901:
52:
40:
197:
1111:
876:
889:
714:
The narrowness of the cerebral aqueduct and foramina means that they can become blocked, for example, by blood following a hemorrhagic stroke. As cerebrospinal fluid is continually produced by the choroid plexus within the ventricles, a blockage of outflow leads to increasingly high pressure in the
705:
The CSF that is produced in the ventricular system is also necessary for chemical stability, and the provision of nutrients needed by the brain. The CSF helps to protect the brain from jolts and knocks to the head and also provides buoyancy and support to the brain against gravity. (Since the brain
318:
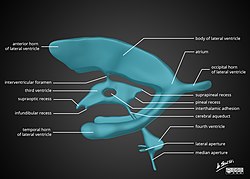
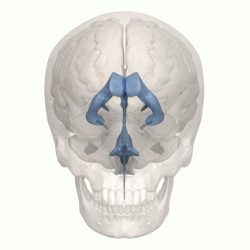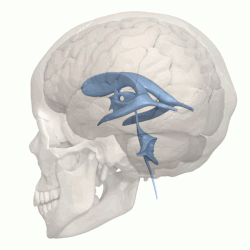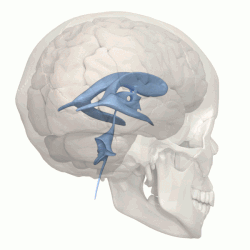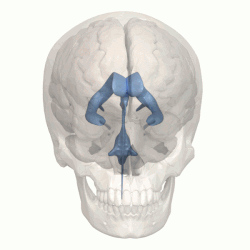
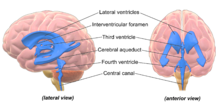
The four cavities of the human brain are called ventricles. The two largest are the lateral ventricles in the cerebrum, the third ventricle is in the diencephalon of the forebrain between the right and left thalamus, and the fourth ventricle is located at the back of the pons and upper half of the
1096:
Cerebrospinal fluid flows in bulk from sites of production to sites of absorption. Fluid formed in the lateral ventricles flows through the paired interventricular foramina (foramen of Monro) into the third ventricle, then through the mesencephalic aqueduct (aqueduct of
Sylvius) into the fourth
835:
and have been explained largely in terms of environmental factors. They have also been found to be extremely diverse between individuals, such that the percentage difference in group averages in schizophrenia studies (+16%) has been described as "not a very profound difference in the context of
615:
According to the traditional understanding of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) physiology, the majority of CSF is produced by the choroid plexus, circulates through the ventricles, the cisterns, and the subarachnoid space to be absorbed into the blood by the arachnoid villi.
503:(CSP), which is a marker for fetal neural maldevelopment. During the fifth month of development, the laminae start to close and this closure completes from about three to six months after birth. Fusion of the septal laminae is attributed to rapid development of the
533:
723:. Medically one would call this post-haemorrhagic acquired hydrocephalus, but is often referred to colloquially by the layperson as "water on the brain". This is an extremely serious condition regardless of the cause of blockage. An
229:, openings acting as channels, that connect the ventricles. The interventricular foramina (also called the foramina of Monro) connect the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle through which the cerebrospinal fluid can flow.
1012:
The ventricles contain the choroid plexus, which produces CSF, and serve as conduits for CSF flow in the CNS. Ventricular walls are lined with ependymal cells, which are connected by tight junctions and constitute a CSF-brain
706:
and CSF are similar in density, the brain floats in neutral buoyancy, suspended in the CSF.) This allows the brain to grow in size and weight without resting on the floor of the cranium, which would destroy nervous tissue.
519:, fornix, corpus callosum and other midline structures. Lack of such limbic development interrupts this posterior-to-anterior fusion, resulting in the continuation of the CSP into adulthood.
1408:
Galarza M, Merlo A, Ingratta A, Albanese E, Albanese A (2004). "Cavum septum pellucidum and its increased prevalence in schizophrenia: a neuroembryological classification".
900:
1125:
Betts, J Gordon; Desaix, Peter; Johnson, Eddie; Johnson, Jody E; Korol, Oksana; Kruse, Dean; Poe, Brandon; Wise, James; Womble, Mark D; Young, Kelly A (July 16, 2023).
