22:
269:
165:. For example, large-scale studies have been conducted for Stable Continental Regions (SCR's), which are defined "as regions of continental crust that have not experienced any major tectonism, magmatism, basement metamorphism or anorogenic intrusion since the early Cretaceous, and no rifting or major extension or transtension since the Paleogene."
138:
168:
Finally there is the common question of what is the maximum magnitude for the whole world. Unfortunately, it cannot really be answered, since this earthquake has most likely not happened in the historical record, and we cannot search beyond the earth for analogs. Answers can again be inferred using
156:
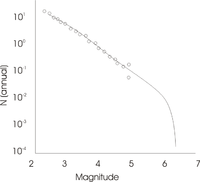
interiors. The circles represent actual earthquake data. Note that the dataset is complete for small magnitudes, but becomes erratic for the larger. At about M5, there are no records, simply because the historical record is usually too short. In some cases paleoseismology can fill some of the gap,
149:) over the region, combined with the expected number (earthquake frequency) of earthquakes, from the smallest to the largest. The integration must close at the maximum magnitude. The figure shows a typical 'earthquake frequency' plot for a given region.
160:
The last part of the curve, perhaps the most important part, can be filled in by inference. This would come from studying similar geology throughout the world (using analogs to extend time), or by a study of
169:
the finite size of the world's plates (plate tectonics), and the possible limits of the various magnitude scales. The specific value, however, is not directly relevant to most people, since, except for
130:) is also one of the more contentious. The choice of the value can greatly influence the final outcome of the results, yet this is most likely a size of
310:
39:
105:
190:
86:
215:
58:
43:
303:
241:
65:
173:, the local shaking effects come to a maximum at about M8, and greater earthquakes simply extend the rupture distance.
72:
334:
296:
54:
32:
127:
329:
79:
162:
280:
194:
119:
323:
191:"USGS Earthquake Hazards Program - Earthquake catalog for Stable Continental Regions"
219:
21:
276:
131:
153:
146:
268:
170:
137:
136:
145:
The seismic hazard calculation involves a double integration (
15:
284:
134:
that has not yet occurred in the region under study.
46:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
304:
118:An important parameter in the calculation of
8:
311:
297:
157:but this is rare for continental regions.
106:Learn how and when to remove this message
216:"Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) Page"
182:
7:
265:
263:
44:adding citations to reliable sources
14:
218:. 4 November 2005. Archived from
267:
20:
31:needs additional citations for
1:
283:. You can help Knowledge by
152:This is a typical plot for
351:
262:
141:Frequency-magnitude plot
142:
128:Moment magnitude scale
140:
246:Eqseis.geosc.psu.edu
40:improve this article
55:"Maximum magnitude"
222:on 4 November 2005
143:
292:
291:
242:"Earthquake Size"
124:maximum magnitude
116:
115:
108:
90:
342:
335:Seismology stubs
313:
306:
299:
271:
264:
257:
256:
254:
252:
238:
232:
231:
229:
227:
212:
206:
205:
203:
202:
193:. Archived from
187:
111:
104:
100:
97:
91:
89:
48:
24:
16:
350:
349:
345:
344:
343:
341:
340:
339:
320:
319:
318:
317:
261:
260:
250:
248:
240:
239:
235:
225:
223:
214:
213:
209:
200:
198:
189:
188:
184:
179:
163:fault mechanics
112:
101:
95:
92:
49:
47:
37:
25:
12:
11:
5:
348:
346:
338:
337:
332:
322:
321:
316:
315:
308:
301:
293:
290:
289:
272:
259:
258:
233:
207:
181:
180:
178:
175:
126:(expressed as
120:seismic hazard
114:
113:
28:
26:
19:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
347:
336:
333:
331:
328:
327:
325:
314:
309:
307:
302:
300:
295:
294:
288:
286:
282:
279:article is a
278:
273:
270:
266:
247:
243:
237:
234:
221:
217:
211:
208:
197:on 2005-12-10
196:
192:
186:
183:
176:
174:
172:
166:
164:
158:
155:
150:
148:
139:
135:
133:
129:
125:
121:
110:
107:
99:
88:
85:
81:
78:
74:
71:
67:
64:
60:
57: –
56:
52:
51:Find sources:
45:
41:
35:
34:
29:This article
27:
23:
18:
17:
285:expanding it
274:
249:. Retrieved
245:
236:
224:. Retrieved
220:the original
210:
199:. Retrieved
195:the original
185:
167:
159:
151:
144:
123:
117:
102:
96:January 2019
93:
83:
76:
69:
62:
50:
38:Please help
33:verification
30:
154:continental
330:Seismology
324:Categories
277:seismology
201:2017-09-04
177:References
132:earthquake
66:newspapers
251:1 January
226:1 January
171:tsunamis
147:integral
80:scholar
82:
75:
68:
61:
53:
275:This
87:JSTOR
73:books
281:stub
253:2019
228:2019
59:news
42:by
326::
244:.
122:,
312:e
305:t
298:v
287:.
255:.
230:.
204:.
109:)
103:(
98:)
94:(
84:·
77:·
70:·
63:·
36:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.