326:
451:
438:
394:
1521:
2506:
185:
1515:
39:
303:
110:
1527:
459:
thereof the active peptide beyond increasing CNS penetration. The innate utilization of sugars as solubilizing moieties in Phase II and III metabolism (glucuronic acids) has remarkably allowed an evolutionary advantage in that mammalian enzymes are not directly evolved to degrade O glycosylated products on larger moieties.
463:
of the plasma membrane. "Hop diffusion" notably combines free diffusion and intercomparmental transitions. Recent examples notably include high permeability of met-enkephalin analogs amongst other peptides. The full mOR agonist pentapeptide DAMGO is also CNS penetrant upon introduction of glycosylation.
502:
nucelobase gets to act like a leaving group. The intermediate produced is a similar oxacarbenium ion where both the hydroxy groups and the nucleobase are still attached to the anomeric carbon. Both mechanisms theoretically yield the same product. Most ribonucleotides are hydrolyzed via the concerted S
501:
ion intermediate. This intermediate rapidly reacts with the nearby water molecule to substitute the N-glycosidic bond of the ribose and the nucleobase with an O-glycosidic bond with a hydroxy group. The concerted mechanism, the water acts as a nucleophile and attacks at the anomeric carbon before the
509:
These reactions are practically irreversible. Due to the fact that the cleavage of the N-glycosidic bond from the DNA backbone can lead to detrimental mutagenic and cytotoxic responses in an organism, have the ability to also catalyze the synthesis of N-glycosidic bonds by way of an abasic DNA site
476:
carbon of the ribose sugar structure through an N-glycosidic bond. Occasionally, the nucleobases attached to the ribose undergo deamination, alkylation, or oxidation which results in cytotoxic lesions along the DNA backbone. These modifications severely threaten the cohesiveness of the DNA molecule,
462:
The peculiar nature of O-linked glycopeptides is that there are numerous examples which are CNS penetrant. The fundamental basis of this effect is thought to involve "membrane hopping" or "hop diffusion". The non-brownian motion driven "hop diffusion" process is thought to occur due to discontinuity
405:
Different biocatalytic approaches have been developed toward the synthesis of glycosides in the past decades, which using "glycosyltransferases" and "glycoside hydrolases" are among the most common catalysis. The former often needs expensive materials and the later often shows low yields, De Winter
430:
Fluorine directed glycosylations represent an encouraging handle for both B selectivity and introduction of a non-natural biomimetic C2 functionality on the carbohydrate. One innovative example provided by Bucher et al. provides a way to utilize a fluoro oxonium ion and the trichloroacetimidate to
426:
The highly substrate specific nature of the selectivity and the overall activity of the pyranoside can provide major synthetic difficulties. The overall specificity of the glycosylation can be improved by utilizing approaches which take into account the relative transition states that the anomeric
293:
which brominates at the 5-position. On addition of the alcohol ROH and lithium carbonate, the OR replaces the bromine and on deprotecting the acetylated hydroxyls the product is synthesized in relatively high purity. It was suggested by Joshi et al. (2001) that lithium acts as the nucleophile that
427:
carbon can undergo during a typical glycosylation. Most notably, recognition and incorporation of Felkin-Ahn-Eisenstein models into rationale chemical design can generally provide reliable results provided the transformation can undergo this type of conformational control in the transition state.
321:
that break glycosidic bonds. Glycoside hydrolases typically can act either on α- or on β-glycosidic bonds, but not on both. This specificity allows researchers to obtain glycosides in high epimeric excess, one example being Wen-Ya Lu's conversion of D-Glucose to Ethyl β-D-glucopyranoside using
458:
O-linked glycopeptides recently have been shown to exhibit excellent CNS permeability and efficacy in multiple animal models with disease states. In addition one of the most intriguing aspects thereof is the capability of O-glycosylation to extend half life, decrease clearance, and improve PK/PD
96:
The term 'glycoside' is now extended to also cover compounds with bonds formed between hemiacetal (or hemiketal) groups of sugars and several chemical groups other than hydroxyls, such as -SR (thioglycosides), -SeR (selenoglycosides), -NRR (N-glycosides), or even -CRRR (C-glycosides).
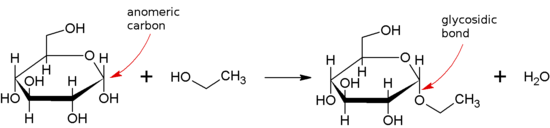
298:
the alcohol is substituted for the bromine group. Advantages of this method as well as its stereoselectivity and low cost of the lithium salt include that it can be done at room temperature and its yield compares relatively well with the conventional
Koenigs-Knorr
471:
DNA molecules contain 5-membered carbon rings called riboses that are directly attached to two phosphate groups and a nucleobase that contains amino groups. The nitrogen atoms from the amino group in the nucleotides are covalently linked to the
979:
Egleton, Richard D.; Bilsky, Edward J.; Tollin, Gordon; Dhanasekaran, Muthu; Lowery, John; Alves, Isabel; Davis, Peg; Porreca, Frank; Yamamura, Henry I. (2005-01-10). "Biousian glycopeptides penetrate the blood–brain barrier".
