505:
The procedure entails removing the segment of cancerous ureter and reattaching the end. Patients with advanced bladder cancer or disease, also often look to bladder reconstruction as a treatment. Current methods of bladder reconstruction include the use of gastrointestinal tissue. However, while this method is effective in improving the function of the bladder, it can actually increases the risk of cancer, and can cause other complications, such as infections, urinary stones, and electrolyte imbalance. Therefore, other methods loom in the future. For example, current research paves the way for use of pluripotent stem cells to derive urothelium, as they are highly and indefinitely proliferative in vitro (i.e. outside of the body).
413:
is due to a highly keratinized cellular membrane synthesized in the Golgi apparatus. The membrane is made up of a hexagonal lattice put together in the Golgi apparatus and implanted into the surface of the cell by reverse pinocytosis, a type of exocytosis. The cells in the superficial layer of the transitional epithelium are highly differentiated, allowing for maintenance of this barrier membrane. The basal layer of the epithelium is much less differentiated; however, it does act as a replacement source for more superficial layer. While the Golgi complex is much less prominent in the cells of the basal layer, these cells are rich in cytoplasmic proteins that bundle together to form
497:, and the second leading cause of cancer of the kidney. Transitional cell carcinoma can develop in two different ways. Should the transitional cell carcinoma grow toward the inner surface of the bladder via finger-like projections, it is known as papillary carcinoma. Otherwise, it is known as flat carcinoma. Either form can transition from non-invasive to invasive by spreading into the muscle layers of the bladder. Transitional cell carcinoma is commonly multifocal, more than one tumor occurring at the time of diagnosis.
698:
304:
40:
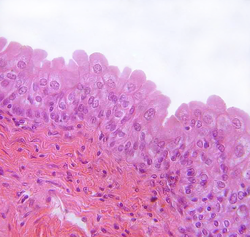
358:(column-shaped), while the cells of the superficial layer vary in appearance depending on the degree of distension. These cells appear to be cuboidal with a domed apex when the organ or the tube in which they reside is not stretched. When the organ or tube is stretched (such as when the bladder is filled with urine), the tissue compresses and the cells become stretched. When this happens, the cells flatten, and they appear to be
686:
52:
710:
722:
438:, or inside hollow space of the tract that it lines and the bloodstream. To help achieve this, the cells of transitional epithelium are connected by tight junctions, or virtually impenetrable junctions that seal together to the cellular membranes of neighboring cells. This barrier prevents re-absorption of toxic wastes and pathogens by the bloodstream.
504:
Transitional cell carcinoma patients have a variety of treatment options. These include nephroureterectomy, or the removal of kidney, ureter, and bladder cuff, and segmental resection of the ureter. This is an option only when the cancer is superficial and infects only the bottom third of the ureter.
520:
is a chronic disease of the bladder that causes feelings of pressure and pain in the bladder among other symptoms which can range from mild to severe. Urinary frequency and urgency are the most common symptoms associated with the disease. The exact causes of IC/BPS are unknown, but there is evidence
412:
The urothelium is the most impermeable membrane in the mammalian body. Because of its importance in acting as an osmotic barrier between the contents of the urinary tract and the surrounding organs and tissues, transitional epithelium is relatively impermeable to water and salts. This impermeability
500:
Transitional cell carcinoma can metastasize, or spread to other parts of the body via the surrounding tissues, the lymph system, and the bloodstream. It can spread to the tissues and fat surrounding the kidney, the fat surrounding the ureter, or, more progressively, lymph nodes and other organs,
403:
The epithelium contains many intimate and delicate connections to neural and connective tissue. These connections allow for communication to tell the cells to expand or contract. The superficial layer of transitional epithelium is connected to the basal layer via cellular projections, such as
923:
Poon, Song Ling; Huang, Mi Ni; Choo, Yang; McPherson, John R.; Yu, Willie; Heng, Hong Lee; Gan, Anna; Myint, Swe Swe; Siew, Ee Yan; Ler, Lian Dee; Ng, Lay Guat; Weng, Wen-Hui; Chuang, Cheng-Keng; Yuen, John SP; Pang, See-Tong; Tan, Patrick; Teh, Bin Tean; Rozen, Steven G. (Dec 2015).
