557:
542:
31:
51:
367:
exists, in terms of length and point of attachment. Despite the classical description, the muscle only solely attaches to the duodenojejunal flexure in about 8% of people; it is far more common, 40 to 60% of the time to attach additionally to the third and fourth parts of the duodenum; and 20 to 30%
395:
The ligament contains a slender band of skeletal muscle from the diaphragm and a fibromuscular band of smooth muscle from the horizontal and ascending parts of the duodenum. When it contracts, by virtue of connections to the third and fourth parts of the duodenum, the suspensory muscle of the
449:, a syndrome often suspected in young children when they have episodes of recurrent vomiting. Visualising a normal location of the ligament of Treitz in radiological images is critical in ruling out malrotation of the gut in a child; it is abnormally located when malrotation is present.
510:(in Latin), and described as consisting of a lower muscular portion with a broad base, and an upper tendinous portion blending with connective tissue around the origins of the superior mesenteric and coeliac arteries. It is commonly termed the
445:, bright red blood or clots in the stool, usually indicates gastrointestinal bleeding from the lower part of the gastrointestinal tract. It is an especially important landmark to note when looking at the bowel for the presence of
856:
Lee, Tae Hee; Lee, Joon Seong; Jo, Yunju; Park, Kyung Sik; Cheon, Jae Hee; Kim, Yong Sung; Jang, Jae Young; Kang, Young Woo (18 October 2012). "Superior
Mesenteric Artery Syndrome: Where Do We Stand Today?".
482:(SMA) is an extremely rare life-threatening condition that can either be congenital and chronic, or induced and acute. SMA Syndrome is characterised by compression of the duodenum between the
277:. The suspensory muscle most often connects to both the third and fourth parts of the duodenum, as well as the duodenojejunal flexure, although the attachment is quite variable.
541:
710:
Kim, Seuk Ky; Cho, C. D.; Wojtowycz, Andrij R. (25 July 2007). "The ligament of Treitz (the suspensory ligament of the
Duodenum): anatomic and radiographic correlation".
918:
355:, inserting into the junction between the duodenum and jejunum, the duodenojejunal flexure. Here, the muscles are continuous with the muscular layers of the duodenum.
299:
rotation of the gut, by offering a point of fixation for the rotating gut. It is also thought to help digestion by widening the angle of the duodenojejunal flexure.
556:
379:
and superior mesenteric artery; and a lower muscular portion from the connective tissue attaching to the duodenum. The superior portion is also described as the
205:
371:
According to some authors, who use the original description by Treitz, the muscle may be divided into two sections: a ligamentous portion attaching the
677:
280:
The suspensory muscle marks the formal division between the duodenum and the jejunum. This division is used to mark the difference between the
762:
648:
181:
911:
486:
and the superior mesenteric artery, and may—when congenital—result from a short suspensory muscle. One surgical treatment is
479:
464:, duodenum, and part of the jejunum, the ligament of Treitz is separated from the duodenum and preserved. When the remaining jejunum is
405:
300:
687:
441:, black tarry stools, usually indicate a gastrointestinal bleed from a location in the upper gastrointestinal tract. In contrast,
904:
368:
of the time it only attaches to the third and fourth parts. Moreover, separate multiple attachments are not that uncommon.
200:
778:
Vernava, Anthony M.; Moore, Beth A.; Longo, Walter E.; Johnson, Frank E. (July 1997). "Lower gastrointestinal bleeding".
323:, respectively. The suspensory muscle of the duodenum marks their formal division. The suspensory muscle arises from the
430:
281:
1432:
1166:
344:
270:
212:
149:
142:
116:
109:
96:
417:. It plays an important role in the embryological rotation of the small intestine as the superior retention band.
1573:
1081:
1076:
896:
821:
Gagner, Michel; Palermo, Mariano (28 July 2009). "Laparoscopic
Whipple procedure: review of the literature".
1490:
1485:
1480:
997:
372:
89:
1271:
1266:
1261:
1182:
1012:
1007:
940:
928:
453:
446:
262:
188:
176:
126:
40:
1508:
970:
396:
duodenum widens the angle of the duodenojejunal flexure, allowing movement of the intestinal contents.
1228:
975:
965:
1276:
980:
548:
1550:
1407:
1351:
1161:
990:
957:
882:
803:
735:
619:
364:
328:
1412:
1206:
874:
838:
795:
758:
727:
683:
644:
638:
611:
457:
336:
324:
285:
266:
101:
1389:
1379:
1315:
1218:
1086:
1050:
1002:
866:
830:
787:
719:
603:
499:
274:
1545:
1516:
1384:
1374:
1369:
1361:
1334:
1310:
1191:
483:
320:
258:
154:
Facilitates movement of food; embryological role in fixating jejunum during gut rotation
1540:
1530:
1475:
1437:
1320:
1136:
1131:
1113:
1055:
1017:
376:
138:
105:
490:, which involves cutting the suspensory muscle, though this is not often carried out.
