267:
278:, which are proteins that regulate transcription. Each transcription factor binds to one specific set of DNA sequences and activates or inhibits the transcription of genes that have these sequences near their promoters. The transcription factors do this in two ways. Firstly, they can bind the RNA polymerase responsible for transcription, either directly or through other mediator proteins; this locates the polymerase at the promoter and allows it to begin transcription. Alternatively, transcription factors can bind
31:
54:
2747:
42:
72:
354:; however, there are exceptions. Protein–DNA interaction are of mainly two types, either specific interaction, or non-specific interaction. Recent single-molecule experiments showed that DNA binding proteins undergo of rapid rebinding in order to bind in correct orientation for recognizing the target site.
303:. Computational methods to identify the DNA binding sequence specificity have been proposed to make a good use of the abundant sequence data in the post-genomic era. In addition, progress has happened on structure-based prediction of binding specificity across protein families using deep learning.
230:
and changing the rate of transcription. Other non-specific DNA-binding proteins in chromatin include the high-mobility group (HMG) proteins, which bind to bent or distorted DNA. Biophysical studies show that these architectural HMG proteins bind, bend and loop DNA to perform its biological functions.
298:
the DNA sequence. Most of these base-interactions are made in the major groove, where the bases are most accessible. Mathematical descriptions of protein-DNA binding taking into account sequence-specificity, and competitive and cooperative binding of proteins of different types are usually performed
456:
has been used to give a highly detailed atomic view of protein–DNA interactions. Besides these methods, other techniques such as SELEX, PBM (protein binding microarrays), DNA microarray screens, DamID, FAIRE or more recently DAP-seq are used in the laboratory to investigate DNA-protein interaction
249:
is the best-understood member of this family and is used in processes where the double helix is separated, including DNA replication, recombination and DNA repair. These binding proteins seem to stabilize single-stranded DNA and protect it from forming
231:
These proteins are important in bending arrays of nucleosomes and arranging them into the larger structures that form chromosomes. Recently FK506 binding protein 25 (FBP25) was also shown to non-specifically bind to DNA which helps in DNA repair.
181:
Structural proteins that bind DNA are well-understood examples of non-specific DNA-protein interactions. Within chromosomes, DNA is held in complexes with structural proteins. These proteins organize the DNA into a compact structure called
473:
The protein–DNA interactions can be modulated using stimuli like ionic strength of the buffer, macromolecular crowding, temperature, pH and electric field. This can lead to reversible dissociation/association of the protein–DNA complex.
285:
These DNA targets can occur throughout an organism's genome. Thus, changes in the activity of one type of transcription factor can affect thousands of genes. Thus, these proteins are often the targets of the
420:. This technique allows the analysis of protein complexes that bind to DNA (DPI-Recruitment-ELISA) or is suited for automated screening of several nucleotide probes due to its standard ELISA plate formate.
294:
and development. The specificity of these transcription factors' interactions with DNA come from the proteins making multiple contacts to the edges of the DNA bases, allowing them to
1875:"A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system"
202:, which contains two complete turns of double-stranded DNA wrapped around its surface. These non-specific interactions are formed through basic residues in the histones making
689:"Nonintercalating DNA-binding ligands: specificity of the interaction and their use as tools in biophysical, biochemical and biological investigations of the genetic material"
1063:
Murugesapillai, Divakaran; McCauley, Micah J.; Huo, Ran; Nelson Holte, Molly H.; Stepanyants, Armen; Maher, L. James; Israeloff, Nathan E.; Williams, Mark C. (2014).
2308:
493:
2016:"The Arabidopsis GAGA-Binding Factor BASIC PENTACYSTEINE6 Recruits the POLYCOMB-REPRESSIVE COMPLEX1 Component LIKE HETEROCHROMATIN PROTEIN1 to GAGA DNA Motifs"
2334:
413:
534:
2382:
2339:
2517:
2522:
2470:
1990:
984:
601:
1576:
Mitra, Raktim; Li, Jinsen; Sagendorf, Jared M.; Jiang, Yibei; Cohen, Ari S.; Chiu, Tsu-Pei; Glasscock, Cameron J.; Rohs, Remo (2024-08-05).
409:
226:. These chemical changes alter the strength of the interaction between the DNA and the histones, making the DNA more or less accessible to
2622:
2689:
2412:
2377:
2301:
2264:
863:
Luger K, Mäder A, Richmond R, Sargent D, Richmond T (1997). "Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 A resolution".
2627:
1161:
Grosschedl R, Giese K, Pagel J (1994). "HMG domain proteins: architectural elements in the assembly of nucleoprotein structures".
274:
In contrast, other proteins have evolved to bind to specific DNA sequences. The most intensively studied of these are the various
2065:
Brand LH, Henneges C, Schüssler A, Kolukisaoglu HÜ, Koch G, Wallmeroth N, Hecker A, Thurow K, Zell A, Harter K, Wanke D (2013).
240:
2782:
432:
DNA target regions of a known transcription factor. This technique when combined with high throughput sequencing is known as
245:
A distinct group of DNA-binding proteins are the DNA-binding proteins that specifically bind single-stranded DNA. In humans,
2553:
2767:
2610:
2372:
2294:
544:
425:
2737:
2724:
2772:
828:
Dame RT (2005). "The role of nucleoid-associated proteins in the organization and compaction of bacterial chromatin".
449:
408:
techniques which are useful in detecting DNA-Protein
Interactions. The following lists some methods currently in use:
385:
362:
Designing DNA-binding proteins that have a specified DNA-binding site has been an important goal for biotechnology.
