157:(EGF)-like domain, a variable number of consensus repeat units (2, 6, and 9 for L-, E-, and P-selectin, respectively), a transmembrane domain (TM) and an intracellular cytoplasmic tail (cyto). The transmembrane and cytoplasmic parts are not conserved across the selectins being responsible for their targeting to different compartments. Though they share common elements, their tissue distribution and binding kinetics are quite different, reflecting their divergent roles in various pathophysiological processes.
338:
In fact, the extravasation of circulating tumor cells in the host organ requires successive adhesive interactions between endothelial cells and their ligands or counter-receptors present on the cancer cells. Metastatic cells that show a high propensity to metastasize to certain organs adhere at higher rates to venular endothelial cells isolated from these target sites. Moreover, they invade the target tissue at higher rates and respond better to paracrine growth factors released from the target site.
210:
similar sugar structures. The cytoplasmic and transmembrane domains are highly conserved between species, but not conserved across the selectins. These parts of the selectin molecules are responsible for their targeting to different compartments: P-selectin to secretory granules, E-selectin to the plasma membrane, and L-selectin to the tips of microfolds on leukocytes.
40:
354:
their adhesion and extravasation into a specific organ. The differential selectin expression profile on endothelium and the specific interactions of selectins expressed by endothelial cells of potential target organs and their ligands expressed on cancer cells are major determinants that underlie the organ-specific distribution of metastases.
316:
affinities are still reduced because the selectin-ligand bond is still a normal slip bond. It is thought that this shear stress threshold helps select for the right diameter of blood vessels to initiate leukocyte extravasation, and may also help prevent inappropriate leukocyte aggregation during vascular stasis.
350:
release by themselves cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β or INF-γ that will directly activate endothelial cells to express E-selectin, P-selectin, ICAM-2 or VCAM. On the other hand, several studies further show that cancer cells may initiate the expression of endothelial adhesion molecules in a more indirect ways.
337:
The selectins and selectin ligands determine the organ selectivity of metastasis. Several factors may explain the seed and soil theory or homing of metastasis. In particular, genetic regulation and activation of specific chemokines, cytokines and proteases may direct metastasis to a preferred organ.
311:
In leukocyte rolling, the ‘open’ conformation of the selectin allows it to bind to inward sialyl Lewis molecules farther up along the PSGL-1 chain, increasing overall binding affinity—if the selectin-sialyl Lewis bond breaks, it can slide and form new bonds with the other sialyl Lewis molecules down
209:
These three types share a significant degree of sequence homology among themselves (except in the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains) and between species. Analysis of this homology has revealed that the lectin domain, which binds sugars, is most conserved, suggesting that the three selectins bind
341:
Typically, the cancer cell/endothelial cell interactions imply first a selectin-mediated initial attachment and rolling of the circulating cancer cells on the endothelium. The rolling cancer cells then become activated by locally released chemokines present at the surface of endothelial cells. This
353:
Since the adhesion of several cancer cells to endothelium requires the presence of endothelial selectins as well as sialyl Lewis carbohydrates on cancer cells, the degree of expression of selectins on the vascular wall and the presence of the appropriate ligand on cancer cells are determinant for
328:
A number of studies have shown increased expression of carbohydrate ligands on metastatic tumor, enhanced E-selectin expression on the surface of endothelial vessels at the site at tumor metastasis, and the capacity of metastatic tumor cells to roll and adhere to endothelial cells, indicating the
349:
The appropriate set of endothelial receptors is sometimes not expressed constitutively and the cancer cells have to trigger their expression. In this context, the culture supernatants of cancer cells can trigger the expression of E- selectin by endothelial cells suggesting that cancer cells may
324:
It is becoming evident that selectin may play a role in inflammation and progression of cancer. Tumor cells exploit the selectin-dependent mechanisms mediating cell tethering and rolling interactions through recognition of carbohydrate ligands on tumor cell to enhance distant organ metastasis,
295:
Ligands for P-selectin on eosinophils and neutrophils are similar sialylated, protease-sensitive, endo-beta-galactosidase-resistant structures, clearly different from those reported for E-selectin, and suggest disparate roles for P-selectin and E-selectin during recruitment during inflammatory
291:
Neutrophils and eosinophils bind to E-selectin. One of the reported ligands for E-selectin is the sialylated Lewis X antigen (SLe). Eosinophils, like neutrophils, use sialylated, protease-resistant structures to bind to E-selectin, although the eosinophil expresses much lower levels of these
315:
The result of such is that selectins exhibit catch and slip bond behavior—under low shear stresses, their bonding affinities are actually increased by an increase in tensile force applied to the bond because of more selectins preferring the ‘open’ conformation. At high stresses, the binding
280:
Selectins bind to the sialyl Lewis X (SLe) determinant “NeuAcα2-3Galβ1-4(Fucα1-3)GlcNAc.” However, SLe, per se, does not constitute an effective selectin receptor. Instead, SLe and related sialylated, fucosylated glycans are components of more extensive binding determinants.
