394:
382:
42:
267:
ground, then they fall into crevices on the floor where they will be safe until they hatch one to ten days later (depending on the environment that they live in, it may take longer to hatch). They hatch into a larva that looks very similar to a worm and is about two millimeters long. It only has a small body and a mouth part. At this stage, the flea does not drink blood; instead it eats dead skin cells, flea droppings, and other smaller parasites lying around them in the dust. When the larva is mature it makes a silken
242:. The flea's body is about one tenth of an inch long (about 2.5 mm). Its body is constructed to make it easier to jump long distances. The flea's body consists of three regions: head, thorax, and abdomen. The head and the thorax have rows of bristles (called combs), and the abdomen consists of eight visible segments. A flea's mouth has two functions: one for squirting saliva or partly digested blood into the bite, and one for sucking up blood from the host. This process mechanically transmits
55:
370:
256:
266:
There are four stages in a flea's life. The first stage is the egg stage. Microscopic white eggs fall easily from the female to the ground or from the animal she lays on. If they are laid on an animal, they soon fall off in the dust or in the animal's bedding. If the eggs do fall immediately on the
246:
that may cause diseases it might carry. Fleas smell exhaled carbon dioxide from humans and animals and jump rapidly to the source to feed on the newly found host. The flea is wingless so it can not fly, but it can jump long distances with the help of small, powerful legs. A flea's leg consists of
282:
Experimentally, it has been shown that the fleas flourish in dry climatic conditions with temperatures of 20–25 °C (68–77 °F), they can live up to a year and can stay in the cocoon stage for up to a year if the conditions are not favourable.
279:. When the flea emerges, it begins the final cycle, called the adult stage. A flea can now suck blood from hosts and mate with other fleas. A single female flea can mate once and lay eggs every day with up to 50 eggs per day.
393:
247:
four parts: the part that is closest to the body is the coxa; next are the femur, tibia, and tarsus. A flea can use its legs to jump up to 200 times its own body length (about 20 in or 50 cm).
381:
995:
1047:
1121:
1126:
1141:
969:
1008:
783:
698:
649:
561:
527:
1136:
430:
300:
230:
The
Oriental rat flea has no genal or pronotal combs. This characteristic can be used to differentiate the Oriental rat flea from the
551:
1116:
369:
1013:
1131:
1034:
767:
891:
868:
948:
54:
1052:
641:
961:
41:
714:
A. Farhang-Azad, R. Traub & S. Baqar (1985). "Transovarial transmission of murine typhus rickettsiae in
846:
808:
222:
that has fed on an infected rodent bites a human, although this flea can live on any warm blooded mammal.
896:
515:
308:
207:
149:
787:
1062:
917:
855:
729:
337:
1026:
1111:
496:
421:
296:
166:
49:
1000:
1083:
904:
745:
720:
694:
688:
645:
557:
523:
488:
480:
1088:
737:
470:
439:
343:
331:
860:
1070:
873:
325:
347:. Diseases can be transmitted from one generation of fleas to the next through the eggs.
733:
956:
943:
320:
255:
211:
610:
1105:
684:
665:
500:
276:
215:
909:
275:. The flea remains a pupa from one week to six months changing in a process called
17:
425:
1039:
1021:
982:
840:
126:
831:
484:
475:
458:
930:
741:
584:
457:
Boyer, Sebastien; Gillespie, Thomas R.; Miarinjara, Adélaïde (1 July 2022).
116:
86:
66:
492:
443:
1075:
883:
749:
825:
243:
235:
231:
193:
974:
197:
987:
292:
202:
96:
76:
802:
935:
272:
268:
239:
219:
106:
922:
806:
553:
Urban
Insects and Arachnids: A Handbook of Urban Entomology
786:. parasitology.informatik.uni-wuerzburg.de. Archived from
514:
Feldman, Sanford H.; Easton, David N. (1 January 2006).
426:"New species of Siphonaptera from Egypt and the Soudan"
522:(Second ed.). Academic Press. pp. 565–586.