1052:
The ventricular system arises from the hollow space within the developing neural tube and gives rise to cisterns within the CNS, from the brain to the spinal cord.
113:
1825:
1603:
1097:
ventricle. The majority of CSF exits from the fourth ventricle into the subarachnoid space; a small amount may enter the central canal of the spinal cord.
573:
400:
have formed within the embryo around the canal, near where the head will develop. The three primary brain vesicles represent different components of the
246:
1908:
888:
831:
Whether enlarged ventricles is a cause or a result of schizophrenia has not yet been established. Enlarged ventricles are also found in organic
416:. These in turn divide into five secondary vesicles. As these sections develop around the neural canal, the inner neural canal becomes known as
973:
The ventricular system is an elaboration of the lumen of cephalic portions of the neural tube, and its development parallels that of the brain.
1134:
1081:
1045:
1005:
966:
358:, whereas the neural canal that does not expand and remains the same at the level of the midbrain superior to the fourth ventricle forms the
1115:
1536:
McKee, AC; Cantu, RC; Nowinski, CJ; Hedley-Whyte, ET; Gavett, BE; Budson, AE; Santini, VE; Lee, HS; Kubilus, CA; Stern, RA (Jul 2009).
1876:
1710:
1189:
1596:
1373:
Allen JS, Damasio H, Grabowski TJ (August 2002). "Normal neuroanatomical variation in the human brain: an MRI-volumetric study".
724:
120:
856:
848:
305:
1445:"Cavum septum pellucidum in monozygotic twins discordant for combat exposure: relationship to posttraumatic stress disorder"
747:, thereby bypassing any obstruction. A surgical procedure to make an entry hole to access any of the ventricles is called a
1150:
828:(MRI) has superseded the use of CT in research in the role of detecting ventricular abnormalities in psychiatric illness.
108:
875:
816:
had (in terms of group averages) larger than usual ventricles. This became the first "evidence" that schizophrenia was
377:
In more detail, around the third week of development, the embryo is a three-layered disc. The embryo is covered on the
1950:
1589:
1314:
Saladin, Kenneth S. Anatomy & Physiology. The Unit of Form and
Function. 5th Edition. McGraw-Hill: New York. 2007
1764:
825:
1444:
1259:"Neurodevelopmental marker for limbic maldevelopment in antisocial personality disorder and psychopathy". BJPsych"
751:. This is done to drain accumulated cerebrospinal fluid either through a temporary catheter or a permanent shunt.
840:
500:
1759:
1747:
1739:
929:
779:
84:
1898:
924:
727:
is a surgical procedure for the treatment of hydrocephalus in which an opening is created in the floor of the
620:
1955:
917:
852:
640:
401:
51:
1028:
Shoykhet, Mish; Clark, Robert S.B. (2011). "Structure, Function, and
Development of the Nervous System".
988:
Shoykhet, Mish; Clark, Robert S.B. (2011). "Structure, Function, and
Development of the Nervous System".
1497:"Increased diffusion in the brain of professional boxers: a preclinical sign of traumatic brain injury?"
624:
601:
504:
499:. During the third month of fetal development, a space forms between two septal laminae, known as the
1720:
860:
794:
775:
101:
1890:
1808:
1705:
1645:
805:
740:
541:
496:
480:
389:. As the ectoderm proliferates, the notochord is dragged into the middle of the developing embryo.
324:
158:
39:
1538:"Chronic traumatic encephalopathy in athletes: progressive tauopathy after repetitive head injury"
1913:
1693:
1624:
1087:
821:
699:
569:
565:
561:
453:
283:
208:
196:
1154:
1903:
1788:
1715:
1662:
1567:
1518:
1477:
1425:
1390:
1355:
1288:
1236:
1185:
1130:
1077:
1041:
1001:
962:
801:
716:
655:
585:
557:
488:
425:
421:
359:
320:
260:
1929:
1855:
1769:
1730:
1640:
1557:
1549:
1508:
1467:
1459:
1417:
1382:
1345:
1337:
1278:
1270:
1226:
1218:
1069:
1033:
993:
954:
663:
609:
581:
476:
429:
355:
295:
219:
1846:
1830:
1793:
1688:
1672:
1119:
1110:
809:
748:
744:
728:
683:
659:
648:
605:
577:
492:
461:
445:
413:
274:
214:
1326:"Genetic influences on human brain structure: A review of brain imaging studies in twins"
1581:
1305:
Klein, S.B., & Thorne, B.M. Biological
Psychology. Worth Publishers: New York. 2007.
