703:
379:. This is because the partial pressure of oxygen is lower at higher altitude which, as a result means that oxygen less readily diffuses into the bloodstream. In response to higher altitude, the body's diffusing capacity increases in order to process more air. Also, due to the lower environmental air pressure at higher altitudes, the air pressure within the breathing system must be lower in order to inhale; in order to meet this requirement, the thoracic diaphragm has a tendency to lower to a greater extent during inhalation, which in turn causes an increase in lung volume.
35:
663:(0.24 for men and 0.28 for women) or in relation to height and age ((0.0275* Age +0.0189*Height −2.6139) litres for normal-mass individuals and (0.0277*Age +0.0138*Height −2.3967) litres for overweight individuals). Standard errors in prediction equations for residual volume have been measured at 579 ml for men and 355 ml for women, while the use of 0.24*FVC gave a standard error of 318 ml.
443:
by 30–40% giving an increase in pulmonary ventilation. This is necessary to meet the increased oxygen requirement of the body, which reaches 50 ml/min, 20 ml of which goes to reproductive tissues. Overall, the net change in maximum breathing capacity is zero.
117:
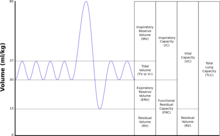
Tidal volume: that volume of air moved into or out of the lungs during quiet breathing (VT indicates a subdivision of the lung; when tidal volume is precisely measured, as in gas exchange calculation, the symbol TV or
53:
Tidal volume: that volume of air moved into or out of the lungs in 1 breath (TV indicates a subdivision of the lung; when tidal volume is precisely measured, as in gas exchange calculation, the symbol TV or
224:
Forced inspiratory flow: (Specific measurement of the forced inspiratory curve is denoted by nomenclature analogous to that for the forced expiratory curve. For example, maximum inspiratory flow is denoted
402:
because their lungs remove adequate amounts of carbon dioxide but they do not take in enough oxygen. (In normal individuals, carbon dioxide is the primary determinant of respiratory drive.)
640:
is more difficult as it is impossible to "completely" breathe out. Therefore, measurement of the residual volume has to be done via indirect methods such as radiographic planimetry,
1518:
1196:
669:
that can compute predicted lung volumes, and other spirometric parameters based on a patient's age, height, weight, and ethnic origin for many reference sources.
405:
Lung function development is reduced in children who grow up near motorways although this seems at least in part reversible. Air pollution exposure affects FEV
267:
416:
1884:
1440:
332:
Several factors affect lung volumes; some can be controlled, and some cannot be controlled. Lung volumes vary with different people as follows:
688:
The mass of one breath is approximately a gram (0.5-5 g). A litre of air weighs about 1.2 g (1.2 kg/m). A half litre ordinary tidal breath
1140:
1115:
889:
862:
777:
1511:
751:
2003:
1212:"Comprehensive integrated spirometry using raised volume passive and forced expirations and multiple-breath nitrogen washout in infants"
1955:
1810:
1172:
702:
260:
1998:
1504:
1874:
1601:
179:
Forced expiratory volume (time): a generic term indicating the volume of air exhaled under forced conditions in the first
1993:
1723:
1269:"The use of actual predicted and constant residual volumes in the assessment of body composition by underwater weighing"
420:
941:
1893:
1842:
1693:
253:
975:
Gauderman, W (2007). "Effect of exposure to traffic on lung development from 10 to 18 years of age: a cohort study".
1847:
801:
1394:
229:. Unless otherwise specified, volume qualifiers indicate the volume inspired from RV at the point of measurement.)
1755:
1686:
1667:
645:
432:
205:
Forced expiratory flow related to some portion of the FVC curve; modifiers refer to amount of FVC already exhaled
1698:
1831:
1662:
1556:
1864:
1733:
629:
245:
Maximal voluntary ventilation: volume of air expired in a specified period during repetitive maximal effort
1681:
1628:
1618:
1527:
984:
74:
Expiratory reserve volume: the maximal volume of air that can be exhaled from the end-expiratory position
1869:
1805:
1044:"Short-term air pollution exposure decreases lung function: a repeated measures study in healthy adults"
168:
Forced vital capacity: the determination of the vital capacity from a maximally forced expiratory effort
1924:
1779:
1743:
1578:
1573:
641:
989:
706:
Scheme of changes in lung volumes in restricted and obstructed lung in comparison with healthy lung.
