273:
131:
25:
287:
A decrease in afferent arteriole diameter causes a decrease in the GFR (glomerular filtration rate), resulting in a decreased concentration of sodium and chloride ions in the filtrate and/or decreased filtrate flow rate. Reduced blood pressure means decreased venous pressure and, hence, a decreased
370:
Damage to the macula densa would impact blood flow to the kidneys because the afferent arterioles would not dilate in response to a decrease in filtrate osmolarity and pressure at the glomerulus would not be increased. As part of the body's blood pressure regulation, the macula densa monitors
319:
release. First, prostaglandins preferentially vasodilate the renal afferent arteriole, decreasing afferent arteriole resistance and, thus, offsetting the decrease in glomerular hydrostatic pressure caused by the drop in blood pressure. Second, prostaglandin activates prostaglandin-sensitive
225:
As such, an increase in sodium chloride concentration would result in vasoconstriction of afferent arterioles, and reduced paracrine stimulation of juxtaglomerular cells. This demonstrates the macula densa feedback, where compensatory mechanisms act in order to return GFR to normal.
202:
in the thick ascending loop of henle. A decrease in sodium chloride concentration initiates a signal from the macula densa that has two effects: (1) it decreases resistance to blood flow in the afferent arterioles, which raises
371:
filtrate osmolarity; if it falls too far, the macula densa causes the efferent arterioles of the kidney to contract, thus increasing the pressure at the glomerulus and increasing the glomerular filtration rate.
336:
lining the arterioles that will release renin if a fall in blood pressure (i.e. decreased stretch of arteriole due to less blood flow) in the arterioles is detected. Furthermore, JG cells contain beta-1
395:
675:
629:
230:
151:
1138:
260:
The close proximity and prominence of the nuclei cause this segment of the distal tubule wall to appear darker in microscopic preparations, hence the name
1133:
192:
284:
to increase or decrease reabsorption of ions and water to the blood (as needed) in order to alter blood volume and return blood pressure to normal.
637:
276:
Schematic depicting how the RAAS works. Here, activation of the RAAS is initiated by a low perfusion pressure in the juxtaglomerular apparatus
668:
479:
553:
464:
108:
311:, where the macula densa is located. The macula densa senses this drop in salt concentration and responds through two mechanisms,
935:
1175:
945:
940:
661:
1102:
1027:
907:
803:
293:
46:
89:
833:
297:
146:
42:
357:
332:
into the bloodstream. The JG cells can also release renin independently of the macula densa. There are stretch-sensitive
61:
887:
793:
1145:
352:(RBF), renal plasma flow (RPF) and GFR due to greater blood flow to the glomerulus. Note that there is no change in
68:
925:
367:
The process triggered by the macula densa helps keep the GFR fairly steady in response to varying artery pressure.
35:
1120:
1097:
1004:
385:
952:
75:
1213:
828:
762:
545:
415:
Gonzalez-Vicente, Agustin; Saez, Fara; Monzon, Casandra M.; Asirwatham, Jessica; Garvin, Jeffrey L. (2019).
1053:
957:
740:
272:
158:
57:
1155:
808:
325:
289:
219:
645:
1017:
207:
1180:
1125:
882:
877:
813:
798:
361:
353:
345:
338:
321:
204:
188:
632:- Comparative Organology at University of California, Davis - "Mammal, kidney cortex (LM, Medium)"
1165:
848:
356:, as both GFR and RPF are increased. It also results in the release of renin, which, through the
191:. Specifically, the macula densa is found in the terminal portion of the distal straight tubule (
1160:
962:
777:
608:
590:
549:
509:
446:
1074:
897:
843:
598:
582:
535:
499:
491:
436:
428:
349:
341:, and so activation of the sympathetic nervous system will further stimulate renin release.
1092:
1063:
869:
757:
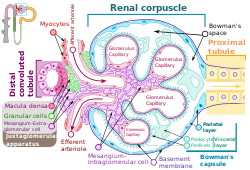
301:
199:
82:
1192:
1185:
1170:
1084:
967:
735:
685:
603:
570:
504:
441:
416:
281:
238:
211:
184:
257:
than surrounding cells of the distal straight tubule (cortical thick ascending limb).
222:
of the afferent and efferent arterioles, which are the major storage sites for renin.
