1517:
44:
1584:
450:
1594:
1511:
615:
232:
403:
In many cases, core network convergence time after a failure is dependent on the length of time a routing protocol requires to successfully converge (change or re-route traffic around the fault). Depending on the specific routing protocol, this convergence time can cause network interruptions ranging
290:
In general, normal network traffic does not traverse the IST unless this is the only path to reach a host which is connected only to the peer switch. By ensuring all devices have SMLT connections to the aggregation switches, traffic never needs to traverse the IST and the total forwarding capacity of
92:
is an important aspect of Multi-Link
Trunking technology. Should any one or more than one link fail, the MLT technology will automatically redistribute traffic across the remaining links. This automatic redistribution is accomplished in less than half a second (typically less than 100 millisecond) so
326:
The use of SMLT not only allows traffic to be load-balanced across all the links in an aggregation group but also allows traffic to be redistributed very quickly in the event of link or switch failure. In general the failure of any one component results in a traffic disruption lasting less than half
246:
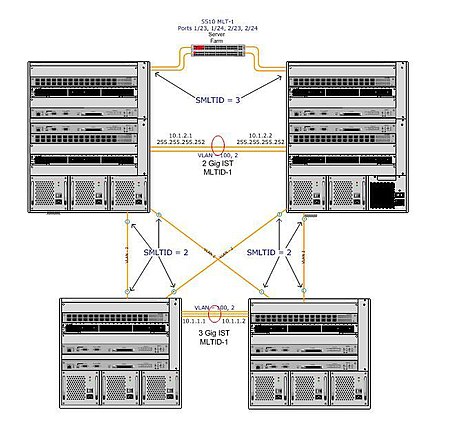
The split may be at one or at both ends of the MLT. If both ends of the link are split, the resulting topology is referred to as an "SMLT square" when there is no cross-connect between diagonally opposite aggregation switches, or an "SMLT mesh" when each aggregation switch has a SMLT connection with
199:
information). For real-world network traffic this generally results in an effective bandwidth for the logical link equal to the sum of the bandwidth of the individual physical links. Redundant links that were once unused due to
Spanning Tree’s loop protection can now be used to their full potential.
334:
of any kind since there are no logical bridging loops introduced by the presence of the IST. This eliminates the need for spanning tree reconvergence or root-bridge failovers in failure scenarios which causes interruptions in network traffic longer than time-sensitive applications are able to cater
548:
Fault-tolerance is a very important aspect of
Distributed Split Multi-Link Trunking (DSMLT) technology. Should any one switch, port, or more than one link fail, the DSMLT technology will automatically redistribute traffic across the remaining links. Automatic redistribution is accomplished in less
183:
Link aggregation or MLT allows multiple physical network links between two network switches and another device (which could be another switch or a network device such as a server) to be treated as a single logical link and load balance the traffic across all available links. For each packet that
81:
MLT allows the use of several links (from 2 up to 8) and combines them to create a single fault-tolerant link with increased bandwidth. This produces server-to-switch or switch-to-switch connections that are up to 8 times faster. Prior to MLT and other aggregation techniques, parallel links were
411:
RSMLT routing topologies providing an active-active router concept to core SMLT networks. The protocol supports networks designed with SMLT or DSMLT triangles, squares, and SMLT or DSMLT full mesh topologies, with routing enabled on the core VLANs. R-SMLT takes care of packet forwarding in core
176:
311:
408:(DSMLT) technologies to provide sub-second failover (normally less than 100 milliseconds) so no outage is noticed by end users. This high speed recovery is required by many critical networks where outages can cause loss of life or very large monetary losses in critical networks.
250:
In an SMLT triangle, the end of the link which is not split does not need to support SMLT. This allows non-Avaya devices including third-party switches and servers to benefit from SMLT. The only requirement is that IEEE 802.3ad static mode must be supported.
549:
than half a second (typically less than 100 milliseconds) so no outage is noticed by end users. This high speed recovery is required by many critical networks where outages can cause loss of life or very large monetary losses in critical networks. Combining
108:
A general limitation of standard MLT is that all the physical ports in the link aggregation group must reside on the same switch. SMLT, DSMLT and R-SMLT technologies removes this limitation by allowing the physical ports to be split between two switches.
