179:
within normal weight ranges. The surgeon uses an incision of just 3-4 inches; a total knee replacement typically requires an incision of 8-12 inches. The partial replacement does not disrupt the knee cap, which makes for a shorter rehabilitation period. A partial replacement also causes minimal blood loss during the procedure, and results in considerably less post-operative pain. The hospitalization time compared with a total knee replacement is also greatly reduced.
212:) are a common complication after surgery. However, a doctor may prescribe certain medications to help prevent blood clots. Infection may occur after surgery. However, antibiotics may be prescribed by a doctor to help prevent infections. Individual factors (e.g., anatomy, weight, prior medical history, prior joint surgeries) should be addressed with the surgery subject. The causes of long-term failure of UKAs include
175:). The surgeon may decide to check if the appropriate amount of bone was removed during the surgery. In order to make sure that the proper size implant is used, a surgeon may choose to use a temporary trial. After making sure the proper size implant is selected, the surgeon will put the implant on the ends of the bone and secure it with pegs. Finally, the surgeon will close the wound with sutures.
28:
158:(e.g., x-rays) to check for degeneration of the other knee compartments and evaluate the knee. The physical exam may also include special tests designed to test the ligaments of the knee and other anatomical structures. Most likely, the surgeon will decide to do a UKA during surgery where he/she can directly see the status of the other compartments.
149:(ACL) should be intact, although this is debated by clinicians for people who need a medial compartment replacement. For people needing a lateral compartment replacement, the ACL should be intact and is contraindicated for people with ACL-deficient knees because the lateral component has more motion than the medial compartment.
196:
In 2018, two of the most significant benefits of UKA or partial knee replacements are: 1. Partial knee replacement subjects report that their replaced knee feels more like their original non-replaced knee as compared to a total knee replacement 2, Partial knee replacements leave other options open to
107:
In the early 1950s, Duncan C. McKeever theorized that osteoarthritis could be isolated to only one compartment of the knee joint, and that replacement of the entire knee might not be necessary if only one knee compartment were affected. The UKA concept was designed to cause less trauma or damage than
141:
of the knee joint, have untreated damage to the knee cap and thigh bone joint (patellofemoral joint), have untreated damage to the opposite compartment or the same side of the knee not being replaced by a device, and/or have instability of the knee ligaments such that the postoperative stability the
178:
The unicompartmental replacement is a minimally invasive option for people whose arthritis is isolated to either the medial or the lateral compartment. The procedure offers several benefits for patients with a moderately active lifestyle, who have arthritis in just one knee compartment, and who are
111:
Initially, UKAs were not always successful, because the implants were poorly designed, people needing the surgery were not thoroughly screened for suitability, and optimal surgical techniques were not developed. Advancements have been made to improve the design of the implants. Also, choosing the
224:
Long-term studies reported excellent outcomes for UKA, partly due to subject screening, minimizing the amount of bone that is removed, and using the proper surgical technique. One study found that at a minimum of 10 years follow up time after the initial surgery, the overall survival rate of the
192:
because less bone is removed. Also, a quicker operation and shorter recovery period may be a result of less bone being removed during the operation and the soft tissue may sustain less trauma. Also, the rehabilitation process may be more progressive. More specific benefits of UKA are that it may
157:
A physical examination and getting the subject's history is performed before getting surgery. A person with pain in one area of the knee may be a candidate for UKA. However, a person with pain in multiple areas of the knee may not be a good candidate for UKA. The doctor may take some radiographs
132:
surgery. People who may not be eligible for a UKA include those with an active or suspected infection in or about the knee joint, may have a known sensitivity to device materials, have bone infections or disease that result in an inability to support or fixate the new implant to the bone, have
399:
Siman, H; Kamath, A. F; Carrillo, N; Harmsen, W. S; Pagnano, M. W; Sierra, R. J (2017). "Unicompartmental Knee
Arthroplasty vs Total Knee Arthroplasty for Medial Compartment Arthritis in Patients Older Than 75 Years: Comparable Reoperation, Revision, and Complication Rates".
225:
implant was 96%. Also, 92% of the people in this study had excellent or good outcome. Another study, reported that at 15 years follow up time after the initial surgery, the overall rate of the implant was 93% and 91% of these people reported good or excellent outcomes.