1871:
1851:
1562:
1537:
1513:
1496:
1472:
1350:
1325:
1283:
1258:
1231:
1206:
1073:
1037:
997:
958:
790:
628:
553:
549:
472:
437:
405:
287:
185:
181:
154:
323:
of the hindbrain. The ventricles are concerned with the production and circulation of
172:
All of the ventricular system and the central canal of the spinal cord are lined with
1944:
1813:
1803:
1752:
1698:
1635:
844:
813:
786:
759:
720:
636:
593:
516:
468:
441:
409:
397:
385:. In the middle of the dorsal surface of the embryo is a linear structure called the
367:
336:
162:
1421:
1091:
1064:
Vernau, William; Vernau, Karen A.; Sue Bailey, Cleta (2008). "Cerebrospinal Fluid".
1683:
1463:
859:. CSP is one of the distinguishing features of individuals displaying symptoms of
644:
632:
457:
449:
340:
138:
17:
1553:
666:
is very small, as are the foramina, which means that they can be easily blocked.
89:
1655:
1616:
771:
754:
Other diseases of the ventricular system include inflammation of the membranes (
597:
545:
508:
371:
344:
166:
532:
1324:
Peper, Jiska S.; Brouwer, RM; Boomsma, DI; Kahn, RS; Hulshoff Pol, HE (2007).
1274:
755:
679:
177:
96:
1495:
Zhang L, Ravdin L, Relkin N, Zimmerman R, Jordan B, Lathan W, Uluğ A (2003).
1180:
Schoenwolf, Gary C. (2009). ""Development of the Brain and
Cranial Nerves"".
763:
736:
732:
687:
386:
351:
1571:
1522:
1481:
1429:
1394:
1359:
1292:
1240:
396:, by the fourth week of embryological development three swellings known as
1129:. Houston: OpenStax CNX. 13.3 Circulation and the Central Nervous System.
832:
695:
675:
589:
512:
382:
226:
173:
428:, line the developing ventricular system in a transient zone called the
378:
1386:
894:
Scheme showing relations of the ventricles to the surface of the brain.
817:
808:
of the ventricles in the late 1970s gave new insight into the study of
491:: a thin, triangular, vertical membrane which runs as a sheet from the
1341:
1207:"Evolution of the neocortex: a perspective from developmental biology"
169:
from the fourth ventricle, allowing for the flow of CSF to circulate.
126:
1222:
1167:
International school of medicine and applied sciences kisumu library
1023:
1021:
906:
Lateral ventricles along with subcortical structures, in glass brain
820:
in origin and led to a renewed interest in its study via the use of
350:
As the part of the primitive neural tube that will develop into the
1257:
Raine, Adrian; Lee, Lydia; Yang, Yaling; Colletti, Patrick (2010).
479:, and the ventricles contained within the mesencephalon become the
836:
normal variation" (ranging from 25% to 350% of the mean average).
767:
691:
531:
393:
195:
150:
72:
983:
981:
556:
found in all components of the ventricular system except for the
475:. The ventricles contained within the rhombencephalon become the
420:
ventricles. These form the ventricular system of the brain: The
1818:
363:
354:, the neural canal expands dorsally and laterally, creating the
1585:
487:
Separating the anterior horns of the lateral ventricles is the
452:. The ventricles contained within the telencephalon become the
1184:(4th ed.). Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier.
639:. CSF within the spinal cord can flow all the way down to the
951:
Fundamental
Neuroscience for Basic and Clinical Applications
56:
Rotating 3D rendering of the four ventricles and connections
1252:
1250:
1443:
May F, Chen Q, Gilbertson M, Shenton M, Pitman R (2004).
1410:
The
Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences
949:
Grow, W.A. (2018). "Development of the
Nervous System".
