301:
is ideal for muscles and joints to maintain neutral positions. Additionally, to prevent hand, wrist, and finger injuries, understanding when to use pinch grips (best for fine motor control and precise movements with low force) and power grips (best for high-force movements done repeatedly) is important for employees and general tasks outside the workplace. The choice of tools should match that of the proper grip and be conducive to neutral postures, which is important for employers to consider when purchasing equipment. In order to reduce injuries to the low back and spine, it is recommended to reduce weight and frequency of lifting cycles as well as decreasing the distance between the body and the load to reduce the
326:
80:
200:. Postures which are less natural, such as twisting of or tension in the upper body, are typically contributors to the development of MSDs due to the unnatural biomechanical load of these postures. There is evidence that posture contributes to MSDs of the neck, shoulder, and back. Repeated motion is another risk factor for MSDs of occupational origin because workers can perform the same movements repeatedly over long periods of time (e.g. typing leading to
204:. Lifting heavy objects is another source of back injury which is common in nurses due to patient lifting. This can lead to both short-term pain and long-term injury leading to herniated discs/slipped discs), which can wear on the joints and muscles involved in the motion in question. Workers doing repetitive motions at a high pace of work with little recovery time and workers with little to no control over the timing of motions (e.g. workers on
49:
220:, for example) and extreme hot or cold temperatures can affect a worker's ability to judge force and strength, which can lead to development of MSDs. Vibration exposure is also associated with hand-arm vibration syndrome, which has symptoms of lack of blood circulation to the fingers, nerve compression, tingling, and/or numbness. Recent epidemiological studies identify
158:
static position. Even activities that do not require a lot of force can result in muscle damage if the activity is repeated often enough at short intervals. MSD risk factors involve doing tasks with heavy force, repetition, or maintaining a nonneutral posture. Of particular concern is the combination of heavy load with repetition. Although
445:, and recreation industries all have incidence rates above 35 per 10,000 full-time workers. For example, a national survey of U.S. nurses found that 38% reported an MSD in the prior year, mainly lower back injury. The neck and back are the most common sites of MSDs in workers, followed by the upper limbs and lower limbs. The
246:
body with various areas labeled and asks the individual to indicate in which areas they have experienced pain, and in which areas has the pain interfered with normal activity. Recent machine learning algorithms can diagnose musculoskeletal disorder from gait patterns captured from 3D motion capture systems.
400:
MSDs are an increasing healthcare issue globally, being the second leading cause of disability. For example, in the U.S. there were more than 16 million strains and sprains treated in 2004, and the total cost for treating MSDs is estimated to be more than $ 125 billion per year. In 2006 approximately
300:
One focus of ergonomic principles is maintaining neutral postures, which are postures in which muscles are at their normal length and able to generate the most force, while reducing stress and possible injury to muscles, tendons, nerves, and bones- therefore, in the workplace or in everyday life, it
296:
not only includes matching the physical ability of the worker with the correct job, but it deals with designing equipment that is correct for the task. Limiting heavy lifting, training, and reporting early signs of injury are examples that can prevent MSD. Employers can provide support for employees
179:
There is a growing consensus that psychosocial factors are another cause of some MSDs. Some theories for this causal relationship found by many researchers include increased muscle tension, increased blood and fluid pressure, reduction of growth functions, pain sensitivity reduction, pupil dilation,
274:
Groups who are at particular risk can be identified, and modifications to the physical and psychosocial environment can be made. Approaches to prevention in workplace settings include matching the person's physical abilities to the tasks, increasing the person's capabilities, changing how tasks are
124:
caused by acute traumatic events like a car accident or fall are not considered musculoskeletal disorders. MSDs can affect many different parts of the body including upper and lower back, neck, shoulders and extremities (arms, legs, feet, and hands). Examples of MSDs include carpal tunnel syndrome,
284:
over, or moving necessary tools within shorter reach of the worker's station. Employers may also utilize administrative controls like reducing number of hours in a certain position, limiting overtime, or including more breaks during shifts in order to reduce amount of time at risk for each worker.
424:
and early retirement in the U.S. The incidence rate for MSDs among the working population in 2014 was 31.9 newly diagnosed MSDs per 10,000 full-time workers. In 2014, the median days away from work due to MSDs was 13, and there were 10.4 cases per 10,000 full-time workers in which an MSD caused a
245:
Doctors look for specific criteria to diagnose each different musculoskeletal disorder, based on location, type, and intensity of pain, as well as what kind of restricted or painful movement a patient is experiencing. A popular measure of MSDs is the Nordic
Questionnaire that has a picture of the
411:
According to recent studies, a significant proportion of older adults experience musculoskeletal pain. This pain can be localized (e.g., back pain, knee pain) or widespread (e.g., fibromyalgia). The prevalence tends to increase with age, affecting a substantial portion of the elderly population.
