress translation and promote degradation of the mRNAs they bind to, although there are examples of microRNAs that stabilise transcripts. Alternative polyadenylation can also shorten the coding region, thus making the mRNA code for a different protein, but this is
316:
The RNA is typically cleaved before transcription termination, as CstF also binds to RNA polymerase II. Through a poorly understood mechanism (as of 2002), it signals for RNA polymerase II to slip off of the transcript. Cleavage also involves the protein CFII, though it is unknown how. The cleavage
627:
contain both stabilising and destabilising poly(A) tails. Destabilising polyadenylation targets both mRNA and noncoding RNAs. The poly(A) tails are 43 nucleotides long on average. The stabilising ones start at the stop codon, and without them the stop codon (UAA) is not complete as the genome only
409:
and remove nucleotides from the poly(A) tail. The level of access to the 5′ cap and poly(A) tail is important in controlling how soon the mRNA is degraded. PARN deadenylates less if the RNA is bound by the initiation factors 4E (at the 5′ cap) and 4G (at the poly(A) tail), which is why translation
663:
of all living organisms, it is presumed, had some form of polyadenylation system. A few organisms do not polyadenylate mRNA, which implies that they have lost their polyadenylation machineries during evolution. Although no examples of eukaryotes that lack polyadenylation are known, mRNAs from the
699:
as an energy currency, making it more likely to be incorporated in this tail in early lifeforms. It has been suggested that the involvement of adenine-rich tails in RNA degradation prompted the later evolution of polyadenylate polymerases (the enzymes that produce poly(A) tails with no other
373:
ribosomal subunit. However, a poly(A) tail is not required for the translation of all mRNAs. Further, poly(A) tailing (oligo-adenylation) can determine the fate of RNA molecules that are usually not poly(A)-tailed (such as (small) non-coding (sn)RNAs etc.) and thereby induce their RNA decay.
770:
in extracts made from cell nuclei that could polymerise ATP, but not ADP, into polyadenine. Although identified in many types of cells, this activity had no known function until 1971, when poly(A) sequences were found in mRNAs. The only function of these sequences was thought at first to be
312:
exist. Two other proteins add specificity to the binding to an RNA: CstF and CFI. CstF binds to a GU-rich region further downstream of CPSF's site. CFI recognises a third site on the RNA (a set of UGUAA sequences in mammals) and can recruit CPSF even if the AAUAAA sequence is missing. The
108:
The poly(A) tail is important for the nuclear export, translation and stability of mRNA. The tail is shortened over time, and, when it is short enough, the mRNA is enzymatically degraded. However, in a few cell types, mRNAs with short poly(A) tails are stored for later activation by
214:
Many eukaryotic non-coding RNAs are always polyadenylated at the end of transcription. There are small RNAs where the poly(A) tail is seen only in intermediary forms and not in the mature RNA as the ends are removed during processing, the notable ones being
172:
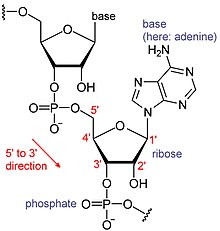
template. By convention, RNA sequences are written in a 5′ to 3′ direction. The 5′ end is the part of the RNA molecule that is transcribed first, and the 3′ end is transcribed last. The 3′ end is also where the poly(A) tail is found on polyadenylated RNAs.
528:(a group of bacterial compounds that trigger an immune response). This results in the selection of weak poly(A) sites and thus shorter transcripts. This removes regulatory elements in the 3′ untranslated regions of mRNAs for defense-related products like
313:
polyadenylation signal – the sequence motif recognised by the RNA cleavage complex – varies between groups of eukaryotes. Most human polyadenylation sites contain the AAUAAA sequence, but this sequence is less common in plants and fungi.
97:; these proteins then synthesize the poly(A) tail at the RNA's 3′ end. In some genes these proteins add a poly(A) tail at one of several possible sites. Therefore, polyadenylation can produce more than one transcript from a single gene (
647:). It can synthesise a 3′ extension where the vast majority of the bases are adenines. Like in bacteria, polyadenylation by polynucleotide phosphorylase promotes degradation of the RNA in plastids and likely also archaea.
5206:
Evguenieva-Hackenberg E, Roppelt V, Finsterseifer P, Klug G (December 2008). "Rrp4 and Csl4 are needed for efficient degradation but not for polyadenylation of synthetic and natural RNA by the archaeal exosome".
536:. These mRNAs then have longer half-lives and produce more of these proteins. RNA-binding proteins other than those in the polyadenylation machinery can also affect whether a polyadenylation site is used, as can
3921:
Alt FW, Bothwell AL, Knapp M, Siden E, Mather E, Koshland M, Baltimore D (June 1980). "Synthesis of secreted and membrane-bound immunoglobulin mu heavy chains is directed by mRNAs that differ at their 3′ ends".
4058:
Ogorodnikov A, Levin M, Tattikota S, Tokalov S, Hoque M, Scherzinger D, Marini F, Poetsch A, Binder H, Macher-Göppinger S, Probst HC, Tian B, Schaefer M, Lackner KJ, Westermann F, Danckwardt S (December 2018).
394:, mRNAs with shortened poly(A) tails are not degraded, but are instead stored and translationally inactive. These short tailed mRNAs are activated by cytoplasmic polyadenylation after fertilisation, during
715:. It is presumed that the horizontal transfer of bacterial CCA-adding enzyme to eukaryotes allowed the archaeal-like CCA-adding enzyme to switch function to a poly(A) polymerase. Some lineages, like
6180:
203:
and aids in transcription termination, export of the mRNA from the nucleus, and translation. Almost all eukaryotic mRNAs are polyadenylated, with the exception of animal replication-dependent
655:
Although polyadenylation is seen in almost all organisms, it is not universal. However, the wide distribution of this modification and the fact that it is present in organisms from all three
186:, tune how active the mRNA is. There are also many RNAs that are not translated, called non-coding RNAs. Like the untranslated regions, many of these non-coding RNAs have regulatory roles.
4019:"Elevated levels of the 64-kDa cleavage stimulatory factor (CstF-64) in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages influence gene expression and induce alternative poly(A) site selection"
512:
The choice of poly(A) site can be influenced by extracellular stimuli and depends on the expression of the proteins that take part in polyadenylation. For example, the expression of
2483:
Tefferi A, Wieben ED, Dewald GW, Whiteman DA, Bernard ME, Spelsberg TC (August 2002). "Primer on medical genomics part II: Background principles and methods in molecular genetics".
3603:
Smibert, Peter; Miura, Pedro; Westholm, Jakub O.; Shenker, Sol; May, Gemma; Duff, Michael O.; Zhang, Dayu; Eads, Brian D.; Carlson, Joe; Brown, James B.; Eisman, Robert C. (2012).
3167:
Sakurai T, Sato M, Kimura M (November 2005). "Diverse patterns of poly(A) tail elongation and shortening of murine maternal mRNAs from fully grown oocyte to 2-cell embryo stages".
199:
In nuclear polyadenylation, a poly(A) tail is added to an RNA at the end of transcription. On mRNAs, the poly(A) tail protects the mRNA molecule from enzymatic degradation in the
628:
encodes the U or UA part. Plant mitochondria have only destabilising polyadenylation. Mitochondrial polyadenylation has never been observed in either budding or fission yeast.
5028:"Domain analysis of the chloroplast polynucleotide phosphorylase reveals discrete functions in RNA degradation, polyadenylation, and sequence homology with exosome proteins"
336:. Another protein, PAB2, binds to the new, short poly(A) tail and increases the affinity of polyadenylate polymerase for the RNA. When the poly(A) tail is approximately 250
116:
mRNA molecules in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have polyadenylated 3′-ends, with the prokaryotic poly(A) tails generally shorter and fewer mRNA molecules polyadenylated.
3010:
Torabi, Seyed-Fakhreddin; Vaidya, Anand T.; Tycowski, Kazimierz T.; DeGregorio, Suzanne J.; Wang, Jimin; Shu, Mei-Di; Steitz, Thomas A.; Steitz, Joan A. (2021-02-05).
616:
to overcome these secondary structures. The poly(A) tail can also recruit RNases that cut the RNA in two. These bacterial poly(A) tails are about 30 nucleotides long.
540:
near the polyadenylation signal. In addition, numerous other components involved in transcription, splicing or other mechanisms regulating RNA biology can affect APA.
469:. Depending on the cell type, the polymerase can be the same type of polyadenylate polymerase (PAP) that is used in the nuclear process, or the cytoplasmic polymerase
454:, which is the strengthening of the signal transmission from a nerve cell to another in response to nerve impulses and is important for learning and memory formation.
5451:"The Functional Role of the 3′ Untranslated Region and Poly(A) Tail of Duck Hepatitis a Virus Type 1 in Viral Replication and Regulation of IRES-Mediated Translation"
5449:
Chen, Jun-Hao; Zhang, Rui-Hua; Lin, Shao-Li; Li, Peng-Fei; Lan, Jing-Jing; Song, Sha-Sha; Gao, Ji-Ming; Wang, Yu; Xie, Zhi-Jing; Li, Fu-Chang; Jiang, Shi-Jin (2018).
211:
structure followed by a purine-rich sequence, termed histone downstream element, that directs where the RNA is cut so that the 3′ end of the histone mRNA is formed.
109:
re-polyadenylation in the cytosol. In contrast, when polyadenylation occurs in bacteria, it promotes RNA degradation. This is also sometimes the case for eukaryotic
6224:
6173:
458:
249:
2754:"sCLIP-an integrated platform to study RNA-protein interactomes in biomedical research: identification of CSTF2tau in alternative processing of small nuclear RNAs"
5647:"Polyadenylic Acid Sequences in the Heterogeneous Nuclear RNA and Rapidly-Labeled Polyribosomal RNA of HeLa Cells: Possible Evidence for a Precursor Relationship"
5245:
Slomovic S, Portnoy V, Yehudai-Resheff S, Bronshtein E, Schuster G (April 2008). "Polynucleotide phosphorylase and the archaeal exosome as poly(A)-polymerases".
341:
DNA template and ⁵'AAUAAA' on the primary transcript), the end of transcription is signaled. The polyadenylation machinery is also physically linked to the
5075:
Slomovic S, Portnoy V, Schuster G (2008). "Chapter 24 Detection and
Characterization of Polyadenylated RNA in Eukarya, Bacteria, Archaea, and Organelles".
6166:
2152:
Stumpf G, Domdey H (November 1996). "Dependence of yeast pre-mRNA 3′-end processing on CFT1: a sequence homolog of the mammalian AAUAAA binding factor".
1306:
Hunt AG, Xu R, Addepalli B, Rao S, Forbes KP, Meeks LR, Xing D, Mo M, Zhao H, Bandyopadhyay A, Dampanaboina L, Marion A, Von Lanken C, Li QQ (May 2008).
5793:
4222:
Danckwardt S, Kaufmann I, Gentzel M, Foerstner KU, Gantzert AS, Gehring NH, Neu-Yilik G, Bork P, Keller W, Wilm M, Hentze MW, Kulozik AE (June 2007).
2440:
Nag A, Narsinh K, Martinson HG (July 2007). "The poly(A)-dependent transcriptional pause is mediated by CPSF acting on the body of the polymerase".
608:. Polynucleotide phosphorylase binds to the 3′ end of RNAs and the 3′ extension provided by the poly(A) tail allows it to bind to the RNAs whose
4930:"PNPase activity determines the efficiency of mRNA 3′-end processing, the degradation of tRNA and the extent of polyadenylation in chloroplasts"
4744:
Slomovic S, Portnoy V, Liveanu V, Schuster G (2006). "RNA Polyadenylation in
Prokaryotes and Organelles; Different Tails Tell Different Tales".
2142:
Molecular
Biology of the Cell, Chapter 6, "From DNA to RNA". 4th edition. Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, et al. New York: Garland Science; 2002.
612:
would otherwise block the 3′ end. Successive rounds of polyadenylation and degradation of the 3′ end by polynucleotide phosphorylase allows the
5282:"Direct Evidence that the Poly(A) Tail of Influenza A Virus mRNA Is Synthesized by Reiterative Copying of a U Track in the Virion RNA Template"
4846:"Kinetics of polynucleotide phosphorylase: comparison of enzymes from Streptomyces and Escherichia coli and effects of nucleoside diphosphates"
2705:"Yeast transcripts cleaved by an internal ribozyme provide new insight into the role of the cap and poly(A) tail in translation and mRNA decay"
300:
cleaves the 3′-most part of a newly produced RNA and polyadenylates the end produced by this cleavage. The cleavage is catalysed by the enzyme
4271:
Danckwardt S, Gantzert AS, Macher-Goeppinger S, Probst HC, Gentzel M, Wilm M, Gröne HJ, Schirmacher P, Hentze MW, Kulozik AE (February 2011).
1892:"Crystal structure of a human cleavage factor CFI(m)25/CFI(m)68/RNA complex provides an insight into poly(A) site recognition and RNA looping"
5961:
5618:
5092:
1201:
4116:
Licatalosi DD, Mele A, Fak JJ, Ule J, Kayikci M, Chi SW, Clark TA, Schweitzer AC, Blume JE, Wang X, Darnell JC, Darnell RB (November 2008).
580:. Poly(A) tails have also been found on human rRNA fragments, both the form of homopolymeric (A only) and heterpolymeric (mostly A) tails.