1567:
1394:
1156:
1151:
1141:
1118:
527:
886:
739:
1470:
1460:
1126:
985:
807:
623:
442:
340:
84:
594:
Meyers, M. A. (September 1995). "Treitz redux: the ligament of Treitz revisited".
1465:
1402:
1238:
1233:
1211:
932:
465:
434:
547:
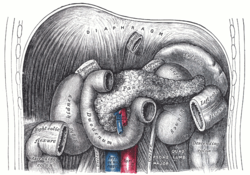
Depiction of the origin of the suspensory muscle, from the fibres of the right
1520:
1455:
1447:
1223:
870:
834:
723:
515:
410:
296:
70:
30:
562:
Suspensory muscle of the duodenum or muscle of Treitz seen in a ventral view.
193:
1535:
1525:
1043:
1038:
1027:
523:
352:
332:
878:
842:
731:
799:
615:
1248:
461:
414:
348:
312:
292:
250:
122:
56:
36:
303:
is a rare abnormality caused by a congenitally short suspensory muscle.
218:
1286:
1146:
1108:
1103:
1098:
1093:
1065:
949:
791:
607:
473:
469:
426:
316:
254:
65:
60:
1424:
438:
383:. These two parts are now considered anatomically distinct, with the
246:
50:
387:
referring solely to the lower structure attaching at the duodenum.
1343:
1302:
164:
133:
498:
The suspensory muscle of the duodenum was first named in 1853 by
757:(6th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 241.
900:
170:
musculus suspensorius duodeni, ligamentum suspensorium duodeni
530: ... a structure that many refer to but few have seen."
288:
as it may determine the source of gastrointestinal bleeding.
73:
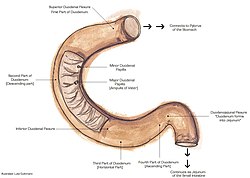
to the duodenojejunal flexure, behind the pancreas, shown.
261:'s first and second parts, respectively), as well as the
413:, the suspensory muscle of the duodenum is derived from
39:. The suspensory muscle of the duodenum attaches to the
429:
landmark of the duodenojejunal flexure, separating the
1507:
1446:
1423:
1360:
1342:
1333:
1301:
1285:
1247:
1199:
1190:
1181:
1064:
1026:
948:
939:
199:
187:
175:
163:
158:
148:
132:
115:
95:
83:
78:
23:
69:. The suspensory muscle of the duodenum connects
912:
8:
823:Journal of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery
589:
587:
585:
583:
581:
579:
577:
671:
669:
667:
640:Oxford textbook of medicine: Sections 18-33
504:
1339:
1196:
1187:
945:
919:
905:
897:
49:
29:
705:
703:
701:
699:
476:, it may be passed through the ligament.
375:to the connective tissue surrounding the
573:
537:
431:upper and lower gastrointestinal tracts
282:upper and lower gastrointestinal tracts
16:Muscle between the duodenum and jejunum
753:Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR (2010).
319:are the first and second parts of the
291:The suspensory muscle is derived from
216:
20:
7:
249:connecting the junction between the
859:Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery
682:. Academic Publishers. p. 48.
480:Superior mesenteric artery syndrome
406:Development of the digestive system
351:, and enters the upper part of the
301:Superior mesenteric artery syndrome
780:Diseases of the Colon & Rectum
14:
526:. It has also been likened to "a
520:suspensory muscle of the duodenum
555:
540:
235:suspensory ligament of duodenum
425:This ligament is an important
1:
506:musculus suspensorius duodeni
231:suspensory muscle of duodenum
24:Suspensory muscle of duodenum
1167:Enterochromaffin-like cells
755:Clinically Oriented Anatomy
643:. Oxford University Press.
1590:
403:
345:superior mesenteric artery
213:Anatomical terms of muscle
143:Superior mesenteric plexus
121:Third and fourth-parts of
110:superior mesenteric artery
871:10.1007/s11605-012-2049-5
835:10.1007/s00534-009-0142-2
724:10.1007/s00261-007-9284-3
679:Anatomy, Combined Edition
637:David A. Warrell (2005).
