456:
480:
468:
504:
492:
307:
The fibers originating from the anterior surface of the anterior aponeurosis insert onto the median septum, and the fibers originating from the posterior surface of the anterior aponeurosis insert onto the posterior aponeurosis. The posterior aponeurosis and median septum join in the lower quarter of
415:
The soleus is the most effective muscle for plantarflexion in a bent knee position. The gastrocnemius originates on the femur, so bending the leg limits its effective tension. During regular movement (i.e., walking) the soleus is the primary muscle utilized for plantarflexion due to the slow-twitch
29:
388:
of the foot (that is, they increase the angle between the foot and the leg). They are powerful muscles vital in walking, running, and keeping balance. The soleus plays an important role in maintaining standing posture; if not for its constant pull, the body would fall forward.
626:
Bojsen-Møller, Jens; Hansen, Philip; Aagaard, Per; Svantesson, Ulla; Kjaer, Michael; Magnusson, S. Peter (2004). "Differential displacement of the human soleus and medial gastrocnemius aponeuroses during isometric plantar flexor contractions in vivo".
411:
Soleus muscles have more slow muscle fibers than many other muscles. In some animals, such as the guinea pig and cat, soleus consists of 100% slow muscle fibers. Human soleus fiber composition is variable, containing between 60% and 100% slow fibers.
41:
295:
from the gastrocnemius muscle. Most soleus muscle fibers originate from each side of the anterior aponeurosis, attached to the tibia and fibula. Other fibers originate from the posterior (back) surfaces of the head of the
375:
Since the anterior compartment of the leg is lateral to the tibia, the bulge of muscle medial to the tibia on the anterior side is the posterior compartment. The soleus is superficial middle of the tibia.
441:. This pathology relates to tissue inflammation affecting blood flow and compressing nerves. If left untreated compartment syndrome can lead to atrophy of muscles, blood clots, and neuropathy.
918:
A. Agur. Architecture of the human soleus muscle, three-dimensional computer modelling of cadaveric muscle and ultrasonographic documentation in vivo. University of
Toronto (PhD Thesis). ((
533:
Agur, Anne M.; Ng-Thow-Hing, Victor; Ball, Kevin A.; Fiume, Eugene; McKee, Nanacy Hunt (2003). "Documentation and Three-Dimensional
Modelling of Human Soleus Muscle Architecture".
583:; Lai, AM; Edgerton, VR; Sinha, S (May 2006). "Influence of structure on the tissue dynamics of the human soleus muscle observed in MRI studies during isometric contractions".
952:
829:
Gollnick PD, Sjödin B, Karlsson J, Jansson E, Saltin B (April 1974). "Human soleus muscle: a comparison of fiber composition and enzyme activities with other leg muscles".
323:
In contrast to some animals, the human soleus and gastrocnemius muscles are relatively separate, so shear can be detected between the soleus and gastrocnemius aponeuroses.
714:"Il potenziamento dell'attività di pompa venosa del tricipite surale in ortopedia e traumatologia mediante l'utilizzo di una nuova apparecchiatura di ginnastica vascolare"
205:
716:[Strengthening of venous pump activity of the sural tricipital in orthopaedics and traumatology by means of a new equipment for vascular exercise]
1686:
945:
1741:
1736:
1647:
1573:
1325:
181:
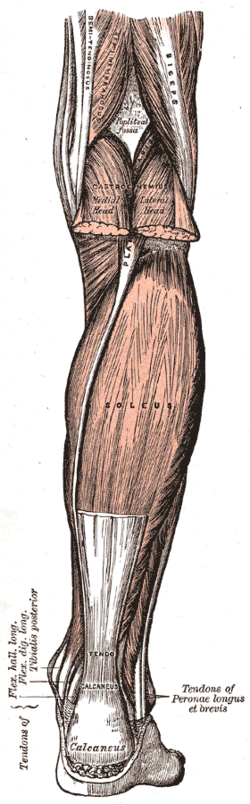
1568:
1330:
1778:
938:
1616:
1387:
925:
1611:
1382:
871:
Saladin, Kenneth S. Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and
Function. 6th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2007. Print.
342:
1642:
1478:
1167:
902:
Saladin, Kenneth S. Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and
Function. 6th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2007. Print.