4061:"Transcriptome 3′ end organization by PCF11 links alternative polyadenylation to formation and neuronal differentiation of neuroblastoma"
146:(for polyadenylic acid tail) reflects the way RNA nucleotides are abbreviated, with a letter for the base the nucleotide contains (A for
6234:
5845:
5825:
4657:
259:
90:
5523:"Polynucleotide Biosynthesis: Formation of a Sequence of Adenylate Units from Adenosine Triphosphate by an Enzyme from Thymus Nuclei"
2203:
Iseli C, Stevenson BJ, de Souza SJ, Samaia HB, Camargo AA, Buetow KH, Strausberg RL, Simpson AJ, Bucher P, Jongeneel CV (July 2002).
497:
data (sequencing of only mRNAs inside ribosomes) has shown that mRNA isoforms with shorter 3’ UTRs are more likely to be translated.
6189:
5933:
1308:"Arabidopsis mRNA polyadenylation machinery: comprehensive analysis of protein-protein interactions and gene expression profiling"
631:
While many bacteria and mitochondria have polyadenylate polymerases, they also have another type of polyadenylation, performed by
3662:"Phylogenetic analysis of mRNA polyadenylation sites reveals a role of transposable elements in evolution of the 3'-end of genes"
1833:"Structural basis of UGUA recognition by the Nudix protein CFI(m)25 and implications for a regulatory role in mRNA 3′ processing"
1409:
Marzluff WF, Gongidi P, Woods KR, Jin J, Maltais LJ (November 2002). "The human and mouse replication-dependent histone genes".
6087:
6031:
501:
387:
3337:"PAP- and GLD-2-type poly(A) polymerases are required sequentially in cytoplasmic polyadenylation and oogenesis in Drosophila"
6026:
489:
Many protein-coding genes have more than one polyadenylation site, so a gene can code for several mRNAs that differ in their
2580:"Poly(A) nuclease interacts with the C-terminal domain of polyadenylate-binding protein domain from poly(A)-binding protein"
2806:"A novel method for poly(A) fractionation reveals a large population of mRNAs with a short poly(A) tail in mammalian cells"
1059:
6114:
6045:
5786:
224:
5392:"Translation of a nonpolyadenylated viral RNA is enhanced by binding of viral coat protein or polyadenylation of the RNA"
208:
5850:
680:
632:
366:
365:. Poly(A)-binding protein also can bind to, and thus recruit, several proteins that affect translation, one of these is
3874:"MicroRNA-mediated up-regulation of an alternatively polyadenylated variant of the mouse cytoplasmic {beta}-actin gene"
6229:
596:
In many bacteria, both mRNAs and non-coding RNAs can be polyadenylated. This poly(A) tail promotes degradation by the
533:
517:
254:
4893:
Nagaike T, Suzuki T, Ueda T (April 2008). "Polyadenylation in mammalian mitochondria: insights from recent studies".
446:. These shortened poly(A) tails are often less than 20 nucleotides, and are lengthened to around 80–150 nucleotides.
6065:
5765:
5118:"RNA polyadenylation in Archaea: not observed in Haloferax while the exosome polynucleotidylates RNA in Sulfolobus"
3967:"Widespread mRNA polyadenylation events in introns indicate dynamic interplay between polyadenylation and splicing"
232:
142:
RNAs are a type of large biological molecules, whose individual building blocks are called nucleotides. The name
1941:"Analysis of a noncanonical poly(A) site reveals a tripartite mechanism for vertebrate poly(A) site recognition"
703:
Polyadenylate polymerases are not as ancient. They have separately evolved in both bacteria and eukaryotes from
6488:
6109:
5897:
5810:
5779:
666:
569:
321:
163:
86:
79:
6435:
6256:
6070:
5887:
5872:
660:
358:
325:
52:
576:, which maintains a tail that is around 4 nucleotides long to the 3′ end. The RNA is then degraded by the
6493:
6075:
6000:
5892:
4644:
Régnier P, Arraiano CM (March 2000). "Degradation of mRNA in bacteria: emergence of ubiquitous features".
3768:"Proliferating cells express mRNAs with shortened 3′ untranslated regions and fewer microRNA target sites"
696:
588:
451:
329:
4175:"Specific trans-acting proteins interact with auxiliary RNA polyadenylation elements in the COX-2 3′-UTR"
2254:"Mechanism of poly(A) polymerase: structure of the enzyme-MgATP-RNA ternary complex and kinetic analysis"
5990:
5975:
5855:
5116:
Portnoy V, Evguenieva-Hackenberg E, Klein F, Walter P, Lorentzen E, Klug G, Schuster G (December 2005).
3719:"Processing and transcriptome expansion at the mRNA 3′ end in health and disease: finding the right end"
692:
443:
177:
71:, the poly(A) tail promotes degradation of the mRNA. It, therefore, forms part of the larger process of
64:
3012:"RNA stabilization by a poly(A) tail 3′-end binding pocket and other modes of poly(A)-RNA interaction"
6319:
6097:
5995:
5913:
5658:
5403:
5344:
4753:
4129:
4072:
3779:
2915:
2393:"Yhh1p/Cft1p directly links poly(A) site recognition and RNA polymerase II transcription termination"
2161:
1844:
1457:
1071:
1016:
739:
442:. This lengthens the poly(A) tail of an mRNA with a shortened poly(A) tail, so that the mRNA will be
102:
4312:
Wood AJ, Schulz R, Woodfine K, Koltowska K, Beechey CV, Peters J, Bourc'his D, Oakey RJ (May 2008).
176:
Messenger RNA (mRNA) is RNA that has a coding region that acts as a template for protein synthesis (
6312:
5923:
609:
3120:"Translational control by neuroguidin, a eukaryotic initiation factor 4E and CPEB binding protein"
2528:"mRNA stabilization by poly(A) binding protein is independent of poly(A) and requires translation"
134:
6058:
5941:
4769:
4669:
4525:
3947:
3317:
3100:
3057:
2619:
Vinciguerra P, Stutz F (June 2004). "mRNA export: an assembly line from genes to nuclear pores".
2508:
2465:
2185:
1993:"An interaction between U2AF 65 and CF I(m) links the splicing and 3′ end processing machineries"
1577:
1097:
1040:
834:
525:
494:
220:
2096:"RNA polymerase II pauses and associates with pre-mRNA processing factors at both ends of genes"
4494:
LaCava J, Houseley J, Saveanu C, Petfalski E, Thompson E, Jacquier A, Tollervey D (June 2005).
4224:"Splicing factors stimulate polyadenylation via USEs at non-canonical 3′ end formation signals"
1991:
Millevoi S, Loulergue C, Dettwiler S, Karaa SZ, Keller W, Antoniou M, Vagner S (October 2006).
1654:
Liu D, Brockman JM, Dass B, Hutchins LN, Singh P, McCarrey JR, MacDonald CC, Graber JH (2006).
592:
Polyadenylation in bacteria helps polynucleotide phosphorylase degrade past secondary structure
6307:
6142:
5740:
5686:
5624:
5614:
5577:
5482:
5431:
5390:
Neeleman, Lyda; Olsthoorn, René C. L.; Linthorst, Huub J. M.; Bol, John F. (4 December 2001).
5372:
5313:
5262:
5224:
5188:
5147:
5098:
5088:
5057:
5008:
4959:
4910:
4875:
4826:
4808:
4723:
4661:
4626:
4577:
4517:
4476:
4427:
4392:
4343:
4294:
4253:
4204:
4155:
4098:
4040:
3996:
3939:
3903:
3854:
3805:
3748:
3699:
3681:
3642:
3624:
3585:
3567:
3526:
3508:
3466:
3417:
3368:
3309:
3268:
3233:
3184:
3149:
3092:
3049:
3031:
2992:
2943:
2884:
2835:
2783:
2734:
2685:
2636:
2601:
2557:
2500:
2457:
2422:
2373:
2332:
2283:
2234:
2177:
2125:
2076:
2047:"Genome level analysis of rice mRNA 3′-end processing signals and alternative polyadenylation"
2022:
1970:
1921:
1872:
1813:
1772:
1720:
1685:
1633:
1569:
1534:
1485:
1426:
1391:
1339:
1285:
1248:
1197:
1170:
1135:
1089:
1032:
989:
940:
886:
826:
561:
476:
289:
6387:
6382:
5167:"Mycoplasma gallisepticum as the first analyzed bacterium in which RNA is not polyadenylated"
4363:"TREND-DB-a transcriptome-wide atlas of the dynamic landscape of alternative polyadenylation"
6392:
6367:
5730:
5722:
5676:
5666:
5606:
5567:
5534:
5472:
5462:
5421:
5411:
5362:
5352:
5303:
5293:
5254:
5216:
5178:
5137:
5129:
5080:
5047:
5039:
4998:
4990:
4979:"RNA polyadenylation and degradation in different Archaea; roles of the exosome and RNase R"
4949:
4941:
4902:
4865:
4857:
4816:
4800:
4761:
4713:
4705:
4653:
4616:
4608:
4567:
4559:
4507:
4466:
4458:
4419:
4382:
4374:
4333:
4325:
4284:
4243:
4235:
4194:
4186:
4145:
4137:
4088:
4080:
4030:
3986:
3978:
3931:
3893:
3885:
3844:
3836:
3795:
3787:
3738:
3730:
3689:
3673:
3632:
3616:
3575:
3557:
3516:
3500:
3456:
3448:
3407:
3399:
3358:
3348:
3299:
3260:
3223:
3215:
3176:
3139:
3131:
3084:
3039:
3023:
2982:
2974:
2933:
2923:
2874:
2866:
2825:
2817:
2773:
2765:
2724:
2716:
2675:
2667:
2628:
2591:
2547:
2539:
2492:
2449:
2412:
2404:
2363:
2322:
2314:
2273:
2265:
2224:
2216:
2169:
2115:
2107:
2066:
2058:
2012:
2004:
1960:
1952:
1911:
1903:
1862:
1852:
1803:
1762:
1754:
1712:
1675:
1667:
1623:
1615:
1561:
1524:
1516:
1475:
1465:
1418:
1381:
1373:
1329:
1319:
1275:
1238:
1230:
1162:
1127:
1079:
1024:
979:
971:
930:
922:
876:
868:
816:
743:
656:
435:
207:
mRNAs. These are the only mRNAs in eukaryotes that lack a poly(A) tail, ending instead in a
5605:. Progress in Nucleic Acid Research and Molecular Biology. Vol. 71. pp. 285–389.
6465:
6266:
6249:
6244:
6119:
5802:
5500:
3075:
Wilusz CJ, Wormington M, Peltz SW (April 2001). "The cap-to-tail guide to mRNA turnover".
688:
644:
577:
537:
362:
274:
269:
94:
72:
4410:
Reinisch KM, Wolin SL (April 2007). "Emerging themes in non-coding RNA quality control".
3219:
2963:"Wispy, the Drosophila homolog of GLD-2, is required during oogenesis and egg activation"
1703:
Lutz CS (October 2008). "Alternative polyadenylation: a twist on mRNA 3′ end formation".
5662:
5407:
5348:
4757:
4133:
4076:
3783:
2919:
2165:
1848:
1461:
1166:
1075:
1020:
320:
When the RNA is cleaved, polyadenylation starts, catalysed by polyadenylate polymerase.
6430:
6329:
6214:
6209:
5946:
5918:
5735:
5710:
5477:
5450:
5367:
5332:
5280:
Poon, Leo L. M.; Pritlove, David C.; Fodor, Ervin; Brownlee, George G. (1 April 1999).
5142:
5117:
5003:
4978:
4870:
4845:
4821:
4788:
4621:
4596:
4572:
4547:
4471:
4446:
4445:
Jia H, Wang X, Liu F, Guenther UP, Srinivasan S, Anderson JT, Jankowsky E (June 2011).
4387:
4362:
4338:
4313:
4248:
4223:
4199:
4174:
4150:
4117:
4093:
4060:
3991:
3966:
3898:
3873:
3849:
3824:
3800:
3767:
3743:
3718:
3694:
3661:
3637:
3604:
3580:
3545:
3521:
3488:
3461:
3436:
3363:
3336:
3228:
3203:
3144:
3119:
3044:
3011:
2987:
2962:
2938:
2903:
2830:
2805:
2778:
2753:
2729:
2704:
2327:
2302:
2278:
2253:
2120:
2095:
2071:
2046:
2017:
1992:
1965:
1940:
1916:
1891:
1867:
1832:
1680:
1655:
1619:
1529:
1504:
1480:
1445:
1386:
1361:
1334:
1307:
1243:
1218:
984:
959:
881:
856:
620:
549:
395:
293:
110:
5711:"3′ end mRNA processing: molecular mechanisms and implications for health and disease"
5681:
5646:
5610:
5539:
5522:
5308:
5281:
5084:
5052:
5027:
4954:
4929:
4718:
4693:
3825:"Expression and function of micro-RNAs in immune cells during normal or disease state"
3437:"3′ end mRNA processing: molecular mechanisms and implications for health and disease"
3412:
3387:
2879:
2854:
2680:
2655:
2552:
2527:
2417:
2392:
2229:
2204:
1808:
1792:"A mechanism for the regulation of pre-mRNA 3′ processing by human cleavage factor Im"
1791:
1767:
1742:
1628:
1603:
1422:
872:
821:
804:
6482:
6147:
5834:
5426:
5391:
5183:
5166:
3935:
3061:
1581:
1131:
935:
910:
720:
624:
573:
557:
431:
411:
333:
304:
and occurs 10–30 nucleotides downstream of its binding site. This site often has the
129:
48:
6158:
5298:
4773:
4673:
4529:
3321:
2189:
1101:
1044:
6276:
6197:
6021:
5951:
5820:
5642:
5598:
5518:
3951:
3104:
2512:
2469:
926:
708:
553:
383:
285:
3872:
Ghosh T, Soni K, Scaria V, Halimani M, Bhattacharjee C, Pillai B (November 2008).