100:
Particularly in naturally occurring glycosides, the compound ROH from which the carbohydrate residue has been removed is often termed the aglycone, and the carbohydrate residue itself is sometimes referred to as the 'glycone'.
481:
are enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis the N-glycosidic bond to free the damaged or modified nucleobase from the DNA, by cleaving the carbon-nitrogen glycosidic bond at the 2' carbon, subsequently initiating the
810:
De Winter K, Van
Renterghem L, Wuyts K, Pelantová H, Křen V, Soetaert W, Desmet T (2015). "Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of β-D Glucosides using Cellobiose Phosphorylase from Clostridium thermocellum".
176:
and is discouraged. All of these modified glycosidic bonds have different susceptibility to hydrolysis, and in the case of C-glycosyl structures, they are typically more resistant to hydrolysis.
497:
2 like mechanism. The stepwise function, the nucleobase acts as a leaving group before the anomeric carbon gets attacked by the water molecule, producing a short-lived unstable
431:
encourage B stereoselectivity through the gauche effect. This reasonable stereoselectivity is clear through visualization of the Felkin-Ahn models of the possible chair forms.
893:
Egleton RD, Mitchell SA, Huber JD, Janders J, Stropova D, Polt R, et al. (October 2000). "Improved bioavailability to the brain of glycosylated Met-enkephalin analogs".
1614:
325:
588:
410:(CP) toward synthesis of alpha-glycosides in ionic liquids. The best condition for use of CP was found to be in the presence of IL AMMOENG 101 and ethyl acetate.
322:
naturally-derived glucosidase. It is worth noting that Wen-Ya Lu utilized glucosidase in a reverse manner opposite to the enzyme's biological functionality:
434:
This method represents an encouraging way to selectivity incorporate B-ethyl, isopropyl and other glycosides with typical trichloroacetimidate chemistry.
1732:
1659:
1340:
1770:
192:
molecule showing how carbons are numbered. The terminal saccharide is linked via a β-1,6 glycosidic bond. The remaining linkages are all β-1,3.
759:
558:
1109:
253:, Nüchter et al. (2001) were able to achieve 100% yield of α- and β-D-glucosides. This method can be performed on a multi-kilogram scale.
1594:
1079:
450:
437:
1579:
378:
or sugar donors. Many biosynthetic pathways use mono- or oligosaccharides activated by a diphosphate linkage to lipids, such as
2540:
1403:
1430:
1391:
1381:
936:
Polt R, Dhanasekaran M, Keyari CM (September 2005). "Glycosylated neuropeptides: a new vista for neuropsychopharmacology?".
1386:
654:
Nüchter, Matthias; Ondruschka, Bernd; Lautenschläger, Werner (2001). "Microwave-Assisted
Synthesis of Alkyl Glycosides".
1333:
1763:
202:
When an anomeric center is involved in a glycosidic bond (as is common in nature) then one can distinguish between
1654:
1649:
210:
by the relative stereochemistry of the anomeric position and the stereocenter furthest from C1 in the saccharide.
2545:
1639:
1629:
1604:
1574:
1830:
1420:
1102:
407:
847:
2323:
1681:
1584:
1556:
1326:
265:
in the stereoselective synthesis of alkyl D-glucopyranosides via glycosylation, with the exception of using
1054:
Marco Brito-Arias, "Synthesis and
Characterization of Glycosides", second edition, Editorial Springer 2016.
2535:
2509:
2317:
1756:
371:
262:
2311:
1725:
1686:
367:
363:
238:
128:
via the formation of an N-glycosidic bond (shown as the vertical line between the N and the sugar cycle)
1720:
350:
in living organisms, they are typically first "activated" by being joined via a glycosidic bond to the
2450:
1644:
1535:
1398:
1357:
489:
Monofunctional glycosylases catalyze the hydrolysis of the N-glycosidic bond via either a stepwise, S
483:
314:
2530:
1546:
1410:
1376:
1095:
393:
383:
359:
86:
1710:
1465:
961:
918:
679:
506:
2 like mechanism, while most deoxyribonucleotides proceed through the stepwise like mechanism.
140:
that links the glycoside to the aglycone or reducing end sugar. In analogy, one also considers
1696:
1485:
1445:
1435:
1302:
1248:
1038:
953:
910:
868:
848:"Fluorine-Directed β-Galactosylation: Chemical Glycosylation Development by Molecular Editing"
827:
792:
755:
697:
Joshi VY, Sawant MR (2006). "A convenient stereoselective synthesis of β-D-glucopyranosides".
671:
636:
564:
554:
274:
266:
1903:
1737:
1520:
1477:
1450:
1028:
1020:
989:
945:
902:
860:
819:
784:
729:
663:
628:
597:
375:
295:
290:
282:
2352:
2298:
2278:
2169:
1589:
1460:
478:
473:
222:
214:
62:
1715:
2339:
2136:
1893:
1870:
1850:
1624:
1425:
1033:
1008:
546:
82:
906:
2524:
2445:
2362:
2250:
2141:
1673:
1633:
1566:
1495:
1368:
1349:
1270:
1253:
346:
Before monosaccharide units are incorporated into glycoproteins, polysaccharides, or
250:
161:
965:
922:
683:
2329:
2210:
2192:
1840:
1780:
1619:
498:
61:. The reaction often favors formation of the α-glycosidic bond as shown due to the
32:
993:
750:
Lu WY, Lin GQ, Yu HL, Tong AM, Xu JH (2009-12-09). Whittall J, Sutton PW (eds.).