329:
role of selectins in metastasis. In addition to E-selectin, the role of P-selectin (expressed on platelets) and L-selectin (on leukocytes) in cancer dissemination has been suggested in the way that they interact with circulating cancer cells at an early stage of metastasis.
230:
Selectins are involved in constitutive lymphocyte homing, and in chronic and acute inflammation processes, including post-ischemic inflammation in muscle, kidney and heart, skin inflammation, atherosclerosis, glomerulonephritis and lupus erythematosus and cancer metastasis.
276:
Each selectin has a carbohydrate recognition domain that mediates binding to specific glycans on apposing cells. They have remarkably similar protein folds and carbohydrate binding residues, leading to overlap in the glycans to which they bind.
205:
of endothelial cells, and is translocated to the cell surface of activated endothelial cells and platelets. E-selectin is not expressed under baseline conditions, except in skin microvessels, but is rapidly induced by inflammatory cytokines.
269:) on the leukocyte, which slows the cell and allows it to leave the blood vessel and enter the site of infection. The low-affinity nature of selectins is what allows the characteristic "rolling" action attributed to leukocytes during the
200:
L-selectin is the smallest of the vascular selectins, expressed on all granulocytes and monocytes and on most lymphocytes, can be found in most leukocytes. P-selectin, the largest selectin, is stored in α-granules of platelets and in
822:
Wein M, Sterbinsky SA, Bickel CA, Schleimer RP, Bochner BS (March 1995). "Comparison of human eosinophil and neutrophil ligands for P-selectin: ligands for P-selectin differ from those for E-selectin".
1087:
Nakamori S, Kameyama M, Imaoka S, Furukawa H, Ishikawa O, Sasaki Y, Izumi Y, Irimura T (April 1997). "Involvement of carbohydrate antigen sialyl Lewis(x) in colorectal cancer metastasis".
1130:
Matsuura N, Narita T, Mitsuoka C, Kimura N, Kannagi R, Imai T, Funahashi H, Takagi H (1997). "Increased concentration of soluble E-selectin in the sera of breast cancer patients".
346:
from the cancer cells allowing their firmer adhesion to members of the Ig-CAM family such as ICAM, initiating the transendothelial migration and extravasation processes.
1640:
1159:"Death receptor-3, a new E-Selectin counter-receptor that confers migration and survival advantages to colon carcinoma cells by triggering p38 and ERK MAPK activation"
724:
Nimrichter L, Burdick MM, Aoki K, Laroy W, Fierro MA, Hudson SA, Von
Seggern CE, Cotter RJ, Bochner BS, Tiemeyer M, Konstantopoulos K, Schnaar RL (November 2008).
312:
the chain. In the ‘closed’ conformation, however, the selectin is only able to bind to one sialyl Lewis molecule, and thus has greatly reduced binding affinity.
153:
All three known members of the selectin family (L-, E-, and P-selectin) share a similar cassette structure: an N-terminal, calcium-dependent lectin domain, an
1200:"Synergistic effects of L- and P-selectin in facilitating tumor metastasis can involve non-mucin ligands and implicate leukocytes as enhancers of metastasis"
2199:
304:
Selectins have hinge domains, allowing them to undergo rapid conformational changes in the nanosecond range between ‘open’ and ‘closed’ conformations.
589:
Cheung LS, Raman PS, Balzer EM, Wirtz D, Konstantopoulos K (February 2011). "Biophysics of selectin-ligand interactions in inflammation and cancer".
1789:
382:
to the bone marrow. E-selectins are constitutively expressed in the bone marrow, and researchers have shown that tagging stem cells with a certain
775:"Differences between human eosinophils and neutrophils in the function and expression of sialic acid-containing counterligands for E-selectin"
1633:
1063:
521:
488:
429:"Insights into the molecular basis of leukocyte tethering and rolling revealed by structures of P- and E-selectin bound to SLe(X) and PSGL-1"
386:
causes these cells to migrate to the bone marrow. Thus, selectins may someday be essential to a regenerative therapy for osteoporosis.
2158:
1352:
708:
1626:
2179:
1688:
258:
stimulate transcription and translation of E-selectin and additional P-selectin, which account for the delay of several hours.