541:
613:, Van Hunter, Joseph Regan, Alfred Nothaft, Akhil Duggal; Regan, Joseph & Nothaft, Alfred et al., "Automatic Load Sharing-Trunking", issued 2004-05-04, assigned to Nortel Networks Limited and Avaya Holdings Limited
274:
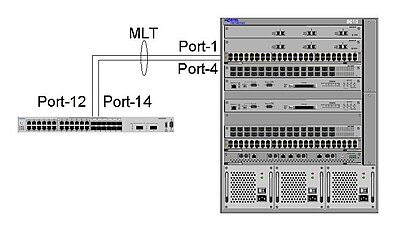
For each SMLT connection, the aggregation switches have a standard MLT or individual port with which an SMLT identifier is associated. For a given SMLT connection, the same SMLT ID must be configured on each of the peer aggregation switches.
741:
131:
260:
722:
534:) protocol. DSMLT allows the ports in a trunk to span multiple units of a stack of switches or to span multiple cards in a chassis, preventing network outages when one switch in a stack fails or one card in a chassis fails.
704:
The network will utilize Nortel's SMLT (Split Multi-Link
Trunking) technology, which provides exceptional resiliency to ensure voice, video and other applications stay connected despite link, switch or site equipment
93:
no outage is noticed by end users. This high speed recovery is required by many critical networks where outages can cause loss of life or very large monetary losses in critical networks. Combining MLT technology with
499:
DMLT allows the ports in a trunk (MLT) to span multiple units of a stack of switches or to span multiple cards in a chassis, preventing network outages when one switch in a stack fails or a card in a chassis fails.
317:
316:
313:
312:
318:
286:
on a port that is part of an SMLT, it will inform its peer switch across the IST and request the peer to update its own ARP table with a record pointing to its own connection with the corresponding SMLT ID.
315:
174:, Lapuh, Roger; Zhao, Yili & Tawbi, Wassim et al., "System, Device, and Method for Improving Communication Network Reliability Using Trunk Splitting", issued 2007-02-06
271:(IST). The IST is a (standard) MLT connection between the aggregation switches which allows the exchange of information regarding traffic forwarding and the status of individual SMLT links.
1516:
243:
The two switches between which the SMLT is split are known as aggregation switches and form a logical cluster which appears to the other end of the SMLT link as a single switch.
140:
SMLT mesh with nine 1Gig paths (all connections active and load balancing traffic) 9 Gbit/s full duplex mesh providing 18 Gbit/s of bandwidth between core switches.
1068:
834:
755:
660:
629:
492:, used to load balance the network traffic across connections and also across multiple switches or modules in a chassis. The protocol is an enhancement to the
1147:
327:
a second (normal less than 100 millisecond) making SMLT appropriate in environments running time- and loss-sensitive applications such as voice and video.
539:, Fite Jr., David B.; Ilyadis, Nicholas & Salett, Ronald M., "Distributed Multi-Link Trunking Method and Apparatus", issued 2002-12-17
867:
Lapuh, Roger & Yili Zhao "System, device, and method for improving communication network reliability using trunk splitting"; (SMLT) issued 2007-02-06
294:
The communication between peer switches across the IST allows both unicast and multicast routing information to be exchanged allowing protocols such as
813:
314:
215:
protocols remove this limitation by allowing the physical ports to be split between two switches, allowing for the creation of Active load sharing
1481:
835:"Evaluation of Resilient Routing Switches for Real-Time Multimedia Traffic with Microsoft Live Communications Server 2005 and Nortel MCS 5100"
756:"Evaluation of Resilient Routing Switches for Real-Time Multimedia Traffic with Microsoft Live Communications Server 2005 and Nortel MCS 5100"
661:"Evaluation of Resilient Routing Switches for Real-Time Multimedia Traffic with Microsoft Live Communications Server 2005 and Nortel MCS 5100"
630:"Evaluation of Resilient Routing Switches for Real-Time Multimedia Traffic with Microsoft Live Communications Server 2005 and Nortel MCS 5100"
1388:
1369:
948:
910:
405:
400:(SMLT) enabling the exchange of Layer 3 information between peer nodes in a switch cluster for resiliency and simplicity for both L3 and L2.
94:
692:"National University of Malaysia Unleashes Student Learning With Nortel; New High Performance Network To Enhance New Educational Approaches"
1000:
343:
SMLT is supported within the following Avaya
Ethernet Routing Switch (ERS) and Virtual Services Platform (VSP) Product Families: ERS 1600,
1036:
864:
1044:
1056:
929:
888:
1065:
449:
1663:
412:
router failures and works with any of the following protocol types: IP Unicast Static Routes, RIP1, RIP2, OSPF, BGP and IPX RIP.