353:
1698:
1676:
1473:
1117:
1108:
357:
200:
1402:
479:
274:
1369:
1360:
1225:
1202:
1041:
467:
334:
The gastrocnemius muscle is superficial to (closer to the skin than) the soleus, which lies below the gastrocnemius.
1746:
1703:
1504:
212:
135:
83:
62:
1483:
1215:
1145:
1130:
1084:
1079:
349:
1681:
1659:
1637:
1377:
1157:
1074:
1064:
152:
455:
1436:
1245:
1140:
361:
104:
1664:
1578:
1240:
1235:
1230:
1190:
491:
188:
176:
1773:
1185:
1180:
1135:
1053:
919:
365:
345:, which separates the superficial posterior compartment of the leg from the deep posterior compartment.
1426:
1421:
438:
397:
285:
258:
254:
781:
1731:
1546:
912:
341:
and a portion of its tendon run between the two muscles. Deep to it (farther from the skin) is the
281:
147:
782:"Motor units in cat soleus muscle: physiological, histochemical and morphological characteristics"
663:
284:
in many species. In some animals, such as the rabbit, it is fused for much of its length with the
1558:
990:
986:
961:
854:
694:
608:
558:
51:. This is a view of the back of the right leg; most of the gastrocnemius muscle has been removed.
308:
the muscle and then join with the anterior aponeuroses of the gastrocnemius muscles to form the
503:
291:
The soleus is a complex, multi-pennate muscle in humans, usually having a separate (posterior)
28:
1512:
1392:
1335:
1089:
846:
811:
762:
686:
644:
600:
550:
47:
1522:
1517:
1490:
1448:
1320:
1210:
1125:
838:
801:
793:
752:
678:
636:
592:
542:
338:
100:
1441:
1296:
1291:
1220:
1150:
1069:
1034:
1024:
1019:
671:
The
Anatomical Record Part A: Discoveries in Molecular, Cellular, and Evolutionary Biology
313:
309:
108:
88:
1723:
1286:
1269:
1029:
995:
806:
713:
385:
242:
140:
1767:
1468:
1274:
858:
698:
640:
612:
562:
1281:
973:
930:
797:
369:
120:
886:
1308:
881:
580:
292:
280:
The soleus exhibits significant morphological differences across species. It is
75:
300:
and its upper quarter, as well as the middle third of the medial border of the
193:
1355:
1175:
981:
965:
317:
690:
648:
604:
554:
257:, and some anatomists consider this combination to be a single muscle, the
850:
815:
766:
1007:
253:
and is involved in standing and walking. It is closely connected to the
218:
842:
682:
596:
396:
blood back into the heart from the periphery, and is often called the
1715:
1534:
1257:
920:
https://tspace.library.utoronto.ca/bitstream/1807/16553/1/NQ59030.pdf
895:
Gray, Henry. Pick, T. Pickering, & Howden, Robert (Eds.) (1995).
546:
297:
262:
234:
95:
67:
757:
740:
437:
Due to the thick fascia covering the leg muscles, they are prone to
40:
1103:
739:
Ariano, M. A.; Armstrong, R. B.; Edgerton, V. R. (7 August 1972).
301:
164:
115:
71:
1596:
392:
Also, in upright posture, the soleus is responsible for pumping
250:
246:
934:
664:"Horse Soleus Muscle: Postural Sensor or Vestigial Structure?"
424:
The soleus is innervated by the tibial nerve (L4, L5, S1, S2)
238:
261:. Its name is derived from the Latin word "solea", meaning "
384:
The action of the calf muscles, including the soleus, is
780:
Burke RE, Levine DN, Salcman M, Tsairis P (May 1974).
712:
Botta G, Piccinetti A, Giontella M, Mancini S (2001).
1714:
1625:
1604:
1595:
1555:
1533:
1503:
1457:
1410:
1401:
1368:
1354:
1305:
1256:
1201:
1166:
1116:
1102:
1050:
1006:
972:
741:"Hindlimb Muscle Fiber Populations Of Five Mammals"
199:
187:
175:
163:
158:
146:
134:
114:
94:
82:
61:
56:
45:The soleus muscle and surrounding structures, from
21:
899:(15th ed.). New York: Barnes & Noble Books.
722:Giornale Italiano di Ortopedia e Traumatologia
316:and inserts onto the posterior surface of the
946:
745:Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry
8:
662:Meyers, Ron A.; Hermanson, John W. (2006).