1472:
1678:
1538:
265:
wall, the distal lectin-like domain of the selectin binds to certain carbohydrate groups presented on proteins (such as
1388:
2106:
270:
104:
1416:
362:
Selectins are involved in projects to treat osteoporosis, a disease that occurs when bone-creating cells called
2194:
2138:
154:
247:
202:
1868:
1661:
1653:
553:
118:
642:"The Interaction of Selectins and PSGL-1 as a Key Component in Thrombus Formation and Cancer Progression"
1845:
1403:
1345:
44:
1259:"Progressive loss of endothelial P-selectin expression with increasing malignancy in colorectal cancer"
1048:
Tumor-microenvironment interactions: the selectin-selectin ligand axis in tumor-endothelium cross talk
1817:
1803:
1211:
598:
558:
238:, P-selectin is expressed on endothelial cells first, followed by E-selectin later. Stimuli such as
1682:
1590:
85:
2189:
1112:
804:
622:
458:
134:
1326:
Computer-generated movie of the mobilization of P-selectin inside a leukocyte at mcb.harvard.edu
1280:
1239:
1180:
1139:
1104:
1069:
1059:
1028:
987:
938:
889:
840:
796:
755:
704:
673:
614:
571:
517:
484:
450:
417:
1618:
378:. Researchers have developed a way to use selectins to direct stem cells introduced into the
2184:
1983:
1649:
1595:
1410:
1338:
1270:
1229:
1219:
1170:
1096:
1051:
1018:
977:
969:
928:
920:
879:
871:
832:
786:
745:
737:
696:
663:
653:
606:
563:
440:
183:
284:
The best-characterized ligand for the three selectins is P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 (
513:
506:
379:
1215:
602:
1585:
982:
957:
933:
908:
884:
859:
750:
725:
668:
641:
610:
130:
1234:
1199:
691:
Jennette, J. Charles; Falk, Ronald J. (2008). "Immunologic
Mechanisms of Vasculitis".
567:
445:
428:
2173:
1965:
1602:
1380:
700:
126:
114:
1116:
808:
462:
1936:
1932:
1928:
1924:
1717:
1528:
1457:
626:
395:
383:
371:
305:
262:
246:
cause endothelial cells to mobilize immediate release of preformed P-selectin from
235:
122:
1175:
1158:
1007:"Interactions between endothelial selectins and cancer cells regulate metastasis"
773:
Bochner BS, Sterbinsky SA, Bickel CA, Werfel S, Wein M, Newman W (January 1994).
741:
90:
78:
2009:
1942:
1902:
1892:
973:
836:
375:
363:
173:
1204:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
791:
774:
2115:
2086:
2081:
2076:
1999:
1920:
1563:
1275:
1258:
367:
189:
179:
169:
48:
1912:
1712:
1398:
1055:
343:
255:
251:
239:
193:
1284:
1243:
1224:
1184:
1073:
1032:
991:
942:
893:
759:
677:
658:
618:
575:
454:
1143:
1108:
924:
875:
844:
800:
288:), which is a mucin-type glycoprotein expressed on all white blood cells.
2121:
1877:
1781:
1670:
1533:
1523:
1507:
1502:
1437:
1432:
1427:
1422:
243:
142:
73:
17:
544:
Ley K (June 2003). "The role of selectins in inflammation and disease".
1580:
1497:
1492:
1487:
1482:
1477:
1361:
1320:
1306:
1100:
219:
1263:
Laboratory
Investigation; A Journal of Technical Methods and Pathology
907:
Yago T, Wu J, Wey CD, Klopocki AG, Zhu C, McEver RP (September 2004).
421:
39:
1978:
1849:
1739:
1702:
1692:
1607:
1449:
1365:
958:"Targeting selectins and selectin ligands in inflammation and cancer"
308:
on the selectin molecule causes it to favor the ‘open’ conformation.
285:
266:
138:
51:
1325:
1330:
909:"Catch bonds govern adhesion through L-selectin at threshold shear"
2153:
2130:
2126:
2054:
2044:
2039:
2034:
2029:
2024:
1973:
1853:
1835:
1831:
1821:
1807:
1793:
1769:
1764:
1759:
1754:
1749:
1744:
1727:
1722:
1696:
1573:
1568:
1393:
1050:. Cancer Treatment and Research. Vol. 130. pp. 125–40.
1023:
1006:
956:
Barthel SR, Gavino JD, Descheny L, Dimitroff CJ (November 2007).
2148:
2143:
2110:
2049:
2019:
2014:
2004:
1954:
1950:
1946:
1897:
1839:
1825:
1811:
1797:
1732:
1707:
1467:
1462:
1622:
1334:
1257:
Peeters CF, Ruers TJ, Westphal JR, de Waal RM (February 2005).
