246:
40:
610:
546:
598:
558:
586:
622:
574:
52:
395:- along a line parallel to the median sulcus; within the floor, motor neurons are located medially of the sulcus limitans, while sensory neurons are located laterally. The elevation between the median sulcus and sulcus limitans (i.e. the region for motor neurons), is known as the
281:(nerve bundles joining the structure on the posterior side of the ventricle to the structures on the anterior side). The caudal tip of the fourth ventricle - where it becomes the
360:. Therefore, the fourth ventricle is the connector between the ventricular system (where CSF is produced) and the subarachnoid space (where CSF is absorbed). The
391:
of the midbrain to the central canal of the spinal cord), dividing the floor into right and left halves. Each half is further divided by a further sulcus - the
150:
1067:
845:
397:
609:
1150:
545:
507:. During the first trimester of pregnancy the central canal expands into the lateral, third and fourth ventricles, connected by thinner channels.
597:
436:
appearance, visible (in a colour closer to teal) through the floor of the ventricle, superiorly to the superior fovea. The internal part of the
748:
126:
460:
647:
344:
is where CSF can escape the ventricle through 3 openings: Near each of the 3 corners of the inferior roof there is an opening into the
1118:
952:
773:
808:
838:
503:
of the neural tube. Specifically, the fourth ventricle originates from the portion of the tube that is present in the developing
157:
736:
480:
145:
500:
464:
213:
The fourth ventricle has a characteristic diamond shape in cross-sections of the human brain. It is located within the
1197:
831:
1006:
792:
1001:
989:
981:
564:
557:
325:
313:
262:
245:
84:
1140:
56:
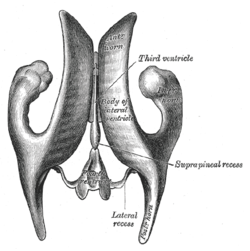
Drawing of a cast of the ventricular cavities, viewed from above. (Fourth ventricle visible at bottom center.)
585:
133:
121:
962:
740:
730:
278:
101:
1132:
1050:
947:
887:
512:
483:, within the medulla oblongata, comprises cells that are spindle shaped, also creating a bulge—the
476:
468:
317:
207:
1192:
1155:
935:
866:
854:
187:
183:
795:
at the
University of Michigan Health System - "Fourth Ventricle, Sagittal Section, Medial View"
1145:
1030:
957:
904:
769:
744:
711:
693:
651:
452:
441:
388:
369:
298:
230:
218:
195:
621:
1171:
1097:
882:
701:
685:
445:
356:
573:
39:
1088:
1072:
1035:
930:
914:
504:
425:
392:
350:
234:
191:
463:
emerge via the median sulcus and run transversely across the floor to become part of the
823:
706:
1113:
1093:
816:
508:
380:
345:
337:
333:
290:
798:
44:
Animation showing the fourth ventricle (in red) in relation to the ventricular system.
1186:
1055:
1045:
994:
940:
877:
516:
484:
479:, located slightly superiorly to the inferior fovea, within the median eminence. The
429:
282:
312:(i.e. of the posterior edge) is formed, in the midline, by a thin lamina called the
925:
528:
437:
221:. CSF entering the fourth ventricle through the cerebral aqueduct can exit to the
114:
89:
897:
858:
302:
294:
226:
179:
401:, while the lateral region (i.e. that for the sensory neurons) is known as the
531:
329:
96:
697:
138:
802:
673:
372:
lies immediately above the roof of the fourth ventricle, in the cerebellum.
715:
615:
Diagram showing the positions of the three principal subarachnoid cisternæ.
515:. If the flow of fluid is blocked ventricles may become enlarged and cause
499:
The ventricular system including the fourth ventricle, develops from the
433:
222:
108:
17:
491:
which overlies them; this is the region inferior of the inferior fovea.
163:
551:
Transverse section of medulla oblongata below the middle of the olive.
689:
297:
and therefore is a marker for the imaginary dividing line between the
603:
Drawing of a cast of the ventricular cavities, viewed from the side.