429:
The transitional epithelium cells stretch readily in order to accommodate fluctuation of volume of the liquid in an organ (the distal part of the urethra becomes non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium in females; the part that lines the bottom of the tissue is called the
396:. This layer is the only fully differentiated layer of the epithelium. It provides an impenetrable barrier between the lumen and the bloodstream, so as not to allow the bloodstream to reabsorb harmful wastes or pathogens. All transitional epithelial cells are covered in
404:
intermediate filaments protruding from the cellular membrane. These structural elements cause the epithelium to allow distension; however, these also cause the tissue to be relatively fragile and, therefore, difficult to study. All cells touch the basement membrane.
521:
of an association between increased permeability of the urothelium and IC. Since the purpose of the urothelium is to act as a highly resistant barrier, the loss of this function has serious clinical implications. Many patients with IC have exhibited a loss of
370:
Transitional epithelium is made up of three types of cell layers: basal, intermediate, and superficial. The basal layer fosters the epithelial stem cells in order to provide constant renewal of the epithelium. These cells' cytoplasm is rich in tonofilaments and
318:. Transitional epithelium is a type of tissue that changes shape in response to stretching (stretchable epithelium). The transitional epithelium usually appears cuboidal when relaxed and squamous when stretched. This tissue consists of multiple layers of
387:
and an array of membrane-bound vesicles. These function in the packaging and transport of proteins, such as keratin, to the superficial cell layer. The cells of the superficial cell layer that lines the lumen are known as
383:. The intermediate cell layer is highly proliferative and, therefore, provides for rapid cell regeneration in response to injury or infection of the organ or tube in which it resides. These cells contain a prominent
501:
including bone. Common risk factors of transitional cell carcinoma include long-term misuse of pain medication, smoking, and exposure to chemicals used in the making of leather, plastic, textiles, and rubber.
1278:
307:
Transitional epithelium animation, highlighting the epithelial layer, then underlying connective tissue. Contrast the messy appearance of the epithelial surface to other epithelial tissues.
815:
913:
Firth, J. A., & Hicks, R. M. (1973). Interspecies variation in the fine structure and enzyme cytochemistry of mammalian transitional epithelium. Journal of
Anatomy, 116(Pt 1), 31–43.
549:
814:
Osborn, S. L., & Kurzrock, E. A. (2015). Production of
Urothelium from Pluripotent Stem Cells for Regenerative Applications. Current Urology Reports, 16(1), 1+. Retrieved from
737:
1020:
975:
466:
mutations and is a cause of liver, urothelial and bladder cancers. Occupational exposure to certain chemicals is also a risk factor for bladder cancer. This can include
446:
Urothelium is susceptible to carcinoma. Because the bladder is in contact with urine for extended periods, chemicals that become concentrated in the urine can cause
1271:
798:
Monis, B., & Zambrano, D. (1968). Ultrastructure of transitional epithelium of man. Zeitschrift für
Zellforschung und Microscopical Anatomie, 87(1), 101-117.
1075:
Hurst, Robert E.; Greenwood-Van
Meerveld, Beverley; Wisniewski, Amy B.; VanGordon, Samuel; Lin, HsuehKung; Kropp, Bradley P.; Towner, Rheal A. (October 2015).
816:
http://go.galegroup.com/ps/i.do?id=GALE%7CA390522720&v=2.1&u=clemsonu_main&it=r&p=AONE&sw=w&asid=bf6961c15c9b9523113dee93fd8df89c
290:
1223:
1162:
1264:
1039:
697:
659:
1247:
989:
1235:
669:
649:
634:
1146:
1415:
174:
644:
322:
cells which can contract and expand in order to adapt to the degree of distension needed. Transitional epithelium lines the organs of the
664:
629:
624:
264:
639:
1017:
100:
654:
591:
564:
471:
559:
1395:
1388:
1381:
283:
197:
169:
146:
60:, known as urothelium. The rounded surface of the apical cells is a distinguishing characteristic of this type of epithelium.