1606:
1471:
946:
428:
98:
Inspiratory vital capacity: the maximum volume of air inhaled from the point of maximum expiration
1934:
1929:
1909:
1767:
1643:
1190:
1010:
747:
440:
424:
82:
Inspiratory reserve volume: the maximal volume that can be inhaled from the end-inspiratory level
659:
have been prepared as a proportion of body mass for infants (18.1 ml/kg), or as a proportion of
1972:
1888:
1854:
1656:
1611:
1593:
1448:
1364:
1323:
1249:
1231:
1178:
1168:
1136:
1111:
1075:
1002:
951:
922:
885:
879:
858:
399:
1105:
852:
1789:
1738:
1648:
1563:
1491:
1354:
1313:
1280:
1239:
1223:
1065:
1055:
994:
914:
789:
often low (asthma can reduce the ratio to 0.6, emphysema can reduce the ratio to 0.78–0.45)
718:
and FRC) can be used to distinguish between restrictive and obstructive pulmonary diseases:
649:
387:
375:
will develop a slightly smaller lung capacity than a person who spends their life at a high
321:
1967:
1815:
1784:
1419:"Pete Reed: Three-time Olympic rowing champion on spinal stroke, paralysis and the future"
382:
When someone living at or near sea level travels to locations at high altitudes (e.g. the
1486:
324:
is 30–60 breaths per minute at birth, decreasing to 12–20 breaths per minute in adults.
237:
Peak expiratory flow: The highest forced expiratory flow measured with a peak flow meter
45:
Total lung capacity: the volume in the lungs at maximal inflation, the sum of VC and RV.
1913:
1903:
1760:
1718:
1583:
1244:
1211:
1070:
1043:
677:
548:
423:
drops 18–20%, typically falling from 1.7 to 1.35 litres, due to the compression of the
998:
1987:
1919:
1675:
1588:
1359:
1343:"Accuracy of measured and predicted residual lung volume on body density measurement"
1342:
1318:
1301:
1285:
1268:
130:
Functional residual capacity: the volume in the lungs at the end-expiratory position
66:
Residual volume: the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a maximal exhalation
1859:
1728:
1568:
755:
676:
is reported to hold the largest recorded lung capacity of 11.68 litres; US swimmer
436:
314:
34:
17:
1014:
881:
Delmar's
Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative and Clinical Competencies
878:
Wilburta Q. Lindh; Marilyn Pooler; Carol
Tamparo; Barbara M. Dahl (9 March 2009).
1898:
194:
Volume that has been exhaled at the end of the first second of forced expiration
1227:
1960:
1879:
1774:
1551:
1546:
1418:
1182:
1060:
1028:
905:
Jones RL, Nzekwu MM (2006). "The effects of body mass index on lung volumes".
807:
624:
317:
is the volume of air that is inhaled or exhaled in only a single such breath.
1452:
1235:
955:
1836:
918:
827:
781:
673:
395:
372:
300:
106:
Vital capacity: the volume of air breathed out after the deepest inhalation.
1253:
1079:
1006:
926:
691:
weighs 0.6 g; a maximal 4.8 litre breath (average vital capacity for males)
1368:
1327:
1496:
711:
376:
160:
Actual volume of the lung including the volume of the conducting airway.
1302:"Derivation of prediction equations for RV in overweight men and women"
1300:
MILLER, WAYNE C.; SWENSEN, THOMAS; WALLACE, JANET P. (February 1998).
666:
1541:
773:
307:
288:
1110:(3rd ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 65–66.
701:
391:
383:
306:
The average total lung capacity of an adult human male is about 6
1938:
1637:
296:
1500:
1167:. Derrickson, Bryan (15th ed.). Hoboken, NJ. p. 874.
1341:
Morrow JR Jr; Jackson AS; Bradley PW; Hartung GH. (Dec 1986).
292:
216:
The maximum instantaneous flow achieved during a FVC maneuver
1381:
English
Institute of Sport, 17 November 2006, test ID 27781
680:
is also said to have a lung capacity of around 12 litres.
786:
volumes are essentially normal but flow rates are impeded
1441:"London 2012 Olympics: Faster. Higher. Longer. Stronger"
427:
by the uterus. The compression also causes a decreased
1135:(11 ed.). Philadelphia: Saunders. pp. 103g.