456:, commonly used to treat
211:
48:
28:
339:around the stems of the
331:as it passes around the
295:and plays a role in the
1491:External anal sphincter
1486:Intersphincteric groove
1481:Internal anal sphincter
998:Pterygomandibular raphe
373:right crus of diaphragm
284:, which is relevant in
1272:Duodenojejunal flexure
1267:Minor duodenal papilla
1262:Major duodenal papilla
1013:Pharyngobasilar fascia
1008:Buccopharyngeal fascia
929:gastrointestinal tract
505:
447:malrotation of the gut
263:duodenojejunal flexure
127:duodenojejunal flexure
41:duodenojejunal flexure
1229:Enteroendocrine cells
421:Clinical significance
404:Further information:
347:, passes behind the
343:(celiac artery) and
1162:Gastric chief cells
454:Whipple's procedure
271:superior mesenteric
792:10.1007/BF02055445
608:10.1007/BF01213262
549:diaphragmatic crus
512:ligament of Treitz
488:Strong's operation
365:anatomic variation
243:ligament of Treitz
1559:
1558:
1551:Muscularis mucosa
1503:
1502:
1499:
1498:
1413:epiploic appendix
1329:
1328:
1257:Suspensory muscle
1219:Intestinal glands
1177:
1176:
865:(12): 2203–2211.
764:978-0-7817-7525-0
712:Abdominal Imaging
676:Mitra, S (2006).
650:978-0-19-856978-7
596:Abdominal Imaging
534:Additional images
458:pancreatic cancer
385:suspensory muscle
337:connective tissue
286:clinical medicine
267:connective tissue
227:
226:
222:
102:Connective tissue
1581:
1574:Digestive system
1433:Transverse folds
1390:Descending colon
1380:Transverse colon
1340:
1294:No substructures
1277:Brunner's glands
1207:Intestinal villi
1197:
1188:
1087:Angular incisure
1003:Pharyngeal raphe
971:retropharyngeal
946:
931:, excluding the
921:
914:
907:
898:
891:
890:
853:
847:
846:
818:
812:
811:
775:
769:
768:
750:
744:
743:
707:
694:
693:
673:
662:
661:
659:
657:
634:
628:
627:
591:
559:
544:
508:
460:by removing the
275:coeliac arteries
269:surrounding the
219:edit on Wikidata
90:Gastrointestinal
53:
33:
21:
1589:
1588:
1584:
1583:
1582:
1580:
1579:
1578:
1564:
1563:
1560:
1555:
1495:
1442:
1419:
1385:Splenic flexure
1375:Hepatic flexure
1370:Ascending colon
1356:
1335:Large intestine
1325:
1321:Microfold cells
1316:Peyer's patches
1311:Ileocecal valve
1297:
1281:
1243:
1192:Small intestine
1173:
1060:
1022:
976:parapharyngeal
966:peripharyngeal
935:
927:Anatomy of the
925:
895:
894:
855:
854:
850:
820:
819:
815:
777:
776:
772:
765:
752:
751:
747:
709:
708:
697:
690:
675:
674:
665:
655:
653:
651:
636:
635:
631:
593:
592:
575:
570:
563:
560:
551:
545:
536:
496:
484:abdominal aorta
433:. For example,
423:
411:Embryologically
408:
402:
393:
361:
335:, continues as
321:small intestine
309:
259:small intestine
239:Treitz's muscle
233:(also known as
223:
74:
44:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1587:
1585:
1577:
1576:
1566:
1565:
1557:
1556:
1554:
1553:
1548:
1543:
1541:Circular folds
1538:
1533:
1531:Muscular layer
1528:
1523:
1513:
1511:
1505:
1504:
1501:
1500:
1497:
1496:
1494:
1493:
1488:
1483:
1478:
1476:Pectinate line
1473:
1468:
1463:
1458:
1452:
1450:
1444:
1443:
1441:
1440:
1435:
1429:
1427:
1421:
1420:
1418:
1417:
1416:
1415:
1410:
1405:
1397:
1392:
1387:
1382:
1377:
1372:
1366:
1364:
1358:
1357:
1355:
1354:
1348:
1346:
1337:
1331:
1330:
1327:
1326:
1324:
1323:
1318:
1313:
1307:
1305:
1299:
1298:
1296:
1295:
1291:
1289:
1283:
1282:
1280:
1279:
1274:
1269:
1264:
1259:
1253:
1251:
1245:
1244:
1242:
1241:
1236:
1231:
1226:
1221:
1216:
1215:
1214:
1203:
1201:
1194:
1185:
1179:
1178:
1175:
1174:
1172:
1171:
1170:
1169:
1164:
1159:
1157:Parietal cells
1154:
1152:Foveolar cells
1149:
1147:Pyloric glands
1144:
1139:
1137:Cardiac glands
1134:
1132:Gastric glands
1129:
1121:
1116:
1114:Gastric mucosa
1111:
1106:
1101:
1096:
1091:
1090:
1089:
1084:
1079:
1070:
1068:
1062:
1061:
1059:
1058:
1053:
1048:
1047:
1046:
1041:
1032:
1030:
1024:
1023:
1021:
1020:
1018:Pyriform sinus
1015:
1010:
1005:
1000:
995:
994:
993:
988:
983:
981:retrovisceral
978:
973:
968:
960:
954:
952:
943:
937:
936:
926:
924:
923:
916:
909:
901:
893:
892:
848:
829:(6): 726–730.