2173:
838:
317:
site associated with a polyadenylation signal can vary up to some 50 nucleotides.
5357:
5258:
4906:
4804:
4496:"RNA degradation by the exosome is promoted by a nuclear polyadenylation complex"
4289:
4272:
3620:
2578:
Siddiqui N, Mangus DA, Chang TC, Palermino JM, Shyu AB, Gehring K (August 2007).
1656:"Systematic variation in mRNA 3′-processing signals during mouse spermatogenesis"
1190:
1007:
Zhuang Y, Zhang H, Lin S (June 2013). "Polyadenylation of 18S rRNA in algae(1)".
426:
There is polyadenylation in the cytosol of some animal cell types, namely in the
6455:
6302:
6261:
6124:
6053:
2978:
735:
731:
684:
597:
342:
4512:
4495:
4462:
4084:
3304:
3287:
3264:
3204:"Virtues and limitations of the preimplantation mouse embryo as a model system"
3180:
2908:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
2671:
1837:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
1450:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
490:
406:
138:
Chemical structure of RNA. The sequence of bases differs between RNA molecules.
6082:
4765:
4423:
3734:
3605:"Global patterns of tissue-specific alternative polyadenylation in Drosophila"
3562:
2804:
Meijer HA, Bushell M, Hill K, Gant TW, Willis AE, Jones P, de Moor CH (2007).
2632:
2352:"Poly(A) tail length control is caused by termination of processive synthesis"
2269:
1907:
1565:
1084:
975:
751:
712:
521:
337:
5726:
5467:
5133:
4812:
4273:"p38 MAPK controls prothrombin expression by regulated RNA 3′ end processing"
4239:
4118:"HITS-CLIP yields genome-wide insights into brain alternative RNA processing"
3685:
3628:
3571:
3512:
3452:
3035:
2008:
5026:
Yehudai-Resheff S, Portnoy V, Yogev S, Adir N, Schuster G (September 2003).
4709:
3791:
3027:
2928:
2656:"Multiple portions of poly(A)-binding protein stimulate translation in vivo"
1857:
1470:
1324:
727:
672:
200:
60:
32:
5744:
5671:
5628:
5572:
5555:
5486:
5435:
5416:
5376:
5317:
5266:
5228:
5192:
5151:
5102:
5061:
5012:
4963:
4945:
4914:
4879:
4830:
4727:
4694:"Comparative genomics and evolution of proteins involved in RNA metabolism"
4665:
4630:
4581:
4521:
4480:
4431:
4396:
4347:
4298:
4257:
4208:
4159:
4102:
4044:
4035:
4018:
4000:
3907:
3858:
3809:
3752:
3703:
3646:
3589:
3530:
3470:
3421:
3372:
3313:
3272:
3237:
3188:
3153:
3096:
3053:
2996:
2947:
2888:
2839:
2787:
2738:
2689:
2640:
2605:
2596:
2579:
2543:
2504:
2461:
2426:
2408:
2391:
Dichtl B, Blank D, Sadowski M, Hübner W, Weiser S, Keller W (August 2002).
2368:
2351:
2336:
2287:
2238:
2129:
2080:
2026:
1974:
1925:
1876:
1817:
1776:
1724:
1689:
1573:
1538:
1489:
1430:
1395:
1343:
1289:
1252:
1174:
1093:
1036:
993:
944:
890:
830:
568:, polyadenylation is a way of marking the RNA for degradation, at least in
17:
5760:
5690:
5581:
4378:
3943:
2561:
2377:
2181:
1637:
1139:
758:) in order to emphasize their own genes' expression over the host cell's.
288:
polyadenylation complex in the nucleus of eukaryotes works on products of
6102:
6092:
6016:
4994:
4658:
10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(200003)22:3<235::AID-BIES5>3.0.CO;2-2
4612:
3889:
3677:
3504:
3403:
3388:"A large-scale analysis of mRNA polyadenylation of human and mouse genes"
3135:
2821:
2769:
2318:
2062:
1758:
1671:
1280:
1267:
529:
505:
427:
415:
216:
151:
68:
4861:
4141:
1956:
1520:
308:
sequence AAUAAA on the RNA, but variants of it that bind more weakly to
6422:
6402:
6397:
5838:
5043:
4563:
4447:"The RNA helicase Mtr4p modulates polyadenylation in the TRAMP complex"
4329:
4190:
3982:
3353:
2870:
1741:
Beaudoing E, Freier S, Wyatt JR, Claverie JM, Gautheret D (July 2000).
1377:
1234:
716:
640:
636:
204:
155:
147:
63:, polyadenylation is part of the process that produces mature mRNA for
56:
5220:
3840:
2720:
1716:
1028:
6377:
6372:
6352:
6288:
6239:
3088:
2496:
2453:
2220:
2111:
1552:
Amaral PP, Mattick JS (August 2008). "Noncoding RNA in development".
767:
755:
565:
439:
391:
346:
264:
159:
5603:
A history of poly A sequences: from formation to factors to function
1505:"A pathway for the biogenesis of trans-acting siRNAs in Arabidopsis"
1153:
Stevens A (1963). "Ribonucleic Acids-Biosynthesis and
Degradation".
2303:"Molecular dissection of mRNA poly(A) tail length control in yeast"
6445:
6440:
6362:
6357:
6347:
6342:
6337:
6297:
5860:
5771:
2301:
Viphakone N, Voisinet-Hakil F, Minvielle-Sebastia L (April 2008).
2045:
Shen Y, Ji G, Haas BJ, Wu X, Zheng J, Reese GJ, Li QQ (May 2008).
747:
704:
513:
509:
much less common than just shortening the 3′ untranslated region.
470:
5501:"Inhibition of host poly(A)-binding protein by virus ~ ViralZone"
5331:
Wu, Hung-Yi; Ke, Ting-Yung; Liao, Wei-Yu; Chang, Nai-Yun (2013).
4314:"Regulation of alternative polyadenylation by genomic imprinting"
3766:
Sandberg R, Neilson JR, Sarma A, Sharp PA, Burge CB (June 2008).
3286:
Piqué M, López JM, Foissac S, Guigó R, Méndez R (February 2008).
2961:
Cui J, Sackton KL, Horner VL, Kumar KE, Wolfner MF (April 2008).
1743:"Patterns of variant polyadenylation signal usage in human genes"
480:
Results of using different polyadenylation sites on the same gene
6460:
6450:
6292:
5333:"Regulation of Coronaviral Poly(A) Tail Length during Infection"
5247:
Biochimica et
Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Gene Regulatory Mechanisms
4895:
Biochimica et
Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Gene Regulatory Mechanisms
4793:
Biochimica et
Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Gene Regulatory Mechanisms
3335:
Benoit P, Papin C, Kwak JE, Wickens M, Simonelig M (June 2008).
1604:"Assembly of a processive messenger RNA polyadenylation complex"
1118:
Sarkar N (June 1997). "Polyadenylation of mRNA in prokaryotes".
780:
466:
462:
402:
309:
301:
228:
83:
6162:
5775:
2094:
Glover-Cutter K, Kim S, Espinosa J, Bentley DL (January 2008).
1503:
Yoshikawa M, Peragine A, Park MY, Poethig RS (September 2005).
5830:
457:
Cytoplasmic polyadenylation requires the RNA-binding proteins
370:
169:
125:
3288:"A combinatorial code for CPE-mediated translational control"
2752:
Kargapolova Y, Levin M, Lackner K, Danckwardt S (June 2017).
93:
segment of the newly made pre-mRNA is first cleaved off by a
2855:"A protein interaction framework for human mRNA degradation"
2654:
Gray NK, Coller JM, Dickson KS, Wickens M (September 2000).
500:
Since alternative polyadenylation changes the length of the
695:
concentrations than other nucleotides as a result of using
504:, it can also change which binding sites are available for
4017:
Shell SA, Hesse C, Morris SM, Milcarek C (December 2005).
5079:. Methods in Enzymology. Vol. 447. pp. 501–20.
1444:
Saini HK, Griffiths-Jones S, Enright AJ (November 2007).
3717:
Ogorodnikov A, Kargapolova Y, Danckwardt S (June 2016).
2205:"Long-range heterogeneity at the 3′ ends of human mRNAs"
1890:
Yang Q, Coseno M, Gilmartin GM, Doublié S (March 2011).
635:
itself. This enzyme is found in bacteria, mitochondria,
4844:
Chang SA, Cozad M, Mackie GA, Jones GH (January 2008).
3251:
Richter JD (June 2007). "CPEB: a life in translation".
1060:"RNA turnover: unexpected consequences of being tailed"
911:"Cytoplasmic polyadenylation in development and beyond"
639:
and as a constituent of the archaeal exosome (in those
55:; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only
4789:"Mitochondrial poly(A) polymerase and polyadenylation"
4173:
Hall-Pogar T, Liang S, Hague LK, Lutz CS (July 2007).
711:. Its catalytic domain is homologous to that of other
5709:
Danckwardt S, Hentze MW, Kulozik AE (February 2008).
3546:"Biased alternative polyadenylation in human tissues"
3435:
Danckwardt S, Hentze MW, Kulozik AE (February 2008).
766:
Poly(A)polymerase was first identified in 1960 as an
572:. This polyadenylation is done in the nucleus by the
1939:
Venkataraman K, Brown KM, Gilmartin GM (June 2005).
707:, which is the enzyme that completes the 3′ ends of
6421:
6328:
6275:
6196:
6135:
6044:
6009:
5983:
5974:
5932:
5906:
5880:
5871:
5809:
4692:Anantharaman V, Koonin EV, Aravind L (April 2002).
4595:Slomovic S, Laufer D, Geiger D, Schuster G (2006).
3169:
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications
1362:"Early evolution of histone mRNA 3′ end processing"
27:
Addition of adenylic acids to 3' end of mature mRNA
5556:"Mechanism and regulation of mRNA polyadenylation"
1189:
465:, and can involve other RNA-binding proteins like
235: – a poly(A) tail is part of the mature RNA.
4597:"Polyadenylation of ribosomal RNA in human cells"
857:"Regulation of mRNA stability in mammalian cells"
5077:RNA Turnover in Bacteria, Archaea and Organelles
3489:"Alternative polyadenylation of mRNA precursors"
1446:"Genomic analysis of human microRNA transcripts"
805:"Integrating mRNA processing with transcription"
803:Proudfoot NJ, Furger A, Dye MJ (February 2002).
5651:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
5396:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
4687:
4685:
4683:
4541:
4539:
2526:Coller JM, Gray NK, Wickens MP (October 1998).
1602:Bienroth S, Keller W, Wahle E (February 1993).
1219:"Trading translation with RNA-binding proteins"
5645:; Vaughan, M. H.; Nakazato, H. (1 June 1971).
4361:Marini F, Scherzinger D, Danckwardt S (2021).
3544:Zhang, Haibo; Lee, Ju Youn; Tian, Bin (2005).
2904:"MicroRNAs direct rapid deadenylation of mRNA"
2573:
2571:
1188:Lehninger AL, Nelson DL, Cox MM, eds. (1993).
357:The poly(A) tail acts as the binding site for
51:(mRNA). The poly(A) tail consists of multiple
6174:
5787:
4928:Walter M, Kilian J, Kudla J (December 2002).
4739:
4737:
3823:Tili E, Michaille JJ, Calin GA (April 2008).
1831:Yang Q, Gilmartin GM, Doublié S (June 2010).
1360:Dávila López M, Samuelsson T (January 2008).
960:"Emerging features of mRNA decay in bacteria"
754:, inhibit the cell's poly-A binding protein (
252:: cleavage/polyadenylation specificity factor
78:The process of polyadenylation begins as the
36:Typical structure of a mature eukaryotic mRNA
8:
2799:
2797:
1736:
1734:
726:Polyadenylate tails are observed in several
723:, never evolved a polyadenylate polymerase.
683:. This enzyme is part of both the bacterial
600:, which contains two RNA-degrading enzymes:
5593:
5591:
4548:"RNA-specific ribonucleotidyl transferases"
3118:Jung MY, Lorenz L, Richter JD (June 2006).
1597:
1595:
1593:
1591:
798:
796:
679:The most ancient polyadenylating enzyme is
6281:
6202:
6181:
6167:
6159:
5980:
5942:Precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA / hnRNA)
5877:
5794:
5780:
5772:
1355:
1353:
915:Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews
5734:
5680:
5670:
5571:
5538:
5476:
5466:
5425:
5415:
5366:
5356:
5307:
5297:
5182:
5141:
5051:
5002:
4953:
4869:
4820:
4717:
4620:
4571:
4511:
4470:
4386:
4337:
4288:
4247:
4198:
4149:
4092:
4034:
3990:
3897:
3848:
3829:International Journal of Medical Sciences
3799:
3742:
3693:
3660:Lee, Ju Youn; Ji, Zhe; Tian, Bin (2008).