1395:"Making sense of breathing, VO2max and lung capacity"
1948:
1824:
1798:
1709:
1627:
1534:
1104:Simpson, Kathleen Rice; Patricia A Creehan (2007).
1099:
1097:
1095:
1093:
1091:
1089:
672:British rower and three-time Olympic gold medalist
241:
233:
220:
209:
198:
187:
172:
164:
153:
142:
134:
126:
110:
102:
94:
86:
78:
70:
62:
49:
41:
313:Tidal breathing is normal, resting breathing; the
1439:Smith, Michael Hanlon and Jennifer (2012-08-03).
439:increases by 30–40%, from 0.5 to 0.7 litres, and
627:. These are the basic elements of a ventilatory
1306:Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise
1029:"Study Findings – USC Children's Health Study"
413:in healthy adults even at low concentrations.
1512:
1487:Lung function fundamentals (anaesthetist.com)
419:in lung volumes also occur during pregnancy.
398:) that person can develop a condition called
261:
8:
409:in asthmatics, but also affects FVC and FEV
138:Residual volume expressed as percent of TLC
90:Inspiratory capacity: the sum of IRV and TV
1519:
1505:
1497:
1195:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
268:
254:
33:
1358:
1317:
1284:
1243:
1216:Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology
1069:
1059:
988:
644:, closed circuit dilution (including the
942:"Living Near Freeways Hurts Kids' Lungs"
720:
520:
451:
334:
819:
1188:
1165:Principles of anatomy & physiology
454:Average lung volumes in healthy adults
29:
1389:
1387:
1158:
1156:
1154:
1152:
340:
337:
7:
1885:oxygen–hemoglobin dissociation curve
1472:Atmosphere of Earth#Density and mass
752:Infant Respiratory Distress Syndrome
857:. Trafford Publishing. p. 30.
851:Scott L. DeBoer (4 November 2004).
357:people who live at lower altitudes
354:people who live at higher altitudes
1811:hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction
763:often in a normal range (0.8–1.0)
371:A person who is born and lives at
25:
884:. Cengage Learning. p. 573.
655:In absence of such, estimates of
523:Lung capacities in healthy adults
476:Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
1360:10.1249/00005768-198612000-00007
1319:10.1097/00005768-199802000-00023
1286:10.1249/00005768-196906000-00006
667:Online calculators are available
623:can be measured directly with a
498:Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
940:Reinberg, Steven (2007-01-26).
1133:Textbook of Medical Physiology
1:
999:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60037-3
578:Functional residual capacity
754:, weak respiratory muscles,
694:weighs approximately 5.8 g.
597:
594:
583:
580:
569:
566:
555:
552:
542:
539:
514:
511:
503:
500:
492:
489:
481:
478:
470:
467:
421:Functional residual capacity
1843:Ventilation/perfusion ratio
1694:pulmonary stretch receptors
1163:Tortora, Gerard J. (2016).
710:The results (in particular
698:Restrictive and obstructive
299:at different phases of the
2020:
2004:Pulmonary function testing
1875:alveolar–arterial gradient
1228:10.1016/j.resp.2009.10.010
802:Pulmonary function testing
431:(TLC) by 5% and decreased
27:Volume of air in the lungs
1756:respiratory minute volume
1668:ventral respiratory group
1061:10.1186/s12940-017-0271-z
646:helium dilution technique
621:expiratory reserve volume
534:
531:
528:
462:
459:
433:expiratory reserve volume
328:Factors affecting volumes
249:
32:
1663:dorsal respiratory group
1557:obligate nasal breathing
1210:Morris, Mohy G. (2010).
1131:Guyton and hall (2005).
1865:pulmonary gas pressures
1267:Wilmore, J. H. (1969).
919:10.1378/chest.130.3.827
630:pulmonary function test
532:Average value (litres)
1999:Respiratory physiology
1619:mechanical ventilation
1528:Respiratory physiology
854:Emergency Newborn Care
707:
1870:alveolar gas equation
1806:pulmonary circulation
1492:Volume of human lungs
1042:Int Panis, L (2017).