1623:
1471:
1378:
1181:
959:
1081:
78:
links into one logical
Ethernet link to provide fault-tolerance and high-speed links between routers, switches, and servers.
1091:
1658:
1436:
1491:
1451:
1446:
1265:
1260:
247:
both aggregation switches in the other pair. If only one end is split, the topology is referred to as an SMLT triangle.
1403:
1329:
1324:
1314:
279:
1336:
841:
762:
667:
636:
1648:
1559:
185:
1643:
1638:
1383:
1364:
1281:
550:
527:
493:
397:
98:
1569:
1486:
295:
1633:
1476:
1153:
720:, Lapuh, Roger & Tamiji, Homma, "Routed Split Multilink Trunking", issued 2008-12-09
1286:
1346:
1290:
1245:
902:
348:
331:
83:
1359:
1233:
1228:
1223:
1218:
1107:
979:
590:
586:
372:
352:
89:
207:
is that all the physical ports in the link aggregation group must reside on the same switch. The SMLT,
736:
717:
610:
536:
171:
1319:
481:
393:
1129:
1021:
356:
1174:
519:
478:
220:
158:
905:, NC: Nortel Press. October 2008. pp. 92, 116–119, 220–225, 423–424, 399, 480–490, 479, 481.
1428:
1205:
268:
1296:
1597:
1628:
1398:
1041:
944:
925:
906:
884:
739:, Lissianoi, Sergei, "Routed Split Multilink Trunking for IPv6", issued 2014-10-14
216:
43:
377:
SMLT is fully interoperable with devices supporting standard MLT (IEEE 802.3ad static mode).
1441:
489:
154:
67:
1653:
1120:
1085:
1072:
1060:
1048:
992:
578:
299:
1510:
1053:
17:
1618:
1587:
1543:
1538:
1533:
1255:
1250:
1240:
1210:
1167:
364:
360:
344:
1612:
1306:
192:
204:
166:
1078:
691:
1408:
283:
196:
809:
787:
1098:
Polishuk, Dr. Paul; Pan, Dr. Hui (May 2003). "European
Telecom Newsletter".
582:
425:
368:
188:
808:
David B. Fite Jr.; Nicholas
Ilyadis; Ronald M. Salett (December 17, 2002).
184:
needs to be transmitted, one of the physical links is selected based on a
130:
105:
technologies create networks that support the most critical applications.
1461:
421:
75:
259:
1564:
1418:
1037:
Technical Brief Split Multi-Link
Trunking Ethernet Routing Switch 8600
565:
technologies create networks that support the most critical networks.
165:
as an enhancement to standard multi-link trunking (MLT) as defined in
1496:
1393:
562:
523:
485:
162:
102:
71:
1413:
1354:
1190:
883:(Second ed.). McGraw-Hill. pp. 92–93, 116–117, 228–233.
574:
330:
In a network using SMLT, it is often no longer necessary to run a
258:
236:
230:
212:
208:
404:
from seconds to minutes. The R-SMLT protocol works with SMLT and
558:
554:
531:
1163:
231:
1130:"Split Multi-link Trunking (SMLT) draft-lapuh-network-smlt-08"
1159:
448:
129:
42:
460:
DMLT between 2 stacked 5530 switches to an ERS 8600 switch
1022:"Split MultiLink Trunking/Routed Split MultiLink Trunking"
453:
DMLT between 2 stacked 5530 switches to an ERS 8600 switch
203:
A general limitation of standard link aggregation, MLT or
420:
R-SMLT is supported on Avaya's
Ethernet Routing Switch
278:
For example, when one switch receives a response to an
810:"Distributed multi-link trunking method and apparatus"
503:
DMLT is described in an expired United States Patent.
1092:
Distributed multi-link trunking method and apparatus
1079:
Distributed multi-link trunking method and apparatus
1066:
Distributed multi-link trunking method and apparatus
1552:
1524:
1460:
1427:
1345:
1305:
1274:
1204:
1197:
53:MLT between ERS 5530 switch and an ERS 8600 switch
239:switches 40 Gbit/s full duplex to edge switch
291:the switches in the cluster is also aggregated.