3636:
3579:
3561:
3520:
3460:
3411:
3362:
3352:
3303:
3227:
3143:
3043:
2986:
2937:
2927:
2878:
2829:
2777:
2728:
2679:
2595:
2551:
2442:Nature Structural & Molecular Biology
2416:
2367:
2326:
2277:
2228:
2119:
2100:Nature Structural & Molecular Biology
2070:
2016:
1964:
1915:
1866:
1856:
1807:
1766:
1679:
1627:
1528:
1479:
1469:
1385:
1333:
1323:
1279:
1242:
1083:
983:
934:
904:
902:
900:
880:
850:
848:
820:
227:RNAs that, for example, includes the RNA
2040:
2038:
2036:
1790:Brown KM, Gilmartin GM (December 2003).
1113:
1111:
587:
475:
133:
31:
3965:Tian B, Pan Z, Lee JY (February 2007).
3386:Tian B, Hu J, Zhang H, Lutz CS (2005).
1986:
1984:
1301:
1299:
792:
5554:Colgan DF, Manley JL (November 1997).
5240:
5238:
3493:Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology
2902:Wu L, Fan J, Belasco JG (March 2006).
1649:
1647:
619:In as different groups as animals and
5962:Histone acetylation and deacetylation
4787:Chang, Jeong Ho; Tong, Liang (2012).
4412:Current Opinion in Structural Biology
4012:
4010:
3482:
3480:
3077:Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology
1266:Mattick JS, Makunin IV (April 2006).
855:Guhaniyogi J, Brewer G (March 2001).
544:Tagging for degradation in eukaryotes
7:
6027:Ribosome-nascent chain complex (RNC)
4546:Martin G, Keller W (November 2007).
3487:Tian, Bin; Manley, James L. (2017).
3220:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2007.09.032
2853:Lehner B, Sanderson CM (July 2004).
5165:Portnoy V, Schuster G (June 2008).
4023:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
2584:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
2356:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
2252:Balbo PB, Bohm A (September 2007).
1167:10.1146/annurev.bi.32.070163.000311
223: – a seemingly large group of
4746:Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences
1620:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05690.x
414:and human cells, most notably the
401:In animals, poly(A) ribonuclease (
324:builds the poly(A) tail by adding
47:to an RNA transcript, typically a
25:
6190:Post-transcriptional modification
2703:Meaux S, Van Hoof A (July 2006).
1217:Abaza I, Gebauer F (March 2008).
1196:(2nd ed.). New York: Worth.
267:: polyadenylate binding protein 2
5759:
5521:; Abrams, Richard (April 1960).
5184:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01157.x
1274:. 15 Spec No 1 (90001): R17-29.
1132:10.1146/annurev.biochem.66.1.173
369:-4G, which in turn recruits the
296:. Here, a multi-protein complex
6032:Post-translational modification
5527:Journal of Biological Chemistry
5299:10.1128/JVI.73.4.3473-3476.1999
2621:Current Opinion in Cell Biology
670:and the salt-tolerant archaean
4977:Portnoy V, Schuster G (2006).
3253:Trends in Biochemical Sciences
3124:Molecular and Cellular Biology
927:10.1128/MMBR.63.2.446-456.1999
661:last universal common ancestor
1:
5611:10.1016/S0079-6603(02)71046-5
5540:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)69494-3
5085:10.1016/S0076-6879(08)02224-6
2174:10.1126/science.274.5292.1517
1809:10.1016/S1097-2765(03)00453-2
1423:10.1016/S0888-7543(02)96850-3
1155:Annual Review of Biochemistry
1120:Annual Review of Biochemistry
873:10.1016/S0378-1119(01)00350-X
822:10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00617-7
584:In prokaryotes and organelles
298:(see components on the right)
257:: cleavage stimulation factor
182:). The rest of the mRNA, the
5358:10.1371/journal.pone.0070548
5259:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2007.12.004
4907:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2008.02.001
4805:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.10.012
4290:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.12.032
3936:10.1016/0092-8674(80)90615-7
3621:10.1016/j.celrep.2012.01.001
681:polynucleotide phosphorylase
633:polynucleotide phosphorylase
602:polynucleotide phosphorylase
2979:10.1534/genetics.107.084558
1058:Anderson JT (August 2005).
518:cleavage stimulatory factor
485:Alternative polyadenylation
422:Cytoplasmic polyadenylation
99:alternative polyadenylation
6510:
4513:10.1016/j.cell.2005.04.029
4463:10.1016/j.cell.2011.05.010
4085:10.1038/s41467-018-07580-5
3305:10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.038
3265:10.1016/j.tibs.2007.04.004
3181:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.08.250
1192:Principles of biochemistry
262:: polyadenylate polymerase
123:
6284:
6205:
5455:Frontiers in Microbiology
5171:FEMS Microbiology Letters
4766:10.1080/07352680500391337
4424:10.1016/j.sbi.2007.03.012
3735:10.1007/s00424-016-1828-3
3563:10.1186/gb-2005-6-12-r100
2633:10.1016/j.ceb.2004.03.013
2350:Wahle E (February 1995).
2270:10.1016/j.str.2007.07.010
1908:10.1016/j.str.2010.12.021
1566:10.1007/s00335-008-9136-7
1085:10.1016/j.cub.2005.08.002
976:10.1017/S1355838200001023
958:Steege DA (August 2000).
659:of life implies that the
345:, a complex that removes
332:to the RNA, cleaving off
233:X chromosome inactivation
6093:sequestration (P-bodies)
5727:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601932
5468:10.3389/fmicb.2018.02250
5134:10.1038/sj.embor.7400571
4240:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601699
3453:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601932
3202:Taft RA (January 2008).
2672:10.1093/emboj/19.17.4723
2009:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601331
1272:Human Molecular Genetics
909:Richter JD (June 1999).
746:. Some viruses, such as
676:lack this modification.
667:Mycoplasma gallisepticum
322:Polyadenylate polymerase
53:adenosine monophosphates
6257:Poly(A)-binding protein
6071:Gene regulatory network
5560:Genes & Development
4850:Journal of Bacteriology
4318:Genes & Development
3792:10.1126/science.1155390
3028:10.1126/science.abe6523
2929:10.1073/pnas.0510928103
2532:Genes & Development
2485:Mayo Clinic Proceedings
1945:Genes & Development
1858:10.1073/pnas.1000848107
1509:Genes & Development
1471:10.1073/pnas.0703890104
1325:10.1186/1471-2164-9-220
359:poly(A)-binding protein
326:adenosine monophosphate
190:Nuclear polyadenylation
6076:cis-regulatory element
5672:10.1073/pnas.68.6.1336
5573:10.1101/gad.11.21.2755
5417:10.1073/pnas.251542798
4983:Nucleic Acids Research
4698:Nucleic Acids Research
4601:Nucleic Acids Research
4367:Nucleic Acids Research
4036:10.1074/jbc.M508848200
3878:Nucleic Acids Research
3666:Nucleic Acids Research
3392:Nucleic Acids Research
2810:Nucleic Acids Research
2758:Nucleic Acids Research
2597:10.1074/jbc.M701256200
2544:10.1101/gad.12.20.3226
2369:10.1074/jbc.270.6.2800
2307:Nucleic Acids Research
2051:Nucleic Acids Research
1660:Nucleic Acids Research
700:nucleotides in them).
593:
481:
452:long-term potentiation
388:3′ untranslated region
330:adenosine triphosphate
306:polyadenylation signal
162:). RNAs are produced (
139:
37:
4710:10.1093/nar/30.7.1427
4065:Nature Communications
591:
520:(CstF), increases in
479:
450:could play a role in
277:: cleavage factor II
137:
124:Further information:
43:is the addition of a
35:
6320:Alternative splicing
6098:alternative splicing
6088:Post-transcriptional
5914:Transcription factor
5768:at Wikimedia Commons
5505:viralzone.expasy.org
4946:10.1093/emboj/cdf686
3505:10.1038/nrm.2016.116
3136:10.1128/MCB.02470-05
2409:10.1093/emboj/cdf390
1759:10.1101/gr.10.7.1001
1705:ACS Chemical Biology
1009:Journal of Phycology
740:Alfalfa mosaic virus
184:untranslated regions
103:alternative splicing
6022:Transfer RNA (tRNA)
5663:1971PNAS...68.1336E
5408:2001PNAS...9814286N
5402:(25): 14286–14291.
5349:2013PLoSO...870548W
5286:Journal of Virology
4862:10.1128/JB.00327-07
4758:2006CRvPS..25...65S
4379:10.1093/nar/gkaa722
4142:10.1038/nature07488
4134:2008Natur.456..464L
4077:2018NatCo...9.5331O
3784:2008Sci...320.1643S
2920:2006PNAS..103.4034W
2166:1996Sci...274.1517S
1957:10.1101/gad.1298605
1849:2010PNAS..10710062Y
1521:10.1101/gad.1352605
1462:2007PNAS..10417719S
1076:2005CBio...15.R635A
1021:2013JPcgy..49..570Z
610:secondary structure
526:lipopolysaccharides
272:: cleavage factor I
221:long noncoding RNAs
6431:5′ cap methylation
6136:Influential people
6115:Post-translational
5934:Post-transcription
5044:10.1105/tpc.013326
4995:10.1093/nar/gkl763
4613:10.1093/nar/gkl357
4564:10.1261/rna.652807
4373:(D1): D:243–D253.
4330:10.1101/gad.473408
4191:10.1261/rna.577707
3983:10.1101/gr.5532707
3890:10.1093/nar/gkn624
3678:10.1093/nar/gkn540
3404:10.1093/nar/gki158
3354:10.1242/dev.021444
3022:(6529): eabe6523.
2871:10.1101/gr.2122004
2822:10.1093/nar/gkm830
2770:10.1093/nar/gkx152
2319:10.1093/nar/gkn080
2063:10.1093/nar/gkn158
1672:10.1093/nar/gkl919
1378:10.1261/rna.782308
1281:10.1093/hmg/ddl046
1235:10.1261/rna.848208
768:enzymatic activity
673:Haloferax volcanii
594:
482:
405:) can bind to the
392:immature egg cells
353:Downstream effects
246:Proteins involved:
140:
38:
6476:
6475:
6417:
6416:
6413:
6412:
6330:pre-mRNA factors
6156:
6155:
6040:
6039:
5970:
5969:
5846:Special transfers
5764:Media related to
5620:978-0-12-540071-8
5221:10.1021/bi8012214
5094:978-0-12-374377-0
4799:(9–10): 992–997.
3841:10.7150/ijms.5.73
3672:(17): 5581–5590.
2764:(10): 6074–6086.
2721:10.1261/rna.46306
2160:(5292): 1517–20.
1717:10.1021/cb800138w
1203:978-0-87901-500-8
1029:10.1111/jpy.12068
705:CCA-adding enzyme
687:and the archaeal
367:initiation factor
290:RNA polymerase II
282:
281:
231:, which mediates
120:Background on RNA
16:(Redirected from
6501:
6282:
6215:5′ cap formation
6203:
6183:
6176:
6169:
6160:
5981:
5878:
5796:
5789:
5782:
5773:
5763:
5748:
5738:
5715:The EMBO Journal
5695:
5694:
5684:
5674:
5657:(6): 1336–1340.
5639:
5633:
5632:
5595:
5586:
5585:
5575:
5551:
5545:
5544:
5542:
5533:(4): 1142–1149.
5515:
5509:
5508:
5497:
5491:
5490:
5480:
5470:
5446:
5440:
5439:
5429:
5419:
5387:
5381:
5380:
5370:
5360:
5328:
5322:
5321:
5311:
5301:
5292:(4): 3473–3476.
5277:
5271:
5270:
5242:
5233:
5232:
5215:(50): 13158–68.
5203:
5197:
5196:
5186:
5162:
5156:
5155:
5145:
5113:
5107:
5106:
5072:
5066:
5065:
5055:
5023:
5017:
5016:
5006:
4974:
4968:
4967:
4957:
4934:The EMBO Journal
4925:
4919:
4918:
4890:
4884:
4883:
4873:
4841:
4835:
4834:
4824:
4784:
4778:
4777:
4741:
4732:
4731:
4721:
4689:
4678:
4677:
4641:
4635:
4634:
4624:
4592:
4586:
4585:
4575:
4543:
4534:
4533:
4515:
4491:
4485:
4484:
4474:
4442:
4436:
4435:
4407:
4401:
4400:
4390:
4358:
4352:
4351:
4341:
4309:
4303:
4302:
4292:
4268:
4262:
4261:
4251:
4228:The EMBO Journal
4219:
4213:
4212:
4202:
4170:
4164:
4163:
4153:
4113:
4107:
4106:
4096:
4055:
4049:
4048:
4038:
4029:(48): 39950–61.
4014:
4005:
4004:
3994:
3962:
3956:
3955:
3918:
3912:
3911:
3901:
3869:
3863:
3862:
3852:
3820:
3814:
3813:
3803:
3778:(5883): 1643–7.
