651:
353:-regulatory modules are called billboards. Their transcriptional output is the summation effect of the bound transcription factors. Enhancers affect the probability of a gene being activated, but have little or no effect on rate. The Binary response model acts like an on/off switch for transcription. This model will increase or decrease the amount of cells that transcribe a gene, but it does not affect the rate of transcription. Rheostatic response model describes cis-regulatory modules as regulators of the initiation rate of transcription of its associated gene.
165:
300:– in this design two different regulatory factors are necessary to make sure that a positive output results. "Toggle Switches" – This design occurs when the signal ligand is absent while the transcription factor is present; this transcription factor ends up acting as a dominant repressor. However, once the signal ligand is present the transcription factor's role as repressor is eliminated and transcription can occur.
3816:
3828:
643:-regulatory modules in a genomic sequence have been difficult to identify. Problems in identification arise because often scientists find themselves with a small set of known transcription factors, so it makes it harder to identify statistically significant clusters of transcription factor binding sites. Additionally, high costs limit the use of large whole genome
543:-regulatory modules can regulate their target genes over large distances. Several models have been proposed to describe the way that these modules may communicate with their target gene promoter. These include the DNA scanning model, the DNA sequence looping model and the facilitated tracking model. In the DNA scanning model, the transcription factor and
394:. It has been found that a single gene can contain multiple promoter sites. In order to initiate transcription of the downstream gene, a host of DNA-binding proteins called transcription factors (TFs) must bind sequentially to this region. Only once this region has been bound with the appropriate set of TFs, and in the proper order, can
606:
user-friendly since it allows automatic retrieval of sequences and several visualizations and links to third-party tools in order to help users to find those instances that are more likely to be true regulatory sites. INSECT 2.0 algorithm was previously published and the algorithm and theory behind it explained in
635:
is applied to the data set to identify possible combinations of transcription factors, which have binding sites that are close to the promoter of the gene set of interest. The possible cis-regulatory modules are then statistically analyzed and the significant combinations are graphically represented
291:
Within the assumption of the
Boolean logic, principles guiding the operation of these modules includes the design of the module which determines the regulatory function. In relation to development, these modules can generate both positive and negative outputs. The output of each module is a product
278:
Additionally, the regulation of chromatin structure and nuclear organization also play a role in determining and controlling the function of cis-regulatory modules. Thus gene-regulation functions (GRF) provide a unique characteristic of a cis-regulatory module (CRM), relating the concentrations of
605:
is a web server that allows to search Cis-regulatory modules in a genome-wide manner. The program relies on the definition of strict restrictions among the
Transcription Factor Binding Sites (TFBSs) that compose the module in order to decrease the false positives rate. INSECT is designed to be
326:-regulatory module regulated by two transcription factors, experimentally determined gene-regulation functions can not be described by the 16 possible Boolean functions of two variables. Non-Boolean extensions of the gene-regulatory logic have been proposed to correct for this issue.
520:-regulatory modules can provide enough information to generate spatial and temporal patterns of gene expression. During development each domain, where each domain represents a different spatial regions of the embryo, of gene expression will be under the control of different
275:, which come into play only during specific situations during development. These inputs can come from different time points, can represent different signal ligands, or can come from different domains or lineages of cells. However, a lot still remains unknown.
226:-regulatory modules as a DNA sequence with transcription factor binding sites which are clustered into modular structures, including -but not limited to- locus control regions, promoters, enhancers, silencers, boundary control elements and other modulators.
416:, or even relatively far away from the gene they regulate. Multiple enhancers can act in a coordinated fashion to regulate transcription of one gene. A number of genome-wide sequencing projects have revealed that enhancers are often transcribed to
619:
use an algorithm that combines site predictions and tissue-specific expression data for transcription factors and target genes of interest. This model also uses regression trees to depict the relationship between the identified
176:
of an organism contains anywhere from a few hundred to thousands of different genes, all encoding a singular product or more. For numerous reasons, including organizational maintenance, energy conservation, and generating
1540:
Wrzodek, Clemens; Schröder, Adrian; Dräger, Andreas; Wanke, Dierk; Berendzen, Kenneth W.; Kronfeld, Marcel; Harter, Klaus; Zell, Andreas (2010). "ModuleMaster: A new tool to decipher transcriptional regulatory networks".
149:-regulatory modules carry out their function by integrating the active transcription factors and the associated co-factors at a specific time and place in the cell where this information is read and an output is given.
563:-regulatory module complex causes the looping of the DNA sequence slowly towards the target promoter and forms a stable looped configuration. The facilitated tracking model combines parts of the two previous models.
3832:
740:
To summarize, cis-regulatory elements are present on the same molecule of DNA as the gene they regulate whereas trans-regulatory elements can regulate genes distant from the gene from which they were transcribed.
307:-regulatory module lead to an output of zero. Additionally, besides influence from the different logic operations, the output of a "cis"-regulatory module will also be influenced by prior events. 4)
2338:
Prud'homme B, Gompel N, Rokas A, Kassner VA, Williams TM, Yeh SD, True JR, Carroll SB (April 2006). "Repeated morphological evolution through cis-regulatory changes in a pleiotropic gene".
279:
transcription factors (input) to the promoter activities (output). The challenge is to predict GRFs. This challenge still remains unsolved. In general, gene-regulation functions do not use
687:, which, in turn, prevents transcription of the adjacent genes on the same DNA molecule. The lac operator is, thus, considered to "act in cis" on the regulation of the nearby genes. The
627:
CRÈME examine clusters of target sites for transcription factors of interest. This program uses a database of confirmed transcription factor binding sites that were annotated across the
493:
arising within a CRE can generate expression variance by changing the way TFs bind. Tighter or looser binding of regulatory proteins will lead to up- or down-regulated transcription.
349:. The architecture and the arrangement of the transcription factor binding sites are critical because disruption of the arrangement could cancel out the function. Functional flexible
2293:
Gompel N, Prud'homme B, Wittkopp PJ, Kassner VA, Carroll SB (February 2005). "Chance caught on the wing: cis-regulatory evolution and the origin of pigment patterns in
Drosophila".
263:
serve as inputs, and the output of the module is the command given to the transcription machinery, which in turn determines the rate of gene transcription or whether it is
613:
to identify statistically significant clusters of transcription factor combinations. It also uses a second related genome to improve the prediction accuracy of the model.
551:-regulatory module and then continues to move along the DNA sequence until it finds the target gene promoter. In the looping model, the transcription factor binds to the
337:-regulatory modules can be characterized by the information processing that they encode and the organization of their transcription factor binding sites. Additionally,
706:
are diffusible factors, usually proteins, that may modify the expression of genes distant from the gene that was originally transcribed to create them. For example, a
367:
Promoters are CREs consisting of relatively short sequences of DNA which include the site where transcription is initiated and the region approximately 35 bp
341:-regulatory modules are also characterized by the way they affect the probability, proportion, and rate of transcription. Highly cooperative and coordinated
3394:
185:
is at the transcriptional level. CREs function to control transcription by acting nearby or within a gene. The most well characterized types of CREs are
3007:
271:. There are two types of transcription factor inputs: those that determine when the target gene is to be expressed and those that serve as functional
453:
of messenger RNA, that binds proteins which suppress translation of that mRNA molecule, but this usage is distinct from its use in describing a CRE.