283:
to prevent injury happening on the job. Implementation of engineering controls is the process of designing or redesigning the workplace to account for strengths, weaknesses, and needs of the working population- examples would be workstation layout changes to be more efficient or reducing bending
157:
load which is the force that must be applied to do tasks, the duration of the force applied, and the frequency with which tasks are performed. Activities involving heavy loads can result in acute injury, but most occupation-related MSDs are from motions that are repetitive, or from maintaining a
1340:
NIOSH . Observation-based posture assessment: review of current practice and recommendations for improvement. By Lowe BD, Weir PL, Andrews DM. Cincinnati, OH: U.S. Department of Health and Human
Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Institute for Occupational Safety and
305:
force on the back for workers and individuals doing repeated lifting to avoid fatigue failure of the spine. The shape of objects being lifted should also be considered, especially by employers, because objects which are easier to grip, lift, and access present less stress on the spine and back
120:, and structures that support limbs, neck and back. MSDs can arise from a sudden exertion (e.g., lifting a heavy object), or they can arise from making the same motions repeatedly (repetitive strain), or from repeated exposure to force, vibration, or awkward posture. Injuries and pain in the
425:
worker to be away from work for 31 or more days. MSDs are widespread in many occupations, including those with heavy biomechanical load like construction and factory work, and those with lighter loads like office work. The transportation and warehousing industries have the highest
236:
Assessment of MSDs is based on self-reports of symptoms and pain as well as physical examination by a doctor. Doctors rely on medical history, recreational and occupational hazards, intensity of pain, a physical exam to locate the source of the pain, and sometimes lab tests,
1687:
Haukkal, Eija; Leino-Arjasl, Päivi; Ojajärvil, Anneli; Takalal, Esa-Pekka; Viikari-Juntural, Eira; Riihimäkil, Hilkka (2011). "Mental stress and psychosocial factors at work in relation to multiple-site musculoskeletal pain: A longitudinal study of kitchen workers".
1731:
Hauke, Angelika; Flintrop, Julia; Brun, Emmanuelle; Rugulies, Reiner (July 2011). "The impact of work-related psychosocial stressors on the onset of musculoskeletal disorders in specific body regions: A review and meta-analysis of 54 longitudinal studies".
170:
People vary in their tendency to get MSDs. Gender is a factor, with women having a higher incidence of MSDs than men. Obesity is also a factor, with overweight individuals having a higher risk of some MSDs, specifically of the lower back.
719:
Gatchel, R. J., & Kishino, N. (2011). Pain, musculoskeletal injuries, and return to work. In J. C. Quick & L. E. Tetrick (Eds.), Handbook of occupational health psychology (2nd ed.). Washington, DC: American
Psychological
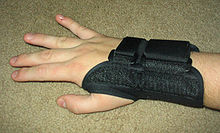
1041:
Hauke A.; Flintrop J.; Brun E.; Rugulies R. (2011). "The impact of work-related psychosocial stressors on the onset of musculoskeletal disorders in specific body regions: A review and meta-analysis of 54 longitudinal studies".
505:
1660:
Singh A, Akkala S, Nayak M, Kotlo A, Poondla N, Raza S, Stankovich J, Antony B. Impact of Pain on
Activities of Daily Living in Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging (KLoSA).
1813:
Shafer, Scott W; Koreerat, Nicholas R; Gordon, Lindsay B; Santillo, Douglas R; Moore, Josef H; Greathouse, David G (1 December 2013). "Median and Ulnar
Neuropathies in U.S. Army Medical Command Band Members".
180:
body remaining at heightened state of sensitivity. Although there is no consensus at this time, some of the workplace stressors found to be associated with MSDs in the workplace include high job demands, low
1005:
Sprigg C. A.; Stride C. B.; Wall T. D.; Holman D. J.; Smith P. R. (2007). "Work characteristics, musculoskeletal disorders, and the mediating role of psychological strain: A study of call center employees".
401:
14.3% of the
Canadian population was living with a disability, with nearly half due to MSDs. Neck pain is one of the most common complaints, with about one fifth of adults worldwide reporting pain annually.
1155:
Martin, P. J., Harvey, J. T., Culvenor, J. F., & Payne, W. R. (2009). Effect of a nurse back injury prevention intervention on the rate of injury compensation claims. Journal of Safety
Research, 40(1),
208:) are also prone to MSDs due to the motion of their work. Force needed to perform actions on the job can also be associated with higher MSD risk in workers, because movements which require more force can
1968:
262:
have been determined, there are several intervention methods which could be used to prevent the development of MSDs. The target of MSD prevention efforts is often the workplace in order to identify
685:
Kuorinka, I.; Jonsson, B.; Kilbom, A.; Vinterberg, H.; Biering-Sørensen, F.; Andersson, G.; Jørgensen, K. (1987). "Standardised Nordic questionnaires for the analysis of musculoskeletal symptoms".
420:
Most workplace MSD episodes involve multiple parts of the body. MSDs are the most frequent health complaint by
European, United States and Asian Pacific workers. and the third leading reason for
2082:
297:
in order to prevent MSD in the workplace by involving the employees in planning, assessing, and developing standards of procedures that will support proper ergonomics and prevent injury.
1938:
310:
1961:
778:"The interaction of force and repetition on musculoskeletal and neural tissue responses and sensorimotor behavior in a rat model of work-related musculoskeletal disorders"
827:
Roffey DM, Wai EK, Bishop P, Kwon BK, Dagenais S (January 2010). "Causal assessment of awkward occupational postures and low back pain: results of a systematic review".
1142:
939:
1354:
Côté, Julie N.; Ngomo, Suzy; Stock, Susan; Messing, Karen; Vézina, Nicole; Antle, David; Delisle, Alain; Bellemare, Marie; Laberge, Marie; St-Vincent, Marie (2013).
1954:
1932:
1912:
1902:
2170:
550:
Kumaraveloo, K Sakthiaseelan; Lunner
Kolstrup, Christina (3 July 2018). "Agriculture and musculoskeletal disorders in low- and middle-income countries".
325:
196:
Because workers maintain the same posture over long work days and often several years, even natural postures like standing can lead to MSDs like low
184:, and overall job strain. Researchers have consistently identified causal relationships between job dissatisfaction and MSDs. For example, improving
2269:
1601:
McLean SM, May S, Klaber-Moffett J, Sharp DM, Gardiner E (July 2010). "Risk factors for the onset of non-specific neck pain: a systematic review".