133:
inflammatory arthritis, have major deformities that can affect the knee mechanical axis, have neuromuscular disorders that may compromise motor control and/or stability, have any mental neuromuscular disorder, are obese, have lost a severe amount of bone from the shin (
879:
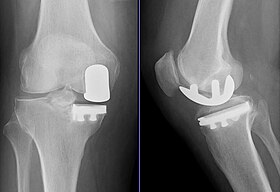
Warwick D, Friedman RJ, Agnelli G, et al. (June 2007). "Insufficient duration of venous thromboembolism prophylaxis after total hip or knee replacement when compared with the time course of thromboembolic events: findings from the Global
Orthopaedic Registry".
112:
best-suited people was emphasized to ensure that surgeons followed the indications and contraindications for partial replacement. Proper selection, following the indications/contraindications, and performing the surgery well are key factors for the success of UKA.
108:
traditional total knee replacement by removing less bone and trying to maintain most of the person's bone and anatomy. The concept was also designed to use smaller implants and thereby keep most of the person's bone, helping them return to normal function faster.
187:
The potential benefits of UKA include a smaller incision because the UKA implants are smaller than the total knee replacements, and the surgeon may make a smaller incision. This may lead to a smaller scar. Another potential benefit is less post-operative
166:
The surgeon may choose which type of incision and implant to use for the subject's knee. During the surgery, the surgeon may align the instruments to determine the amount of bone to remove. The surgeon removes bone from the
197:
further advances. By not replacing the rest of the knee with metal and plastic, if other options exist in years to come for arthritis in these areas then a partial knee replacement does not burn that bridge.
1076:
1069:
644:
774:
Mullaji AB, Sharma A, Marawar S (June 2007). "Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: functional recovery and radiographic results with a minimally invasive technique".
1062:
265:"Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty, is it superior to high tibial osteotomy in treating unicompartmental osteoarthritis? A meta-analysis and systemic review"
661:
Geller JA, Yoon RS, Macaulay W (January 2008). "Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: a controversial history and a rationale for contemporary resurgence".
80:
compartments in which the damaged parts of the knee are replaced. UKA surgery may reduce post-operative pain and have a shorter recovery period than a
1469:
734:
1421:
1004:
965:
Berger RA, Meneghini RM, Jacobs JJ, et al. (May 2005). "Results of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty at a minimum of ten years of follow-up".
1581:
46:
1327:
1322:
923:
Ritter MA, Olberding EM, Malinzak RA (September 2007). "Ultraviolet lighting during orthopaedic surgery and the rate of infection".
1381:
1376:
435:
Riddle DL, Jiranek WA, McGlynn FJ (April 2008). "Yearly incidence of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in the United States".
193:
improve range of motion, reduce blood loss during surgery, reduce the person's time spent in the hospital, and decrease costs.
1273:
1586:
752:
523:
1310:
146:
1414:
1596:
1436:
1227:
32:
475:"Better clinical outcomes after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty when comparing with high tibial osteotomy"
1346:
1217:
1185:
738:
81:
1315:
638:
96:
1493:
1591:
1404:
1124:
209:
1556:
1366:
1288:
557:
348:
1498:
1431:
1232:
1180:
1096:
1028:
905:
592:
376:
69:
1534:
1488:
1283:
1278:
1129:
1050:
1020:
982:
940:
897:
856:
826:
791:
716:
678:
626:
573:
504:
452:
417:
368:
296:
92:
85:
41:
847:
Colwell CW (September 2007). "Rationale for thromboprophylaxis in lower joint arthroplasty".
84:
procedure, particularly in people over 75 years of age. Moreover, UKAs may require a smaller
1474:
1399:
1012:
974:
932:
889:
818:
783:
708:
670:
616:
608:
565:
494:
486:
444:
409:
360:
286:
276:
1459:
1454:
1237:
1054:
1549:
1464:
1409:
1268:
1222:
621:
596:
499:
474:
291:
264:
121:
822:
1575:
1359:
1258:
1201:
1119:
1016:
569:
364:
1032:
1005:"Long-term clinical results of the medial Oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty"
380:
1519:
1483:
1426:
1175:
1160:
1145:
909:
216:
wear, loosening of the implant, and degeneration of the adjacent knee compartment.