412:
Enhancers are CREs that influence (enhance) the transcription of genes on the same molecule of DNA and can be found upstream, downstream, within the
218:
The original definition presented cis-regulatory modules as enhancers of cis-acting DNA, which increased the rate of transcription from a linked
2976:
2449:
3175:
2427:
1343:
311:-regulatory modules must interact with other regulatory elements. For the most part, even with the presence of functional overlap between
3419:
2941:
1362:
Wittkopp PJ, Kalay G (December 2011). "Cis-regulatory elements: molecular mechanisms and evolutionary processes underlying divergence".
989:
2514:
3738:
3441:
3059:
3039:
2786:
2025:"Molecular control of vertebrate iron metabolism: mRNA-based regulatory circuits operated by iron, nitric oxide, and oxidative stress"
86:
3730:
3670:
3147:
2486:
322:, detailed studies show that in general the logic of gene regulation is not Boolean. This means, for example, that in the case of a
303:
Other
Boolean logic operations can occur as well, such as sequence specific transcriptional repressors, which when they bind to the
2529:
2524:
575:
algorithms for predicting them. Most algorithms try to search for significant combinations of transcription factor binding sites (
2743:
3792:
3675:
3387:
3301:
3245:
450:
3240:
2920:
215:-regulatory modules are non-random clusters at their specified target site that contain transcription factor binding sites.
3797:
3787:
3774:
3328:
3259:
3000:
2771:
1013:
650:
368:
182:
120:
92:
CREs are found in the vicinity of the genes that they regulate. CREs typically regulate gene transcription by binding to
3414:
3064:
1251:
Jeziorska DM, Jordan KW, Vance KW (2009). "A systems biology approach to understanding cis-regulatory module function".
977:
806:
181:
variance, it is important that genes are only expressed when they are needed. The most efficient way for an organism to
1974:
Mokrejs M, Vopálenský V, Kolenaty O, Masek T, Feketová Z, Sekyrová P, Skaloudová B, Kríz V, Pospísek M (January 2006).
1890:
Chung BY, Firth AE, Atkins JF (March 2010). "Frameshifting in alphaviruses: a diversity of 3' stimulatory structures".
2738:
137:, which refers to effects on genes not located on the same strand or farther away, such as transcription factors. One
70:
583:
sequences of co-expressed genes. More advanced methods combine the search for significant motifs with correlation in
3820:
3380:
3279:
2930:
2796:
2628:
2623:
3323:
3111:
3024:
2993:
2458:
772:
703:
153:
132:
62:
3869:
3859:
3459:
3284:
3101:
3086:
2864:
2801:
2776:
2659:
2579:
1023:
544:
505:
559:
of the DNA sequence and allows for the interaction with the target gene promoter. The transcription factor-
3214:
3106:
2748:
2733:
2702:
2603:
529:
482:
207:. Regulatory elements are binding sites for transcription factors, which are involved in gene regulation.
2454:
3618:
3613:
3555:
3469:
3204:
3189:
3069:
2960:
2854:
2781:
2680:
2618:
2613:
2544:
2479:
2213:"A novel RNA structural motif in the selenocysteine insertion element of eukaryotic selenoprotein mRNAs"
850:
830:
588:
509:
96:. A single transcription factor may bind to many CREs, and hence control the expression of many genes (
3718:
3575:
3424:
3311:
3209:
3127:
2869:
2712:
2707:
2589:
2584:
2571:
2347:
2302:
2168:
Kortmann J, Narberhaus F (March 2012). "Bacterial RNA thermometers: molecular zippers and switches".
2126:
2036:
1138:
707:
655:
602:
481:
among organisms; yet different organisms display marked phenotypic diversity. It has been found that
442:
256:
237:
116:
93:
449:, thereby preventing transcription of a gene. The term "silencer" can also refer to a region in the
3587:
3582:
3560:
3506:
3137:
2965:
1038:
1018:
676:
659:
438:
433:
417:
407:
391:
362:
264:
204:
190:
186:
131:
because they are typically located on the same DNA strand as the genes they control as opposed to
3272:
3155:
2654:
2371:
2326:
2281:
2193:
2150:
1387:
1033:
972:
688:
580:
478:
219:
17:
3759:
3403:
3356:
2915:
2899:
2695:
2690:
2599:
2423:
2406:
2363:
2318:
2273:
2234:
2185:
2142:
2099:
2064:
2005:
1956:
1907:
1872:
1823:
1774:
1720:
1668:
1617:
1566:
1558:
1522:
1487:
1438:
1379:
1339:
1314:
1268:
1206:
1164:
387:
1333:
1202:
296:– this design indicates that in an output will be given when either input is given , and the
2925:
2894:
2889:
2844:
2472:
2396:
2355:
2310:
2265:
2224:
2177:
2134:
2091:
2054:
2044:
1995:
1987:
1946:
1938:
1899:
1862:
1854:
1813:
1805:
1764:
1754:
1710:
1702:
1658:
1648:
1607:
1597:
1550:
1514:
1477:
1469:
1428:
1418:
1371:
1304:
1260:
1198:
1183:
1154:
1146:
616:
576:
383:
168:
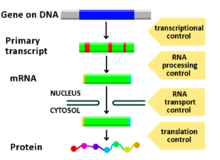
Diagram showing at which stages in the DNA-mRNA-protein pathway expression can be controlled
1293:"The RNA polymerase II core promoter: a key component in the regulation of gene expression"
592:
3723:
3449:
3333:
3170:
3016:
2935:
2839:
2649:
2445:
Gene
Regulation Info – manually curated lists of resources, reviews, community discussions
1000:
994:
892:
729:
There are cis-regulatory and trans-regulatory elements. Cis-regulatory elements are often
584:
486:
141:-regulatory element can regulate several genes, and conversely, one gene can have several
58:
424:(eRNA), whose changes in levels frequently correlate with those of the target gene mRNA.
108:
means "on this side", i.e. on the same molecule of DNA as the gene(s) to be transcribed.
2351:
2306:
2130:
2095:
2040:
1142:
315:-regulatory modules of a gene, the modules' inputs and outputs tend to not be the same.
164:
3754:
3705:
3665:
3160:
3132:
2401:
2384:
2229:
2212:
2000:
1975:
1951:
1926:
1867:
1842:
1769:
1742:
1715:
1690:
1482:
1457:
1433:
1406:
1159:
1126:
920:
572:
395:
268:
245:
194:
54:
1818:
1793:
485:
occurring within non-coding sequences have a profound effect on phenotype by altering
283:, although in some cases the approximation of the Boolean logic is still very useful.
3848:
3764:
3655:
3570:
3361:
3048:
2903:
2817:
2685:
2519:
2496:
2059:
2024:
1554:
1518:
911:
780:
730:
715:
684:
477:
CREs have an important evolutionary role. The coding regions of genes are often well
280:
211:-regulatory modules perform a large amount of developmental information processing.
152:
CREs are often but not always upstream of the transcription site. CREs contrast with
82:
74:
2330:
2197:
2154:
1976:"IRESite: the database of experimentally verified IRES structures (www.iresite.org)"
1653:
1636:
1602:
1585:
1505:
Aerts, S.; et al. (2003). "Computational detection of cis-regulatory modules".
1391:
3864:
3854:
3700:
3608:
3603:
3235:
3165:
3034:
2728:
2549:
2539:
2375:
2256:
Wray GA (March 2007). "The evolutionary significance of cis-regulatory mutations".
2082:
Platt T (1986). "Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression".
1942:
734:
711:
644:
628:
610:
421:
346:
2285:
1841:
Bekaert M, Firth AE, Zhang Y, Gladyshev VN, Atkins JF, Baranov PV (January 2010).