614:
569:
241:
889:
Hicks, R. (1966). THE FUNCTION OF THE GOLGI COMPLEX IN TRANSITIONAL EPITHELIUM: Synthesis of the Thick Cell
Membrane.
539:
486:
376:
1361:
1354:
1335:
586:
246:
192:
164:
141:
601:
1624:
1191:
1040:
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases_conditions/hic_Transitional_Cell_Cancer_of_Renal_Pelvis_and_Ureter
534:
276:
581:
1312:
1307:
1302:
1214:
1199:
www.urothelium.com is an online resource for information about Human
Urothelium and the "Biomimetic Urothelium"
183:
155:
132:
88:
709:
1220:
1180:
618:
576:
350:
The appearance of transitional epithelium differs according to its cell layer. Cells of the basal layer are
1420:
721:
685:
596:
218:
969:
513:
223:
93:
1244:
1187:
609:
544:
493:, occurring in 9 out of 10 cases. It is also the leading cause of cancer of the ureter, urethra, and
213:
1201:
1051:
303:
1475:
1232:
379:. The tonofilaments play a role in the attachment of the basal layer to the basement membrane via
1561:
454:
leads to the concentration of carcinogens in the urine and is a leading cause of bladder cancer.
233:
852:
853:"Membranes and membrane surfaces: Dynamics of cytoplasmic membranes in pancreatic acinar cells"
1588:
1578:
1142:
1114:
1096:
1018:
http://www.cancer.org/cancer/bladdercancer/detailedguide/bladder-cancer-what-is-bladder-cancer
957:
872:
455:
451:
431:
39:
1104:
1088:
947:
937:
864:
459:
1566:
1497:
1492:
1251:
1239:
1227:
1205:
1173:
1167:
1024:
435:
384:
1092:
1599:
1573:
1520:
1109:
1076:
952:
925:
490:
467:
447:
418:
323:
76:
17:
1210:
1618:
1583:
1515:
1052:"What is Interstitial Cystitis(IC)/Bladder Pain Syndrome? - Urology Care Foundation"
759:
1541:
1536:
1016:
American Cancer
Society. (2014). Bladder cancer. Retrieved November 25, 2014, from
897:
831:
Hicks, R. (1965). The Fine
Structure Of The Transitional Epithelium Of Rat Ureter.
372:
71:
1077:"Increased bladder permeability in interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome"
839:
1136:
857:
Philosophical
Transactions of the Royal Society of London. B, Biological Sciences
1345:
1340:
414:
51:
926:"Mutation signatures implicate aristolochic acid in bladder cancer development"
1434:
1287:
1038:
Transitional Cell Cancer. (2012, April 13). Retrieved
December 14, 2014, from
942:
522:
397:
389:
380:
319:
315:
125:
1100:
1487:
1470:
482:
1118:
961:
868:
876:
851:
Meldolesi, J.; Markham, Roy; Horne, R. W.; Hicks, R. Marian (1974-07-04).
1482:
359:
355:
351:
1176:
at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center - "urinary bladder"
106:
494:
339:
57:
1595:
760:"Transitional epithelium- definition, structure, functions, examples"
553:
1256:
434:). Transitional epithelium also functions as a barrier between the
302:
1260:
1170:
at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center - "ureter"
463:
1198:
660:
Urothelial carcinoma with syncitiotrophoblastic giant cells
670:
Urothelial carcinoma similar to giant cell tumor of bone
650:
Urothelial carcinoma, clear cell (glycogen-rich) variant
635:
Urothelial carcinoma with villoglandular differentiation
550:
Papillary urothelial neoplasm of low malignant potential
485:
is a type of cancer that occurs in epithelial cells.
645:
Urothelial carcinoma, lymphoepithelioma-like variant
1554:
1529:
1508:
1463:
1456:
1449:
1408:
1374:
1328:
1321:
1295:
738:
List of distinct cell types in the adult human body
87:
82:
70:
65:
32:
1181:Anatomy Atlases – Microscopic Anatomy, plate 02.24
665:Urothelial carcinoma with rhabdoid differentiation
630:Urothelial carcinoma with squamous differentiation
1012:
1010:
625:Urothelial carcinoma with inverted growth pattern
898:http://jcb.rupress.org/content/30/3/623.abstract
896:(3), 623-643. Retrieved November 25, 2014, from
342:, for example, has a need for great distension.
