40:
341:
synapse at the periaqueductal grey matter which in turn projects to the nucleus raphe magnus, which when stimulated directly inhibits pain fibers in the posterior grey column, alleviating pain. All of this seems to indicate that the nucleus raphe magnus is part of the endogenous opiate system, and
387:
Hermann, Dirk M. et al. Afferent projections to the rat nuclei raphe magnus, raphe pallidus and reticularis gigantocellularis pars demonstrated by iontophoretic application of choleratoxin (subunit b). Journal of
Chemical Neuroanatomy Volume 13, Issue 1, June 1997, Pages
418:
Hellman, Kevin et al., Opioid microinjection into raphe magnus modulates cardiorespiratory function in mice and rats. American
Journal of Physiology Regulator Integratory Comp Physiology. Volume 297, Issue 5, November 2009, Pages
321:, sends efferent stimuli to the nucleus raphe magnus when stimulated by opioids (endogenous or otherwise); electrical stimulation of the PAG as well as administration of opioid agonists to the PAG or nucleus raphe magnus produces
277:
The nucleus raphe magnus seems to participate in the endogenous analgesia system. Mounting evidence suggests that the nucleus raphe magnus plays an important role in homeostatic regulation. Its afferents from the
409:
Hellman, Kevin et al. Activity of murine magnus raphe cells predicts tachypnea and on-going nociceptive responsiveness. Journal of
Neurophysiology Volume 98, Issue 6, December 2007, Pages 3121-33.
763:
138:
823:
798:
803:
372:
254:
114:
238:
400:
Haines, Duane E., and M. D. Ard. Fundamental
Neuroscience for Basic and Clinical Applications. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders, 2013.
855:
446:
202:
145:
860:
768:
250:
703:
698:
688:
683:
209:. This neural path thus mediates pain perception through pre-synaptic inhibition of first-order afferent (sensory) neurons.
44:
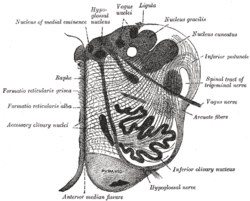
Section of the medulla oblongata at about the middle of the olive. (Raphe nuclei not labeled, but 'raphe' labeled at left.)
561:
307:
266:
206:
201:
neurons of the NRM then bilaterally project efferents to the enkephalinergic and dynorphin-containing interneurons of the
133:
875:
828:
624:
566:
529:
925:
519:
234:
870:
865:
619:
614:
596:
524:
253:
and the prelimbic, infralimbic, medial and lateral precentral cortices. It is one of the afferent targets of the
780:
502:
72:
634:
904:
897:
887:
183:
121:
109:
724:
473:
439:
89:
850:
818:
758:
729:
678:
668:
551:
338:
334:
314:
298:
The main function of the nucleus raphe magnus is pain mediation. The nucleus raphe magnus releases
194:
930:
629:
514:
509:
456:
368:
673:
556:
492:
432:
591:
586:
497:
326:
919:
813:
808:
882:
775:
650:
287:
246:
171:
102:
77:
842:
464:
279:
223:
303:
283:
227:
190:
84:
329:
effects of electrical stimulation of the PAG can be blocked by administering
126:
322:
318:
299:
198:
179:
17:
151:
424:
330:
242:
96:
337:) to the nucleus raphe magnus. Similarly, afferent fibres from the
39:
60:
175:
428:
367:(2nd ed.). Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell.
841:
791:
751:
744:
714:
658:
649:
605:
579:
540:
481:
472:
463:
132:
120:
108:
95:
83:
71:
59:
54:
49:
32:
363:Patestas, Maria A.; Gartner, Leslie P. (2016).
358:
356:
354:
440:
317:, an area of the brain involved in mediating
302:when stimulated. It sends projections to the
8:
189:The NRM receives afferent stimuli from the
748:
655:
478:
469:
447:
433:
425:
233:It receives descending afferents from the
38:
699:Descending dorsal longitudinal fasciculus
342:acts to inhibit pain in the spinal cord.
