51:
31:
307:
is unusual in becoming endemic to
Australia, whereas the other genera are found in Africa and Madagascar, and the fossil record supports the terrestrial radiation of the family. One hypothesis is they may have aerially dispersed to new regions by island hopping, a proposed explanation for Allodapine
242:
are sometimes found to be contrary in morphological and molecular analyses, yet resolving the phylogeny of these speciose and poorly defined groups has implication in several areas of research. The synonymy includes earlier combinations that elevated the rank through subtribe, tribe then subfamily.
401:. The three groups, the hipposiderid, rhinolophid and rhinonycterid families, were tested by several genomic and morphological studies that strongly supported monophyletic lineages. The families all appear to have diverged from a common ancestor around 42
286:
A common name for what Gray referred as 'leaf-nosed bats' in establishing the
Rhinonycterina, and later authors labelled 'Old World leaf-nosed bats' in transposing the name for hipposiderid species, has been proposed as
270:
in earlier morphological classifications. Aside from anticipating and detecting the sources of zoonotic disease, as carriers of the potentially lethal coronavirus species (especially those of human-lethal
262:
outbreak. The reviewing authors also emphasise the strong support for elevation to family rank of
Rhinonycteridae and reconsideration as a taxonomic equivalent to family
308:
bees that dispersed from Africa to
Australia during the same epochs. The earliest dates for the arrival of the family in Australia coïncides with the arrival of
228:
in a 1982 revision that compared the nose-leaf morphology of the species. This name was again proposed to accommodate the fossil and extant species of the genus
868:
379:
The 2014 revision presents a separation as three families, equivalent to other mammalian taxonomic arrangements, and incorporates a clade identifying the type
669:
Hand, Suzanne J.; Benda, Petr; Goodman, Steven M.; Armstrong, Kyle N. (28 October 2016). "A common name for the bat family
Rhinonycteridae—the Trident Bats".
500:
Hill J. A review of the leaf-nosed bats
Rhinonycteris, Cloeotis and Triaenops (Chiroptera: Hipposideridae), Bonn Zool Beitr., 1982, vol. 33 (pg. 165-186)
192:
for the subfamilial group, and these provide diagnosis to distinguish the species from other families. Molecular analysis also provides a distinctive
829:
932:
855:
405:, and the Hipposideridae and Rhinonycteridae at approximately 39 Ma. The origin of the family is determined to be the African continent.
250:
The hipposiderid and rhinolophid bats are of especial interest to research into potential public health concerns, and the opportunity for a
314:, and both are thought to have migrated through Europe and Asia to arrive and diverge at the Australian continent around 15 to 20 Ma.
560:
Foley, Nicole M.; Thong, Vu Dinh; Soisook, Pipat; Goodman, Steven M.; Armstrong, Kyle N.; Jacobs, David S.; Puechmaille, Sébastien J.;
247:
Benda & Vallo, 2009 was also reduced to a synonym for this family by the authors of the 2014 revision that elevated this taxon.
259:
860:
645:(Chiroptera: Hipposideridae) with description of a new species from southern Arabia and definitions of a new genus and tribe"
354:
50:
276:
310:
803:
318:
873:
922:
937:
756:
367:
347:
166:
144:
927:
894:
371:
Hand, 1993. A fossil taxon of the
Miocene period, the earliest of the Australian rhinonycterid lineage.
794:
566:"How and Why Overcome the Impediments to Resolution: Lessons from rhinolophid and hipposiderid Bats"
408:
The arrangement of the family, with the subsequent inclusion of
Miocene taxa, may be summarised as:
702:
161:
45:
899:
881:
816:
737:
694:
686:
595:
886:
515:
678:
585:
577:
453:
205:
127:
721:
272:
193:
726:(Brachipposideros) (Microchiroptera: Hipposideridae). from Australian Miocene sediments"
808:
613:
590:
565:
263:
235:
213:
112:
30:
916:
469:
461:
385:
338:
239:
230:
180:
706:
640:
821:
561:
442:
136:
238:, and was elevated in 2014. The affinities within the families Hipposideridae and
779:
842:
788:
255:
682:
741:
690:
581:
478:
402:
391:
267:
224:
189:
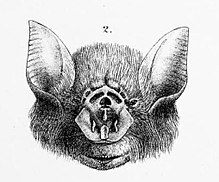
188:. The revision of Hill in 1982 follows Gray to describe the features of the
185:
62:
698:
599:
773:
431:
397:
218:
82:
208:'s 1866 arrangement of known microbat taxa, first published as subtribe
834:
847:
92:
72:
750:
266:, based on the time of divergence and phylogenies that indicated
251:
754:
102:
254:-like outbreak from species that act as reservoirs for the
178:
The family accords with the description to the type genus
234:, separating it from the unstable arrangements of family
164:. The type species, the orange nose-leafed species group
258:
implicated in conditions like the
Chinese epidemic and
275:-b group), the treatment allows the identification of
216:
of family. The taxon combined the poorly known genera
449:
438:
763:
184:, and its classification of the morphology of the
664:
662:
321:recognised extant taxa occurring in Australia;
279:within the hipposiderid, rhinolophid and the
8:
555:
553:
551:
549:
547:
545:
543:
541:
539:
537:
751:
620:. Department of the Environment and Energy
522:. Department of the Environment and Energy
170:, is found across the north of Australia.