840:http://jcb.rupress.org/content/26/1/25.abstract
838:(1), 25-48. Retrieved November 25, 2014, from
421:to attach the cells at the basement membrane.
1272:
974:: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of March 2024 (
284:
8:
1034:
1032:
827:
825:
823:
640:Urothelial carcinoma, micropapillary variant
794:
792:
458:, a compound found in plants of the family
1460:
1453:
1405:
1371:
1325:
1279:
1265:
1257:
291:
277:
116:
50:
38:
1213:at the U.S. National Library of Medicine
1108:
951:
941:
703:Schematic view of transitional epithelium
655:Urothelial carcinoma, lipoid cell variant
592:Urothelial atypia of unknown significance
565:High-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma
810:
808:
806:
804:
786:(9th ed., pp. 122-124). Boston: Pearson.
560:Low-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma
909:
907:
905:
747:
681:
256:
205:
182:
154:
131:
124:
967:
104:
29:
7:
1416:Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
782:Marieb, E., & Hoehn, K. (2013).
753:
751:
1184:- "Transitional Epithelium", Ureter
1093:10.3978/j.issn.2223-4683.2015.10.03
1081:Translational Andrology and Urology
331:
120:This article is part of a series on
265:Table of epithelia of human organs
25:
715:Vertical section of bladder wall.
720:
708:
696:
684:
540:Papillary urothelial hyperplasia
472:polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
417:. These tonofibrils converge at
101:Anatomical terms of microanatomy
758:Sapkota, Anupama (2020-09-28).
56:Transitional epithelium of the
1396:Stratified columnar epithelium
1389:Stratified cuboidal epithelium
1382:Stratified squamous epithelium
784:Human anatomy & physiology
1:
1135:Andersson, Karl-Erik (2011).
990:"Bladder cancer risk factors"
727:Transverse section of ureter.
615:Invasive urothelial carcinoma
587:Urothelial inverted papilloma
570:Invasive urothelial carcinoma
474:, and diesel engine exhaust.
400:and a fibrillar mucous coat.
891:The Journal of Cell Biology,
833:The Journal of Cell Biology,
602:Urothelial carcinoma in situ
535:Papillary urothelial lesions
375:; however, they contain few
487:Transitional cell carcinoma
377:rough endoplasmic reticulum
1641:
1362:Simple columnar epithelium
1355:Simple cuboidal epithelium
1336:Simple squamous epithelium
582:Reactive urothelial atypia
943:10.1186/s13073-015-0161-3
99:
49:
37:
1215:Medical Subject Headings
518:painful bladder syndrome
184:Cuboidal epithelial cell
156:Columnar epithelial cell
133:Squamous epithelial cell
1430:Transitional epithelium
1221:Histology at qmul.ac.uk
946:(inactive 2024-03-19).