1198:
Borsig L, Wong R, Hynes RO, Varki NM, Varki A (February 2002).
860:"For catch bonds, it all hinges on the interdomain region"
825:
American
Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology
427:
Somers WS, Tang J, Shaw GD, Camphausen RT (October 2000).
222:," which are a type of carbohydrate-recognizing protein.
133:
and calcium-dependent binding. Selectins bind to sugar
1046:
218:
The name selectin comes from the words "selected" and "
370:, and scientists hope to eventually be able to treat
512:(2nd ed.). New York: Garland Science. pp.
2099:
2067:
1992:
1964:
1911:
1885:
1876:
1867:
1780:
1669:
1660:
1556:
1516:
1448:
1379:
1372:
1157:Gout S, Morin C, Houle F, Huot J (September 2006).
84:
72:
64:
59:
32:
505:
1297:In the lab of Robert Sackstein Harvard University
121:). All selectins are single-chain transmembrane
1634:
1346:
412:
410:
366:become too scarce. Osteoblasts develop from
8:
1882:
1873:
1666:
1641:
1627:
1619:
1376:
1353:
1339:
1331:
726:"E-selectin receptors on human leukocytes"
539:
537:
535:
533:
474:
472:
1274:
1233:
1223:
1174:
1022:
981:
932:
883:
790:
749:
667:
657:
557:
444:
141:, cell adhesion proteins that bind sugar
406:
165:There are three subsets of selectins:
483:. Philadelphia: W.B Saunders Company.
137:and so are considered to be a type of
29:
962:Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets
7:
374:by adding stem cells to a patient’s
481:Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease
2200:Single-pass transmembrane proteins
25:
261:As the leukocyte rolls along the
125:that share similar properties to
27:Family of cell adhesion molecules
1089:Diseases of the Colon and Rectum
701:10.1016/B978-012088488-9.50085-1
693:Seldin and Giebisch's the Kidney
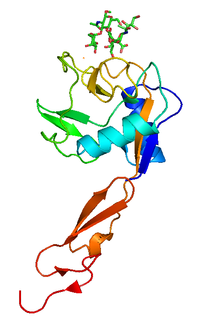
54:bound to sugar, shown in sticks.
38:
479:Cotran; Kumar, Collins (1998).
1473:Myelin-associated glycoprotein
640:Kappelmayer J, Nagy B (2017).
1:
1176:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4605
646:BioMed Research International
568:10.1016/S1471-4914(03)00071-6
446:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00138-0
325:showing ‘leukocyte mimicry’.
1539:N-Acetylglucosamine receptor
742:10.1182/blood-2008-04-149641
611:10.1088/1478-3975/8/1/015013
546:Trends in Molecular Medicine
1389:Asialoglycoprotein receptor
974:10.1517/14728222.11.11.1473
913:The Journal of Cell Biology
864:The Journal of Cell Biology
858:Thomas W (September 2006).
837:10.1165/ajrcmb.12.3.7532979
342:triggers the activation of
292:structures on its surface.
2216:
2107:Lymphocyte homing receptor
792:10.4049/jimmunol.152.2.774
271:leukocyte adhesion cascade
105:cluster of differentiation
45:Crystallographic structure
1417:proteochondroitin sulfate
1321:Sackstein Lab of Research
1276:10.1038/labinvest.3700217
37:
2139:Carcinoembryonic antigen
1993:Unconventional/ungrouped
1005:St Hill CA (June 2011).
1654:cell adhesion molecules
1056:10.1007/0-387-26283-0_6
1011:Frontiers in Bioscience
155:epidermal growth factor
2180:Cell adhesion proteins
1225:10.1073/pnas.261704098
695:. pp. 2315–2338.
504:Parham, Peter (2005).
196:and endothelial cells)
1846:Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa
1404:Mannan-binding lectin
925:10.1083/jcb.200403144
876:10.1083/jcb.200609029
779:Journal of Immunology
236:inflammatory response
1818:Macrophage-1 antigen
1804:Integrin alphaXbeta2
659:10.1155/2017/6138145
248:Weible-Palade bodies
203:Weibel–Palade bodies
1683:Myelin protein zero
1662:Calcium-independent
1591:Phytohaemagglutinin
1216:2002PNAS...99.2193B
1132:Anticancer Research
603:2011PhBio...8a5013S
1101:10.1007/BF02258386
300:Bonding mechanisms
113:) are a family of
2167:
2166:
2095:
2094:
2063:
2062:
1869:Calcium-dependent
1863:
1862:
1650:Membrane proteins
1616:
1615:
1552:
1551:
1065:978-0-387-26282-6
523:978-0-8153-4093-5
508:The immune system
490:978-0-7216-7335-6
333:Organ selectivity
250:inside the cell.