29:
20:
589:
160:is a family of bats, within the suborder
196:insertion expressed in a gene fragment.
507:
493:
7:
639:Benda, Petr; Vallo, Peter (2009).
14:
641:"Taxonomic revision of the genus
730:Memoirs of the Queensland Museum
516:"Names List for RHINONYCTERIDAE"
360:recognised as an isolated group
260:Middle East respiratory syndrome
49:
570:Molecular Biology and Evolution
933:Taxa named by John Edward Gray
277:Evolutionary Significant Units
1:
722:"First skull of a species of
311:Brachipposideros nooraleebus
212:, and elevating this to the
618:Australian Faunal Directory
520:Australian Faunal Directory
319:Australian Faunal Directory
954:
720:Hand, Suzanne J. (1993).
683:10.11646/zootaxa.4179.1.7
142:
135:
46:Scientific classification
44:
37:
28:
23:
614:"Family RHINONYCTERIDAE"
204:The alliance resurrects
649:Folia Zoologica -Praha
412:family Hipposideridae.
381:Rhinonicteris aurantia
368:Rhinonicteris tedfordi
356:Rhinonicteris aurantia
348:Rhinonicteris aurantia
167:Rhinonicteris aurantia
39:Rhinonicteris aurantia
895:Paleobiology Database
582:10.1093/molbev/msu329
422:. elevated by Foley,
415:family Rhinolophidae.
329:. elevated by Foley,
145:Rhinolophus aurantius
351:(J.E. Gray, 1845).
162:Yinpterochiroptera
923:Bats of Australia
910:
909:
882:Open Tree of Life
757:Taxon identifiers
564:(February 2015).
155:
154:
131:
945:
903:
902:
890:
889:
877:
876:
864:
863:
851:
850:
838:
837:
825:
824:
812:
811:
799:
798:
797:
784:
783:
782:
752:
746:
745:
717:
711:
710:
666:
657:
656:
636:
630:
629:
627:
625:
610:
604:
603:
593:
562:Teeling, Emma C.
557:
532:
531:
529:
527:
512:
501:
498:
454:Brachipposideros
451:
440:
342:J.E. Gray, 1847
206:John Edward Gray
126:
54:
53:
33:
24:Rhinonycteridae
21:
953:
952:
948:
947:
946:
944:
943:
942:
938:Rhinonycteridae
913:
912:
911:
906:
898:
893:
885:
880:
872:
867:
859:
854:
846:
841:
833:
828:
820:
815:
809:Rhinonycteridae
807:
802:
795:Rhinonycteridae
793:
792:
787:
778:
777:
772:
765:Rhinonycteridae
759:
749:
719:
718:
714:
668:
667:
660:
638:
637:
633:
623:
621:
612:
611:
607:
559:
558:
535:
525:
523:
514:
513:
509:
505:
504:
499:
495:
490:
473:J.E. Gray, 1847
420:Rhinonycteridae
327:Rhinonycteridae
301:
273:Betacoronavirus
202:
194:retrotransposon
176:
158:Rhinonycteridae
151:
148:
125:
123:Rhinonycteridae
48:
17:
12:
11:
5:
951:
949:
941:
940:
935:
930:
925:
915:
914:
908:
907:
905:
904:
891:
878:
865:
852:
839:
826:
813:
800:
785:
769:
767:
761:
760:
755:
748:
747:
712:
677:(1): 115–117.
658:
631:
605:
576:(2): 313–333.