213:
893:
1529:
1524:
1354:
1170:
1155:
490:
205:
138:
27:
787:
448:
413:
1544:
1514:
1371:
1165:
1150:
712:
612:
558:"Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in patients sixty years of age or younger"
281:
120:
UKA may be suitable for people with moderate joint disease caused by painful
1302:
1263:
1253:
737:. Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, NH, USA. 2017. Archived from
73:
1024:
986:
944:
901:
860:
830:
795:
720:
682:
674:
630:
577:
508:
456:
421:
372:
300:
124:
or traumatic injury, a history of unsuccessful surgical procedures or poor
978:
936:
55:
597:"How to Treat the Stiff Total Knee Arthroplasty?: A Systematic Review"
91:
In the United States, the procedure constitutes approximately 8% of
1337:
172:
168:
134:
95:. In comparisons with a more extensive surgical procedure called
1104:
1086:
189:
129:
125:
77:
1058:
809:
Newman JH (April 2000). "Unicompartmental knee replacement".
699:
Bert JM (October 2005). "Unicompartmental knee replacement".
473:
Han, S. B; Kyung, H. S; Seo, I. W; Shin, Y. S (2017).
137:) or have severe tibial deformities, have recurring
1507:
1447:
1392:
1345:
1336:
1301:
1246:
1210:
1194:
1138:
1112:
1103:
40:
20:
556:Swienckowski JJ, Pennington DW (September 2004).
88:, less tissue damage, and faster recovery times.
35:of a knee arthroplasty of the medial compartment
998:
996:
960:
958:
956:
954:
874:
872:
870:
842:
840:
694:
692:
342:
340:
338:
336:
334:
332:
330:
656:
654:
551:
549:
547:
545:
543:
541:
328:
326:
324:
322:
320:
318:
316:
314:
312:
310:
1070:
8:
643:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
269:Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research
1342:
1109:
1077:
1063:
1055:
26:
1470:Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
1003:Price AJ, Waite JC, Svard U (June 2005).
755:. North Yorkshire Orthopaedic Specialists
620:
526:. North Yorkshire Orthopaedic Specialists
498:
290:
280:
1422:Ulnar collateral ligament reconstruction
394:
392:
390:
234:
636:
128:density that precludes other types of
17:
468:
466:
347:Borus T, Thornhill T (January 2008).
258:
7:
349:"Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty"
256:
254:
252:
250:
248:
246:
244:
242:
240:
238:
99:, UKA has equal or better outcomes.
1328:Autologous chondrocyte implantation
51:
1479:Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty
1323:Knee cartilage replacement therapy
66:Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty
21:Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty
14:
116:Indications and contraindications
1017:10.1097/00003086-200506000-00024
570:10.2106/00004623-200409001-00004
365:10.5435/00124635-200801000-00003
153:History and physical examination
564:. 86-A Suppl 1 (Pt 2): 131–42.
1582:Orthopedic surgical procedures
1:
823:10.1016/S0968-0160(99)00032-0
263:Santoso, M. B; Wu, L (2017).
894:10.1302/0301-620X.89B6.18844
591:Fitzsimmons SE, Vazquez EA,
491:10.1097/MD.0000000000009268
402:The Journal of Arthroplasty
1613:
1311:Articular cartilage repair
788:10.1016/j.arth.2006.12.109
753:"Partial Knee Replacement"
735:"Partial Knee Replacement"
524:"Partial Knee Replacement"
449:10.1016/j.arth.2007.04.012
414:10.1016/j.arth.2017.01.020
147:anterior cruciate ligament
142:UKA would be compromised.
1094:
1009:Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res.
713:10.1016/j.ocl.2005.05.001
613:10.1007/s11999-010-1230-y
282:10.1186/s13018-017-0552-9
52:
25:
1437:Finger joint replacement
1228:Distraction osteogenesis
601:Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res
1218:Femoral head ostectomy
1186:Vertebral augmentation
701:Orthop. Clin. North Am
675:10.1055/s-0030-1247785
82:total knee replacement
1415:Weaver–Dunn procedure
1316:Microfracture surgery
1085:Procedures involving
353:J Am Acad Orthop Surg
97:high tibial osteotomy
1405:Shoulder replacement
1367:Intervertebral discs
1125:Orthognathic surgery
979:10.2106/JBJS.C.00568
967:J Bone Joint Surg Am
937:10.2106/JBJS.F.01037
925:J Bone Joint Surg Am
882:J Bone Joint Surg Br
562:J Bone Joint Surg Am
210:deep vein thrombosis
162:Surgical information
1587:Implants (medicine)
1557:Arthroscopic lavage
1289:Tension band wiring
782:(4 Suppl 1): 7–11.