527:
35:(sugar) molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
2487:
2475:
2347:
2258:
2006:
2001:
1941:
1705:
1455:
1258:
1215:
1205:
387:
286:
189:
51:
1514:
184:
2263:
2205:
2200:
2073:
2026:
1220:
1200:
733:
632:
355:
278:
218:
78:
70:
38:
28:
831:
675:
640:
601:
2421:
2417:
2372:
2286:
2268:
2235:
2220:
2041:
1964:
1926:
1440:
1415:
1307:
1290:
1285:
1280:
1275:
1265:
1243:
1210:
1192:
1118:
1072:
351:
242:
226:
113:
90:
74:
54:
1042:
957:
914:
872:
864:
823:
796:
788:
568:
667:
302:
2438:
2399:
2384:
2357:
2306:
2240:
2113:
2108:
2093:
2078:
1994:
1989:
1809:
1804:
1748:
1235:
1225:
386:, which transfer the sugar unit from the activated donor to an accepting
379:
157:
1064:
775:
Bucher C, Gilmour R (November 2010). "Fluorine-directed glycosylation".
269:
which is less expensive and toxic than the conventional method of using
2480:
2460:
2428:
2403:
2393:
2389:
2367:
2230:
2225:
2215:
2125:
2088:
2083:
2061:
2046:
2036:
1953:
1931:
1915:
1297:
1182:
1177:
1172:
1167:
1024:
125:
47:
43:
949:
446:
O-linked glycopeptides; pharmaceutical uses of O-glycosylated peptides
2470:
2465:
2455:
2432:
2409:
2377:
2164:
2159:
2103:
2066:
2051:
2031:
2018:
1979:
1974:
1969:
1882:
1835:
1825:
1799:
1794:
1159:
318:
270:
246:
197:
169:
149:
137:
121:
717:
616:
583:
109:
1526:
1009:"Mechanisms for enzymatic cleavage of the N-glycosidic bond in DNA"
845:
Durantie, Estelle; Bucher, Christoph; Gilmour, Ryan (16 May 2012).
2056:
1859:
1068:
449:
436:
382:. These activated donors are then substrates for enzymes known as
347:
324:
301:
183:
173:
58:
1318:
617:"Ueber die Verbindungen der Zucker mit den Alkoholen und Ketonen"
454:
Control of oxonium ion – Felkin-Ahn stereoselectivity chair forms
1752:
1322:
1091:
418:
Multiple chemical approaches exist to encourage selectivity of
374:(CMP). These activated biochemical intermediates are known as
148:), where the oxygen of the glycosidic bond is replaced with a
117:
1087:
160:. Substances containing N-glycosidic bonds are also known as
1084:
Cold Spring Harbor
Laboratory Press; 1999. Searchable online
718:"Ueber einige Derivate des Traubenzuckers und der Galactose"
132:
Glycosidic bonds of the form discussed above are known as
752:
Practical
Methods for Biocatalysis and Biotransformations
331:
549:. In Varki A, Cummings RD, Esko JD, et al. (eds.).
532:
Department of
Chemistry, Queen Mary University of London
1149:
1144:
1139:
1134:
477:
leading to the development of diseases such as cancer.
16:
Covalent bond joining a sugar molecule to another group
528:"Nomenclature of Carbohydrates (Recommendations 1996)"
217:
via glycosidic bonds in order to increase their water
553:(2nd ed.). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
441:
Control of
Oxonium ion – Felkin-Ahn stereoselectivity
172:; the term "C-glycoside" is considered a misnomer by
2338:
2295:
2277:
2249:
2191:
2184:
2152:
2124:
2017:
1952:
1914:
1881:
1858:
1849:
1818:
1787:
1695:
1672:
1603:
1565:
1545:
1534:
1494:
1476:
1367:
1356:
1234:
1191:
1158:
1125:
294:attacks the carbon at the 5-position and through a
277:salts. D-glucose is first protected by forming the
237:Nüchter et al. (2001) have shown a new approach to
846:
180:Numbering, and α/β distinction of glycosidic bonds
81:(or a molecule derived from a saccharide) and the
156:, have the glycosidic bond oxygen replaced with
89:. A substance containing a glycosidic bond is a
168:bonds have the glycosidic oxygen replaced by a
722:Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft
621:Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft
589:Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft
1764:
1334:
1103:
8:
754:. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 236–239.
2188:
1855:
1771:
1757:
1749:
1542:
1364:
1341:
1327:
1319:
1110:
1096:
1088:
1071:Compendium of Chemical Terminology, the "
1032:
213:Pharmacologists often join substances to
1733:Polyhedral skeletal electron pair theory
392:
229:have important physiological functions.