3763:
3757:
3756:
3746:
3714:
3708:
3707:
3697:
3657:
3651:
3650:
3640:
3600:
3594:
3593:
3583:
3565:
3541:
3535:
3534:
3524:
3484:
3475:
3474:
3464:
3441:The EMBO Journal
3432:
3426:
3425:
3415:
3383:
3377:
3376:
3366:
3356:
3332:
3326:
3325:
3307:
3283:
3277:
3276:
3248:
3242:
3241:
3231:
3199:
3193:
3192:
3164:
3158:
3157:
3147:
3115:
3109:
3108:
3089:10.1038/35067025
3072:
3066:
3065:
3047:
3007:
3001:
3000:
2990:
2958:
2952:
2951:
2941:
2931:
2899:
2893:
2892:
2882:
2850:
2844:
2843:
2833:
2801:
2792:
2791:
2781:
2749:
2743:
2742:
2732:
2700:
2694:
2693:
2683:
2660:The EMBO Journal
2651:
2645:
2644:
2616:
2610:
2609:
2599:
2590:(34): 25067–75.
2575:
2566:
2565:
2555:
2523:
2517:
2516:
2497:10.4065/77.8.785
2480:
2474:
2473:
2454:10.1038/nsmb1253
2437:
2431:
2430:
2420:
2397:The EMBO Journal
2388:
2382:
2381:
2371:
2347:
2341:
2340:
2330:
2298:
2292:
2291:
2281:
2249:
2243:
2242:
2232:
2221:10.1101/gr.62002
2200:
2194:
2193:
2149:
2143:
2140:
2134:
2133:
2123:
2112:10.1038/nsmb1352
2091:
2085:
2084:
2074:
2042:
2031:
2030:
2020:
1997:The EMBO Journal
1988:
1979:
1978:
1968:
1936:
1930:
1929:
1919:
1887:
1881:
1880:
1870:
1860:
1828:
1822:
1821:
1811:
1787:
1781:
1780:
1770:
1738:
1729:
1728:
1700:
1694:
1693:
1683:
1651:
1642:
1641:
1631:
1608:The EMBO Journal
1599:
1586:
1585:
1554:Mammalian Genome
1549:
1543:
1542:
1532:
1500:
1494:
1493:
1483:
1473:
1456:(45): 17719–24.
1441:
1435:
1434:
1406:
1400:
1399:
1389:
1357:
1348:
1347:
1337:
1327:
1303:
1294:
1293:
1283:
1268:"Non-coding RNA"
1263:
1257:
1256:
1246:
1214:
1208:
1207:
1195:
1185:
1179:
1178:
1150:
1144:
1143:
1115:
1106:
1105:
1087:
1055:
1049:
1048:
1004:
998:
997:
987:
955:
949:
948:
938:
906:
895:
894:
884:
852:
843:
842:
824:
800:
744:Duck Hepatitis A
243:
242:
219:. But, for many
21:
6509:
6508:
6504:
6503:
6502:
6500:
6499:
6498:
6489:Gene expression
6479:
6478:
6477:
6472:
6409:
6324:
6271:
6267:Polyuridylation
6220:Polyadenylation
6192:
6187:
6157:
6152:
6131:
6066:Transcriptional
6036:
6005:
5966:
5957:Polyadenylation
5928:
5902:
5867:
5861:Protein→Protein
5812:
5805:
5803:Gene expression
5800:
5766:Polyadenylation
5756:
5751:
5708:
5704:
5702:Further reading
5699:
5698:
5641:
5640:
5636:
5621:
5597:
5596:
5589:
5566:(21): 2755–66.
5553:
5552:
5548:
5517:
5516:
5512:
5499:
5498:
5494:
5448:
5447:
5443:
5389:
5388:
5384:
5330:
5329:
5325:
5279:
5278:
5274:
5244:
5243:
5236:
5205:
5204:
5200:
5164:
5163:
5159:
5128:(12): 1188–93.
5115:
5114:
5110:
5095:
5074:
5073:
5069:
5025:
5024:
5020:
4989:(20): 5923–31.
4976:
4975:
4971:
4940:(24): 6905–14.
4927:
4926:
4922:
4892:
4891:
4887:
4843:
4842:
4838:
4786:
4785:
4781:
4743:
4742:
4735:
4691:
4690:
4681:
4643:
4642:
4638:
4607:(10): 2966–75.
4594:
4593:
4589:
4558:(11): 1834–49.
4545:
4544:
4537:
4493:
4492:
4488:
4444:
4443:
4439:
4409:
4408:
4404:
4360:
4359:
4355:
4311:
4310:
4306:
4270:
4269:
4265:
4234:(11): 2658–69.
4221:
4220:
4216:
4172:
4171:
4167:
4128:(7221): 464–9.
4115:
4114:
4110:
4057:
4056:
4052:
4016:
4015:
4008:
3971:Genome Research
3964:
3963:
3959:
3920:
3919:
3915:
3884:(19): 6318–32.
3871:
3870:
3866:
3822:
3821:
3817:
3765:
3764:
3760:
3729:(6): 993–1012.
3723:Pflügers Archiv
3716:
3715:
3711:
3659:
3658:
3654:
3602:
3601:
3597:
3543:
3542:
3538:
3486:
3485:
3478:
3434:
3433:
3429:
3385:
3384:
3380:
3347:(11): 1969–79.
3334:
3333:
3329:
3285:
3284:
3280:
3250:
3249:
3245:
3201:
3200:
3196:
3166:
3165:
3161:
3130:(11): 4277–87.
3117:
3116:
3112:
3074:
3073:
3069:
3009:
3008:
3004:
2960:
2959:
2955:
2901:
2900:
2896:
2859:Genome Research
2852:
2851:
2847:
2803:
2802:
2795:
2751:
2750:
2746:
2702:
2701:
2697:
2666:(17): 4723–33.
2653:
2652:
2648:
2618:
2617:
2613:
2577:
2576:
2569:
2538:(20): 3226–35.
2525:
2524:
2520:
2482:
2481:
2477:
2439:
2438:
2434:
2403:(15): 4125–35.
2390:
2389:
2385:
2349:
2348:
2344:
2300:
2299:
2295:
2251:
2250:
2246:
2209:Genome Research
2202:
2201:
2197:
2151:
2150:
2146:
2141:
2137:
2093:
2092:
2088:
2044:
2043:
2034:
2003:(20): 4854–64.
1990:
1989:
1982:
1951:(11): 1315–27.
1938:
1937:
1933:
1889:
1888:
1884:
1843:(22): 10062–7.
1830:
1829:
1825:
1789:
1788:
1784:
1747:Genome Research
1740:
1739:
1732:
1702:
1701:
1697:
1653:
1652:
1645:
1601:
1600:
1589:
1560:(7–8): 454–92.
1551:
1550:
1546:
1515:(18): 2164–75.
1502:
1501:
1497:
1443:
1442:
1438:
1408:
1407:
1403:
1359:
1358:
1351:
1305:
1304:
1297:
1265:
1264:
1260:
1216:
1215:
1211:
1204:
1187:
1186:
1182:
1152:
1151:
1147:
1117:
1116:
1109:
1064:Current Biology
1057:
1056:
1052:
1006:
1005:
1001:
957:
956:
952:
908:
907:
898:
854:
853:
846:
802:
801:
794:
789:
777:
764:
653:
586:
550:non-coding RNAs
546:
538:DNA methylation
524:in response to
516:, a subunit of
495:Ribo-sequencing
487:
430:, during early
424:
390:of an mRNA. In
380:
355:
273:
268:
263:
258:
253:
247:
241:
197:
192:
132:
122:
111:non-coding RNAs
95:set of proteins
73:gene expression
41:Polyadenylation
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
6507:
6505:
6497:
6496:
6491:
6481:
6480:
6474:
6473:
6471:
6470:
6469:
6468:
6463:
6458:
6453:
6448:
6443:
6436:mRNA decapping
6433:
6427:
6425:
6419:
6418:
6415:
6414:
6411:
6410:
6408:
6407:
6406:
6405:
6400:
6395:
6390:
6385:
6380:
6375:
6370:
6365:
6360:
6355:
6350:
6345:
6334:
6332:
6326:
6325:
6323:
6322:
6317:
6316:
6315:
6310:
6300:
6295:
6285:
6279:
6273:
6272:
6270:
6269:
6264:
6259:
6254:
6253:
6252:
6247:
6242:
6237:
6232:
6227:
6217:
6212:
6210:Precursor mRNA
6206:
6200:
6194:
6193:
6188:
6186:
6185:
6178:
6171:
6163:
6154:
6153:
6151:
6150:
6145:
6143:François Jacob
6139:
6137:
6133:
6132:
6130:
6129:
6128:
6127:
6122:
6112:
6107:
6106:
6105:
6100:
6095:
6085:
6080:
6079:
6078:
6073:
6063:
6062:
6061:
6050:
6048:
6042:
6041:
6038:
6037:
6035:
6034:
6029:
6024:
6019:
6013:
6011:
6007:
6006:
6004:
6003:
5998:
5993:
5987:
5985:
5978:
5972:
5971:
5968:
5967:
5965:
5964:
5959:
5954:
5949:
5944:
5938:
5936:
5930:
5929:
5927:
5926:
5921:
5919:RNA polymerase
5916:
5910:
5908:
5904:
5903:
5901:
5900:
5895:
5890:
5884:
5882:
5875:
5869:
5868:
5866:
5865:
5864:
5863:
5858:
5853:
5843:
5842:
5841:
5823:
5817:
5815:
5807:
5806:
5801:
5799:
5798:
5791:
5784:
5776:
5770:
5769:
5755:
5754:External links
5752:
5750:
5749:
5705:
5703:
5700:
5697:
5696:
5634:
5619:
5587:
5546:
5510:
5492:
5441:
5382:
5323:
5272:
5234:
5198:
5157:
5108:
5093:
5067:
5038:(9): 2003–19.
5032:The Plant Cell
5018:
4969:
4920:
4885:
4836:
4779:
4733:
4704:(7): 1427–64.
4679:
4636:
4587:
4535:
4486:
4457:(6): 890–901.
4437:
4402:
4353:
4304:
4283:(3): 298–310.
4277:Molecular Cell
4263:
4214:
4185:(7): 1103–15.
4165:
4108:
4050:
4006:
3957:
3930:(2): 293–301.
3913:
3864:
3815:
3758:
3709:
3652:
3615:(3): 277–289.
3595:
3550:Genome Biology
3536:
3476:
3427:
3378:
3327:
3278:
3243:
3208:Theriogenology
3194:
3159:
3110:
3067:
3002:
2973:(4): 2017–29.
2953:
2914:(11): 4034–9.
2894:
2865:(7): 1315–23.
2845:
2793:
2744:
2715:(7): 1323–37.
2695:
2646:
2611:
2567:
2518:
2491:(8): 785–808.
2475:
2432:
2383:
2342:
2313:(7): 2418–33.
2293:
2264:(9): 1117–31.
2244:
2215:(7): 1068–74.
2195:
2144:
2135:
2086:
2057:(9): 3150–61.
2032:
1980:
1931:
1882:
1823:
1802:(6): 1467–76.
1796:Molecular Cell
1782:
1753:(7): 1001–10.
1730:
1711:(10): 609–17.
1695:
1643:
1587:
1544:
1495:
1436:
1401:
1349:
1295:
1258:
1209:
1202:
1180:
1145:
1107:
1070:(16): R635-8.
1050:
999:
970:(8): 1079–90.
950:
896:
867:(1–2): 11–23.
844:
791:
790:
788:
785:
784:
783:
776:
773:
763:
760:
652:
649:
585:
582:
545:
542:
486:
483:
423:
420:
396:egg activation
382:In eukaryotic
379:
376:
354:
351:
294:precursor mRNA
280:
279:
240:
237:
196:
193:
191:
188:
121:
118:
101:), similar to
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
6506:
6495:
6494:Messenger RNA
6492:
6490:
6487:
6486:
6484:
6467:
6464:
6462:
6459:
6457:
6454:
6452:
6449:
6447:
6444:
6442:
6439:
6438:
6437:
6434:
6432:
6429:
6428:
6426:
6424:
6420:
6404:
6401:
6399:
6396:
6394:
6391:
6389:
6386:
6384:
6381:
6379:
6376:
6374:
6371:
6369:
6366:
6364:
6361:
6359:
6356:
6354:
6351:
6349:
6346:
6344:
6341:
6340:
6339:
6336:
6335:
6333:
6331:
6327:
6321:
6318:
6314:
6311:
6309:
6306:
6305:
6304:
6301:
6299:
6296:
6294:
6290:
6287:
6286:
6283:
6280:
6278:
6274:
6268:
6265:
6263:
6260:
6258:
6255:
6251:
6248:
6246:
6243:
6241:
6238:
6236:
6233:
6231:
6228:
6226:
6223:
6222:
6221:
6218:
6216:
6213:
6211:
6208:
6207:
6204:
6201:
6199:
6195:
6191:
6184:
6179:
6177:
6172:
6170:
6165:
6164:
6161:
6149:
6148:Jacques Monod
6146:
6144:
6141:
6140:
6138:
6134:
6126:
6123:
6121:
6118:
6117:
6116:
6113:
6111:
6110:Translational
6108:
6104:
6101:
6099:
6096:
6094:
6091:
6090:
6089:
6086:
6084:
6081:
6077:
6074:
6072:
6069:
6068:
6067:
6064:
6060:
6057:
6056:
6055:
6052:
6051:
6049:
6047:
6043:
6033:
6030:
6028:
6025:
6023:
6020:
6018:
6015:
6014:
6012:
6008:
6002:
5999:
5997:
5994:
5992:
5989:
5988:
5986:
5982:
5979:
5977:
5973:
5963:
5960:
5958:
5955:
5953:
5950:
5948:
5945:
5943:
5940:
5939:
5937:
5935:
5931:
5925:
5922:
5920:
5917:
5915:
5912:
5911:
5909:
5905:
5899:
5896:
5894:
5891:
5889:
5886:
5885:
5883:
5879:
5876:
5874:
5873:Transcription
5870:
5862:
5859:
5857:
5854:
5852:
5849:
5848:
5847:
5844:
5840:
5836:
5832:
5829:
5828:
5827:
5826:Central dogma
5824:
5822:
5819:
5818:
5816:
5814:
5808:
5804:
5797:
5792:
5790:
5785:
5783:
5778:
5777:
5774:
5767:
5762:
5758:
5757:
5753:
5746:
5742:
5737:
5732:
5728:
5724:
5721:(3): 482–98.