1601:
1539:
1407:
1365:
1262:
1113:
1012:
953:
939:
931:
473:Bones of the right leg. Posterior surface.
39:
27:
805:
756:
574:
572:
273:The soleus is located in the superficial
348:On the other side of the fascia are the
16:Muscle in the back part of the lower leg
522:
451:
528:
526:
326:The soleus is vestigial in the horse.
229:In humans and some other mammals, the
216:
18:
1326:Lateral intermuscular septum of thigh
7:
1331:Medial intermuscular septum of thigh
915:at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
485:Cross-section through middle of leg.
14:
926:Soleus Muscle - Your Second Heart
502:
490:
478:
466:
454:
275:posterior compartment of the leg
641:10.1152/japplphysiol.00084.2004
343:transverse intermuscular septum
245:). It runs from just below the
798:10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010540
354:flexor digitorum longus muscle
237:in the back part of the lower
1:
497:Back of left lower extremity.
358:flexor hallucis longus muscle
123:, specifically, nerve roots L
1513:Fibularis (peroneus) muscles
1393:Fibularis (peroneus) tertius
1687:Flexor digiti minimi brevis
1795:
416:fibers resisting fatigue.
213:Anatomical terms of muscle
33:Muscles of lower extremity
1779:Muscles of the lower limb
1617:Extensor digitorum brevis
1542:
1388:Extensor digitorum longus
1265:
1015:
786:The Journal of Physiology
350:tibialis posterior muscle
211:
38:
26:
1612:Extensor hallucis brevis
1383:Extensor hallucis longus
913:Anatomy photo:15:st-0414
882:MedlinePlus Encyclopedia
1643:Flexor digitorum brevis
1479:Flexor digitorum longus
406:sural (tricipital) pump
362:posterior tibial artery
105:posterior tibial artery
1677:Flexor hallucis brevis
1648:Abductor digiti minimi
1474:Flexor hallucis longus
1054:Lateral rotator group
428:Clinical significance
366:posterior tibial vein
1042:Tensor fasciae latae
887:Compartment syndrome
439:compartment syndrome
398:skeletal muscle pump
286:gastrocnemius muscle
255:gastrocnemius muscle
1559:Intermuscular septa
70:, medial border of
1704:Plantar interossei
1484:Tibialis posterior
1216:External obturator
1146:Vastus intermedius
1085:External obturator
1080:Internal obturator
962:Muscles of the hip
843:10.1007/BF00587415
683:10.1002/ar.a.20377
597:10.1002/jmor.10421
1761:
1760:
1757:
1756:
1742:Superior extensor
1737:Inferior extensor
1699:Dorsal interossei
1682:Adductor hallucis
1660:Quadratus plantae
1638:Abductor hallucis
1591:
1590:
1587:
1586:
1499:
1498:
1378:Tibialis anterior
1350:
1349:
1346:
1345:
1336:Cribriform fascia
1158:Articularis genus
1098:
1097:
1075:Superior gemellus
1070:Inferior gemellus
1065:Quadratus femoris
677:(10): 1068–1076.
445:Additional images
360:, along with the
227:
226:
222:
153:Tibialis anterior
1786:
1665:Lumbrical muscle
1602:
1562:
1540:
1462:
1437:Accessory soleus
1415:
1408:
1366:
1321:Iliotibial tract
1312:
1263:
1141:Vastus lateralis
1114:
1058:
1013:
955:
948:
941:
932:
889:
878:
872:
869:
863:
862:
826:
820:
819:
809:
777:
771:
770:
760:
736:
730:
729:
719:
709:
703:
702:
668:
659:
653:
652:
635:(5): 1908–1914.
623:
617:
616:
576:
567:
566:
547:10.1002/ca.10112
535:Clinical Anatomy
530:
506:
494:
482:
470:
458:
402:peripheral heart
339:plantaris muscle
320:, or heel bone.