108:
69:A glycosidic bond is formed between the
37:
777:Angewandte Chemie International Edition
519:
547:"Structural Basis of Glycan Diversity"
7:
1013:Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry
1007:Drohat AC, Maiti A (November 2014).
745:
743:
493:1 like mechanism, or a concerted, S
812:Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis
584:"Ueber die Glucoside der Alkohole"
105:S-, N-, C-, and O-glycosidic bonds
14:
136:, in reference to the glycosidic
2505:
2504:
1525:
1519:
1513:
984:. Carbohydrate Science. Part 1.
261:Joshi et al. (2006) propose the
853:Chemistry – A European Journal
42:Formation of ethyl glucoside:
1:
907:10.1016/S0006-8993(00)02794-3
545:Bertozzi C, Rabuka D (2009).
994:10.1016/j.tetasy.2004.11.038
85:of some compound such as an
1081:Essentials of Glycobiology.
716:Koenigs W, Knorr E (1901).
699:Indian Journal of Chemistry
510:and a specific nucleobase.
406:et al. investigated use of
401:Disaccharide phosphorylases
2562:
1431:Metal–ligand multiple bond
938:Medicinal Research Reviews
551:Essentials of Glycobiology
390:(the acceptor substrate).
195:
120:, results from the sugar
2500:
1511:
734:10.1002/cber.190103401162
633:10.1002/cber.189502801248
467:N-Glycosidic bonds in DNA
1831:Cyclohexane conformation
1065:Definition of glycosides
656:Synthetic Communications
602:10.1002/cber.18930260327
408:cellobiose phosphorylase
249:in a rotor reactor with
2324:Isomaltooligosaccharide
1281:Anthraquinone glycoside
414:Directed glycosylations
317:(or glycosidases), are
289:, and then addition of
257:Vishal Y Joshi's method
152:atom. In the same way,
2541:Carbohydrate chemistry
2318:Galactooligosaccharide
982:Tetrahedron: Asymmetry
865:10.1002/chem.201200468
824:10.1002/adsc.201500077
789:10.1002/anie.201004467
615:Fischer, Emil (1895).
582:Fischer, Emil (1893).
455:
442:
397:
372:cytidine monophosphate
338:
306:
263:Koenigs-Knorr reaction
256:
193:
129:
66:
2312:Fructooligosaccharide
668:10.1081/scc-100104035
453:
440:
396:
368:thymidine diphosphate
364:guanosine diphosphate
328:
305:
239:Fischer glycosidation
187:
112:
41:
1421:Coordinate (dipolar)
1266:Cyanogenic glycoside
484:base excision repair
384:glycosyltransferases
342:Glycosyltransferases
315:Glycoside hydrolases
310:Glycoside hydrolases
1595:C–H···O interaction
1377:Electron deficiency
1291:Flavonoid glycoside
1244:Alcoholic glycoside
424:β-glycosidic bonds.
360:uridine diphosphate
247:refluxing apparatus
245:oven equipped with
233:Chemical approaches
221:; this is known as
1580:Resonance-assisted
1286:Coumarin glycoside
1276:Phenolic glycoside
1025:10.1039/c4ob01063a
456:
443:
398:
339:
329:Lu, Wen-Ya et al.
307:
208:β-glycosidic bonds
194:
154:N-glycosidic bonds
142:S-glycosidic bonds
134:O-glycosidic bonds
130:
67:
25:glycosidic linkage
2518:
2517:
2496:
2495:
2180:
2179:
1746:
1745:
1697:Electron counting
1668:
1667:
1557:London dispersion
1509:
1508:
1486:Metal aromaticity
1316:
1315:
1303:Steviol glycoside
1249:Cardiac glycoside
1150:C-glycosidic bond
1145:S-glycosidic bond
1140:N-glycosidic bond
1135:O-glycosidic bond
1019:(42): 8367–8378.
950:10.1002/med.20039
859:(26): 8208–8215.
761:978-0-470-74859-6
560:978-0-87969-770-9
376:sugar nucleotides
267:lithium carbonate
116:, a component of
2553:
2546:Chemical bonding
2508:
2507:
2299:oligosaccharides
2279:Tetrasaccharides
2189:
1904:Dihydroxyacetone
1856:
1773:
1766:
1759:
1750:
1738:Jemmis mno rules
1590:Dihydrogen bonds
1543:
1529:
1523:
1517:
1451:Hyperconjugation
1365:
1343:
1336:
1329:
1320:
1112:
1105:
1098:
1089:
1047:
1046:
1036:
1004:
998:
997:
976:
970:
969:
933:
927:
926:
890:
884:
883:
881:
879:
850:
842:
836:
835:
818:(8): 1961–1969.
807:
801:
800:
772:
766:
765:
747:
738:
737:
713:
707:
706:
694:
688:
687:
662:(9): 1277–1283.
651:
645:
644:
627:(1): 1145–1167.
612:
606:
605:
596:(3): 2400–2412.
