61:
287:, and that they were raised to a full theme some time after 695, probably in the early years of the 8th century, but the phrasing of the sources does not make clear whether that had been done by 711. Some modern scholars, like Ralph-Johannes Lilie and John Haldon, however, have argued that the Thracesian army is to be identified with the
245:, after which it was named, it was one of the larger and more important themes of the Empire throughout its existence based on its proximity to Constantinople. The Thracesian Theme was one of the longest-lived themes, surviving until the region was conquered by the
592:
in the south. The theme contained some 20 cities, although most of them were much reduced from their late antique status. Smyrna and
Ephesus (known as "Theologos" at the time) were probably the largest among them. The Persian geographer
403:, especially the monks, so that by 772, in the words of historian Warren Treadgold, he seems to have succeeded in "eradicating monasticism within his theme". Other notable governors of the theme include
1519:
1261:
509:
of
Pyrgion and Kaloe in the upper Kaystros valley. Basil Chrysomalles is the first known governor after 1204, and the list of governors from 1233 until 1260 is almost complete. The theme of
450:
In the 10th century, as the threat of Arab raids subsided, the soldiers of the
Thracesians appear to have been used more and more in overseas expeditions, such as those sent against the
392:
by the emperor on suspicion of conspiracy. Constantine took care to appoint a series of governors loyal to him and his policies, the most prominent among them being the ardent
1254:
1524:
1247:
961:
909:
893:
841:
820:
720:
389:
1534:
520:, and played an important role as a bulwark against their raids. By the early 14th century, however, it had been restricted to the area around
1119:
Catalogue of
Byzantine Seals at Dumbarton Oaks and in the Fogg Museum of Art, Volume 3: West, Northwest, and Central Asia Minor and the Orient
1160:
1031:
295:
army") mentioned in a decree of 687, and that consequently the
Thracesian theme was one of the original themes established in Asia Minor.
1209:
1181:
1127:
1079:
1055:
1010:
455:
316:. This is further supported by the fact that units that are known to have been part of the latter in the 4th/5th centuries, the
351:
in the 10th century. This provides the
Thracesian theme with the distinction of fielding some of the oldest known units of the
257:
As with the other themes, the exact date of foundation is unclear. The
Thracesians are first securely attested in 711, when a "
1070:
612:, who wrote a generation earlier, puts them as high as 10,000. In 949, its senior-most officers were, in order of rank, the
454:
in 911, 949 and 960. The same process saw the theme gradually becoming a peaceful backwater; when the formidable general
604:
ranked in the first tier of thematic governors and received an annual salary of 40 pounds of gold. The Arab geographer
1529:
234:
41:
1239:
1270:
597:, who wrote c. 847, mentions Ephesus as the capital, but this is not certain; it may instead have been at Chonae.
1201:
517:
321:
241:(modern Turkey). Created either in the mid-7th or the early 8th century as the settlement of the former Army of
470:
298:
The name of the theme derives from the fact that the themes were formed in the mid-7th century, following the
1230:(1965). "L'Histoire et la Géographie de la région de Smyrne entre les deux occupations turques (1081–1317)".
492:
436:
416:
299:
277:
is only attested as late as 741. It is hence traditionally assumed that the
Thracesians were initially a
585:
541:
396:
481:(r. 1118–1143) re-established the theme as an administrative unit, albeit with a reduced size, under a
462:
in 1029, the appointment was seen as a demotion, intended to curb his suspected designs on the throne.
1234:(in French). Paris, France: Centre de recherche d'histoire et civilisation de Byzance. pp. 1–204.