548:
within their bony confines. CSF is produced by modified
200:
3D rendering of ventricles (lateral and anterior views)
161:(CSF). The ventricular system is continuous with the
1922:
1889:
1864:
1839:
1778:
1738:
1729:
1671:
1623:
719:. As a consequence, this commonly leads in turn to
107:
95:
83:
71:
66:
61:
32:
145:is a set of four interconnected cavities known as
592:. From the fourth ventricle it can pass into the
572:. CSF flows from the lateral ventricles via the
735:placed within the ventricular system through a
702:between the pia mater and the arachnoid mater.
694:and spine provides further protection and also
678:, the three protective membranes of the tough
544:(CSF) which bathes and cushions the brain and
1597:
674:The brain and spinal cord are covered by the
335:The structures of the ventricular system are
8:
1175:
1173:
812:. Researchers found that individuals with
690:. The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the
1735:
1604:
1590:
1582:
50:
38:
1561:
1512:
1471:
1375:American Journal of Physical Anthropology
1349:
1282:
1230:
1066:Clinical Biochemistry of Domestic Animals
27:Structures containing cerebrospinal fluid
231:
211:right and left (one for each hemisphere)
941:
870:
366:(in the caudal medulla), to become the
153:. Within each ventricle is a region of
604:via three small foramina: the central
362:. The fourth ventricle narrows at the
204:The system comprises four ventricles:
124:
29:
424:of the developing brain, principally
7:
631:, after which it passes through the
467:The rhombencephalon divides into a
381:surface by a layer of cells called
1501:American Journal of Neuroradiology
1074:10.1016/b978-0-12-370491-7.00026-x
1038:10.1016/b978-0-323-07307-3.10057-6
998:10.1016/b978-0-323-07307-3.10057-6
959:10.1016/b978-0-323-39632-5.00005-0
643:at the end of the cord around the
25:
1263:The British Journal of Psychiatry
843:has been loosely associated with
186:blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier
1114: This article incorporates
1109:
899:
887:
873:
725:endoscopic third ventriculostomy
619:The fluid then flows around the
456:, and the ventricles within the
448:of the developed brain, and the
121:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
1422:10.1176/appi.neuropsych.16.1.41
953:. Elsevier. pp. 72–90.e1.
857:antisocial personality disorder
540:The ventricles are filled with
157:which produces the circulating
1464:10.1016/j.biopsych.2003.09.018
1068:. Elsevier. pp. 769–819.
1032:. Elsevier. pp. 783–804.
992:. Elsevier. pp. 783–804.
882:3D model of ventricular system
849:post-traumatic stress disorder
627:(or arachnoid villi) into the
306:cistern of great cerebral vein
1:
1151:National Institutes of Health
1554:10.1097/NEN.0b013e3181a9d503
1211:Nature Reviews. Neuroscience
528:Flow of cerebrospinal fluid
304:subarachnoid space via the
1972:
915:
826:Magnetic resonance imaging
44:Ventricular system anatomy
1909:Interventricular foramina
1275:10.1192/bjp.bp.110.078485
1205:Rakic, P (October 2009).
1182:Larsen's human embryology
1155:"Ventricles of the brain"
841:cave of septum pellucidum
623:to be reabsorbed via the
574:interventricular foramina
501:cave of septum pellucidum
247:interventricular foramina
119:
49:
37:
1760:Inferior medullary velum
1748:Superior medullary velum
1127:Anatomy & Physiology
930:Circumventricular organs
780:subarachnoid haemorrhage
758:) or of the ventricles (
743:to flow directly to the
176:, a specialised form of
1030:Pediatric Critical Care
990:Pediatric Critical Care
766:or the introduction of
670:Protection of the brain
621:superior sagittal sinus
536:MRI showing flow of CSF
1542:Neuropathol Exp Neurol
918:anatomical terminology
853:traumatic brain injury
698:, and is found in the
625:arachnoid granulations
537:
402:central nervous system
201:
1153:(December 13, 2011).