533:
506:
503:
502:
492:
491:
489:
486:
485:
484:
483:
482:
474:
465:
457:
446:
435:
416:
413:
377:
376:
375:
374:
373:
372:
363:
362:
361:
358:(Pilbara form)
300:
297:
264:Hipposideridae
236:Hipposideridae
210:Rhinonycterina
201:
198:
175:
172:
153:
152:
149:
140:
139:
133:
132:
120:
116:
115:
113:Rhinolophoidea
110:
106:
105:
100:
96:
95:
90:
86:
85:
80:
76:
75:
70:
66:
65:
60:
56:
55:
42:
41:
35:
34:
26:
25:
16:Family of bats
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
950:
939:
936:
934:
931:
929:
926:
924:
921:
920:
918:
901:
896:
892:
888:
883:
879:
875:
870:
866:
862:
857:
853:
849:
844:
840:
836:
831:
827:
823:
818:
814:
810:
805:
801:
796:
790:
786:
781:
775:
771:
770:
768:
766:
762:
758:
753:
743:
739:
735:
731:
727:
725:
716:
713:
708:
704:
700:
696:
692:
688:
684:
680:
676:
672:
665:
663:
659:
654:
650:
646:
644:
635:
632:
619:
615:
609:
606:
601:
597:
592:
587:
583:
579:
575:
571:
567:
563:
556:
554:
552:
550:
548:
546:
544:
542:
540:
538:
534:
521:
517:
511:
508:
497:
494:
487:
481:
480:
475:
472:
471:
470:Rhinonicteris
466:
464:
463:
462:Paratriaenops
458:
456:
455:
447:
445:
444:
436:
434:
433:
428:
427:
425:
421:
417:
414:
411:
410:
409:
406:
404:
400:
399:
394:
393:
388:
387:
386:Paratriaenops
382:
370:
369:
364:
359:
357:
353:
352:
350:
349:
344:
343:
341:
340:
339:Rhinonicteris
335:
334:
332:
328:
324:
323:
322:
320:
315:
313:
312:
306:
305:Rhinonicteris
298:
296:
294:
290:
284:
282:
281:rhinonycterid
278:
274:
269:
265:
261:
257:
256:coronaviruses
253:
248:
246:
241:
240:Rhinolophidae
237:
233:
232:
231:Rhinonicteris
227:
226:
221:
220:
215:
211:
207:
199:
197:
195:
191:
187:
183:
182:
181:Rhinonicteris
173:
171:
169:
168:
163:
159:
147:
146:
141:
138:
134:
129:
124:
121:
118:
117:
114:
111:
109:Superfamily:
108:
107:
104:
101:
98:
97:
94:
91:
88:
87:
84:
81:
78:
77:
74:
71:
68:
67:
64:
61:
58:
57:
52:
47:
43:
40:
36:
32:
27:
22:
19:
928:Bat families
764:
733:
729:
724:Hipposideros
723:
715:
674:
670:
652:
648:
642:
634:
622:. Retrieved
617:
608:
573:
569:
524:. Retrieved
519:
510:
496:
477:
468:
460:
452:
443:Brevipalatus
441:
430:
423:
419:
407:
396:
390:
384:
383:with genera
380:
378:
366:
355:
346:
337:
330:
326:
316:
309:
304:
302:
292:
291:(Armstrong,
289:trident bats
288:
285:
280:
249:
244:
229:
223:
217:
209:
203:
179:
177:
165:
157:
156:
143:
137:Type species
122:
38:
18:
843:iNaturalist
789:Wikispecies
736:: 179–192.
245:Triaenopini
174:Description
917:Categories
624:29 January
526:29 January
488:References
303:The genus
283:lineages.
243:The taxon
150:Gray, 1845
103:Chiroptera
780:Q19409100
742:0079-8835
691:1175-5334
643:Triaenops
479:Triaenops
426:, 2014.
392:Triaenops
333:, 2014.
299:Diversity
295:, 2016).
268:paraphyly
225:Triaenops
190:nose-leaf
186:rhinarium
128:J.E. Gray
69:Kingdom:
63:Eukaryota
774:Wikidata
707:20906819
699:27811695
600:25433366
432:Cloeotis
398:Cloeotis
365:species
345:species
219:Cloeotis
200:Taxonomy
119:Family:
93:Mammalia
83:Chordata
79:Phylum:
73:Animalia
59:Domain:
887:5819794
874:1677019
861:1141256
835:4832037
671:Zootaxa
591:4769323
418:family
325:family
99:Order:
89:Class:
900:477221
848:446817
740:
705:
697:
689:
598:
588:
476:genus
467:genus
459:genus
448:genus
437:genus
429:genus
336:genus
130:, 1866
822:7NDGQ
703:S2CID
424:et al
331:et al
293:et al
869:NCBI
856:ITIS
830:GBIF
738:ISSN
695:PMID
687:ISSN
675:4179
626:2019
596:PMID
528:2019
395:and
317:The
252:SARS
222:and
214:rank
817:CoL
804:AFD
679:doi
586:PMC
578:doi
919::
897::
884::
871::
858::
845::
832::
819::
806::
791::
776::
734:33
732:.
728:.
701:.
693:.
685:.
673:.
661:^
653:58
651:.
647:.
616:.
594:.
584:.
574:32
572:.
568:.
536:^
518:.
403:Ma
389:,
744:.
709:.
681::
655:.
628:.
602:.
580::
530:.
450:†
439:†
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.