310:calcaneal tendon
219:edit on Wikidata
101:Popliteal artery
43:
31:
19:
1794:
1793:
1789:
1788:
1787:
1785:
1784:
1783:
1764:
1763:
1762:
1753:
1710:
1621:
1583:
1556:
1551:
1529:
1495:
1458:
1453:
1442:Achilles tendon
1411:
1397:
1359:
1342:
1306:
1301:
1297:Muscular lacuna
1292:Adductor hiatus
1252:
1197:
1191:Semimembranosus
1162:
1151:Vastus medialis
1107:
1094:
1051:
1046:
1020:Gluteal muscles
1002:
968:
959:
909:
892:
879:
875:
870:
866:
831:Pflügers Archiv
828:
827:
823:
779:
778:
774:
758:10.1177/21.1.51
738:
737:
733:
717:
711:
710:
706:
666:
661:
660:
656:
625:
624:
620:
578:
577:
570:
532:
531:
524:
520:
515:
514:
513:
510:
509:Posterior view.
507:
498:
495:
486:
483:
474:
471:
462:
459:
447:
435:
430:
422:
382:
332:
314:Achilles tendon
271:
223:
170:musculus soleus
130:
126:
109:peroneal artery
89:Tendo calcaneus
52:
34:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1792:
1790:
1782:
1781:
1776:
1766:
1765:
1759:
1758:
1755:
1754:
1752:
1751:
1750:
1749:
1744:
1739:
1734:
1726:
1724:Plantar fascia
1720:
1718:
1712:
1711:
1709:
1708:
1707:
1706:
1701:
1691:
1690:
1689:
1684:
1679:
1669:
1668:
1667:
1662:
1652:
1651:
1650:
1645:
1640:
1629:
1627:
1623:
1622:
1620:
1619:
1614:
1608:
1606:
1599:
1593:
1592:
1589:
1588:
1585:
1584:
1582:
1581:
1576:
1571:
1565:
1563:
1553:
1552:
1550:
1549:
1543:
1537:
1531:
1530:
1528:
1527:
1526:
1525:
1520:
1509:
1507:
1501:
1500:
1497:
1496:
1494:
1493:
1488:
1487:
1486:
1481:
1476:
1465:
1463:
1455:
1454:
1452:
1451:
1446:
1445:
1444:
1439:
1434:
1429:
1418:
1416:
1405:
1399:
1398:
1396:
1395:
1390:
1385:
1380:
1374:
1372:
1363:
1352:
1351:
1348:
1347:
1344:
1343:
1341:
1340:
1339:
1338:
1333:
1328:
1323:
1315:
1313:
1303:
1302:
1300:
1299:
1294:
1289:
1287:Adductor canal
1284:
1279:
1278:
1277:
1270:Femoral sheath
1266:
1260:
1254:
1253:
1251:
1250:
1249:
1248:
1243:
1238:
1233:
1223:
1218:
1213:
1207:
1205:
1199:
1198:
1196:
1195:
1194:
1193:
1188:
1186:Semitendinosus
1183:
1181:Biceps femoris
1172:
1170:
1164:
1163:
1161:
1160:
1155:
1154:
1153:
1148:
1143:
1138:
1136:Rectus femoris
1128:
1122:
1120:
1111:
1100:
1099:
1096:
1095:
1093:
1092:
1087:
1082:
1077:
1072:
1067:
1061:
1059:
1048:
1047:
1045:
1044:
1039:
1038:
1037:
1032:
1027:
1016:
1010:
1004:
1003:
1001:
1000:
999:
998:
993:
978:
976:
970:
969:
960:
958:
957:
950:
943:
935:
929:
928:
923:
916:
908:
907:External links
905:
904:
903:
900:
897:Gray's Anatomy
891:
890:
873:
864:
821:
772:
731:
724:(in Italian).
704:
654:
629:J Appl Physiol
618:
591:(5): 584–601.
568:
541:(4): 285–293.
