98:
43:
153:. A more significant problem with earlier designs was their failure to prevent collapse or rotation in inherently unstable fractures. This was addressed by the introduction of the concept of 'locking' the nails, where bolts on each end of the nail fix it to the bony cortex, preventing rotation among the fragments. This led to the emergence of locked IM nailing, which is the standard today.
31:
97:
179:
Lower screws holding intramedullary rods can sometimes cause limited dorsiflexion as a result of damage and subsequent healing and fibrotic developments around that area. If the bone breaks more medially, there is scope to position the nails further from the ankle joint which would prevent/reduce
156:
The extension mechanism of intramedullary can be of two types: ratcheting, such as in the
Bliskunov, Albizzia, and the Internal Skeletal Kinetic Distractor (ISKD, removed from market in 2015) nails; and rotating spindle, as in the Fitbone, Phenix, PRECICE, and PRECICE 2 nails.
125:
The earliest IM nails were triangular or V-shaped in cross-section. Later they were modified to their present and more rotationally stable clover-leaf shape. Several modifications and shapes were introduced subsequently for various bones such as V-nails for
94:, both of which required long periods of inactivity. IM nails resulted in earlier return to activity for the soldiers, sometimes even within a span of a few weeks, since they share the load with the bone, rather than entirely supporting the bone.
165:
At a median 14 years after tibial nailing of isolated tibial fractures, patients' function is comparable to population norms, but objective and subjective evaluation shows persistent
528:
249:
455:
Lefaivre, K. A.; Guy, P.; Chan, H.; Blachut, P. A. (2008). "Long-Term Follow-up of Tibial Shaft
Fractures Treated with Intramedullary Nailing".
394:
Leung, Kwok-Sui; Kempf, Ivan; Alt, Volker; Taglang, Gilbert; Haarman, H. J. Th. M.; Seidel, Hartmut; Schnettler, Reinhard (15 February 2006).
405:
214:
321:
495:
439:
117:
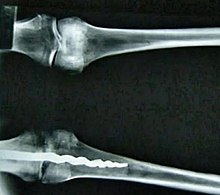
man from more than 3,500 years ago. Researchers believe the pin was inserted after the man's death, but before his burial.
523:
58:(IM nail) or inter-locking nail or Küntscher nail (without proximal or distal fixation), is a metal rod forced into the
299:
538:
533:
189:
87:
272:
46:
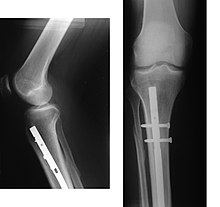
Proximal femur nail with locking and stabilisation screws for treatment of femur fractures of left thigh
348:
349:"Defining the role of intramedullary nailing for fractures of the distal radius: a systematic review"
75:
176:, where the broken bone is fixated out of alignment and heals incorrectly, causing a rotated limb.
221:
472:
435:
401:
395:
376:
368:
264:
110:
464:
360:
173:
150:
59:
499:
142:
91:
397:
Practice of intramedullary locked nails: new developments in techniques and applications
194:
517:
131:
114:
67:
79:
42:
364:
300:"Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics - Intramedullary Nailing of Femoral Shaft Frx"
468:
429:
17:
149:
has several advantages, including lower mechanical failure rates and improved
71:
372:
476:
380:
268:
172:
One potential complication of intramedullary nailing after a fracture is
166:
146:
101:
An intramedullary nail found in the left knee of a mummified
Egyptian man
30:
322:"BYU professor finds evidence of advanced surgery in ancient mummy"
127:
106:
96:
83:
41:
35:
29:
135:
63:
105:
The oldest intramedullary nail was found in the left knee of a
248:
Bong, Matthew R.; Koval, Kenneth J.; Egol, Kenneth A. (2006).
78:
is credited with the first use of this device in 1939, during
86:. Prior to that, treatment of such fractures was limited to
431:
Intramedullary Limb
Lengthening: Principles and Practice
34:X-ray showing the proximal portion of a fractured
243:
241:
215:"AO Dialogue 2206: The magazine of AO community"
263:(3/4). NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases: 94–97.
257:Bulletin of the NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases
8:
347:Jordan, R. W.; Saithna, A. (October 2015).
220:. AO Foundation. p. 42. Archived from
294:
292:
428:Green, Stuart A.; Dahl, Mark T. (2017).
66:. IM nails have long been used to treat
250:"The History of Intramedullary Nailing"
206:
82:, for soldiers with fractures of the
27:Metal rod inserted to treat fractures
7:
529:German inventions of the Nazi period
25:
1:
457:Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma
365:10.1302/0301-620X.97B10.35297
169:which are not insignificant.