1423:
1264:
3782:
3511:
3338:
3267:
2664:
2644:
1743:"Comparing sequences without using alignments: application to HIV/SIV subtyping"
952:
260:
2464:
2029:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
3538:
3533:
3528:
3296:
2908:
2608:
2561:
1903:
1150:
883:
869:
680:
193:. Both of these sequence elements are structural regions of DNA that serve as
97:
29:
Region of non-coding DNA that regulates the transcription of neighboring genes
1562:
1127:"Predicting Gene-Regulation Functions: Lessons from Temperate Bacteriophages"
3565:
2859:
2827:
2594:
2500:
2420:
From DNA to
Diversity: Molecular Genetics and the Evolution of Animal Design
2138:
2049:
1586:"INSECT 2.0: a web-server for genome-wide cis-regulatory modules prediction"
1105:
The
Regulatory Genome: Gene Regulatory Networks in Development and Evolution
1048:
967:
841:
821:
817:
797:
793:
632:
466:
446:
372:
233:
178:
2410:
2367:
2322:
2277:
2189:
2146:
2009:
1960:
1911:
1876:
1827:
1778:
1724:
1672:
1621:
1570:
1526:
1491:
1442:
1383:
1318:
1272:
1210:
1168:
2238:
2103:
2068:
1759:
624:-regulatory module and the possible binding set of transcription factors.
591:
and target genes. Both methods have been implemented, for example, in the
3628:
3623:
3516:
3316:
3306:
3230:
2822:
2791:
1991:
1858:
1809:
1706:
962:
947:
902:
879:
860:
789:
663:
525:
490:
376:
297:
292:
of the various operations performed on it. Common operations include the
2359:
2314:
2181:
1309:
1292:
524:-regulatory modules. The design of regulatory modules help in producing
461:
Operators are CREs in prokaryotes and some eukaryotes that exist within
3734:
3709:
3684:
3680:
3660:
3473:
3052:
2554:
1691:"Stubb: a program for discovery and analysis of cis-regulatory modules"
1663:
1612:
1473:
957:
925:
785:
692:
293:
78:
3545:
3523:
2534:
1028:
462:
413:
173:
3372:
2269:
1407:"Transcriptional enhancers: Transcription, function and flexibility"
1375:
3747:
3074:
2985:
1584:
Parra RG, Rohr CO, Koile D, Perez-Castro C, Yankilevich P (2015).
649:
595:. Other programs created for the identification and prediction of
380:
163:
101:
2385:"Evolutionary developmental biology and the problem of variation"
1637:"INSECT: IN-silico SEarch for Co-occurring Transcription factors"
3550:
2832:
1043:
124:
66:
3376:
2989:
2468:
115:, usually 100–1000 DNA base pairs in length, where a number of
3463:
3453:
3044:
2444:
696:
112:
1843:"Recode-2: new design, new search tools, and many more genes"
1794:"CREME: Cis-Regulatory Module Explorer for the human genome"
375:, promoters usually have the following four components: the
127:
and regulate their transcription rates. They are labeled as
571:
Besides experimentally determining CRMs, there are various
203:-regulatory modules are one of several types of functional
857:
Regulates transcription of associated genes and/or operons
1635:
Rohr CO, Parra RG, Yankilevich P, Perez-Castro C (2013).
240:, which work indirectly by interacting with other nearby
1927:"Frameshifting RNA pseudoknots: structure and mechanism"
318:
While the assumption of
Boolean logic is important for
232:-regulatory modules can be divided into three classes;
1184:"Gene regulation: gene control network in development"
814:
Initiates translation in the middle of a messenger RNA
2389:
Evolution; International
Journal of Organic Evolution
2211:
Walczak R, Westhof E, Carbon P, Krol A (April 1996).
1338:. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 78.
1792:
Sharan R, Ben-Hur A, Loots GG, Ovcharenko I (2004).
3773:
3693:
3648:
3641:
3596:
3483:
3440:
3433:
3349:
3258:
3223:
3197:
3188:
3146:
3120:
3094:
3085:
3023:
2953:
2882:
2810:
2764:
2757:
2721:
2673:
2637:
2570:
2507:
1405:Melamed P, Yosefzun Y, et al. (2 March 2016).
1357:
1355:
714:might itself have been transcribed from a gene on
2117:Breaker RR (March 2008). "Complex riboswitches".
1458:"Building Developmental Gene Regulatory Networks"
919:Directs the cell to translate UGA stop-codons as
838:Regulates the expression of iron associated genes
222:. However, this definition has changed to define
2418:Weatherbee SD, Carroll SB, Grenier JK (2004).
512:, whose function is dependent on the multiple
3388:
3001:
2480:
500:-regulatory module in gene regulatory network
236:, which regulate gene expression positively;
8:
1684:
1682:
1286:
1284:
1282:
1246:
1244:
1242:
1240:
1736:
1734:
1238:
1236:
1234:
1232:
1230:
1228:
1226:
1224:
1222:
1220:
567:Identification and computational prediction
3645:
3437:
3395:
3381:
3373:
3194:
3156:Precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA / hnRNA)
3091:
3008:
2994:
2986:
2761:
2487:
2473:
2465:
1120:
1118:
1116:
1114:
748:
654:Binding sites of gene regulatory factors.
555:-regulatory module, which then causes the
2457:at the U.S. National Library of Medicine
2400:
2228:
2058:
2048:
1999:
1950:
1866:
1817:
1768:
1758:
1714:
1662:
1652:
1611:
1601:
1481:
1432:
1422:
1308:
1182:Ben-Tabou de-Leon S, Davidson EH (2007).
1158:
1925:Giedroc DP, Cornish PV (February 2009).
1203:10.1146/annurev.biophys.35.040405.102002
2422:. Cambridge, MA: Blackwell Publishers.
1291:Butler JE, Kadonaga JT (October 2002).
1098:
1096:
1094:
1092:
1090:
1088:
1086:
1062:
156:. TREs code for transcription factors.
2977:Index of evolutionary biology articles
1084:
1082:
1080:
1078:
1076:
1074:
1072:
1070:
1068:
1066:
465:, where they can bind proteins called
398:bind and begin transcribing the gene.
345:-regulatory modules are classified as
3176:Histone acetylation and deacetylation
779:Regulates alternative frame use with
7:
3241:Ribosome-nascent chain complex (RNC)
683:. This DNA sequence is bound by the
3827:
2096:10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011
1689:Sinha S, Liang Y, Siggia E (2006).
990:List of cis-regulatory RNA elements
722:is constructed from the Latin root
516:-regulatory modules. The layout of
508:depends on the architecture of the
248:that turn off expression of genes.
2787:Evolutionary developmental biology
2402:10.1111/j.0014-3820.2000.tb00544.x
2023:Hentze MW, Kühn LC (August 1996).
371:from the initiation site (bp). In
87:evolutionary developmental biology
25:
3671:Post-transcriptional modification
912:Selenocysteine insertion sequence
255:-regulatory modules is such that
18:Transcription factor-binding site
3826:
3815:
3814:
2744:Evolution of sexual reproduction
1555:10.1016/j.biosystems.2009.09.005
443:transcription regulation factors
154:trans-regulatory elements (TREs)
3676:Post-translational modification
3246:Post-translational modification
1804:(Web Server issue): W253–W256.
1701:(Web Server issue): W555–W559.
1549:(1). Ireland: Elsevier: 79–81.
1335:Introduction to Systems Biology
69:. CREs are vital components of
2515:Genotype–phenotype distinction
1943:10.1016/j.virusres.2008.06.008
1519:10.1093/bioinformatics/btg1052
1191:Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct
532:, and cross-regulatory loops.