579:
573:
572:
542:
536:
535:
524:
479:DNA glycosylases
296:transition state
291:hydrogen bromide
283:acetic anhydride
50:combine to form
2561:
2560:
2556:
2555:
2554:
2552:
2551:
2550:
2521:
2520:
2519:
2514:
2492:
2353:Oat beta-glucan
2340:Polysaccharides
2334:
2297:
2291:
2273:
2245:
2176:
2170:Neuraminic acid
2148:
2120:
2013:
1948:
1910:
1877:
1851:Monosaccharides
1845:
1814:
1783:
1777:
1747:
1742:
1691:
1664:
1607:
1599:
1561:
1548:
1538:
1530:
1524:
1518:
1505:
1490:
1472:
1360:
1352:
1347:
1317:
1312:
1230:
1187:
1154:
1121:
1116:
1078:Varki A et al.
1061:
1051:
1050:
1006:
1005:
1001:
978:
977:
973:
935:
934:
930:
892:
891:
887:
877:
875:
844:
843:
839:
809:
808:
804:
774:
773:
769:
762:
749:
748:
741:
715:
714:
710:
696:
695:
691:
653:
652:
648:
614:
613:
609:
581:
580:
576:
561:
544:
543:
539:
526:
525:
521:
516:
505:
496:
492:
486:(BER) pathway.
469:
448:
416:
403:
344:
312:
281:by addition of
259:
235:
223:glucuronidation
215:glucuronic acid
200:
182:
107:
63:anomeric effect
21:glycosidic bond
17:
12:
11:
5:
2559:
2557:
2549:
2548:
2543:
2538:
2533:
2523:
2522:
2516:
2515:
2513:
2512:
2501:
2498:
2497:
2494:
2493:
2491:
2490:
2485:
2484:
2483:
2478:
2468:
2463:
2458:
2453:
2451:Levan beta 2→6
2448:
2443:
2442:
2441:
2425:
2414:
2413:
2412:
2396:
2387:
2382:
2381:
2380:
2375:
2370:
2365:
2360:
2355:
2344:
2342:
2336:
2335:
2333:
2332:
2327:
2321:
2315:
2309:
2303:
2301:
2293:
2292:
2290:
2289:
2283:
2281:
2275:
2274:
2272:
2271:
2266:
2261:
2255:
2253:
2251:Trisaccharides
2247:
2246:
2244:
2243:
2238:
2233:
2228:
2223:
2218:
2213:
2208:
2203:
2197:
2195:
2186:
2182:
2181:
2178:
2177:
2175:
2174:
2173:
2172:
2162:
2156:
2154:
2150:
2149:
2147:
2146:
2145:
2144:
2139:
2137:Mannoheptulose
2130:
2128:
2122:
2121:
2119:
2118:
2117:
2116:
2111:
2106:
2098:
2097:
2096:
2091:
2086:
2081:
2071:
2070:
2069:
2064:
2059:
2054:
2049:
2044:
2039:
2034:
2023:
2021:
2015:
2014:
2012:
2011:
2010:
2009:
1999:
1998:
1997:
1992:
1984:
1983:
1982:
1977:
1972:
1967:
1958:
1956:
1950:
1949:
1947:
1946:
1945:
1944:
1936:
1935:
1934:
1929:
1920:
1918:
1912:
1911:
1909:
1908:
1907:
1906:
1898:
1897:
1896:
1894:Glyceraldehyde
1887:
1885:
1879:
1878:
1876:
1875:
1874:
1873:
1871:Glycolaldehyde
1864:
1862:
1853:
1847:
1846:
1844:
1843:
1838:
1833:
1828:
1822:
1820:
1816:
1815:
1813:
1812:
1807:
1802:
1797:
1791:
1789:
1785:
1784:
1778:
1776:
1775:
1768:
1761:
1753:
1744:
1743:
1741:
1740:
1735:
1730:
1729:
1728:
1723:
1718:
1713:
1702:
1700:
1693:
1692:
1690:
1689:
1684:
1678:
1676:
1670:
1669:
1666:
1665:
1663:
1662:
1657:
1652:
1647:
1642:
1637:
1627:
1622:
1617:
1611:
1609:
1601:
1600:
1598:
1597:
1592:
1587:
1582:
1577:
1571:
1569:
1563:
1562:
1560:
1559:
1553:
1551:
1540:
1536:Intermolecular
1532:
1531:
1512:
1510:
1507:
1506:
1504:
1503:
1500:
1498:
1492:
1491:
1489:
1488:
1482:
1480:
1474:
1473:
1471:
1470:
1469:
1468:
1463:
1453:
1448:
1443:
1438:
1433:
1428:
1423:
1418:
1413:
1408:
1407:
1406:
1396:
1395:
1394:
1389:
1384:
1373:
1371:
1362:
1358:Intramolecular
1354:
1353:
1350:Chemical bonds
1348:
1346:
1345:
1338:
1331:
1323:
1314:
1313:
1311:
1310:
1305:
1300:
1295:
1294:
1293:
1288:
1283:
1273:
1268:
1263:
1262:
1261:
1256:
1246:
1240:
1238:
1232:
1231:
1229:
1228:
1223:
1218:
1213:
1208:
1203:
1197:
1195:
1189:
1188:
1186:
1185:
1180:
1175:
1170:
1164:
1162:
1156:
1155:
1153:
1152:
1147:
1142:
1137:
1131:
1129:
1123:
1122:
1117:
1115:
1114:
1107:
1100:
1092:
1086:
1085:
1076:
1060:
1059:External links
1057:
1056:
1055:
1049:
1048:
999:
971:
944:(5): 557–585.