2543:
2488:
2452:
300:
1973:
Fischer SM, Böser A, Hirsch JP, Wanke D (2016). "Quantitative
Analysis of Protein–DNA Interaction by qDPI-ELISA".
2387:
2642:
2777:
2704:
2440:
2280:
421:
291:
282:
that modify the histones at the promoter. This alters the accessibility of the DNA template to the polymerase.
206:
to the acidic sugar-phosphate backbone of the DNA, and are therefore largely independent of the base sequence.
2273:
Uses a curated set of DNA-binding domains to predict transcription factors in all completely sequenced genomes
1924:"DPI-ELISA: a fast and versatile method to specify the binding of plant transcription factors to DNA in vitro"
412:(EMSA) is a widespread qualitative technique to study protein–DNA interactions of known DNA binding proteins.
266:
2527:
2354:
1198:"Structural basis of nucleic acid recognition by FK506-binding protein 25 (FKBP25), a nuclear immunophilin"
2699:
2654:
2493:
1466:
Teif V.B.; Rippe K. (2010). "Statistical-mechanical lattice models for protein-DNA binding in chromatin".
923:
529:
452:(B1H) is used to identify which protein binds to a particular DNA fragment. Structure determination using
344:
169:(among many others) that facilitate binding to nucleic acid. There are also more unusual examples such as
453:
371:
367:
332:
246:
1826:"Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis"
2600:
2548:
2498:
2349:
2325:
2213:
2078:
1485:
1385:
872:
737:
661:
445:
275:
227:
130:
34:
2787:
928:
539:
287:
424:
can be used to identify the specific sites of binding of a protein to DNA at basepair resolution.
2694:
1806:
1509:
1475:
1354:
1065:"DNA bridging and looping by HMO1 provides a mechanism for stabilizing nucleosome-free chromatin"
1002:
949:
896:
810:
498:
320:
94:
76:
2276:
2173:
Hianik T, Wang J (2009). "Electrochemical
Aptasensors – Recent Achievements and Perspectives".
1677:"DNA binding proteins explore multiple local configurations during docking via rapid rebinding"
1675:
Ganji, Mahipal; Docter, Margreet; Le Grice, Stuart F. J.; Abbondanzieri, Elio A. (2016-09-30).
30:
27:
Proteins that bind with DNA, such as transcription factors, polymerases, nucleases and histones
2239:
2155:
2106:
2047:
1996:
1986:
1955:
1904:
1855:
1798:
1763:
1714:
1696:
1654:
1595:
1558:
1501:
1448:
1413:
1346:
1305:
1270:
1235:
1217:
1178:
1143:
1094:
1045:
990:
980:
941:
888:
845:
802:
753:
710:
634:
597:
580:
568:
416:
allows the qualitative and quantitative analysis of DNA-binding preferences of known proteins
2714:
2344:
2229:
2221:
2182:
2145:
2137:
2096:
2086:
2037:
2027:
1978:
1945:
1935:
1894:
1886:
1845:
1837:
1790:
1753:
1745:
1704:
1688:
1644:
1636:
1603:
1585:
1548:
1540:
1493:
1440:
1403:
1393:
1336:
1297:
1262:
1225:
1209:
1170:
1133:
1125:
1084:
1076:
1037:
972:
933:
880:
837:
792:
784:
745:
700:
669:
626:
508:
503:
339:
that form part of the structure of DNA and bind to it less specifically. Also proteins that
198:, multiple types of proteins are involved. The histones form a disk-shaped complex called a
162:
110:
64:
2573:
2395:
1253:
Iftode C, Daniely Y, Borowiec J (1999). "Replication protein A (RPA): the eukaryotic SSB".
2719:
2480:
2126:"DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity"
1112:
Murugesapillai, Divakaran; McCauley, Micah J.; Maher, L. James; Williams, Mark C. (2017).
1014:
324:
219:
134:
2014:
Hecker A, Brand LH, Peter S, Simoncello N, Kilian J, Harter K, Gaudin V, Wanke D (2015).
1497:
2217:
2082:
1608:
1489:
1444:
1389:
876:
797:
772:
741:
665:
630:
2751:
2359:
2234:
2201:
2101:
2066:
2042:
2015:
1950:
1923:
1758:
1733:
1709:
1676:
1649:
1625:"Minor groove-binding architectural proteins: structure, function, and DNA recognition"
1624:
1553:
1528:
1230:
1138:
1113:
1089:
1064:
518:
366:
proteins have been designed to bind to specific DNA sequences and this is the basis of
166:
17:
2150:
2125:
1899:
1874:
1850:
1825:
1408:
1373:
673:
53:
2761:
2067:"Screening for protein-DNA interactions by automatable DNA-protein interaction ELISA"
1640:
1577:
1301:
1174:
1114:"Single-molecule studies of high-mobility group B architectural DNA bending proteins"
841:
705:
688:
49:(blue). These proteins' basic amino acids bind to the acidic phosphate groups on DNA.
2202:"Electrical Stimulus Controlled Binding/Unbinding of Human Thrombin-Aptamer Complex"
1358:
814:
953:
900:
351:
170:
154:
102:
58:
2260:
Protein-DNA binding: data, tools & models (annotated list, constantly updated)
2259:
1810:
1513:
190:, this structure involves DNA binding to a complex of small basic proteins called
2091:
1781:
Cai YH, Huang H (July 2012). "Advances in the study of protein–DNA interaction".