710:Clinical significance
602:subarachnoid cisterns
535:
199:
1721:Posterior commissure
1118:available under the
861:dementia pugilistica
795:choroid plexus cysts
776:cerebral haemorrhage
770:following trauma or
343:, the centre of the
1899:Blood–brain barrier
1891:Cerebrospinal fluid
1809:Hypoglossal trigone
1706:Hypothalamic sulcus
1689:Infundibular recess
1646:Collateral eminence
1330:Human Brain Mapping
925:Blood–brain barrier
793:of the ventricles,
741:cerebrospinal fluid
542:cerebrospinal fluid
481:aqueduct of Sylvius
325:cerebrospinal fluid
159:cerebrospinal fluid
147:cerebral ventricles
1951:Ventricular system
1914:Perilymphatic duct
1694:Suprapineal recess
1625:Lateral ventricles
1613:Ventricular system
1387:10.1002/ajpa.10092
916:This article uses
855:, as well as with
822:imaging techniques
739:. This allows the
717:lateral ventricles
700:subarachnoid space
570:lateral ventricles
538:
454:lateral ventricles
444:, which forms the
426:radial glial cells
284:subarachnoid space
252:lateral ventricles
225:There are several
209:lateral ventricles
202:
143:ventricular system
78:ventriculi cerebri
33:Ventricular system
18:Ventricles (brain)
1938:
1937:
1904:Cerebral aqueduct
1885:
1884:
1789:Facial colliculus
1716:Subfornical organ
1663:Septum pellucidum
1342:10.1002/hbm.20398
1136:978-1-947172-04-3
1083:978-0-12-370491-7
1047:978-0-323-07307-3
1007:978-0-323-07307-3
968:978-0-323-39632-5
664:fourth ventricles
656:cerebral aqueduct
610:lateral apertures
586:cerebral aqueduct
558:cerebral aqueduct
489:septum pellucidum
440:divides into the
422:neural stem cells
360:cerebral aqueduct
339:derived from the
321:medulla oblongata
311:
310:
296:lateral apertures
269:fourth ventricle
261:Cerebral aqueduct
184:that make up the
135:
134:
130:
16:(Redirected from
1963:
1930:Ventriculomegaly
1736:
1731:Fourth ventricle
1641:Stria terminalis
1606:
1599:
1592:
1583:
1576:
1575:
1565:
1533:
1527:
1526:
1516:
1492:
1486:
1485:
1475:
1452:Biol. Psychiatry
1449:
1440:
1434:
1433:
1405:
1399:
1398:
1370:
1364:
1363:
1353:
1321:
1315:
1312:
1306:
1303:
1297:
1296:
1286:
1254:
1245:
1244:
1234:
1202:
1196:
1195:
1177:
1168:
1165:
1159:
1158:
1147:
1141:
1140:
1113:
1106:
1100:
1099:
1061:
1055:
1054:
1025:
1016:
1015:
985:
976:
975:
946:
903:
891:
879:
878:
867:Additional media
810:mental disorders
649:lumbar punctures
582:fourth ventricle
477:fourth ventricle
430:ventricular zone
356:fourth ventricle
301:fourth ventricle
280:fourth ventricle
255:third ventricle
232:
220:fourth ventricle
127:edit on Wikidata
54:
42:
30:
21:
1971:
1970:
1966:
1965:
1964:
1962:
1961:
1960:
1941:
1940:
1939:
1934:
1918:
1881:
1860:
1856:Lateral/Luschka
1847:Median/Magendie
1835:
1831:Sulcus limitans
1826:Medial eminence
1794:Locus coeruleus
1774:
1725:
1673:Third ventricle
1667:
1652:Occipital horn
1619:
1610:
1580:
1579:
1535:
1534:
1530:
1494:
1493:
1489:
1447:
1442:
1441:
1437:
1407:
1406:
1402:
1372:
1371:
1367:
1323:
1322:
1318:
1313:
1309:
1304:
1300:
1256:
1255:
1248:
1223:10.1038/nrn2719
1204:
1203:
1199:
1192:
1179:
1178:
1171:
1166:
1162:
1149:
1148:
1144:
1137:
1124:
1107:
1103:
1084:
1063:
1062:
1058:
1048:
1027:
1026:
1019:
1008:
987:
986:
979:
969:
948:
947:
943:
938:
921:
914:
907:
904:
895:
892:
883:
880:
874:
869:
749:ventriculostomy
729:third ventricle
712:
684:arachnoid mater
672:
651:are performed.