928:
895:Brain Research
885:
837:
802:
783:(46): 8724–8.
767:
760:
739:
728:(1): 957–981.
708:
689:
646:
607:
574:
559:
537:
518:
517:
515:
512:
503:
494:
490:
468:
465:
447:
444:
415:
412:
402:
399:
343:
340:
311:
308:
258:
255:
251:pressure bombs
241:. Employing a
234:
231:
196:Main article:
181:
178:
162:glycosylamines
146:thioglycosides
106:
103:
83:hydroxyl group
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2558:
2547:
2544:
2542:
2539:
2537:
2536:Carbohydrates
2534:
2532:
2529:
2528:
2526:
2511:
2503:
2502:
2499:
2489:
2486:
2482:
2479:
2477:
2474:
2473:
2472:
2469:
2467:
2464:
2462:
2459:
2457:
2454:
2452:
2449:
2447:
2446:Hemicellulose
2444:
2440:
2437:
2436:
2435:
2434:
2430:
2426:
2424:
2423:
2419:
2415:
2411:
2408:
2407:
2406:
2405:
2401:
2397:
2395:
2391:
2388:
2386:
2383:
2379:
2376:
2374:
2371:
2369:
2366:
2364:
2361:
2359:
2356:
2354:
2351:
2350:
2349:
2346:
2345:
2343:
2341:
2337:
2331:
2328:
2325:
2322:
2319:
2316:
2313:
2310:
2308:
2305:
2304:
2302:
2300:
2294:
2288:
2285:
2284:
2282:
2280:
2276:
2270:
2267:
2265:
2262:
2260:
2257:
2256:
2254:
2252:
2248:
2242:
2239:
2237:
2234:
2232:
2229:
2227:
2224:
2222:
2219:
2217:
2214:
2212:
2209:
2207:
2204:
2202:
2199:
2198:
2196:
2194:
2193:Disaccharides
2190:
2187:
2183:
2171:
2168:
2167:
2166:
2163:
2161:
2158:
2157:
2155:
2151:
2143:
2142:Sedoheptulose
2140:
2138:
2135:
2134:
2133:Ketoheptoses
2132:
2131:
2129:
2127:
2123:
2115:
2112:
2110:
2107:
2105:
2102:
2101:
2100:Deoxy sugars
2099:
2095:
2092:
2090:
2087:
2085:
2082:
2080:
2077:
2076:
2075:
2072:
2068:
2065:
2063:
2060:
2058:
2055:
2053:
2050:
2048:
2045:
2043:
2040:
2038:
2035:
2033:
2030:
2029:
2028:
2025:
2024:
2022:
2020:
2016:
2008:
2005:
2004:
2003:
2000:
1996:
1993:
1991:
1988:
1987:
1986:Ketopentoses
1985:
1981:
1978:
1976:
1973:
1971:
1968:
1966:
1963:
1962:
1961:Aldopentoses
1960:
1959:
1957:
1955:
1951:
1943:
1940:
1939:
1937:
1933:
1930:
1928:
1925:
1924:
1923:Aldotetroses
1922:
1921:
1919:
1917:
1913:
1905:
1902:
1901:
1899:
1895:
1892:
1891:
1889:
1888:
1886:
1884:
1880:
1872:
1869:
1868:
1866:
1865:
1863:
1861:
1857:
1854:
1852:
1848:
1842:
1839:
1837:
1834:
1832:
1829:
1827:
1824:
1823:
1821:
1817:
1811:
1808:
1806:
1803:
1801:
1798:
1796:
1793:
1792:
1790:
1786:
1782:
1781:carbohydrates
1774:
1769:
1767:
1762:
1760:
1755:
1754:
1751:
1739:
1736:
1734:
1731:
1727:
1724:
1722:
1719:
1717:
1714:
1712:
1711:Hückel's rule
1709:
1708:
1707:
1704:
1703:
1701:
1698:
1694:
1688:
1685:
1683:
1680:
1679:
1677:
1675:
1674:Bond cleavage
1671:
1661:
1658:
1656:
1653:
1651:
1648:
1646:
1643:
1641:
1640:Intercalation
1638:
1635:
1631:
1630:Metallophilic
1628:
1626:
1623:
1621:
1618:
1616:
1613:
1612:
1610:
1606:
1602:
1596:
1593:
1591:
1588:
1586:
1583:
1581:
1578:
1576:
1573:
1572:
1570:
1568:
1564:
1558:
1555:
1554:
1552:
1550:
1547:Van der Waals
1544:
1541:
1537:
1533:
1528:
1522:
1516:
1502:
1501:
1499:
1497:
1493:
1487:
1484:
1483:
1481:
1479:
1475:
1467:
1464:
1462:
1459:
1458:
1457:
1454:
1452:
1449:
1447:
1444:
1442:
1439:
1437:
1434:
1432:
1429:
1427:
1424:
1422:
1419:
1417:
1414:
1412:
1409:
1405:
1402:
1401:
1400:
1397:
1393:
1390:
1388:
1385:
1383:
1380:
1379:
1378:
1375:
1374:
1372:
1370:
1366:
1363:
1359:
1355:
1351:
1344:
1339:
1337:
1332:
1330:
1325:
1324:
1321:
1309:
1308:Thioglycoside
1306:
1304:
1301:
1299:
1296:
1292:
1289:
1287:
1284:
1282:
1279:
1278:
1277:
1274:
1272:
1271:Glycosylamine
1269:
1267:
1264:
1260:
1257:
1255:
1254:Bufadienolide
1252:
1251:
1250:
1247:
1245:
1242:
1241:
1239:
1237:
1233:
1227:
1224:
1222:
1219:
1217:
1214:
1212:
1209:
1207:
1204:
1202:
1199:
1198:
1196:
1194:
1190:
1184:
1183:1,6-Glycoside
1181:
1179:
1178:1,4-Glycoside
1176:
1174:
1171:
1169:
1166:
1165:
1163:
1161:
1157:
1151:
1148:
1146:
1143:
1141:
1138:
1136:
1133:
1132:
1130:
1128:
1124:
1120:
1113:
1108:
1106:
1101:
1099:
1094:
1093:
1090:
1083:
1082:
1077:
1074:
1070:
1066:
1063:
1062:
1058:
1053:
1052:
1044:
1040:
1035:
1030:
1026:
1022:
1018:
1014:
1010:
1003:
1000:
995:
991:
987:
983:
975:
972:
967:
963:
959:
955:
951:
947:
943:
939:
932:
929:
924:
920:
916:
912:
908:
904:
900:
896:
889:
886:
874:
870:
866:
862:
858:
854:
849:
841:
838:
833:
829:
825:
821:
817:
813:
806:
803:
798:
794:
790:
786:
782:
778:
771:
768:
763:
757:
753:
746:
744:
740:
735:
731:
727:
723:
719:
712:
709:
704:
700:
693:
690:
685:
681:
677:
673:
669:
665:
661:
657:
650:
647:
642:
638:
634:
630:
626:
622:
618:
611:
608:
603:
599:
595:
591:
590:
585:
578:
575:
570:
566:
562:
556:
552:
548:
541:
538:
533:
529:
523:
520:
513:
511:
507:
500:
487:
485:
480:
475:
466:
464:
460:
452:
445:
439:
435:
432:
428:
425:
421:
413:
411:
409:
400:
395:
391:
389:
385:
381:
377:
373:
369:
365:
361:
357:
353:
349:
341:
336:
332:
327:
323:
320:
316:
309:
304:
300:
297:
292:
288:
284:
280:
276:
272:
268:
264:
254:
252:
248:
244:
240:
232:
230:
228:
225:. Many other
224:
220:
216:
211:
209:
205:
199:
191:
186:
179:
177:
175:
171:
167:
163:
159:
155:
151:
147:
143:
139:
135:
127:
123:
119:
115:
111:
104:
102:
98:
94:
92:
88:
84:
80:
76:
72:
64:
60:
56:
53:
49:
45:
40:
36:
34:
31:that joins a
30:
27:is a type of
26:
22:
2427:
2416:
2398:
2330:Maltodextrin
2211:Isomaltulose
2002:Deoxy sugars
1938:Ketotetrose
1841:Mutarotation
1716:Baird's rule
1436:Charge-shift
1399:Hypervalence
1126:
1080:
1016:
1012:
1002:
988:(1): 65–75.
985:
981:
974:
941:
937:
931:
901:(1): 37–46.
898:
894:
888:
876:. Retrieved
856:
852:
840:
815:
811:
805:
780:
776:
770:
751:
725:
721:
711:
702:
698:
692:
659:
655:
649:
624:
620:
610:
593:
587:
577:
550:
540:
531:
522:
508:
499:oxacarbenium
488:
470:
461:
457:
433:
429:
423:
419:
417:
404:
345:
334:
330:
313:
260:
236:
212:
207:
203:
201:
165:
153:
145:
144:(which form
141:
133:
131:
99:
95:
68:
33:carbohydrate
24:
20:
18:
2488:Xanthan gum
2476:Amylopectin
2348:Beta-glucan
2259:Maltotriose
2074:Ketohexoses
2027:Aldohexoses
2007:Deoxyribose
1942:Erythrulose
1900:Ketotriose
1890:Aldotriose
1706:Aromaticity
1682:Heterolysis
1660:Salt bridge
1605:Noncovalent
1575:Low-barrier
1456:Aromaticity
1446:Conjugation
1426:Pi backbond
1259:Cardenolide
1216:Glucuronide
1206:Galactoside
1173:β-Glycoside
1168:α-Glycoside
1067:, from the
388:nucleophile
354:group of a
287:acetic acid
77:group of a
2531:Glycosides
2525:Categories
2264:Melezitose
2206:Isomaltose
2201:Cellobiose
1867:Aldodiose
1634:aurophilic
1615:Mechanical
1221:Rhamnoside
1201:Fructoside
1119:Glycosides
705:: 461–465.