521:
519:
516:
512:
511:
508:
501:
499:
496:
489:
487:
484:
477:
475:
472:
465:
463:
460:
453:
450:
449:
448:
446:
443:
434:
431:
429:
426:
421:
418:
386:plantarflexion
381:
378:
331:
328:
270:
267:
233:is a powerful
225:
224:
215:
209:
208:
203:
197:
196:
191:
185:
184:
179:
173:
172:
167:
161:
160:
156:
155:
150:
144:
143:
141:Plantarflexion
138:
132:
131:
128:
124:
118:
112:
111:
98:
92:
91:
86:
80:
79:
65:
59:
58:
54:
53:
48:Gray's Anatomy
44:
36:
35:
32:
24:
23:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1791:
1780:
1777:
1775:
1772:
1771:
1769:
1748:
1745:
1743:
1740:
1738:
1735:
1733:
1730:
1729:
1727:
1725:
1722:
1721:
1719:
1717:
1713:
1705:
1702:
1700:
1697:
1696:
1695:
1692:
1688:
1685:
1683:
1680:
1678:
1675:
1674:
1673:
1670:
1666:
1663:
1661:
1658:
1657:
1656:
1653:
1649:
1646:
1644:
1641:
1639:
1636:
1635:
1634:
1631:
1630:
1628:
1624:
1618:
1615:
1613:
1610:
1609:
1607:
1603:
1600:
1598:
1594:
1580:
1577:
1575:
1572:
1570:
1567:
1566:
1564:
1561:
1560:
1554:
1548:
1547:Pes anserinus
1545:
1544:
1541:
1538:
1536:
1532:
1524:
1521:
1519:
1516:
1515:
1514:
1511:
1510:
1508:
1506:
1502:
1492:
1489:
1485:
1482:
1480:
1477:
1475:
1472:
1471:
1470:
1469:tarsal tunnel
1467:
1466:
1464:
1461:
1456:
1450:
1447:
1443:
1440:
1438:
1435:
1433:
1430:
1428:
1427:Gastrocnemius
1425:
1424:
1423:
1422:Triceps surae
1420:
1419:
1417:
1414:
1409:
1406:
1404:
1400:
1394:
1391:
1389:
1386:
1384:
1381:
1379:
1376:
1375:
1373:
1371:
1367:
1364:
1362:
1357:
1353:
1337:
1334:
1332:
1329:
1327:
1324:
1322:
1319:
1318:
1317:
1316:
1314:
1311:
1310:
1304:
1298:
1295:
1293:
1290:
1288:
1285:
1283:
1280:
1276:
1275:Femoral canal
1273:
1272:
1271:
1268:
1267:
1264:
1261:
1259:
1255:
1247:
1244:
1242:
1239:
1237:
1234:
1232:
1229:
1228:
1227:
1224:
1222:
1219:
1217:
1214:
1212:
1209:
1208:
1206:
1204:
1200:
1192:
1189:
1187:
1184:
1182:
1179:
1178:
1177:
1174:
1173:
1171:
1169:
1165:
1159:
1156:
1152:
1149:
1147:
1144:
1142:
1139:
1137:
1134:
1133:
1132:
1129:
1127:
1124:
1123:
1121:
1119:
1115:
1112:
1110:
1105:
1101:
1091:
1088:
1086:
1083:
1081:
1078:
1076:
1073:
1071:
1068:
1066:
1063:
1062:
1060:
1057:
1055:
1049:
1043:
1040:
1036:
1033:
1031:
1028:
1026:
1023:
1022:
1021:
1018:
1017:
1014:
1011:
1009:
1005:
997:
994:
992:
988:
985:
984:
983:
980:
979:
977:
975:
971:
967:
963:
956:
951:
949:
944:
942:
937:
936:
933:
927:
924:
921:
917:
914:
911:
910:
906:
901:
898:
894:
893:
888:
884:
883:
877:
874:
868:
865:
860:
856:
852:
848:
844:
840:
837:(3): 247–55.
836:
832:
825:
822:
817:
813:
808:
803:
799:
795:
792:(3): 503–14.
791:
787:
783:
776:
773:
768:
764:
759:
754:
750:
746:
742:
735:
732:
727:
723:
715:
708:
705:
700:
696:
692:
688:
684:
680:
676:
672:
665:
658:
655:
650:
646:
642:
638:
634:
630:
622:
619:
614:
610:
606:
602:
598:
594:
590:
586:
582:
579:Hodgson, JA;
575:
573:
569:
564:
560:
556:
552:
548:
544:
540:
536:
529:
527:
523:
517:
505:
500:
493:
488:
481:
476:
469:
464:
457:
452:
444:
442:
440:
432:
427:
425:
419:
417:
413:
409:
407:
403:
399:
395:
390:
387:
379:
377:
373:
371:
367:
363:
359:
355:
351:
346:
344:
340:
335:
329:
327:
324:
321:
319:
315:
311:
305:
303:
299:
294:
289:
287:
283:
278:
276:
268:
266:
264:
260:
259:triceps surae
256:
252:
248:
244:
240:
236:
232:
220:
214:
210:
207:
204:
202:
198:
195:
192:
190:
186:
183:
180:
178:
174:
171:
168:
166:
162:
157:
154:
151:
149:
145:
142:
139:
137:
133:
122:
119:
117:
113:
110:
106:
102:
99:
97:
93:
90:
87:
85:
81:
77:
73:
69:
66:
64:
60:
55:
50:
49:
42:
37:
30:
25:
22:Soleus muscle
20:
1774:Calf muscles
1693:
1671:
1654:
1632:
1557:
1459:
1431:
1412:
1361:compartments
1307:
1282:Femoral ring
1109:compartments
1052:
974:Iliac region
896:
880:
876:
867:
834:
830:
824:
789:
785:
775:
751:(1): 51–55.