270:
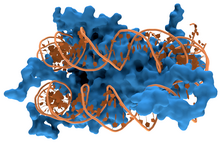
DNA contacts of different types of DNA-binding domains from transcription factors
2595:
2508:
1982:
1374:"A global transcriptional regulatory role for c-Myc in Burkitt's lymphoma cells"
976:
773:"Diversity of prokaryotic chromosomal proteins and the origin of the nucleosome"
549:
523:
483:
437:
380:
363:
223:
215:
158:
2746:
1590:
1341:
1324:
971:. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology. Vol. 274. pp. 1–22.
2664:
2637:
2462:
2417:
1794:
1266:
1129:
340:
211:
203:
199:
195:
150:
138:
2605:
1700:
1599:
1221:
728:
Dervan PB (April 1986). "Design of sequence-specific DNA-binding molecules".
2435:
2422:
1890:
1841:
1398:
937:
749:
448:(Y1H) is used to identify which protein binds to a particular DNA fragment.
441:
251:
187:
183:
114:
61:
2243:
2186:
2141:
2110:
2051:
2000:
1959:
1940:
1802:
1767:
1718:
1562:
1505:
1417:
1350:
1309:
1274:
1239:
1147:
1098:
1049:
994:
945:
849:
1908:
1859:
1749:
1658:
1452:
1182:
892:
806:
788:
757:
714:
638:
2445:
2159:
1692:
1544:
1213:
1080:
488:
433:
336:
255:
207:
142:
2032:
1196:
Prakash, Ajit; Shin, Joon; Rajan, Sreekanth; Yoon, Ho Sup (2016-04-07).
41:
2286:
1041:
513:
414:
DNA-Protein-Interaction - Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbant Assay (DPI-ELISA)
375:
312:
191:
146:
126:
90:
71:
46:
2225:
1288:
Myers L, Kornberg R (2000). "Mediator of transcriptional regulation".
335:
that activate or repress gene expression by binding to DNA motifs and
2615:
1197:
279:
101:. Sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins generally interact with the
1325:"Biological control throughs regulated transcriptional coactivators"
1028:
Thomas J (2001). "HMG1 and 2: architectural DNA-binding proteins".
2684:
2679:
2674:
2585:
2568:
2563:
2558:
2430:
2270:
1480:
884:
389:
265:
106:
79:
70:
52:
40:
29:
2709:
2659:
2647:
2632:
2590:
2405:
2400:
328:
2290:
2669:
2578:
2364:
316:
98:
290:
processes that control responses to environmental changes or
1578:"Geometric deep learning of protein–DNA binding specificity"
1372:
Li Z, Van Calcar S, Qu C, Cavenee W, Zhang M, Ren B (2003).
914:
Jenuwein T, Allis C (2001). "Translating the histone code".
652:
Dickerson R.E. (1983). "The DNA helix and how it is read".
157:. DNA-binding proteins can incorporate such domains as the
1922:
Brand LH, Kirchler T, Hummel S, Chaban C, Wanke D (2010).
1734:"A TALE of two nucleases: gene targeting for the masses?"
374:(TALENs) have been created which are based on natural
2735:
1977:. Methods Mol. Biol. Vol. 1482. pp. 49–66.
617:
Pabo CO, Sauer RT (1984). "Protein-DNA recognition".
967:
Ito T (2003). "Nucleosome assembly and remodeling".
2536:
2507:
2479:
2461:
2429:(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts:
2324:
1431:Pabo C, Sauer R (1984). "Protein-DNA recognition".
235:
Proteins that specifically bind single-stranded DNA
97:and thus have a specific or general affinity for
1732:Clark KJ, Voytas DF, Ekker SC (September 2011).
1529:"DNA Motif Elucidation using belief propagation"
1527:Wong KC, Chan TM, Peng C, Li Y, Zhang Z (2013).
535:Protein–DNA interaction site prediction software
2271:DBD database of predicted transcription factors
372:transcription activator-like effector nucleases
494:Comparison of nucleic acid simulation software
2302:
8:
2335:basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors
67:transcription factor bound to its DNA target
1623:Bewley CA, Gronenborn AM, Clore GM (1998).
82:(green) in a complex with its substrate DNA
2383:early growth response transcription factor
2340:basic-leucine zipper transcription factors
2309:
2295:
2287:
2267:tool for modeling DNA-ligand interactions.
1670:
1668:
331:. Among the proteins that bind to DNA are
2279:at the U.S. National Library of Medicine
2233:
2149:
2100:
2090:
2041:
2031:
1949:
1939:
1898:
1849:
1757:
1708:
1648:
1607:
1589:
1552:
1479:
1407:
1397:
1340:
1229:
1137:
1088:
927:
796:
704:
2518:factor for inversion stimulation protein
350:In general, proteins bind to DNA in the
2742:
969:Protein Complexes that Modify Chromatin
560:
2554:erythroid-specific DNA-binding factors
2371:(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains:
1010:
1000:
771:Sandman K, Pereira S, Reeve J (1998).
311:Protein–DNA interactions occur when a
171:transcription activator like effectors
137:the process of transcription, various
2523:leucine-responsive regulatory protein
2471:xeroderma pigmentosum group a protein
526:(a semi-synthetic DNA-binding ligand)
177:Non-specific DNA-protein interactions
7:
1468:Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter
410:Electrophoretic mobility shift assay
2623:Methyl-CpG-binding domain protein 2
1445:10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453
631:10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453
153:packaging and transcription in the
2690:receptors, cytoplasmic and nuclear
2413:winged-helix transcription factors
2378:kruppel-like transcription factors
25:
2638:myeloid-lymphoid leukemia protein
2628:muts dna mismatch-binding protein
1323:Spiegelman B, Heinrich R (2004).