760:volumes are decreased
705:
636:Determination of the
564:Inspiratory capacity
509:Residual volume (RV)
1925:respiratory quotient
1780:body plethysmography
1699:Hering–Breuer reflex
1574:pulmonary surfactant
1347:Med Sci Sports Exerc
1048:Environmental Health
769:obstructive diseases
743:restrictive diseases
642:body plethysmography
617:inspiratory capacity
601:IRV + TV + ERV + RV
592:Total lung capacity
1994:Respiratory therapy
1768:Lung function tests
1602:hyperresponsiveness
947:The Washington Post
525:
456:
429:total lung capacity
149:Alveolar gas volume
18:Total lung capacity
1935:diffusion capacity
1930:arterial blood gas
1910:carbonic anhydrase
1644:pneumotaxic center
748:pulmonary fibrosis
708:
521:
487:Tidal volume (TV)
452:
441:minute ventilation
320:The average human
1981:
1980:
1889:Oxygen saturation
1855:zones of the lung
1594:airway resistance
1142:978-81-8147-920-4
1117:978-0-7817-6759-0
1107:Perinatal Nursing
983:(9561): 571–577.
891:978-1-4354-1914-8
864:978-1-4120-3089-2
793:
792:
605:
604:
519:
518:
400:altitude sickness
369:
368:
301:respiratory cycle
278:
277:
16:(Redirected from
2011:
1790:nitrogen washout
1649:apneustic center
1564:respiratory rate
1521:
1514:
1507:
1498:
1474:
1469:
1463:
1462:
1460:
1459:
1436:
1430:
1429:
1427:
1426:
1415:
1409:
1408:
1406:
1405:
1391:
1382:
1379:
1373:
1372:
1362:
1338:
1332:
1331:
1321:
1297:
1291:
1290:
1288:
1264:
1258:
1257:
1247:
1207:
1201:
1200:
1194:
1186:
1160:
1147:
1146:
1128:
1122:
1121:
1101:
1084:
1083:
1073:
1063:
1039:
1033:
1032:
1025:
1019:
1018:
992:
972:
966:
965:
963:
962:
937:
931:
930:
902:
896:
895:
875:
869:
868:
848:
842:
841:
839:
838:
824:
721:
684:Weight of breath
650:nitrogen washout
526:
457:
417:Specific changes
388:Denver, Colorado
341:Smaller volumes
335:
322:respiratory rate
270:
263:
256:
37:
30:
21:
2019:
2018:
2014:
2013:
2012:
2010:
2009:
2008:
1984:
1983:
1982:
1977:
1968:oxygen toxicity
1944:
1832:ventilation (V)
1820:
1816:pulmonary shunt
1794:
1785:peak flow meter
1705:
1623:
1530:
1525:
1483:
1478:
1477:
1470:
1466:
1457:
1455:
1445:Daily Telegraph
1438:
1437:
1433:
1424:
1422:
1417:
1416:
1412:
1403:
1401:
1399:worldrowing.com
1393:
1392:
1385:
1380:
1376:
1340:
1339:
1335:
1299:
1298:
1294:
1266:
1265:
1261:
1209:
1208:
1204:
1187:
1175:
1162:
1161:
1150:
1143:
1130:
1129:
1125:
1118:
1103:
1102:
1087:
1041:
1040:
1036:
1027:
1026:
1022:
990:10.1.1.541.1258
974:
973:
969:
960:
958:
939:
938:
934:
904:
903:
899:
892:
877:
876:
872:
865:
850:
849:
845:
836:
834:
826:
825:
821:
816:
798:
736:
715:
700:
686:
657:residual volume
638:residual volume
559:IRV + TV + ERV
463:Value (litres)
450:
412:
408:
349:shorter people
330:
285:lung capacities
274:
228:
213:
202:
191:
176:
157:
146:
121:
114:
57:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2017:
2015:
2007:
2006:
2001:
1996:
1986:
1985:
1979:
1978:
1976:
1975:
1970:
1965:
1964:
1963:
1952:
1950:
1946:
1945:
1943:
1942:
1932:
1927:
1922:
1917:
1914:chloride shift
1907:
1904:Haldane effect
1901:
1896:
1891:
1882:
1877:
1872:
1867:
1862:
1857:
1852:
1851:
1850:
1845:
1834:
1828:
1826:
1822:
1821:
1819:
1818:
1813:
1808:
1802:
1800:
1796:
1795:
1793:
1792:
1787:
1782:
1777:
1772:
1770:
1764:
1763:
1761:FEV1/FVC ratio
1758:
1753:
1751:
1747:
1746:
1741:
1736:
1731:
1726:
1721:
1715:
1713:
1707:
1706:
1704:
1703:
1702:
1701:
1691:
1690:
1689:
1684:
1676:chemoreceptors
1672:
1671:
1670:
1665:
1653:
1652:
1651:
1646:
1633:
1631:
1625:
1624:
1622:
1621:
1616:
1615:
1614:
1609:
1604:
1596:
1591:
1586:
1584:elastic recoil
1581:
1576:
1571:
1566:
1561:
1560:
1559:
1554:
1549:
1538:
1536:
1532:
1531:
1526:
1524:
1523:
1516:
1509:
1501:
1495:
1494:
1489:
1482:
1481:External links
1479:
1476:
1475:
1464:
1431:
1410:
1383:
1374:
1333:
1312:(2): 322–327.