577:Flat urothelial lesions
489:is the leading type of
312:Transitional epithelium
44:Transitional epithelium
33:Transitional epithelium
18:Transitional epithelial
1421:Respiratory epithelium
1174:Histology image: 37_02
1168:Histology image: 36_02
869:10.1098/rstb.1974.0014
308:
1245:Histology at wisc.edu
1163:Histology at utmb.edu
1056:www.urologyhealth.org
514:Interstitial cystitis
509:Interstitial cystitis
442:Clinical significance
326:and is known here as
316:stratified epithelium
306:
206:Specialised epithelia
1233:Diagram at umich.edu
610:urothelial carcinoma
597:Urothelial dysplasia
545:Urothelial papilloma
691:Types of epithelium
1562:Myoepithelial cell
1250:2008-06-10 at the
1238:2006-09-10 at the
1226:2011-07-21 at the
1204:2011-02-01 at the
1023:2016-12-01 at the
994:Cancer Research UK
529:Urothelial lesions
354:(cube-shaped), or
309:
94:H2.00.02.0.02033
1612:
1611:
1608:
1607:
1550:
1549:
1445:
1444:
1404:
1403:
1370:
1369:
1188:Histology at KUMC
1148:978-3-642-16498-9
456:Aristolochic acid
452:cigarette smoking
432:basement membrane
301:
300:
115:
114:
110:
16:(Redirected from
1632:
1625:Epithelial cells
1461:
1454:
1406:
1372:
1326:
1281:
1274:
1267:
1258:
1152:
1123:
1122:
1112:
1072:
1066:
1065:
1063:
1062:
1048:
1042:
1036:
1027:
1014:
1005:
1004:
1002:
1000:
986:
980:
979:
973:
965:
955:
945:
920:
914:
911:
900:
887:
881:
880:
848:
842:
829:
818:
812:
799:
796:
787:
780:
774:
773:
771:
770:
755:
724:
712:
700:
688:
460:Aristolochiaceae
450:. For example,
333:
293:
286:
279:
175:Pseudostratified
117:
107:edit on Wikidata
54:
42:
30:
27:A type of tissue
21:
1640:
1639:
1635:
1634:
1633:
1631:
1630:
1629:
1615:
1614:
1613:
1604:
1567:Serous demilune
1546:
1525:
1504:
1441:
1400:
1366:
1317:
1291:
1285:
1252:Wayback Machine
1240:Wayback Machine
1228:Wayback Machine
1206:Wayback Machine
1192:urinary-renal16
1159:
1149:
1134:
1131:
1126:
1074:
1073:
1069:
1060:
1058:
1050:
1049:
1045:
1037:
1030:
1025:Wayback Machine
1015:
1008:
998:
996:
988:
987:
983:
966:
930:Genome Medicine
922:
921:
917:
912:
903:
888:
884:
850:
849:
845:
830:
821:
813:
802:
797:
790:
781:
777:
768:
766:
757:
756:
749:
745:
735:
728:
725:
716:
713:
704:
701:
692:
689:
680:
531:
516:(IC) a type of
511:
480:
470:(aniline dye),
468:aromatic amines
444:
427:
410:
385:Golgi apparatus
368:
362:and irregular.
348:
297:
111:
61:
45:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1638:
1636:
1628:
1627:
1617:
1616:
1610:
1609:
1606:
1605:
1603:
1602:
1593:
1592:
1591:
1586:
1581:
1570:
1569:
1564:
1558:
1556:
1552:
1551:
1548:
1547:
1545:
1544:
1539:
1533:
1531:
1527:
1526:
1524:
1523:
1521:Alveolar gland
1518:
1512:
1510:
1506:
1505:
1503:
1502:
1501:
1500:
1495:
1485:
1480:
1479:
1478:
1467:
1465:
1458:
1451:
1447:
1446:
1443:
1442:
1440:
1439:
1438:
1437:
1426:
1425:
1424:
1423:
1412:
1410:
1402:
1401:
1399:
1398:
1392:
1391:
1385:
1384:
1378:
1376:
1368:
1367:
1365:
1364:
1358:
1357:
1351:
1350:
1349:
1348:
1343:
1332:
1330:
1323:
1319:
1318:
1316:
1315:
1310:
1305:
1299:
1297:
1293:
1292:
1286:
1284:
1283:
1276:
1269:
1261:
1255:
1254:
1242:
1230:
1218:
1208:
1196:
1185:
1177:
1171:
1165:
1158:
1157:External links
1155:
1154:
1153:
1147:
1130:
1127:
1125:
1124:
1087:(5): 563–571.
1067:
1043:
1028:
1006:
981:
915:
901:
882:
863:(891): 39–53.