730:
Barriera-Viruet H.; Sobeih T. M.; Daraiseh N.; Salem S. (2006). "Questionnaires vs observational and direct measurements: A systematic review".
460:) were the center of a study which concluded that musicians have a high rate of MSDs and that it exceeds percentages in the general population.
188:
can reduce 17-69 per cent of work-related back disorders and improving job control can reduce 37-84 per cent of work-related wrist disorders.
449:
reports that 31.8 new cases of MSDs per 10,000 full-time workers per year are due to overexertion, bodily reaction, or repetitive motions.
2572:
453:
1192:"CDC - NIOSH Publications and Products - Criteria for a Recommended Standard: Occupational Exposure to Hand-Arm Vibration (89-106)"
2098:
254:
Prevention of MSDs relies upon identification of risk factors, either by self-report, observation on the job, or measurement of
255:
408:, 8.9 million working days were lost due to work-related musculoskeletal disorders and 480,000 workers have these disorders.
2194:
1166:
2165:
145:
MSDs can arise from the interaction of physical factors with ergonomic, psychological, social, and occupational factors.
2482:
480:
475:
293:
121:
97:
485:
2131:
776:
Barbe, Mary F; Gallagher, Sean; Massicotte, Vicky S; Tytell, Michael; Popoff, Steven N; Barr-Gillespie, Ann E (2013).
405:
1505:"Examining the Interaction of Force and Repetition on Musculoskeletal Disorder Risk: A Systematic Literature Review"
1276:
658:
2477:
1227:"Work-related musculoskeletal disorders and associated risk factors among urban metropolitan hairdressers in India"
446:
242:
162:
is often blamed for lower back pain, a systematic review of the literature failed to find a consistent connection.
2262:
2523:
1465:
Moore, S.M., Torma-Krajewski, J., & Steiner, L.J. (2011). Practical
Demonstrations of Ergonomic Principles.
1302:"Automatic Musculoskeletal and Neurological Disorder Diagnosis with Relative Joint Displacement from Human Gait"
2436:
2121:
1868:
1803:
American Nurses Association. (2001). Nursingworld organizational health & safety survey. Silver Spring, MD.
500:
426:
263:
953:
Courvoisier DS, Genevay S, Cedraschi C, Bessire N, Griesser-Delacretaz AC, Monnin D, Perneger TV (July 2011).
2255:
280:
317:
for several industries, including construction, mining, agriculture, healthcare, and retail, among others.
2454:
2431:
2400:
2189:
2116:
470:
212:
muscles quicker which can lead to injury and/or pain. Additionally, exposure to vibration (experienced by
201:
56:
31:
2377:
429:
rate of musculoskeletal disorders, with an incidence rate of 89.9 cases per 10,000 full-time workers.
2518:
2464:
2177:
1077:
Punnett (2004). "Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders: The Epidemiologic Evidence and the Debate".
276:
224:
as a significant risk factor in occurrence of MSDs among workers in gender-related occupations, e.g.
659:"CDC - Workplace Health - Implementation - Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders (WMSD) Prevention"
79:
2577:
2546:
2487:
2418:
2351:
2229:
2182:
2111:
2069:
1406:
915:
217:
1554:"A population-based profile of adult Canadians living with participation and activity limitations"
609:"CDC - NIOSH Publications and Products - Musculoskeletal Disorders and Workplace Factors (97-141)"
2333:
2144:
2106:
1749:
1713:
1626:
1323:
1059:
982:
747:
575:
2224:
2405:
2323:
2292:
2077:
1831:
1705:
1618:
1583:
1534:
1258:
1136:
1094:
1023:
974:
933:
893:
844:
809:
702:
567:
68:
60:
2449:
2054:
2046:
1823:
1741:
1697:
1610:
1573:
1565:
1524:
1516:
1367:
1313:
1248:
1238:
1199:
1086:
1051:
1015:
966:
883:
875:
836:
799:
789:
739:
694:
624:
616:
559:
259:
209:
185:
527:"CDC - NIOSH Program Portfolio : Musculoskeletal Disorders : Program Description"
2364:
2338:
2027:
1480:"CDC - Ergonomics and Musculoskeletal Disorders - NIOSH Workplace Safety and Health Topic"
862:
Kerr MS, Frank JW, Shannon HS, Norman RW, Wells RP, Neumann WP, Bombardier C (July 2001).
457:
2149:
1674:
954:
17:
2459:
2219:
2001:
1578:
1553:
1529:
1504:
1253:
1226:
888:
863:
804:
777:
181:
1118:
2566:
2551:
2006:
1996:
1753:
1717:
1063:
986:
698:
490:
434:
205:
126:
1644:
1630:
1327:
751:
579:
48:
2533:
2528:
2500:
2328:
2305:
2214:
2059:
2037:
1928:
1300:
Worasak, Rueangsirarak; Jingtian, Zhang; Nauman, Aslam; Hubert P. H., Shum (2018).
629:
225:
213:
159:
154:
73:
1645:"Work related musculoskeletal disorder statistics (WRMSDs) in Great Britain, 2020"
1433:
1119:"Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders (WMSDs) - Risk Factors : OSH Answers"
1090:
955:"Job strain, work characteristics and back pain: a study in a university hospital"
563:
1873:
1745:
1701:
1055:
970:
840:
2387:
2382:
1977:
1908:
1019:
438:
430:
238:
1479:
1318:
1301:
314:
2234:
2022:
743:
421:
130:
1614:
1520:
794:
2287:
1991:
1879:
1827:
1670:
1666:
1243:
197:
134:
1929:
Hazards and risks associated with manual handling of loads in the workplace
1835:
1709:
1622:
1587:
1538:
1262:
1204:
1117:
Safety, Government of Canada, Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and.