1:
3798:Post-translational regulation
2772:Regulation of gene expression
2455:Regulation of Gene Expression
2084:Annual Review of Biochemistry
1741:Chen X, Blanchette M (2007).
1654:10.1093/bioinformatics/btt506
1603:10.1093/bioinformatics/btv726
1424:10.1080/21541264.2015.1128517
1014:Regulation of gene expression
726:, which means "across from".
691:itself does not code for any
599:-regulatory modules include:
3746:High-throughput technique ("
2942:Endless Forms Most Beautiful
2722:Evolution of genetic systems
2530:Gene–environment correlation
2525:Gene–environment interaction
2170:Nature Reviews. Microbiology
1986:(Database issue): D125–130.
1892:Journal of Molecular Biology
1265:10.1016/j.semcdb.2009.07.007
978:Upstream activation sequence
807:Internal ribosome entry site
287:The Boolean logic assumption
3624:Functional biology/medicine
2921:Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard
675:An example of a cis-acting
71:genetic regulatory networks
3886:
2797:Hedgehog signaling pathway
2674:Developmental architecture
1853:(Database issue): D69–74.
1456:Li E, Davidson EH (2009).
1107:. Elsevier. pp. 1–86.
431:
405:
360:
195:transcriptional regulators
3810:
3410:
2974:
2624:Transgressive segregation
1904:10.1016/j.jmb.2010.01.044
1151:10.1016/j.bpj.2009.11.046
710:that regulates a gene on
704:trans-regulatory elements
469:to affect transcription.
244:-regulatory modules; and
3307:sequestration (P-bodies)
2459:Medical Subject Headings
2383:Stern DL (August 2000).
261:epigenetic modifications
183:regulate gene expression
73:, which in turn control
3285:Gene regulatory network
2802:Notch signaling pathway
2777:Gene regulatory network
2660:Dual inheritance theory
2258:Nature Reviews Genetics
2139:10.1126/science.1152621
2050:10.1073/pnas.93.16.8175
1364:Nature Reviews Genetics
1297:Genes & Development
1024:Gene regulatory network
679:is the operator in the
506:gene regulatory network
441:are CREs that can bind
81:, and other aspects of
3290:cis-regulatory element
2850:cis-regulatory element
2758:Control of development
2638:Non-genetic influences
2604:evolutionary landscape
1980:Nucleic Acids Research
1847:Nucleic Acids Research
1332:Choi S (17 May 2008).
667:
451:3' untranslated region
369:upstream or downstream
169:
111:CRMs are stretches of
3619:Developmental biology
3614:Computational biology
2961:Nature versus nurture
2865:Cell surface receptor
2782:Evo-devo gene toolkit
2681:Developmental biology
2619:Polygenic inheritance
2545:Quantitative genetics
1760:10.1186/1471-2105-8-1
1253:Semin. Cell Dev. Biol
831:Iron response element
656:Transcription factors
653:
589:transcription factors
392:core promoter element
390:, and the downstream
257:transcription factors
167:
145:-regulatory modules.
117:transcription factors
94:transcription factors
83:embryonic development
77:, the development of
3793:Post-transcriptional
3312:alternative splicing
3302:Post-transcriptional
3128:Transcription factor
2870:Transcription factor
2585:Genetic assimilation
2572:Genetic architecture
1103:Davidson EH (2006).
708:transcription factor
660:RNA-binding proteins
547:complex form at the
36:-regulatory elements
3588:Histone methylation
3236:Transfer RNA (tRNA)
2966:Morphogenetic field
2883:Influential figures
2360:10.1038/nature04597
2352:2006Natur.440.1050P
2346:(7087): 1050–1053.
2315:10.1038/nature03235
2307:2005Natur.433..481G
2182:10.1038/nrmicro2730
2131:2008Sci...319.1795B
2125:(5871): 1795–1797.
2041:1996PNAS...93.8175H
1513:(Suppl 2): ii5–14.
1310:10.1101/gad.1026202
1143:2010BpJ....98.1247T
1131:Biophysical Journal
1039:Trans-acting factor
1019:Cis-trans isomerism
751:
677:regulatory sequence
434:Silencer (genetics)
418:long non-coding RNA
408:Enhancer (genetics)
363:Promoter (genetics)
205:regulatory elements
121:regulate expression
47:-regulatory modules
3350:Influential people
3329:Post-translational
3148:Post-transcription
2655:Genomic imprinting
2450:Cellular Darwinism
1992:10.1093/nar/gkj081
1859:10.1093/nar/gkp788
1810:10.1093/nar/gkh385
1747:BMC Bioinformatics
1707:10.1093/nar/gkl224
1474:10.1002/bdrc.20152
1125:Teif V.B. (2010).
973:Operator (biology)
773:Frameshift element
749:
668:
609:Stubb uses hidden
504:The function of a
445:(proteins) called
170:
3842:
3841:
3821:Molecular biology
3806:
3805:
3760:Mass spectrometry
3637:
3636:
3404:Molecular biology
3370:
3369:
3254:
3253:
3184:
3183:
3060:Special transfers
2983:
2982:
2916:Eric F. Wieschaus
2878:
2877:
2696:Pattern formation
2600:Fitness landscape
2429:978-1-4051-1950-4
2301:(7025): 481–487.
2035:(16): 8175–8182.
1798:Nucleic Acids Res
1695:Nucleic Acids Res
1462:Birth Defects Res
1345:978-1-59745-531-2
1303:(20): 2583–2592.
933:
932:
617:Bayesian Networks
587:datasets between
577:DNA binding sites
473:Evolutionary role
53:) are regions of
16:(Redirected from
3877:
3830:
3829:
3818:
3817:
3751:
3646:
3499:
3494:
3438:
3397:
3390:
3383:
3374:
3195:
3092:
3010:
3003:
2996:
2987:
2926:William McGinnis
2895:Richard Lewontin
2890:C. H. Waddington
2762:
2739:Neutral networks
2489:
2482:
2475:
2466:
2433:
2414:
2404:
2395:(4): 1079–1091.