1175:
577:'s Ethernet Routing Switch 1600, 5500, 8300,
74:in 1999. It allows grouping several physical
8:
920:Edwards, James; Jensen, Matthews S. (2001).
924:. McGraw-Hill. pp. 113, 353–354, 364.
1201:
1182:
1168:
1160:
1154:See IEEE.org for info on 802.3ad standard
300:Protocol Independent Multicast-Sparse Mode
814:United States Patent and Trademark Office
396:developed at Nortel as an enhancement to
899:Nortel Ethernet Routing Switch Solutions
459:
447:
438:
309:
267:The key to the operation of SMLT is the
195:operating on the source and destination
139:
128:
119:
52:
41:
32:
881:Nortel networks: The Complete Reference
602:
1116:
1105:
988:
977:
435:
116:
29:
1054:Using Distributed Multi-Link Trunking
512:Distributed split multi-link trunking
507:Distributed split multi-link trunking
441:Avaya Distributed Multi-Link Trunking
406:distributed Split Multi-Link Trunking
95:Distributed Split Multi-Link Trunking
7:
1593:
922:Nortel Networks: A Beginner's Guide
27:Network link aggregation technology
1492:Proactive Voice Quality Management
424:, ERS 8800, VSP9000, ERS 8300 and
25:
1482:Unified Communications Management
1355:Auto Detection Auto Configuration
1102:(5). Information Gatekeepers: 16.
840:. The Tolly Group. Archived from
761:. The Tolly Group. Archived from
666:. The Tolly Group. Archived from
635:. The Tolly Group. Archived from
1592:
1583:
1582:
1515:
1509:
1472:Agile Communication Environment
1370:Simple Loop Prevention Protocol
1337:Avaya 9600-series IP Deskphones
939:Roebuck, Kevin (May 30, 2011).
467:Distributed multi-link trunking
437:
432:Distributed multi-link trunking
302:(PIM-SM) to operate correctly.
118:
31:
1:
1024:. Network World. January 2008
960:"In light of buy, Bay builds"
694:. M2 Presswire. June 17, 2009
1128:Lapuh, Roger (8 July 2008).
1315:Avaya 1100-series IP phones
958:Duffy, Jim (May 18, 1998).
518:) or Distributed SMLT is a
392:) is a computer networking
223:availability requirements.
1680:
1560:Avaya Government Solutions
1001:"Next-Generation Networks"
219:network designs that meet
35:Nortel Multi-Link Trunking
1578:
1507:
1487:Enterprise Switch Manager
1365:Nortel Discovery Protocol
551:Multi-Link Trunking (MLT)
528:Split Multi-Link Trunking
494:Multi-Link Trunking (MLT)
398:split multi-link trunking
147:Split multi-link trunking
122:Split Multi-Link Trunking
113:Split multi-link trunking
99:Split multi-link trunking
18:Split multi-link trunking
1570:Wellfleet Communications
879:Knapp, James R. (2001).
786:Nortel Networks (2008).
522:technology developed at
296:Open Shortest Path First
235:SMLT triangle between 3
161:originally developed by
70:technology developed at
1664:Reliability engineering
1156:-Retrieved 29 July 2011
1150:-Retrieved 29 July 2011
966:(20). Network World: 64
1624:Communication circuits
1477:Communications Manager
1115:Cite journal requires
987:Cite journal requires
903:Research Triangle Park
454:
332:spanning tree protocol
323:
264:
240:
134:
84:Spanning Tree Protocol
47:
1287:Secure Network Access
941:Ethernet MAN Services
611:US patent 6731599
573:SMLT is supported on
452:
321:
262:
234:
191:(usually involving a
133:
90:Fault-tolerant design
82:underutilized due to
46:
1659:Network architecture
1042:Desktop Connectivity
263:Server SMLT triangle
86:’s loop protection.
520:computer networking
488:, and now owned by
479:computer networking
159:computer networking
60:Multi-link trunking
1282:Secure Router 4134
1084:2016-09-16 at the
1071:2012-03-28 at the
1059:2016-09-18 at the
1047:2016-03-03 at the
901:(First ed.).