684:Ascending dorsal longitudinal fasciculus
396:
394:
207:posterior grey column of the spinal cord
350:
149:
29:
255:ascending reticular activating system
7:
239:paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus
27:Cluster of nuclei in the brain stem
25:
286:suggest it may be a part of the
146:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
306:-releasing interneurons of the
251:parvocellular reticular nucleus
222:It receives afferents from the
704:Medial longitudinal fasciculus
689:Medial longitudinal fasciculus
1:
562:Dorsal nucleus of vagus nerve
265:It projects efferents to the
829:Inferior cerebellar peduncle
625:Rostral ventromedial medulla
273:Neurophysiology and function
567:Inferior salivatory nucleus
947:
620:Arcuate nucleus of medulla
365:A Textbook of Neuroanatomy
310:to directly inhibit pain.
235:periaqueductal grey matter
615:Ventral respiratory group
597:Accessory cuneate nucleus
315:periaqueductal gray (PAG)
241:, central nucleus of the
144:
37:
781:Inferior olivary nucleus
503:Dorsal respiratory group
174:. It is situated in the
799:Posterior median sulcus
764:Anterior median fissure
170:) is one of the seven
905:Perihypoglossal nuclei
184:nucleus raphe obscurus
182:, just rostral to the
804:Posterolateral sulcus
725:Olivocerebellar tract
635:Pre-Bötzinger complex
308:posterior grey column
267:posterior grey column
203:substantia gelatinosa
66:nucleus raphes magnus
769:Anterolateral sulcus
269:(to modulate pain).
164:nucleus raphe magnus
33:Nucleus raphe magnus
851:Reticular formation
819:Hypoglossal trigone
730:Rubro-olivary tract
679:Juxtarestiform body
669:Sensory decussation
552:Hypoglossal nucleus
339:spinothalamic tract
195:periaqueductal gray
721:Descending tracts
926:Medulla oblongata
913:
912:
837:
836:
740:
739:
645:
644:
630:Botzinger complex
575:
574:
515:Vestibular nuclei
510:Gustatory nucleus
374:978-1-118-67746-9
160:
159:
155:
16:(Redirected from
938:
749:
674:Medial lemniscus
656:
557:Nucleus ambiguus
545:
493:Solitary nucleus
486:
479:
470:
449:
442:
435:
426:
420:
416:
410:
407:
401:
398:
389:
385:
379:
378:
360:
152:edit on Wikidata
42:
30:
21:
946:
945:
941:
940:
939:
937:
936:
935:
916:
915:
914:
909:
856:Gigantocellular
833:
824:Medial eminence
787:
736:
710:
641:
601:
592:Cuneate nucleus
587:Gracile nucleus
571:
541:
536:
482:
459:
455:Anatomy of the
453:
423:
417:
413:
408:
404:
399:
392:
386:
382:
375:
362:
361:
352:
348:
296:
294:Pain modulation
275:
263:
220:
215:
193:neurons of the
191:enkephalinergic
156:
45:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
944:
942:
934:
933:
928:
918:
917:
911:
910:
908:
907:
902:
901:
900:
895:
890:
880:
879:
878:
873:
868:
863:
858:
847:
845:
839:
838:
835:
834:
832:
831:
826:
821:
816:
811:
806:
801:
795:
793:
789:
788:
786:
785:
784:
783:
773:
772:
771:
766:
755:
753:
746:
742:
741:
738:
737:
735:
734:
733:
732:
727:
718:
716:
712:
711:
709:
708:
707:
706:
701:
693:
692:
691:
686:
681:
676:
671:
662:
660:
653:
647:
646:
643:
642:
640:
639:
638:
637:
632:
627:
622:
617:
609:
607:
603:
602:
600:
599:
594:
589:
583:
581:
577:
576:
573:
572:
570:
569:
564:
559:
554:
548:
546:
538:
537:
535:
534:
533:
532:
527:
522:
512:
507:
506:
505:
500:
489:
487:
476:
474:Cranial nuclei
467:
461:
460:
454:
452:
451:
444:
437:
429:
422:
421:
411:
402:
390:
380:
373:
349:
347:
344:
327:antinociceptic
295:
292:
274:
271:
262:
259:
219:
216:
214:
211:
158:
157:
148:
142:
141:
136:
130:
129:
124:
118:
117:
112:
106:
105:
100:
93:
92:
87:
81:
80:
75:
69:
68:
63:
57:
56:
52:
51:
47:
46:
43:
35:
34:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
943:
932:
929:
927:
924:
923:
921:
906:
903:
899:
896:
894:
891:
889:
886:
885:
884:
881:
877:
874:
872:
869:
867:
864:
862:
861:Parvocellular
859:
857:
854:
853:
852:
849:
848:
846:
844:
840:
830:
827:
825:
822:
820:
817:
815:
814:Vagal trigone
812:
810:
809:Area postrema
807:
805:
802:
800:
797:
796:
794:
790:
782:
779:
778:
777:
774:
770:
767:
765:
762:
761:
760:
757:
756:
754:
750:
747:
743:
731:
728:
726:
723:
722:
720:
719:
717:
713:
705:
702:
700:
697:
696:
694:
690:
687:
685:
682:
680:
677:
675:
672:
670:
667:
666:
664:
663:
661:
657:
654:
652:
648:
636:
633:
631:
628:
626:
623:
621:
618:
616:
613:
612:
611:
610:
608:
604:
598:
595:
593:
590:
588:
585:
584:
582:
578:
568:
565:
563:
560:
558:
555:
553:
550:
549:
547:
544:
539:
531:
528:
526:
523:
521:
518:
517:
516:
513:
511:
508:
504:
501:
499:
496:
495:
494:
491:
490:
488:
485:
480:
477:
475:
471:
468:
466:
462:
458:
450:
445:
443:
438:
436:
431:
430:
427:
415:
412:
406:
403:
397:
395:
391:
384:
381:
376:
370:
366:
359:
357:
355:
351:
345:
343:
340:
336:
332:
328:
324:
320:
316:
311:
309:
305:
301:
293:
291:
289:
285:
281:
272:
270:
268:
260:
258:
256:
252:
248:
244:
240:
236:
231:
229:
225:
217:
212:
210:
208:
204:
200:
196:
192:
187:
185:
181:
177:
173:
169:
165:
153:
147:
143:
140:
137:
135:
131:
128:
125:
123:
119:
116:
113:
111:
107:
104:
101:
98:
94:
91:
88:
86:
82:
79:
76:
74:
70:
67:
64:
62:
58:
53:
48:
41:
36:
31:
19:
892:
883:Raphe nuclei
651:White matter
542:
483:
414:
405:
383:
364:
312:
297:
288:motor system
276:
264:
247:hypothalamic
232:
221:
199:serotonergic
188:
172:raphe nuclei
167:
163:
161:
115:A14.1.04.321
103:birnlex_1363
65:
18:Raphe magnus
465:Grey matter
333:(an opiate
280:spinal cord
237:(PAG), the
224:spinal cord
55:Identifiers
920:Categories
876:Paramedian
346:References
335:antagonist
304:enkephalin
284:cerebellum
245:, lateral
228:cerebellum
85:NeuroNames
931:Serotonin
543:efferent:
484:afferent:
323:analgesia
319:analgesia
300:serotonin
261:Efferents
218:Afferents
180:brainstem
898:Pallidus
888:Obscurus
665:Sensory
530:Inferior
419:R1400-8.
331:naloxone
243:amygdala
97:NeuroLex
871:Lateral
866:Ventral
759:Pyramid
745:Surface
715:Ventral
606:Ventral
520:Lateral
457:medulla
213:Anatomy
205:of the
178:in the
78:D065846
50:Details
893:Magnus
695:Motor
659:Dorsal
580:Dorsal
525:Medial
371:
325:; the
249:area,
197:; the
776:Olive
752:Front
498:tract
150:[
139:72584
61:Latin
843:Grey
792:Back
388:1-21
369:ISBN
313:The
282:and
226:and
176:pons
162:The
127:6038
110:TA98
73:MeSH
168:NRM
134:FMA
122:TA2
90:739
922::
393:^
353:^
290:.
257:.
230:.
186:.
99:ID
448:e
441:t
434:v
377:.
166:(
154:]
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.