510:
1436:
605:
444:
393:
516:
The
Thracesian Theme was one of the last Byzantine territories in Asia Minor to fall to the various
1466:
1454:
1448:
1353:
1341:
1113:
1401:
1306:
1003:
A Byzantine
Government in Exile: Government and Society Under the Laskarids of Nicaea (1204-1261)
428:
525:
1460:
1424:
1383:
1365:
1335:
1205:
1177:
1156:
1123:
1075:
1065:
1051:
1027:
1006:
589:
553:
370:
312:
246:
242:
164:
1490:
1377:
1359:
1274:
1227:
1191:
1146:
478:
451:
404:
331:
308:
231:
45:
1484:
1430:
420:
356:
303:
20:
1472:
1442:
1418:
1389:
1302:
1296:
649:
594:
577:
569:
496:
440:
352:
284:
209:
193:
1513:
1395:
1279:
653:
474:
381:
361:
1502:
Thrace and Macedonia were counted among the Eastern themes for hierarchical purposes
60:
609:
466:
424:
412:
268:
1195:
1171:
1150:
1117:
1045:
1021:
1478:
1041:
614:
565:
501:
488:
432:
400:
264:
259:
91:
302:, as military encampment areas for the remnants of the old field armies of the
1310:
557:
385:
318:
238:
1329:
640:
366:
273:
1371:
1323:
71:
491:. The southern portion of the old theme became part of the new theme of
1347:
608:, who wrote c. 930, gives the troops under his command as 6,000, while
561:
131:
83:
581:
573:
521:
355:. This origin is reflected in the mythical story narrated by Emperor
292:
279:
95:
87:
513:, with its seat at Antioch-on-the-Maeander, was subordinated to it.
447:, Michael III's protégé who eventually usurped the throne from him.
1090:
1122:. Washington, DC: Dumbarton Oaks Research Library and Collection.
549:
545:
537:
1023:
Byzantium in the Seventh Century: The Transformation of a Culture
1243:
435:(r. 842–867) and the Empire's leading general, in 856–863; and
536:
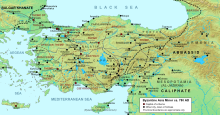
The theme of the Thracesians comprised the ancient regions of
483:
469:
in the late 1070s, but most of its territory was recovered by
263:
of the Thracesians" named Christopher was dispatched against
221:
31:
1047:
Warfare, State and Society in the Byzantine World, 565–1204
644:. The coast was also under the parallel authority of the
306:; in the case of the Thracesians, the field army of the
572:
in the north, probably along the valley of the river
1099:(in Greek). Athens: Foundation of the Hellenic World
505:
of Smyrna and Anaia along the Aegean coast, and the
443:
George Peganes tried to oppose the growing power of
1410:
1288:
1155:. Stanford, California: Stanford University Press.
1141:(in Italian). Rome: Biblioteca Apostolica Vaticana.
380:of the Thracesians, a certain Sisinnios, supported
161:
146:
128:
118:
106:
79:
28:
1520:States and territories disestablished in the 1330s
701:
399:. Lachanodrakon launched a brutal persecution of
1074:. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press.
1097:Encyclopedia of the Hellenic World, Asia Minor
1255:
427:in 841 and married into the imperial family;
369:settled there in the early 6th century BC by
8:
1197:A History of the Byzantine State and Society
556:. The theme was bordered on the west by the
1262:
1248:
1240:
365:, whereby the region was named after some
237:(a military-civilian province) in western
59:
25:
1026:. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
985:
877:
865:
853:
780:
33:Θρᾳκήσιον θέμα, θέμα Θρᾳκησίων, Θρᾳκήσιοι
1139:Constantino Porfirogenito: De Thematibus
1089:Lambakis, Stylianos (October 17, 2003).
957:
905:
889:
837:
816:
716:
712:
710:
697:
695:
693:
691:
1176:. Stanford: Stanford University Press.
973:
945:
833:
831:
829:
804:
768:
732:
664:
656:, who drew crews and ships from there.
465:The theme was briefly conquered by the
78:
933:
921:
792:
756:
744:
678:
676:
674:
672:
670:
668:
560:, with its coastline stretching from
439:, who along with the governor of the
339:, are attested again as the thematic
181:
177:
160:
145:
127:
117:
113:
101:
7:
499:, and by this time consisted of the
388:(r. 741–742), but was himself later
16:Byzantine military-civilian province
1525:7th century in the Byzantine Empire
1005:. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
524:, until that city also fell to the
1071:The Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium
685:, "Thrakesion" (C. Foss), p. 2080.