788:"Patent US6496502"
455:
324:
269:Inter-Switch Trunk
265:
241:
135:
48:
1649:Bonding protocols
1606:
1605:
1505:
1504:
1006:. CDW. March 2010
950:978-1-74304-426-1
912:978-0-9815218-1-7
868:
477:is a proprietary
464:
463:
319:
306:Failure scenarios
217:high availability
144:
143:
57:
56:
16:(Redirected from
1671:
1644:Nortel protocols
1639:Network topology
1596:
1595:
1586:
1585:
1519:
1513:
1275:Security devices
1202:
1184:
1177:
1170:
1161:
1148:Tolly Benchmarks
1137:
1134:Ietf Datatracker
1124:
1118:
1113:
1111:
1103:
1033:
1031:
1029:
1015:
1013:
1011:
1005:
996:
990:
985:
983:
975:
973:
971:
954:
935:
916:
894:
863:
856:
855:
853:
852:
846:
839:
831:
825:
824:
822:
820:
805:
799:
798:
796:
794:
783:
777:
776:
774:
773:
767:
760:
752:
746:
745:
744:
740:
733:
727:
726:
725:
721:
714:
708:
707:
701:
699:
688:
682:
681:
679:
678:
672:
665:
657:
651:
650:
648:
647:
641:
634:
626:
620:
619:
618:
614:
607:
545:
544:
540:
490:Extreme Networks
443:
436:
320:
282:request from an
180:
179:
175:
155:link aggregation
124:
117:
68:link aggregation
37:
30:
21:
1679:
1678:
1674:
1673:
1672:
1670:
1669:
1668:
1609:
1608:
1607:
1602:
1574:
1548:
1526:
1520:
1514:
1501:
1464:
1456:
1423:
1372:
1341:
1301:
1270:
1266:ERS 2500 series
1261:ERS 3500 series
1256:ERS 4000 series
1251:ERS 5500 series
1246:ERS 5600 series
1241:ERS 8800 series
1234:VSP 4000 series
1229:VSP 7000 series
1224:VSP 8000 series
1219:VSP 9000 series
1209:
1193:
1188:
1144:
1127:
1114:
1104:
1097:
1086:Wayback Machine
1073:Wayback Machine
1061:Wayback Machine
1049:Wayback Machine
1027:
1025:
1020:
1009:
1007:
1003:
999:
986:
976:
969:
967:
957:
951:
938:
932:
919:
913:
897:
891:
878:
875:
873:Further reading
860:
859:
850:
848:
844:
837:
833:
832:
828:
818:
816:
807:
806:
802:
792:
790:
785:
784:
780:
771:
769:
765:
758:
754:
753:
749:
742:
735:
734:
730:
723:
716:
715:
711:
697:
695:
690:
689:
685:
676:
674:
670:
663:
659:
658:
654:
645:
643:
639:
632:
628:
627:
623:
616:
609:
608:
604:
599:
571:
569:Product support
542:
535:
526:to enhance the
509:
486:Nortel Networks
475:distributed MLT
439:
434:
418:
416:Product support
383:
341:
339:Product support
310:
308:
257:
229:
227:SMLT topologies
177:
170:
153:) is a Layer-2
120:
115:
33:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1677:
1675:
1667:
1666:
1661:
1656:
1651:
1646:
1641:
1636:
1634:Link protocols
1631:
1626:
1621:
1611:
1610:
1604:
1603:
1601:
1600:
1590:
1579:
1576:
1575:
1573:
1572:
1567:
1562:
1556:
1554:
1550:
1549:
1547:
1546:
1541:
1536:
1534:1A2 Key System
1530:
1528:
1522:
1521:
1508:
1506:
1503:
1502:
1500:
1499:
1494:
1489:
1484:
1479:
1474:
1468:
1466:
1458:
1457:
1455:
1454:
1449:
1444:
1439:
1433:
1431:
1425:
1424:
1422:
1421:
1416:
1411:
1406:
1401:
1396:
1391:
1386:
1381:
1376:
1367:
1362:
1357:
1351:
1349:
1343:
1342:
1340:
1339:
1334:
1333:
1332:
1327:
1322:
1311:
1309:
1303:
1302:
1300:
1299:
1294:
1284:
1278:
1276:
1272:
1271:
1269:
1268:
1263:
1258:
1253:
1248:
1243:
1237:
1236:
1231:
1226:
1221:
1215:
1213:
1199:
1195:
1194:
1189:
1187:
1186:
1179:
1172:
1164:
1158:
1157:
1151:
1143:
1142:External links
1140:
1139:
1138:
1125:
1117:|journal=
1095:
1089:
1076:
1075:Google Patents
1063:
1051:
1039:
1034:
1017:
1016:
997:
989:|journal=
955:
949:
936:
930:
917:
911:
895:
889:
874:
871:
870:
869:
858:
857:
826:
800:
778:
747:
728:
709:
683:
652:
621:
601:
600:
598:
595:
570:
567:
508:
505:
462:
461:
457:
456:
445:
444:
433:
430:
417:
414:
382:
379:
340:
337:
307:
304:
256:
253:
228:
225:
186:load-balancing
157:technology in
142:
141:
137:
136:
126:
125:
114:
111:
55:
54:
50:
49:
39:
38:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1676:
1665:
1662:
1660:
1657:
1655:
1652:
1650:
1647:
1645:
1642:
1640:
1637:
1635:
1632:
1630:
1627:
1625:
1622:
1620:
1617:
1616:
1614:
1599:
1591:
1589:
1581:
1580:
1577:
1571:
1568:
1566:
1563:
1561:
1558:
1557:
1555:
1551:
1545:
1542:
1540:
1537:
1535:
1532:
1531:
1529:
1523:
1518:
1512:
1498:
1495:
1493:
1490:
1488:
1485:
1483:
1480:
1478:
1475:
1473:
1470:
1469:
1467:
1463:
1459:
1453:
1450:
1448:
1445:
1443:
1440:
1438:
1435:
1434:
1432:
1430:
1426:
1420:
1417:
1415:
1412:
1410:
1407:
1405:
1402:
1400:
1397:
1395:
1392:
1390:
1387:
1385:
1382:
1380:
1377:
1375:
1371:
1368:
1366:
1363:
1361:
1360:FAST Stacking
1358:
1356:
1353:
1352:
1350:
1348:
1344:
1338:
1335:
1331:
1328:
1326:
1323:
1321:
1318:
1317:
1316:
1313:
1312:
1310:
1308:
1307:IP telephones
1304:
1298:
1295:
1292:
1288:
1285:
1283:
1280:
1279:
1277:
1273:
1267:
1264:
1262:
1259:
1257:
1254:
1252:
1249:
1247:
1244:
1242:
1239:
1238:
1235:
1232:
1230:
1227:
1225:
1222:
1220:
1217:
1216:
1214:
1212:
1207:
1203:
1200:
1196:
1192:
1185:
1180:
1178:
1173:
1171:
1166:
1165:
1162:
1155:
1152:
1149:
1146:
1145:
1141:
1135:
1131:
1126:
1122:
1109:
1101:
1096:
1093:
1090:
1088:Patent Genius
1087:
1083:
1080:
1077:
1074:
1070:
1067:
1064:
1062:
1058:
1055:
1052:
1050:
1046:
1043:
1040:
1038:
1035:
1023:
1019:
1018:
1002:
998:
994:
981:
965:
961:
956:
952:
946:
942:
937:
933:
931:0-07-213089-X
927:
923:
918:
914:
908:
904:
900:
896:
892:
890:0-07-219281-X
886:
882:
877:
876:
872:
866:
862:
861:
847:on 2011-07-25
843:
836:
830:
827:
815:
811:
804:
801:
789:
782:
779:
768:on 2011-07-25
764:
757:
751:
748:
738:
732:
729:
719:
713:
710:
706:
693:
687:
684:
673:on 2011-07-25
669:
662:
656:
653:
642:on 2011-07-25
638:
631:
625:
622:
612:
606:
603:
596:
594:
592:
588:
584:
580:
576:
568:
566:
564:
560:
556:
552:
546:
538:
533:
529:
525:
521:
517:
513:
506:
504:
501:
497:
495:
491:
487:
483:
480:
476:
472:
468:
458:
451:
446:
442:
431:
429:
427:
423:
415:
413:
409:
407:
401:
399:
395:
391:
387:
380:
378:
375:
374:
370:
366:
362:
358:
354:
350:
346:
338:
336:
333:
328:
305:
303:
301:
297:
292:
288:
285:
281:
276:
272:
270:
261:
254:
252:
248:
244:
238:
233:
226:
224:
222:
218:
214:
210:
206:
201:
198:
194:
193:hash function
190:
187:
181:
173:
168:
164:
160:
156:
152:
148:
138:
132:
127:
123:
112:
110:
106:
104:
100:
96:
91:
87:
85:
79:
77:
73:
69:
65:
61:
51:
45:
40:
36:
19:
1373:
1133:
1108:cite journal
1099:
1094:Patent Storm
1026:. Retrieved
1008:. Retrieved
980:cite journal
968:. Retrieved
963:
940:
921:
898:
880:
849:. Retrieved
842:the original
829:
817:. Retrieved
803:
791:. Retrieved
781:
770:. Retrieved
763:the original
750:
731:
712:
703:
696:. Retrieved
686:
675:. Retrieved
668:the original
655:
644:. Retrieved
637:the original
624:
605:
572:
561:, DSMLT and
547:
515:
511:
510:
502:
498:
484:designed by
474:
470:
466:
465:
440:
419:
410:
402:
389:
385:
384:
376:
342:
329:
325:
293:
289:
277:
273:
266:
249:
245:
242:
205:EtherChannel
202:
182:
167:IEEE 802.3ad
150:
146:
145:
121:
107:
101:(SMLT), and
88:
80:
63:
59:
58:
34:
1465:and systems
1409:IP-VPN Lite
386:Routed-SMLT
298:(OSPF) and
284:end station
197:MAC address
1613:Categories
1297:VPN router
1191:Avaya Inc.