5720:
5716:
5712:
5707:
5706:
5701:
5692:
5688:
5683:
5678:
5673:
5668:
5664:
5660:
5656:
5652:
5648:
5644:
5638:
5635:
5630:
5626:
5622:
5616:
5612:
5608:
5604:
5600:
5594:
5592:
5588:
5583:
5579:
5574:
5569:
5565:
5561:
5557:
5550:
5547:
5541:
5536:
5532:
5528:
5524:
5520:
5519:Edmonds, Mary
5514:
5511:
5506:
5502:
5496:
5493:
5488:
5484:
5479:
5474:
5469:
5464:
5460:
5456:
5452:
5445:
5442:
5437:
5433:
5428:
5423:
5418:
5413:
5409:
5405:
5401:
5397:
5393:
5386:
5383:
5378:
5374:
5369:
5364:
5359:
5354:
5350:
5346:
5343:(7): e70548.
5342:
5338:
5334:
5327:
5324:
5319:
5315:
5310:
5305:
5300:
5295:
5291:
5287:
5283:
5276:
5273:
5268:
5264:
5260:
5256:
5253:(4): 247–55.
5252:
5248:
5241:
5239:
5235:
5230:
5226:
5222:
5218:
5214:
5210:
5202:
5199:
5194:
5190:
5185:
5180:
5177:(1): 97–103.
5176:
5172:
5168:
5161:
5158:
5153:
5149:
5144:
5139:
5135:
5131:
5127:
5123:
5119:
5112:
5109:
5104:
5100:
5096:
5090:
5086:
5082:
5078:
5071:
5068:
5063:
5059:
5054:
5049:
5045:
5041:
5037:
5033:
5029:
5022:
5019:
5014:
5010:
5005:
5000:
4996:
4992:
4988:
4984:
4980:
4973:
4970:
4965:
4961:
4956:
4951:
4947:
4943:
4939:
4935:
4931:
4924:
4921:
4916:
4912:
4908:
4904:
4900:
4896:
4889:
4886:
4881:
4877:
4872:
4867:
4863:
4859:
4856:(1): 98–106.
4855:
4851:
4847:
4840:
4837:
4832:
4828:
4823:
4818:
4814:
4810:
4806:
4802:
4798:
4794:
4790:
4783:
4780:
4775:
4771:
4767:
4763:
4759:
4755:
4751:
4747:
4740:
4738:
4734:
4729:
4725:
4720:
4715:
4711:
4707:
4703:
4699:
4695:
4688:
4686:
4684:
4680:
4675:
4671:
4667:
4663:
4659:
4655:
4652:(3): 235–44.
4651:
4647:
4640:
4637:
4632:
4628:
4623:
4618:
4614:
4610:
4606:
4602:
4598:
4591:
4588:
4583:
4579:
4574:
4569:
4565:
4561:
4557:
4553:
4549:
4542:
4540:
4536:
4531:
4527:
4523:
4519:
4514:
4509:
4506:(5): 713–24.
4505:
4501:
4497:
4490:
4487:
4482:
4478:
4473:
4468:
4464:
4460:
4456:
4452:
4448:
4441:
4438:
4433:
4429:
4425:
4421:
4418:(2): 209–14.
4417:
4413:
4406:
4403:
4398:
4394:
4389:
4384:
4380:
4376:
4372:
4368:
4364:
4357:
4354:
4349:
4345:
4340:
4335:
4331:
4327:
4324:(9): 1141–6.
4323:
4319:
4315:
4308:
4305:
4300:
4296:
4291:
4286:
4282:
4278:
4274:
4267:
4264:
4259:
4255:
4250:
4245:
4241:
4237:
4233:
4229:
4225:
4218:
4215:
4210:
4206:
4201:
4196:
4192:
4188:
4184:
4180:
4176:
4169:
4166:
4161:
4157:
4152:
4147:
4143:
4139:
4135:
4131:
4127:
4123:
4119:
4112:
4109:
4104:
4100:
4095:
4090:
4086:
4082:
4078:
4074:
4070:
4066:
4062:
4054:
4051:
4046:
4042:
4037:
4032:
4028:
4024:
4020:
4013:
4011:
4007:
4002:
3998:
3993:
3988:
3984:
3980:
3977:(2): 156–65.
3976:
3972:
3968:
3961:
3958:
3953:
3949:
3945:
3941:
3937:
3933:
3929:
3925:
3917:
3914:
3909:
3905:
3900:
3895:
3891:
3887:
3883:
3879:
3875:
3868:
3865:
3860:
3856:
3851:
3846:
3842:
3838:
3834:
3830:
3826:
3819:
3816:
3811:
3807:
3802:
3797:
3793:
3789:
3785:
3781:
3777:
3773:
3769:
3762:
3759:
3754:
3750:
3745:
3740:
3736:
3732:
3728:
3724:
3720:
3713:
3710:
3705:
3701:
3696:
3691:
3687:
3683:
3679:
3675:
3671:
3667:
3663:
3656:
3653:
3648:
3644:
3639:
3634:
3630:
3626:
3622:
3618:
3614:
3610:
3606:
3599:
3596:
3591:
3587:
3582:
3577:
3573:
3569:
3564:
3559:
3555:
3551:
3547:
3540:
3537:
3532:
3528:
3523:
3518:
3514:
3510:
3506:
3502:
3498:
3494:
3490:
3483:
3481:
3477:
3472:
3468:
3463:
3458:
3454:
3450:
3447:(3): 482–98.
3446:
3442:
3438:
3431:
3428:
3423:
3419:
3414:
3409:
3405:
3401:
3398:(1): 201–12.
3397:
3393:
3389:
3382:
3379:
3374:
3370:
3365:
3360:
3355:
3350:
3346:
3342:
3338:
3331:
3328:
3323:
3319:
3315:
3311:
3306:
3301:
3298:(3): 434–48.
3297:
3293:
3289:
3282:
3279:
3274:
3270:
3266:
3262:
3259:(6): 279–85.
3258:
3254:
3247:
3244:
3239:
3235:
3230:
3225:
3221:
3217:
3213:
3209:
3205:
3198:
3195:
3190:
3186:
3182:
3178:
3175:(4): 1181–9.
3174:
3170:
3163:
3160:
3155:
3151:
3146:
3141:
3137:
3133:
3129:
3125:
3121:
3114:
3111:
3106:
3102:
3098:
3094:
3090:
3086:
3083:(4): 237–46.
3082:
3078:
3071:
3068:
3063:
3059:
3055:
3051:
3046:
3041:
3037:
3033:
3029:
3025:
3021:
3017:
3013:
3006:
3003:
2998:
2994:
2989:
2984:
2980:
2976:
2972:
2968:
2964:
2957:
2954:
2949:
2945:
2940:
2935:
2930:
2925:
2921:
2917:
2913:
2909:
2905:
2898:
2895:
2890:
2886:
2881:
2876:
2872:
2868:
2864:
2860:
2856:
2849:
2846:
2841:
2837:
2832:
2827:
2823:
2819:
2815:
2811:
2807:
2800:
2798:
2794:
2789:
2785:
2780:
2775:
2771:
2767:
2763:
2759:
2755:
2748:
2745:
2740:
2736:
2731:
2726:
2722:
2718:
2714:
2710:
2706:
2699:
2696:
2691:
2687:
2682:
2677:
2673:
2669:
2665:
2661:
2657:
2650:
2647:
2642:
2638:
2634:
2630:
2627:(3): 285–92.
2626:
2622:
2615:
2612:
2607:
2603:
2598:
2593:
2589:
2585:
2581:
2574:
2572:
2568:
2563:
2559:
2554:
2549:
2545:
2541:
2537:
2533:
2529:
2522:
2519:
2514:
2510:
2506:
2502:
2498:
2494:
2490:
2486:
2479:
2476:
2471:
2467:
2463:
2459:
2455:
2451:
2447:
2443:
2436:
2433:
2428:
2424:
2419:
2414:
2410:
2406:
2402:
2398:
2394:
2387:
2384:
2379:
2375:
2370:
2365:
2362:(6): 2800–8.
2361:
2357:
2353:
2346:
2343:
2338:
2334:
2329:
2324:
2320:
2316:
2312:
2308:
2304:
2297:
2294:
2289:
2285:
2280:
2275:
2271:
2267:
2263:
2259:
2255:
2248:
2245:
2240:
2236:
2231:
2226:
2222:
2218:
2214:
2210:
2206:
2199:
2196:
2191:
2187:
2183:
2179:
2175:
2171:
2167:
2163:
2159:
2155:
2148:
2145:
2139:
2136:
2131:
2127:
2122:
2117:
2113:
2109:
2105:
2101:
2097:
2090:
2087:
2082:
2078:
2073:
2068:
2064:
2060:
2056:
2052:
2048:
2041:
2039:
2037:
2033:
2028:
2024:
2019:
2014:
2010:
2006:
2002:
1998:
1994:
1987:
1985:
1981:
1976:
1972:
1967:
1962:
1958:
1954:
1950:
1946:
1942:
1935:
1932:
1927:
1923:
1918:
1913:
1909:
1905:
1902:(3): 368–77.
1901:
1897:
1893:
1886:
1883:
1878:
1874:
1869:
1864:
1859:
1854:
1850:
1846:
1842:
1838:
1834:
1827:
1824:
1819:
1815:
1810:
1805:
1801:
1797:
1793:
1786:
1783:
1778:
1774:
1769:
1764:
1760:
1756:
1752:
1748:
1744:
1737:
1735:
1731:
1726:
1722:
1718:
1714:
1710:
1706:
1699:
1696:
1691:
1687:
1682:
1677:
1673:
1669:
1666:(1): 234–46.
1665:
1661:
1657:
1650:
1648:
1644:
1639:
1635:
1630:
1625:
1621:
1617:
1614:(2): 585–94.
1613:
1609:
1605:
1598:
1596:
1594:
1592:
1588:
1583:
1579:
1575:
1571:
1567:
1563:
1559:
1555:
1548:
1545:
1540:
1536:
1531:
1526:
1522:
1518:
1514:
1510:
1506:
1499:
1496:
1491:
1487:
1482:
1477:
1472:
1467:
1463:
1459:
1455:
1451:
1447:
1440:
1437:
1432:
1428:
1424:
1420:
1417:(5): 487–98.
1416:
1412:
1405:
1402:
1397:
1393:
1388:
1383:
1379:
1375:
1371:
1367:
1363:
1356:
1354:
1350:
1345:
1341:
1336:
1331:
1326:
1321:
1317:
1313:
1309:
1302:
1300:
1296:
1291:
1287:
1282:
1277:
1273:
1269:
1262:
1259:
1254:
1250:
1245:
1240:
1236:
1232:
1228:
1224:
1220:
1213:
1210:
1205:
1199:
1194:
1193:
1184:
1181:
1176:
1172:
1168:
1164:
1160:
1156:
1149:
1146:
1141:
1137:
1133:
1129:
1126:(1): 173–97.
1125:
1121:
1114:
1112:
1108:
1103:
1099:
1095:
1091:
1086:
1081:
1077:
1073:
1069:
1065:
1061:
1054:
1051:
1046:
1042:
1038:
1034:
1030:
1026:
1022:
1018:
1014:
1010:
1003:
1000:
995:
991:
986:
981:
977:
973:
969:
965:
961:
954:
951:
946:
942:
937:
932:
928:
924:
921:(2): 446–56.
920:
916:
912:
905:
903:
901:
897:
892:
888:
883:
878:
874:
870:
866:
862:
858:
851:
849:
845:
840:
836:
832:
828:
823:
818:
815:(4): 501–12.