1098:
1027:
978:
914:
Safety, Government of Canada, Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and.
897:
879:
848:
813:
706:
620:
571:
1942:
1552:
Goodridge, D.; Lawson, J.; Marciniuk, D.; Rennie, D. (20 September 2011).
608:
526:
1277:"Musculoskeletal Pain: Tendonitis, Myalgia & More | Cleveland Clinic"
1191:
306:
muscles than objects which are awkwardly shaped and difficult to access.
105:
1860:
1569:
506:
Ischemia-repurfusion injuries of the appendicular musculoskeletal system
2247:
864:"Biomechanical and psychosocial risk factors for low back pain at work"
1918:
1778:
1509:
Human Factors: The Journal of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society
1372:
1355:
2310:
1946:
916:"Musculoskeletal Disorders - Psychosocial Factors : OSH Answers"
495:
442:
404:
According to the Labour Force Survey 2019/20 carried out by the UK's
302:
221:
117:
109:
1898:
1387:
Rostykus W.; Ip W.; Mallon J. (2013). "Musculoskeletal disorders".
1306:
IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering
324:
113:
101:
59:
is a common musculoskeletal disorder, and is often treated with a
329:
Deaths from musculoskeletal diseases per million persons in 2012
2088:
2251:
1950:
1884:
2139:
1779:"Occupational Injuries/Illnesses and Fatal Injuries Profiles"
275:
performed, or changing the tasks. Employers can also utilize
311:
National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
1356:"Quebec Research on Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders"
266:
rates of both disorders and exposure to unsafe conditions.
137:, tension neck syndrome, and hand-arm vibration syndrome.
1922:
1407:"Hospital eTool: Healthcare Wide Hazards - Ergonomics"
1939:
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
1850:
1503:
Gallagher, Sean; Heberger, John R. (February 2013).
2207:
2158:
2130:
2097:
2068:
2045:
2036:
2015:
1984:
1909:
Good Practices to prevent Musculoskeletal disorders
1854:
67:
41:
1167:"Herniated Disc and Social Security Disability"
1341:Health, DHHS (NIOSH) Publication No. 2014–131.
2263:
1962:
1933:European Agency for Safety and Health at Work
1913:European Agency for Safety and Health at Work
1903:European Agency for Safety and Health at Work
657:Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and.
8:
2171:Systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis
1899:Musculoskeletal disorders Single Entry Point
1603:Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health
1141:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
938:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
680:
678:
1428:
1426:
1079:Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology
2270:
2256:
2248:
2042:
1969:
1955:
1947:
1851:
78:
47:
38:
1785:. United States Department of Labor. 2014
1577:
1528:
1371:
1317:
1252:
1242:
1203:
1000:
998:
996:
909:
907:
887:
803:
793:
628:
732:Theoretical Issues in Ergonomics Science
27:Pain in the muscular or skeletal systems
1434:"Safety and Health Topics | Ergonomics"
1349:
1347:
771:
769:
767:
765:
763:
761:
518:
1816:Medical Problems of Performing Artists
1134:
931:
1773:
1771:
1769:
1767:
1765:
1763:
1461:
1459:
1457:
1455:
1453:
1112:
1110:
1108:
7:
1558:Canadian Medical Association Journal
1225:Mishra SD, Sarkar K (January 2021).
652:
650:
648:
646:
603:
601:
599:
597:
595:
593:
591:
589:
1919:Musculoskeletal disorders homepage
454:United States Army Medical Command
25:
1469:. NIOSH. Retrieved 24 March 2016.
868:American Journal of Public Health
406:Health and Safety Executive (HSE)
1941:Musculoskeletal Health Program
258:which could lead to MSDs. Once
1231:Journal of Occupational Health
292:Encouraging the use of proper
96:) are injuries or pain in the
1:
2166:Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
1467:Report of Investigations 9684
1091:10.1016/j.jelekin.2003.09.015
1008:Journal of Applied Psychology
782:BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders
564:10.1080/1059924X.2018.1458671
2483:Obstetric labor complication
1746:10.1080/02678373.2011.614069
1702:10.1016/j.ejpain.2010.09.005
1056:10.1080/02678373.2011.614069
971:10.1016/j.ejpain.2010.11.012
841:10.1016/j.spinee.2009.09.003
699:10.1016/0003-6870(87)90010-x
481:Human musculoskeletal system
476:Human factors and ergonomics
98:human musculoskeletal system
2195:Adult-onset Still's disease
2132:Connective tissue disorders
1923:Health and Safety Executive
1020:10.1037/0021-9010.92.5.1456
2594:
2478:Complications of pregnancy
1783:Bureau of Labor Statistics
1319:10.1109/TNSRE.2018.2880871
447:Bureau of Labor Statistics
29:
2573:Musculoskeletal disorders
2542:
2524:Connective tissue disease
2509:
2496:
2473:
2445:
2427:
2414:
2396:
2373:
2360:
2347:
2319:
2301:
2283:
1667:10.3390/geriatrics9030065
744:10.1080/14639220500090661
90:Musculoskeletal disorders
55:
46:
42:Musculoskeletal disorders
18:Musculoskeletal disorders
2514:Musculoskeletal disorder
2437:Gastrointestinal disease
2122:Enteropathic arthropathy
1690:European Journal of Pain
1615:10.1136/jech.2009.090720
1521:10.1177/0018720812449648
959:European Journal of Pain
795:10.1186/1471-2474-14-303
501:Repetitive strain injury
452:In 2013, members of the
313:has published ergonomic
1828:10.21091/mppa.2013.4038
1360:Relations Industrielles
1244:10.1002/1348-9585.12200
630:2027/coo.31924078629387
552:Journal of Agromedicine
486:Ehlers–Danlos syndromes
281:administrative controls
2455:Female genital disease
2432:Maxillofacial disorder
2401:Cardiovascular disease
2190:Palindromic rheumatism
2117:Ankylosing spondylitis
2060:Tuberculosis arthritis
1281:my.clevelandclinic.org
1205:10.26616/NIOSHPUB89106
1171:CitizensDisability.com
880:10.2105/AJPH.91.7.1069
621:10.26616/NIOSHPUB97141
392:
202:carpal tunnel syndrome
166:Individual differences
122:musculoskeletal system
57:Carpal tunnel syndrome
32:Musculoskeletal injury
2378:Neurological disorder
1665:. 2024;9(3):65. doi:
328:
2519:Soft tissue disorder
2465:Male genital disease
2278:Major Disease groups
2178:Rheumatoid arthritis
277:engineering controls
218:construction workers
2547:Congenital disorder
2488:Postpartum disorder
2419:Respiratory disease
2352:Hematologic disease
2112:Psoriatic arthritis
1570:10.1503/cmaj.110153
1564:(13): E1017–E1024.
