62:
42:
318:
is unusual in becoming endemic to
Australia, whereas the other genera are found in Africa and Madagascar, and the fossil record supports the terrestrial radiation of the family. One hypothesis is they may have aerially dispersed to new regions by island hopping, a proposed explanation for Allodapine
253:
are sometimes found to be contrary in morphological and molecular analyses, yet resolving the phylogeny of these speciose and poorly defined groups has implication in several areas of research. The synonymy includes earlier combinations that elevated the rank through subtribe, tribe then subfamily.
412:. The three groups, the hipposiderid, rhinolophid and rhinonycterid families, were tested by several genomic and morphological studies that strongly supported monophyletic lineages. The families all appear to have diverged from a common ancestor around 42
297:
A common name for what Gray referred as 'leaf-nosed bats' in establishing the
Rhinonycterina, and later authors labelled 'Old World leaf-nosed bats' in transposing the name for hipposiderid species, has been proposed as
281:
in earlier morphological classifications. Aside from anticipating and detecting the sources of zoonotic disease, as carriers of the potentially lethal coronavirus species (especially those of human-lethal
273:
outbreak. The reviewing authors also emphasise the strong support for elevation to family rank of
Rhinonycteridae and reconsideration as a taxonomic equivalent to family
319:
bees that dispersed from Africa to
Australia during the same epochs. The earliest dates for the arrival of the family in Australia coïncides with the arrival of
239:
in a 1982 revision that compared the nose-leaf morphology of the species. This name was again proposed to accommodate the fossil and extant species of the genus
879:
390:
The 2014 revision presents a separation as three families, equivalent to other mammalian taxonomic arrangements, and incorporates a clade identifying the type
680:
Hand, Suzanne J.; Benda, Petr; Goodman, Steven M.; Armstrong, Kyle N. (28 October 2016). "A common name for the bat family
Rhinonycteridae—the Trident Bats".
511:
Hill J. A review of the leaf-nosed bats
Rhinonycteris, Cloeotis and Triaenops (Chiroptera: Hipposideridae), Bonn Zool Beitr., 1982, vol. 33 (pg. 165-186)
203:
for the subfamilial group, and these provide diagnosis to distinguish the species from other families. Molecular analysis also provides a distinctive
840:
943:
866:
416:, and the Hipposideridae and Rhinonycteridae at approximately 39 Ma. The origin of the family is determined to be the African continent.
261:
The hipposiderid and rhinolophid bats are of especial interest to research into potential public health concerns, and the opportunity for a
325:, and both are thought to have migrated through Europe and Asia to arrive and diverge at the Australian continent around 15 to 20 Ma.
571:
Foley, Nicole M.; Thong, Vu Dinh; Soisook, Pipat; Goodman, Steven M.; Armstrong, Kyle N.; Jacobs, David S.; Puechmaille, Sébastien J.;
258:
Benda & Vallo, 2009 was also reduced to a synonym for this family by the authors of the 2014 revision that elevated this taxon.
270:
871:
656:(Chiroptera: Hipposideridae) with description of a new species from southern Arabia and definitions of a new genus and tribe"
365:
61:
287:
321:
814:
329:
884:
933:
948:
767:
378:
358:
177:
155:
938:
905:
382:
Hand, 1993. A fossil taxon of the
Miocene period, the earliest of the Australian rhinonycterid lineage.
805:
577:"How and Why Overcome the Impediments to Resolution: Lessons from rhinolophid and hipposiderid Bats"
419:
The arrangement of the family, with the subsequent inclusion of
Miocene taxa, may be summarised as:
713:
172:
56:
910:
892:
827:
748:
705:
697:
606:
897:
526:
689:
596:
588:
464:
216:
138:
732:
283:
204:
737:(Brachipposideros) (Microchiroptera: Hipposideridae). from Australian Miocene sediments"
819:
624:
601:
576:
274:
246:
224:
123:
41:
927:
480:
472:
396:
349:
250:
241:
191:
717:
651:
832:
572:
453:
147:
249:, and was elevated in 2014. The affinities within the families Hipposideridae and
790:
853:
799:
266:
693:
752:
701:
592:
489:
413:
402:
278:
235:
200:
199:. The revision of Hill in 1982 follows Gray to describe the features of the
196:
73:
709:
610:
17:
784:
442:
408:
229:
93:
219:'s 1866 arrangement of known microbat taxa, first published as subtribe
845:
858:
103:
83:
761:
277:, based on the time of divergence and phylogenies that indicated
262:
765:
113:
265:-like outbreak from species that act as reservoirs for the
189:
The family accords with the description to the type genus
245:, separating it from the unstable arrangements of family
175:. The type species, the orange nose-leafed species group
269:
implicated in conditions like the
Chinese epidemic and
286:-b group), the treatment allows the identification of
227:
of family. The taxon combined the poorly known genera
460:
449:
774:
195:, and its classification of the morphology of the
675:
673:
332:recognised extant taxa occurring in Australia;
290:within the hipposiderid, rhinolophid and the
8:
566:
564:
562:
560:
558:
556:
554:
552:
550:
548:
762:
631:. Department of the Environment and Energy
533:. Department of the Environment and Energy
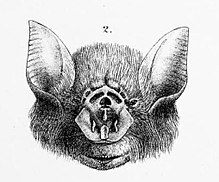
181:, is found across the north of Australia.