93:knee arthroplasties
1499:Triple arthrodesis
1494:Broström procedure
1432:Brunelli procedure
1233:Ilizarov apparatus
1181:Vertebral fixation
1097:Orthopedic surgery
171:) and thigh bone (
70:surgical procedure
1569:
1568:
1565:
1564:
1535:Joint replacement
1489:Ankle replacement
1297:
1296:
1284:External fixation
1279:Internal fixation
1130:Chin augmentation
855:(9 Suppl): 11–3.
741:on 4 August 2018.
220:Long-term results
63:
62:
1604:
1475:Knee replacement
1400:Shoulder surgery
1343:
1110:
1079:
1072:
1065:
1056:
1037:
1036:
1000:
991:
990:
962:
949:
948:
920:
914:
913:
876:
865:
864:
844:
835:
834:
806:
800:
799:
771:
765:
764:
762:
760:
749:
743:
742:
731:
725:
724:
696:
687:
686:
658:
649:
648:
642:
634:
624:
588:
582:
581:
553:
536:
535:
533:
531:
519:
513:
512:
502:
470:
461:
460:
432:
426:
425:
408:(6): 1792–1797.
396:
385:
384:
344:
305:
304:
294:
284:
260:
72:used to relieve
56:edit on Wikidata
30:
18:
1612:
1611:
1607:
1606:
1605:
1603:
1602:
1601:
1597:Knee treatments
1572:
1571:
1570:
1561:
1503:
1460:Hip replacement
1455:Hip resurfacing
1443:
1388:
1332:
1293:
1242:
1238:Phemister graft
1206:
1190:
1134:
1099:
1090:
1083:
1046:
1041:
1040:
1011:(435): 171–80.
1002:
1001:
994:
973:(5): 999–1006.
964:
963:
952:
922:
921:
917:
878:
877:
868:
846:
845:
838:
808:
807:
803:
773:
772:
768:
758:
756:
751:
750:
746:
733:
732:
728:
698:
697:
690:
660:
659:
652:
635:
607:(4): 1096–106.
590:
589:
585:
555:
554:
539:
529:
527:
521:
520:
516:
472:
471:
464:
434:
433:
429:
398:
397:
388:
346:
345:
308:
262:
261:
236:
231:
222:
208:(also known as
203:
185:
164:
155:
118:
105:
59:
36:
12:
11:
5:
1610:
1608:
1600:
1599:
1594:
1589:
1584:
1574:
1573:
1567:
1566:
1563:
1562:
1560:
1559:
1554:
1553:
1552:
1550:Arthrocentesis
1547:
1537:
1532:
1527:
1522:
1517:
1511:
1509:
1505:
1504:
1502:
1501:
1496:
1491:
1486:
1481:
1472:
1467:
1465:Rotationplasty
1462:
1457:
1451:
1449:
1445:
1444:
1442:
1441:
1440:
1439:
1434:
1424:
1419:
1418:
1417:
1412:
1410:Bankart repair
1407:
1396:
1394:
1390:
1389:
1387:
1386:
1385:
1384:
1379:
1374:
1364:
1363:
1362:
1351:
1349:
1340:
1334:
1333:
1331:
1330:
1325:
1320:
1319:
1318:
1307:
1305:
1299:
1298:
1295:
1294:
1292:
1291:
1286:
1281:
1276:
1271:
1269:Epiphysiodesis
1266:
1261:
1256:
1250:
1248:
1244:
1243:
1241:
1240:
1235:
1230:
1225:
1223:Astragalectomy
1220:
1214:
1212:
1208:
1207:
1205:
1204:
1198:
1196:
1192:
1191:
1189:
1188:
1183:
1178:
1173:
1168:
1163:
1158:
1153:
1148:
1142:
1140:
1136:
1135:
1133:
1132:
1127:
1122:
1116:
1114:
1107:
1101:
1100:
1095:
1092:
1091:
1084:
1082:
1081:
1074:
1067:
1059:
1053:
1052:
1045:
1044:External links
1042:
1039:
1038:
992:
950:
931:(9): 1935–40.
915:
888:(6): 799–807.