514:References
370:(TDP), or
356:nucleotide
337:, 236–239.
279:peracetate
227:glycosides
219:solubility
166:C-glycosyl
79:saccharide
71:hemiacetal
29:ether bond
2418:Galactose
2373:Cellulose
2363:Sizofiran
2287:Stachyose
2269:Raffinose
2236:Trehalose
2221:Lactulose
2042:Galactose
1965:Arabinose
1927:Erythrose
1779:Types of
1726:spherical
1687:Homolysis
1650:Cation–pi
1625:Chalcogen
1585:Symmetric
1441:Hapticity
1211:Glucoside
1073:Gold Book
832:1615-4150
676:0039-7911
641:1099-0682
352:phosphate
243:microwave
114:Adenosine
91:glycoside
75:hemiketal
55:glucoside
2510:Category
2439:Glycogen
2422:Galactan
2400:Fructose
2385:Chitosan
2358:Lentinan
2307:Acarbose
2241:Turanose
2185:Multiple
2126:Heptoses
2114:Rhamnose
2109:Fuculose
2094:Tagatose
2079:Fructose
1995:Xylulose
1990:Ribulose
1954:Pentoses
1916:Tetroses
1819:Geometry
1810:Pyranose
1805:Furanose
1655:Anion–pi
1645:Stacking
1567:Hydrogen
1478:Metallic
1369:Covalent
1361:(strong)
1236:Aglycone
1226:Riboside
1160:Geometry
1043:25181003
966:38798797
958:16075406
923:18102579
915:11033091
878:24 April
873:22592962
797:20886497
684:93986043
569:20301274
474:anomeric
380:dolichol
358:such as
188:A β-1,6
158:nitrogen
2481:Amylose
2429:Glucose
2404:Fructan
2394:Dextran
2390:Dextrin
2368:Zymosan
2231:Sucrose
2226:Maltose
2216:Lactose
2165:Nonoses
2160:Octoses
2153:Above 7
2089:Sorbose
2084:Psicose
2062:Mannose
2047:Glucose
2037:Altrose
2019:Hexoses
1932:Threose
1883:Trioses
1788:General
1620:Halogen
1466:bicyclo
1411:Agostic
1298:Saponin
1193:Glycone
1034:4238931
366:(GDP),
362:(UDP),
319:enzymes
299:method.
275:mercury
126:adenine
87:alcohol
48:ethanol
44:Glucose
2471:Starch
2466:Pectin
2461:Mannan
2456:Lignin
2433:Glucan
2410:Inulin
2378:Chitin
2104:Fucose
2067:Talose
2052:Gulose
2032:Allose
1980:Xylose
1975:Ribose
1970:Lyxose
1860:Dioses
1836:Epimer
1826:Anomer
1800:Ketose
1795:Aldose
1721:Möbius
1549:forces
1539:(weak)
1041:
1031:
964:
956:
921:
913:
871:
830:
795:
758:
682:
674:
639:
567:
557:
348:lipids
271:silver
198:Anomer
190:glucan
170:carbon
150:sulfur
138:oxygen
122:ribose
2326:(IMO)
2320:(GOS)
2314:(FOS)
2296:Other
2057:Idose
1699:rules
1608:other
1496:Ionic
1404:3c–4e
1392:8c–2e
1387:4c–2e
1382:3c–2e
1069:IUPAC
962:S2CID
919:S2CID
680:S2CID
174:IUPAC
59:water
52:ethyl
1461:homo
1416:Bent
1127:Bond
1039:PMID
954:PMID
911:PMID
880:2022
869:PMID
828:ISSN
793:PMID
756:ISBN
672:ISSN
637:ISSN
565:PMID
555:ISBN
422:and
335:2010
206:and
124:and
57:and
46:and
1029:PMC
1021:doi
990:doi
946:doi
903:doi
899:881
861:doi
820:doi
816:357
785:doi
730:doi
703:45B
664:doi
629:doi
598:doi
285:in
273:or
118:RNA
73:or
23:or
2527::
2431:/
2420:/
2402:/
2392:/
1037:.
1027:.
1017:12
1015:.
1011:.
986:16
960:.
952:.
942:25
940:.
917:.
909:.
897:.
867:.
857:18
855:.
851:.
826:.
814:.
791:.
781:49
779:.
742:^
726:34
724:.
720:.
701:.
678:.
670:.
660:31
658:.
635:.
625:28
623:.
619:.
594:26
592:.
586:.
563:.
530:.
420:α-
333:.
204:α-
164:.
93:.
19:A
1772:e
1765:t
1758:v
1636:)
1632:(
1342:e
1335:t
1328:v
1111:e
1104:t
1097:v
1075:"
1045:.
1023::
996:.
992::
968:.
948::
925:.
905::
882:.
863::
834:.
822::
799:.
787::
764:.
736:.
732::
686:.
666::
643:.
631::
604:.
600::
571:.
534:.
504:N
495:N
491:N
65:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.