814:
810:
806:
799:
797:
793:
786:
782:
779:
778:
774:
772:
769:
761:
759:
757:
753:
749:
745:
741:
737:
733:
729:
724:
722:
721:cyanobacteria
718:
714:
710:
706:
701:
698:
694:
690:
686:
682:
677:
675:
674:
669:
668:
662:
658:
650:
648:
646:
643:that have an
642:
638:
634:
629:
626:
622:
617:
615:
611:
607:
603:
599:
590:
583:
581:
579:
575:
574:TRAMP complex
571:
567:
563:
559:
555:
551:
543:
541:
539:
535:
531:
527:
523:
519:
515:
510:
507:
503:
498:
496:
492:
484:
478:
474:
472:
468:
464:
460:
455:
453:
447:
445:
441:
437:
433:
432:embryogenesis
429:
421:
419:
417:
413:
412:budding yeast
408:
404:
399:
397:
393:
389:
385:
384:somatic cells
378:Deadenylation
377:
375:
372:
368:
364:
360:
352:
350:
348:
344:
339:
335:
334:pyrophosphate
331:
327:
323:
318:
314:
311:
307:
303:
299:
295:
291:
287:
278:
276:
271:
266:
261:
256:
251:
245:
244:
238:
236:
234:
230:
226:
222:
218:
212:
210:
206:
202:
194:
189:
187:
185:
181:
180:
174:
171:
167:
166:
161:
157:
153:
149:
145:
136:
131:
130:Messenger RNA
127:
119:
117:
114:
112:
106:
104:
100:
96:
92:
88:
85:
81:
80:transcription
76:
74:
70:
66:
62:
58:
54:
50:
49:messenger RNA
46:
42:
34:
30:
19:
6291: /
6277:RNA splicing
6219:
6125:irreversible
6010:Key elements
5956:
5907:Key elements
5821:Genetic code
5811:Introduction
5718:
5714:
5654:
5650:
5637:
5602:
5563:
5559:
5549:
5530:
5526:
5513:
5504:
5495:
5458:
5454:
5444:
5399:
5395:
5385:
5340:
5336:
5326:
5289:
5285:
5275:
5250:
5246:
5212:
5209:Biochemistry
5208:
5201:
5174:
5170:
5160:
5125:
5122:EMBO Reports
5121:
5111:
5076:
5070:
5035:
5031:
5021:
4986:
4982:
4972:
4937:
4933:
4923:
4901:(4): 266–9.
4898:
4894:
4888:
4853:
4849:
4839:
4796:
4792:
4782:
4752:(1): 65–77.
4749:
4745:
4701:
4697:
4649:
4645:
4639:
4604:
4600:
4590:
4555:
4551:
4503:
4499:
4489:
4454:
4450:
4440:
4415:
4411:
4405:
4370:
4366:
4356:
4321:
4317:
4307:
4280:
4276:
4266:
4231:
4227:
4217:
4182:
4178:
4168:
4125:
4121:
4111:
4068:
4064:
4053:
4026:
4022:
3974:
3970:
3960:
3927:
3923:
3916:
3881:
3877:
3867:
3832:
3828:
3818:
3775:
3771:
3761:
3726:
3722:
3712:
3669:
3665:
3655:
3612:
3609:Cell Reports
3608:
3598:
3556:(12): R100.
3553:
3549:
3539:
3499:(1): 18–30.
3496:
3492:
3444:
3440:
3430:
3395:
3391:
3381:
3344:
3340:
3330:
3295:
3291:
3281:
3256:
3252:
3246:
3211:
3207:
3197:
3172:
3168:
3162:
3127:
3123:
3113:
3080:
3076:
3070:
3019:
3015:
3005:
2970:
2966:
2956:
2911:
2907:
2897:
2862:
2858:
2848:
2816:(19): e132.
2813:
2809:
2761:
2757:
2747:
2712:
2708:
2698:
2663:
2659:
2649:
2624:
2620:
2614:
2587:
2583:
2535:
2531:
2521:
2488:
2484:
2478:
2448:(7): 662–9.
2445:
2441:
2435:
2400:
2396:
2386:
2359:
2355:
2345:
2310:
2306:
2296:
2261:
2257:
2247:
2212:
2208:
2198:
2157:
2153:
2147:
2138:
2103:
2099:
2089:
2054:
2050:
2000:
1996:
1948:
1944:
1934:
1899:
1895:
1885:
1840:
1836:
1826:
1799:
1795:
1785:
1750:
1746:
1708:
1704:
1698:
1663:
1659:
1611:
1607:
1557:
1553:
1547:
1512:
1508:
1498:
1453:
1449:
1439:
1414:
1410:
1404:
1369:
1365:
1315:
1312:BMC Genomics
1311:
1271:
1261:
1229:(3): 404–9.
1226:
1222:
1212:
1191:
1183:
1158:
1154:
1148:
1123:
1119:
1067:
1063:
1053:
1015:(3): 570–9.
1012:
1008:
1002:
967:
963:
953:
918:
914:
864:
860:
812:
808:
765:
730:, including
725:
702:
678:
671:
665:
654:
630:
625:mitochondria
621:trypanosomes
618:
613:
605:
601:
595:
552:, including
547:
511:
499:
488:
456:
448:
434:and in post-
425:
400:
381:
356:
319:
315:
305:
297:
283:
248:
213:
198:
183:
178:
175:
164:
144:poly(A) tail
143:
141:
115:
107:
98:
77:
45:poly(A) tail
44:
40:
39:
29:
6303:Spliceosome
6262:RNA editing
5976:Translation
5813:to genetics
5643:Edmonds, M.
4071:(1): 5331.
3835:(2): 73–9.
3341:Development
3214:(1): 10–6.
2106:(1): 71–8.
1372:(1): 1–10.
736:Coronavirus
732:Influenza A
728:RNA viruses
713:polymerases
685:degradosome
614:degradosome
598:degradosome
522:macrophages
440:nerve cells
349:from RNAs.
343:spliceosome
338:nucleotides
328:units from
179:translation
165:transcribed
65:translation
18:Poly-A tail
6483:Categories
6120:reversible
6083:lac operon
6059:imprinting
6054:Epigenetic
6046:Regulation
6001:Eukaryotic
5947:5' capping
5898:Eukaryotic
5599:Edmonds, M
787:References
752:Poliovirus
664:bacterium
444:translated
292:, such as
286:processive
225:regulatory
158:and U for
87:terminates
67:. In many
61:eukaryotes
59:bases. In
6423:Cytosolic
5991:Bacterial
5888:Bacterial
4813:0006-3002
4646:BioEssays
3686:1362-4962
3629:2211-1247
3572:1474-760X
3513:1471-0080
3062:231195473
3036:0036-8075
2258:Structure
1896:Structure
1582:206956408
1161:: 15–42.
651:Evolution
548:For many
506:microRNAs
438:sites of
418:complex.
239:Mechanism
217:microRNAs
209:stem-loop
201:cytoplasm
168:) from a
6103:microRNA
6017:Ribosome
5996:Archaeal
5952:Splicing
5924:Promoter
5893:Archaeal
5837: →
5833: →
5745:18256699
5629:12102557
5601:(2002).
5487:30319572
5461:: 2250.
5436:11717411
5377:23923003
5337:PLOS ONE
5318:10074205
5267:18177749
5229:19053279
5193:18399989
5152:16282984
5103:19161858
5062:12953107
5013:17065466
4964:12486011
4915:18312863
4880:17965156
4831:22172994
4774:86607431
4728:11917006
4674:26109164
4666:10684583
4631:16738135
4582:17872511
4530:14898055
4522:15935758
4481:21663793
4432:17395456
4397:32976578
4348:18451104
4299:21292162
4258:17464285
4209:17507659
4160:18978773
4103:30552333
4045:16207706
4001:17210931
3908:18835850
3859:18392144
3810:18566288
3753:27220521
3704:18757892
3647:22685694
3590:16356263
3531:27677860
3471:18256699
3422:15647503
3373:18434412
3322:16092673
3314:18267074
3273:17481902
3238:18023855
3189:16169522
3154:16705177
3097:11283721
3054:33414189
2997:18430932
2967:Genetics
2948:16495412
2889:15231747
2840:17933768
2788:28334977
2739:16714281
2690:10970864
2641:15145353
2606:17595167
2505:12173714
2462:17572685
2427:12145212
2337:18304944
2288:17850751
2239:12097343
2190:34840144
2130:18157150
2081:18411206
2027:17024186
1975:15937220
1926:21295486
1877:20479262
1818:14690600
1777:10899149
1725:18817380
1690:17158511
1574:18839252
1539:16131612
1490:17965236
1431:12408966
1411:Genomics
1396:17998288
1344:18479511
1290:16651366
1253:18212021
1175:14140701
1102:19003617
1094:16111937
1045:19863143
1037:27007045
994:10943888
945:10357857
891:11255003
831:11909521
775:See also
637:plastids
530:lysozyme
436:synaptic
428:germline
416:CCR4-Not
195:Function
154:, G for
152:cytosine
150:, C for
69:bacteria
6403:PRPF40B
6398:PRPF40A
6388:PRPF38B
6383:PRPF38A
6198:Nuclear
5856:RNA→DNA
5851:RNA→RNA
5839:Protein
5736:2241648
5691:5288383
5659:Bibcode
5582:9353246
5478:6167517
5404:Bibcode
5368:3726627
5345:Bibcode
5143:1369208
5004:1635327
4871:2223728
4822:3307840
4754:Bibcode
4622:1474067
4573:2040100
4472:3115544
4388:7778938
4339:2335310
4249:1888663
4200:1894925
4151:2597294
4130:Bibcode
4094:6294251
4073:Bibcode
3992:1781347
3952:7448467
3944:6771018
3899:2577349
3850:2288788
3801:2587246
3780:Bibcode
3772:Science
3744:4893057
3695:2553571
3638:3368434
3581:1414089
3522:5483950
3462:2241648
3364:9154023
3229:2239213
3145:1489097
3105:9734550
3045:9491362
3016:Science
2988:2323793
2939:1449641
2916:Bibcode
2831:2095794
2779:5449641
2730:1484436
2562:9784497
2513:2237085
2470:5777074
2378:7852352
2328:2367721
2279:2032019
2182:8929410
2162:Bibcode
2154:Science
2121:2836588
2072:2396415
2018:1618107
1966:1142555
1917:3056899
1868:2890493
1845:Bibcode
1681:1802579
1638:8440247
1530:1221887
1481:2077053
1458:Bibcode
1387:2151031
1335:2391170
1318:: 220.