866:
836:
801:
776:J Arthroplasty
766:
744:
726:
688:
650:
595:(April 2010).
583:
537:
522:Gibbon, Tony.
514:
462:
437:J Arthroplasty
427:
386:
306:
233:
232:
230:
227:
221:
218:
202:
199:
184:
181:
163:
160:
154:
151:
122:osteoarthritis
117:
114:
104:
101:
76:in one of the
61:
60:
53:
50:
49:
44:
38:
37:
31:
23:
22:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1609:
1598:
1595:
1593:
1590:
1588:
1585:
1583:
1580:
1579:
1577:
1558:
1555:
1551:
1548:
1546:
1543:
1542:
1541:
1538:
1536:
1533:
1531:
1528:
1526:
1523:
1521:
1518:
1516:
1513:
1512:
1510:
1506:
1500:
1497:
1495:
1492:
1490:
1487:
1485:
1482:
1480:
1476:
1473:
1471:
1468:
1466:
1463:
1461:
1458:
1456:
1453:
1452:
1450:
1446:
1438:
1435:
1433:
1430:
1429:
1428:
1425:
1423:
1420:
1416:
1413:
1411:
1408:
1406:
1403:
1402:
1401:
1398:
1397:
1395:
1391:
1383:
1380:
1378:
1375:
1373:
1370:
1369:
1368:
1365:
1361:
1360:Spinal fusion
1358:
1357:
1356:
1353:
1352:
1350:
1348:
1344:
1341:
1339:
1335:
1329:
1326:
1324:
1321:
1317:
1314:
1313:
1312:
1309:
1308:
1306:
1304:
1300:
1290:
1287:
1285:
1282:
1280:
1277:
1275:
1272:
1270:
1267:
1265:
1262:
1260:
1259:Bone grafting
1257:
1255:
1252:
1251:
1249:
1245:
1239:
1236:
1234:
1231:
1229:
1226:
1224:
1221:
1219:
1216:
1215:
1213:
1209:
1203:
1202:Acromioplasty
1200:
1199:
1197:
1193:
1187:
1184:
1182:
1179:
1177:
1174:
1172:
1169:
1167:
1164:
1162:
1159:
1157:
1154:
1152:
1149:
1147:
1144:
1143:
1141:
1137:
1131:
1128:
1126:
1123:
1121:
1120:Jaw reduction
1118:
1117:
1115:
1111:
1108:
1106:
1102:
1098:
1093:
1088:
1080:
1075:
1073:
1068:
1066:
1061:
1060:
1057:
1051:
1049:Medline Plus
1048:
1047:
1043:
1034:
1030:
1026:
1022:
1018:
1014:
1010:
1006:
999:
997:
993:
988:
984:
980:
976:
972:
968:
961:
959:
957:
955:
951:
946:
942:
938:
934:
930:
926:
919:
916:
911:
907:
903:
899:
895:
891:
887:
883:
875:
873:
871:
867:
862:
858:
854:
850:
849:Am. J. Orthop
843:
841:
837:
832:
828:
824:
820:
816:
812:
805:
802:
797:
793:
789:
785:
781:
777:
770:
767:
754:
748:
745:
740:
736:
730:
727:
722:
718:
714:
710:
707:(4): 513–22.
706:
702:
695:
693:
689:
684:
680:
676:
672:
668:
664:
657:
655:
651:
646:
640:
632:
628:
623:
618:
614:
610:
606:
602:
598:
594:
587:
584:
579:
575:
571:
567:
563:
559:
552:
550:
548:
546:
544:
542:
538:
525:
518:
515:
510:
506:
501:
496:
492:
488:
485:(50): e9268.
484:
480:
476:
469:
467:
463:
458:
454:
450:
446:
443:(3): 408–12.
442:
438:
431:
428:
423:
419:
415:
411:
407:
403:
395:
393:
391:
387:
382:
378:
374:
370:
366:
362:
358:
354:
350:
343:
341:
339:
337:
335:
333:
331:
329:
327:
325:
323:
321:
319:
317:
315:
313:
311:
307:
302:
298:
293:
288:
283:
278:
274:
270:
266:
259:
257:
255:
253:
251:
249:
247:
245:
243:
241:
239:
235:
228:
226:
219:
217:
215:
211:
207:
200:
198:
194:
191:
182:
180:
176:
174:
170:
161:
159:
152:
150:
148:
143:
140:
136:
131:
127:
123:
115:
113:
109:
102:
100:
98:
94:
89:
87:
83:
79:
75:
71:
67:
57:
48:
45:
43:
39:
34:
29:
24:
19:
16:
1539:
1520:Arthroplasty
1484:Ankle fusion
1478:
1427:Hand surgery
1382:Arthroplasty
1377:Annuloplasty
1176:Foraminotomy
1161:Laminoplasty
1146:Coccygectomy
1008:
970:
966:
928:
924:
918:
885:
881:
852:
848:
817:(2): 63–70.