1292:
1273:Med Sci Sports
1259:
1222:(2): 123–140.
1202:
1174:978-1119447979
1173:
1148:
1141:
1123:
1116:
1085:
1034:
1020:
967:
932:
897:
890:
870:
863:
843:
828:"Lung Volumes"
818:
817:
815:
812:
811:
810:
805:
797:
794:
791:
790:
787:
784:
771:
765:
764:
761:
758:
745:
739:
738:
734:
731:
728:
725:
713:
699:
696:
685:
682:
678:Michael Phelps
661:vital capacity
613:vital capacity
603:
602:
599:
596:
593:
589:
588:
585:
582:
579:
575:
574:
571:
568:
565:
561:
560:
557:
554:
551:
549:Vital capacity
545:
544:
541:
537:
536:
533:
530:
517:
516:
513:
510:
506:
505:
502:
499:
495:
494:
491:
488:
484:
483:
480:
477:
473:
472:
469:
465:
464:
461:
449:
446:
410:
406:
367:
366:
363:
359:
358:
355:
351:
350:
347:
343:
342:
339:
338:Larger volume
329:
326:
276:
275:
273:
272:
265:
258:
250:
247:
246:
243:
239:
238:
235:
231:
230:
226:
222:
218:
217:
214:
211:
207:
206:
203:
200:
196:
195:
192:
189:
185:
184:
177:
174:
170:
169:
166:
162:
161:
158:
155:
151:
150:
147:
144:
140:
139:
136:
132:
131:
128:
124:
123:
119:
115:
112:
108:
107:
104:
100:
99:
96:
92:
91:
88:
84:
83:
80:
76:
75:
72:
68:
67:
64:
60:
59:
55:
51:
47:
46:
43:
39:
38:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2016:
2005:
2002:
2000:
1997:
1995:
1992:
1991:
1989:
1974:
1971:
1969:
1966:
1962:
1959:
1958:
1957:
1956:high altitude
1954:
1953:
1951:
1949:Insufficiency
1947:
1940:
1936:
1933:
1931:
1928:
1926:
1923:
1921:
1920:oxyhemoglobin
1918:
1915:
1911:
1908:
1905:
1902:
1900:
1897:
1895:
1892:
1890:
1886:
1883:
1881:
1878:
1876:
1873:
1871:
1868:
1866:
1863:
1861:
1858:
1856:
1853:
1849:
1846:
1844:
1841:
1840:
1838:
1835:
1833:
1830:
1829:
1827:
1823:
1817:
1814:
1812:
1809:
1807:
1804:
1803:
1801:
1797:
1791:
1788:
1786:
1783:
1781:
1778:
1776:
1773:
1771:
1769:
1766:
1765:
1762:
1759:
1757:
1754:
1752:
1749:
1748:
1745:
1742:
1740:
1737:
1735:
1732:
1730:
1727:
1725:
1722:
1720:
1717:
1716:
1714:
1712:
1708:
1700:
1697:
1696:
1695:
1692:
1688:
1685:
1683:
1680:
1679:
1678:
1677:
1673:
1669:
1666:
1664:
1661:
1660:
1659:
1658:
1654:
1650:
1647:
1645:
1642:
1641:
1640:
1639:
1635:
1634:
1632:
1630:
1626:
1620:
1617:
1613:
1610:
1608:
1605:
1603:
1600:
1599:
1597:
1595:
1592:
1590:
1589:hysteresivity
1587:
1585:
1582:
1580:
1577:
1575:
1572:
1570:
1567:
1565:
1562:
1558:
1555:
1553:
1550:
1548:
1545:
1544:
1543:
1540:
1539:
1537:
1533:
1529:
1522:
1517:
1515:
1510:
1508:
1503:
1502:
1499:
1493:
1490:
1488:
1485:
1484:
1480:
1473:
1468:
1465:
1454:
1450:
1446:
1442:
1435:
1432:
1420:
1414:
1411:
1400:
1396:
1390:
1388:
1384:
1378:
1375:
1370:
1366:
1361:
1356:
1353:(6): 647–52.