2379:
2334:
2289:
2243:
2242:
2232:
2208:
2202:
2201:
2165:
2159:
2158:
2114:
2108:
2107:
2079:
2073:
2072:
2062:
2052:
2020:
2014:
2013:
2003:
1971:
1965:
1964:
1954:
1922:
1916:
1915:
1887:
1881:
1880:
1870:
1838:
1832:
1831:
1821:
1789:
1783:
1782:
1772:
1762:
1738:
1729:
1728:
1718:
1686:
1677:
1676:
1666:
1656:
1632:
1626:
1625:
1615:
1605:
1581:
1575:
1574:
1537:
1531:
1530:
1502:
1496:
1495:
1485:
1453:
1447:
1446:
1436:
1426:
1402:
1396:
1395:
1359:
1350:
1349:
1329:
1323:
1322:
1312:
1288:
1277:
1276:
1248:
1215:
1214:
1188:
1179:
1173:
1172:
1162:
1122:
1109:
1108:
1100:
752:
733:for one or more
720:trans-regulatory
384:recognition site
21:
3885:
3884:
3880:
3879:
3878:
3876:
3875:
3874:
3845:
3844:
3843:
3838:
3802:
3775:Gene regulation
3769:
3745:
3706:Model organisms
3689:
3666:Cell signalling
3633:
3592:
3497:
3492:
3479:
3450:DNA replication
3429:
3406:
3401:
3371:
3366:
3345:
3280:Transcriptional
3250:
3219:
3180:
3171:Polyadenylation
3142:
3116:
3081:
3075:Protein→Protein
3026:
3019:
3017:Gene expression
3014:
2984:
2979:
2970:
2949:
2936:Sean B. Carroll
2874:
2806:
2753:
2717:
2669:
2650:Maternal effect
2633:
2566:
2503:
2493:
2441:
2436:
2430:
2417:
2382:
2337:
2292:
2270:10.1038/nrg2063
2255:
2251:
2249:Further reading
2246:
2210:
2209:
2205:
2167:
2166:
2162:
2116:
2115:
2111:
2081:
2080:
2076:
2022:
2021:
2017:
1973:
1972:
1968:
1924:
1923:
1919:
1889:
1888:
1884:
1840:
1839:
1835:
1791:
1790:
1786:
1740:
1739:
1732:
1688:
1687:
1680:
1634:
1633:
1629:
1583:
1582:
1578:
1539:
1538:
1534:
1504:
1503:
1499:
1455:
1454:
1450:
1404:
1403:
1399:
1376:10.1038/nrg3095
1361:
1360:
1353:
1346:
1331:
1330:
1326:
1290:
1289:
1280:
1250:
1249:
1218:
1186:
1181:
1180:
1176:
1124:
1123:
1112:
1102:
1101:
1064:
1060:
1055:
1001:AU-rich element
995:Polyadenylation
938:
921:selenocysteines
899:Gene regulation
893:RNA thermometer
876:Gene regulation
747:
745:Examples in RNA
673:
585:gene expression
569:
538:
502:
487:gene expression
475:
459:
436:
430:
410:
404:
365:
359:
332:
320:systems biology
289:
162:
65:of neighboring
30:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
3883:
3881:
3873:
3872:
3870:Non-coding DNA
3867:
3862:
3860:Non-coding RNA
3857:
3847:
3846:
3840:
3839:
3837:
3836:
3824:
3811:
3808:
3807:
3804:
3803:
3801:
3800:
3795:
3790:
3785:
3779:
3777:
3771:
3770:
3768:
3767:
3762:
3757:
3755:DNA microarray
3752:
3742:
3741:
3728:
3727:
3726:
3721:
3713:
3703:
3697:
3695:
3691:
3690:
3688:
3687:
3678:
3673:
3668:
3663:
3658:
3652:
3650:
3643:
3639:
3638:
3635:
3634:
3632:
3631:
3626:
3621:
3616:
3611:
3606:
3600:
3598:
3594:
3593:
3591:
3590:
3585:
3580:
3579:
3578:
3573:
3563:
3558:
3553:
3548:
3543:
3542:
3541:
3536:
3531:
3521:
3520:
3519:
3514:
3503:
3502:
3501:
3500:
3495:
3487:
3485:
3481:
3480:
3478:
3477:
3467:
3457:
3446:
3444:
3435:
3431:
3430:
3428:
3427:
3422:
3417:
3411:
3408:
3407:
3402:
3400:
3399:
3392:
3385:
3377:
3368:
3367:
3365:
3364:
3359:
3357:François Jacob
3353:
3351:
3347:
3346:
3344:
3343:
3342:
3341:
3336:
3326:
3321:
3320:
3319:
3314:
3309:
3299:
3294:
3293:
3292:
3287:
3277:
3276:
3275:
3264:
3262:
3256:
3255:
3252:
3251:
3249:
3248:
3243:
3238:
3233:
3227:
3225:
3221:
3220:
3218:
3217:
3212:
3207:
3201:
3199:
3192:
3186:
3185:
3182:
3181:
3179:
3178:
3173:
3168:
3163:
3158:
3152:
3150:
3144:
3143:
3141:
3140:
3135:
3133:RNA polymerase
3130:
3124:
3122:
3118:
3117:
3115:
3114:
3109:
3104:
3098:
3096:
3089:
3083:
3082:
3080:
3079:
3078:
3077:
3072:
3067:
3057:
3056:
3055:
3037:
3031:
3029:
3021:
3020:
3015:
3013:
3012:
3005:
2998:
2990:
2981:
2980:
2975:
2972:
2971:
2969:
2968:
2963:
2957:
2955:
2951:
2950:
2948:
2947:
2946:
2945:
2933:
2928:
2923:
2918:
2913:
2912:
2911:
2900:François Jacob
2897:
2892:
2886:
2884:
2880:
2879:
2876:
2875:
2873:
2872:
2867:
2862:
2857:
2852:
2847:
2842:
2837:
2836:
2835:
2825:
2820:
2814:
2812:
2808:
2807:
2805:
2804:
2799:
2794:
2789:
2784:
2779:
2774:
2768:
2766:
2759:
2755:
2754:
2752:
2751:
2746:
2741:
2736:
2731:
2725:
2723:
2719:
2718:
2716:
2715:
2710:
2705:
2700:
2699:
2698:
2693:
2683:
2677:
2675:
2671:
2670:
2668:
2667:
2662:
2657:
2652:
2647:
2641:
2639:
2635:
2634:
2632:
2631:
2629:Sequence space
2626:
2621:
2616:
2611:
2606:
2597:
2592:
2587:
2582:
2576:
2574:
2568:
2567:
2565:
2564:
2559:
2558:
2557:
2547:
2542:
2537:
2532:
2527:
2522:
2517:
2511:
2509:
2505:
2504:
2494:
2492:
2491:
2484:
2477:
2469:
2463:
2462:
2452:
2447:
2440:
2439:External links
2437:
2435:
2434:
2428:
2415:
2380:
2335:
2290:
2264:(3): 206–216.
2252:
2250:
2247:
2245:
2244:
2223:(4): 367–379.
2203:
2176:(4): 255–265.
2160:
2109:
2074:
2015:
1966:
1937:(2): 193–208.
1931:Virus Research
1917:
1898:(2): 448–456.
1882:
1833:
1784:
1730:
1678:
1647:(22): 2852–8.
1641:Bioinformatics
1627:
1596:(8): 1229–31.
1590:Bioinformatics
1576:
1532:
1507:Bioinformatics
1497:
1468:(2): 123–130.
1448:
1397:
1351:
1344:
1324:
1278:
1259:(7): 856–862.
1216:
1174:
1137:(7): 1247–56.