606:median aperture
580:, and then the
578:third ventricle
550:ependymal cells
530:
525:
493:corpus callosum
462:third ventricle
414:rhombencephalon
337:embryologically
333:
316:
294:Right and left
275:Median aperture
266:third ventricle
215:third ventricle
194:
182:tight junctions
131:
57:
45:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1969:
1967:
1959:
1958:
1953:
1943:
1942:
1936:
1935:
1933:
1932:
1926:
1924:
1920:
1919:
1917:
1916:
1911:
1906:
1901:
1895:
1893:
1887:
1886:
1883:
1882:
1880:
1879:
1877:Tela choroidea
1874:
1872:Rhomboid fossa
1868:
1866:
1862:
1861:
1859:
1858:
1852:Lateral recess
1849:
1843:
1841:
1837:
1836:
1834:
1833:
1828:
1823:
1822:
1821:
1816:
1811:
1806:
1798:
1797:
1796:
1791:
1782:
1780:
1776:
1775:
1773:
1772:
1767:
1762:
1757:
1756:
1755:
1744:
1742:
1733:
1727:
1726:
1724:
1723:
1718:
1713:
1711:Tela choroidea
1708:
1703:
1702:
1701:
1696:
1691:
1686:
1677:
1675:
1669:
1668:
1666:
1665:
1660:
1659:
1658:
1650:
1649:
1648:
1643:
1638:
1629:
1627:
1621:
1620:
1611:
1609:
1608:
1601:
1594:
1586:
1578:
1577:
1528:
1487:
1435:
1400:
1365:
1316:
1307:
1298:
1269:(3): 186–192.
1246:
1217:(10): 724–35.
1197:
1190:
1169:
1160:
1142:
1135:
1101:
1082:
1056:
1046:
1017:
1006:
977:
967:
940:
939:
937:
934:
933:
932:
927:
913:
910:
909:
908:
905:
898:
896:
893:
886:
884:
881:
872:
868:
865:
791:choroid plexus
745:basal cisterns
711:
708:
671:
668:
641:lumbar cistern
629:venous sinuses
566:anterior horns
554:choroid plexus
529:
526:
524:
521:
485:
484:
473:myelencephalon
465:
438:prosencephalon
406:prosencephalon
398:brain vesicles
394:brain develops
332:
329:
315:
312:
309:
308:
302:
299:
291:
290:
288:cisterna magna
281:
278:
271:
270:
267:
264:
257:
256:
253:
250:
243:
242:
239:
236:
223:
222:
217:
212:
193:
190:
155:choroid plexus
133:
132:
123:
117:
116:
111:
105:
104:
99:
93:
92:
87:
81:
80:
75:
69:
68:
64:
63:
59:
58:
55:
47:
46:
43:
35:
34:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1968:
1957:
1956:Brain anatomy
1954:
1952:
1949:
1948:
1946:
1931:
1928:
1927:
1925:
1921:
1915:
1912:
1910:
1907:
1905:
1902:
1900:
1897:
1896:
1894:
1892:
1888:
1878:
1875:
1873:
1870:
1869:
1867:
1863:
1857:
1853:
1850:
1848:
1845:
1844:
1842:
1838:
1832:
1829:
1827:
1824:
1820:
1817:
1815:
1814:Area postrema
1812:
1810:
1807:
1805:
1804:Vagal trigone
1802:
1801:
1799:
1795:
1792:
1790:
1787:
1786:
1784:
1783:
1781:
1777:
1771:
1768:
1766:
1763:
1761:
1758:
1754:
1751:
1750:
1749:
1746:
1745:
1743:
1741:
1737:
1734:
1732:
1728:
1722:
1719:
1717:
1714:
1712:
1709:
1707:
1704:
1700:
1699:Pineal recess
1697:
1695:
1692:
1690:
1687:
1685:
1682:
1681:
1679:
1678:
1676:
1674:
1670:
1664:
1661:
1657:
1654:
1653:
1651:
1647:
1644:
1642:
1639:
1637:
1636:Lamina affixa
1634:
1633:
1631:
1630:
1628:
1626:
1622:
1618:
1614:
1607:
1602:
1600:
1595:
1593:
1588:
1587:
1584:
1573:
1569:
1564:
1559:
1555:
1551:
1548:(7): 709–35.