40:
31:
600:
171:is a family of bats, within the suborder
207:insertion expressed in a gene fragment.
518:
504:
7:
650:Benda, Petr; Vallo, Peter (2009).
25:
652:"Taxonomic revision of the genus
741:Memoirs of the Queensland Museum
527:"Names List for RHINONYCTERIDAE"
371:recognised as an isolated group
271:Middle East respiratory syndrome
60:
581:Molecular Biology and Evolution
944:Taxa named by John Edward Gray
288:Evolutionary Significant Units
1:
733:"First skull of a species of
322:Brachipposideros nooraleebus
223:, and elevating this to the
629:Australian Faunal Directory
531:Australian Faunal Directory
330:Australian Faunal Directory
965:
731:Hand, Suzanne J. (1993).
694:10.11646/zootaxa.4179.1.7
153:
146:
57:Scientific classification
55:
48:
39:
34:
625:"Family RHINONYCTERIDAE"
215:The alliance resurrects
660:Folia Zoologica -Praha
423:family Hipposideridae.
392:Rhinonicteris aurantia
379:Rhinonicteris tedfordi
367:Rhinonicteris aurantia
359:Rhinonicteris aurantia
178:Rhinonicteris aurantia
50:Rhinonicteris aurantia
906:Paleobiology Database
593:10.1093/molbev/msu329
433:. elevated by Foley,
426:family Rhinolophidae.
340:. elevated by Foley,
156:Rhinolophus aurantius
362:(J.E. Gray, 1845).
173:Yinpterochiroptera
934:Bats of Australia
921:
920:
893:Open Tree of Life
768:Taxon identifiers
575:(February 2015).
166:
165:
142:
16:(Redirected from
956:
914:
913:
901:
900:
888:
887:
875:
874:
862:
861:
849:
848:
836:
835:
823:
822:
810:
809:
808:
795:
794:
793:
763:
757:
756:
728:
722:
721:
677:
668:
667:
647:
641:
640:
638:
636:
621:
615:
614:
604:
573:Teeling, Emma C.
568:
543:
542:
540:
538:
523:
512:
509:
465:Brachipposideros
462:
451:
353:J.E. Gray, 1847
217:John Edward Gray
137:
65:
64:
44:
35:Rhinonycteridae
32:
21:
964:
963:
959:
958:
957:
955:
954:
953:
949:Rhinonycteridae
924:
923:
922:
917:
909:
904:
896:
891:
883:
878:
870:
865:
857:
852:
844:
839:
831:
826:
820:Rhinonycteridae
818:
813:
806:Rhinonycteridae
804:
803:
798:
789:
788:
783:
776:Rhinonycteridae
770:
760:
730:
729:
725:
679:
678:
671:
649:
648:
644:
634:
632:
623:
622:
618:
570:
569:
546:
536:
534:
525:
524:
520:
516:
515:
510:
506:
501:
484:J.E. Gray, 1847
431:Rhinonycteridae
338:Rhinonycteridae
312:
284:Betacoronavirus
213:
205:retrotransposon
187:
169:Rhinonycteridae
162:
159:
136:
134:Rhinonycteridae
59:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
962:
960:
952:
951:
946:
941:
936:
926:
925:
919:
918:
916:
915:
902:
889:
876:
863:
850:
837:
824:
811:
796:
780:
778:
772:
771:
766:
759:
758:
723:
688:(1): 115–117.
669:
642:
616:
587:(2): 313–333.