748:
744:
734:
725:
721:
707:
674:
670:
657:
632:
628:
621:
588:
584:
538:
534:
436:
423:
414:
410:
405:
401:
393:
391:
383:
374:
370:tibial nerve
347:
336:
333:
325:
322:
306:
290:
279:
272:
230:
228:
182:A04.7.02.047
169:
121:Tibial nerve
46:
1728:retinacula
1413:Superficial
1309:Fascia lata
991:Psoas minor
987:Psoas major
420:Innervation
293:aponeurosis
159:Identifiers
76:soleal line
1768:Categories
1579:Transverse
1131:Quadriceps
1090:Piriformis
518:References
461:Animation.
356:, and the
282:unipennate
148:Antagonist
1694:4th layer
1672:3rd layer
1655:2nd layer
1633:1st layer
1574:Posterior
1491:Popliteus
1449:Plantaris
1403:Posterior
1211:Pectineus
1176:Hamstring
1168:Posterior
1126:Sartorius
982:Iliopsoas
966:human leg
585:J Morphol
330:Relations
318:calcaneus
269:Structure
84:Insertion
1732:Peroneal
1569:Anterior
1370:Anterior
1226:Adductor
1221:Gracilis
1118:Anterior
1008:Buttocks
859:29365931
699:13867533
691:16952170
649:15220297
613:25645433
605:16453292
581:Finni, T
563:31122290
555:12794910
380:Function
368:and the
1626:Plantar
1505:Lateral
1246:Minimus
1035:Minimus
1025:Maximus
996:Iliacus
851:4275915
816:4277582
807:1330899
767:4348494
728:: 84–8.
433:Disease
404:or the
249:to the
136:Actions
57:Details
1747:Flexor
1716:Fascia
1605:Dorsal
1535:Fascia
1523:Brevis
1518:Longus
1432:Soleus
1258:Fascia
1241:Magnus
1236:Brevis
1231:Longus
1203:Medial
1030:Medius
857:
849:
814:
804:
765:
697:
689:
647:
611:
603:
561:
553:
394:venous
352:, the
298:fibula
263:sandal
235:muscle
231:soleus
96:Artery
68:Fibula
63:Origin
1104:Thigh
855:S2CID
718:(PDF)
695:S2CID
667:(PDF)
609:S2CID
559:S2CID
302:tibia
241:(the
217:[
206:22542
165:Latin
116:Nerve
72:tibia
1597:Foot
1460:Deep
964:and
847:PMID
812:PMID
763:PMID
687:PMID
645:PMID
601:PMID
551:PMID
364:and
337:The
251:heel
247:knee
243:calf
194:2660
177:TA98
1356:Leg
839:doi
835:348
802:PMC
794:doi
790:238
753:doi
679:doi
675:288
637:doi
593:doi
589:267
543:doi
312:or
265:".
239:leg
201:FMA
189:TA2
1770::
922:))
885::
853:.
845:.
833:.
810:.
800:.
788:.
784:.
761:.
749:21
747:.
743:.
726:27
720:.
693:.
685:.
673:.
669:.
643:.
633:97
631:.
607:.
599:.
587:.
571:^
557:.
549:.
539:16
537:.
525:^
408:.
400:,
372:.
304:.
288:.
277:.
127:–S
107:,
103:,
1358:/
1106:/
1056::
989:/
954:e
947:t
940:v
861:.
841::
818:.
796::
769:.
755::
701:.
681::
651:.
639::
615:.
595::
565:.
545::
221:]
129:2
125:5
78:)
74:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.