1547:
1543:
1539:
1532:
1529:
1524:
1520:
1515:
1510:
1506:
1502:
1498:
1491:
1488:
1483:
1479:
1474:
1469:
1465:
1461:
1457:
1453:
1446:
1439:
1436:
1431:
1427:
1423:
1419:
1415:
1411:
1404:
1401:
1396:
1392:
1388:
1384:
1381:(4): 341–58.
1380:
1376:
1369:
1366:
1361:
1357:
1352:
1347:
1343:
1339:
1336:(6): 464–73.
1335:
1331:
1327:
1320:
1317:
1311:
1308:
1302:
1299:
1294:
1290:
1285:
1280:
1276:
1272:
1268:
1264:
1260:
1253:
1251:
1247:
1242:
1238:
1233:
1228:
1224:
1220:
1216:
1212:
1208:
1201:
1198:
1193:
1191:9780443068119
1187:
1183:
1176:
1174:
1170:
1164:
1161:
1156:
1152:
1146:
1143:
1138:
1132:
1128:
1123:
1121:
1117:
1112:
1105:
1102:
1098:
1093:
1089:
1085:
1079:
1075:
1071:
1067:
1060:
1057:
1053:
1049:
1043:
1039:
1035:
1031:
1024:
1022:
1018:
1014:
1009:
1003:
999:
995:
991:
984:
982:
978:
974:
970:
964:
960:
956:
952:
945:
942:
935:
931:
928:
926:
923:
922:
919:
911:
902:
897:
890:
885:
877:
871:
866:
864:
862:
858:
854:
850:
846:
845:schizophrenia
842:
837:
834:
829:
827:
823:
819:
815:
814:schizophrenia
811:
807:
803:
798:
796:
792:
788:
787:embryogenesis
783:
781:
777:
773:
769:
765:
761:
760:ventriculitis
757:
752:
750:
746:
742:
738:
734:
730:
726:
722:
721:hydrocephalus
718:
709:
707:
703:
701:
697:
693:
689:
685:
681:
677:
669:
667:
665:
661:
657:
652:
650:
646:
642:
638:
637:venous system
634:
630:
626:
622:
617:
613:
611:
607:
603:
599:
595:
594:central canal
591:
587:
583:
579:
575:
571:
567:
563:
559:
555:
551:
547:
543:
534:
527:
522:
520:
518:
517:septal nuclei
514:
510:
506:
502:
498:
494:
490:
482:
478:
474:
470:
469:metencephalon
466:
463:
459:
455:
451:
447:
443:
442:telencephalon
439:
435:
434:
433:
431:
427:
423:
419:
415:
411:
410:mesencephalon
407:
403:
399:
395:
390:
388:
384:
380:
375:
373:
369:
368:central canal
365:
361:
357:
353:
348:
346:
342:
338:
330:
328:
326:
322:
313:
307:
303:
300:
297:
293:
292:
289:
285:
282:
279:
276:
273:
272:
268:
265:
262:
259:
258:
254:
251:
248:
245:
244:
240:
237:
234:
233:
230:
228:
221:
218:
216:
213:
210:
207:
206:
205:
198:
191:
189:
187:
183:
180:connected by
179:
175:
170:
168:
164:
163:central canal
160:
156:
152:
148:
144:
140:
128:
122:
118:
115:
112:
110:
106:
103:
100:
98:
94:
91:
88:
86:
82:
79:
76:
74:
70:
65:
60:
53:
48:
41:
36:
31:
19:
1684:Optic recess
1612:
1545:
1541:
1531:
1504:
1500:
1490:
1458:(6): 656–8.
1455:
1451:
1438:
1413:
1409:
1403:
1378:
1374:
1368:
1333:
1329:
1319:
1310:
1301:
1266:
1262:
1214:
1210:
1200:
1181:
1163:
1145:
1126:
1108:
1104:
1095:
1065:
1059:
1051:
1029:
1011:
989:
972:
950:
944:
838:
830:
799:
784:
762:) caused by
753:
713:
704:
673:
658:between the
653:
645:cauda equina
633:jugular vein
618:
614:
608:and the two
600:or into the
539:
495:down to the
486:
458:diencephalon
450:diencephalon
417:
391:
376:
349:
341:neural canal
334:
317:
224:
203:
171:
146:
142:
139:neuroanatomy
136:
77:
1656:Calcar avis
1617:human brain
1507:(1): 52–7.