1389:Professional Safety
441:, wholesale trade,
153:MSDs are caused by
2334:Metabolic disorder
2145:systemic sclerosis
2107:Reactive arthritis
1978:Diseases of joints
1663:Geriatrics (Basel)
1650:. 19 October 2021.
687:Applied Ergonomics
396:General population
393:
270:Workplace controls
2560:
2559:
2406:Lymphatic disease
2324:Endocrine disease
2293:Parasitic disease
2245:
2244:
2203:
2202:
2078:Chondrocalcinosis
1894:
1893:
1734:Work & Stress
1373:10.7202/1023009ar
1312:(12): 2387–2396.
1044:Work & Stress
829:The Spine Journal
87:
86:
36:Medical condition
16:(Redirected from
2585:
2450:Urologic disease
2272:
2265:
2258:
2249:
2230:Bouchard's nodes
2183:Felty's syndrome
2055:Septic arthritis
2043:
1971:
1964:
1957:
1948:
1852:
1840:
1839:
1810:
1804:
1801:
1795:
1794:
1792:
1790:
1775:
1758:
1757:
1728:
1722:
1721:
1684:
1678:
1658:
1652:
1651:
1649:
1641:
1635:
1634:
1598:
1592:
1591:
1581:
1549:
1543:
1542:
1532:
1500:
1494:
1493:
1491:
1490:
1476:
1470:
1463:
1448:
1447:
1445:
1444:
1430:
1421:
1420:
1418:
1417:
1403:
1397:
1396:
1384:
1378:
1377:
1375:
1351:
1342:
1338:
1332:
1331:
1321:
1297:
1291:
1290:
1288:
1287:
1273:
1267:
1266:
1256:
1246:
1222:
1216:
1215:
1213:
1212:
1207:
1188:
1182:
1181:
1179:
1177:
1163:
1157:
1153:
1147:
1146:
1140:
1132:
1130:
1129:
1114:
1103:
1102:
1074:
1068:
1067:
1038:
1032:
1031:
1014:(5): 1456–1466.
1002:
991:
990:
950:
944:
943:
937:
929:
927:
926:
911:
902:
901:
891:
859:
853:
852:
824:
818:
817:
807:
797:
773:
756:
755:
727:
721:
717:
711:
710:
682:
673:
672:
670:
669:
654:
641:
640:
638:
637:
632:
605:
584:
583:
547:
541:
540:
538:
537:
523:
388:
382:
376:
370:
364:
358:
352:
346:
340:
334:
186:job satisfaction
100:, including the
83:
82:
51:
39:
21:
2593:
2592:
2588:
2587:
2586:
2584:
2583:
2582:
2563:
2562:
2561:
2556:
2538:
2505:
2492:
2469:
2441:
2423:
2410:
2392:
2369:
2365:Mental disorder
2356:
2343:
2339:Immune disorder
2315:
2297:
2279:
2276:
2246:
2241:
2225:Heberden's node
2208:Noninflammatory
2199:
2154:
2126:
2093:
2064:
2032:
2028:Joint stiffness
2011:
1980:
1975:
1895:
1890:
1889:
1863:
1849:
1844:
1843:
1812:
1811:
1807:
1802:
1798:
1788:
1786:
1777:
1776:
1761:
1730:
1729:
1725:
1686:
1685:
1681:
1659:
1655:
1647:
1643:
1642:
1638:
1600:
1599:
1595:
1551:
1550:
1546:
1502:
1501:
1497:
1488:
1486:
1478:
1477:
1473:
1464:
1451:
1442:
1440:
1432:
1431:
1424:
1415:
1413:
1405:
1404:
1400:
1386:
1385:
1381:
1353:
1352:
1345:
1339:
1335:
1299:
1298:
1294:
1285:
1283:
1275:
1274:
1270:
1224:
1223:
1219:
1210:
1208:
1190:
1189:
1185:
1175:
1173:
1165:
1164:
1160:
1154:
1150:
1133:
1127:
1125:
1116:
1115:
1106:
1076:
1075:
1071:
1040:
1039:
1035:
1004:
1003:
994:
952:
951:
947:
930:
924:
922:
913:
912:
905:
861:
860:
856:
826:
825:
821:
775:
774:
759:
729:
728:
724:
718:
714:
684:
683:
676:
667:
665:
656:
655:
644:
635:
633:
607:
606:
587:
549:
548:
544:
535:
533:
525:
524:
520:
515:
510:
466:
458:323rd Army Band
418:
398:
391:
390:
386:
384:
380:
378:
374:
372:
368:
366:
362:
360:
356:
354:
350:
348:
344:
342:
338:
336:
332:
323:
315:recommendations
290:
272:
252:
234:
194:
177:
168:
151:
143:
77:
37:
34:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2591:
2589:
2581:
2580:
2575:
2565:
2564:
2558:
2557:
2555:
2554:
2549:
2543:
2540:
2539:
2537:
2536:
2531:
2526:
2521:
2516:
2510:
2507:
2506:
2504:
2503:
2497:
2494:
2493:
2491:
2490:
2485:
2480:
2474:
2471:
2470:
2468:
2467:
2462:
2460:Breast disease
2457:
2452:
2446:
2443:
2442:
2440:
2439:
2434:
2428:
2425:
2424:
2422:
2421:
2415:
2412:
2411:
2409:
2408:
2403:
2397:
2394:
2393:
2391:
2390:
2385:
2380:
2374:
2371:
2370:
2368:
2367:
2361:
2358:
2357:
2355:
2354:
2348:
2345:
2344:
2342:
2341:
2336:
2331:
2326:
2320:
2317:
2316:
2314:
2313:
2308:
2302:
2299:
2298:
2296:
2295:
2290:
2284:
2281:
2280:
2277:
2275:
2274:
2267:
2260:
2252:
2243:
2242:
2240:
2239:
2238:
2237:
2232:
2227:
2220:Osteoarthritis
2217:
2211:
2209:
2205:
2204:
2201:
2200:
2198:
2197:
2192:
2187:
2186:
2185:
2175:
2174:
2173:
2162:
2160:
2156:
2155:
2153:
2152:
2147:
2142:
2136:
2134:
2128:
2127:
2125:
2124:
2119:
2114:
2109:
2103:
2101:
2095:
2094:
2092:
2091:
2086:
2080:
2074:
2072:
2066:
2065:
2063:
2062:
2057:
2051:
2049:
2040:
2034:
2033:
2031:
2030:
2025:
2019:
2017:
2013:
2012:
2010:
2009:
2004:
2002:Oligoarthritis
1999:
1994:
1988:
1986:
1982:
1981:
1976:
1974:
1973:
1966:
1959:
1951:
1945:
1944:
1936:
1926:
1916:
1906:
1892:
1891:
1888:
1887:
1876:
1864:
1859:
1858:
1856:
1855:Classification
1848:
1847:External links
1845:
1842:
1841:
1822:(4): 188–194.
1805:
1796:
1759:
1740:(3): 243–256.
1723:
1679:
1653:
1636:
1593:
1544:
1515:(1): 108–124.
1495:
1471:
1449:
1422:
1398:
1379:
1343:
1333:
1292:
1268:
1217:
1183:
1158:
1148:
1104:
1069:
1050:(3): 243–256.
1033:
992:
945:
903:
874:(7): 1069–75.
854:
819:
757:
738:(3): 261–284.
722:
712:
674:
642:
585:
558:(3): 227–248.
542:
517:
516:
514:
511:
509:
508:
503:
498:
493:
488:
483:
478:
473:
467:
465:
462:
456:Band (now the
417:
414:
397:
394:
385:
379:
373:
367:
361:
355:
349:
343:
337:
331:
330:
322:
319:
289:
286:
271:
268:
251:
248:
233:
230:
206:assembly lines
193:
190:
182:social support
176:
173:
167:
164:
150:
147:
142:
139:
85:
84:
71:
65:
64:
53:
52:
44:
43:
35:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2590:
2579:
2576:
2574:
2571:
2570:
2568:
2553:
2552:Fetal disease
2550:
2548:
2545:
2544:
2541:
2535:
2532:
2530:
2527:
2525:
2522:
2520:
2517:
2515:
2512:
2511:
2508:
2502:
2499:
2498:
2495:
2489:
2486:
2484:
2481:
2479:
2476:
2475:
2472:
2466:
2463:
2461:
2458:
2456:
2453:
2451:
2448:
2447:
2444:
2438:
2435:
2433:
2430:
2429:
2426:
2420:
2417:
2416:
2413:
2407:
2404:
2402:
2399:
2398:
2395:
2389:
2386:
2384:
2381:
2379:
2376:
2375:
2372:
2366:
2363:
2362:
2359:
2353:
2350:
2349:
2346:
2340:
2337:
2335:
2332:
2330:
2327:
2325:
2322:
2321:
2318:
2312:
2309:
2307:
2304:
2303:
2300:
2294:
2291:
2289:
2286:
2285:
2282:
2273:
2268:
2266:
2261:
2259:
2254:
2253:
2250:
2236:
2233:
2231:
2228:
2226:
2223:
2222:
2221:
2218:
2216:
2213:
2212:
2210:
2206:
2196:
2193:
2191:
2188:
2184:
2181:
2180:
2179:
2176:
2172:
2169:
2168:
2167:
2164:
2163:
2161:
2157:
2151:
2148:
2146:
2143:
2141:
2138:
2137:
2135:
2133:
2129:
2123:
2120:
2118:
2115:
2113:
2110:
2108:
2105:
2104:
2102:
2100:
2096:
2090:
2087:
2084:
2081:
2079:
2076:
2075:
2073:
2071:
2067:
2061:
2058:
2056:
2053:
2052:
2050:
2048:
2044:
2041:
2039:
2035:
2029:
2026:
2024:
2021:
2020:
2018:
2014:
2008:
2007:Polyarthritis
2005:
2003:
2000:
1998:
1997:Monoarthritis
1995:
1993:
1990:
1989:
1987:
1983:
1979:
1972:
1967:
1965:
1960:
1958:
1953:
1952:
1949:
1943:
1940:
1937:
1934:
1930:
1927:
1924:
1920:
1917:
1914:
1910:
1907:
1904:
1900:
1897:
1896:
1886:
1882:
1881:
1877:
1875:
1871:
1870:
1866:
1865:
1862:
1857:
1853:
1846:
1837:
1833:
1829:
1825:
1821:
1817:
1809:
1806:
1800:
1797:
1784:
1780:
1774:
1772:
1770:
1768:
1766:
1764:
1760:
1755:
1751:
1747:
1743:
1739:
1735:
1727:
1724:
1719:
1715:
1711:
1707:
1703:
1699:
1695:
1691:
1683:
1680:
1676:
1672:
1668:
1664:
1657:
1654:
1646:
1640:
1637:
1632:
1628:
1624:
1620:
1616:
1612:
1609:(7): 565–72.