843:
819:
800:
788:
775:
746:
744:
741:
734:
731:
730:
729:
726:
719:
717:
714:
707:
705:
702:
695:
693:
690:
683:
679:
676:
675:
674:
673:
672:
667:
662:
657:
652:
647:
642:
637:
632:
627:
622:
606:
605:
604:
599:
594:
589:
584:
574:
573:
572:
567:
562:
557:
547:
542:
530:
527:
523:umbrella cells
510:
507:
491:bladder cancer
479:
476:
462:, also causes
448:bladder cancer
443:
440:
426:
423:
419:hemidesmosomes
409:
406:
394:umbrella cells
367:
364:
347:
344:
324:urinary system
299:
298:
296:
295:
288:
281:
273:
270:
269:
268:
267:
259:
258:
254:
253:
252:
251:
250:
249:
244:
236:
231:
226:
221:
216:
208:
207:
203:
202:
201:
200:
195:
187:
186:
180:
179:
178:
177:
172:
167:
159:
158:
152:
151:
150:
149:
144:
136:
135:
129:
128:
122:
121:
113:
112:
103:
97:
96:
91:
85:
84:
80:
79:
77:Urinary system
74:
68:
67:
63:
62:
55:
47:
46:
43:
35:
34:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1637:
1626:
1623:
1622:
1620:
1601:
1597:
1594:
1590:
1589:Intercalated
1587:
1585:
1582:
1580:
1577:
1576:
1575:
1572:
1571:
1568:
1565:
1563:
1560:
1559:
1557:
1553:
1543:
1542:Mucous glands
1540:
1538:
1537:Serous glands
1535:
1534:
1532:
1528:
1522:
1519:
1517:
1516:Tubular gland
1514:
1513:
1511:
1507:
1499:
1496:
1494:
1491:
1490:
1489:
1486:
1484:
1481:
1477:
1474:
1473:
1472:
1469:
1468:
1466:
1462:
1459:
1455:
1452:
1448:
1436:
1433:
1432:
1431:
1428:
1427:
1422:
1419:
1418:
1417:
1414:
1413:
1411:
1407:
1397:
1394:
1393:
1390:
1387:
1386:
1383:
1380:
1379:
1377:
1373:
1363:
1360:
1359:
1356:
1353:
1352:
1347:
1344:
1342:
1339:
1338:
1337:
1334:
1333:
1331:
1327:
1324:
1320:
1314:
1311:
1309:
1306:
1304:
1301:
1300:
1298:
1294:
1289:
1282:
1277:
1275:
1270:
1268:
1263:
1262:
1259:
1253:
1249:
1246:
1243:
1241:
1237:
1234:
1231:
1229:
1225:
1222:
1219:
1216:
1212:
1209:
1207:
1203:
1200:
1197:
1194:
1193:
1189:
1186:
1183:
1182:
1178:
1175:
1172:
1169:
1166:
1164:
1161:
1160:
1156:
1150:
1144:
1140:
1139:
1138:Urinary Tract
1133:
1132:
1128:
1120:
1116:
1111:
1106:
1102:
1098:
1094:
1090:
1086:
1082:
1078:
1071:
1068:
1057:
1053:
1047:
1044:
1041:
1035:
1033:
1029:
1026:
1022:
1019:
1013:
1011:
1007:
995:
991:
985:
982:
977:
971:
963:
959:
954:
949:
944:
939:
935:
931:
927:
919:
916:
910:
908:
906:
902:
899:
895:
892:
886:
883:
878:
874:
870:
866:
862:
858:
854:
847:
844:
841:
837:
834:
828:
826:
824:
820:
817:
811:
809:
807:
805:
801:
795:
793:
789:
785:
779:
776:
765:
764:Microbe Notes
761:
754:
752:
748:
742:
740:
739:
732:
723:
718:
711:
706:
699:
694:
687:
682:
677:
671:
668:
666:
663:
661:
658:
656:
653:
651:
648:
646:
643:
641:
638:
636:
633:
631:
628:
626:
623:
620:
616:
613:
612:
611:
607:
603:
600:
598:
595:
593:
590:
588:
585:
583:
580:
579:
578:
575:
571:
568:
566:
563:
561:
558:
555:
551:
548:
546:
543:
541:
538:
537:
536:
533:
532:
528:
526:
524:
519:
515:
508:
506:
502:
498:
496:
492:
488:
484:
477:
475:
473:
469:
465:
461:
457:
453:
449:
441:
439:
437:
433:
424:
422:
420:
416:
408:Cell membrane
407:
405:
401:
399:
395:
391:
386:
382:
378:
374:
365:
363:
361:
357:
353:
345:
343:
341:
337:
329:
325:
321:
317:
314:is a type of
313:
305:
294:
289:
287:
282:
280:
275:
274:
272:
271:
266:
263:
262:
261:
260:
255:
248:
245:
243:
240:
239:
237:
235:
232:
230:
227:
225:
222:
220:
217:
215:
212:
211:
210:
209:
204:
199:
196:
194:
191:
190:
189:
188:
185:
181:
176:
173:
171:
168:
166:
163:
162:
161:
160:
157:
153:
148:
145:
143:
140:
139:
138:
137:
134:
130:
127:
123:
119:
118:
108:
102:
98:
95:
92:
90:
86:
81:
78:
75:
73:
69:
64:
59:
53:
48:
41:
36:
31:
19:
1579:Intralobular
1429:
1190:
1179:
1141:. Springer.