815:
638:A History of Bubonic Plague in the British Isles
387:Close-up of a female slide-mounted plague flea
516:"Chapter 17 – Occupational Health and Safety"
8:
399:Close-up of a male slide-mounted plague flea
556:. Cambridge University Press. p. 378.
803:
615:Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
40:
31:
474:
335:and also act as a host for the tapeworms
768:"Xenopsylla cheopis (oriental rat flea)"
254:
413:
365:
291:The Oriental rat flea was collected in
693:. Chatto & Windus. pp. 147–.
550:Robinson, William H. (14 April 2005).
375:A whole slide image of the plague flea
319:This species can act as a vector for
7:
1063:3a7147b5-e778-4052-8dee-ca48273ce749
962:61b5e34f-0ace-430f-9d3f-641c788428c5
303:and described in 1903. He named it
1122:Insect vectors of animal pathogens
25:
1127:Insect vectors of human pathogens
1142:Taxa named by Charles Rothschild
611:"How fleas spread disease | CDC"
392:
380:
368:
53:
459:"Xenopsylla cheopis (rat flea)"
431:Entomologist's Monthly Magazine
1:
636:J. F. D. Shrewsbury (2005).
1158:
642:Cambridge University Press
1137:Insects described in 1903
200:, primarily of the genus
155:
148:
50:Scientific classification
48:
39:
34:
476:10.1016/j.pt.2022.03.006
1117:Rodent-carried diseases
742:10.1126/science.3966162
770:. Animal Diversity Web
463:Trends in Parasitology
444:10.5962/bhl.part.17671
263:
258:
218:. This occurs when a
184:), also known as the
1132:Parasites of rodents
957:Fauna Europaea (new)
790:on 25 September 2007
585:"CDC - DPDx - Fleas"
338:Hymenolepis diminuta
315:Disease transmission
784:"Oriental rat flea"
734:1985Sci...227..543F
206:, and is a primary
18:Xenopsylla cheopsis
874:Xenopsylla_cheopis
861:Xenopsylla_cheopis
847:Xenopsylla cheopis
817:Xenopsylla cheopis
716:Xenopsylla cheopis
520:The Laboratory Rat
359:Xenopsylla cheopis
297:Charles Rothschild
271:around itself and
264:
261:Xenopsylla cheopis
182:Xenopsylla cheopis
159:Xenopsylla cheopis
35:Oriental rat flea
1099:
1098:
1084:Open Tree of Life
809:Taxon identifiers
728:(4686): 543–545.
700:978-0-7011-8180-2
651:978-0-521-02247-7
591:. 16 January 2019
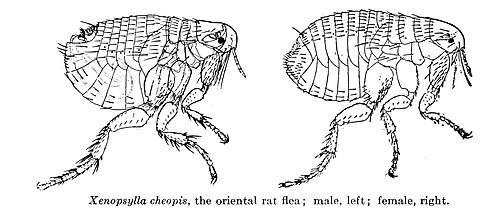
563:978-1-139-44347-0
529:978-0-12-074903-4
186:tropical rat flea
178:Oriental rat flea
174:
173:
16:(Redirected from
1149:
1092:
1091:
1079:
1078:
1066:
1065:
1056:
1055:
1043:
1042:
1040:NBNSYS0000013088
1030:
1029:
1017:
1016:
1004:
1003:
991:
990:
978:
977:
965:
964:
952:
951:
939:
938:
926:
925:
913:
912:
900:
899:
887:
886:
877:
876:
864:
863:
851:
850:
849:
836:
835:
834:
804:
799:
797:
795:
779:
777:
775:
754:
753:
711:
705:
704:
680:
674:
673:
662:
656:
655:
633:
627:
626:
624:
622:
617:. 13 August 2020
607:
601:
600:
598:
596:
581:
575:
574:
572:
570:
547:
541:
540:
538:
536:
511:
505:
504:
478:
454:
448:
447:
422:N. C. Rothschild
418:
396:
384:
372:
344:Hymenolepis nana
332:Rickettsia typhi
259:Male and female
161:
58:
57:
44:
32:
21:
1157:
1156:
1152:
1151:
1150:
1148:
1147:
1146:
1102:
1101:
1100:
1095:
1087:
1082:
1074:
1071:Observation.org
1069:
1061:
1059:
1051:
1046:
1038:
1033:
1025:
1020:
1012:
1007:
999:
994:
986:
981:
973:
968:
960:
955:
947:
942:
934:
929:
921:
916:
908:
903:
895:
890:
882:
880:
872:
867:
859:
854:
845:
844:
839:
830:
829:
824:
811:
793:
791:
782:
773:
771:
766:
763:
758:
757:
713:
712:
708:
701:
690:Bugs Britannica
683:Marren, Peter;
682:
681:
677:
664:
663:
659:
652:
635:
634:
630:
620:
618:
609:
608:
604:
594:
592:
583:
582:
578:
568:
566:
564:
549:
548:
544:
534:
532:
530:
513:
512:
508:
456:
455:
451:
420:
419:
415:
410:
405:
404:
403:
400:
397:
388:
385:
376:
373:
362:
361:
353:
326:Yersinia pestis
317:
309:Cheops pyramids
289:
253:
228:
170:
163:
157:
144:
141:X. cheopis
52:
28:
27:Species of flea
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1155:
1153:
1145:
1144:
1139:
1134:
1129:
1124:
1119:
1114:
1104:
1103:
1097:
1096:
1094:
1093:
1080:
1067:
1057:
1044:
1031:
1018:
1005:
992:
979:
966:
953:
944:Fauna Europaea
940:
927:
914:
901:
888:
878:
865:
852:
837:
821:
819:
813:
812:
807:
801:
800:
780:
762:
761:External links
759:
756:
755:
706:
699:
685:Mabey, Richard
675:
657:
650:
628:
602:
576:
562:
542:
528:
506:
469:(7): 607–608.
449:
412:
411:
409:
406:
402:
401:
398:
391:
389:
386:
379:
377:
374:
367:
364:
363:
356:
355:
354:
352:
349:
316:
313:
288:
285:
252:
249:
227:
226:Body structure
224:
212:bubonic plague
172:
171:
164:
153:
152:
146:
145:
138:
136:
132:
131:
124:
120:
119:
114:
110:
109:
104:
100:
99:
94:
90:
89:
84:
80:
79:
74:
70:
69:
64:
60:
59:
46:
45:
37:
36:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1154:
1143:
1140:
1138:
1135:
1133:
1130:
1128:
1125:
1123:
1120:
1118:
1115:
1113:
1110:
1109:
1107:
1090:
1085:
1081:
1077:
1072:
1068:
1064:
1058:
1054:
1049:
1045:
1041:
1036:
1032:
1028:
1023:
1019:
1015:
1010:
1006:
1002:
997:
993:
989:
984:
980:
976:
971:
967:
963:
958:
954:
950:
945:
941:
937:
932:
928:
924:
919:
915:
911:
906:
902:
898:
893:
889:
885:
879:
875:
870:
866:
862:
857:
853:
848:
842:
838:
833:
827:
823:
822:
820:
818:
814:
810:
805:
789:
785:
781:
769:
765:
764:
760:
751:
747:
743:
739:
735:
731:
727:
723:
722:
717:
710:
707:
702:
696:
692:
691:
686:
679:
676:
671:
670:www.nhm.ac.uk
667:
666:"Collections"
661:
658:
653:
647:
644:. p. 3.