1608:
1604:
1597:
1594:
1589:
1585:
1580:
1575:
1571:
1567:
1563:
1559:
1555:
1548:
1545:
1540:
1536:
1531:
1526:
1522:
1518:
1514:
1510:
1506:
1499:
1496:
1485:
1481:
1475:
1472:
1468:
1462:
1460:
1458:
1456:
1454:
1450:
1439:
1435:
1429:
1427:
1423:
1412:
1408:
1402:
1399:
1394:
1390:
1383:
1380:
1374:
1369:
1365:
1361:
1357:
1350:
1348:
1344:
1337:
1334:
1329:
1325:
1320:
1315:
1311:
1307:
1303:
1296:
1293:
1282:
1278:
1272:
1269:
1264:
1260:
1255:
1250:
1245:
1240:
1237:(1): e12200.
1236:
1232:
1228:
1221:
1218:
1206:
1201:
1197:
1193:
1187:
1184:
1172:
1168:
1162:
1159:
1152:
1149:
1144:
1138:
1124:
1120:
1113:
1111:
1109:
1105:
1100:
1096:
1092:
1088:
1084:
1080:
1073:
1070:
1065:
1061:
1057:
1053:
1049:
1045:
1037:
1034:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1017:
1013:
1009:
1001:
999:
997:
993:
988:
984:
980:
976:
972:
968:
965:(6): 634–40.
964:
960:
956:
949:
946:
941:
935:
921:
917:
910:
908:
904:
899:
895:
890:
885:
881:
877:
873:
869:
865:
858:
855:
850:
846:
842:
838:
834:
830:
823:
820:
815:
811:
806:
801:
796:
791:
787:
783:
779:
772:
770:
768:
766:
764:
762:
758:
753:
749:
745:
741:
737:
733:
726:
723:
716:
713:
708:
704:
700:
696:
692:
688:
681:
679:
675:
664:
660:
653:
651:
649:
647:
643:
631:
626:
622:
618:
614:
610:
604:
602:
600:
598:
596:
594:
592:
590:
586:
581:
577:
573:
569:
565:
561:
557:
553:
546:
543:
532:
528:
522:
519:
512:
507:
504:
502:
499:
497:
494:
492:
491:Low back pain
489:
487:
484:
482:
479:
477:
474:
472:
471:Carpal Tunnel
469:
468:
463:
461:
459:
455:
450:
448:
444:
440:
436:
435:manufacturing
432:
428:
423:
415:
413:
409:
407:
402:
395:
327:
320:
318:
316:
312:
307:
304:
298:
295:
287:
285:
282:
278:
269:
267:
265:
261:
257:
249:
247:
244:
240:
231:
229:
227:
223:
219:
215:
214:truck drivers
211:
207:
203:
199:
191:
189:
187:
183:
174:
172:
165:
163:
161:
156:
155:biomechanical
149:Biomechanical
148:
146:
140:
138:
136:
132:
128:
127:epicondylitis
123:
119:
115:
111:
107:
103:
99:
95:
91:
81:
75:
72:
70:
66:
62:
58:
54:
50:
45:
40:
33:
19:
2534:Chondropathy
2529:Bone disease
2513:
2501:Skin disease
2329:Malnutrition
2306:Benign tumor
2215:Hemarthrosis
2099:Seronegative
2085:(Pseudogout)
2038:Inflammatory
1878:
1867:
1819:
1815:
1808:
1799:
1787:. Retrieved
1782:
1737:
1733:
1726:
1696:(4): 432–8.
1693:
1689:
1682:
1662:
1656:
1639:
1606:
1602:
1596:
1561:
1557:
1547:
1512:
1508:
1498:
1487:. Retrieved
1483:
1474:
1466:
1441:. Retrieved
1438:www.osha.gov
1437:
1414:. Retrieved
1411:www.osha.gov
1410:
1401:
1395:(12): 35–42.
1392:
1388:
1382:
1363:
1359:
1336:
1309:
1305:
1295:
1284:. Retrieved
1280:
1271:
1234:
1230:
1220:
1209:. Retrieved
1195:
1186:
1174:. Retrieved
1170:
1161:
1151:
1126:. Retrieved
1123:www.ccohs.ca
1122:
1085:(1): 13–23.
1082:
1078:
1072:
1047:
1043:
1036:
1011:
1007:
962:
958:
948:
923:. Retrieved
920:www.ccohs.ca
919:
871:
867:
857:
835:(1): 89–99.
832:
828:
822:
785:
781:
735:
731:
725:
720:Association.
715:
693:(3): 233–7.