51:
244:
194:, and the fourth ventricle. The fourth ventricle extends from the
72:
27:
One of four central brain cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid
799:
Stained brain slice images which include the "fourth%20ventricle"
379:(i.e. the anterior edge) of the fourth ventricle constitutes the
1060:
417:
286:
214:
203:
827:
178:
is one of the four connected fluid-filled cavities within the
732:
First Aid for the USMLE Step 1: 2010 20th
Anniversary Edition
383:, and comprises a number of general features. A sulcus - the
249:
Fourth ventricle location shown in red (E), pons (B); the
420:
is located behind the middle and superior portion of the
405:. The sulcus limitans bifurcates at either end - the
1164:
1131:
1106:
1081:
1020:
980:
971:
913:
865:
144:
132:
120:
107:
95:
83:
71:
66:
61:
32:
674:"The debated neuroanatomy of the fourth ventricle"
364:rises (i.e. posteriorly) to a peak, known as the
289:; the obex is also a marker for the level of the
277:(anterior) surface, and side walls formed by the
527:The fourth ventricle is a common location of an
387:- extends the length of the ventricle (from the
455:is located behind the inferior portion of the
839:
729:Le, Tao; Bhushan, Vikas; Vasan, Neil (2010).
8:
766:Human Embryology & Developmental Biology
424:. In the superior region of the pons is the
182:. These cavities, known collectively as the
459:(and continues caudally of the ventricle).
977:
846:
832:
824:
50:
38:
705:
448:within the inferior region of the Pons.
638:
541:
511:appear in the ventricles which produce
444:, in the process of looping around the
440:bulges into the ventricle, forming the
253:of the ventricle is to the right, the
161:
29:
813:Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator
354:, while the lateral openings are the
7:
428:, which due to its concentration of
591:Median sagittal section of brain.
25:
620:
608:
596:
584:
572:
556:
544:
186:, consist of the left and right
158:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
737:The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
348:, the caudal opening being the
809:"Anatomy diagram: 13048.000-3"
340:. The inferior portion of the
320:. The inferior portion of the
1:
481:dorsal nucleus of vagus nerve
465:inferior cerebellar peduncle
324:is formed superiorly by the
308:The superior portion of the
217:or in the upper part of the
768:. Mosby. pp. 237–238.
261:The fourth ventricle has a
1214:
815:. Elsevier. Archived from
764:Carlson, Bruce M. (1999).
368:(Latin for "summit"); the
269:(posterior) surface and a
1151:Interventricular foramina
646:Dr. M. A. (Toby) Arnold.
336:), and inferiorly by the
156:
49:
37:
1002:Inferior medullary velum
990:Superior medullary velum
565:roof of fourth ventricle
314:superior medullary velum
672:Spierer, Ronen (2023).
326:inferior medullary veli
316:, and laterally by the
487:—in the region of the
328:and the vermis of the
258:
233:and a single, midline
523:Clinical significance
248:
206:, and is filled with
963:Posterior commissure
409:cerebrally, and the
318:cerebellar peduncles
279:cerebellar peduncles
1141:Blood–brain barrier
1133:Cerebrospinal fluid
1051:Hypoglossal trigone
948:Hypothalamic sulcus
931:Infundibular recess
888:Collateral eminence
793:Atlas image: n2a8p1
513:cerebrospinal fluid
477:hypoglossal trigone
469:hypoglossal nucleus
357:foramina of Luschka
208:cerebrospinal fluid
200:aqueduct of Sylvius
78:ventriculus quartus
1198:Ventricular system
1156:Perilymphatic duct
936:Suprapineal recess
867:Lateral ventricles
855:Ventricular system
678:Journal of Anatomy
648:"Anatomy Glossary"
285:- is known as the
259:
223:subarachnoid space
188:lateral ventricles
184:ventricular system
1180:
1179:
1146:Cerebral aqueduct
1127:
1126:
1031:Facial colliculus
958:Subfornical organ
905:Septum pellucidum
803:BrainMaps project
750:978-0-07-163340-6
690:10.1111/joa.13885
538:Additional images
453:medulla oblongata
442:facial colliculus
389:cerebral aqueduct
370:fastigial nucleus
231:lateral apertures
219:medulla oblongata
196:cerebral aqueduct
172:
171:
167:
16:(Redirected from
1205:
1172:Ventriculomegaly
978:
973:Fourth ventricle
883:Stria terminalis
848:
841:
834:
825:
820:
780:
779:
761:
755:
754:
726:
720:
719:
709:
669:
663:
662:
660:
659:
650:. Archived from
643:
627:Fourth ventricle
624:
612:
600:
588:
576:
560:
548:
509:Choroid plexuses
471:bulges into the
461:Medullary striae
446:abducens nucleus
351:foramen Magendie
176:fourth ventricle
164:edit on Wikidata
54:
42:
33:Fourth ventricle
30:
21:
1213:
1212:
1208:
1207:
1206:
1204:
1203:
1202:
1183:
1182:
1181:
1176:
1160:
1123:
1102:
1098:Lateral/Luschka
1089:Median/Magendie
1077:
1073:Sulcus limitans
1068:Medial eminence
1036:Locus coeruleus
1016:
967:
915:Third ventricle
909:
894:Occipital horn
861:
852:
807:
789:
784:
783:
776:
763:
762:
758:
751:
728:
727:
723:
671:
670:
666:
657:
655:
645:
644:
640:
635:
628:
625:
616:
613:
604:
601:
592:
589:
580:
579:Rhomboid fossa.