1110:
1061:
1059:
1056:
1054:
1053:
1052:
1051:
1046:
1041:
1036:
1031:
1026:
1021:
1016:
1006:
1005:
1004:
998:
992:
982:
981:
980:
975:
970:
965:
960:
955:
950:
939:
937:
934:
931:
930:
928:
923:
917:
914:
908:
907:
905:
900:
897:
895:
889:
888:
886:
877:
874:
872:
866:
865:
863:
858:
855:
853:
851:Leader peptide
847:
846:
844:
839:
836:
833:
827:
826:
824:
815:
812:
809:
803:
802:
800:
783:
781:messenger RNAs
777:
775:
769:
768:
765:
762:
759:
756:
746:
743:
672:
669:
573:bioinformatics
568:
565:
537:
536:Mode of action
534:
501:
495:
474:
471:
458:
455:
432:Main article:
429:
426:
406:Main article:
403:
400:
396:RNA polymerase
361:Main article:
358:
355:
331:
330:Classification
328:
288:
285:
251:The design of
161:
158:
55:non-coding DNA
28:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3882:
3871:
3868:
3866:
3863:
3861:
3858:
3856:
3853:
3852:
3850:
3835:
3834:
3825:
3823:
3822:
3813:
3812:
3809:
3799:
3796:
3794:
3791:
3789:
3786:
3784:
3781:
3780:
3778:
3776:
3772:
3766:
3765:Lab-on-a-chip
3763:
3761:
3758:
3756:
3753:
3749:
3744:
3743:
3740:
3739:Radioactivity
3736:
3732:
3729:
3725:
3722:
3720:
3717:
3716:
3714:
3711:
3707:
3704:
3702:
3699:
3698:
3696:
3692:
3686:
3682:
3679:
3677:
3674:
3672:
3669:
3667:
3664:
3662:
3659:
3657:
3656:Cultured meat
3654:
3653:
3651:
3647:
3644:
3640:
3630:
3627:
3625:
3622:
3620:
3617:
3615:
3612:
3610:
3607:
3605:
3602:
3601:
3599:
3595:
3589:
3586:
3584:
3581:
3577:
3576:trp repressor
3574:
3572:
3571:lac repressor
3569:
3568:
3567:
3564:
3562:
3559:
3557:
3554:
3552:
3549:
3547:
3544:
3540:
3537:
3535:
3532:
3530:
3527:
3526:
3525:
3522:
3518:
3515:
3513:
3510:
3509:
3508:
3505:
3504:
3496:
3491:
3490:
3489:
3488:
3486:
3482:
3475:
3471:
3468:
3465:
3461:
3460:Transcription
3458:
3455:
3451:
3448:
3447:
3445:
3443:
3442:Central dogma
3439:
3436:
3432:
3426:
3423:
3421:
3418:
3416:
3413:
3412:
3409:
3405:
3398:
3393:
3391:
3386:
3384:
3379:
3378:
3375:
3363:
3362:Jacques Monod
3360:
3358:
3355:
3354:
3352:
3348:
3340:
3337:
3335:
3332:
3331:
3330:
3327:
3325:
3324:Translational
3322:
3318:
3315:
3313:
3310:
3308:
3305:
3304:
3303:
3300:
3298:
3295:
3291:
3288:
3286:
3283:
3282:
3281:
3278:
3274:
3271:
3270:
3269:
3266:
3265:
3263:
3261:
3257:
3247:
3244:
3242:
3239:
3237:
3234:
3232:
3229:
3228:
3226:
3222:
3216:
3213:
3211:
3208:
3206:
3203:
3202:
3200:
3196:
3193:
3191:
3187:
3177:
3174:
3172:
3169:
3167:
3164:
3162:
3159:
3157:
3154:
3153:
3151:
3149:
3145:
3139:
3136:
3134:
3131:
3129:
3126:
3125:
3123:
3119:
3113:
3110:
3108:
3105:
3103:
3100:
3099:
3097:
3093:
3090:
3088:
3087:Transcription
3084:
3076:
3073:
3071:
3068:
3066:
3063:
3062:
3061:
3058:
3054:
3050:
3046:
3043:
3042:
3041:
3040:Central dogma
3038:
3036:
3033:
3032:
3030:
3028:
3022:
3018:
3011:
3006:
3004:
2999:
2997:
2992:
2991:
2988:
2978:
2973:
2967:
2964:
2962:
2959:
2958:
2956:
2952:
2944:
2943:
2939:
2938:
2937:
2934:
2932:
2929:
2927:
2924:
2922:
2919:
2917:
2914:
2910:
2907:
2906:
2905:
2904:Jacques Monod
2901:
2898:
2896:
2893:
2891:
2888:
2887:
2885:
2881:
2871:
2868:
2866:
2863:
2861:
2858:
2856:
2853:
2851:
2848:
2846:
2843:
2841:
2838:
2834:
2831:
2830:
2829:
2826:
2824:
2821:
2819:
2818:Homeotic gene
2816:
2815:
2813:
2809:
2803:
2800:
2798:
2795:
2793:
2790:
2788:
2785:
2783:
2780:
2778:
2775:
2773:
2770:
2769:
2767:
2763:
2760:
2756:
2750:
2747:
2745:
2742:
2740:
2737:
2735:
2732:
2730:
2727:
2726:
2724:
2720:
2714:
2711:
2709:
2706:
2704:
2701:
2697:
2694:
2692:
2689:
2688:
2687:
2686:Morphogenesis
2684:
2682:
2679:
2678:
2676:
2672:
2666:
2663:
2661:
2658:
2656:
2653:
2651:
2648:
2646:
2643:
2642:
2640:
2636:
2630:
2627:
2625:
2622:
2620:
2617:
2615:
2612:
2610:
2607:
2605:
2601:
2598:
2596:
2593:
2591:
2588:
2586:
2583:
2581:
2578:
2577:
2575:
2573:
2569:
2563:
2560:
2556:
2553:
2552:
2551:
2548:
2546:
2543:
2541:
2538:
2536:
2533:
2531:
2528:
2526:
2523:
2521:
2520:Reaction norm
2518:
2516:
2513:
2512:
2510:
2506:
2502:
2498:
2490:
2485:
2483:
2478:
2476:
2471:
2470:
2467:
2460:
2456:
2453:
2451:
2448:
2446:
2443:
2442:
2438:
2431:
2425:
2421:
2416:
2412:
2408:
2403:
2398:
2394:
2390:
2386:
2381:
2377:
2373:
2369:
2365:
2361:
2357:
2353:
2349:
2345:
2341:
2336:
2332:
2328:
2324:
2320:
2316:
2312:
2308:
2304:
2300:
2296:
2291:
2287:
2283:
2279:
2275:
2271:
2267:
2263:
2259:
2254:
2253:
2248:
2240:
2236:
2231:
2226:
2222:
2218:
2214:
2207:
2204:
2199:
2195:
2191:
2187:
2183:
2179:
2175:
2171:
2164:
2161:
2156:
2152:
2148:
2144:
2140:
2136:
2132:
2128:
2124:
2120:
2113:
2110:
2105:
2101:
2097:
2093:
2089:
2085:
2078:
2075:
2070:
2066:
2061:
2056:
2051:
2046:
2042:
2038:
2034:
2030:
2026:
2019:
2016:
2011:
2007:
2002:
1997:
1993:
1989:
1985:
1981:
1977:
1970:
1967:
1962:
1958:
1953:
1948:
1944:
1940:
1936:
1932:
1928:
1921:
1918:
1913:
1909:
1905:
1901:
1897:
1893:
1886:
1883:
1878:
1874:
1869:
1864:
1860:
1856:
1852:
1848:
1844:
1837:
1834:
1829:
1825:
1820:
1815:
1811:
1807:
1803:
1799:
1795:
1788:
1785:
1780:
1776:
1771:
1766:
1761:
1756:
1752:
1748:
1744:
1737:
1735:
1731:
1726:
1722:
1717:
1712:
1708:
1704:
1700:
1696:
1692:
1685:
1683:
1679:
1674:
1670:
1665:
1660:
1655:
1650:
1646:
1642:
1638:
1631:
1628:
1623:
1619:
1614:
1609:
1604:
1599:
1595:
1591:
1587:
1580:
1577:
1572:
1568:
1564:
1560:
1556:
1552:
1548:
1544:
1536:
1533:
1528:
1524:
1520:
1516:
1512:
1508:
1501:
1498:
1493:
1489:
1484:
1479:
1475:
1471:
1467:
1463:
1459:
1452:
1449:
1444:
1440:
1435:
1430:
1425:
1420:
1416:
1412:
1411:Transcription
1408:
1401:
1398:
1393:
1389:
1385:
1381:
1377:
1373:
1369:
1365:
1358:
1356:
1352:
1347:
1341:
1337:
1336:
1328:
1325:
1320:
1316:
1311:
1306:
1302:
1298:
1294:
1287:
1285:
1283:
1279:
1274:
1270:
1266:
1262:
1258:
1254:
1247:
1245:
1243:
1241:
1239:
1237:
1235:
1233:
1231:
1229:
1227:
1225:
1223:
1221:
1217:
1212:
1208:
1204:
1200:
1196:
1192:
1185:
1178:
1175:
1170:
1166:
1161:
1156:
1152:
1148:
1144:
1140:
1136:
1132:
1128:
1121:
1119:
1117:
1115:
1111:
1106:
1099:
1097:
1095:
1093:
1091:
1089:
1087:
1085:
1083:
1081:
1079:
1077:
1075:
1073:
1071:
1069:
1067:
1063:
1057:
1050:
1047:
1045:
1042:
1040:
1037:
1035:
1032:
1030:
1027:
1025:
1022:
1020:
1017:
1015:
1012:
1011:
1010:
1007:
1002:
999:
997:signals, mRNA
996:
993:
991:
988:
987:
986:
983:
979:
976:
974:
971:
969:
966:
964:
961:
959:
956:
954:
951:
949:
946:
945:
944:
941:
940:
935:
929:
927:
924:
922:
918:
915:
913:
910:
909:
906:
904:
901:
898:
896:
894:
891:
890:
887:
885:
881:
878:
875:
873:
871:
868:
867:
864:
862:
859:
856:
854:
852:
849:
848:
845:
843:
840:
837:
834:
832:
829:
828:
825:
823:
819:
816:
813:
810:
808:
805:
804:
801:
799:
795:
791:
787:
784:
782:
778:
776:
774:
771:
770:
766:
763:
760:
757:
754:
753:
750:RNA elements
744:
742:
738:
736:
732:
731:binding sites
727:
725:
721:
717:
716:chromosome 11
713:
709:
705:
702:In contrast,
700:
698:
694:
690:
686:
685:lac repressor
682:
678:
670:
665:
661:
658:binding DNA,
657:
652:
648:
646:
645:tiling arrays
642:
637:
634:
630:
625:
623:
618:
614:
612:
611:Markov models
607:
604:
600:
598:
594:
590:
586:
582:
578:
574:
566:
564:
562:
558:
554:
550:
546:
542:
535:
533:
531:
527:
523:
519:
515:
511:
507:
499:
496:
494:
492:
488:
484:
483:polymorphisms
480:
472:
470:
468:
464:
456:
454:
452:
448:
444:
440:
435:
427:
425:
423:
419:
415:
409:
401:
399:
397:
393:
389:
385:
382:
378:
374:
370:
364:
356:
354:
352:
348:
347:enhanceosomes
344:
340:
336:
329:
327:
325:
321:
316:
314:
310:
306:
301:
299:
295:
286:
284:
282:
281:Boolean logic
276:
274:
270:
266:
262:
258:
254:
249:
247:
243:
239:
235:
231:
227:
225:
221:
216:
214:
210:
206:
202:
198:
196:
192:
188:
184:
180:
175:
166:
159:
157:
155:
150:
148:
144:
140:
136:
135:
130:
126:
122:
119:can bind and
118:
114:
109:
107:
103:
99:
95:
90:
88:
85:, studied in
84:
80:
76:
75:morphogenesis
72:
68:
64:
63:transcription
60:
56:
52:
48:
46:
41:
37:
35:
27:
19:
3831:
3819:
3731:Fluorescence
3719:Nucleic acid
3710:C57BL/6 mice
3701:Cell culture
3609:Biochemistry
3604:Cell biology
3339:irreversible
3289:
3224:Key elements
3121:Key elements
3035:Genetic code
3025:Introduction
2940:
2849:
2833:eyeless gene
2729:Evolvability
2703:Segmentation
2580:Canalisation
2550:Heterochrony
2540:Heritability
2508:Key concepts
2419:
2392:
2388:
2343:
2339:
2298:
2294:
2261:
2257:
2220:
2216:
2206:
2173:
2169:
2163:
2122:
2118:
2112:
2087:
2083:
2077:
2032:
2028:
2018:
1983:
1979:
1969:
1934:
1930:
1920:
1895:
1891:
1885:
1850:
1846:
1836:
1801:
1797:
1787:
1750:
1746:
1698:
1694:
1644:
1640:
1630:
1593:
1589:
1579:
1546:
1542:
1535:
1510:
1506:
1500:
1465:
1461:
1451:
1417:(1): 26–31.
1414:
1410:
1400:
1370:(1): 59–69.
1367:
1363:
1334:
1327:
1300:
1296:
1256:
1252:
1194:
1190:
1177:
1134:
1130:
1104:
1008:
984:
942:
764:Distribution
739:
735:trans-acting
728:
723:
719:
712:chromosome 6
701:
674:
640:
638:
629:human genome
626:
621:
615:
608:
601:
596:
593:ModuleMaster
570:
560:
556:
552:
548:
540:
539:
530:feed forward
521:
517:
513:
503:
497:
476:
460:
437:
422:enhancer RNA
420:(lncRNA) or
411:
366:
350:
342:
338:
334:
333:
323:
319:
317:
312:
308:
304:
302:
290:
277:
272:
252:
250:
241:
229:
228:
223:
217:
212:
208:
200:
199:
171:
151:
146:
142:
138:
133:
128:
110:
105:
91:
50:
44:
43:
39:
33:
32:
31:
26:
3833:WikiProject
3642:Engineering
3597:Linked life
3512:Pribnow box
3470:Translation
3190:Translation
3027:to genetics
2931:Mike Levine
2840:Distal-less
2665:Polyphenism
2645:Epigenetics
2497:development
2090:: 339–372.
1664:11336/12301
1613:11336/37980
1197:: 191–212.
953:Pribnow box
798:RNA viruses
718:. The term
666:binding RNA
631:. A search
3849:Categories
3783:Epigenetic
3694:Techniques
3556:Terminator
3539:trp operon
3534:lac operon
3529:gal operon
3334:reversible
3297:lac operon
3273:imprinting
3268:Epigenetic
3260:Regulation
3215:Eukaryotic
3161:5' capping
3112:Eukaryotic
2909:Lac operon
2734:Robustness
2713:Modularity
2708:Metamerism
2614:Plasticity
2609:Pleiotropy
2562:Heterotopy
1543:Biosystems
1058:References
870:Riboswitch
681:lac operon
603:INSECT 2.0
467:repressors
447:repressors
373:eukaryotes
238:insulators
179:phenotypic
123:of nearby
98:pleiotropy
3708:(such as
3566:Repressor
3205:Bacterial
3102:Bacterial
2860:Morphogen
2845:Engrailed
2828:Pax genes
2749:Tinkering
2595:Epistasis
2590:Dominance
2501:phenotype
1563:0303-2647
1049:Transterm
968:CCAAT box
884:Eukaryota
842:Eukaryota
822:Eukaryota
818:RNA virus
794:Eukaryota
737:factors.
664:microRNAs
633:algorithm
491:Mutations
479:conserved
457:Operators
439:Silencers
428:Silencers
402:Enhancers
388:initiator
265:turned on
246:silencers
234:enhancers
191:promoters
187:enhancers
3715:Methods
3649:Concepts
3629:Genetics
3583:Silencer
3561:Enhancer
3517:TATA box
3507:Promoter
3498:Heredity
3434:Overview
3425:Glossary
3317:microRNA
3231:Ribosome
3210:Archaeal
3166:Splicing
3138:Promoter
3107:Archaeal
3051: →
3047: →
2823:Hox gene
2811:Elements
2792:Homeobox
2411:11005278
2368:16625197
2331:16422483
2323:15690032
2278:17304246
2198:29414695
2190:22421878
2155:45588146
2147:18369140
2010:16381829
1961:18621088
1912:20114053
1877:19783826
1828:15215390
1779:17199892
1753:: 1–17.