1352:
1348:
1344:
1337:
1334:
1329:
1325:
1320:
1315:
1311:
1307:
1303:
1296:
1293:
1287:
1282:
1278:
1274:
1270:
1263:
1260:
1255:
1251:
1246:
1241:
1237:
1233:
1229:
1225:
1221:
1217:
1213:
1206:
1203:
1198:
1192:
1184:
1180:
1176:
1170:
1166:
1159:
1157:
1155:
1153:
1149:
1144:
1138:
1134:
1127:
1124:
1119:
1113:
1109:
1108:
1100:
1098:
1096:
1094:
1092:
1090:
1086:
1081:
1077:
1072:
1067:
1062:
1057:
1053:
1049:
1045:
1038:
1035:
1030:
1024:
1021:
1016:
1012:
1008:
1004:
1000:
996:
991:
986:
982:
978:
971:
968:
957:
953:
949:
948:
943:
936:
933:
928:
924:
920:
916:
913:(3): 827–33.
912:
908:
901:
898:
893:
887:
883:
882:
874:
871:
866:
860:
856:
855:
847:
844:
833:
829:
823:
820:
813:
809:
806:
803:
800:
799:
795:
788:
785:
783:
779:
775:
772:
770:
767:
766:
762:
759:
757:
753:
749:
746:
744:
741:
740:
732:
729:
726:
723:
722:
719:
717:
704:
697:
695:
693:
690:
683:
681:
679:
675:
670:
668:
664:
662:
658:
653:
651:
647:
643:
639:
634:
632:
631:
626:
622:
618:
614:
610:
600:
591:
590:
586:
577:
576:
572:
563:
562:
558:
550:
547:
546:
538:
527:
524:
508:
507:
497:
496:
486:
485:
475:
474:
466:
458:
455:
447:
445:
442:
438:
434:
430:
426:
422:
418:
414:
403:
401:
397:
393:
389:
385:
380:
378:
374:
364:
361:
360:
356:
353:
352:
348:
346:taller people
345:
344:
336:
333:
327:
325:
323:
318:
316:
311:
309:
304:
302:
298:
294:
290:
287:refer to the
286:
282:
271:
266:
264:
259:
257:
252:
251:
248:
244:
240:
236:
232:
223:
219:
215:
208:
204:
197:
193:
186:
182:
178:
171:
167:
163:
159:
152:
148:
141:
137:
133:
129:
125:
116:
109:
105:
101:
97:
93:
89:
85:
81:
77:
73:
69:
65:
61:
52:
48:
44:
40:
36:
31:
19:
1860:gas exchange
1825:Interactions
1750:calculations
1711:Lung volumes
1710:
1674:
1655:
1636:
1607:constriction
1569:respirometer
1467:
1456:. Retrieved
1444:
1434:
1423:. Retrieved
1421:. 2019-11-28
1413:
1402:. Retrieved
1398:
1377:
1350:
1346:
1336:
1309:
1305:
1295:
1279:(2): 87–90.