577:
568:
561:
552:
549:
540:
525:
505:rhombencephalon
497:
475:, creating the
426:locus coeruleus
403:vestibular area
398:medial eminence
393:sulcus limitans
243:
235:median aperture
192:third ventricle
168:
57:
45:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1211:
1209:
1201:
1200:
1195:
1185:
1184:
1178:
1177:
1175:
1174:
1168:
1166:
1162:
1161:
1159:
1158:
1153:
1148:
1143:
1137:
1135:
1129:
1128:
1125:
1124:
1122:
1121:
1119:Tela choroidea
1116:
1114:Rhomboid fossa
1110:
1108:
1104:
1103:
1101:
1100:
1094:Lateral recess
1091:
1085:
1083:
1079:
1078:
1076:
1075:
1070:
1065:
1064:
1063:
1058:
1053:
1048:
1040:
1039:
1038:
1033:
1024:
1022:
1018:
1017:
1015:
1014:
1009:
1004:
999:
998:
997:
986:
984:
975:
969:
968:
966:
965:
960:
955:
953:Tela choroidea
950:
945:
944:
943:
938:
933:
928:
919:
917:
911:
910:
908:
907:
902:
901:
900:
892:
891:
890:
885:
880:
871:
869:
863:
862:
853:
851:
850:
843:
836:
828:
822:
821:
819:on 2012-07-22.
805:
796:
788:
787:External links
785:
782:
781:
774:
756:
749:
721:
684:(4): 555–563.
664:
637:
636:
634:
631:
630:
629:
626:
619:
617:
614:
607:
605:
602:
595:
593:
590:
583:
581:
578:
571:
569:
562:
555:
553:
550:
543:
539:
536:
524:
521:
496:
493:
411:inferior fovea
407:superior fovea
381:rhomboid fossa
346:cisterna magna
334:choroid plexus
332:(covered with
291:foramen magnum
242:
239:
170:
169:
160:
154:
153:
148:
142:
141:
136:
130:
129:
124:
118:
117:
112:
105:
104:
99:
93:
92:
87:
81:
80:
75:
69:
68:
64:
63:
59:
58:
55:
47:
46:
43:
35:
34:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1210:
1199:
1196:
1194:
1191:
1190:
1188:
1173:
1170:
1169:
1167:
1163:
1157:
1154:
1152:
1149:
1147:
1144:
1142:
1139:
1138:
1136:
1134:
1130:
1120:
1117:
1115:
1112:
1111:
1109:
1105:
1099:
1095:
1092:
1090:
1087:
1086:
1084:
1080:
1074:
1071:
1069:
1066:
1062:
1059:
1057:
1056:Area postrema
1054:
1052:
1049:
1047:
1046:Vagal trigone
1044:
1043:
1041:
1037:
1034:
1032:
1029:
1028:
1026:
1025:
1023:
1019:
1013:
1010:
1008:
1005:
1003:
1000:
996:
993:
992:
991:
988:
987:
985:
983:
979:
976:
974:
970:
964:
961:
959:
956:
954:
951:
949:
946:
942:
941:Pineal recess
939:
937:
934:
932:
929:
927:
924:
923:
921:
920:
918:
916:
912:
906:
903:
899:
896:
895:
893:
889:
886:
884:
881:
879:
878:Lamina affixa
876:
875:
873:
872:
870:
868:
864:
860:
856:
849:
844:
842:
837:
835:
830:
829:
826:
818:
814:
810:
806:
804:
800:
797:
794:
791:
790:
786:
777:
775:0-8151-1458-3
771:
767:
760:
757:
752:
746:
742:
738:
734:
733:
725:
722:
717:
713:
708:
703:
699:
695:
691:
687:
683:
679:
675:
668:
665:
654:on 2017-03-01
653:
649:
642:
639:
632:
623:
618:
611:
606:
599:
594:
587:
582:
575:
570:
566:
559:
554:
547:
542:
537:
535:
533:
530:
522:
520:
518:
517:hydrocephalus
514:
510:
506:
502:
501:central canal
494:
492:
490:
486:
485:vagal trigone
482:
478:
474:
470:
466:
462:
458:
454:
449:
447:
443:
439:
435:
431:
430:noradrenaline
427:
423:
419:
414:
412:
408:
404:
400:
399:
394:
390:
386:
385:median sulcus
382:
378:
373:
371:
367:
363:
359:
358:
353:
352:
347:
343:
339:
335:
331:
327:
323:
319:
315:
311:
306:
304:
300:
296:
292:
288:
284:
283:central canal
280:
276:
272:
268:
264:
256:
252:
247:
240:
238:
236:
232:
228:
224:
220:
216:
211:
209:
205:
201:
197:
193:
189:
185:
181:
177:
165:
159:
155:
152:
149:
147:
143:
140:
137:
135:
131:
128:
125:
123:
119:
116:
113:
110:
106:
103:
100:
98:
94:
91:
88:
86:
82:
79:
76:
74:
70:
65:
60:
53:
48:
41:
36:
31:
19:
1011:
972:
926:Optic recess
817:the original
812:
765:
759:
731:
724:
681:
677:
667:
656:. Retrieved
652:the original
641:
529:intracranial
526:
498:
488:
472:
456:
450:
438:facial nerve
421:
415:
410:
406:
402:
396:
384:
376:
374:
365:
361:
355:
349:
341:
321:
309:
307:
274:
270:
266:
260:
254:
250:
229:through two
212:
199:
175:
173:
127:A14.1.05.701
115:birnlex_1256
77:
898:Calcar avis
859:human brain
532:ependymomal
495:Development
303:spinal cord
257:to the left
227:spinal cord
180:human brain
67:Identifiers
1187:Categories
658:2015-07-28
633:References
563:Scheme of
413:caudally.
330:Cerebellum
241:Boundaries
97:NeuroNames
1193:Brainstem
1082:Apertures
1012:Fastigium
922:Recesses
739:pp.
698:1469-7580
366:fastigium
202:) to the
18:Fastigium
995:Frenulum
716:37170923
707:10485575
534:tumour.
434:sky blue
109:NeuroLex
1165:Related
857:of the
801:at the
735:. USA:
299:medulla
293:of the
273:at its
265:at its
225:of the
210:(CSF).
90:D020546
62:Details
1042:Lower
1027:Upper
1007:Taenia
772:
747:
714:
704:
696:
467:. The
432:has a
190:, the
1107:Other
1021:Floor
874:Body
489:floor
473:floor
457:floor
422:floor
377:floor
295:skull
275:lower
271:floor
267:upper
251:floor
162:[
151:78469
73:Latin
1061:Obex
982:Roof
770:ISBN
745:ISBN
712:PMID
694:ISSN
451:The
418:pons
416:The
375:The
362:roof
342:roof
338:tela
322:roof
310:roof
301:and
287:obex
263:roof
255:roof
215:pons
204:obex
174:The
139:5966
122:TA98
85:MeSH
1096:to
741:126
702:PMC
686:doi
682:243
146:FMA
134:TA2
102:621
1189::
811:.
743:.
710:.
700:.
692:.
680:.
676:.
519:.
305:.
237:.
111:ID
847:e
840:t
833:v
778:.
753:.
718:.
688::
661:.
567:.
198:(
166:]
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.