674:10.1038/scientificamerican1283-94
262:Binding to specific DNA sequences
45:Interaction of DNA (orange) with
2745:
2423:paired box transcription factors
1641:10.1146/annurev.biophys.27.1.105
1302:10.1146/annurev.biochem.69.1.729
842:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04598.x
145:which cleave DNA molecules, and
241:Single-stranded binding protein
2394:(3) Helix-turn-helix domains:
1629:Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct
1498:10.1088/0953-8984/22/41/414105
99:single- or double-stranded DNA
1:
2611:interferon regulatory factors
2373:general transcription factors
2200:Gosai A, et al. (2016).
1824:Fried M, Crothers DM (1981).
545:Single-strand binding protein
469:Manipulating the interactions
426:Chromatin immunoprecipitation
210:modifications of these basic
2725:tumor suppressor protein p53
2124:Galas DJ, Schmitz A (1978).
2092:10.1371/journal.pone.0075177
1873:Garner MM, Revzin A (1981).
1175:10.1016/0168-9525(94)90232-1
706:10.1016/0079-6107(86)90005-2
687:Zimmer C, Wähnert U (1986).
1983:10.1007/978-1-4939-6396-6_4
977:10.1007/978-3-642-55747-7_1
450:Bacterial one-hybrid system
2804:
2643:nuclear respiratory factor
2544:butyrate response factor 1
2489:origin recognition complex
2453:hepatocyte nuclear factors
1591:10.1038/s41592-024-02372-w
1342:10.1016/j.cell.2004.09.037
347:interact closely with it.
238:
109:, because it exposes more
2441:tcf transcription factors
2436:SOX transcription factors
2388:GATA transcription factor
2350:transcription factor ap-2
2345:NFI transcription factors
1975:Plant Synthetic Promoters
1795:10.1007/s00726-012-1377-9
1267:10.1080/10409239991209255
1255:Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol
1130:10.1007/s12551-016-0236-4
388:when they infect various
386:type III secretion system
2705:Telomere-binding protein
2281:Medical Subject Headings
693:Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol
594:DNA-protein interactions
428:is used to identify the
422:DNase footprinting assay
319:, often to regulate the
307:Protein–DNA interactions
292:cellular differentiation
37:protein complex with DNA
2528:integration host factor
1399:10.1073/pnas.1332764100
938:10.1126/science.1063127
750:10.1126/science.2421408
592:Travers, A. A. (1993).
446:Yeast one-hybrid System
436:and when combined with
18:Protein–DNA interaction
2700:retinoblastoma protein
2494:Replication protein A1
2187:10.1002/elan.200904566
1941:10.1186/1746-4811-6-25
1681:Nucleic Acids Research
1533:Nucleic Acids Research
1378:Proc Natl Acad Sci USA
1202:Nucleic Acids Research
1069:Nucleic Acids Research
530:Deoxyribonucleoprotein
345:uracil-DNA glycosylase
271:
149:which are involved in
83:
68:
50:
38:
2783:Transcription factors
2431:T-box domain proteins
2355:g-box binding factors
2326:Transcription factors
1891:10.1093/nar/9.13.3047
1842:10.1093/nar/9.23.6505
1750:10.1089/zeb.2011.9993
789:10.1007/s000180050259
454:X-ray crystallography
368:zinc finger nucleases
333:transcription factors
299:with the help of the
276:transcription factors
269:
254:or being degraded by
247:replication protein A
239:Further information:
228:transcription factors
131:transcription factors
74:
56:
44:
33:
2768:DNA-binding proteins
2710:toll-like receptor 9
2655:oncogene protein p55
2601:homeodomain proteins
2549:centromere protein b
2499:Replication factor C
2318:DNA-binding proteins
2277:DNA-Binding+Proteins
2142:10.1093/nar/5.9.3157
596:. London: Springer.
323:of DNA, usually the
315:binds a molecule of
87:DNA-binding proteins
2333:(1) Basic domains:
2218:2016NatSR...637449G
2083:2013PLoSO...875177B
2033:10.1104/pp.15.00409
1490:2010JPCM...22O4105T
1390:2003PNAS..100.8164L
1118:Biophysical Reviews
877:1997Natur.389..251L
742:1986Sci...232..464D
666:1983SciAm.249f..94D
540:RNA-binding protein
384:bacteria via their
321:biological function
288:signal transduction
95:DNA-binding domains
2773:Molecular genetics
2695:repressor proteins
1693:10.1093/nar/gkw666
1545:10.1093/nar/gkt574
1214:10.1093/nar/gkw001
1081:10.1093/nar/gku635
1042:10.1042/BST0290395
619:Annu. Rev. Biochem
499:DNA-binding domain
272:
84:
77:restriction enzyme
69:
51:
39:
2733:
2732:
2226:10.1038/srep37449
2181:(11): 1223–1235.
2130:Nucleic Acids Res
1992:978-1-4939-6394-2
1885:(13): 3047–3060.
1879:Nucleic Acids Res
1836:(23): 6505–6525.
1830:Nucleic Acids Res
1687:(17): 8376–8384.
1075:(14): 8996–9004.
1036:(Pt 4): 395–401.
1030:Biochem Soc Trans
986:978-3-642-62909-9
922:(5532): 1074–80.
777:Cell Mol Life Sci
603:978-0-412-25990-6
396:Detection methods
214:residues include
111:functional groups
16:(Redirected from
2795:
2750:
2749:
2741:
2715:trans-activators
2311:
2304:
2297:
2288:
2248:
2247:
2237:
2197:
2191:
2190:
2170:
2164:
2163:
2153:
2136:(9): 3157–3170.