1137:
1129:Bibliography
1084:
1080:
1070:
1059:. Retrieved
1055:
1046:
997:. Retrieved
993:
984:
970:cite journal
933:
929:
918:
893:
890:
885:
860:
856:
846:
835:
832:
783:
778:
767:. Retrieved
763:
736:
517:
512:
503:
499:
481:
445:
428:
411:
402:
393:
373:mitochondria
369:
349:
335:
327:
311:
310:
229:Transitional
228:
1346:Mesothelium
1341:Endothelium
415:tonofibrils
390:facet cells
366:Cell layers
219:Respiratory
83:Identifiers
1555:Components
1435:Urothelium
1375:stratified
1288:Epithelial
1211:Urothelium
1061:2021-07-12
769:2021-10-17
743:References
398:microvilli
381:desmosomes
328:urothelium
320:epithelial
224:Intestinal
198:Stratified
170:Stratified
147:Stratified
1584:Striated
1530:Secretion
1498:Meibomian
1493:Sebaceous
1488:Holocrine
1471:Merocrine
1464:Mechanism
1308:Cuboidal
1303:Squamous
1101:2223-4691
936:(1): 38.
608:Invasive
483:Carcinoma
478:Carcinoma
346:Structure
336:urothelia
238:Germinal
214:Olfactory
126:Epithelia
1619:Category
1483:Apocrine
1313:Columnar
1248:Archived
1236:Archived
1224:Archived
1202:Archived
1195:"ureter"
1119:26751576
1021:Archived
962:26015808
733:See also
425:Function
360:squamous
356:columnar
352:cuboidal
1476:Eccrine
1110:4706376
999:27 July
953:4443665
877:4155089
678:Gallery
495:urachus
340:bladder
338:). The
234:Vaginal
66:Details
58:bladder
1596:Acinus
1450:Glands
1329:Simple
1290:tissue
1217:(MeSH)
1145:
1117:
1107:
1099:
960:
950:
875:
554:PUNLMP
242:female
193:Simple
165:Simple
142:Simple
72:System
1574:Ducts
1509:Shape
1457:Types
1409:Other
1322:Types
1296:Cells
436:lumen
257:Other
105:[
1600:Lobe
1143:ISBN
1115:PMID
1097:ISSN
1001:2014
976:link
958:PMID
873:PMID
247:male
1105:PMC
1089:doi
948:PMC
938:doi
865:doi
861:268
619:NOS
464:DNA
392:or
332:pl.
1621::
1113:.
1103:.
1095:.
1083:.
1079:.
1054:.
1031:^
1009:^
992:.
972:}}
968:{{
956:.
932:.
928:.
904:^
894:30
871:.
859:.
855:.
836:26
822:^
803:^
791:^
762:.
750:^
525:.
334::
89:TH
1598:/
1280:e
1273:t
1266:v
1151:.
1121:.
1091::
1085:4
1064:.
1003:.
978:)
964:.
940::
934:7
879:.
867::
772:.
621:)
617:(
556:)
552:(
330:(
292:e
285:t
278:v
109:]
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.