813:
786:(7): 846–858.
770:
763:
745:
718:(4): 395–397.
695:
688:
663:
649:
629:
602:(5): 421–424.
572:
571:
569:
566:
565:
564:
561:
554:
552:
546:
539:
535:
532:
495:
492:
422:
419:
401:
398:
392:
389:
377:coeliac artery
360:
357:
308:
305:
225:
224:
215:
209:
208:
203:
197:
196:
191:
185:
184:
179:
173:
172:
167:
161:
160:
156:
155:
152:
146:
145:
139:Coeliac plexus
136:
130:
129:
119:
113:
112:
106:coeliac artery
99:
93:
92:
87:
81:
80:
76:
75:
54:
46:
45:
34:
26:
25:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1586:
1575:
1572:
1571:
1569:
1562:
1552:
1549:
1547:
1544:
1542:
1539:
1537:
1534:
1532:
1529:
1527:
1524:
1522:
1518:
1515:
1514:
1512:
1510:
1506:
1492:
1489:
1487:
1484:
1482:
1479:
1477:
1474:
1472:
1469:
1467:
1464:
1462:
1459:
1457:
1454:
1453:
1451:
1449:
1445:
1439:
1436:
1434:
1431:
1430:
1428:
1426:
1422:
1414:
1411:
1409:
1406:
1404:
1401:
1400:
1398:
1396:
1395:Sigmoid colon
1393:
1391:
1388:
1386:
1383:
1381:
1378:
1376:
1373:
1371:
1368:
1367:
1365:
1363:
1359:
1353:
1350:
1349:
1347:
1345:
1341:
1338:
1336:
1332:
1322:
1319:
1317:
1314:
1312:
1309:
1308:
1306:
1304:
1300:
1293:
1292:
1290:
1288:
1284:
1278:
1275:
1273:
1270:
1268:
1265:
1263:
1260:
1258:
1255:
1254:
1252:
1250:
1246:
1240:
1237:
1235:
1232:
1230:
1227:
1225:
1222:
1220:
1217:
1213:
1210:
1209:
1208:
1205:
1204:
1202:
1198:
1195:
1193:
1189:
1186:
1184:
1180:
1168:
1165:
1163:
1160:
1158:
1155:
1153:
1150:
1148:
1145:
1143:
1142:Fundic glands
1140:
1138:
1135:
1133:
1130:
1128:
1125:
1124:
1123:Microanatomy
1122:
1120:
1119:Gastric folds
1117:
1115:
1112:
1110:
1107:
1105:
1102:
1100:
1097:
1095:
1092:
1088:
1085:
1083:
1080:
1078:
1075:
1074:
1072:
1071:
1069:
1067:
1063:
1057:
1054:
1052:
1049:
1045:
1042:
1040:
1037:
1036:
1034:
1033:
1031:
1029:
1025:
1019:
1016:
1014:
1011:
1009:
1006:
1004:
1001:
999:
996:
992:
989:
987:
984:
982:
979:
977:
974:
972:
969:
967:
964:
963:
961:
959:
956:
955:
953:
951:
947:
944:
942:
938:
934:
930:
922:
917:
915:
910:
908:
903:
902:
899:
888:
884:
880:
876:
872:
868:
864:
860:
852:
849:
844:
840:
836:
832:
828:
824:
817:
814:
809:
805:
801:
797:
793:
789:
785:
781:
774:
771:
766:
760:
756:
749:
746:
741:
737:
733:
729:
725:
721:
717:
713:
706:
704:
702:
700:
696:
691:
689:81-87504-95-1
685:
681:
680:
672:
670:
668:
664:
652:
646:
642:
641:
633:
630:
625:
621:
617:
613:
609:
605:
601:
597:
590:
588:
586:
584:
582:
580:
578:
574:
567:
558:
553:
550:
543:
538:
533:
531:
529:
528:polar ice cap
525:
521:
517:
513:
509:
507:
501:
500:Václav Treitz
493:
491:
489:
485:
481:
477:
475:
471:
467:
463:
459:
455:
450:
448:
444:
440:
436:
432:
428:
420:
418:
416:
412:
407:
399:
397:
390:
388:
386:
382:
378:
374:
369:
366:
363:Considerable
358:
356:
354:
350:
346:
342:
338:
334:
330:
326:
322:
318:
314:
306:
304:
302:
298:
297:embryological
294:
289:
287:
283:
278:
276:
272:
268:
264:
260:
256:
252:
248:
244:
240:
236:
232:
220:
214:
210:
207:
204:
202:
198:
195:
192:
190:
186:
183:
180:
178:
174:
171:
168:
166:
162:
157:
153:
151:
147:
144:
140:
137:
135:
131:
128:
124:
120:
118:
114:
111:
107:
103:
100:
98:
94:
91:
88:
86:
82:
77:
72:
68:
67:
62:
58:
52:
47:
42:
38:
32:
27:
22:
19:
1561:
1471:Anal sinuses
1461:Anal columns
1256:
1239:Paneth cells
1234:Goblet cells
1200:Microanatomy
1127:Gastric pits
991:prevertebral
862:
858:
851:
826:
822:
816:
783:
779:
773:
754:
748:
715:
711:
678:
654:. Retrieved
639:
632:
599:
595:
519:
511:
503:
497:
487:
478:
451:
443:hematochezia
435:bloody vomit
424:
409:
394:
384:
380:
370:
362:
341:celiac trunk
310:
290:
279:
245:) is a thin
242:
238:
234:
230:
228:
182:A05.6.02.011
169:
104:surrounding
64:
18:
1466:Anal valves
1403:taenia coli
1399:Continuous
1224:Enterocytes
1073:Curvatures
1035:Sphincters
518:and as the
466:anastamosed
381:Hilfsmuskel
159:Identifiers
71:posteriorly
1521:Adventitia
1448:Anal canal
1212:Microvilli
568:References
524:anatomists
516:clinicians
427:anatomical
400:Embryology
325:right crus
1536:Submucosa
1526:Subserosa
1028:Esophagus
502:, as the
468:with the
452:During a
359:Variation
353:mesentery
333:esophagus
329:diaphragm
307:Structure
117:Insertion
63:depicted
1568:Category
1352:Appendix
1249:Duodenum
887:40701151
879:23076975
843:19636494
740:11858260
732:17653583
462:pancreas
415:mesoderm
391:Function
349:pancreas
315:and the
313:duodenum
293:mesoderm
251:duodenum
123:duodenum
57:duodenum
43:, shown.
37:duodenum
1438:Ampulla
1408:haustra
1287:Jejunum
1109:Pylorus
1077:greater
1066:Stomach
962:Spaces
958:Muscles
950:Pharynx
808:6971032
800:9221865
624:4381790
616:7580775
494:History
474:stomach
472:of the
470:pylorus
327:of the
317:jejunum
255:jejunum
150:Actions
79:Details
66:in situ
61:jejunum
1546:Mucosa
1517:Serosa
1425:Rectum
1104:Fundus
1094:Cardia
1082:lesser
1051:glands
986:danger
885:
877:
841:
806:
798:
761:
738:
730:
686:
656:1 July
647:
622:
614:
439:melena
247:muscle
97:Origin
85:System
1362:Colon
1344:Cecum
1303:Ileum
1183:Lower
1044:lower
1039:upper
941:Upper
933:mouth
883:S2CID
804:S2CID
736:S2CID
620:S2CID
257:(the
217:[
206:20509
165:Latin
134:Nerve
1509:Wall
1456:Anus
1099:Body
1056:crop
875:PMID
839:PMID
796:PMID
759:ISBN
728:PMID
684:ISBN
658:2010
645:ISBN
612:PMID
311:The
273:and
253:and
229:The
194:3781
177:TA98
108:and
59:and
55:The
35:The
867:doi
831:doi
788:doi
720:doi
604:doi
522:by
514:by
437:or
265:to
241:or
201:FMA
189:TA2
1570::
1519:/
881:.
873:.
863:16
861:.
837:.
827:16
825:.
802:.
794:.
784:40
782:.
734:.
726:.
716:33
714:.
698:^
666:^
618:.
610:.
600:20
598:.
576:^
237:,
141:,
125:,
920:e
913:t
906:v
889:.
869::
845:.
833::
810:.
790::
767:.
742:.
722::
692:.
660:.
626:.
606::
221:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.