145:was used for older IM nails,
469:10.1097/BOT.0b013e318180e646
353:The Bone & Joint Journal
498:. About.com. Archived from
400:. Birkhäuser. p. 100.
38:with an intramedullary nail
555:
328:. Brigham Young University
494:Cluett, Jonathan (M.D.).
434:. Springer. p. 180.
320:Snow, Karen (June 1996).
190:Distraction osteogenesis
180:this dorsiflexion loss.
138:nails, Rusch nails etc.
102:
47:
39:
100:
45:
33:
496:"Intramedullary Rod"
113:, the remains of an
524:Orthopedic implants
302:. Duke Orthopaedics
56:intramedullary nail
54:, also known as an
103:
52:intramedullary rod
48:
40:
407:978-3-540-25349-5
359:(10): 1370–1376.
76:Gerhard Küntscher
16:(Redirected from
546:
510:
508:
507:
481:
480:
452:
446:
445:
425:
419:
418:
416:
414:
391:
385:
384:
344:
338:
337:
335:
333:
317:
311:
310:
308:
307:
296:
287:
286:
284:
283:
277:
271:. Archived from
254:
245:
236:
235:
233:
232:
226:
219:
211:
174:bone malrotation
151:biocompatibility
60:medullary cavity
21:
554:
553:
549:
548:
547:
545:
544:
543:
539:1939 in Germany
534:1939 in science
514:
513:
505:
503:
493:
490:
485:
484:
454:
453:
449:
442:
427:
426:
422:
412:
410:
408:
393:
392:
388:
346:
345:
341:
331:
329:
319:
318:
314:
305:
303:
298:
297:
290:
281:
279:
275:
252:
247:
246:
239:
230:
228:
224:
217:
213:
212:
208:
203:
186:
163:
143:stainless steel
123:
28:
23:
22:
18:Rodding surgery
15:
12:
11:
5:
552:
550:
542:
541:
536:
531:
526:
516:
515:
512:
511:
489:
488:External links
486:
483:
482:
463:(8): 525–529.
447:
440:
420:
406:
386:
339:
312:
288:
237:
205:
204:
202:
199:
198:
197:
195:Cannulated bar
192:
185:
182:
162:
159:
122:
119:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
551:
540:
537:
535:
532:
530:
527:
525:
522:
521:
519:
502:on 2009-01-26
501:
497:
492:
491:
487:
478:
474:
470:
466:
462:
458:
451:
448:
443:
441:9783319602974
437:
433:
432:
424:
421:
409:
403:
399:
398:
390:
387:
382:
378:
374:
370:
366:
362:
358:
354:
350:
343:
340:
327:
323:
316:
313:
301:
295:
293:
289:
278:on 2015-01-21
274:
270:
266:
262:
258:
251:
244:
242:
238:
227:on 2015-01-21
223:
216:
210:
207:
200:
196:
193:
191:
188:
187:
183:
181:
177:
175:
170:
168:
161:Complications
160:
158:
154:
152:
148:
144:
139:
137:
133:
129:
120:
118:
116:
112:
108:
99:
95:
93:
89:
85:
81:
77:
74:of the body.
73:
69:
65:
61:
57:
53:
44:
37:
32:
19:
504:. Retrieved
500:the original
460:
456:
450:
430:
423:
411:. Retrieved
396:
389:
356:
352:
342:
330:. Retrieved
326:BYU Magazine
325:
315:
304:. Retrieved
280:. Retrieved
273:the original
260:
256:
229:. Retrieved
222:the original
209:
178:
171:
164:
155:
140:
124:
104:
80:World War II
55:
51:
49:
413:20 December
518:Categories
506:2008-12-19
306:2011-08-04
282:2013-03-12
231:2013-03-12
201:References
72:long bones
373:2049-4394
141:Although
111:Usermontu
68:fractures
477:18758282
381:26430012
269:17155917
184:See also
167:sequelae
147:titanium
115:Egyptian
88:traction
332:May 27,
92:plaster
475:
438:
404:
379:
371:
267:
132:radius
121:Design
109:named
276:(PDF)
253:(PDF)
225:(PDF)
218:(PDF)
128:tibia
107:mummy
84:femur
62:of a
36:tibia
473:PMID
436:ISBN
415:2011
402:ISBN
377:PMID
369:ISSN
357:97-B
334:2015
265:PMID
136:ulna
134:and
64:bone
465:doi
361:doi
90:or
70:of
50:An
520::
471:.
461:22
459:.
375:.
367:.
355:.
351:.
324:.
291:^
261:64
259:.
255:.
240:^
130:,
509:.
479:.
467::
444:.
417:.
383:.
363::
336:.
309:.
285:.
234:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.