544:
517:
514:
513:
503:
502:
500:
497:
496:
495:
494:
493:
485:
476:
468:
457:
446:
427:
424:
388:
387:
386:
385:
384:
383:
374:
373:
372:
369:(Pilbara form)
311:
308:
275:Hipposideridae
247:Hipposideridae
221:Rhinonycterina
212:
209:
186:
183:
164:
163:
160:
151:
150:
144:
143:
131:
127:
126:
124:Rhinolophoidea
121:
117:
116:
111:
107:
106:
101:
97:
96:
91:
87:
86:
81:
77:
76:
71:
67:
66:
53:
52:
46:
45:
37:
36:
27:Family of bats
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
961:
950:
947:
945:
942:
940:
937:
935:
932:
931:
929:
912:
907:
903:
899:
894:
890:
886:
881:
877:
873:
868:
864:
860:
855:
851:
847:
842:
838:
834:
829:
825:
821:
816:
812:
807:
801:
797:
792:
786:
782:
781:
779:
777:
773:
769:
764:
754:
750:
746:
742:
738:
736:
727:
724:
719:
715:
711:
707:
703:
699:
695:
691:
687:
683:
676:
674:
670:
665:
661:
657:
655:
646:
643:
630:
626:
620:
617:
612:
608:
603:
598:
594:
590:
586:
582:
578:
574:
567:
565:
563:
561:
559:
557:
555:
553:
551:
549:
545:
532:
528:
522:
519:
508:
505:
498:
492:
491:
486:
483:
482:
481:Rhinonicteris
477:
475:
474:
473:Paratriaenops
469:
467:
466:
458:
456:
455:
447:
445:
444:
439:
438:
436:
432:
428:
425:
422:
421:
420:
417:
415:
411:
410:
405:
404:
399:
398:
397:Paratriaenops
393:
381:
380:
375:
370:
368:
364:
363:
361:
360:
355:
354:
352:
351:
350:Rhinonicteris
346:
345:
343:
339:
335:
334:
333:
331:
326:
324:
323:
317:
316:Rhinonicteris
309:
307:
305:
301:
295:
293:
292:rhinonycterid
289:
285:
280:
276:
272:
268:
267:coronaviruses
264:
259:
257:
252:
251:Rhinolophidae
248:
244:
243:
242:Rhinonicteris
238:
237:
232:
231:
226:
222:
218:
210:
208:
206:
202:
198:
194:
193:
192:Rhinonicteris
184:
182:
180:
179:
174:
170:
158:
157:
152:
149:
145:
140:
135:
132:
129:
128:
125:
122:
120:Superfamily:
119:
118:
115:
112:
109:
108:
105:
102:
99:
98:
95:
92:
89:
88:
85:
82:
79:
78:
75:
72:
69:
68:
63:
58:
54:
51:
47:
43:
38:
33:
30:
19:
939:Bat families
775:
744:
740:
735:Hipposideros
734:
726:
685:
681:
663:
659:
653:
645:
633:. Retrieved
628:
619:
584:
580:
535:. Retrieved
530:
521:
507:
488:
479:
471:
463:
454:Brevipalatus
452:
441:
434:
430:
418:
407:
401:
395:
394:with genera
391:
389:
377:
366:
357:
348:
341:
337:
327:
320:
315:
313:
303:
302:(Armstrong,
300:trident bats
299:
296:
291:
260:
255:
240:
234:
228:
220:
214:
190:
188:
176:
168:
167:
154:
148:Type species
133:
49:
29:
854:iNaturalist
800:Wikispecies
747:: 179–192.
256:Triaenopini
185:Description
18:Triaenopini
928:Categories
635:29 January
537:29 January
499:References
314:The genus
294:lineages.
254:The taxon
161:Gray, 1845
114:Chiroptera
791:Q19409100
753:0079-8835
702:1175-5334
654:Triaenops
490:Triaenops
437:, 2014.
403:Triaenops
344:, 2014.
310:Diversity
306:, 2016).
279:paraphyly
236:Triaenops
201:nose-leaf
197:rhinarium
139:J.E. Gray
80:Kingdom:
74:Eukaryota
785:Wikidata
718:20906819
710:27811695
611:25433366
443:Cloeotis
409:Cloeotis
376:species
356:species
230:Cloeotis
211:Taxonomy
130:Family:
104:Mammalia
94:Chordata
90:Phylum:
84:Animalia
70:Domain:
898:5819794
885:1677019
872:1141256
846:4832037
682:Zootaxa
602:4769323
429:family
336:family
110:Order:
100:Class:
911:477221
859:446817
751:
716:
708:
700:
609:
599:
487:genus
478:genus
470:genus
459:genus
448:genus
440:genus
347:genus
141:, 1866
833:7NDGQ
714:S2CID
435:et al
342:et al
304:et al
880:NCBI
867:ITIS
841:GBIF
749:ISSN
706:PMID
698:ISSN
686:4179
637:2019
607:PMID
539:2019
406:and
328:The
263:SARS
233:and
225:rank
828:CoL
815:AFD
690:doi
597:PMC
589:doi
930::
908::
895::
882::
869::
856::
843::
830::
817::
802::
787::
745:33
743:.
739:.
712:.
704:.
696:.
684:.
672:^
664:58
662:.
658:.
627:.
605:.
595:.
585:32
583:.
579:.
547:^
529:.
414:Ma
400:,
755:.
720:.
692::
666:.
639:.
613:.
591::
541:.
461:†
450:†
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.