865:US 7173934
851:2007-06-25
772:2007-06-25
737:US 8861338
718:US 7463579
677:2007-06-25
646:2007-06-25
597:References
593:products.
537:US 6496502
496:protocol.
428:products.
221:five nines
172:US 7173934
1347:Protocols
943:. Tebbo.
705:failures.
583:MERS 8600
426:MERS 8600
369:MERS 8600
255:Operation
189:algorithm
97:(DSMLT),
1629:Ethernet
1588:Category
1539:Definity
1527:products
1462:Software
1211:switches
1198:Products
1082:Archived
1069:Archived
1057:Archived
1045:Archived
793:July 10,
591:VSP-9000
587:VSP-7000
579:ERS 8600
482:protocol
422:ERS 8600
394:protocol
373:VSP 9000
365:ERS 8600
361:ERS 8800
357:ERS 8300
353:ERS 7000
349:ERS 5600
345:ERS 5500
76:Ethernet
1598:Commons
1565:Tenovis
1525:Retired
1452:CS1000M
1447:CS1000E
1429:Servers
1419:UNIStim
1206:Routers
1136:. IETF.
1028:29 July
1010:29 July
66:) is a
1654:Nortel
1544:Merlin
1497:Scopia
1442:CS2100
1437:AS5300
1330:1120SA
947:
928:
909:
887:
743:
724:
617:
563:R-SMLT
543:
524:Nortel
390:R-SMLT
381:R-SMLT
178:
163:Nortel
103:R-SMLT
72:Nortel
1619:Avaya
1553:Other
1414:VLACP
1394:RSMLT
1389:DSMLT
1325:1120E
1320:1140E
1004:(PDF)
970:3 Sep
845:(PDF)
838:(PDF)
819:3 Sep
766:(PDF)
759:(PDF)
698:2 Sep
671:(PDF)
664:(PDF)
640:(PDF)
633:(PDF)
575:Avaya
516:DSMLT
473:) or
335:for.
237:Avaya
213:RSMLT
209:DSMLT
1384:SMLT
1379:DMLT
1121:help
1030:2011
1012:2011
993:help
972:2011
945:ISBN
926:ISBN
907:ISBN
885:ISBN
821:2011
795:2012
700:2011
589:and
559:SMLT
555:DMLT
532:SMLT
471:DMLT
322:SMLT
211:and
151:SMLT
1404:PBT
1399:IST
1374:MLT
1291:NAC
1208:and
280:ARP
64:MLT
1615::
1132:.
1112::
1110:}}
1106:{{
984::
982:}}
978:{{
964:15
962:.
812:.
702:.
585:,
581:,
557:,
553:,
371:,
367:,
363:,
359:,
355:,
351:,
347:,
169:.
1293:)
1289:(
1183:e
1176:t
1169:v
1123:)
1119:(
1100:8
1032:.
1014:.
995:)
991:(
974:.
953:.
934:.
915:.
893:.
854:.
823:.
797:.
775:.
680:.
649:.
530:(
514:(
469:(
388:(
149:(
62:(
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.