2121:
2115:
2114:
2104:
2094:
2062:
2056:
2055:
2045:
2035:
2026:(3): 1013–1024.
2011:
2005:
2004:
1970:
1964:
1963:
1953:
1943:
1919:
1913:
1912:
1902:
1870:
1864:
1863:
1853:
1821:
1815:
1814:
1778:
1772:
1771:
1761:
1729:
1723:
1722:
1712:
1672:
1663:
1662:
1652:
1620:
1614:
1613:
1611:
1593:
1573:
1567:
1566:
1556:
1524:
1518:
1517:
1483:
1463:
1457:
1456:
1433:Annu Rev Biochem
1428:
1422:
1421:
1411:
1401:
1369:
1363:
1362:
1344:
1320:
1314:
1313:
1290:Annu Rev Biochem
1285:
1279:
1278:
1250:
1244:
1243:
1233:
1208:(6): 2909–2925.
1193:
1187:
1186:
1158:
1152:
1151:
1141:
1109:
1103:
1102:
1092:
1060:
1054:
1053:
1025:
1019:
1018:
1012:
1008:
1006:
998:
964:
958:
957:
931:
911:
905:
904:
871:(6648): 251–60.
860:
854:
853:
825:
819:
818:
800:
768:
762:
761:
736:(4749): 464–71.
725:
719:
718:
708:
684:
678:
677:
649:
643:
642:
614:
608:
607:
589:
583:
577:
571:
565:
509:Helix-turn-helix
504:Helix-loop-helix
163:helix-turn-helix
113:that identify a
65:helix-turn-helix
21:
2803:
2802:
2798:
2797:
2796:
2794:
2793:
2792:
2778:DNA replication
2758:
2757:
2756:
2744:
2736:
2734:
2729:
2720:tristetraprolin
2537:Other/ungrouped
2532:
2503:
2481:DNA replication
2475:
2457:
2320:
2315:
2256:
2251:
2199:
2198:
2194:
2175:Electroanalysis
2172:
2171:
2167:
2123:
2122:
2118:
2064:
2063:
2059:
2013:
2012:
2008:
1993:
1972:
1971:
1967:
1921:
1920:
1916:
1872:
1871:
1867:
1823:
1822:
1818:
1780:
1779:
1775:
1731:
1730:
1726:
1674:
1673:
1666:
1622:
1621:
1617:
1575:
1574:
1570:
1526:
1525:
1521:
1465:
1464:
1460:
1430:
1429:
1425:
1371:
1370:
1366:
1322:
1321:
1317:
1287:
1286:
1282:
1252:
1251:
1247:
1195:
1194:
1190:
1160:
1159:
1155:
1111:
1110:
1106:
1062:
1061:
1057:
1027:
1026:
1022:
1009:
999:
987:
966:
965:
961:
913:
912:
908:
862:
861:
857:
827:
826:
822:
783:(12): 1350–64.
770:
769:
765:
727:
726:
722:
686:
685:
681:
651:
650:
646:
616:
615:
611:
604:
591:
590:
586:
578:
574:
566:
562:
558:
480:
471:
440:it is known as
400:There are many
398:
360:
309:
264:
243:
237:
220:phosphorylation
179:
123:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2801:
2799:
2791:
2790:
2785:
2780:
2775:
2770:
2760:
2759:
2755:
2754:
2731:
2730:
2728:
2727:
2722:
2717:
2712:
2707:
2702:
2697:
2692:
2687:
2682:
2677:
2672:
2667:
2662:
2657:
2652:
2651:
2650:
2640:
2635:
2630:
2625:
2620:
2619:
2618:
2608:
2603:
2598:
2593:
2588:
2583:
2582:
2581:
2576:
2571:
2566:
2561:
2551:
2546:
2540:
2538:
2534:
2533:
2531:
2530:
2525:
2520:
2514:
2512:
2505:
2504:
2502:
2501:
2496:
2491:
2485:
2483:
2477:
2476:
2474:
2473:
2467:
2465:
2459:
2458:
2456:
2455:
2449:
2448:
2443:
2438:
2433:
2426:
2425:
2420:
2415:
2410:
2409:
2408:
2403:
2391:
2390:
2385:
2380:
2375:
2368:
2367:
2362:
2357:
2352:
2347:
2342:
2337:
2330:
2328:
2322:
2321:
2316:
2314:
2313:
2306:
2299:
2291:
2285:
2284:
2274:
2268:
2262:
2255:
2254:External links
2252:
2250:
2249:
2192:
2165:
2116:
2077:(10): e75177.
2057:
2006:
1991:
1965:
1914:
1865:
1816:
1773:
1724:
1664:
1615:
1582:Nature Methods
1568:
1519:
1474:(41): 414105.
1458:
1439:(1): 293–321.
1423:
1384:(14): 8164–9.
1364:
1315:
1280:
1245:
1188:
1153:
1104:
1055:
1020:
1011:|journal=
985:
959:
929:10.1.1.453.900
906:
855:
830:Mol. Microbiol
820:
763:
720:
679:
644:
625:(1): 293–321.