1416:(1): 41–6.
772:haemorrhage
598:spinal cord
546:spinal cord
509:hippocampus
460:become the
372:spinal cord
345:neural tube
331:Development
167:spinal cord
67:Identifiers
1945:Categories
1157:. nih.gov.
936:References
818:biological
802:scientific
797:can form.
756:meningitis
680:dura mater
635:and major
314:Ventricles
277:(Magendie)
178:epithelium
97:NeuroNames
1840:Apertures
1770:Fastigium
1680:Recesses
1120:CC BY 4.0
804:study of
764:infection
737:burr hole
733:endoscope
731:using an
688:pia mater
576:into the
562:posterior
418:primitive
387:notochord
352:brainstem
298:(Luschka)
263:(Sylvius)
192:Structure
1753:Frenulum
1572:19535999
1523:12533327
1482:15013837
1430:14990758
1395:12124914
1360:17415783
1293:20807962
1241:19763105
1122:license.
1092:71013935
1013:barrier.
912:See also
833:dementia
806:CT scans
696:buoyancy
686:and the
676:meninges
590:midbrain
584:via the
560:and the
523:Function
513:amygdala
383:ectoderm
286:via the
227:foramina
174:ependyma
1923:Related
1615:of the
1563:2945234
1514:8148951
1473:2794416
1351:6871295
1284:2930915
1232:2913577
789:in the
785:During
596:of the
588:in the
568:of the
552:of the
507:of the
392:As the
370:of the
249:(Monro)
165:of the
149:in the
90:D002552
62:Details
1800:Lower
1785:Upper
1765:Taenia
1570:
1560:
1521:
1511:
1480:
1470:
1428:
1393:
1358:
1348:
1291:
1281:
1239:
1229:
1188:
1133:
1090:
1080:
1044:
1004:
965:
682:, the
647:where
497:fornix
446:cortex
404:: the
379:dorsal
141:, the
114:242787
1865:Other
1779:Floor
1632:Body
1448:(PDF)
1088:S2CID
768:blood
692:skull
660:third
505:alvei
151:brain
125:[
73:Latin
1819:Obex
1740:Roof
1568:PMID
1519:PMID
1478:PMID
1426:PMID
1391:PMID
1356:PMID
1289:PMID
1237:PMID
1186:ISBN
1131:ISBN
1116:text
1078:ISBN
1042:ISBN
1002:ISBN
963:ISBN
839:The
800:The
662:and
654:The
564:and
471:and
436:The
412:and
364:obex
238:From
235:Name
102:2497
85:MeSH
1854:to
1558:PMC
1550:doi
1509:PMC
1468:PMC
1460:doi
1418:doi
1383:doi
1379:118
1346:PMC
1338:doi
1279:PMC
1271:doi
1267:197
1227:PMC
1219:doi
1070:doi
1034:doi
994:doi
955:doi
782:).
778:or
241:To
137:In
109:FMA
1947::
1566:.
1556:.
1546:68
1544:.
1540:.
1517:.
1505:24
1503:.
1499:.
1476:.
1466:.
1456:55
1454:.
1450:.
1424:.
1414:16
1412:.
1389:.
1377:.
1354:.
1344:.
1334:28
1332:.
1328:.
1287:.
1277:.
1265:.
1261:.
1249:^
1235:.
1225:.
1215:10
1213:.
1209:.
1172:^
1094:.
1086:.
1076:.
1050:.
1040:.
1020:^
1010:.
1000:.
980:^
971:.
961:.
863:.
851:,
847:,
824:.
612:.
515:,
511:,
432:.
408:,
374:.
347:.
327:.
188:.
1605:e
1598:t
1591:v
1574:.
1552::
1525:.
1484:.
1462::
1432:.
1420::
1397:.
1385::
1362:.
1340::
1295:.
1273::
1243:.
1221::
1194:.
1139:.
1072::
1036::
996::
957::
920:.
774:(
483:.
464:.
129:]
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.