129:due to a related
96:
95:
16:(Redirected from
2207:
1883:
1874:
1667:
1643:
1636:
1629:
1620:
1596:Pokeweed mitogen
1411:Mannose receptor
1377:
1355:
1348:
1341:
1332:
1309:
1304:
1298:
1295:
1289:
1288:
1278:
1254:
1248:
1247:
1237:
1227:
1195:
1189:
1188:
1178:
1154:
1148:
1147:
1127:
1121:
1120:
1084:
1078:
1077:
1043:
1037:
1036:
1026:
1002:
996:
995:
985:
953:
947:
946:
936:
904:
898:
897:
887:
855:
849:
848:
819:
813:
812:
794:
770:
764:
763:
753:
721:
715:
714:
688:
682:
681:
671:
661:
637:
631:
630:
591:Physical Biology
586:
580:
579:
561:
541:
528:
527:
511:
501:
495:
494:
476:
467:
466:
448:
424:
414:
42:
30:
21:
2215:
2214:
2210:
2209:
2208:
2206:
2205:
2204:
2195:Protein domains
2170:
2169:
2168:
2163:
2091:
2059:
1988:
1960:
1907:
1859:
1776:
1656:
1647:
1617:
1612:
1548:
1512:
1444:
1368:
1359:
1317:
1312:
1305:
1301:
1296:
1292:
1256:
1255:
1251:
1197:
1196:
1192:
1169:(18): 9117–24.
1163:Cancer Research
1156:
1155:
1151:
1138:(2B): 1367–72.
1129:
1128:
1124:
1086:
1085:
1081:
1066:
1045:
1044:
1040:
1004:
1003:
999:
968:(11): 1473–91.
955:
954:
950:
906:
905:
901:
857:
856:
852:
821:
820:
816:
772:
771:
767:
723:
722:
718:
711:
690:
689:
685:
639:
638:
634:
588:
587:
583:
559:10.1.1.407.6232
543:
542:
531:
524:
503:
502:
498:
491:
478:
477:
470:
426:
416:
415:
408:
404:
392:
380:vascular system
360:
335:
322:
302:
228:
216:
163:
151:
55:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2213:
2211:
2203:
2202:
2197:
2192:
2187:
2182:
2172:
2171:
2165:
2164:
2162:
2161:
2156:
2151:
2146:
2141:
2135:
2134:
2118:
2113:
2103:
2101:
2097:
2096:
2093:
2092:
2090:
2089:
2084:
2079:
2073:
2071:
2065:
2064:
2061:
2060:
2058:
2057:
2052:
2047:
2042:
2037:
2032:
2027:
2022:
2017:
2012:
2007:
2002:
1996:
1994:
1990:
1989:
1987:
1986:
1981:
1976:
1970:
1968:
1962:
1961:
1959:
1958:
1940:
1917:
1915:
1909:
1908:
1906:
1905:
1900:
1895:
1889:
1887:
1880:
1871:
1865:
1864:
1861:
1860:
1858:
1857:
1843:
1829:
1815:
1801:
1786:
1784:
1778:
1777:
1775:
1774:
1773:
1772:
1767:
1762:
1757:
1752:
1747:
1737:
1736:
1735:
1730:
1725:
1720:
1710:
1705:
1700:
1686:
1675:
1673:
1664:
1658:
1657:
1648:
1646:
1645:
1638:
1631:
1623:
1614:
1613:
1611:
1610:
1605:
1600:
1599:
1598:
1593:
1588:
1586:Concanavalin A
1578:
1577:
1576:
1571:
1560:
1558:
1554:
1553:
1550:
1549:
1547:
1546:
1541:
1536:
1531:
1526:
1520:
1518:
1514:
1513:
1511:
1510:
1505:
1500:
1495:
1490:
1485:
1480:
1475:
1470:
1465:
1460:
1454:
1452:
1446:
1445:
1443:
1442:
1441:
1440:
1435:
1430:
1425:
1413:
1408:
1407:
1406:
1396:
1391:
1385:
1383:
1381:C-type lectins
1374:
1370:
1369:
1360:
1358:
1357:
1350:
1343:
1335:
1329:
1328:
1323:
1316:
1315:External links
1313:
1311:
1310:
1299:
1290:
1249:
1190:
1149:
1122:
1079:
1064:
1038:
1017:(9): 3233–51.
997:
948:
899:
850:
814:
765:
736:(9): 3744–52.
