338:
282:
298:
22:
127:
156:. The word "sector" is used in the geometric sense; some portion of the circumference of a circle measured in degrees of arc. 60°, 90° and 120° designs are typical, often with a few degrees 'extra' to ensure overlap and mounted in multiples when wider or full-circle coverage is required (see photos below). The largest use of these antennas is as antennas for
265:, which is determined by the projection of the radiation pattern on the ground, can be adjusted by changing the downtilt of the pattern. In some models this is done mechanically by manually adjusting the tilt of the antenna with an adjustable mounting bracket. In more recent sector antennas the pattern can be electronically tilted, by adjustable
349:
In a picture on the right, there are two sector antennas with different mechanical downtilts. Note that a more vertical antenna is less visible than a mechanically tilted one - the use of purely electrical tilt with no mechanical tilt is therefore an attractive choice for aesthetic reasons which are
345:
A well-chosen downtilt setting strategy can lower the overall interference in the network. A too-aggressive downtilting strategy will however lead to an overall loss of coverage due to cells not overlapping. Downtilting can be used to solve specific problems, for example local interference problems
180:
290:
323:, but setting a correct downtilt as well. By restricting emitted energy to a sub-circular arc and narrow vertical coverage the design makes efficient use of relatively low power transmitter equipment. Though absolute range is limited, this configuration allows for good
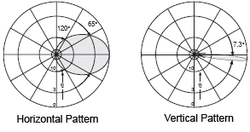
239:. This means that the signal strength at the ±33° directions is half (3 dB down) from its peak value at the center. At the ±60° directions, it is suggested to be a border of a sector and antenna gain is negligible there.
183:
Horizontal and vertical radiation patterns. The antenna radiates a horizontal fan-shaped beam, sharp in the vertical axis so it doesn't spill over into neighboring sectors.
231:, wide in the horizontal direction and relatively narrow in the vertical direction. According to the radiation patterns depicted, typical antennas used in a three-sector
327:(digital information transfer measured in bits/second, sometimes given as total minus error-correction overhead), and good signal consistency within the coverage area.
316:
antenna, though sometimes for brevity "sector antenna" is used as well. It has several angularly-separated sector antennas as shown on the figures at right.
305:
To increase or widen the coverage area, and thus the number of served clients, several sector antennas are installed on the same supporting structure, e.g.
422:
319:
Once the antenna unit is attached to a supporting structure, it has to be positioned. Positioning means not only setting a correct direction or
877:
395:
851:
669:
113:
330:
Prior to positioning, grounding and lightning protection are required. As seen in the pictures, all supporting constructions have
619:
43:
94:
47:
66:
491:
415:
73:
32:
51:
36:
882:
754:
247:
80:
749:
659:
649:
511:
458:
243:
62:
831:
769:
506:
408:
306:
486:
373:
794:
694:
566:
541:
217:
164:
179:
714:
606:
561:
139:
856:
704:
644:
639:
536:
448:
254:
or downtilt so that the base station can more effectively cover its immediate area and not cause
337:
242:
Vertical beamwidth is not wider than 15°, meaning 7.5° in each direction. Unlike antennas for
841:
734:
654:
576:
471:
228:
153:
350:
very important for operators seeking acceptance of integrated antennas in visible locations.
815:
629:
591:
556:
87:
289:
273:
circuit from the ground, eliminating the need for a technician to climb the antenna tower.
187:
A typical sector antenna is depicted in the figure on the right. At the bottom, there are
821:
784:
759:
684:
674:
531:
501:
481:
466:
431:
364:
359:
262:
255:
149:
145:
297:
281:
846:
779:
739:
614:
571:
546:
496:
270:
221:
871:
826:
719:
709:
664:
551:
385:
369:
331:
266:
192:
774:
744:
729:
724:
699:
689:
596:
581:
526:
521:
516:
200:
188:
624:
476:
390:
21:
324:
208:
171:
networks. They are used for limited-range distances of around 4 to 5 km.
157:
126:
346:
or cells that are too large. Electrical tilting slightly reduces beam width.
679:
586:
251:
236:
232:
160:
142:
836:
634:
440:
214:
enclosure to keep its operation stable regardless of weather conditions.