814:
810:
804:
779:
775:
769:
757:. Retrieved
747:
739:the original
729:
704:
700:
666:
662:
639:cite journal
604:
600:
586:
561:
528:. Retrieved
517:
482:
478:
440:
436:
430:
405:
401:
356:
352:
272:
268:
223:
214:polyethylene
204:
195:
186:
177:
165:
156:
144:
119:
110:
106:
90:
65:
64:
15:
1592:Prosthetics
1530:Arthroscopy
1525:Synovectomy
1355:Arthrodesis
1171:Facetectomy
1156:Laminectomy
669:(1): 7–14.
663:J Knee Surg
359:(1): 9–18.
206:Blood clots
139:subluxation
68:(UKA) is a
33:Radiographs
1576:Categories
1545:Arthrogram
1515:Arthrotomy
1372:Discectomy
1166:Corpectomy
1151:Laminotomy
1089:and joints
759:5 February
593:Bronson MJ
530:1 February
229:References
103:Background
1303:Cartilage
1274:Reduction
1264:Osteotomy
1254:Ostectomy
275:(1): 50.
74:arthritis
1540:imaging:
1033:12178609
1025:15930935
987:15866962
945:17768189
902:17613508
861:17948162
831:10788767
796:17570269
721:16164956
683:18300665
631:20087698
578:15466754
509:29390376
479:Medicine
457:18358380
422:28215968
381:22536661
373:18180388
301:28351371
183:Benefits
86:incision
42:ICD-9-CM
1508:General
1247:General
910:1966988
622:2835585
500:5815788
292:5371236
1338:Joints
1031:
1023:
985:
943:
908:
900:
859:
829:
794:
719:
681:
629:
619:
576:
507:
497:
455:
420:
379:
371:
299:
289:
1347:Spine
1139:Spine
1105:Bones
1087:bones
1029:S2CID
906:S2CID
377:S2CID
201:Risks
173:femur
169:tibia
135:tibia
54:[
47:81.54
1113:Face
1021:PMID
983:PMID
941:PMID
898:PMID
857:PMID
827:PMID
811:Knee
792:PMID
761:2013
717:PMID
679:PMID
645:link
627:PMID
574:PMID
532:2013
505:PMID
453:PMID
418:PMID
369:PMID
297:PMID
190:pain
145:The
130:knee
126:bone
78:knee
1448:Leg
1393:Arm
1211:Leg
1195:Arm
1013:doi
975:doi
933:doi
890:doi
819:doi
784:doi
709:doi
671:doi
617:PMC
609:doi
605:468
566:doi
495:PMC
487:doi
445:doi
410:doi
361:doi
287:PMC
277:doi
1578::
1027:.
1019:.
1007:.
995:^
981:.
971:87
969:.
953:^
939:.
929:89
927:.
904:.
896:.
886:89
884:.
869:^
853:36
851:.
839:^
825:.
813:.
790:.
780:22
778:.
715:.
705:36
703:.
691:^
677:.
667:21
665:.
653:^
641:}}
637:{{
625:.
615:.
603:.
599:.
572:.
560:.
540:^
503:.
493:.
483:96
481:.
477:.
465:^
451:.
441:23
439:.
416:.
406:32
404:.
389:^
375:.
367:.
357:16
355:.
351:.
309:^
295:.
285:.
273:12
271:.
267:.
237:^
1477:/
1078:e
1071:t
1064:v
1035:.
1015::
989:.
977::
947:.
935::
912:.
892::
863:.
833:.
821::
815:7
798:.
786::
763:.
723:.
711::
685:.
673::
647:)
633:.
611::
580:.
568::
534:.
511:.
489::
459:.
447::
424:.
412::
383:.
363::
303:.
279::
167:(
58:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.