716:
709:
683:
632:
581:
529:
522:
496:
489:
468:
405:
403:
400:
399:
398:
391:
388:
359:
356:
334:
331:
321:
320:Role in cancer
318:
301:
298:
227:
224:
215:
212:
198:
197:
187:
177:
162:
159:
150:
147:
131:amino terminus
127:C-type lectins
117:molecules (or
94:
93:
88:
82:
81:
76:
70:
69:
66:
62:
61:
57:
56:
43:
35:
34:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2212:
2201:
2198:
2196:
2193:
2191:
2188:
2186:
2183:
2181:
2178:
2177:
2175:
2160:
2157:
2155:
2152:
2150:
2147:
2145:
2142:
2140:
2137:
2136:
2132:
2128:
2124:
2123:
2119:
2117:
2114:
2112:
2108:
2105:
2104:
2102:
2098:
2088:
2085:
2083:
2080:
2078:
2075:
2074:
2072:
2070:
2066:
2056:
2053:
2051:
2048:
2046:
2043:
2041:
2038:
2036:
2033:
2031:
2028:
2026:
2023:
2021:
2018:
2016:
2013:
2011:
2008:
2006:
2003:
2001:
1998:
1997:
1995:
1991:
1985:
1982:
1980:
1977:
1975:
1972:
1971:
1969:
1967:
1966:Protocadherin
1963:
1956:
1952:
1948:
1944:
1941:
1938:
1934:
1930:
1926:
1922:
1919:
1918:
1916:
1914:
1910:
1904:
1901:
1899:
1896:
1894:
1891:
1890:
1888:
1884:
1881:
1879:
1875:
1872:
1870:
1866:
1855:
1851:
1847:
1844:
1841:
1837:
1833:
1830:
1827:
1823:
1819:
1816:
1813:
1809:
1805:
1802:
1799:
1795:
1791:
1788:
1787:
1785:
1783:
1779:
1771:
1768:
1766:
1763:
1761:
1758:
1756:
1753:
1751:
1748:
1746:
1743:
1742:
1741:
1738:
1734:
1731:
1729:
1726:
1724:
1721:
1719:
1716:
1715:
1714:
1711:
1709:
1706:
1704:
1701:
1698:
1694:
1690:
1687:
1684:
1680:
1677:
1676:
1674:
1672:
1668:
1665:
1663:
1659:
1655:
1651:
1644:
1639:
1637:
1632:
1630:
1625:
1624:
1621:
1609:
1606:
1604:
1603:Legume lectin
1601:
1597:
1594:
1592:
1589:
1587:
1584:
1583:
1582:
1579:
1575:
1572:
1570:
1567:
1566:
1565:
1562:
1561:
1559:
1555:
1545:
1542:
1540:
1537:
1535:
1532:
1530:
1527:
1525:
1522:
1521:
1519:
1515:
1509:
1506:
1504:
1501:
1499:
1496:
1494:
1491:
1489:
1486:
1484:
1481:
1479:
1476:
1474:
1471:
1469:
1466:
1464:
1461:
1459:
1456:
1455:
1453:
1451:
1447:
1439:
1436:
1434:
1431:
1429:
1426:
1424:
1421:
1420:
1419:
1418:
1414:
1412:
1409:
1405:
1402:
1401:
1400:
1397:
1395:
1392:
1390:
1387:
1386:
1384:
1382:
1378:
1375:
1371:
1367:
1363:
1356:
1351:
1349:
1344:
1342:
1337:
1336:
1333:
1327:
1324:
1322:
1319:
1318:
1314:
1308:
1307:Sackstein Lab
1303:
1300:
1294:
1291:
1286:
1282:
1277:
1272:
1269:(2): 248–56.
1268:
1264:
1260:
1253:
1250:
1245:
1241:
1236:
1231:
1226:
1221:
1217:
1213:
1210:(4): 2193–8.
1209:
1205:
1201:
1194:
1191:
1186:
1182:
1177:
1172:
1168:
1164:
1160:
1153:
1150:
1145:
1141:
1137:
1133:
1126:
1123:
1118:
1114:
1110:
1106:
1102:
1098:
1095:(4): 420–31.
1094:
1090:
1083:
1080:
1075:
1071:
1067:
1061:
1057:
1053:
1049:
1042:
1039:
1034:
1030:
1025:
1020:
1016:
1012:
1008:
1001:
998:
993:
989:
984:
979:
975:
971:
967:
963:
959:
952:
949:
944:
940:
935:
930:
926:
922:
919:(6): 913–23.