204:
196:
269:
in the feed of the individual dipole elements. These are adjusted by a
320:
810:
211:
199:), and adjustment mechanisms. For its outdoor placement, the main
789:
336:
296:
288:
280:
178:
168:
125:
386:
Deploying
License-Free Wireless Wide-Area Networks by Cisco Press
400:
220:
is very important for an outdoor antenna so all metal parts are
404:
15:
396:
P-CPICH Power and
Antenna Tilt Optimization in UMTS networks
301:
Sector antennas are often installed on existing structures.
250:
over many miles or kilometers, there is usually a downward
246:- AM, FM and television for example - which must achieve
293:
Top of cellular base station tower with sector antennas
227:
The antenna's long narrow form gives it a fan-shaped
803:
605:
457:
439:
341:
An antenna at bottom has bigger mechanical downtilt
416:
8:
207:, and all internal parts are housed into a
50:. Unsourced material may be challenged and
423:
409:
401:
285:Sector antennas installed on a short mast
163:. They are also used for other types of
114:Learn how and when to remove this message
130:Typical GSM sector antenna outdoor unit
312:Such a construction is often called a
391:Antenna Tilt Control in CDMA Networks
7:
48:adding citations to reliable sources
14:
852:Circularly disposed antenna array
670:Folded inverted conformal antenna
20:
1:
878:Radio frequency antenna types
492:Dielectric resonator antenna
899:
755:Regenerative loop antenna
372:, a similar type used in
750:Reflective array antenna
660:Corner reflector antenna
650:Collinear antenna array
244:commercial broadcasting
235:have 66° of horizontal
832:Reconfigurable antenna
795:Yagi–Uda antenna
770:Short backfire antenna
507:Folded unipole antenna
342:
302:
294:
286:
184:
131:
487:Crossed field antenna
374:broadcast engineering
340:
300:
292:
284:
182:
165:mobile communications
129:
804:Application-specific
695:Log-periodic antenna
567:Rubber ducky antenna
542:Inverted vee antenna
517:Ground-plane antenna
44:improve this article
715:Offset dish antenna
562:Random wire antenna
857:Television antenna
705:Microstrip antenna
645:Choke ring antenna
640:Cassegrain antenna
537:Inverted-F antenna
449:Isotropic radiator
343:
303:
295:
287:
258:to distant cells.
185:
161:base-station sites
132:
865:
864:
842:Reference antenna
735:Parabolic antenna
655:Conformal antenna
577:Turnstile antenna
472:Biconical antenna
229:radiation pattern
203:is produced from
167:, for example in
154:radiation pattern
124:
123:
116:
98:
890:
883:Antennas (radio)
816:Corner reflector
630:Beverage antenna
592:Umbrella antenna
557:Monopole antenna
512:Franklin antenna
425:
418:
411:
402:
201:reflector screen
119:
112:
108:
105:
99:
97:
63:"Sector antenna"
56:
24:
16:
898:
897:
893:
892:
891:
889:
888:
887:
868:
867:
866:
861:
822:Evolved antenna
799:
785:Vivaldi antenna
760:Rhombic antenna
685:Helical antenna
675:Fractal antenna
620:AS-2259 Antenna
601:
532:Helical antenna
502:Discone antenna
482:Coaxial antenna
467:Batwing antenna
459:Omnidirectional
453:
435:
429:
382:
365:Radio frequency
356:
279:
256:RF interference
177:
120:
109:
103:
100:
57:
55:
41:
25:
12:
11:
5:
896:
894:
886:
885:
880:
870:
869:
863:
862:
860:
859:
854:
849:
847:Spiral antenna
844:
839:
834:
829:
824:
819:
813:
807:
805:
801:
800:
798:
797:
792:
787:
782:
780:Sterba antenna
777:
772:
767:
765:Sector antenna
762:
757:
752:
747:
742:
740:Plasma antenna
737:
732:
727:
722:
717:
712:
707:
702:
697:
692:
687:
682:
677:
672:
667:
662:
657:
652:
647:
642:
637:
632:
627:
622:
617:
615:Adcock antenna
611:
609:
603:
602:
600:
599:
594:
589:
584:
579:
574:
572:Sloper antenna
569:
564:
559:
554:
549:
547:J-pole antenna
544:
539:
534:
529:
524:
519:
514:
509:
504:
499:
497:Dipole antenna
494:
489:
484:
479:
474:
469:
463:
461:
455:
454:
452:
451:
445:
443:
437:
436:
430:
428:
427:
420:
413:
405:
399:
398:
393:
388:
381:
380:External links
378:
377:
376:
367:
362:
355:
352:
332:lightning rods
278:
275:
271:remote control
267:phase shifters
176:
173:
136:sector antenna
122:
121:
28:
26:
19:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
895:
884:
881:
879:
876:
875:
873:
858:
855:
853:
850:
848:
845:
843:
840:
838:
835:
833:
830:
828:
827:Ground dipole
825:
823:
820:
817:
814:
812:
809:
808:
806:
802:
796:
793:
791:
788:
786:
783:
781:
778:
776:
773:
771:
768:
766:
763:
761:
758:
756:
753:
751:
748:
746:
743:
741:
738:
736:
733:
731:
728:
726:
723:
721:
720:Patch antenna
718:
716:
713:
711:
710:Moxon antenna
708:
706:
703:
701:
698:
696:
693:
691:
688:
686:
683:
681:
678:
676:
673:
671:
668:
666:
665:Curtain array
663:
661:
658:
656:
653:
651:
648:
646:
643:
641:
638:
636:
633:
631:
628:
626:
623:
621:
618:
616:
613:
612:
610:
608:
604:
598:
595:
593:
590:
588:
585:
583:
580:
578:
575:
573:
570:
568:
565:
563:
560:
558:
555:
553:
552:Mast radiator
550:
548:
545:
543:
540:
538:
535:
533:
530:
528:
525:
523:
520:
518:
515:
513:
510:
508:
505:
503:
500:
498:
495:
493:
490:
488:
485:
483:
480:
478:
475:
473:
470:
468:
465:
464:
462:
460:
456:
450:
447:
446:
444:
442:
438:
433:
426:
421:
419:
414:
412:
407:
406:
403:
397:
394:
392:
389:
387:
384:
383:
379:
375:
371:
370:panel antenna
368:
366:
363:
361:
358:
357:
353:
351:
347:
339:
335:
333:
328:
326:
322:
317:
315:
310:
308:
307:tower or mast
299:
291:
283:
276:
274:
272:
268:
264:
263:coverage area
259:
257:
253:
249:
248:line-of-sight
245:
240:
238:
234:
230:
225:
223:
219:
215:
213:
210:
206:
202:
198:
194:
193:coaxial cable
190:
189:RF connectors
181:
174:
172:
170:
166:
162:
159:
155:
151:
147:
144:
141:
138:is a type of
137:
128:
118:
115:
107:
104:February 2013
96:
93:
89:
86:
82:
79:
75:
72:
68:
65: –
64:
60:
59:Find sources:
53:
49:
45:
39:
38:
34:
29:This article
27:
23:
18:
17:
775:Slot antenna
764:
745:Quad antenna
730:Planar array
725:Phased array
700:Loop antenna
690:Horn antenna
597:Whip antenna
582:T2FD antenna
527:Halo antenna
522:G5RV antenna
348:
344:
329:
318:
313:
311:
304:
260:
241:
233:base station
226:
216:
186:
135:
133:
110:
101:
91:
84:
77:
70:
58:
42:Please help
30:
625:AWX antenna
607:Directional
477:Cage aerial
224:-grounded.
140:directional
872:Categories
325:data rates
314:sectorized
209:fiberglass
158:cell phone
74:newspapers
818:(passive)
680:Gizmotchy
587:T-antenna
441:Isotropic
252:beam tilt
237:beamwidth
218:Grounding
143:microwave
31:does not
837:Rectenna
635:Cantenna
354:See also
205:aluminum
197:feedline
152:-shaped
432:Antenna
360:Antenna
321:azimuth
148:with a
146:antenna
88:scholar
52:removed
37:sources
811:ALLISS
212:radome
175:Design
150:sector
90:
83:
76:
69:
61:
790:WokFi
434:types
169:Wi-Fi
95:JSTOR
81:books
261:The
191:for
67:news
35:any
33:cite
277:Use
46:by
874::
334:.
309:.
222:DC
134:A
424:e
417:t
410:v
195:(
117:)
111:(
106:)
102:(
92:·
85:·
78:·
71:·
54:.
40:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.