1244:2248257
1140:9242905
1072:Bibcode
1017:Bibcode
985:1369983
882:3340483
762:History
717:archaea
689:exosome
657:domains
645:exosome
641:archaea
606:RNase E
578:exosome
514:CstF-64
467:Pumilio
363:exosome
347:introns
205:histone
156:guanine
148:adenine
91:3′-most
57:adenine
6393:PRPF39
6378:PRPF31
6373:PRPF19
6368:PRPF18
6353:PRPF4B
6289:Intron
5743:
5733:
5689:
5682:389184
5679:
5627:
5617:
5580:
5485:
5475:
5434:
5424:
5375:
5365:
5316:
5309:104115
5306:
5265:
5227:
5191:
5150:
5140:
5101:
5091:
5060:
5053:181327
5050:
5011:
5001:
4962:
4955:139106
4952:
4913:
4878:
4868:
4829:
4819:
4811:
4772:
4726:
4719:101826
4716:
4672:
4664:
4629:
4619:
4580:
4570:
4528:
4520:
4479:
4469:
4430:
4395:
4385:
4346:
4336:
4297:
4256:
4246:
4207:
4197:
4158:
4148:
4122:Nature
4101:
4091:
4043:
3999:
3989:
3950:
3942:
3906:
3896:
3857:
3847:
3808:
3798:
3751:
3741:
3702:
3692:
3684:
3645:
3635:
3627:
3588:
3578:
3570:
3529:
3519:
3511:
3469:
3459:
3420:
3413:546146
3410:
3371:
3361:
3320:
3312:
3271:
3236:
3226:
3187:
3152:
3142:
3103:
3095:
3060:
3052:
3042:
3034:
2995:
2985:
2946:
2936:
2887:
2880:442147
2877:
2838:
2828:
2786:
2776:
2737:
2727:
2688:
2681:302064
2678:
2639:
2604:
2560:
2553:317214
2550:
2511:
2503:
2468:
2460:
2425:
2418:126137
2415:
2376:
2335:
2325:
2286:
2276:
2237:
2230:186619
2227:
2188:
2180:
2128:
2118:
2079:
2069:
2025:
2015:
1973:
1963:
1924:
1914:
1875:
1865:
1816:
1775:
1768:310884
1765:
1723:
1688:
1678:
1636:
1629:413241
1626:
1580:
1572:
1537:
1527:
1488:
1478:
1429:
1394:
1384:
1342:
1332:
1288:
1251:
1241:
1200:
1173:
1138:
1100:
1092:
1043:
1035:
992:
982:
943:
933:
889:
879:
839:478260
837:
829:
756:PABPC1
742:, and
623:, the
566:snoRNA
564:, and
502:3' UTR
491:3′ end
407:5′ cap
160:uracil
89:. The
6446:DCP1B
6441:DCP1A
6363:PRPF8
6358:PRPF6
6348:PRPF4
6343:PRPF3
6338:PLRG1
6308:minor
6298:snRNP
5984:Types
5881:Types
5427:64674
4770:S2CID
4670:S2CID
4526:S2CID
3948:S2CID
3318:S2CID
3101:S2CID
3058:S2CID
2509:S2CID
2466:S2CID
2186:S2CID
1578:S2CID
1098:S2CID
1041:S2CID
936:98972
835:S2CID
748:HIV-1
709:tRNAs
570:yeast
562:snRNA
534:TNF-α
471:GLD-2
265:PABII
82:of a
6466:EDC4
6461:EDC3
6456:DCPS
6451:DCP2
6293:Exon
6250:CFII
6240:PAB2
6230:CstF
6225:CPSF
5741:PMID
5687:PMID
5625:PMID
5615:ISBN
5578:PMID
5483:PMID
5432:PMID
5373:PMID
5314:PMID
5263:PMID
5251:1779
5225:PMID
5189:PMID
5148:PMID
5099:PMID
5089:ISBN
5058:PMID
5009:PMID
4960:PMID
4911:PMID
4899:1779
4876:PMID
4827:PMID
4809:ISSN
4797:1819
4724:PMID
4662:PMID
4627:PMID
4578:PMID
4518:PMID
4500:Cell
4477:PMID
4451:Cell
4428:PMID
4393:PMID
4344:PMID
4295:PMID
4254:PMID
4205:PMID
4156:PMID
4099:PMID
4041:PMID
3997:PMID
3940:PMID
3924:Cell
3904:PMID
3855:PMID
3806:PMID
3749:PMID
3700:PMID
3682:ISSN
3643:PMID
3625:ISSN
3586:PMID
3568:ISSN
3527:PMID
3509:ISSN
3467:PMID
3418:PMID
3369:PMID
3310:PMID
3292:Cell
3269:PMID
3234:PMID
3185:PMID
3150:PMID
3093:PMID
3050:PMID
3032:ISSN
2993:PMID
2944:PMID
2885:PMID
2836:PMID
2784:PMID
2735:PMID
2686:PMID
2637:PMID
2602:PMID
2558:PMID
2501:PMID
2458:PMID
2423:PMID
2374:PMID
2333:PMID
2284:PMID
2235:PMID
2178:PMID
2126:PMID
2077:PMID
2023:PMID
1971:PMID
1922:PMID
1873:PMID
1814:PMID
1773:PMID
1721:PMID
1686:PMID
1634:PMID
1570:PMID
1535:PMID
1486:PMID
1427:PMID
1392:PMID
1340:PMID
1286:PMID
1249:PMID
1198:ISBN
1171:PMID
1136:PMID
1090:PMID
1033:PMID
990:PMID
941:PMID
887:PMID
861:Gene
827:PMID
809:Cell
781:SV40
750:and
719:and
604:and
558:rRNA
554:tRNA
532:and
463:CPEB
461:and
459:CPSF
403:PARN
310:CPSF
302:CPSF
284:The
275:CFII
255:CstF
250:CPSF
229:Xist
128:and
84:gene
6245:CFI
6235:PAP
5835:RNA
5831:DNA
5731:PMC
5723:doi
5677:PMC
5667:doi
5607:doi
5568:doi
5535:doi
5531:235
5473:PMC
5463:doi
5422:PMC
5412:doi
5363:PMC
5353:doi
5304:PMC
5294:doi
5255:doi
5217:doi
5179:doi
5175:283
5138:PMC
5130:doi
5081:doi
5048:PMC
5040:doi
4999:PMC
4991:doi
4950:PMC
4942:doi
4903:doi
4866:PMC
4858:doi
4854:190
4817:PMC
4801:doi
4762:doi
4714:PMC
4706:doi
4654:doi
4617:PMC
4609:doi
4568:PMC
4560:doi
4552:RNA
4508:doi
4504:121
4467:PMC
4459:doi
4455:145
4420:doi
4383:PMC
4375:doi
4334:PMC
4326:doi
4285:doi
4244:PMC
4236:doi
4195:PMC
4187:doi
4179:RNA
4146:PMC
4138:doi
4126:456
4089:PMC
4081:doi
4031:doi
4027:280
3987:PMC
3979:doi
3932:doi
3894:PMC
3886:doi
3845:PMC
3837:doi
3796:PMC
3788:doi
3776:320
3739:PMC
3731:doi
3727:468
3690:PMC
3674:doi
3633:PMC
3617:doi
3576:PMC
3558:doi
3517:PMC
3501:doi
3457:PMC
3449:doi
3408:PMC
3400:doi
3359:PMC
3349:doi
3345:135
3300:doi
3296:132
3261:doi
3224:PMC
3216:doi
3177:doi
3173:336
3140:PMC
3132:doi
3085:doi
3040:PMC
3024:doi
3020:371
2983:PMC
2975:doi
2971:178
2934:PMC
2924:doi
2912:103
2875:PMC
2867:doi
2826:PMC
2818:doi
2774:PMC
2766:doi
2725:PMC
2717:doi
2709:RNA
2676:PMC
2668:doi
2629:doi
2592:doi
2588:282
2548:PMC
2540:doi
2493:doi
2450:doi
2413:PMC
2405:doi
2364:doi
2360:270
2323:PMC
2315:doi
2274:PMC
2266:doi
2225:PMC
2217:doi
2170:doi
2158:274
2116:PMC
2108:doi
2067:PMC
2059:doi
2013:PMC
2005:doi
1961:PMC
1953:doi
1912:PMC
1904:doi
1863:PMC
1853:doi
1841:107
1804:doi
1763:PMC
1755:doi
1713:doi
1676:PMC
1668:doi
1624:PMC
1616:doi
1562:doi
1525:PMC
1517:doi
1476:PMC
1466:doi
1454:104
1419:doi
1382:PMC
1374:doi
1366:RNA
1330:PMC
1320:doi
1276:doi
1239:PMC
1231:doi
1223:RNA
1163:doi
1128:doi
1080:doi
1025:doi
980:PMC
972:doi
964:RNA
931:PMC
923:doi
877:PMC
869:doi
865:265
817:doi
813:108
697:ATP
693:ADP
371:40S
270:CFI
260:PAP
170:DNA
126:RNA
6485::
6313:U1
5739:.
5729:.
5719:27
5717:.
5713:.
5685:.
5675:.
5665:.
5655:68
5653:.
5649:.
5623:.
5613:.
5590:^
5576:.
5564:11
5562:.
5558:.
5529:.
5525:.
5503:.
5481:.
5471:.
5457:.
5453:.
5430:.
5420:.
5410:.
5400:98
5398:.
5394:.
5371:.
5361:.
5351:.
5339:.
5335:.
5312:.
5302:.
5290:73
5288:.
5284:.
5261:.
5249:.
5237:^
5223:.
5213:47
5211:.
5187:.
5173:.
5169:.
5146:.
5136:.
5124:.
5120:.
5097:.
5087:.
5056:.
5046:.
5036:15
5034:.
5030:.
5007:.
4997:.
4987:34
4985:.
4981:.
4958:.
4948:.
4938:21
4936:.
4932:.
4909:.
4897:.
4874:.
4864:.
4852:.
4848:.
4825:.
4815:.
4807:.
4795:.
4791:.
4768:.
4760:.
4750:25
4748:.
4736:^
4722:.
4712:.
4702:30
4700:.
4696:.
4682:^
4668:.
4660:.
4650:22
4648:.
4625:.
4615:.
4605:34
4603:.
4599:.
4576:.
4566:.
4556:13
4554:.
4550:.
4538:^
4524:.
4516:.
4502:.
4498:.
4475:.
4465:.
4453:.
4449:.
4426:.
4416:17
4414:.
4391:.
4381:.
4371:49
4369:.
4365:.
4342:.
4332:.
4322:22
4320:.
4316:.
4293:.
4281:41
4279:.
4275:.
4252:.
4242:.
4232:26
4230:.
4226:.
4203:.
4193:.
4183:13
4181:.
4177:.
4154:.
4144:.
4136:.
4124:.
4120:.
4097:.
4087:.
4079:.
4067:.
4063:.
4039:.
4025:.
4021:.
4009:^
3995:.
3985:.
3975:17
3973:.
3969:.
3946:.
3938:.
3928:20
3926:.
3902:.
3892:.
3882:36
3880:.
3876:.
3853:.
3843:.
3831:.
3827:.
3804:.
3794:.
3786:.
3774:.
3770:.
3747:.
3737:.
3725:.
3721:.
3698:.
3688:.
3680:.
3670:36
3668:.
3664:.
3641:.
3631:.
3623:.
3611:.
3607:.
3584:.
3574:.
3566:.
3552:.
3548:.
3525:.
3515:.
3507:.
3497:18
3495:.
3491:.
3479:^
3465:.
3455:.
3445:27
3443:.
3439:.
3416:.
3406:.
3396:33
3394:.
3390:.
3367:.
3357:.
3343:.
3339:.
3316:.
3308:.
3294:.
3290:.
3267:.
3257:32
3255:.
3232:.
3222:.
3212:69
3210:.
3206:.
3183:.
3171:.
3148:.
3138:.
3128:26
3126:.
3122:.
3099:.
3091:.
3079:.
3056:.
3048:.
3038:.
3030:.
3018:.
3014:.
2991:.
2981:.
2969:.
2965:.
2942:.
2932:.
2922:.
2910:.
2906:.
2883:.
2873:.
2863:14
2861:.
2857:.
2834:.
2824:.
2814:35
2812:.
2808:.
2796:^
2782:.
2772:.
2762:45
2760:.
2756:.
2733:.
2723:.
2713:12
2711:.
2707:.
2684:.
2674:.
2664:19
2662:.
2658:.
2635:.
2625:16
2623:.
2600:.
2586:.
2582:.
2570:^
2556:.
2546:.
2536:12
2534:.
2530:.
2507:.
2499:.
2489:77
2487:.
2464:.
2456:.
2446:14
2444:.
2421:.
2411:.
2401:21
2399:.
2395:.
2372:.
2358:.
2354:.
2331:.
2321:.
2311:36
2309:.
2305:.
2282:.
2272:.
2262:15
2260:.
2256:.
2233:.
2223:.
2213:12
2211:.
2207:.
2184:.
2176:.
2168:.
2156:.
2124:.
2114:.
2104:15
2102:.
2098:.
2075:.
2065:.
2055:36
2053:.
2049:.
2035:^
2021:.
2011:.
2001:25
1999:.
1995:.
1983:^
1969:.
1959:.
1949:19
1947:.
1943:.
1920:.
1910:.
1900:19
1898:.
1894:.
1871:.
1861:.
1851:.
1839:.
1835:.
1812:.
1800:12
1798:.
1794:.
1771:.
1761:.
1751:10
1749:.
1745:.
1733:^
1719:.
1707:.
1684:.
1674:.
1664:35
1662:.
1658:.
1646:^
1632:.
1622:.
1612:12
1610:.
1606:.
1590:^
1576:.
1568:.
1558:19
1556:.
1533:.
1523:.
1513:19
1511:.
1507:.
1484:.
1474:.
1464:.
1452:.
1448:.
1425:.
1415:80
1413:.
1390:.
1380:.
1370:14
1368:.
1364:.
1352:^
1338:.
1328:.
1314:.
1310:.
1298:^
1284:.
1270:.
1247:.
1237:.
1227:14
1225:.
1221:.
1169:.
1159:32
1157:.
1134:.
1124:66
1122:.
1110:^
1096:.
1088:.
1078:.
1068:15
1066:.
1062:.
1039:.
1031:.
1023:.
1013:49
1011:.
988:.
978:.
966:.
962:.
939:.
929:.
919:63
917:.
913:.
899:^
885:.
875:.
863:.
859:.
847:^
833:.
825:.
811:.
807:.
795:^
738:,
734:,
560:,
556:,
398:.
113:.
105:.
75:.
6182:e
6175:t
6168:v
5795:e
5788:t
5781:v
5747:.
5725::
5693:.
5669::
5661::
5631:.
5609::
5584:.
5570::
5543:.
5537::
5507:.
5489:.
5465::
5459:9
5438:.
5414::
5406::
5379:.
5355::
5347::
5341:8
5320:.
5296::
5269:.
5257::
5231:.
5219::
5195:.
5181::
5154:.
5132::
5126:6
5105:.
5083::
5064:.
5042::
5015:.
4993::
4966:.
4944::
4917:.
4905::
4882:.
4860::
4833:.
4803::
4776:.
4764::
4756::
4730:.
4708::
4676:.
4656::
4633:.
4611::
4584:.
4562::
4532:.
4510::
4483:.
4461::
4434:.
4422::
4399:.
4377::
4350:.
4328::
4301:.
4287::
4260:.
4238::
4211:.
4189::
4162:.
4140::
4132::
4105:.
4083::
4075::
4069:9
4047:.
4033::
4003:.
3981::
3954:.
3934::
3910:.
3888::
3861:.
3839::
3833:5
3812:.
3790::
3782::
3755:.
3733::
3706:.
3676::
3649:.
3619::
3613:1
3592:.
3560::
3554:6
3533:.
3503::
3473:.
3451::
3424:.
3402::
3375:.
3351::
3324:.
3302::
3275:.
3263::
3240:.
3218::
3191:.
3179::
3156:.
3134::
3107:.
3087::
3081:2
3064:.
3026::
2999:.
2977::
2950:.
2926::
2918::
2891:.
2869::
2842:.
2820::
2790:.
2768::
2741:.
2719::
2692:.
2670::
2643:.
2631::
2608:.
2594::
2564:.
2542::
2515:.
2495::
2472:.
2452::
2429:.
2407::
2380:.
2366::
2339:.
2317::
2290:.
2268::
2241:.
2219::
2192:.
2172::
2164::
2132:.
2110::
2083:.
2061::
2029:.
2007::
1977:.
1955::
1928:.
1906::
1879:.
1855::
1847::
1820:.
1806::
1779:.
1757::
1727:.
1715::
1709:3
1692:.
1670::
1640:.
1618::
1584:.
1564::
1541:.
1519::
1492:.
1468::
1460::
1433:.
1421::
1398:.
1376::
1346:.
1322::
1316:9
1292:.
1278::
1255:.
1233::
1206:.
1177:.
1165::
1142:.
1130::
1104:.
1082::
1074::
1047:.
1027::
1019::
996:.
974::
968:6
947:.
925::
893:.
871::
841:.
819::
473:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.