918:
914:
910:
903:
900:
895:
891:
886:
881:
877:
873:
869:
865:
861:
854:
851:
846:
842:
838:
834:
830:
826:
818:
815:
810:
806:
802:
798:
793:
788:
785:(2): 774–82.
784:
780:
776:
769:
766:
761:
757:
752:
747:
743:
739:
735:
731:
727:
720:
717:
712:
710:9780120884889
706:
702:
698:
694:
687:
684:
679:
675:
670:
665:
660:
655:
651:
647:
643:
636:
633:
628:
624:
620:
616:
612:
608:
604:
600:
597:(1): 015013.
596:
592:
585:
582:
577:
573:
569:
565:
560:
555:
551:
547:
540:
538:
536:
534:
530:
525:
519:
515:
510:
509:
500:
497:
492:
486:
482:
475:
473:
469:
464:
460:
456:
452:
447:
442:
439:(3): 467–79.
438:
434:
430:
423:
419:
413:
411:
407:
401:
397:
394:
393:
389:
387:
385:
381:
377:
373:
369:
365:
357:
355:
351:
347:
345:
339:
332:
330:
326:
319:
317:
313:
309:
307:
299:
297:
293:
289:
287:
282:
278:
274:
272:
268:
264:
259:
257:
253:
249:
245:
241:
237:
232:
225:
223:
221:
213:
211:
207:
204:
195:
191:
188:
185:
181:
178:
175:
171:
168:
167:
166:
160:
158:
156:
148:
146:
144:
140:
136:
132:
128:
124:
123:glycoproteins
120:
116:
115:cell adhesion
112:
108:
106:
101:
92:
89:
87:
83:
80:
77:
75:
71:
67:
63:
58:
53:
50:
46:
41:
36:
31:
19:
2120:
2068:
1543:
1529:Calreticulin
1458:Sialoadhesin
1415:
1302:
1293:
1266:
1262:
1252:
1207:
1203:
1193:
1166:
1162:
1152:
1135:
1131:
1125:
1092:
1088:
1082:
1047:
1041:
1024:10.2741/3909
1014:
1010:
1000:
965:
961:
951:
916:
912:
902:
870:(7): 911–3.
867:
863:
853:
831:(3): 315–9.
828:
824:
817:
782:
778:
768:
733:
729:
719:
692:
686:
649:
645:
635:
594:
590:
584:
552:(6): 263–8.
549:
545:
507:
499:
480:
436:
432:
396:Sushi domain
384:glycoprotein
372:osteoporosis
361:
352:
348:
340:
336:
327:
323:
314:
310:
306:Shear stress
303:
294:
290:
283:
279:
275:
263:blood vessel
260:
233:
229:
217:
208:
199:
164:
152:
110:
103:
99:
97:
1943:Desmocollin
1564:Toxalbumins
652:: 6138145.
376:bone marrow
364:osteoblasts
296:responses.
174:endothelial
60:Identifiers
2174:Categories
2116:L-selectin
2087:P-selectin
2082:L-selectin
2077:E-selectin
2000:T-cadherin
1921:Desmoglein
1913:Desmosomal
402:References
368:stem cells
234:During an
190:P-selectin
184:leukocytes
180:L-selectin
170:E-selectin
86:Membranome
49:P-selectin
2190:Selectins
2069:Selectins
1886:Classical
1878:Cadherins
1782:Integrins
1713:L1 family
1399:Collectin
554:CiteSeerX
425:;
344:integrins
256:TNF-alpha
252:Cytokines
240:histamine
214:Etymology
194:platelets
149:Structure
100:selectins
79:IPR002396
18:Selectins
2122:integrin
1671:IgSF CAM
1581:Mitogens
1544:Selectin
1534:Galectin
1524:Calnexin
1508:SIGLEC12
1503:SIGLEC10
1438:Neurocan
1433:Brevican
1428:Versican
1423:Aggrecan
1285:15640834
1244:11854515
1185:16982754
1117:24770173
1074:16610706
1033:21622232
992:18028011
943:15364963
894:17000873
809:45677380
760:18579791
678:28680883
619:21301059
576:12829015
463:12719907
455:11081633
390:See also
358:Research
254:such as
244:thrombin
226:Function
143:polymers
135:moieties
74:InterPro
68:Selectin
33:Selectin
2185:Lectins