1276:
1272:
1262:
1219:
1215:
1205:
1164:
1132:
1126:
1106:
1051:
1047:
1037:
1023:
980:
976:
970:
959:. Retrieved
945:
935:
910:
906:
900:
880:
873:
853:
846:
835:. Retrieved
831:
822:
768:
756:pneumothorax
742:
709:
692:
689:
687:
671:
665:
660:
656:
654:
637:
635:
628:
620:
616:
612:
609:tidal volume
608:
606:
522:
453:
437:Tidal volume
415:
404:
381:
370:
331:
319:
315:tidal volume
312:
305:
284:
281:Lung volumes
280:
279:
180:
1899:Bohr effect
1799:Circulation
1535:Respiration
832:Physiopedia
730:Description
535:Derivation
1988:Categories
1961:death zone
1880:hemoglobin
1775:spirometry
1734:dead space
1687:peripheral
1612:dilatation
1598:bronchial
1579:compliance
1552:exhalation
1547:inhalation
1458:2019-11-28
1425:2019-11-28
1404:2019-11-28
1183:1020568457
977:The Lancet
961:2023-04-26
837:2023-04-14
814:References
808:Spirometry
625:spirometer
1837:Perfusion
1453:0307-1235
1236:1569-9048
1191:cite book
1054:(1): 60.
985:CiteSeerX
956:0190-8286
782:emphysema
674:Pete Reed
587:ERV + RV
573:IRV + TV
543:In women
471:In women
425:diaphragm
396:Himalayas
373:sea level
122:is used.)
58:is used.)
1848:V/Q scan
1254:19897058
1080:28615020
1007:17307103
927:16963682
796:See also
727:Examples
435:by 20%.
377:altitude
310:of air.
1973:hypoxia
1894:2,3-BPG
1682:central
1657:medulla
1629:Control
1369:3784877
1328:9502364
1245:2858579
1071:5471732
540:In men
529:Volume
468:In men
460:Volume
295:in the
183:seconds
135:RV/TLC%
1542:breath
1451:
1367:
1326:
1252:
1242:
1234:
1181:
1171:
1139:
1114:
1078:
1068:
1015:852646
1013:
1005:
987:
954:
925:
888:
861:
774:asthma
648:) and
448:Values
394:; the
365:obese
308:litres
289:volume
1011:S2CID
907:Chest
804:(PFT)
737:/FVC
392:Tibet
384:Andes
297:lungs
1939:DLCO
1839:(Q)
1638:pons
1449:ISSN
1365:PMID
1324:PMID
1250:PMID
1232:ISSN
1197:link
1179:OCLC
1169:ISBN
1137:ISBN
1112:ISBN
1076:PMID
1003:PMID
952:ISSN
923:PMID
886:ISBN
859:ISBN
778:COPD
724:Type
716:/FVC
619:and
607:The
598:4.2
595:6.0
584:1.8
581:2.4
570:2.4
567:3.8
556:3.1
553:4.8
515:1.1
512:1.2
504:0.7
501:1.1
493:0.5
490:0.5
482:1.9
479:3.3
283:and
1744:PEF
1724:FRC
1355:doi
1314:doi
1281:doi
1240:PMC
1224:doi
1220:170
1066:PMC
1056:doi
995:doi
981:369
915:doi
911:130
733:FEV
712:FEV
362:fit
293:air
291:of
242:MVV
234:PEF
227:max
225:FIF
221:FIF
212:max
210:FEF
199:FEF
188:FEV
173:FEV
165:FVC
127:FRC
95:IVC
79:IRV
71:ERV
42:TLC
1990::
1739:CC
1729:Vt
1719:VC
1447:.
1443:.
1397:.
1386:^
1363:.
1351:18
1349:.
1345:.
1322:.
1310:30
1308:.
1304:.
1275:.
1271:.
1248:.
1238:.
1230:.
1218:.
1214:.
1193:}}
1189:{{
1177:.
1151:^
1088:^
1074:.
1064:.
1052:16
1050:.
1046:.
1009:.
1001:.
993:.
979:.
950:.
944:.
921:.
909:.
830:.
780:,
776:,
750:,
652:.
633:.
615:,
611:,
390:;
386:;
303:.
103:VC
87:IC
63:RV
50:TV
1941:)
1937:(
1916:)
1912:(
1906:)
1887:(
1520:e
1513:t
1506:v
1461:.
1428:.
1407:.
1371:.
1357::
1330:.
1316::
1289:.
1283::
1277:1
1256:.
1226::
1199:)
1185:.
1145:.
1120:.
1082:.
1058::
1031:.
1017:.
997::
964:.
929:.
917::
894:.
867:.
840:.
735:1
714:1
411:1
407:1
269:e
262:t
255:v
201:x
190:1
181:t
175:t
156:L
154:V
145:A
143:V
120:T
118:V
113:T
111:V
56:T
54:V
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.