609:
602:
584:
572:
559:
557:
554:
553:
552:
547:
542:
537:
532:
527:
521:
519:Leucine zipper
516:
511:
506:
501:
496:
491:
486:
479:
476:
470:
467:
397:
394:
359:
356:
308:
305:
301:lattice models
263:
260:
236:
233:
178:
175:
167:leucine zipper
122:
119:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2800:
2789:
2786:
2784:
2781:
2779:
2776:
2774:
2771:
2769:
2766:
2765:
2763:
2753:
2748:
2743:
2739:
2726:
2723:
2721:
2718:
2716:
2713:
2711:
2708:
2706:
2703:
2701:
2698:
2696:
2693:
2691:
2688:
2686:
2683:
2681:
2678:
2676:
2673:
2671:
2668:
2666:
2663:
2661:
2658:
2656:
2653:
2649:
2646:
2645:
2644:
2641:
2639:
2636:
2634:
2631:
2629:
2626:
2624:
2621:
2617:
2614:
2613:
2612:
2609:
2607:
2604:
2602:
2599:
2597:
2594:
2592:
2589:
2587:
2584:
2580:
2577:
2575:
2572:
2570:
2567:
2565:
2562:
2560:
2557:
2556:
2555:
2552:
2550:
2547:
2545:
2542:
2541:
2539:
2535:
2529:
2526:
2524:
2521:
2519:
2516:
2515:
2513:
2510:
2506:
2500:
2497:
2495:
2492:
2490:
2487:
2486:
2484:
2482:
2478:
2472:
2469:
2468:
2466:
2464:
2460:
2454:
2451:
2450:
2447:
2444:
2442:
2439:
2437:
2434:
2432:
2428:
2427:
2424:
2421:
2419:
2416:
2414:
2411:
2407:
2404:
2402:
2399:
2398:
2397:
2393:
2392:
2389:
2386:
2384:
2381:
2379:
2376:
2374:
2370:
2369:
2366:
2363:
2361:
2360:SMAD proteins
2358:
2356:
2353:
2351:
2348:
2346:
2343:
2341:
2338:
2336:
2332:
2331:
2329:
2327:
2323:
2319:
2312:
2307:
2305:
2300:
2298:
2293:
2292:
2289:
2282:
2278:
2275:
2272:
2269:
2266:
2263:
2261:
2258:
2257:
2253:
2245:
2241:
2236:
2231:
2227:
2223:
2219:
2215:
2211:
2207:
2203:
2196:
2193:
2188:
2184:
2180:
2176:
2169:
2166:
2161:
2157:
2152:
2147:
2143:
2139:
2135:
2131:
2127:
2120:
2117:
2112:
2108:
2103:
2098:
2093:
2088:
2084:
2080:
2076:
2072:
2068:
2061:
2058:
2053:
2049:
2044:
2039:
2034:
2029:
2025:
2021:
2020:Plant Physiol
2017:
2010:
2007:
2002:
1998:
1994:
1988:
1984:
1980:
1976:
1969:
1966:
1961:
1957:
1952:
1947:
1942:
1937:
1933:
1929:
1928:Plant Methods
1925:
1918:
1915:
1910:
1906:
1901:
1896:
1892:
1888:
1884:
1880:
1876:
1869:
1866:
1861:
1857:
1852:
1847:
1843:
1839:
1835:
1831:
1827:
1820:
1817:
1812:
1808:
1804:
1800:
1796:
1792:
1789:(3): 1141–6.
1788:
1784:
1777:
1774:
1769:
1765:
1760:
1755:
1751:
1747:
1743:
1739:
1735:
1728:
1725:
1720:
1716:
1711:
1706:
1702:
1698:
1694:
1690:
1686:
1682:
1678:
1671:
1669:
1665:
1660:
1656:
1651:
1646:
1642:
1638:
1634:
1630:
1626:
1619:
1616:
1610:
1605:
1601:
1597:
1592:
1587:
1583:
1579:
1572:
1569:
1564:
1560:
1555:
1550:
1546:
1542:
1538:
1534:
1530:
1523:
1520:
1515:
1511:
1507:
1503:
1499:
1495:
1491:
1487:
1482:
1477:
1473:
1469:
1462:
1459:
1454:
1450:
1446:
1442:
1438:
1434:
1427:
1424:
1419:
1415:
1410:
1405:
1400:
1395:
1391:
1387:
1383:
1379:
1375:
1368:
1365:
1360:
1356:
1352:
1348:
1343:
1338:
1335:(2): 157–67.
1334:
1330:
1326:
1319:
1316:
1311:
1307:
1303:
1299:
1296:(1): 729–49.
1295:
1291:
1284:
1281:
1276:
1272:
1268:
1264:
1261:(3): 141–80.
1260:
1256:
1249:
1246:
1241:
1237:
1232:
1227:
1223:
1219:
1215:
1211:
1207:
1203:
1199:
1192:
1189:
1184:
1180:
1176:
1172:
1169:(3): 94–100.
1168:
1164:
1157:
1154:
1149:
1145:
1140:
1135:
1131:
1127:
1123:
1119:
1115:
1108:
1105:
1100:
1096:
1091:
1086:
1082:
1078:
1074:
1070:
1066:
1059:
1056:
1051:
1047:
1043:
1039:
1035:
1031:
1024:
1021:
1016:
1004:
996:
992:
988:
982:
978:
974:
970:
963:
960:
955:
951:
947:
943:
939:
935:
930:
925:
921:
917:
910:
907:
902:
898:
894:
890:
886:
885:10.1038/38444
882:
878:
874:
870:
866:
859:
856:
851:
847:
843:
839:
836:(4): 858–70.
835:
831:
824:
821:
816:
812:
808:
804:
799:
794:
790:
786:
782:
778:
774:
767:
764:
759:
755:
751:
747:
743:
739:
735:
731:
724:
721:
716:
712:
707:
702:
699:(1): 31–112.