69:in c. 780, after the split of the
14:
495:. It was reconstituted under the
411:in the 790s and rebelled against
384:(r. 740–775) against the usurper
1173:Byzantium and Its Army, 284–1081
682:
580:in the east (somewhere east of
52:640s–660s / 700s–710s – c. 1078
1535:Themes of the Byzantine Empire
1152:The Byzantine Revival, 780–842
702:Nesbitt & Oikonomides 1996
204:), more properly known as the
23:, which was located in Europe.
1:
1170:Treadgold, Warren T. (1995).
152:
137:
532:Geography and administration
327:Equites Theodosiaci Iuniores
19:Not to be confused with the
249:in the early 14th century.
1551:
1411:Western or European themes
222:
148:• Byzantine recovery
32:
18:
1500:
1202:Stanford University Press
868:, pp. 325, 355, 454.
540:(the late Roman province
359:(reigned 913–959) in his
213:
197:
182:
178:
174:
124:640s–660s or c. 700s–710s
114:
102:
58:
51:
40:
1200:. Stanford, California:
1091:
1020:Haldon, John F. (1997).
1001:Angold, Michael (1975).
206:Theme of the Thracesians
29:Theme of the Thracesians
1289:Eastern or Asian themes
548:, the northern half of
600:The theme's governing
493:Mylasa and Melanoudion
437:Symbatios the Armenian
417:Constantine Kontomytes
90:(7th–11th centuries),
1232:Travaux et mémoires 1
1050:. London: UCL Press.
586:Laodicea on the Lycus
473:with the help of the
415:(r. 803–811) in 803;
397:Michael Lachanodrakon
98:(12th–14th centuries)
1137:Pertusi, A. (1952).
1114:Oikonomides, Nicolas
456:Constantine Diogenes
445:Basil the Macedonian
289:Thracianus exercitus
271:, while a governing
880:, pp. 450–451.
856:, pp. 364–365.
747:, pp. 212–214.
477:in the late 1090s.
419:, who defeated the
163:• Fall to the
130:• Fall to the
120:• Established
1530:Byzantine Anatolia
1066:Kazhdan, Alexander
936:, pp. 246–248
783:, pp. 97–100.
735:, pp. 124–125
332:auxilium palatinum
283:(division) of the
1507:
1506:
1384:Cibyrrhaeot Theme
1336:Bucellarian Theme
1228:Ahrweiler, Hélène
1192:Treadgold, Warren
1162:978-0-8047-1462-4
1147:Treadgold, Warren
1033:978-0-521-31917-1
634:of the seacoast (
606:Qudama ibn Ja'far
590:Cibyrrhaeot Theme
554:Phrygia Pacatiana
371:Alyattes of Lydia
186:
185:
1542:
1318:Thracesian Theme
1275:Byzantine Empire
1264:
1257:
1250:
1241:
1235:
1215:
1187:
1166:
1142:
1133:
1108:
1106:
1104:
1085:
1061:
1037:
1016:
989:
983:
977:
971:
965:
955:
949:
943:
937:
931:
925:
919:
913:
903:
897:
887:
881:
875:
869:
863:
857:
851:
845:
835:
824:
814:
808:
802:
796:
790:
784:
778:
772:
766:
760:
754:
748:
742:
736:
730:
724:
714:
705:
699:
686:
680:
479:John II Komnenos
452:Emirate of Crete
405:Bardanes Tourkos
376:The first known
309:magister militum
300:Muslim conquests
225:
224:
218:thema Thrakēsiōn
215:
202:Thrakēsion thema
199:
190:Thracesian Theme
157:
154:
142:
139:
63:
46:Byzantine Empire
35:
34:
26:
1550:
1549:
1545:
1544:
1543:
1541:
1540:
1539:
1510:
1509:
1508:
1503:
1496:
1485:Cherson/Klimata
1406:
1284:
1268:
1238:
1226:
1222:
1220:Further reading
1212:
1190:
1184:
1169:
1163:
1145:
1136:
1130:
1116:, eds. (1996).