1207:
1079:
979:
974:
930:
730:
713:
333:
316:
308:
994:
917:
838:
788:
723:
718:
708:
307:
Hence, a decrease in blood pressure results in less sodium chloride present at the
254:
242:
130:
989:
984:
747:
653:
24:
432:
280:
Macula densa cells sense changes in sodium chloride level, and will trigger an
823:
752:
594:
1022:
902:
612:
586:
513:
450:
417:"Thick Ascending Limb Sodium Transport in the Pathogenesis of Hypertension"
344:
Thus, a drop in blood pressure results in preferential vasodilation of the
892:
495:
164:
1112:
860:
767:
390:
1045:
693:
465:"Tubuloglomerular Feedback - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics"
380:
364:, which ultimately increases hydrostatic pressure in the glomerulus.
176:
198:
The cells of the macula densa are sensitive to the concentration of
526:
Guyton & Hall
Textbook Of Physiology, 11th Edition 2006, p. 324
329:
215:
253:
The cells of the macula densa are taller and have more prominent
571:"Macula Densa Sensing and Signaling Mechanisms of Renin Release"
657:
296:, which causes an increased absorption of sodium ions into the
18:
187:
lining the wall of the distal tubule where it touches the
16:
A region of juxtaglomerular apparatus in nephron of kidney
484:
Clinical
Journal of the American Society of Nephrology
229:
The release of renin is an essential component of the
569:
Peti-Peterdi, János; Harris, Raymond C. (July 2010).
195:), after which the distal convoluted tubule begins.
1111:
1062:
1044:
1003:
916:
868:
859:
776:
701:
692:
396:
List of distinct cell types in the adult human body
145:
140:
123:
49:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
542:A Learning System in Histology: CD-ROM and Guide
669:
630:Anatomy photo: Urinary/mammal/cortex1/cortex5
575:Journal of the American Society of Nephrology
320:specialized smooth muscle cells of the renal
8:
480:"Thick Ascending Limb of the Loop of Henle"
865:
698:
676:
662:
654:
650:- "The Nephron: Juxtaglomerular Apparatus"
214:(GFR) toward normal, and (2) it increases
129:
602:
503:
440:
193:thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle
183:is an area of closely packed specialized
135:Renal corpuscle showing the macula densa.
109:Learn how and when to remove this message
271:
407:
162:
120:
7:
292:pressure. This results in a smaller
231:renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system
47:adding citations to reliable sources
14:
23:
34:needs additional citations for
1028:Extraglomerular mesangial cell
908:Intraglomerular mesangial cell
642:Essentials of Human Physiology
294:capillary hydrostatic pressure
1:
360:, causes constriction of the
888:Glomerular basement membrane
1230:
926:Proximal convoluted tubule
638:"Section 7/7ch03/7ch03p17"
433:10.1152/physrev.00055.2017
212:glomerular filtration rate
1121:Internal urethral orifice
1098:Median umbilical ligament
1005:Juxtaglomerular apparatus
540:Vaughan, Deborah (2002).
386:Juxtaglomerular apparatus
315:of which are mediated by
157:
128:
953:Distal convoluted tubule
536:Histology image:16010loa
478:Mount, David B. (2014).
358:renin–angiotensin system
829:Peritubular capillaries
546:Oxford University Press
328:(JG cells), to release
282:autoregulatory response
1054:Ureteropelvic junction
958:Collecting duct system
741:medullary interstitium
587:10.1681/ASN.2009070759
277:
159:Anatomical terminology
1018:Juxtaglomerular cells
421:Physiological Reviews
326:juxtaglomerular cells
290:peritubular capillary
275:
220:juxtaglomerular cells
210:and helps return the
496:10.2215/CJN.04480413
339:adrenergic receptors
208:hydrostatic pressure
43:improve this article
1181:Lacunae of Morgagni
1126:Urethral sphincters
362:efferent arterioles
354:filtration fraction
346:afferent arterioles
322:afferent arterioles
237:), which regulates
278:
1201:
1200:
1040:
1039:
1036:
1035:
963:Connecting tubule
636:Nosek, Thomas M.
490:(11): 1974–1986.
218:release from the
173:
172:
168:
119:
118:
111:
93:
1221:
1075:Vesical arteries
898:Filtration slits
883:Bowman's capsule
866:
699:
678:
671:
664:
655:
649:
644:. Archived from
617:
616:
606:
581:(7): 1093–1096.