698:
694:
690:
683:
680:
675:
671:
667:
663:
660:(6): 94–111.
659:
655:
648:
645:
640:
636:
632:
628:
624:
620:
613:
610:
605:
599:
595:
588:
585:
582:
579:Created from
576:
573:
570:
567:Created from
564:
561:
555:
551:
548:
546:
543:
541:
538:
536:
533:
531:
528:
525:
522:
520:
517:
515:
512:
510:
507:
505:
502:
500:
497:
495:
492:
490:
487:
485:
482:
481:
477:
475:
468:
466:
464:
460:
455:
451:
447:
443:
439:
435:
431:
427:
423:
419:
415:
411:
407:
403:
395:
393:
391:
387:
383:
382:
377:
373:
369:
365:
357:
355:
353:
348:
346:
342:
338:
334:
330:
326:
322:
318:
314:
306:
304:
302:
297:
293:
289:
283:
281:
277:
268:
261:
259:
257:
253:
248:
242:
234:
232:
229:
225:
221:
217:
213:
209:
205:
201:
197:
193:
189:
185:
176:
174:
172:
168:
164:
160:
156:
152:
148:
144:
140:
136:
132:
128:
120:
118:
116:
112:
108:
104:
100:
96:
92:
88:
81:
78:
73:
66:
63:
60:
55:
48:
43:
36:
32:
19:
2317:
2209:
2205:
2195:
2178:
2174:
2168:
2133:
2129:
2119:
2074:
2070:
2060:
2023:
2019:
2009:
1974:
1968:
1931:
1927:
1917:
1882:
1878:
1868:
1833:
1829:
1819:
1786:
1782:
1776:
1744:(3): 147–9.
1741:
1737:
1727:
1684:
1680:
1632:
1628:
1618:
1581:
1571:
1539:(16): e153.
1536:
1532:
1522:
1471:
1467:
1461:
1436:
1432:
1426:
1381:
1377:
1367:
1332:
1328:
1318:
1293:
1289:
1283:
1258:
1254:
1248:
1205:
1201:
1191:
1166:
1163:Trends Genet
1162:
1156:
1124:(1): 17–40.
1121:
1117:
1107:
1072:
1068:
1058:
1033:
1029:
1023:
968:
962:
919:
915:
909:
868:
864:
858:
833:
829:
823:
780:
776:
766:
733:
729:
723:
696:
692:
682:
657:
653:
647:
622:
618:
612:
593:
587:
575:
563:
472:
462:
458:
429:
417:
405:
401:
399:
379:
378:secreted by
361:
352:major groove
349:
310:
295:
284:
273:
244:
180:
155:cell nucleus
125:DNA-binding
124:
103:major groove
86:
85:
2596:HMG protein
2509:Prokaryotic
1783:Amino Acids
550:Zinc finger
524:Lexitropsin
484:bZIP domain
438:microarrays
381:Xanthomonas
370:. Recently
364:Zinc finger
224:acetylation
216:methylation
204:ionic bonds
196:prokaryotes
159:zinc finger
139:polymerases
2788:Biophysics
2762:Categories
2463:DNA repair
2418:POU family
1635:: 105–31.
556:References
341:repair DNA
325:expression
252:stem-loops
212:amino acid
200:nucleosome
188:eukaryotes
165:, and the
151:chromosome
93:that have
2212:: 37449.
1934:(6): 25.
1738:Zebrafish
1701:0305-1048
1600:1548-7091
1481:1004.5514
1222:0305-1048
1013:ignored (
1003:cite book
924:CiteSeerX
442:ChIP-chip
392:species.
256:nucleases
184:chromatin
143:nucleases
115:base pair
62:repressor
2244:27874042
2206:Sci. Rep
2111:24146751
2071:PLOS ONE
2052:26025051
2001:27557760
1960:21108821
1803:22842750
1768:21929364
1719:27471033
1609:11399107
1584:: 1–10.
1563:23814189
1506:21386588
1418:12808131
1359:14668705
1351:15479634
1310:10966474
1275:10473346
1240:26762975
1148:28303166
1099:25063301
1050:11497996
995:12596902
946:11498575
850:15853876
815:21101836
798:11147202
581:PDB 1RVA
569:PDB 1LMB
489:ChIP-exo
478:See also
463:in vitro
434:ChIP-Seq
418:in vitro
402:in vitro
376:proteins
343:such as
337:histones
208:Chemical
192:histones
147:histones
135:modulate
129:include
127:proteins
121:Examples
91:proteins
47:histones
2752:Biology
2265:Abalone
2235:5118750
2214:Bibcode
2102:3795721
2079:Bibcode
2043:4741334
1951:3003642
1909:6269071
1860:6275366
1759:3174730
1710:5041478
1659:9646864
1650:4781445
1554:3763557
1486:Bibcode
1453:6236744
1386:Bibcode
1231:4824100
1183:8178371
1139:5331113
1090:4132745
954:1883924
916:Science
901:4328827
893:9305837
873:Bibcode
807:9893710
758:2421408
738:Bibcode
730:Science
715:2422697
662:Bibcode
639:6236744
514:HMG-box
459:in vivo
430:in vivo
406:in vivo
313:protein