1112:Nesbitt, John;
1111:
1102:
1100:
1093:
1088:
1082:
1064:
1058:
1040:
1034:
1019:
1013:
1000:
997:
992:
984:
980:
972:
968:
956:
952:
944:
940:
932:
928:
920:
916:
904:
900:
888:
884:
876:
872:
864:
860:
852:
848:
836:
827:
815:
811:
803:
799:
791:
787:
779:
775:
767:
763:
755:
751:
743:
739:
731:
727:
715:
708:
700:
689:
681:
666:
662:
534:
526:Beylik of Aydın
518:Turkish beyliks
431:, the uncle of
421:Cretan Saracens
357:Constantine VII
304:East Roman army
255:
220:, often simply
167:
155:
149:
140:
134:
121:
64:
53:
36:
24:
21:Theme of Thrace
17:
12:
11:
5:
1548:
1546:
1538:
1537:
1532:
1527:
1522:
1512:
1511:
1505:
1504:
1501:
1498:
1497:
1495:
1494:
1487:
1481:
1475:
1469:
1463:
1457:
1451:
1445:
1439:
1433:
1427:
1421:
1414:
1412:
1408:
1407:
1405:
1404:
1398:
1392:
1386:
1380:
1374:
1368:
1362:
1356:
1350:
1344:
1338:
1332:
1326:
1324:Opsician Theme
1320:
1314:
1303:Armeniac Theme
1299:
1297:Anatolic Theme
1292:
1290:
1286:
1285:
1269:
1267:
1266:
1259:
1252:
1244:
1237:
1236:
1223:
1221:
1218:
1217:
1216:
1210:
1188:
1182:
1167:
1161:
1143:
1134:
1128:
1109:
1092:Θρακησίων Θέμα
1086:
1080:
1068:, ed. (1991).
1062:
1056:
1038:
1032:
1017:
1011:
996:
993:
991:
990:
986:Treadgold 1995
978:
976:, p. 126.
966:
950:
948:, p. 125.
938:
926:
914:
898:
882:
878:Treadgold 1997
870:
866:Treadgold 1988
858:
854:Treadgold 1997
846:
825:
809:
797:
795:, p. 112.
785:
781:Treadgold 1995
773:
771:, p. 124.
761:
749:
737:
725:
706:
687:
663:
661:
658:
595:Ibn Khordadbeh
578:Anatolic Theme
570:Opsician Theme
552:, and part of
533:
530:
497:Nicaean Empire
458:was named its
441:Opsician Theme
407:, who was its
353:Byzantine army
285:Anatolic Theme
254:
251:
214:θέμα Θρᾳκησίων
198:Θρᾳκήσιον θέμα
184:
183:
180:
179:
176:
175:
172:
171:
168:
162:
159:
158:
150:
147:
144:
143:
135:
129:
126:
125:
122:
119:
116:
115:
112:
111:
108:
107:Historical era
104:
103:
100:
99:
81:
77:
76:
65:The Byzantine
56:
55:
49:
48:
38:
37:
30:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1547:
1536:
1533:
1531:
1528:
1526:
1523:
1521:
1518:
1517:
1515:
1499:
1492:
1488:
1486:
1482:
1480:
1476:
1474:
1470:
1468:
1464:
1462:
1458:
1456:
1452:
1450:
1446:
1444:
1440:
1438:
1434:
1432:
1428:
1426:
1422:
1420:
1416:
1415:
1413:
1409:
1403:
1399:
1397:
1393:
1391:
1387:
1385:
1381:
1379:
1375:
1373:
1369:
1367:
1363:
1361:
1357:
1355:
1351:
1349:
1345:
1343:
1339:
1337:
1333:
1331:
1327:
1325:
1321:
1319:
1315:
1312:
1308:
1304:
1300:
1298:
1294:
1293:
1291:
1287:
1282:
1281:
1280:De Thematibus
1277:according to
1276:
1272:
1265:
1260:
1258:
1253:
1251:
1246:
1245:
1242:
1233:
1229:
1225:
1224:
1219:
1213:
1211:0-8047-2630-2
1207:
1203:
1199:
1198:
1193:
1189:
1185:
1183:0-8047-3163-2
1179:
1175:
1174:
1168:
1164:
1158:
1154:
1153:
1148:
1144:
1140:
1135:
1131:
1129:0-88402-250-1
1125:
1121:
1120:
1115:
1110:
1098:
1094:
1087:
1083:
1081:0-19-504652-8
1077:
1073:
1072:
1067:
1063:
1059:
1057:1-85728-495-X
1053:
1049:
1048:
1043:
1039:
1035:
1029:
1025:
1024:
1018:
1014:
1012:0-19-821854-0
1008:
1004:
999:
998:
994:
988:, p. 99.