690:
686:
666:. Retrieved
662:
634:. Retrieved
612:
555:
551:
545:
534:. Retrieved
530:
521:
451:
419:
410:
403:
399:
389: 55-104
321:Epidemiology
308:
299:
291:
273:
260:risk factors
253:
235:
226:hairdressers
195:
192:Occupational
178:
175:Psychosocial
169:
160:poor posture
152:
144:
93:
89:
88:
74:Rheumatology
2388:Ear disease
2383:Eye disease
1675:PMC11130898
1484:www.cdc.gov
1196:www.cdc.gov
663:www.cdc.gov
613:www.cdc.gov
531:www.cdc.gov
439:agriculture
383: 47-54
377: 37-46
371: 31-36
365: 25-30
359: 21-24
353: 16-20
347: 12-15
2578:Ergonomics
2567:Categories
2235:Osteophyte
2047:Infectious
2023:Joint pain
1489:2016-03-25
1443:2016-04-07
1416:2016-04-07
1366:(4): 643.
1286:2016-03-24
1211:2016-03-25
1128:2016-03-25
925:2016-04-07
668:2016-03-24
636:2016-03-24
536:2016-03-24
513:References
431:Healthcare
422:disability
341: 8-11
294:ergonomics
288:Ergonomics
250:Prevention
131:tendinitis
30:See also:
2288:Infection
2150:Sjögren's
1992:Arthritis
1880:SNOMED CT
1754:146625767
1718:221681876
1673:; PMCID:
1176:9 October
1064:146625767
987:221675567
427:incidence
416:Workplace
335: 0-7
264:incidence
232:Diagnosis
198:back pain
135:back pain
106:ligaments
69:Specialty
2016:Symptoms
1836:24337029
1789:25 March
1710:20932789
1671:38804322
1669:. PMID:
1631:25220241
1623:20466711
1588:21825051
1539:23516797
1328:53566279
1263:33586840
1198:. 1989.
1137:cite web
1099:14759746
1028:17845098
979:21186129
934:cite web
898:11441733
849:19910263
814:24156755
752:71927954
707:15676628
615:. 1997.
580:51719997
572:30047854
464:See also
241:, or an
2070:Crystal
1985:General
1874:D009140
1579:3176864
1530:4495348
1254:7883474
889:1446725
805:3924406
788:: 303.
256:posture
210:fatigue
118:tendons
110:muscles
2311:Cancer
1935:(OSHA)
1915:(OSHA)
1905:(OSHA)
1885:928000
1834:
1752:
1716:
1708:
1629:
1621:
1586:
1576:
1537:
1527:
1326:
1261:
1251:
1156:13-19.
1097:
1062:
1026:
985:
977:
896:
886:
847:
812:
802:
750:
705:
578:
570:
496:Sprain
443:retail
387:
381:
375:
369:
363:
357:
351:
345:
339:
333:
303:torque
239:X-rays
222:gender
141:Causes
114:nerves
102:joints
76:
61:splint
2159:Other
1925:(HSE)
1750:S2CID
1714:S2CID
1648:(PDF)
1627:S2CID
1324:S2CID
1060:S2CID
983:S2CID
748:S2CID
576:S2CID
2089:Gout
2083:CPPD
1869:MeSH
1832:PMID
1791:2016
1706:PMID
1619:PMID
1584:PMID
1535:PMID
1259:PMID
1178:2019
1143:link
1095:PMID
1024:PMID
975:PMID
940:link
894:PMID
845:PMID
810:PMID
703:PMID
568:PMID
309:The
279:and
94:MSDs
2140:SLE
1824:doi
1742:doi
1698:doi
1611:doi
1574:PMC
1566:doi
1562:183
1525:PMC
1517:doi
1368:doi
1314:doi
1249:PMC
1239:doi
1200:doi
1087:doi
1052:doi
1016:doi
967:doi
884:PMC
876:doi
837:doi
800:PMC
790:doi
740:doi
695:doi
625:hdl
617:doi
560:doi
243:MRI
216:or
2569::
1931:,
1921:,
1911:,
1901:,
1883::
1872::
1830:.
1820:28
1818:.
1781:.
1762:^
1748:.
1738:25
1736:.
1712:.
1704:.
1694:15
1692:.
1625:.
1617:.
1607:64
1605:.
1582:.
1572:.
1560:.
1556:.
1533:.
1523:.
1513:55
1511:.
1507:.
1482:.
1452:^
1436:.
1425:^
1409:.
1393:58
1391:.
1364:68
1362:.
1358:.
1346:^
1322:.
1310:26
1308:.
1304:.
1279:.
1257:.
1247:.
1235:63
1233:.
1229:.
1194:.
1169:.
1139:}}
1135:{{
1121:.
1107:^
1093:.
1083:14
1081:.
1058:.
1048:25
1046:.
1022:.
1012:92
1010:.
995:^
981:.
973:.
963:15
961:.
957:.
936:}}
932:{{
918:.
906:^
892:.
882:.
872:91
870:.
866:.
843:.
833:10
831:.
808:.
798:.
786:14
784:.
780:.
760:^
746:.
734:.
701:.
691:18
689:.
677:^
661:.
645:^
623:.
611:.
588:^
574:.
566:.
556:23
554:.
529:.
437:,
433:,
228:.
133:,
129:,
116:,
112:,
108:,
104:,
2271:e
2264:t
2257:v
1970:e
1963:t
1956:v
1861:D
1838:.
1826::
1793:.
1756:.
1744::
1720:.
1700::
1677:.
1633:.
1613::
1590:.
1568::
1541:.
1519::
1492:.
1446:.
1419:.
1376:.
1370::
1330:.
1316::
1289:.
1265:.
1241::
1214:.
1202::
1180:.
1145:)
1131:.
1101:.
1089::
1066:.
1054::
1030:.
1018::
989:.
969::
942:)
928:.
900:.
878::
851:.
839::
816:.
792::
754:.
742::
736:7
709:.
697::
671:.
639:.
627::
619::
582:.
562::
539:.
92:(
63:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.