1498:SIGLEC9
1493:SIGLEC8
1488:SIGLEC7
1483:SIGLEC6
1478:SIGLEC5
1366:lectins
1362:Protein
1212:Bibcode
1144:9137500
1109:9106690
983:2559865
934:2172126
885:2064382
845:7532979
801:7506734
751:2572800
669:5478826
627:3909905
599:Bibcode
514:244–245
220:lectins
1984:PCDH19
1979:PCDH15
1850:ITGA2B
1740:Nectin
1718:L1-CAM
1708:PE-CAM
1703:VCAM-1
1608:BanLec
1450:SIGLEC
1373:Animal
1283:
1242:
1235:122341
1232:
1183:
1142:
1115:
1107:
1072:
1062:
1031:
990:
980:
941:
931:
892:
882:
843:
807:
799:
758:
748:
707:
676:
666:
625:
617:
574:
556:
520:
487:
461:
453:
286:PSGL-1
267:PSGL-1
176:cells)
139:lectin
65:Symbol
52:lectin
2159:EpCAM
2154:CD146
2131:LFA-1
2127:VLA-4
2100:Other
2055:CDH10
2045:CDH17
2040:CDH16
2035:CDH15
2030:CDH12
2025:CDH11
1974:PCDH1
1854:ITGB3
1836:CD49d
1832:VLA-4
1822:CD11b
1808:CD11c
1794:CD11a
1790:LFA-1
1770:CD155
1765:CADM3
1760:CADM1
1755:PVRL3
1750:PVRL2
1745:PVRL1
1728:NFASC
1723:NRCAM
1679:N-CAM
1574:Ricin
1569:Abrin
1557:Plant
1517:Other
1394:KLRD1
1113:S2CID
805:S2CID
730:Blood
623:S2CID
459:S2CID
161:Types
2149:CD44
2144:CD24
2111:CD44
2050:CDH9
2020:CDH8
2015:CDH6
2010:CDH5
2005:CDH4
1955:DSC3
1951:DSC2
1947:DSC1
1937:DSG4
1933:DSG3
1929:DSG2
1925:DSG1
1903:CDH3
1898:CDH2
1893:CDH1
1840:CD29
1826:CD18
1812:CD18
1798:CD18
1733:CHL1
1689:ICAM
1468:CD33
1463:CD22
1281:PMID
1240:PMID
1181:PMID
1140:PMID
1105:PMID
1070:PMID
1060:ISBN
1029:PMID
988:PMID
939:PMID
890:PMID
841:PMID
797:PMID
756:PMID
705:ISBN
674:PMID
650:2017
615:PMID
572:PMID
518:ISBN
485:ISBN
451:PMID
433:Cell
422:1G1R
242:and
192:(in
182:(in
172:(in
119:CAMs
111:CD62
98:The
1271:doi
1230:PMC
1220:doi
1171:doi
1097:doi
1052:doi
1019:doi
978:PMC
970:doi
929:PMC
921:doi
917:166
880:PMC
872:doi
868:174
833:doi
787:doi
783:152
746:PMC
738:doi
734:112
697:doi
664:PMC
654:doi
607:doi
564:doi
441:doi
437:103
418:PDB
109:or
47:of
2176::
2129:,
2109::
1953:,
1949:,
1935:,
1931:,
1927:,
1695:,
1652::
1364::
1279:.
1267:85
1265:.
1261:.
1238:.
1228:.
1218:.
1208:99
1206:.
1202:.
1179:.
1167:66
1165:.
1161:.
1136:17
1134:.
1111:.
1103:.
1093:40
1091:.
1068:.
1058:.
1027:.
1015:16
1013:.
1009:.
986:.
976:.
966:11
964:.
960:.
937:.
927:.
915:.
911:.
888:.
878:.
866:.
862:.
839:.
829:12
827:.
803:.
795:.
781:.
777:.
754:.
744:.
732:.
728:.
703:.
672:.
662:.
648:.
644:.
621:.
613:.
605:.
593:.
570:.
562:.
548:.
532:^
516:.
471:^
457:.
449:.
435:.
431:.
420::
409:^
273:.
145:.
107:62
91:12
2133:)
2125:(
1957:)
1945:(
1939:)
1923:(
1856:)
1852:+
1848:(
1842:)
1838:+
1834:(
1828:)
1824:+
1820:(
1814:)
1810:+
1806:(
1800:)
1796:+
1792:(
1699:)
1697:5
1693:1
1691:(
1685:)
1681:(
1642:e
1635:t
1628:v
1354:e
1347:t
1340:v
1287:.
1273::
1246:.
1222::
1214::
1187:.
1173::
1146:.
1119:.
1099::
1076:.
1054::
1035:.
1021::
994:.
972::
945:.
923::
896:.
874::
847:.
835::
811:.
789::
762:.
740::
713:.
699::
680:.
656::
629:.
609::
601::
595:8
578:.
566::
550:9
526:.
493:.
465:.
443::
186:)
102:(
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.