643:
639:
632:
629:
616:
612:
606:
603:
590:
586:
580:
577:
565:
559:
555:
554:
546:
543:
531:
525:
521:
517:
510:
507:
502:
498:
494:
490:
486:
482:
477:
472:
468:
464:
460:
453:
450:
445:
441:
437:
433:
432:
427:
423:
417:
414:
407:
395:
390:
383:
378:
371:
366:
360:
350:
348:
346:
345:
340:
339:
334:
333:
328:
327:
322:
314:
312:
310:
306:
302:
298:
294:
286:
284:
280:
278:
277:metamorphosis
274:
270:
262:
257:
250:
248:
245:
241:
237:
233:
225:
223:
221:
217:
216:murine typhus
213:
209:
205:
204:
199:
195:
191:
187:
183:
179:
168:
162:
160:
154:
151:
150:Binomial name
147:
143:
142:
137:
134:
133:
130:
129:
125:
122:
121:
118:
115:
112:
111:
108:
105:
102:
101:
98:
95:
92:
91:
88:
85:
82:
81:
78:
75:
72:
71:
68:
65:
62:
61:
56:
51:
47:
43:
38:
33:
30:
19:
816:
792:. Retrieved
788:the original
772:. Retrieved
725:
719:
715:
709:
689:
678:
669:
660:
637:
631:
619:. Retrieved
614:
605:
593:. Retrieved
588:
579:
567:. Retrieved
552:
545:
533:. Retrieved
519:
509:
466:
462:
452:
435:
429:
416:
358:
342:
336:
330:
324:
318:
304:
290:
281:
265:
260:
238:, and other
229:
201:
189:
185:
181:
177:
175:
158:
156:
140:
139:
127:
107:Siphonaptera
29:
1022:NatureServe
983:iNaturalist
841:Wikispecies
794:3 September
774:3 September
621:27 December
595:27 December
589:www.cdc.gov
569:27 December
535:27 December
301:Karl Jordan
299:along with
295:, Sudan by
1106:Categories
408:References
357:Images of
307:after the
251:Life cycle
167:Rothschild
128:Xenopsylla
87:Arthropoda
1112:Pulicidae
1027:2.1013051
501:248570009
485:1471-4922
438:: 83–87.
244:pathogens
135:Species:
117:Pulicidae
73:Kingdom:
67:Eukaryota
1001:10160865
881:BioLib:
826:Wikidata
718:fleas".
687:(2010).
493:35527197
424:(1903).
236:dog flea
232:cat flea
194:parasite
190:rat flea
113:Family:
83:Phylum:
77:Animalia
63:Domain:
975:1419435
832:Q499106
750:3966162
730:Bibcode
721:Science
351:Gallery
305:cheopis
287:History
273:pupates
198:rodents
192:, is a
188:or the
169:, 1903)
123:Genus:
103:Order:
97:Insecta
93:Class:
1089:174929
1076:837053
1060:NZOR:
1053:163159
1014:189334
988:271312
949:170080
936:XENOCH
923:704445
897:127312
884:104623
748:
697:
648:
560:
526:
499:
491:
483:
321:plague
293:Shendi
269:cocoon
208:vector
203:Rattus
996:IRMNG
910:5CB97
497:S2CID
240:fleas
1048:NCBI
1009:ITIS
970:GBIF
931:EPPO
892:BOLD
796:2016
776:2016
746:PMID
695:ISBN
646:ISBN
623:2022
597:2022
571:2022
558:ISBN
537:2022
524:ISBN
489:PMID
481:ISSN
341:and
220:flea
214:and
210:for
176:The
1035:NBN
918:EoL
905:CoL
869:AFD
856:ADW
738:doi
726:227
471:doi
440:doi
196:of
1108::
1086::
1073::
1050::
1037::
1024::
1011::
998::
985::
972::
959::
946::
933::
920::
907::
894::
871::
858::
843::
828::
744:.
736:.
724:.
668:.
640:.
613:.
587:.
518:.
495:.
487:.
479:.
467:38
465:.
461:.
436:39
434:.
428:.
329:,
323:,
311:.
234:,
798:.
778:.
752:.
740::
732::
703:.
672:.
654:.
625:.
599:.
573:.
539:.
503:.
473::
446:.
442::
180:(
165:(
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.