280:enzymes
2738:Portal
2616:ISGF3G
2283:(MeSH)
2242:
2232:
2160:212715
2158:
2151:342238
2148:
2109:
2099:
2050:
2040:
1999:
1989:
1958:
1948:
1907:
1900:327330
1897:
1858:
1851:327619
1848:
1811:310256
1809:
1801:
1766:
1756:
1717:
1707:
1699:
1657:
1647:
1606:
1598:
1561:
1551:
1514:103345
1512:
1504:
1451:
1416:
1409:166200
1406:
1357:
1349:
1308:
1273:
1238:
1228:
1220:
1181:
1146:
1136:
1097:
1087:
1048:
993:
983:
952:
944:
926:
899:
891:
865:Nature
848:
813:
805:
795:
756:
713:
654:Sci Am
637:
600:
358:Design
161:, the
133:which
59:lambda
2685:RAD52
2680:RAD51
2675:c-sis
2586:HNRPK
2574:NF-E2
2569:GATA3
2564:GATA2
2559:GATA1
2446:NF-κB
2396:c-ets
2365:c-myc
1807:S2CID
1510:S2CID
1476:arXiv
1355:S2CID
950:S2CID
897:S2CID
811:S2CID
390:plant
327:of a
194:. In
186:. In
107:B-DNA
80:EcoRV
2660:BCL6
2648:NRF1
2633:MSH2
2606:IκBα
2591:HMGA
2511:only
2406:ETS2
2401:ETS1
2240:PMID
2156:PMID
2107:PMID
2048:PMID
1997:PMID
1987:ISBN
1956:PMID
1905:PMID
1856:PMID
1799:PMID
1764:PMID
1715:PMID
1697:ISSN
1655:PMID
1596:ISSN
1559:PMID
1502:PMID
1449:PMID
1414:PMID
1347:PMID
1329:Cell
1306:PMID
1271:PMID
1236:PMID
1218:ISSN
1179:PMID
1144:PMID
1095:PMID
1046:PMID
1015:help
991:PMID
981:ISBN
942:PMID
889:PMID
846:PMID
803:PMID
754:PMID
711:PMID
635:PMID
598:ISBN
461:and
404:and
329:gene
296:read
222:and
89:are
75:The
57:The
2670:REL
2665:MYB
2579:YY1
2230:PMC
2222:doi
2183:doi
2146:PMC
2138:doi
2097:PMC
2087:doi
2038:PMC
2028:doi
2024:163
1979:doi
1946:PMC
1936:doi
1895:PMC
1887:doi
1846:PMC
1838:doi
1791:doi
1754:PMC
1746:doi
1705:PMC
1689:doi
1645:PMC
1637:doi
1604:PMC
1586:doi
1549:PMC
1541:doi
1494:doi
1441:doi
1404:PMC
1394:doi
1382:100
1337:doi
1333:119
1298:doi
1263:doi
1226:PMC
1210:doi
1171:doi
1134:PMC
1126:doi
1085:PMC
1077:doi
1038:doi
973:doi
934:doi
920:293
881:doi
869:389
838:doi
793:PMC
785:doi
746:doi
734:232
701:doi
670:doi
658:249
627:doi
317:DNA
105:of
35:Cro
2764::
2238:.
2228:.
2220:.
2208:.
2204:.
2179:21
2177:.
2154:.
2144:.
2132:.
2128:.
2105:.
2095:.
2085:.
2073:.
2069:.
2046:.
2036:.
2022:.
2018:.
1995:.
1985:.
1954:.
1944:.
1932:25
1930:.
1926:.
1903:.
1893:.
1881:.
1877:.
1854:.
1844:.
1832:.
1828:.
1805:.
1797:.
1787:43
1785:.
1762:.
1752:.
1740:.
1736:.
1713:.
1703:.
1695:.
1685:44
1683:.
1679:.
1667:^
1653:.
1643:.
1633:27
1631:.
1627:.
1602:.
1594:.
1580:.
1557:.
1547:.
1537:41
1535:.
1531:.
1508:.
1500:.
1492:.
1484:.
1472:22
1470:.
1447:.
1437:53
1435:.
1412:.
1402:.
1392:.
1380:.
1376:.
1353:.
1345:.
1331:.
1327:.
1304:.
1294:69
1292:.
1269:.
1259:34
1257:.
1234:.
1224:.
1216:.
1206:44
1204:.
1200:.
1177:.
1167:10
1165:.
1142:.
1132:.
1120:.
1116:.
1093:.
1083:.
1073:42
1071:.
1067:.
1044:.
1034:29
1032:.
1007::
1005:}}
1001:{{
989:.
979:.
948:.
940:.
932:.
918:.
895:.
887:.
879:.
867:.
844:.
834:56
832:.
809:.
801:.
791:.
781:54
779:.
775:.
752:.
744:.
732:.
709:.
697:47
695:.
691:.
668:.
656:.
633:.
623:53
621:.
465:.
444:.
258:.
218:,
173:.
141:,
117:.
2740::
2310:e
2303:t
2296:v
2246:.
2224::
2216::
2210:6
2189:.
2185::
2162:.
2140::
2134:5
2113:.
2089::
2081::
2075:8
2054:.
2030::
2003:.
1981::
1962:.
1938::
1911:.
1889::
1883:9
1862:.
1840::
1834:9
1813:.
1793::
1770:.
1748::
1742:8
1721:.
1691::
1661:.
1639::
1612:.
1588::
1565:.
1543::
1516:.
1496::
1488::
1478::
1455:.
1443::
1420:.
1396::
1388::
1361:.
1339::
1312:.
1300::
1277:.
1265::
1242:.
1212::
1185:.
1173::
1150:.
1128::
1122:9
1101:.
1079::
1052:.
1040::
1017:)
997:.
975::
956:.
936::
903:.
883::
875::
852:.
840::
817:.
787::
760:.
748::
740::
717:.
703::
676:.
672::
664::
641:.
629::
606:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.