1725:16845069
1673:24008418
1622:26656931
1571:19819296
1527:14534164
1492:19530131
1443:26934309
1392:13513643
1384:22143240
1319:12381658
1273:19660565
1211:17291181
1169:20371324
1034:Promoter
963:CAAT box
948:TATA box
936:See also
903:Bacteria
880:Bacteria
861:Bacteria
790:bacteria
761:Function
689:operator
671:Examples
581:promoter
545:cofactor
526:feedback
377:TATA box
357:Promoter
298:AND gate
220:promoter
160:Overview
59:regulate
3788:Genetic
3735:Pigment
3724:Protein
3685:Wet lab
3681:Dry lab
3661:Mitosis
3493:Genetic
3484:Element
3474:protein
3415:History
3070:RNA→DNA
3065:RNA→RNA
3053:Protein
2954:Debates
2765:Systems
2691:Eyespot
2555:Neoteny
2376:9581516
2348:Bibcode
2303:Bibcode
2239:8634917
2230:1369379
2127:Bibcode
2119:Science
2104:3527045
2069:8710843
2037:Bibcode
2001:1347444
1952:2670756
1868:2808893
1770:1766362
1716:1538799
1483:2747644
1434:4802784
1160:2849075
1139:Bibcode
958:SOS box
926:Metazoa
786:Archaea
693:protein
639:Active
557:looping
463:operons
414:introns
294:OR gate
273:drivers
104:prefix
100:). The
79:anatomy
3748:-omics
3737:&
3546:Intron
3524:Operon
2855:Ligand
2535:Operon
2461:(MeSH)
2426:
2409:
2374:
2366:
2340:Nature
2329:
2321:
2295:Nature
2286:560067
2284:
2276:
2237:
2227:
2196:
2188:
2153:
2145:
2102:
2067:
2057:
2008:
1998:
1959:
1949:
1910:
1875:
1865:
1826:
1819:441523
1816:
1777:
1767:
1723:
1713:
1671:
1620:
1569:
1561:
1525:
1490:
1480:
1441:
1431:
1390:
1382:
1342:
1317:
1271:
1209:
1167:
1157:
1029:Operon
1003:, mRNA
174:genome
57:which
3420:Index
3198:Types
3095:Types
2372:S2CID
2327:S2CID
2282:S2CID
2194:S2CID
2151:S2CID
2060:38642
1388:S2CID
1187:(PDF)
1009:Other
916:SECIS
767:Ref.
758:Abbr.
724:trans
579:) in
510:nodes
386:, an
381:TFIIB
134:trans
125:genes
102:Latin
67:genes
42:) or
3551:Exon
2495:The
2424:ISBN
2407:PMID
2364:PMID
2319:PMID
2274:PMID
2235:PMID
2186:PMID
2143:PMID
2100:PMID
2065:PMID
2006:PMID
1957:PMID
1908:PMID
1873:PMID
1824:PMID
1775:PMID
1721:PMID
1669:PMID
1618:PMID
1567:PMID
1559:ISSN
1523:PMID
1488:PMID
1439:PMID
1380:PMID
1340:ISBN
1315:PMID
1269:PMID
1207:PMID
1165:PMID
1044:Rfam
811:IRES
755:Type
662:and
379:, a
259:and
189:and
172:The
61:the
51:CRMs
40:CREs
3865:DNA
3855:RNA
3464:RNA
3454:DNA
3049:RNA
3045:DNA
2499:of
2397:doi
2356:doi
2344:440
2311:doi
2299:433
2266:doi
2225:PMC
2217:RNA
2178:doi
2135:doi
2123:319
2092:doi
2055:PMC
2045:doi
1996:PMC
1988:doi
1947:PMC
1939:doi
1935:139
1900:doi
1896:397
1863:PMC
1855:doi
1814:PMC
1806:doi
1765:PMC
1755:doi
1711:PMC
1703:doi
1659:hdl
1649:doi
1608:hdl
1598:doi
1551:doi
1515:doi
1478:PMC
1470:doi
1429:PMC
1419:doi
1372:doi
1305:doi
1261:doi
1199:doi
1155:PMC
1147:doi
985:RNA
943:DNA
835:IRE
697:RNA
695:or
641:cis
622:cis
597:cis
561:cis
553:cis
549:cis
541:Cis
522:cis
518:cis
514:cis
498:Cis
351:cis
343:cis
339:cis
335:Cis
324:cis
313:cis
309:Cis
305:cis
269:off
267:or
253:cis
242:cis
230:Cis
224:cis
213:Cis
209:Cis
201:Cis
147:Cis
143:cis
139:cis
129:cis
113:DNA
106:cis
45:cis
34:Cis
3851::
3750:")
3733:,
3683:/
2902:+
2405:.
2393:54
2391:.
2387:.
2370:.
2362:.
2354:.
2342:.
2325:.
2317:.
2309:.
2297:.
2280:.
2272:.
2260:.
2233:.
2219:.
2215:.
2192:.
2184:.
2174:10
2172:.
2149:.
2141:.
2133:.
2121:.
2098:.
2088:55
2086:.
2063:.
2053:.
2043:.
2033:93
2031:.
2027:.
2004:.
1994:.
1984:34
1982:.
1978:.
1955:.
1945:.
1933:.
1929:.
1906:.
1894:.
1871:.
1861:.
1851:38
1849:.
1845:.
1822:.
1812:.
1802:32
1800:.
1796:.
1773:.
1763:.
1749:.
1745:.
1733:^
1719:.
1709:.
1699:34
1697:.
1693:.
1681:^
1667:.
1657:.
1645:29
1643:.
1639:.
1616:.
1606:.
1594:32
1592:.
1588:.
1565:.
1557:.
1547:99
1545:.
1521:.
1511:19
1509:.
1486:.
1476:.
1466:87
1464:.
1460:.
1437:.
1427:.
1413:.
1409:.
1386:.
1378:.
1368:13
1366:.
1354:^
1313:.
1301:16
1299:.
1295:.
1281:^
1267:.
1257:20
1255:.
1219:^
1205:.
1195:36
1193:.
1189:.
1163:.
1153:.
1145:.
1135:98
1133:.
1129:.
1113:^
1065:^
882:,
820:,
796:,
792:,
788:,
699:.
647:.
528:,
489:.
197:.
89:.
3712:)
3476:)
3472:(
3466:)
3462:(
3456:)
3452:(
3396:e
3389:t
3382:v
3009:e
3002:t
2995:v
2602:/
2488:e
2481:t
2474:v
2432:.
2413:.
2399::
2378:.
2358::
2350::
2333:.
2313::
2305::
2288:.
2268::
2262:8
2241:.
2221:2
2200:.
2180::
2157:.
2137::
2129::
2106:.
2094::
2071:.
2047::
2039::
2012:.
1990::
1963:.
1941::
1914:.
1902::
1879:.
1857::
1830:.
1808::
1781:.
1757::
1751:8
1727:.
1705::
1675:.
1661::
1651::
1624:.
1610::
1600::
1573:.
1553::
1529:.
1517::
1494:.
1472::
1445:.
1421::
1415:7
1394:.
1374::
1348:.
1321:.
1307::
1275:.
1263::
1213:.
1201::
1171:.
1149::
1141::
49:(
38:(
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.