566:
560:
559:
533:
527:
524:
518:
517:
507:
475:
469:
468:
461:
455:
454:
444:
412:
350:renal blood flow
165:edit on Wikidata
133:
121:
114:
107:
103:
100:
94:
92:
51:
27:
19:
1229:
1228:
1224:
1223:
1222:
1220:
1219:
1218:
1204:
1203:
1202:
1197:
1176:navicular fossa
1107:
1093:Detrusor muscle
1058:
1032:
999:
946:Thick ascending
912:
870:Renal corpuscle
855:
772:
758:Cortical lobule
688:
684:Anatomy of the
682:
635:
626:
621:
620:
568:
567:
563:
556:
539:
534:
530:
525:
521:
477:
476:
472:
463:
462:
458:
414:
413:
409:
404:
377:
302:proximal tubule
270:
251:
200:sodium chloride
169:
136:
115:
104:
98:
95:
52:
50:
40:
28:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1227:
1225:
1217:
1216:
1214:Kidney anatomy
1206:
1205:
1199:
1198:
1196:
1195:
1193:Urinary meatus
1190:
1189:
1188:
1186:urethral gland
1183:
1178:
1173:
1168:
1163:
1158:
1150:
1149:
1148:
1143:
1142:
1141:
1136:
1123:
1117:
1115:
1109:
1108:
1106:
1105:
1100:
1095:
1090:
1089:
1088:
1085:Vaginal artery
1082:
1077:
1068:
1066:
1060:
1059:
1057:
1056:
1050:
1048:
1042:
1041:
1038:
1037:
1034:
1033:
1031:
1030:
1025:
1020:
1015:
1009:
1007:
1001:
1000:
998:
997:
992:
987:
982:
977:
972:
971:
970:
968:Papillary duct
965:
955:
950:
949:
948:
943:
941:Thin ascending
938:
928:
922:
920:
914:
913:
911:
910:
905:
900:
895:
890:
885:
880:
874:
872:
863:
857:
856:
854:
853:
852:
851:
846:
841:
836:
831:
826:
818:
817:
816:
811:
806:
801:
796:
791:
782:
780:
774:
773:
771:
770:
765:
760:
755:
750:
745:
744:
743:
738:
728:
727:
726:
716:
711:
705:
703:
696:
690:
689:
686:urinary system
683:
681:
680:
673:
666:
658:
652:
651:
648:on 2016-03-24.
633:
625:
624:External links
622:
619:
618:
561:
555:978-0195151732
554:
528:
519:
470:
456:
427:(1): 235–309.
406:
405:
403:
400:
399:
398:
393:
388:
383:
376:
373:
269:
266:
250:
247:
239:blood pressure
171:
170:
161:
155:
154:
149:
143:
142:
138:
137:
134:
126:
125:
117:
116:
58:"Macula densa"
31:
29:
22:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1226:
1215:
1212:
1211:
1209:
1194:
1191:
1187:
1184:
1182:
1179:
1177:
1174:
1172:
1169:
1167:
1164:
1162:
1159:
1157:
1156:pre-prostatic
1154:
1153:
1152:Male urethra
1151:
1147:
1144:
1140:
1137:
1135:
1132:
1131:
1129:
1128:
1127:
1124:
1122:
1119:
1118:
1116:
1114:
1110:
1104:
1101:
1099:
1096:
1094:
1091:
1086:
1083:
1081:
1080:Vesical veins
1078:
1076:
1073:
1072:
1070:
1069:
1067:
1065:
1061:
1055:
1052:
1051:
1049:
1047:
1043:
1029:
1026:
1024:
1021:
1019:
1016:
1014:
1011:
1010:
1008:
1006:
1002:
996:
993:
991:
988:
986:
983:
981:
980:Renal papilla
978:
976:
975:Tubular fluid
973:
969:
966:
964:
961:
960:
959:
956:
954:
951:
947:
944:
942:
939:
937:
934:
933:
932:
931:Loop of Henle
929:
927:
924:
923:
921:
919:
915:
909:
906:
904:
901:
899:
896:
894:
891:
889:
886:
884:
881:
879:
876:
875:
873:
871:
867:
864:
862:
858:
850:
847:
845:
842:
840:
837:
835:
832:
830:
827:
825:
822:
821:
819:
815:
812:
810:
807:
805:
802:
800:
797:
795:
792:
790:
787:
786:
784:
783:
781:
779:
775:
769:
766:
764:
763:Medullary ray
761:
759:
756:
754:
751:
749:
746:
742:
739:
737:
734:
733:
732:
729:
725:
722:
721:
720:
717:
715:
712:
710:
707:
706:
704:
700:
697:
695:
691:
687:
679:
674:
672:
667:
665:
660:
659:
656:
647:
643:
639:
634:
631:
628:
627:
623:
614:
610:
605:
600:
596:
592:
588:
584:
580:
576:
572:
565:
562:
557:
551:
547:
543:
537:
532:
529:
523:
520:
515:
511:
506:
501:
497:
493:
489:
485:
481:
474:
471:
466:
460:
457:
452:
448:
443:
438:
434:
430:
426:
422:
418:
411:
408:
401:
397:
394:
392:
389:
387:
384:
382:
379:
378:
374:
372:
368:
365:
363:
359:
355:
351:
348:, increasing
347:
342:
340:
335:
334:baroreceptors
331:
327:
323:
318:
317:prostaglandin
314:
310:
309:distal tubule
305:
303:
299:
295:
291:
285:
283:
274:
267:
265:
263:
258:
256:
248:
246:
244:
240:
236:
232:
227:
223:
221:
217:
213:
209:
206:
201:
196:
194:
190:
186:
182:
178:
166:
160:
156:
153:
150:
148:
144:
139:
132:
127:
122:
113:
110:
102:
91:
88:
84:
81:
77:
74:
70:
67:
63:
60: –
59:
55:
54:Find sources:
48:
44:
38:
37:
32:This article
30:
26:
21:
20:
1166:intermediate
1071:Circulation
1013:Macula densa
1012:
995:Renal pelvis
918:Renal tubule
809:interlobular
789:Renal artery
646:the original
641:
578:
574:
564:
541:
531:
522:
487:
483:
473:
459:
424:
420:
410:
369:
366:
343:
312:
306:
286:
279:
262:macula densa
261:
259:
252:
234:
228:
224:
197:
181:macula densa
180:
174:
124:Macula densa
105:
96:
86:
79:
72:
65:
53:
41:Please help
36:verification
33:
990:Major calyx
985:Minor calyx
778:Circulation
141:Identifiers
936:Descending
878:Glomerulus
844:interlobar
834:Vasa recta
824:Renal vein
799:interlobar
402:References
298:vasa recta
205:glomerular
189:glomerulus
69:newspapers
1161:prostatic
1130:External
1023:Mesangium
903:Mesangium
794:segmental
785:Arteries
595:1046-6673
249:Histology
1208:Category
1146:Internal
1087:(female)
893:Podocyte
849:efferent
814:afferent
736:pyramids
613:20360309
514:25318757
451:30354966
375:See also
268:Function
99:May 2015
1113:Urethra
1103:Trigone
1064:Bladder
1046:Ureters
861:Nephron
839:arcuate
804:arcuate
768:Nephron
731:Medulla
714:Capsule
694:Kidneys
604:4577295
505:4220766
442:6335098
391:Nephron
300:at the
175:In the
83:scholar
1171:spongy
1139:female
820:Veins
724:column
719:Cortex
709:Fascia
702:Layers
611:
601:
593:
552:
512:
502:
449:
439:
381:Kidney
255:nuclei
243:volume
179:, the
177:kidney
85:
78:
71:
64:
56:
748:Sinus
538:from
330:renin
216:renin
185:cells
163:[
152:86333
90:JSTOR
76:books
1134:male
753:Lobe
609:PMID
591:ISSN
550:ISBN
510:PMID
447:PMID
313:both
241:and
235:RAAS
62:news
599:PMC
583:doi
500:PMC
492:doi
437:PMC
429:doi
147:FMA
45:by
1210::
640:.
607:.
597:.
589:.
579:21
577:.
573:.
548:.
544:.
508:.
498:.
486:.
482:.
445:.
435:.
425:99
423:.
419:.
324:,
304:.
264:.
245:.
677:e
670:t
663:v
615:.
585::
558:.
516:.
494::
488:9
467:.
453:.
431::
233:(
167:]
112:)
106:(
101:)
97:(
87:·
80:·
73:·
66:·
39:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.