987:
982:
979:
975:
970:
967:
963:
959:
958:Lambakis 2003
954:
951:
947:
942:
939:
935:
930:
927:
924:, p. 97.
923:
918:
915:
911:
907:
906:Lambakis 2003
902:
899:
895:
891:
890:Lambakis 2003
886:
883:
879:
874:
871:
867:
862:
859:
855:
850:
847:
843:
839:
838:Lambakis 2003
834:
832:
830:
826:
822:
818:
817:Lambakis 2003
813:
810:
807:, p. 60.
806:
801:
798:
794:
789:
786:
782:
777:
774:
770:
765:
762:
759:, p. 73.
758:
753:
750:
746:
741:
738:
734:
729:
726:
722:
718:
717:Lambakis 2003
713:
711:
707:
703:
698:
696:
694:
692:
688:
684:
679:
677:
675:
673:
671:
669:
665:
659:
657:
655:
651:
647:
643:
642:
637:
633:
629:
625:
621:
617:
616:
611:
607:
603:
598:
596:
591:
587:
583:
579:
575:
571:
567:
563:
559:
555:
551:
547:
543:
539:
531:
529:
527:
523:
519:
514:
512:
508:
504:
503:
498:
494:
490:
486:
485:
480:
476:
475:First Crusade
472:
468:
463:
461:
457:
453:
448:
446:
442:
438:
434:
430:
426:
422:
418:
414:
410:
406:
402:
398:
395:
391:
387:
383:
382:Constantine V
379:
374:
372:
368:
364:
363:
362:De Thematibus
358:
354:
350:
346:
342:
338:
334:
333:
328:
324:
323:
320:
315:
314:
310:
305:
301:
296:
294:
290:
286:
282:
281:
276:
275:
270:
266:
262:
261:
252:
250:
248:
244:
240:
236:
233:
229:
219:
211:
207:
203:
195:
191:
173:
169:
166:
151:
136:
133:
123:
109:
105:
97:
93:
89:
85:
82:
74:
73:
68:
62:
57:
50:
47:
43:
39:
27:
22:
1437:Thessalonica
1317:
1278:
1231:
1196:
1172:
1151:
1138:
1118:
1101:. Retrieved
1096:
1069:
1046:
1042:Haldon, John
1022:
1002:
981:
974:Pertusi 1952
969:
953:
946:Pertusi 1952
941:
929:
917:
901:
885:
873:
861:
849:
812:
805:Pertusi 1952
800:
788:
776:
769:Pertusi 1952
764:
752:
740:
733:Pertusi 1952
728:
704:, p. 4.
645:
639:
636:tēs paraliou
635:
631:
627:
623:
620:Theodosiakoi
619:
613:
610:Ibn al-Faqih
601:
599:
535:
515:
506:
500:
489:Philadelphia
482:
467:Seljuk Turks
464:
459:
449:
425:Mount Latros
413:Nikephoros I
408:
377:
375:
360:
348:
345:Theodosiakoi
344:
340:
336:
330:
326:
317:
307:
297:
288:
278:
272:
269:Justinian II
258:
256:
227:
217:
205:
201:
189:
187:
92:Philadelphia
70:
66:
1479:Longobardia
1467:Dyrrhachium
1455:Cephallenia
1449:Peloponnese
1354:Mesopotamia
1342:Paphlagonia
962:Chapter 2.2
934:Angold 1975
922:Haldon 1999
793:Haldon 1999
757:Haldon 1999
745:Haldon 1997
721:Chapter 2.1
632:tourmarchēs
624:tourmarchēs
615:tourmarchēs
588:), and the
566:Adramyttion
502:katepanikia
471:John Doukas
433:Michael III
401:iconophiles
267:by Emperor
260:tourmarchēs
156: 1097
141: 1078
110:Middle Ages
1514:Categories
1489:(omitted:
1402:Aegean Sea
1311:Charsianon
1307:Cappadocia
660:References
641:meriarchēs
558:Aegean Sea
394:iconoclast
386:Artabasdos
319:vexillatio
239:Asia Minor
228:Thrakēsioi
94:and later
1461:Nicopolis
1425:Macedonia
1366:Sebasteia
1330:Optimates
1103:7 October
910:Chapter 5
894:Chapter 4
842:Chapter 3
821:Chapter 1
652:theme of
646:stratēgos
638:), and a
602:stratēgos
528:in 1330.
487:based at
460:stratēgos
409:stratēgos
378:stratēgos
367:Thracians
274:stratēgos
232:Byzantine
230:), was a
223:Θρᾳκήσιοι
54:1097–1330
1491:Dalmatia
1378:Seleucia
1372:Lykandos
1360:Koloneia
1283:(c. 950)
1194:(1997).
1149:(1988).
1044:(1999).
628:Viktores
511:Maeander
429:Petronas
349:Viktores
337:Victores
329:and the
322:palatina
313:Thracias
293:Thracian
72:Opsikion
1431:Strymon
1348:Chaldia
1305:(incl.
1273:of the
995:Sources
648:of the
626:of the
618:of the
576:), the
562:Ephesus
390:blinded
343:of the
341:tourmai
335:of the
325:of the
265:Cherson
253:History
132:Seljuks
84:Ephesus
80:Capital
67:themata
44:of the
1473:Sicily
1443:Hellas
1419:Thrace
1390:Cyprus
1271:Themes
1208:
1180:
1159:
1126:
1078:
1054:
1030:
1009:
630:, the
622:, the
582:Chonae
574:Caicus
568:, the
522:Smyrna
280:tourma
243:Thrace
96:Smyrna
88:Chonae
1396:Samos
654:Samos
650:naval
550:Caria
546:Lydia
538:Ionia
507:chora
247:Turks
235:theme
210:Greek
194:Greek
165:Turks
42:Theme
1483:12.
1477:11.
1471:10.
1400:17.
1394:16.
1388:15.
1382:14.
1376:13.
1370:12.
1364:11.
1358:10.
1309:and
1206:ISBN
1178:ISBN
1157:ISBN
1124:ISBN
1105:2009
1076:ISBN
1052:ISBN
1028:ISBN
1007:ISBN
584:and
542:Asia
484:doux
347:and
311:per
188:The
170:1330
1465:9.
1459:8.
1453:7.
1447:6.
1441:5.
1435:4.
1429:3.
1423:2.
1417:1.
1352:9.
1346:8.
1340:7.
1334:6.
1328:5.
1322:4.
1316:3.
1301:2.
1295:1.
683:ODB
564:to
544:),
423:at
86:or
1516::
1204:.
1095:.
960:,
908:,
892:,
840:,
828:^
819:,
719:,
709:^
690:^
667:^
373:.
291:("
226:,
216:,
212::
200:,
196::
153:c.
138:c.
1493:)
1313:)
1263:e
1256:t
1249:v
1214:.
1186:.
1165:.
1132:.
1107:.
1084:.
1060:.
1036:.
1015:.
964:.
912:.
896:.
844:.
823:.
723:.
208:(
192:(
75:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.